f. 2nd/3rd Tri Path P2
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
microcephaly is defined as HC measuring more than ___ standard deviations from the normal mean for the expected GA
a) 4
b) 2
c) 3
d) 1
b) 2
multiple echogenic foci within the anterior abd of the fetus are indicative of
a) bowel perforation or meconium peritonitis
b) biliary atresia
c) anal or intestinal atresia
d) mesenchymal hamartoma
a) bowel perforation or meconium peritonitis

which can present as unilateral fetal hydronephrosis
a) ureteropelvic junction obstruction
b) posterior urethral valves
c) bladder extrophy
d) cloacal extrophy
a) ureteropelvic junction obstruction

which correctly describes oligohydramnios
a) fluid levels below the 20th percentile for GA
b) AFI <8cm or single pocket <2cm
c) <1cm pocket of fluid found, not containing fetal anatomy/cord
d) AFI <5cm or single pocket <2cm
d) AFI <5cm or single pocket <2cm

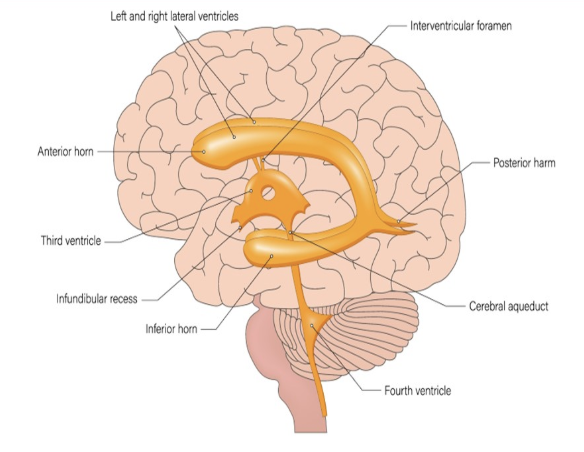
the most common cause of cerebrospinal fluid obstruction + ventriculomegaly
.
a) cerebellar agenesis
b) congenital hydrocephalus
c) aqueductal stenosis
d) dandy walker malformation
c) aqueductal stenosis

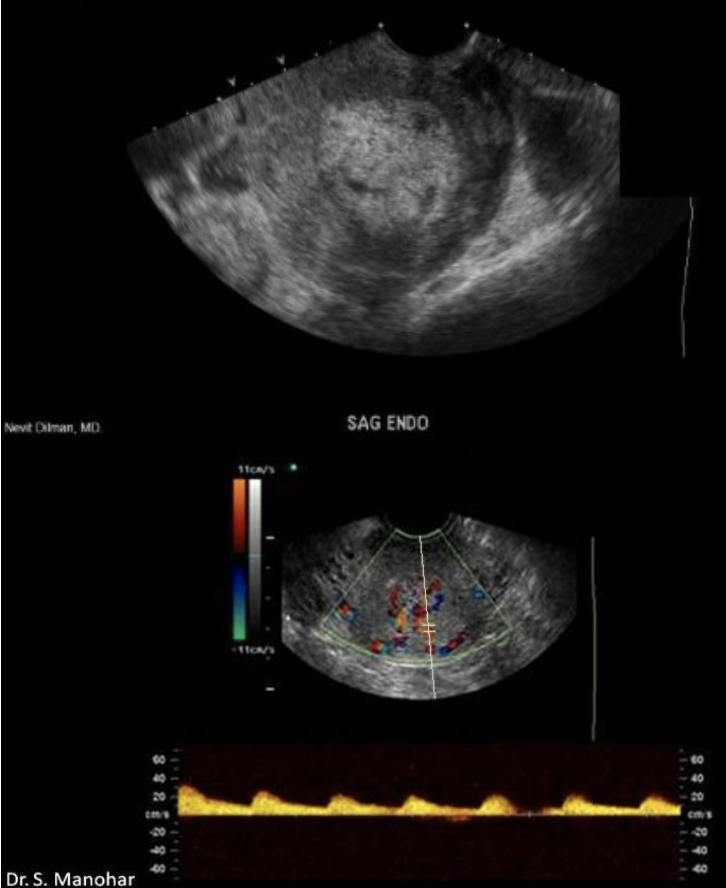
27 yo pregnant pt has bleeding + pain. lab testing shows lower bHCG than reported 2w ago.
a) molar pregnancy
b) endometrial carcinoma
c) endometrial hyperplasia
d) retained products of conception
d) retained products of conception

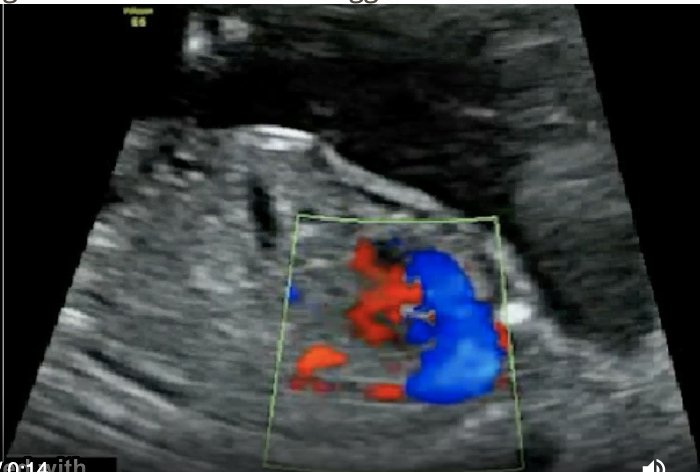
a) congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation
b) pulmonary sequestration
c) diaphragmatic hernia
d) echogenic bowel
b) pulmonary sequestration
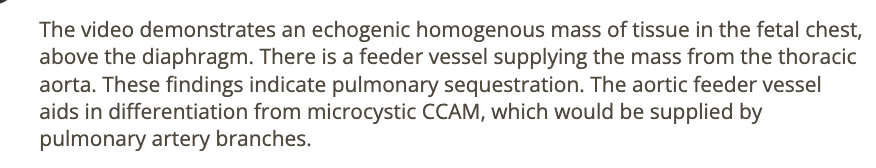
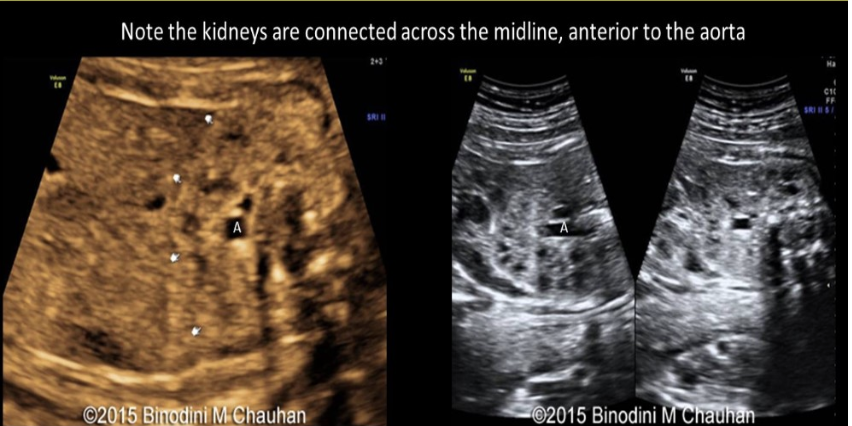
an abn of renal fusion where the lower pole of kidneys are connected across the midline of abd called
a) horseshoe kidney
b) epispadias
c) cross fused renal ectopia
d) persistent cloaca
a) horseshoe kidney

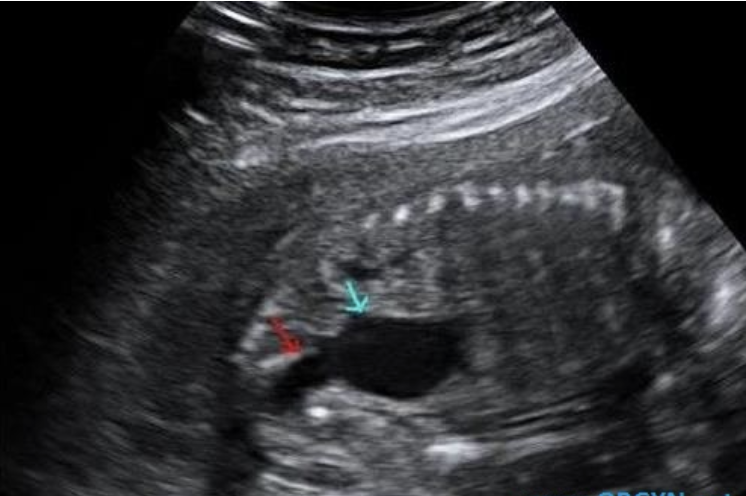
what congenital anomaly is shown
a) renal agenesis
b) duodenal atresia
c) anal atresia
d) posterior urethral valves
d) posterior urethral valves

which is the least likely maternal complication of multifetal pregnancy
a) preeclampsia
b) hydronephrosis
c) renal calculus
d) postpartum hemorrhage
c) renal calculus

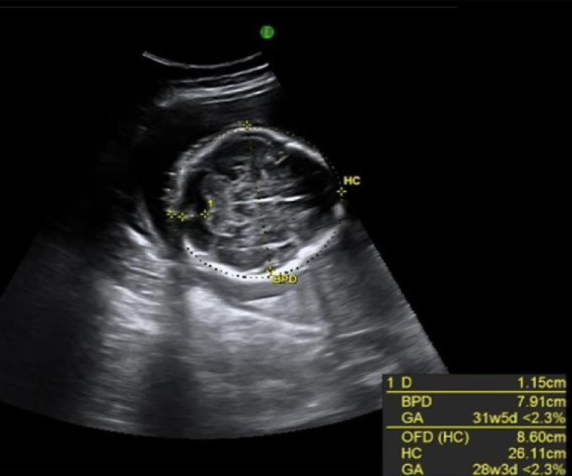
what cranial abn is usually a normal variant but has been assoc w/trisomy 21 + spina bifida
.
a) encephalocele
b) exencephaly
c) dolichocephaly
d) brachycephaly
d) brachycephaly

which is strongly assoc w/supernumerary [3+] vessels in the umbilical cord
.
a) trisomy 18
b) twin to twin transfusion syndrome
c) turner syndrome
d) conjoined twins
d) conjoined twins

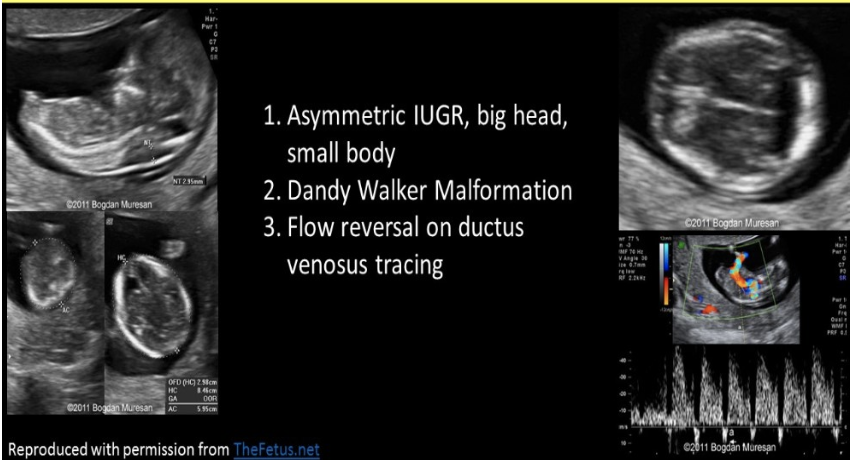
an 18w fetus shows syndactyly, dandy walker malformation, asymmetric IUGR, and flow reversal in ductus venosus.
.
a) trisomy 13
b) triploidy
c) apert syndrome
d) turner syndrome
b) triploidy

