prokaryotes
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
what are the three key parameters of microscopy?
Magnification, Resolution, and Contrast.
What does magnification mean in microscopy?
It refers to the ability to enlarge an image.
What does resolution mean in microscopy?
It refers to the clarity of an image or the ability to distinguish between two close points.
What does contrast mean in microscopy?
It refers to the difference in brightness or color between parts of an image, making structures more visible.
What types of microscopy technologies have evolved since the 1590s?
Light microscopy,
fluorescent microscopy,
super-resolution microscopy,
electron microscopy.
Which type of microscope is best for imaging living specimens?
Light microscope.
What is fluorescent microscopy used for?
To visualize specific compartments or macromolecules.
What is the purpose of super-resolution microscopy?
To image processes smaller than the wavelength of light.
What can electron microscopy visualize?
The smallest cellular structures.
What are prokaryotes?
Single-celled organisms including bacteria and archaea, typically 1–10 μm in diameter with no membrane-bound organelles.
What are the four macromolecules that make up prokaryotic cell structures?
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What is the role of the peptidoglycan cell wall in prokaryotes?
It supports bacterial shape and is located outside the membrane.
What is the function of flagella in prokaryotes?
enable cell motility, allowing cells to move through liquid environments
What are pili and fimbriae?
Short, hollow, thread-like structures help bacteria adhere to surfaces or each other allow DNA exchange via conjugation.
What distinguishes eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles; prokaryotic cells do not.
Why is there a limit to cell size?
diffusion limitations; as cells grow, the surface area to volume ratio decreases, making transport less efficient.
What determines the efficiency of diffusion in cells?
The surface area to volume ratio.
Why are smaller cells more efficient?
They have a more favorable surface area to volume ratio, allowing better diffusion of substances like oxygen.
What else sets a limit on cell size besides diffusion?
Metabolic requirements and the plasma membrane’s ability to regulate substance passage.
Do larger animals like whales have bigger cells or more cells?
More cells, not bigger cells.
What is Gram staining used for?
To distinguish between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria based on cell wall structure.
What characterizes Gram-positive (Gram+) bacteria?
Thick peptidoglycan wall that absorbs purple dye.
What characterizes Gram-negative (Gram−) bacteria?
Thinner peptidoglycan wall covered by an outer membrane; does not absorb purple dye.
Why is the distinction between Gram+ and Gram− important?
It affects antibiotic effectiveness and bacterial classification.
What are phototrophs?
Organisms that obtain energy from sunlight.
What are chemotrophs?
Organisms that obtain energy from chemical compounds.
What are autotrophs?
organisms that can produce their own food from inorganic substances, using energy from sources like sunlight or chemical reactions
What are heterotrophs?
organisms that cannot produce their own food and must obtain nutrients by consuming other organisms or organic matter
What are the three tenets of Cell Theory?
1) Cells are the fundamental units of life.
2) All organisms are composed of cells.
3) All cells arise from preexisting cells.
Who first observed cells and when?
Robert Hooke in 1665 (Micrographia).
Who observed living cells under a microscope in 1682?
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek.
What are the three domains of life?
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
Which domains contain only prokaryotic organisms?
Bacteria and Archaea
What type of organisms are prokaryotes?
Single-celled organisms
Which domains include prokaryotes?
Bacteria and Archaea
What is the typical size range of prokaryotic cells?
1–10 μm in diameter.
Do prokaryotes have membrane-bound organelles?
No
What macromolecules make up prokaryotic cellular structures?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids.
What is peptidoglycan and where is it found?
It supports bacterial shape and is located outside the plasma membrane
What makes up a bacterial cell wall?
Plasma membrane and peptidoglycan
How do Gram+ bacteria appear after staining and why?
They absorb purple dye because they have a thicker peptidoglycan layer
Why don’t Gram- bacteria retain the purple dye?
They have a thin peptidoglycan layer covered by an outer membrane
True or False: Gram- bacterial cell walls contain more peptidoglycan than Gram+ cell walls.
