Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis Of Inheritance
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
How does DNA replication transmit genetic information?
DNA replication allows for genetic information to be inherited from parent self to daughter cells by mitosis and from generation to generation starting with meiosis.
Transformation
Change in genotype and phenotype due to a simulation of foreign DNA
Bacteria phages and viruses
Bacteriaphages-viruses that infect bacteria
Viruses-DNA (sometimes RNA) enclosed by protective coat, often simple protein.
The structural model of DNA
Found pairing was more specific and dictated by the base
adenine (a) paired only with thymine(t)
Guanine (g) paired only with cytosine ( c )
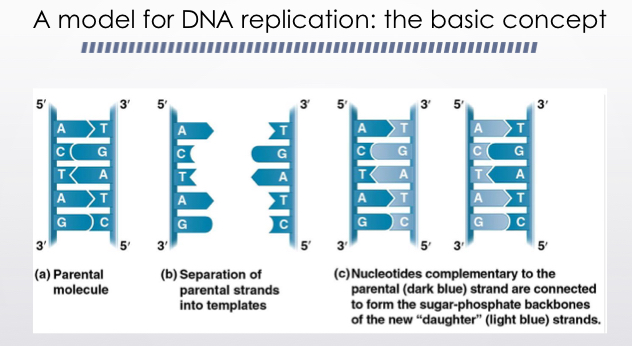
A model for DNA replication the basic concept
Semi conservative model, conservative model, dispersive model
Semi conservative predicts each daughter molecule will have one old strand, derived or conserve from the parent molecule in 1 newly made strand.
Conservative model the two parent stands rejoin
Dispersive model each strand is a mix of old and new
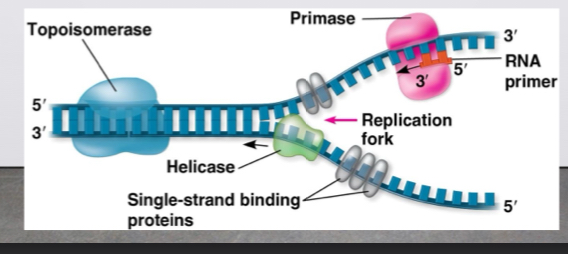
DNA Replications
Origins of Replication-where two DNA strands are separated, opening up a replication bubble.
Proceeds in both directions from origin until the entire molecule copied
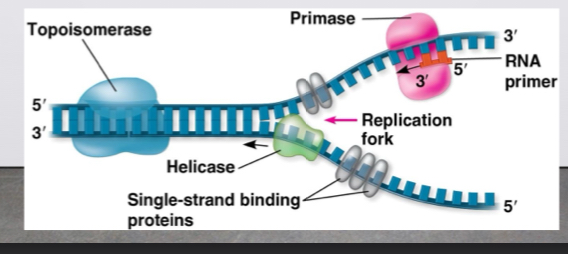
The start of DNA replication
At the end of each bubble is a replication fork which is a wise shaped region where parental DNA stands are unwound
Helicases on twist the double helix at replication forks
Single strand binding proteins bind two and stabilize single stranded DNA
Topoisomerase relieves the strain of twisting of the double helix by breaking swiveling and rejoining DNA strands
The three are enzymes/proteins
Synthesizing a new DNA strand
Enzymes DNA polymerase is catalyze the elongation of new DNA at a replication fork. can only add nucleotides to the 3’ end of a growing DNA strand.
EnzymesMost enable the nurses require a primer to which they can add nucleotides, which is synthesized by Primase.
Leading Strand
DNA polymerase add nucleotides only to the 3’ end of a growing strand therefore it can long only in 5’ to 3’ prime direction
along one strand, the DNA polymer synthesizes, a leading strand continuously moving toward the replication fork
Lagging strand
To elongate the lagging strand, DNA polymerase must work away from the replication fork
The lagging strand is synthesized as series of Okazaki fragments, which are joined together by DNA ligase
Telomere
is repetitive DNA at the end of the eukaryotic chromosomes DNA molecule.
telomerase catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres in germ cells
Eukaryotic chromosomes
DNA is precisely combined with proteins in a complex called chromatin
Chromosomes fit into the nucleus through an elaborate multilevel system of packing
Proteins called histones are responsible for the main level of DNA packing and interphase chromatin
Euchromatin and Heterochromatin
(E)loosely packed chromatin
(H)Highly condensed chromatin