![<p>a) twin reversed arterial perfusion sequence [<strong>TRAP</strong>]</p><p>b) twin anemia polycythemia sequence (<strong>TAP</strong>)</p><p>c) a triploidy fetus + normal fetus</p><p>d) vanishing twin syndrome</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/93193faf-e189-4587-9739-07cd68e6222a.png)
a) twin reversed arterial perfusion sequence [TRAP]
b) twin anemia polycythemia sequence (TAP)
c) a triploidy fetus + normal fetus
d) vanishing twin syndrome
a) twin reversed arterial perfusion sequence

which is strongly assoc w/ fetal dysphagia + polyhydramnios
.
a) potter syndrome
b) meckel gruber syndrome
c) ebstein anomaly
d) beckwith wiedemann syndrome
d) beckwith wiedemann syndrome

the fetal structures within an omphalocele are protected by a membrane composed of
a) peritoneum + rectus sheath muscle
b) amnion + rectus sheath muscle
c) amnion + peritoneum
d) peritoneum + retroperitoneum
c) amnion + peritoneum
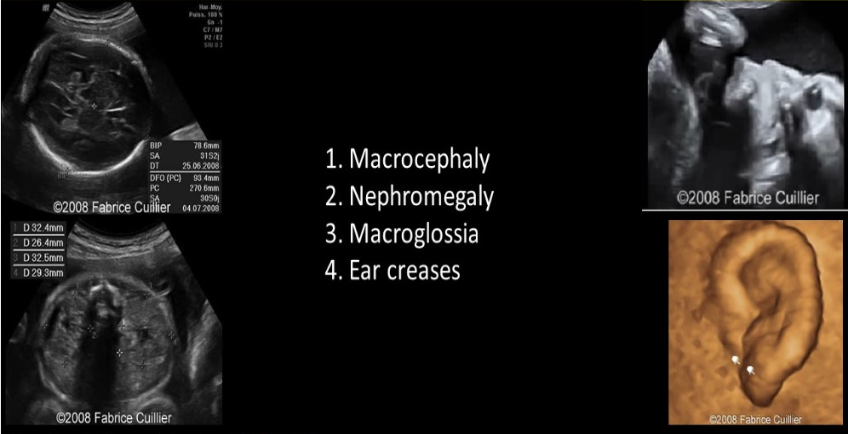
which trisomies has been significant assoc w/choroid plexus cysts after 28w
.
a) 18
b) 21
c) 9
d) 13
a) 18
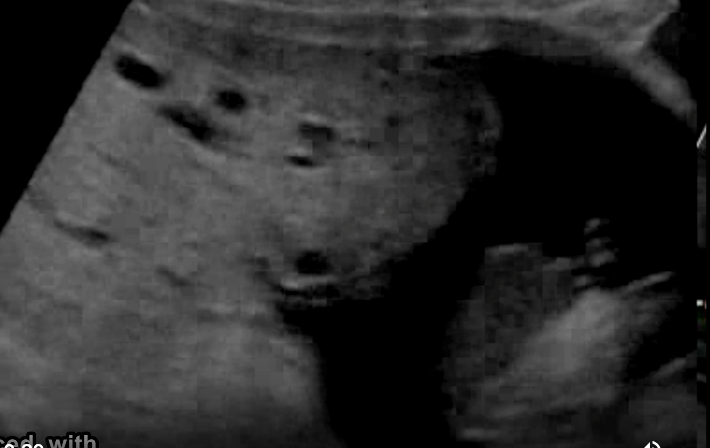
a pregnant pt w/recent acute onset of hypertension, nausea, vomit. she has no pain, cramping, or vaginal bleeding.
.
a prior US exam at 6w shows the pregnancy should now be 17w6d GA.
.
what maternal serum level is abn elevated
.
a) acetylcholinesterase
b) bHCG
c) AFP
d) inhibin A
b) bHCG

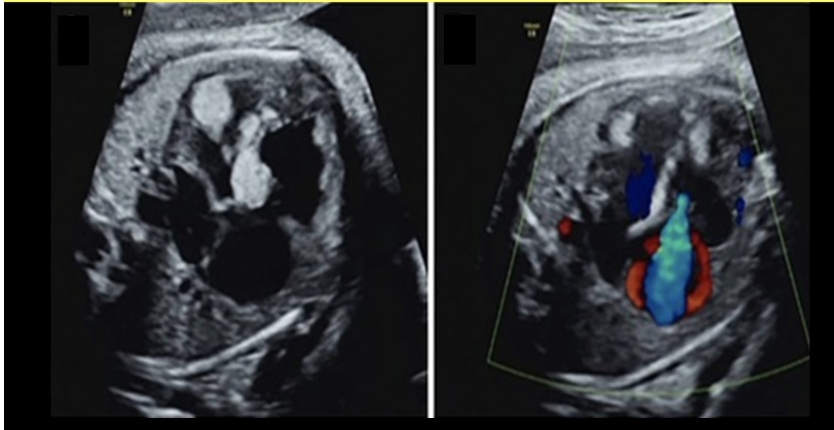
the most common intracardiac mass seen in fetus is
a) myxoma
b) fibroelastoma
c) rhabdomyoma
d) sarcoma
c) rhabdomyoma

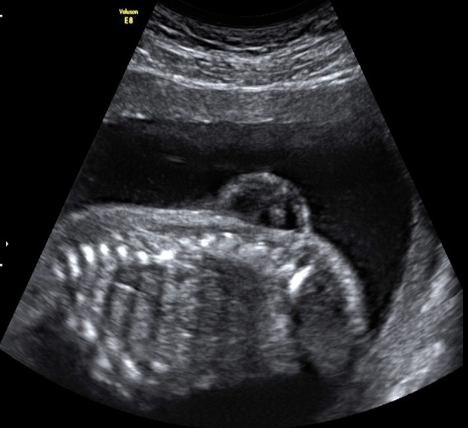
a myelomeningocele refers to
a) herniation of neural tissue through cranial opening
b) herniation of meninges through cranial opening
c) herniation of meninges + neural tissue through vertebral opening
d) herniation of meninges through vertebral opening
c) herniation of meninges + neural tissue through vertebral opening

a fetus w/male genitalia + ovaries would be described as
a) 45XO
b) 46XY intersex
c) ambiguous genitalia
d) 46XX intersex
d) 46XX intersex

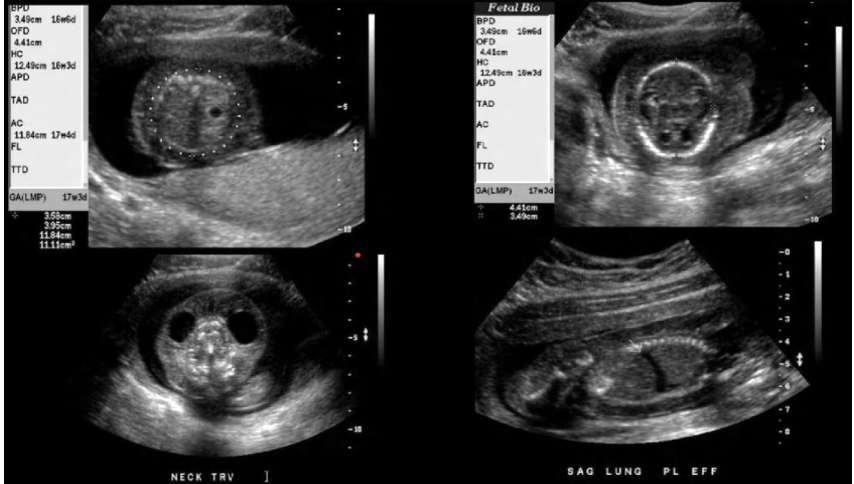
which are signs of fetal hydrops
a) pleural effusion + macrocystic lungs
b) scalp edema + ascites
c) theca lutein cyst + anasarca
d) skin edema + facial clefting
b) scalp edema + ascites

_____ is/are the most common fetal arrhythmia but is clinically insignificant in nearly all cases
a) sinus bradycardia
b) supraventricular tachycardia
c) premature atrial contraction
d) complete heart block
c) premature atrial contraction
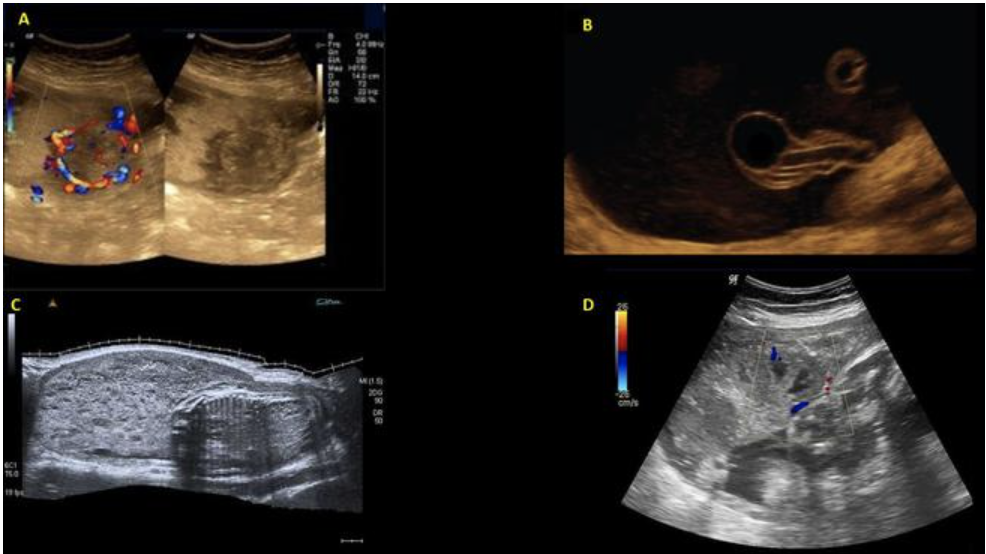
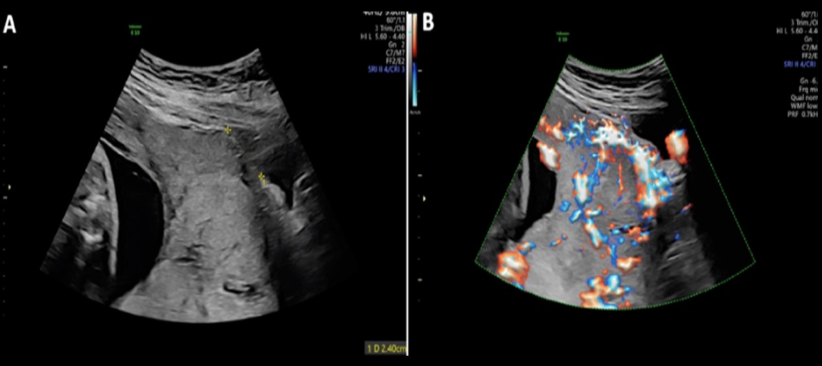
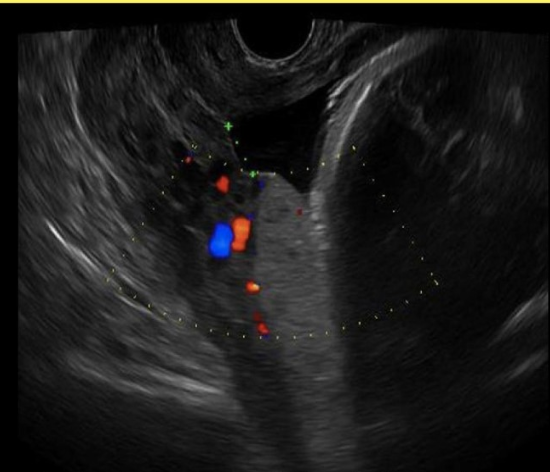
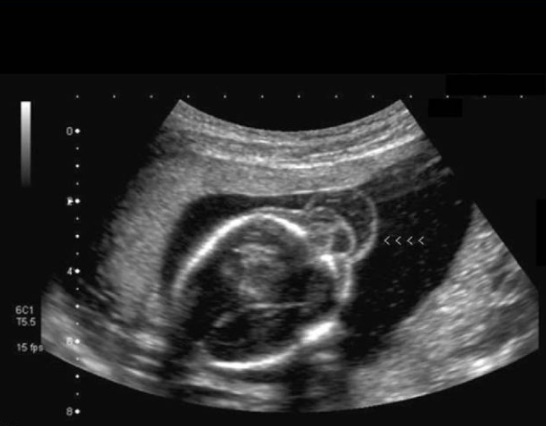
chorioangioma is supected. which image shows it
a) A
b) B
c) C
d) D
a) A

