Chromosomes, The Cell Cycle and an Introduction to its Regulation 22/10
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is chromatin and what does it consist of?
It is scattered during cell cycle progression, it coils into chromosomes. Chromosomal DNA, RNA and proteins.
What are the 2 types of proteins in chromatin?
Basic (mostly histones) and acidic proteins. Chromatin is also associated w/ phospholipids and enzymes.
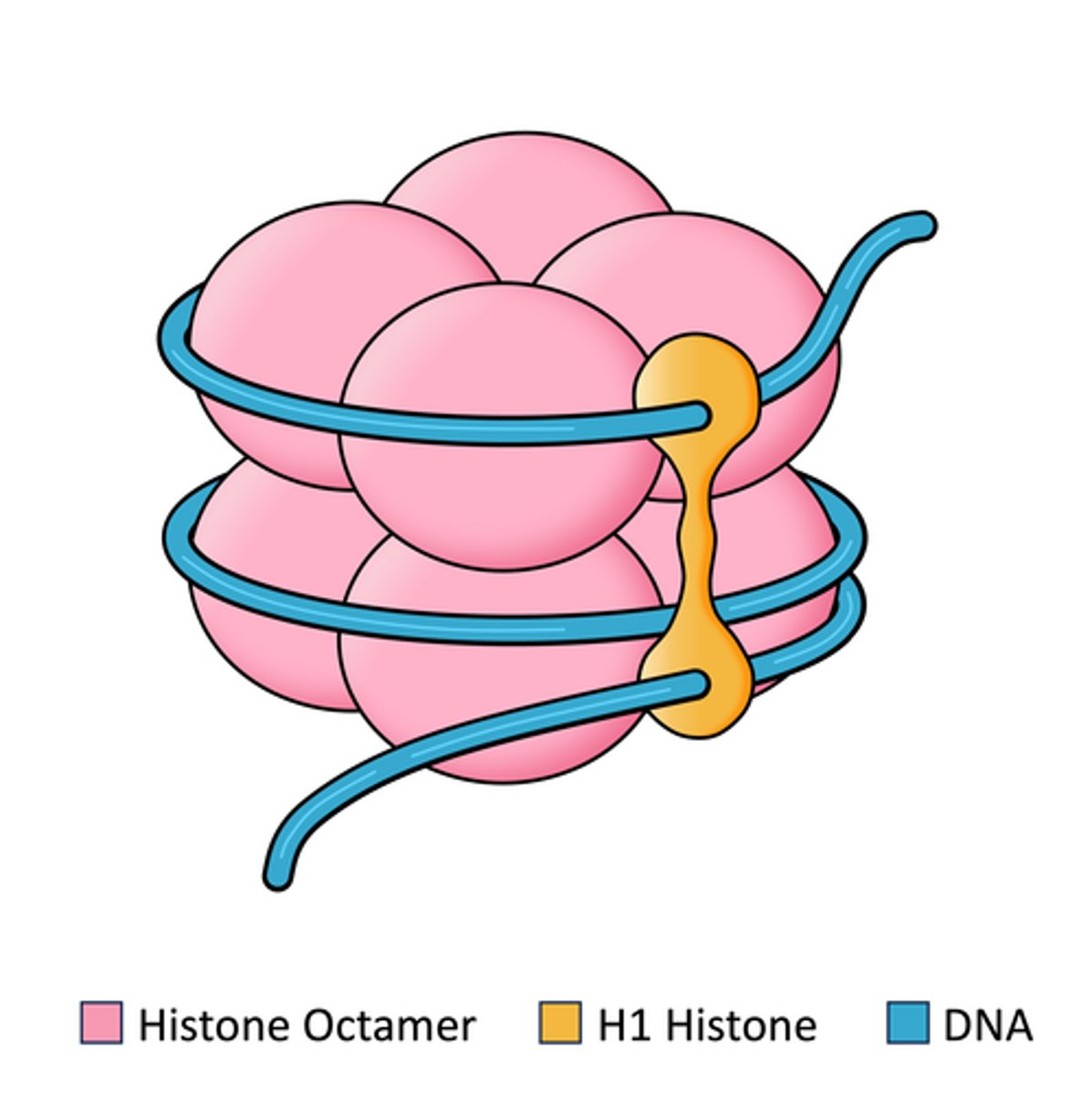
What are nucleosomes?
Bead-like structures which chromatin is packed into - each nucleosome has 2 loops of DNA double helix wrapped around an 8 histone cluster.
How are visible chromosomes formed?
Through supercoiling + condensation of chromatin.
What are genes on the chromosomes?
Specialised functional sites.
What is nucleosome packing?
Several nucleosomes packed together.
Explain nucleosomes structure
Nucleosomes are the basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotic cells, consisting of a segment of DNA wound around the Octameric core of histone proteins.
Then it joins to neighbouring nucleosomes by linker DNA with H1 bound to the linker.
What happens to nucleosomes during replication and DNA synthesis
Replication - they are disassembled
DNA synthesis - reassembled
Which amino acids are histones rich in?
Basic amino acids eg. Lys and Arg.
What are the core histones in chromosomal DNA?
H2A, H2B, H3 and H4.