False. Gram+ walls contain more peptidoglycan
What is the shape of cocci bacteria and an example?
Round; e.g., Staphylococcus aureus.
What is the shape of bacilli bacteria and an example?
Rod-shaped; e.g., Pseudomonas aeruginosa
What is the shape of comma-shaped bacteria and an example?
Comma; e.g., Vibrio cholerae
What is the shape of spiral bacteria and an example?
Spiral; e.g., Borrelia burgdorferi.
Can different bacterial shapes be either Gram+ or Gram-?
Yes
What are antibiotics?
Chemicals that inhibit bacterial growth and survival by disrupting essential cell functions.
What does penicillin target in bacteria?
It inhibits transpeptidase, preventing cell wall synthesis.
What are the four essential bacterial pathways targeted by antibiotics?
Cell-wall synthesis or membrane function DNA replication/RNA transcription Translation (protein synthesis)Metabolism
What is a bacterial flagellum
A hair-like appendage that provides motility.
What powers bacterial flagellar motion?
Motor proteins and cellular energy.
What direction of flagellar rotation leads to forward movement?
Counterclockwise
What direction of flagellar rotation leads to tumbling?
Clockwise
Does flagellar motion require cellular energy?
Yes
What method would best study flagellar function in real-time?
Light microscopy to observe movement of mutant vs. wild-type bacteria
What are the functions of pili and fimbriae?
Adhere to each other Adhere to surfaces Form bridges for DNA exchange
What is bacterial conjugation?
The transfer of DNA between bacteria without cell division
What is commonly transferred during bacterial conjugation?
Plasmid DNA carrying traits like antibiotic resistance or virulence
Which experiment demonstrated bacterial genetic transfer?
Griffith’s Experiment.
Are larger animals larger due to bigger cells, more cells, or both?
More cells (not bigger cells).
Why does diffusion limit cell size?
Because it becomes inefficient as surface area to volume ratio decreases.
Which cell has a more favorable surface area to volume ratio, smaller or larger?
Smaller
What limits maximum cell size?
Metabolic requirements and diffusion efficiency
What role does the plasma membrane play in cell size limitation?
It acts as a selective barrier for substance exchange.
What genetic material is used by all living things?
DNA
What is the base unit of all living organisms?
Membrane-bound cells
What structures do all cells use to make proteins
Ribosomes
List key characteristics shared by all living organisms
DNA as genetic material
Membrane-bound cells
Ribosomes
Growth, development, reproduction
Response to environment
Homeostasis
Energy harvesting and processing
Common macromolecular systems suggesting common ancestry
What are unicellular organisms
Organisms made of a single cell, self-sufficient but limited in capability.
What are multicellular organisms?
Organisms made of many specialized cells with distinct functions
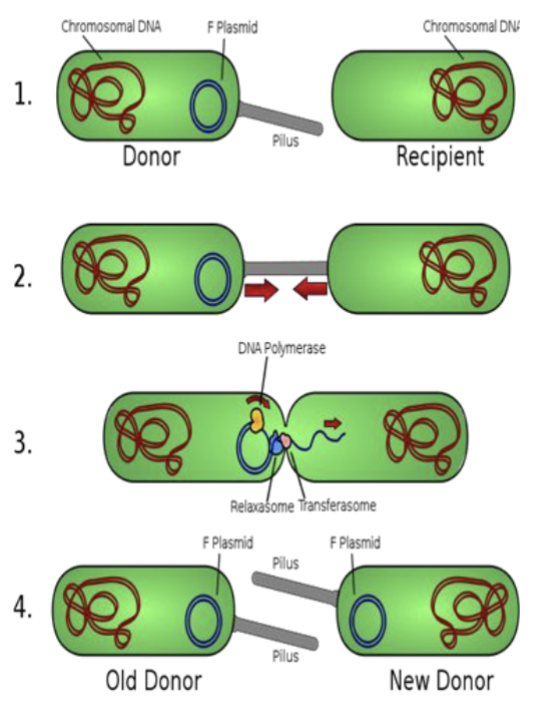
what is this process
horizontal gene transfer