a fetus has pleural effusion, anasarca [skin edema >5mm], and an enlarged liver. which is most likely cause?
.
a) maternal HTN
b) erythroblastosis fetalis
c) ovarian vein thrombosis
d) maternal diabetes
b) erythroblastosis fetalis

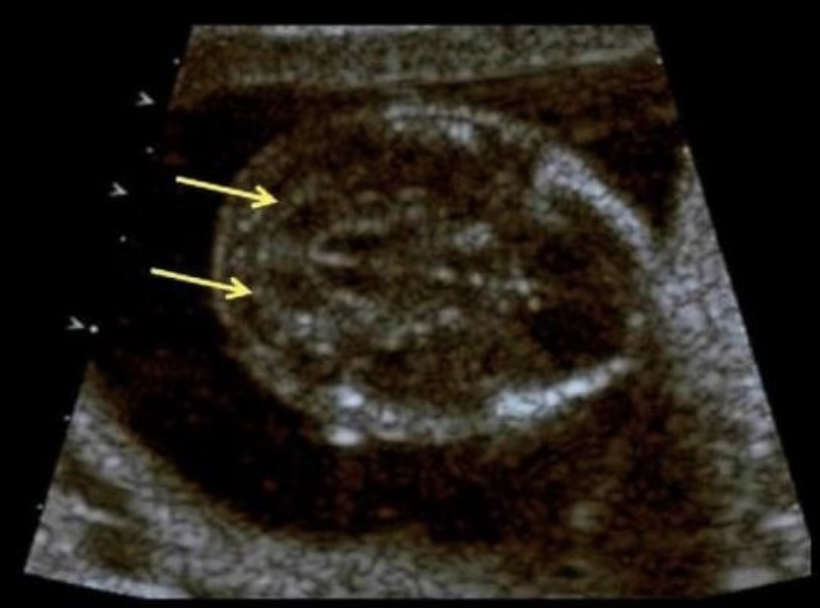
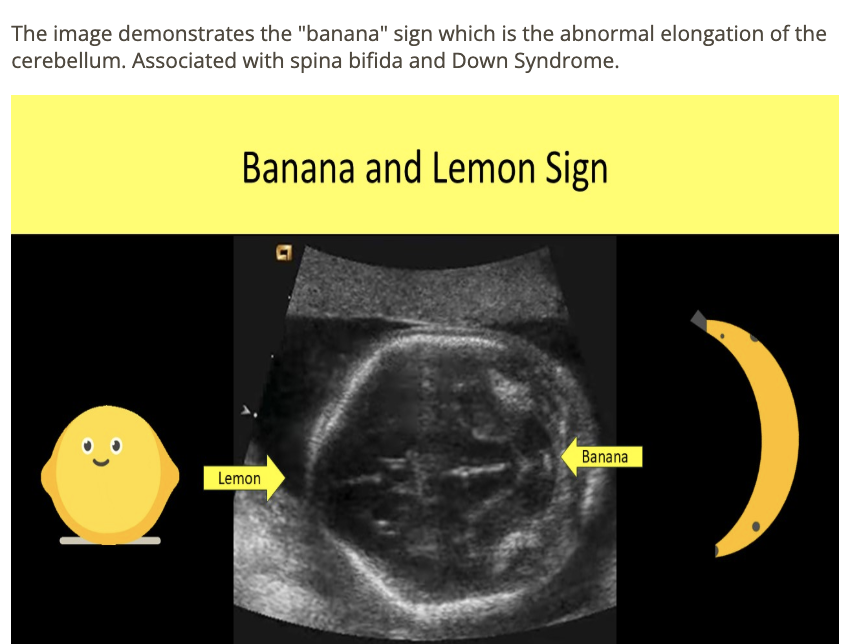
the cerebellum shows what sono sign
a) fruit salad
b) banana sign
c) lemon sign
d) string of pearls sign
b) banana sign
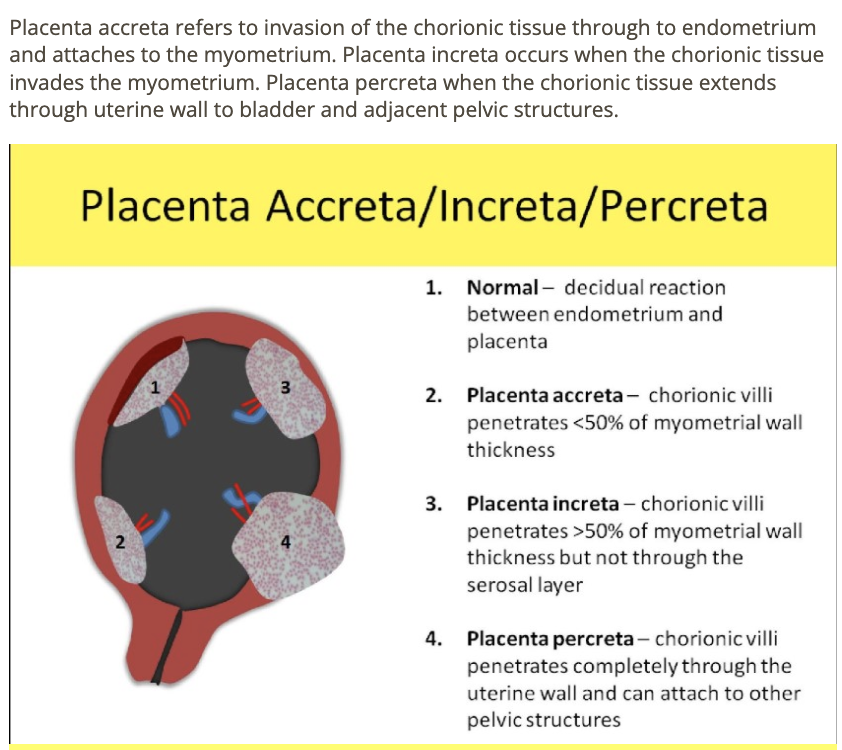
which is described as invasion of placental chorionic villus through myometrium + uterine wall
a) placenta increta
b) adenomyosis
c) placenta accreta
d) placenta percreta
d) placenta percreta
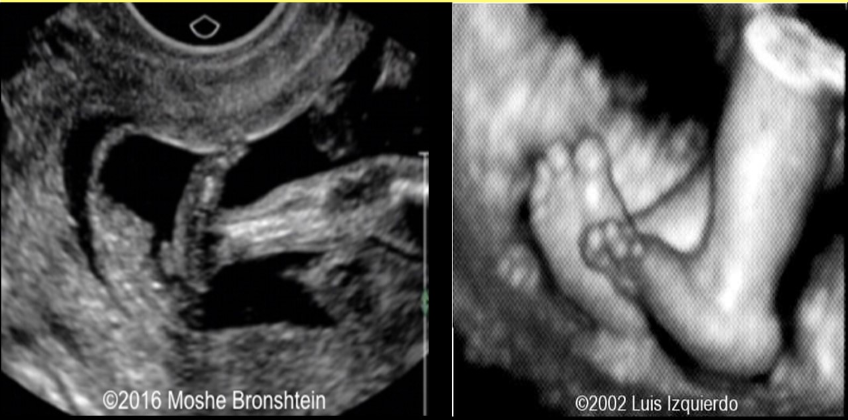
what pedal abn is assoc w/trisomy 13 + 18
a) talipes equinovarus
b) polydactyly
c) club foot
d) rocker bottom foot
d) rocker bottom foot
what are the common fetal findings when the mother has a hx of HIV
a) macrocephaly, macroglossia, renal abn
b) severe cardiac defects
c) IUGR, hepatomegaly
d) polyhydramnios, anencephaly
c) IUGR, hepatomegaly
what type of CCAM is this
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
c) 3

most cases of duodenal atresia [double bubble] are assoc w/
.
a) polyhydramnios + symmetrical growth restriction
b) oligohydramnios + asymmetric growth restriction
c) trisomy 13
d) turner syndrome
.
poly vs oli hydramnios - 1 is renal, 1 is GI related
a) polyhydramnios + symmetrical growth restriction