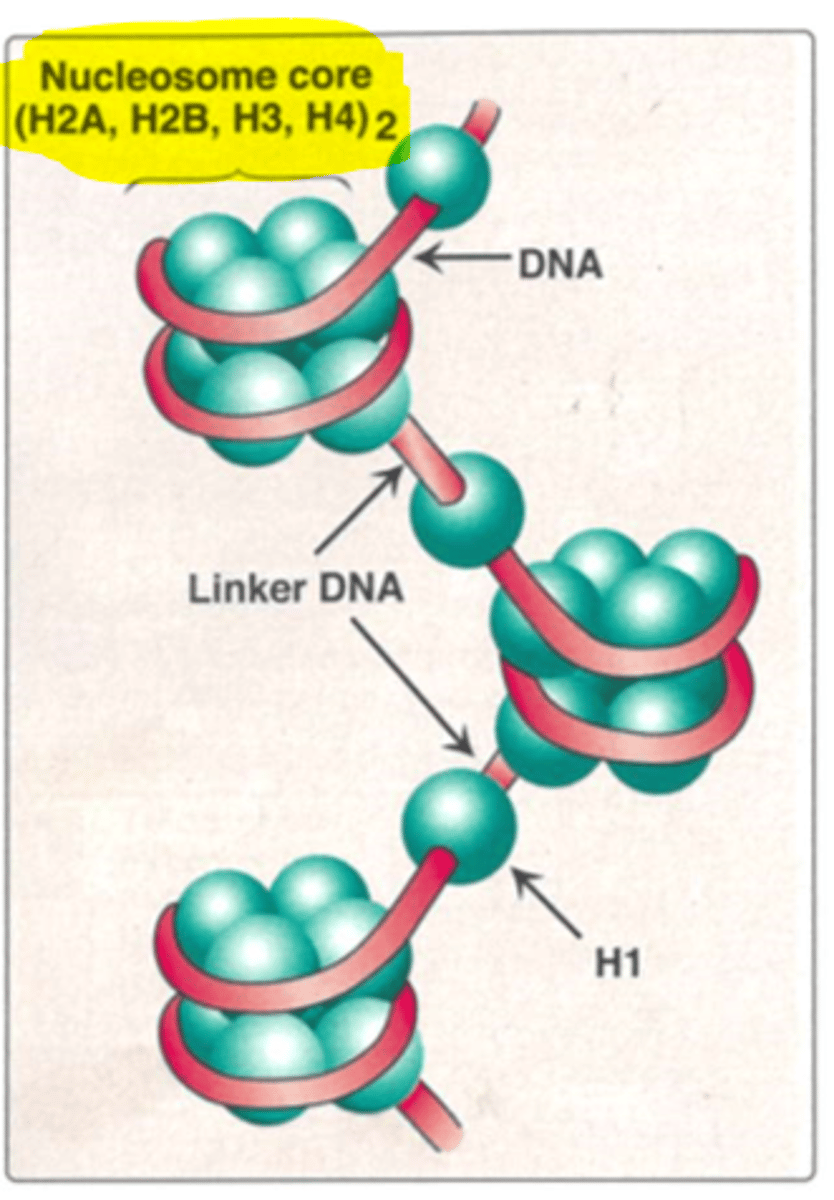
What are the linker histones in chromosomal DNA?
H1 and H5 (hold structures together).
What effect does the packing of chromatin have on DNA translation?
Tightly packed chromatin is important to prevent DNA translation. -Make sure only the right genes are expressed at the right time
What are the 2 forms that chromatin appears in?
1. heterochromatin
2. euchromatin
What are features of heterochromatin?
1. more condensed
2. dense staining
3.Heterochromatin is in a transcriptionally inactive state

What are features of euchromatin?
1. less condensed
2. light staining
3.Euchromatin is in a transcriptionally active state
What are cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases?
Regulatory molecules which co-ordinate cell's entry into cell cycle, and different types are needed at different stages.
Cyclin - regulate CDK activity
Order of cell cycle
G1 , S , G2 , M
What is the definition of meiosis?
Sexual reproduction, producing genetically distinct haploid cells.
Meiosis involves 2 rounds of segregation. what are they ?
Meiosis 1 = Segregates homologus chromosomes - 2 haploid
Meiosis 2 =segregates sister chromatids - 4 haploid
What is trisomy 21, trisomy 13. Trisomy 18 and XXY?
Down's syndrome, Patau's syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Kleinfelter's syndrome.
What are some challanges that can occur in S phase
Ensuring exact replication and preventing gene amplification.
Replicated chromosomes consist of sister chromatids glued by WHAT ?
cohesion proteins and DNA catenation
What increases histone production
S-CDK - By triggers DNA replication at the start of S phase
In mitosis : Prophase ?
Chromosome condensation, mitotic spindle assembly
In mitosis : Prophasemetaphase ?
Nuclear envelope breakdown, chromosome attachment to spindle.
In mitosis : metaphase ?
Metaphase: Chromosomes align at the equator, kinetochore microtubules attach to chromatids.
in mitosis : anaphase ?
Chromatid separation and movement towards spindle poles.
in mitosis : telophase ?
Telophase: Chromosomes decondense, nuclear envelope reassembles, cytokinesis occurs
Meiosis 1 : prophase 1
Homologous chromosomes recognition and pairing, crossing over, formation of bivalents and tetrads, and appearance of chiasmata.
Meiosis 1 : metaphase 1
Tetrads align at metaphase plate
Meiosis 1 : anaphase 1
Homologs segregate to opposite poles
Meiosis 1 : telophase 1
Nuclear membranes form around dyads.
Meiosis 2: prophase 2
Chromosomes condense
Meiosis 2: metaphase 2
Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate
Meiosis 2: anaphase 2
Sister chromatids segregate to opposite poles
Meiosis 2: telophase 2
Four haploid gametes are formed
Monosomy
Missing chromosomes