Skill Acquisition
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Skill
Learned ability to bring about predetermined results
ACE FACE
Aesthetically pleasing
Consistent
Efficient
Fluent
Accurate
Controlled
Economical
Ability
A persons natural potential to perform a specific activity/sport
Skill Continua - Swimming - Triple jump - Serve
Continuous - Serial - Discrete
Skill Continua - Rock Climbing - Sailing
Self paced - Externally paced
Skill Continua - Dribbling - Gymnastics routine
Open - Closed
Skill Continua - Rugby tackle - Darts
Gross - Fine
Skill Continua - Backflip - Swimming
High - Low organisation
Skill Continua - Roly poly - Diving
Simple - Complex
6 skill continua
Continuous - serial - discrete
Self paced - Externally paced
Open - closed
Gross - fine
High - low organisation
Simple - complex
Learning
Permanent change in behaviour as a result of practice or experience
Plateau
No change in the performance as measured
3 stages of leaning
Cognitive - associative - autonomous
Stimulus response theory
Stimulus - Information entering sensory system
Response - An action
Practice - Makes SR bond stronger
Operant conditioning + Who
Skinner
trial and error
behaviour is shaped and maintained by consequences
What do positive and negative reinforcement do
Strengthen behaviour
Hulls drive reduction theory
When an individual completes a task, their drive to complete It again is reduced so a new challenge must be introduced
Positive transfer
One skill helps learning of another
Negative transfer
One skill hinders learning of another
Zero transfer
One skill has no effect on learning of another
Bi-lateral transfer
Learning transfered from limb to limb
Proactive transfer
When a skill or task presently being learned has an effect on future skills or tasks
Retroactive transfer
When a skill or task presently being learned has an effect on previously learned
Guidance
Helps learners learn new skills effectively
3 types of guidance
Visual
Verbal
Manual / Mechanical
Methods of practice
Whole
Part
Thole-part-whole