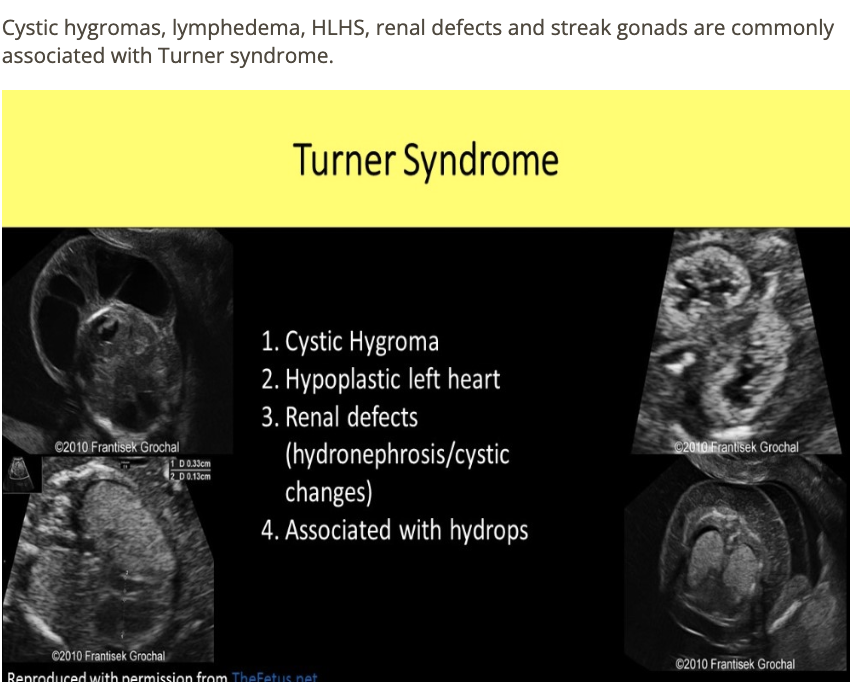
which is NOT commonly seen with turner syndrome
a) renal agenesis
b) duodenal atresia
c) hypoplastic left heart
d) streak gonads
b) duodenal atresia
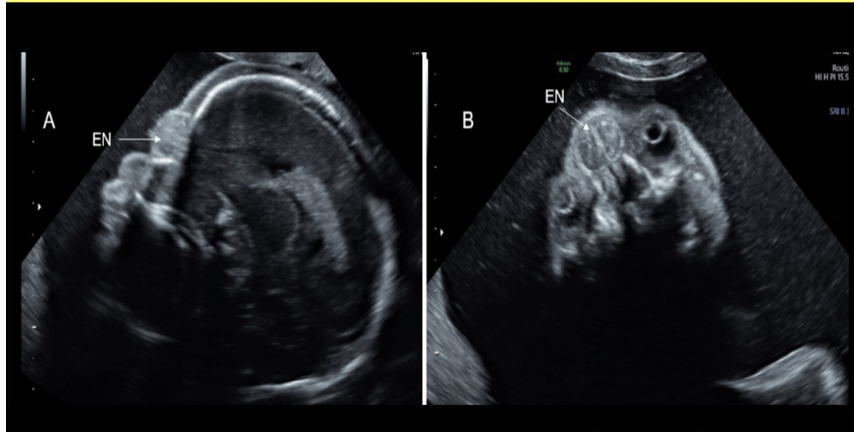
hypertelorism is most commonly caused by
a) spina bifida
b) posterior encephalocele
c) anterior encephalocele
d) cystic hygroma
c) anterior encephalocele
which trisomy is most commonly seen w/micrognathia
a) 18
b) 13
c) 21
d) 9
a) 18
while scanning fetal cord insertion on a 15w fetus,
.
a small herniation of the fetal bowel is seen in the base of the cord
.
a) after 12w, this is omphalocele
b) after 12w, this is gastroschisis
c) this is a normal finding + should resolved by 16w
d) an allantoic cyst of the umbilical cord, normal variant until 16w
a) after 12w, this is omphalocele
which abn is considered the most severe form of a twin to twin transfusion
a) acrania
b) holoprosencephaly
c) conjoined twins
d) acardia
d) acardia

which type of placenta previa is defined as placement of the placental tip within 2cm of crossing the internal os
.
a) partial previa
b) low lying placenta
c) velamentous previa
d) vasa previa
b) low lying placenta

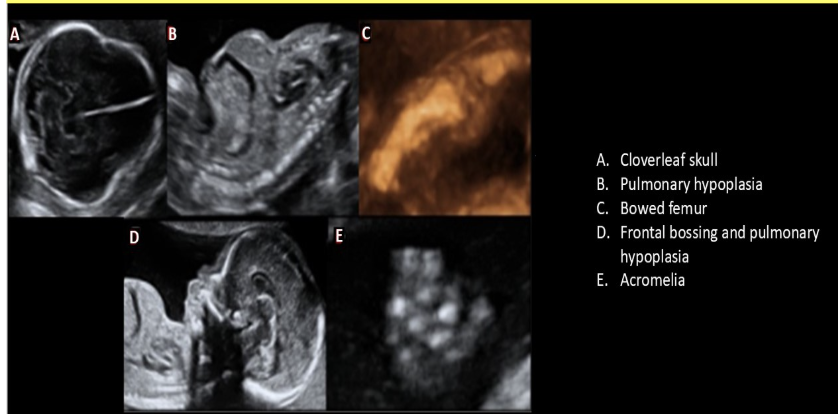
a clover-leaf skull is most commonly assoc w/
a) club foot
b) spina bifida
c) achondrogenesis
d) thanatophoric dysplasia
d) thanatophoric dysplasia

a midline facial cleft is most commonly assoc w/what intracranial abn
a) hydranencephaly
b) dandy walker malformation
c) hydrocephalus
d) holoprosencephaly
d) holoprosencephaly
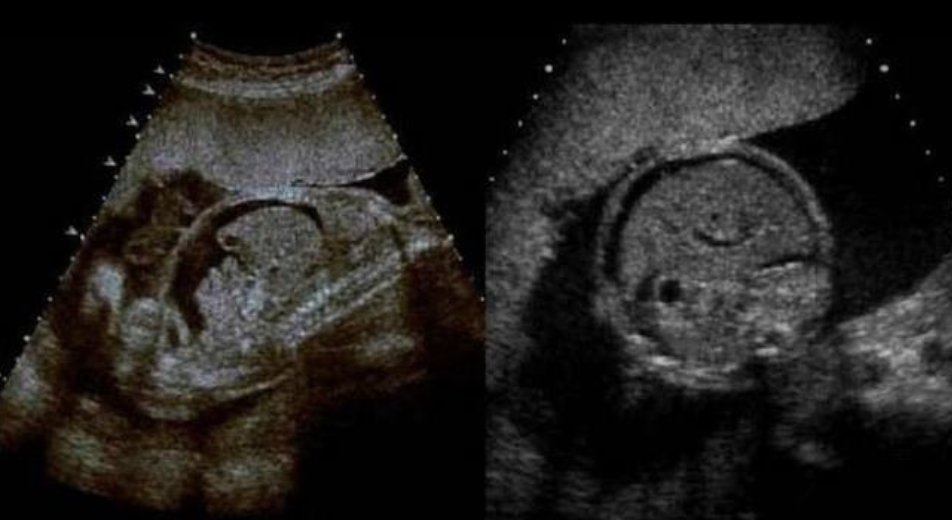
a) fetal ascites + skin edema of the abd
b) fetal ascites + pleural effusions
c) skin edema of fetal abd
d) fetal ascites
d) fetal ascites

which pedal abn is commonly seen w/spina bifida
a) polydactyly
b) splayed digits
c) talipes equinovarus [club foot]
d) rocker bottom foot
c) talipes equinovarus

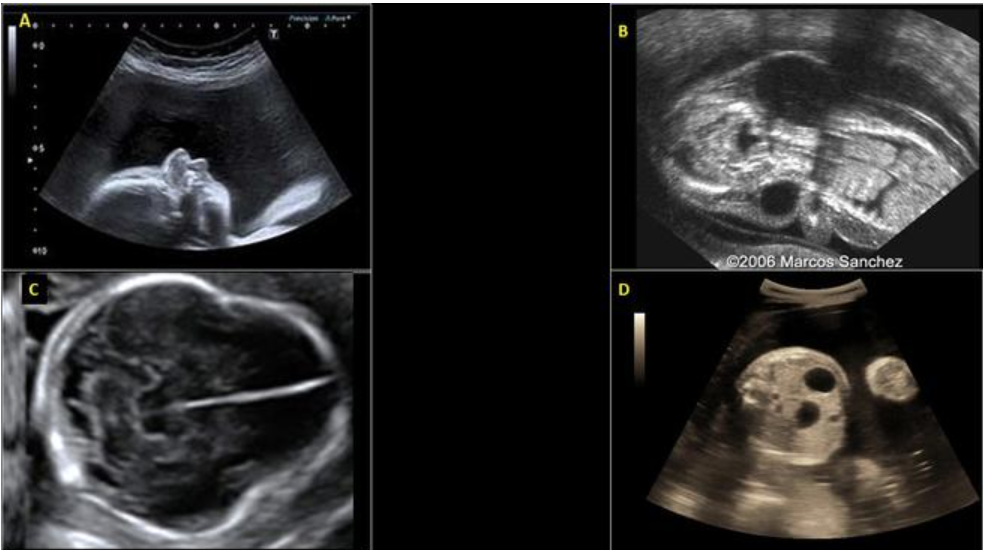
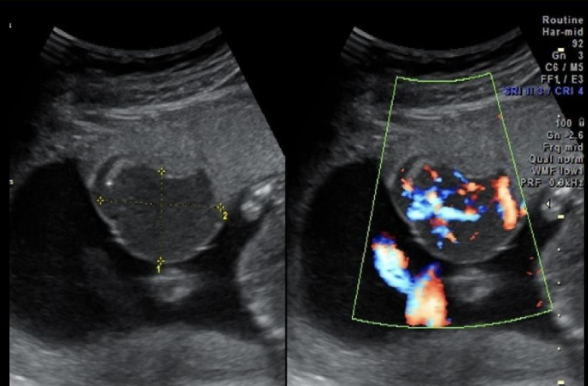
which image is turner syndrome
a) A
b) B
c) C
d) D
b) B

which has the greatest risk of maternal death
a) lupus
b) preeclampsia
c) gestational diabetes
d) eclampsia
d) eclampsia

![<p>an abd wall abn that occurs w/abd contents <strong>herniating <em>through abd wall</em> [as in not covered]</strong>layers outside the fetus is</p><p>.</p><p>a) allantoic cyst</p><p>b) omphalocele</p><p>c) gastroschisis</p><p>d) cloacal extrophy</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fd44542a-011f-4c00-afe9-6ec2cde36bed.png)
an abd wall abn that occurs w/abd contents herniating through abd wall [as in not covered]layers outside the fetus is
.
a) allantoic cyst
b) omphalocele
c) gastroschisis
d) cloacal extrophy
c) gastroschisis

the majority of encephalocele are located in the ___ region of the cranium
a) occipital
b) temporal
c) frontal
d) parietal
a) occipital
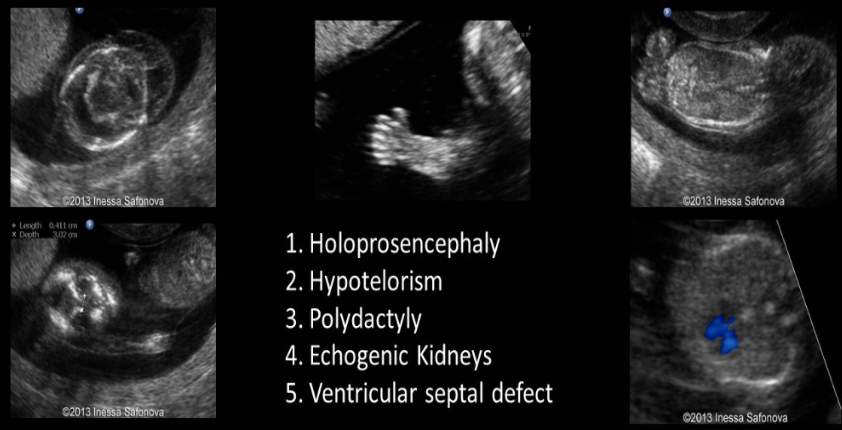
holoprosencephaly is commonly assoc w
a) noonan
b) trisomy 13
c) turner
d) trisomy 21
b) trisomy 13

which type of osteogenesis imperfecta has the poorest prognosis
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
b) 2

