chapter 7- cofactors
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
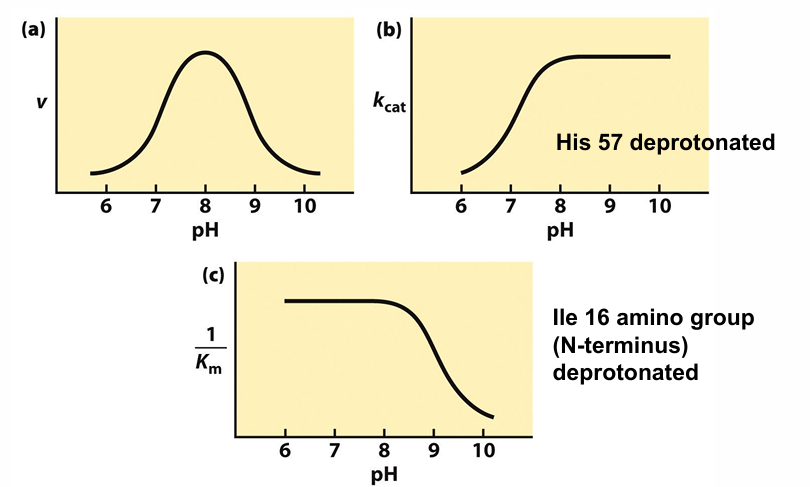
explain what the plots mean
a) chymotrypsin works best near neutral to slight basic conditions
b) peak at ph 8 → His57 being deprotonated
His57 acts a general base
if His57 is protonated → slow catalysis
c) low pH → binding is stron
after pH 8 → amino groups of lle becomes deprotonated
so weak substrate binding
what is another name for cofactors?
vitamins
important to understand because a deficiency can create disease
cofactor vs coenzyme
cofactor:
coenzyme: helps an enzyme catalyze a reaction by transferring atoms or electrons
non protein chemical helpers that enzymes need to fucntion properly
What is SAM?
S-adenosylmethionine
synthesized by the reaction of methionine with ATP
reacts readily with the nucleophilic acceptors
donor of almost all the methyl group
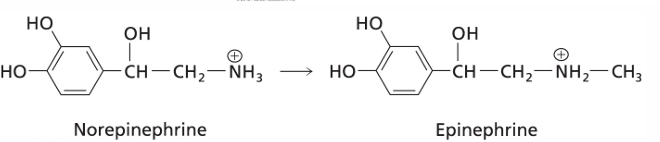
what is this reaction important?
SAM is required for conversion of norepinephrine to epinephrine
what are NAD(P)+ and NAD(P)H? why are they important?
NAD+ → nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (accepts electrons to become NADH)
NADP+ → nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (accepts electrons to become NADPH)
Important as they are used in redox reactions
what is niacin?
wear NAD+ and NADP+ come from
two forms: nicotinic acid and nicotinamide
vitatmin B3
need 12-14 mg/day
in animals, fruit, seeds, fungi
can synthesize from tryptophan but we can not synthesize tryptophan
how do the structures of NAD+(NADP+) and NADH (NADPH)differ?
NAD+ : is in oxidized form so it has one H
NADH: is in reduced form so it has two H
what is lactate dehyrogenesase (LDH)?
a NAD-dependent dehydrogenase
NAD+ is reduced to NADH
gains electrons from lactate
lactate is oxides to pyruvate
loses electrons
shows how NAD+ is important for electron flow
what so dehydrogenases contain?
rossman fold motifcation
so beta-alpha-beta-alpha-beta units
hoe does ethanol metabolism work?
1: ethanol to acetaldehyde
uses alcohol dehydrogenase
NAD+ reduced to NADH
ethanol oxidized to acetaldehyde → toxic!!
2: acetaldehyde to acetate
uses acetaldehyde dehydrogenase
NAD+ is reduced to NADH
acetaldehyde is oxidized to acetate
what is FAD and FMN?
FAD: flavin adenine mononucleotide
FMN: flavin mononucleotide
it is from riboflavin (vitamin B2)
used by flavoproteins