Types of practice
Fixed / variable
Massed / Distributed
Mental practice
Uses of fixed / variable practice
Fixed for closed skills
Variable for open skills
Fixed practice
Practicing same skill in stable and predictable environment
Variable practice
Practicing skills in different conditions
Massed practice
Long continuous sessions designed to increase repetition and build motor programmes
Distributed practice
Short frequent sessions - allows rest
mental practice
Visualisation
Feedback
Information available to a performer during or after performing to alter performance
Reasons for feedback (MRI)
Motivate
Reinforce
Inform
Types of Intrinsic feedback (3)
Kinaesthetic
Equilibrium
Proprioception
Types of extrinsic feedback (2)
Tangible - Facts + figures
Intangible - advice + motivation
Positive feedback…
Reinforces skill learning
Negative feedback
Information about unsuccessful action
Knowledge of performance
Information about why a performance went well
Terminal feedback
Feedback after performance
allows athlete to analyse themself
Concurrent feedback
Feedback given during performance
Basic model of information processing
Input - decision making - output
6 types of input detection
Audition
Vision
Proprioreception
Touch
Equilibrium
Kinaethesis
Selective attention
The process of filtering out unnecessary information and picking important bits from a display
Perception (input)
Brain interpreting and making sense of the information given
Describe DCR process (perception)
Detection - comparison - recognition
detected by senses
compared
match due to previous experience
Where is selecting attention along the memory stores
Between STSS and STM
STSS functions
stores all information for max 1 second
if attention paid then transfers to STM
STM fucntions (2)
Working memory where info processed
Holds 5-9 pieces info for 30 seconds
LTM functions (3)
Permanent store of info
Unlimited capacity and can store forever
Information encoded through repetition + practice
CALORI memory processing
Chunking - grouping common things together