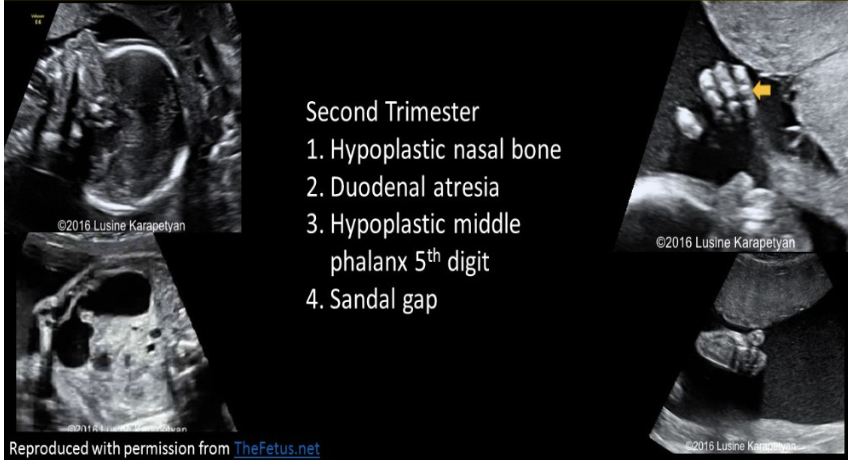
which type of aneuploidy is most assoc w/shortened middle phalanx of the 5th digit
a) trisomy 21
b) triploidy
c) trisomy 18
d) trisomy 13
a) trisomy 21

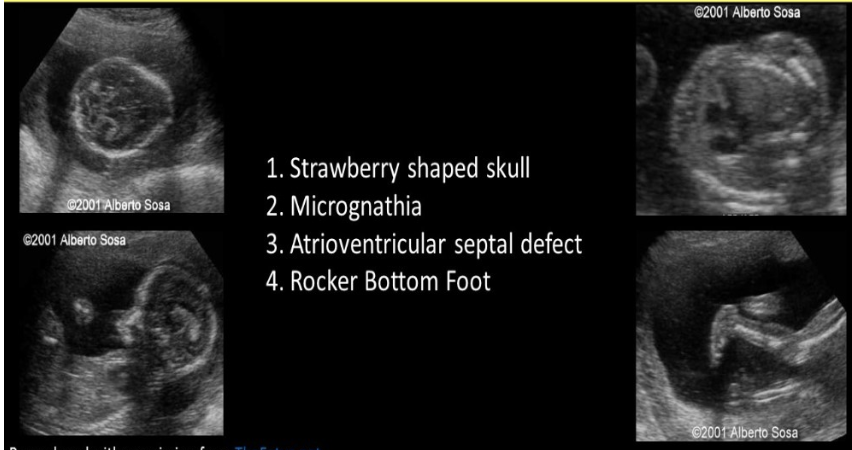
which trisomy is most commonly assoc w/strawberry shaped fetal skull
a) 9
b) 18
c) 13
d) 21
b) 18

____ describes a thoracic defect where the heart has herniated outside the chest wall
a) allantoic cyst
b) ectopia cordis
c) cloacal extrophy
d) omphalocele
b) ectopia cordis

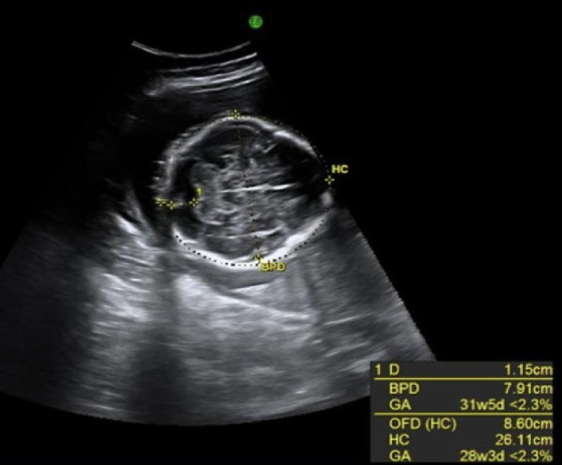
which describes a rounded head w/cephalic index >85%
a) bradycephaly
b) dolicephaly
c) brachycephaly
d) microcephaly
c) brachycephaly

which skeletal abn is defined by the presence of webbing between the digits
a) clinodactyly
b) syndactyly
c) micromelia
d) polydactyly
b) syndactyly

parenti-franco [type 1, auto recessive] and langer-saldino [type 2, auto dominant] are what types of skeletal anomaly
.
a) achondrogenesis
b) campomelic dysplasia
c) thanatophoric dysplasia
d) osteogenesis imperfecta
a) achondrogenesis

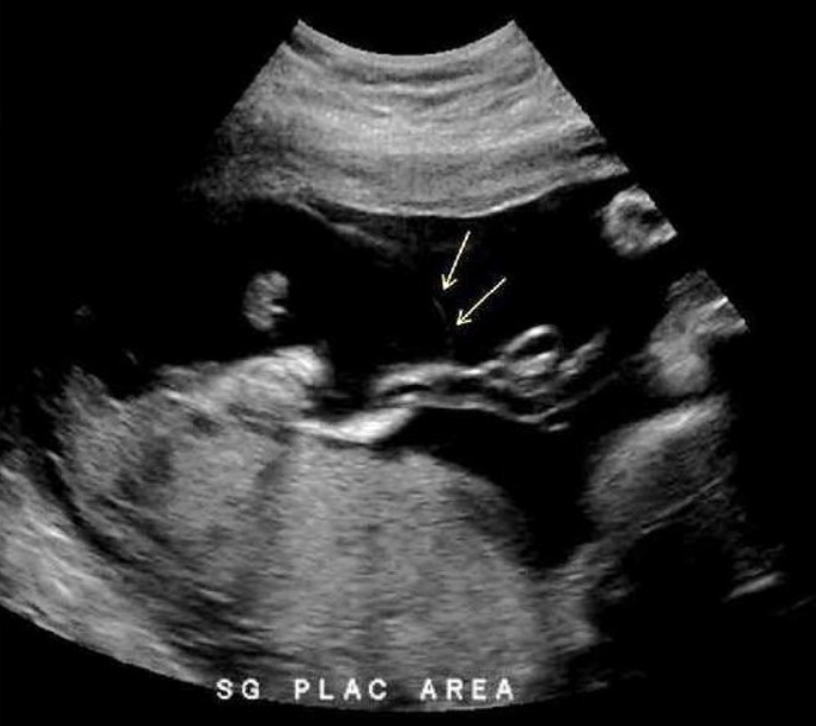
a) umbilical cord cyst
b) placental abruption
c) chorioangioma
d) vasa previa
a) umbilical cord cyst

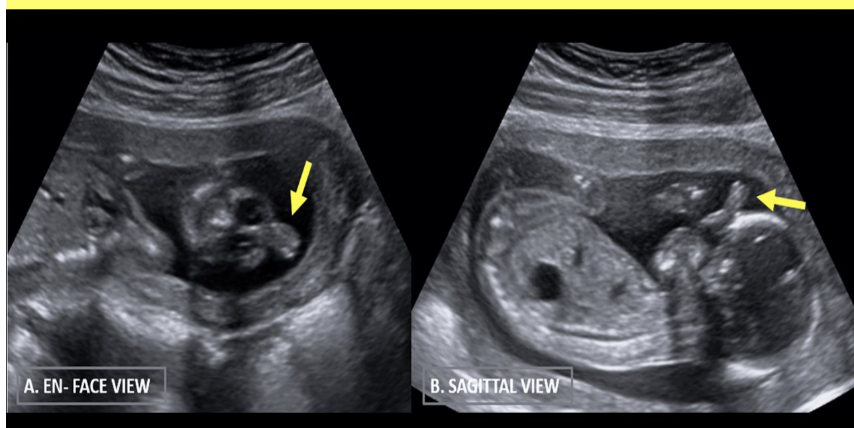
which describes as an abn homogenous, soft tissue mass usually protruding from the anterior cranium or face w/assoc arhinia
a) teratoma
b) anostomia
c) proboscis
d) epidermal cyst
c) proboscis
all are signs of fetal demise except
a) scalp edema
b) meckel sign
c) debris in amniotic fluid
d) spalding sign
b) meckel sign
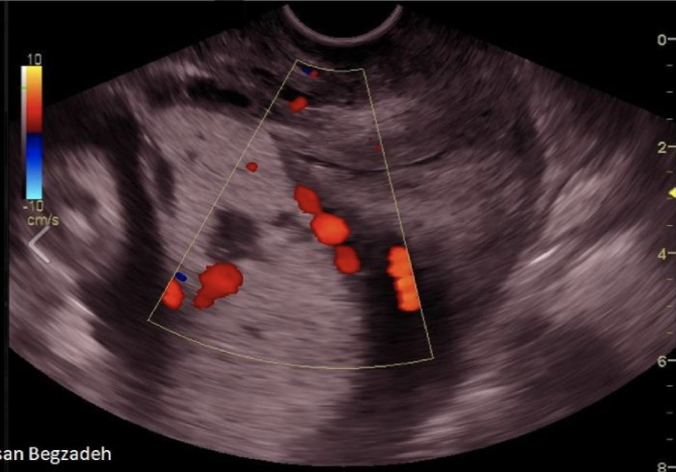
a pt has 33w gestation w/recent onset intermittent bleeding that is bright red. she does not have any associated pain or cramping
.
a) placenta previa
b) placental abruption
c) premature rupture of membranes
d) placenta accreta
a) placenta previa

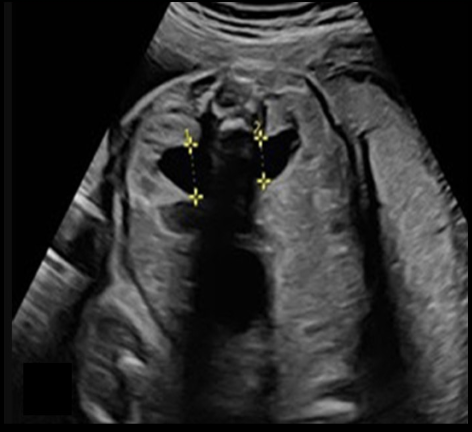
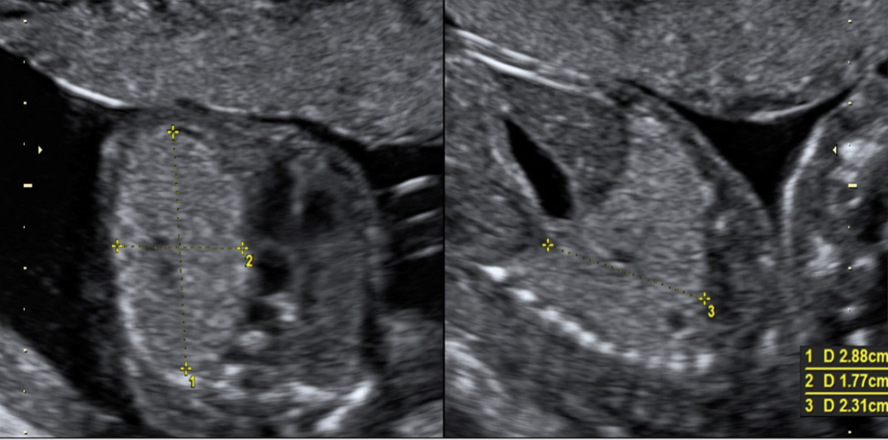
when fetal hydronephrosis is suspected, how is it properly documented by US
.
a) coronal image of both kidneys, measure minimum diameter of dilation
b) transverse image w/fetal spine at 12 or 6 o’clock, measure the minimum diameter of dilation
c) transverse image w/fetal spine at 9 or 3 o’clock, measure maximum diameter of dilation
d) transverse image w/fetal spine at 12 or 6 o’clock, measure the maximum diameter of dilation
d) transverse image w/fetal spine at 12 or 6 o’clock, measure the maximum diameter of dilation

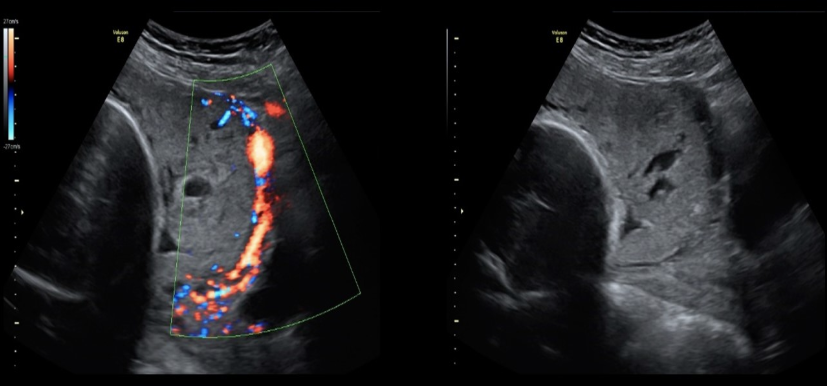
which is described as invasion of the placental chorionic villus “deep” into the uterine myometrium
.
a) placenta increta
b) placenta percreta
c) placenta accreta
d) placenta myocreta
a) placenta increta
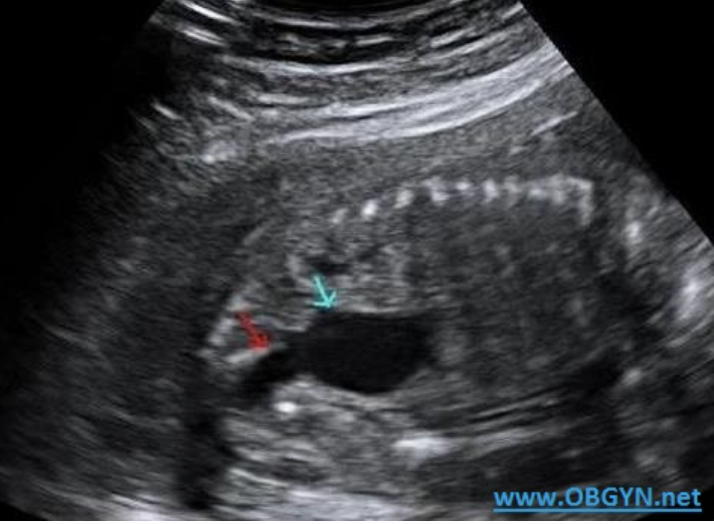
a) dilated urinary bladder
b) cystic hygroma
c) double bubble
d) normal fetal abd/pelvis
a) dilated urinary bladder

which is most suggestive of holoprosencephaly
a) bilateral cleft lip
b) ethmocephaly [midline facial defects]
c) promient falx cerebri
d) bilateral cleft palate
b) ethmocephaly

which defines foreshortening of proximal long bones (femur + humerus)
a) achondroplasia
b) rhizomelia
c) micromelia
d) acromelia
b) rhizomelia

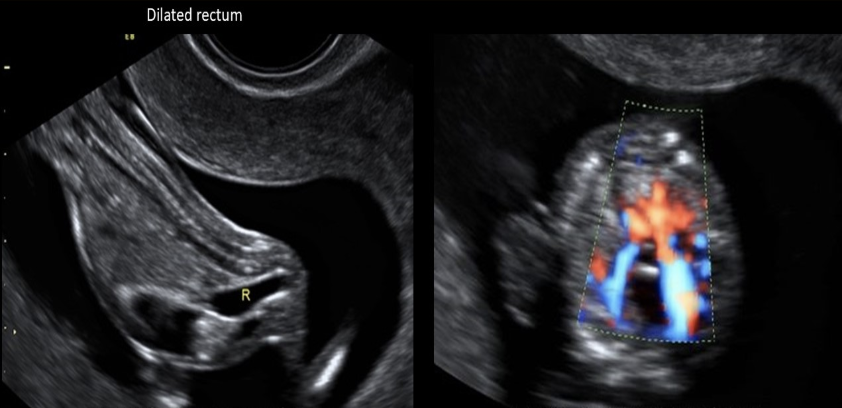
a dilated fetal rectum should raise strong suspicion of
a) posterior urethral valves
b) cystic fibrosis
c) anal atresia
d) jejunal atresia
c) anal atresia

omphaloceles are assoc w/all except
a) cardiac abn
b) decreased AFP
c) chromosomal abn
d) advanced maternal age
b) decreased AFP

which types of placenta previa is defined as placental vessels crossing the internal os
a) velamentous previa
b) vasa previa
c) partial previa
d) marginal previa
b) vasa previa

pentalogy of cantrell consists of a
sternum defect
diaphragm defect
omphalocele
intracardiac anomalies
and ____
.
a) renal agenesis
b) ectopia cordis
c) club foot
d) bladder extrophy
b) ectopia cordis
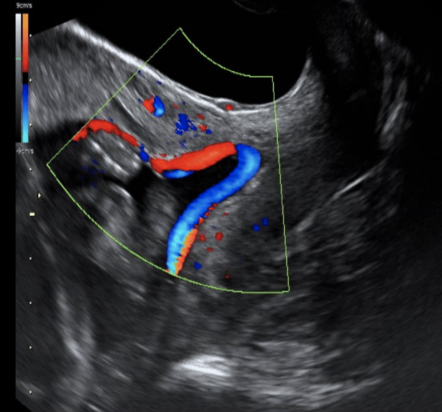
which describes a hypoechoic vascular mass adjacent to the cord insertion into the placenta
a) choriocarcinoma destruens
b) chorioangioma
c) placental lake
d) placenta accreta
b) chorioangioma

the most common type of conjoined twins is
a) craniopagus
b) omphalopagus
c) thoracopagus
d) pyopagus
c) thoracopagus
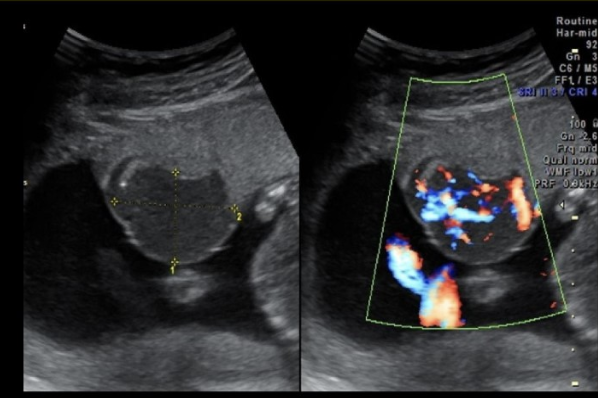
which is assoc w/polyhydramnios
a) premature rupture of membranes
b) chorioangioma
c) renal hypoplasia
d) renal agenesis
b) chorioangioma

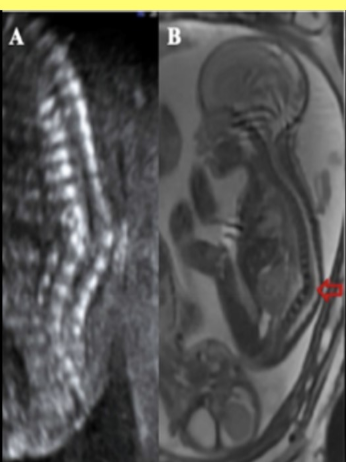
which usually requires serial exams in the 2nd + 3rd trimester to make an accurate dx
a) kyphosis
b) corrected transposition of great arteries
c) complete transposition of great arteries
d) omphalocele
a) kyphosis

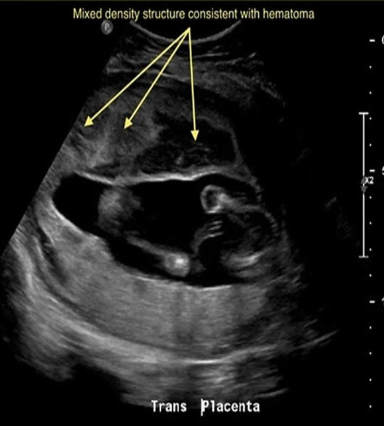
a pt has 36w gestation w/acute onset of pain + bright red bleeding. she had 2 prior scans that were normal. what is the most common cause for the acute symptoms
a) placenta accreta
b) placenta abruption
c) placenta percreta
d) placenta previa
b) placenta abruption

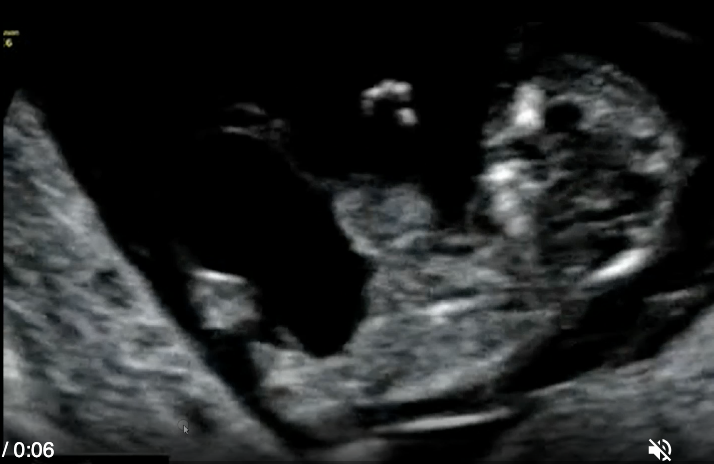
this is a routine 1st trimester scan. this shows
a) omphalocele + ectopia cordis
b) cloacal extrophy
c) normal midgut herniation
d) vanishing twin syndrome
a) omphalocele + ectopia cordis