Association - linking new info to old knowledge
Linking - Connecting similar concepts
Organisation - Structured info
Repetition - more practice, improves
Imagery - visualisation
Response time
Reaction time + movement time
Reaction time
Time form onset of stimulus to first movement
Movement time
Time form initiation to completion
Simple reaction time
1 stimulus, 1 response
Choice reaction time
having to respond to several stimuli
Hicks law - reaction time
More choices you have to process, longer reaction time is
Spatial anticipation
Predicting what the actions of their opponents will be
Temporal anticipation
Predicting when an action will take place
Anticipation
Draw on past experiences to predict what is going to happen
Single channel hypothesis theory
The brain can only deal with one piece of info at a time - so when multiple stimuli it causes the bottleneck effect
Psychological refractory period
If second stimulus follows closely behind the first, reaction time - reaction time is slowed due to increased information processing
Motot programme
A set of movements stored in the memory
How does a motor programme run
subroutines are put into movement by the effector mechanism
Where are motor programmes stored
In the LTM
Executive programme
A series of subroutines organised in correct sequence to perform a movement

Closed loop control theory
Possible feedback and correcting during performance

Open loop control theory
All info sent as a single message before hand
Schema theory
General motor programme which can be adapted (e.g. throwing/kicking schema)
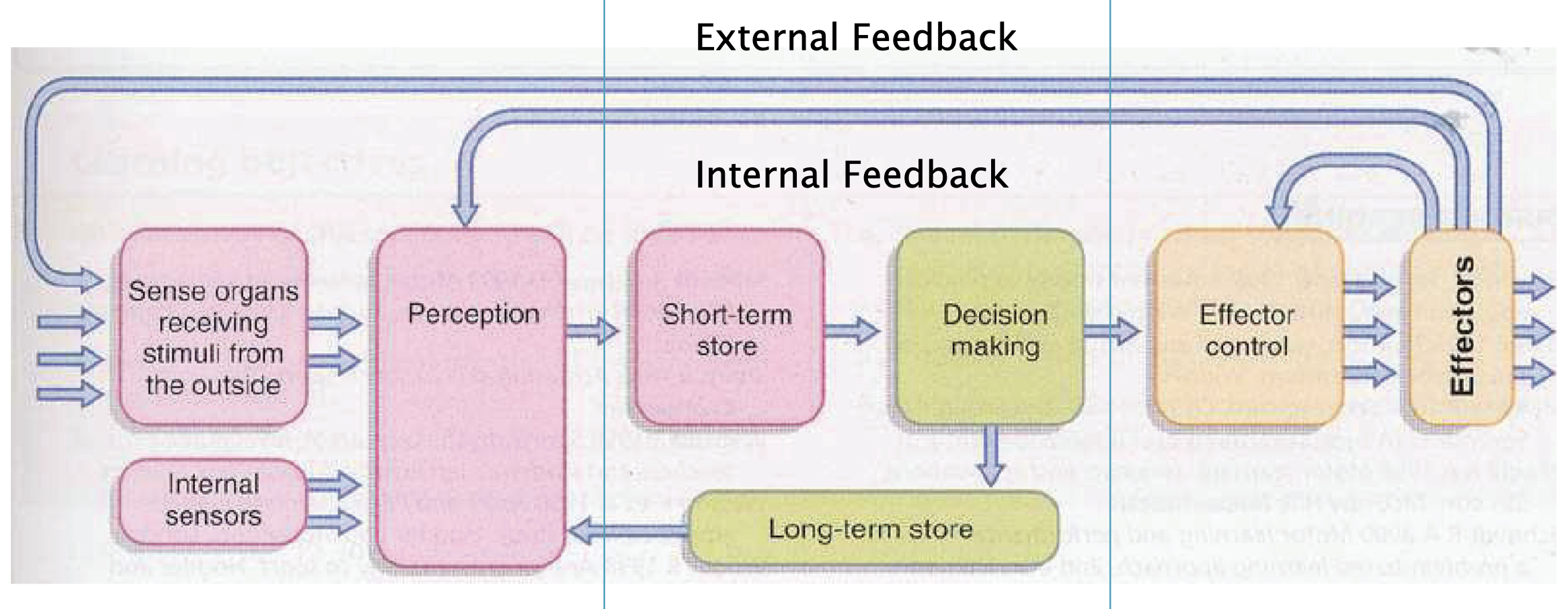
What are the 3 stages information processing and what doe they include in Welfords model
Perception - including sense organs + DCR
Translation - STM - LTM relationship
Effectors - motor programmes
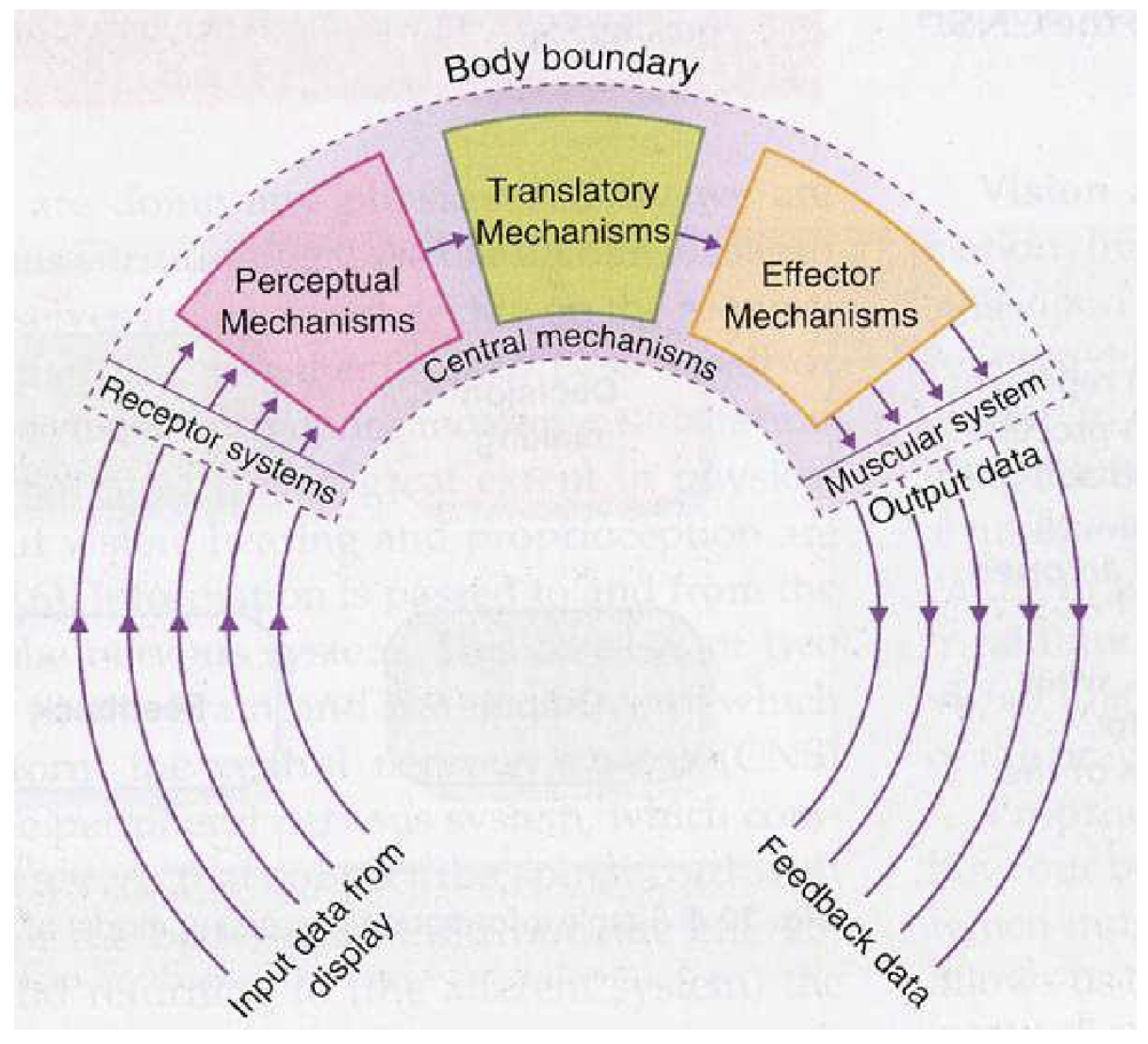
What does Whiting call his 3 stages
Perceptual mechanism
Translatory mechanism
Effector mechanism
Guidance for cognitive
Visual + Verbal in conjunction
Manual = Gain feel
Mechanical = safety