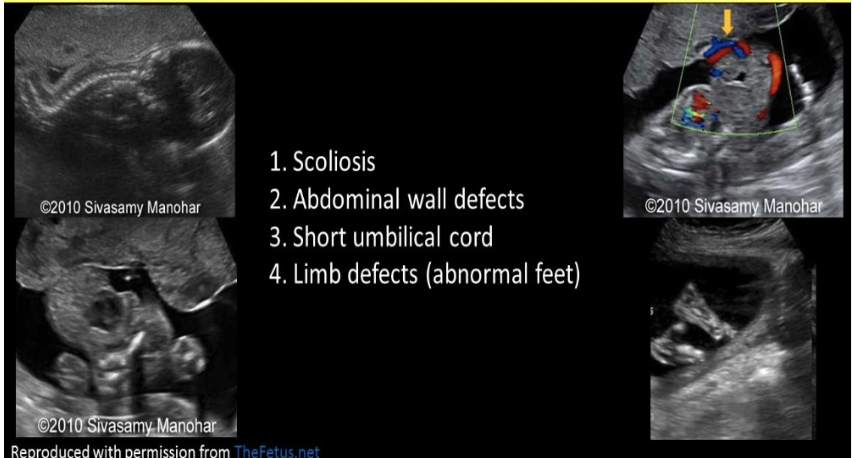
you identify a facial cleft, scoliosis, gastroschisis, and a very short or absent umbilical cord on a 25w fetus
.
a) tetralogy of fallot
b) trisomy 21
c) shone complex
d) limb-wall-body complex
d) limb-wall-body complex

the most common cause of fetal bladder rupture is
a) posterior urethral valves
b) ureterocele
c) urethral calculi
d) renal calculi
a) posterior urethral valves

which intracranial anomalies is most commonly assoc w/fetal hydrops, ascites, and congestive heart failure
a) schizencephaly
b) holoprosencephaly
c) intracranial bleed
d) vein of galen aneurysm
d) vein of galen aneurysm

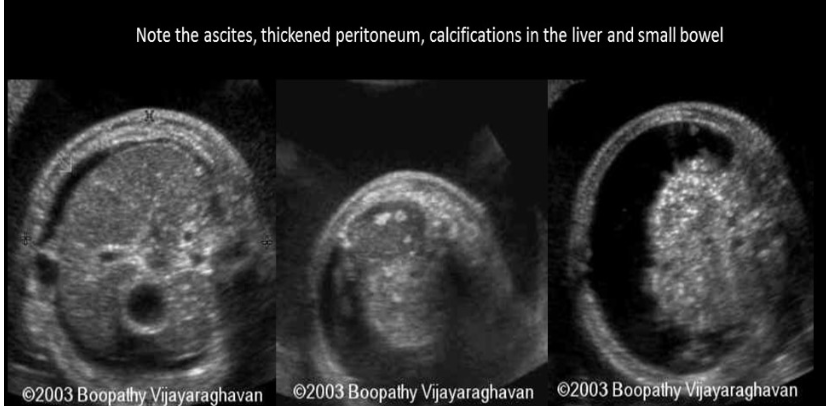
a calcification in the liver is commonly assoc w
a) ambiguous genitalia
b) umbilical vein thrombosis
c) meconium peritonitis
d) renal calculi
c) meconium peritonitis

Asherman syndrome is related to what 2nd trimester OB finding
.
a) uterine synechia
b) limb body stalk
c) skeletal dysplasia
d) increased thickness of nuchal skin fold
a) uterine synechia

which describes the placenta in a fetus w/triploidy
a) small, atrophic, and malformed
b) AP thickness >4cm
c) AP thickness <1.5cm
d) contains 5+ placental lakes
b) AP thickness >4cm
which defines the foreshortening of the bones of hands + feet
a) acromelia
b) micromelia
c) rhizomelia
d) mesomelia
a) acromelia

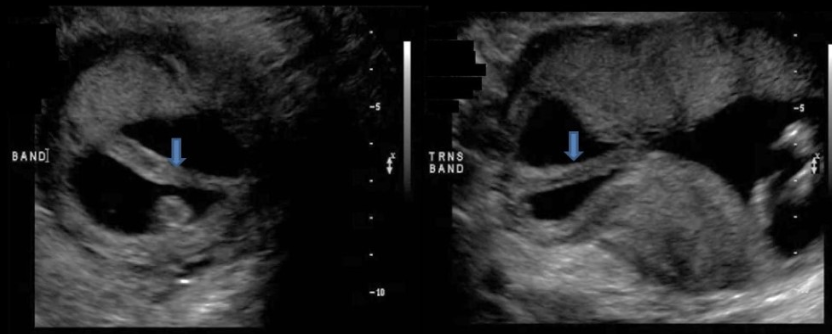
the sono look of hydranencephaly is
.
a) the cerebellum is usually absent or malformed w/enlarged cisterna magna
b) fluid filled sacs of cerebrospinal fluid in cranial cavity, varying amounts of tissue may remain as atrophy + necrosis occurs
c) an abn brain stem is usually identified w/cisterna magna <2mm
d) single large c-shaped ventricle is present
b) fluid filled sacs of cerebrospinal fluid in cranial cavity, varying amounts of tissue may remain as atrophy + necrosis occurs

the autosomal recessive genetic disorder that is associated w/meconium ileus + fetal bowel obstruction is
a) multicystic kidney disease
b) cystic fibrosis
c) erythroblastosis fetalis
d) polycystic kidney disease
b) cystic fibrosis
which describes foreshortened radius, ulna, tibia, and fibula
a) micromelia
b) acromelia
c) mesomelia
d) rhizomelia
c) mesomelia

bilaterally enlarged, echogenic fetal kidneys w/normal bladder is
a) renal failure
b) autosomal dominant polycystic disease
c) multicystic dysplastic kidney disease
d) autosomal recessive polycystic disease
b) autosomal dominant polycystic disease
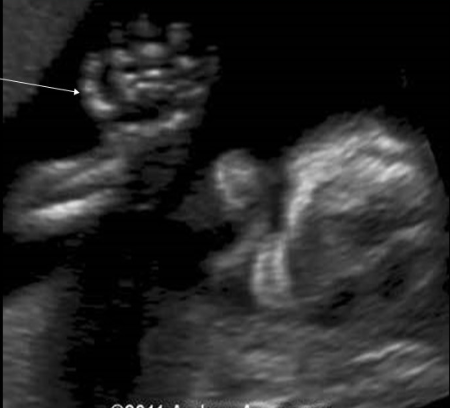
which skeletal abn is defined by the arching/curving of 4th/5th digits toward the thumb, along the axis of palm curvature
a) polydactyly
b) syndactyly
c) clinodactyly
d) rocker bottom foot
c) clinodactyly

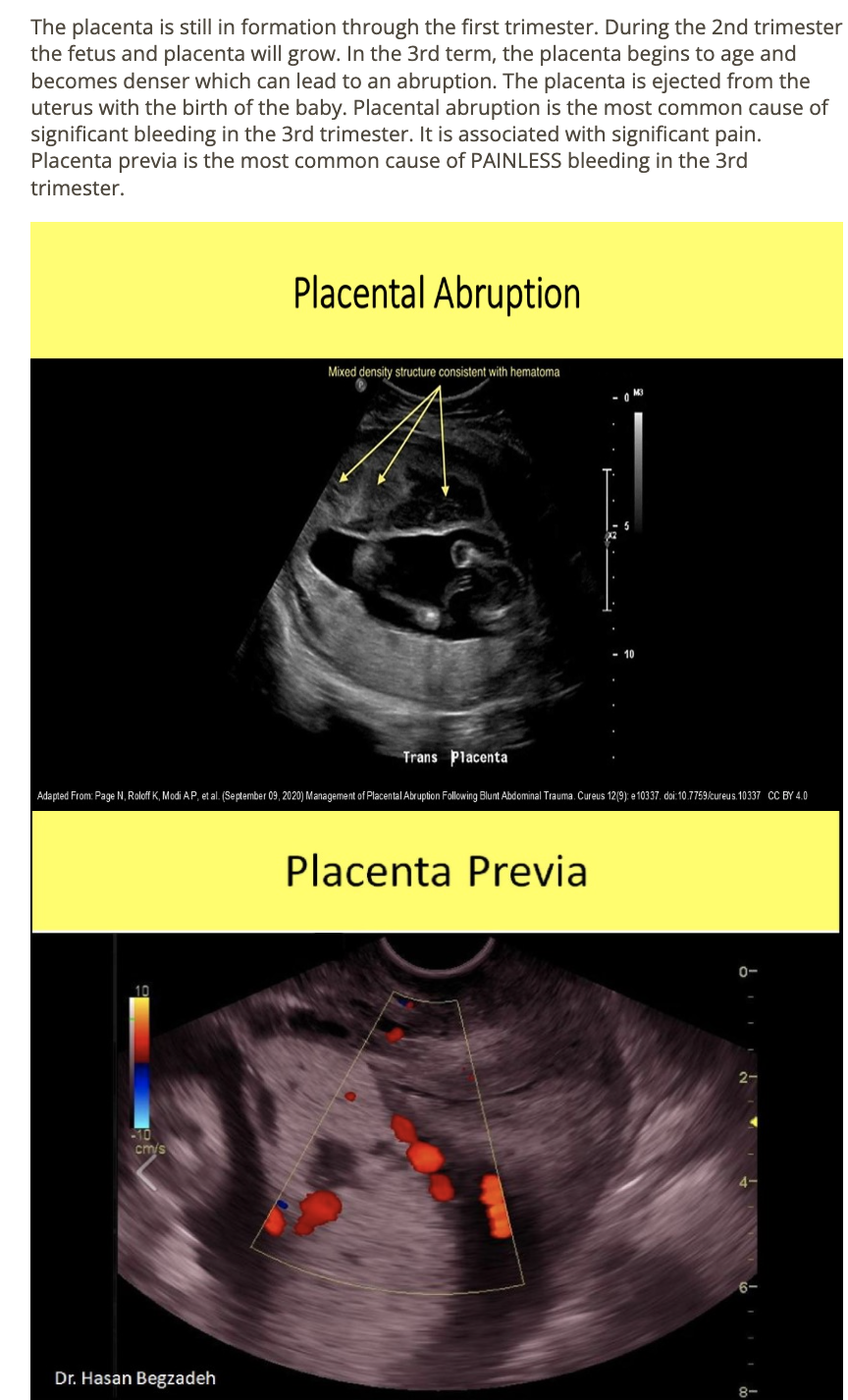
_____ is the most common pathologic cause of significant 3rd trimester bleeding
.
_____ is the most common cause of painless 3rd trimester bleeding
.
a) placental abruption, placenta previa
b) placental previa, placental abruption
c) placental percreta, placenta accreta
d) placenta accreta, placenta percreta
a) placental abruption, placenta previa
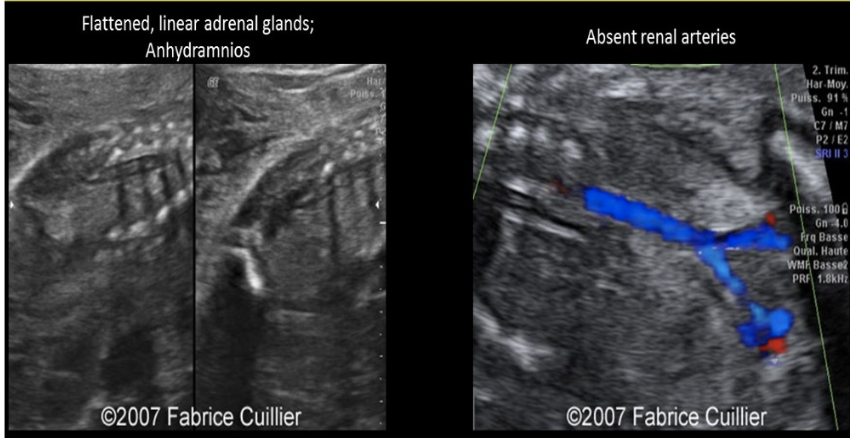
which is assoc w/ oligohydramnios/anhydramnios
.
a) chorioangioma
b) duodenal atresia
c) potter syndrome
d) twins
c) potter syndrome

while scanning the umbilical cord of a 28w gestation, the cord appears abn thickened but contains vessels of normal size + number
a) fetal HTN
b) excessive wharton jelly in the cord
c) placental hypertension
d) flow reversal in the umbilical vein causing cord edema
b) excessive wharton jelly in the cord

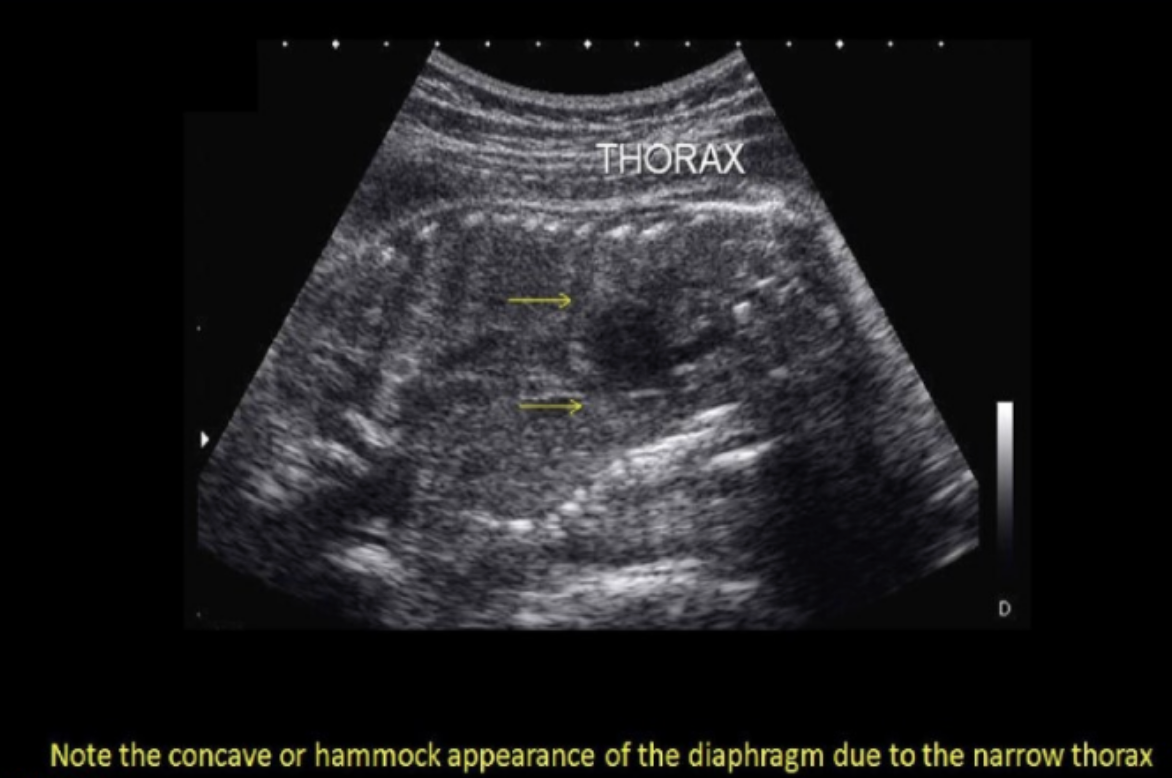
if the radiologist suspects potter syndrome + requests that you perform a thoracic circumference. how will this measurement assist in the dx? Potter syndrome usually shows
.
a) cardiomegaly + diaphragmatic hernia, which will increase the size of thoracic cavity
b) pulmonary hyperplasia, which leads to enlarged thorax
c) a narrow thorax due to acardia
d) a bell-shaped thorax that is much more narrow than the abd cavity
d) a bell-shaped thorax that is much more narrow than the abd cavity

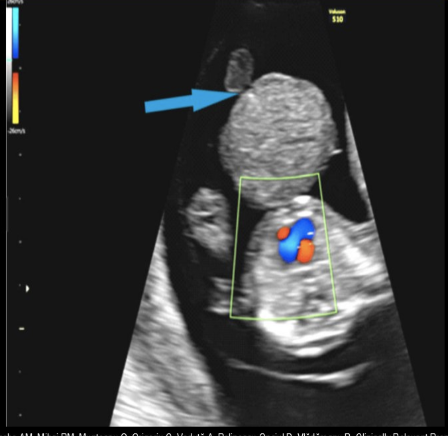
an abd wall defect where the abd contents herniate into the base of umbilical cord is called
a) allantoic cyst
b) omphalocele
c) gastroschisis
d) marginal cord insertion
b) omphalocele

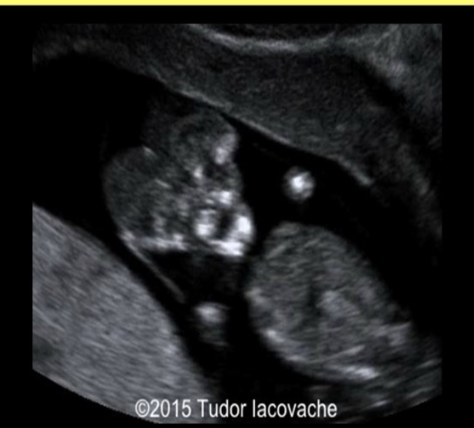
during a fetal head scan of a 16w fetus, the calvarium is found to be absent
.
cerebral tissue is there but has an irregular appearance. this is
.
a) dandy walker malformaiton
b) encephalocele
c) arhinia
d) acrania
d) acrania

streak gonads + infertility are assoc w/what fetal syndrome
a) noonan syndrome
b) holt oram syndrome
c) edward syndrome
d) turner syndrome
d) turner syndrome

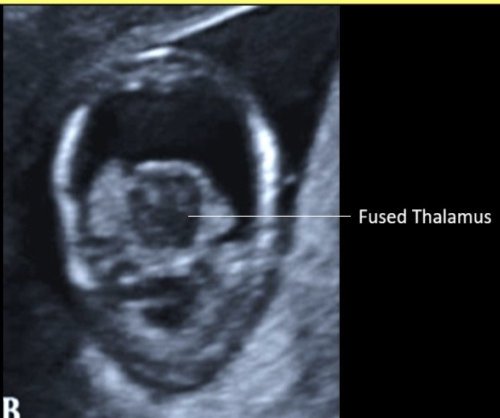
a fused thalamus is identified in which cranial abn
a) semilobar holoprosencephaly only
b) alobar holoprosencephaly only
c) agenesis of corpus callosum + alobar holoprosencephaly
d) alobar + semilobar holoprosencephaly
d) alobar + semilobar holoprosencephaly

which would be most consistent w/unilateral increase in AP renal pelvic diameter between 2nd and 3rd trimester
a) normal variant
b) autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease
c) ureterocele
d) autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
c) ureterocele

a cystic hygroma contains
a) lymphatic fluid
b) amniotic fluid
c) meninges + cerebrospinal fluid
d) cerebrospinal fluid
a) lymphatic fluid
postpartum hemorrhage is a complication of all except
a) macrosomia
b) twin gestation
c) polyhydramnios
d) IUGR
d) IUGR

![<p>mother says fetal <strong>motion</strong> has been very <strong>limited</strong></p><p>a) arthrogryposis [contraction/fixation]</p><p>b) osteogenesis imperfecta [brittle bone disease]</p><p>c) achrondroplasia [dwafism]</p><p>d) rhizomelia [femur/humerus shortening]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2907bea5-0605-4222-827c-d522cd89efaf.png)
mother says fetal motion has been very limited
a) arthrogryposis [contraction/fixation]
b) osteogenesis imperfecta [brittle bone disease]
c) achrondroplasia [dwafism]
d) rhizomelia [femur/humerus shortening]
a) arthrogryposis

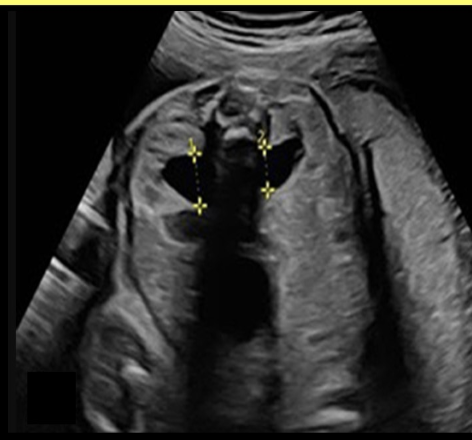
what is the most common abn of the fetal urinary system
a) posterior urethral valves
b) polycystic kidney disease
c) multicystic kidney disease
d) hydronephrosis
d) hydronephrosis
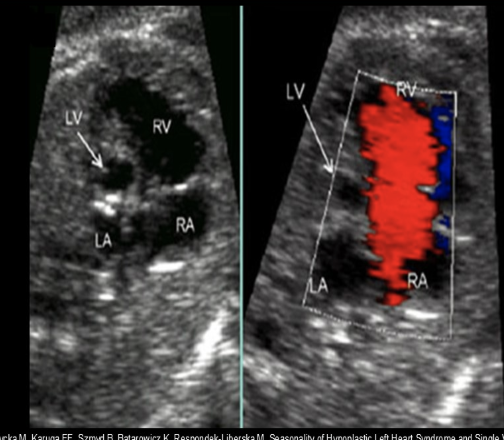
while scanning the 4 chamber heart view, you see an enlarged right heart w/very small left ventricle + atrium. you move to the LVOT view and the ascending AO is much smaller than normal
.
a) marfan syndrome
b) pulmonary HTN
c) Ebstein anomaly
d) hypoplastic left heart
d) hypoplastic left heart

midline facial defects, such as cyclopia + proboscis, are commonly assoc w/
a) oligohydramnios
b) ellis van creveld syndrome
c) amniotic band sequence
d) alobar holoprosencephaly
d) alobar holoprosencephaly

a triploidy fetus has
a) an extra chromosome 13
b) 3 sets of chromosome 13
c) 3 sets of chromosome 3
d) 3 sets of all 23 chromosomes
d) 3 sets of all 23 chromosomes
