Electricity, Magnetism, Electromagnetism
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Smallest unit of electrical charge is the…
electron
electrons are measured with…
coulomb
1 coulomb =
6.3 × 1018 electron charges
Electrification
too few or much electrons (protons unmoved)
Electrostatics means…
study of electric charges in stationary form
3 methods of electrification
friction
contact
induction
friction
like rubbing fur on a rod

contact
friction-charged body comes in CONTACT with another object
induction
arranged electrons on uncharged object in presence of charged object
when object is electrically charged, it’ll manifest…
an electrical field or force around i
There’s how many laws of electrostatics?
4
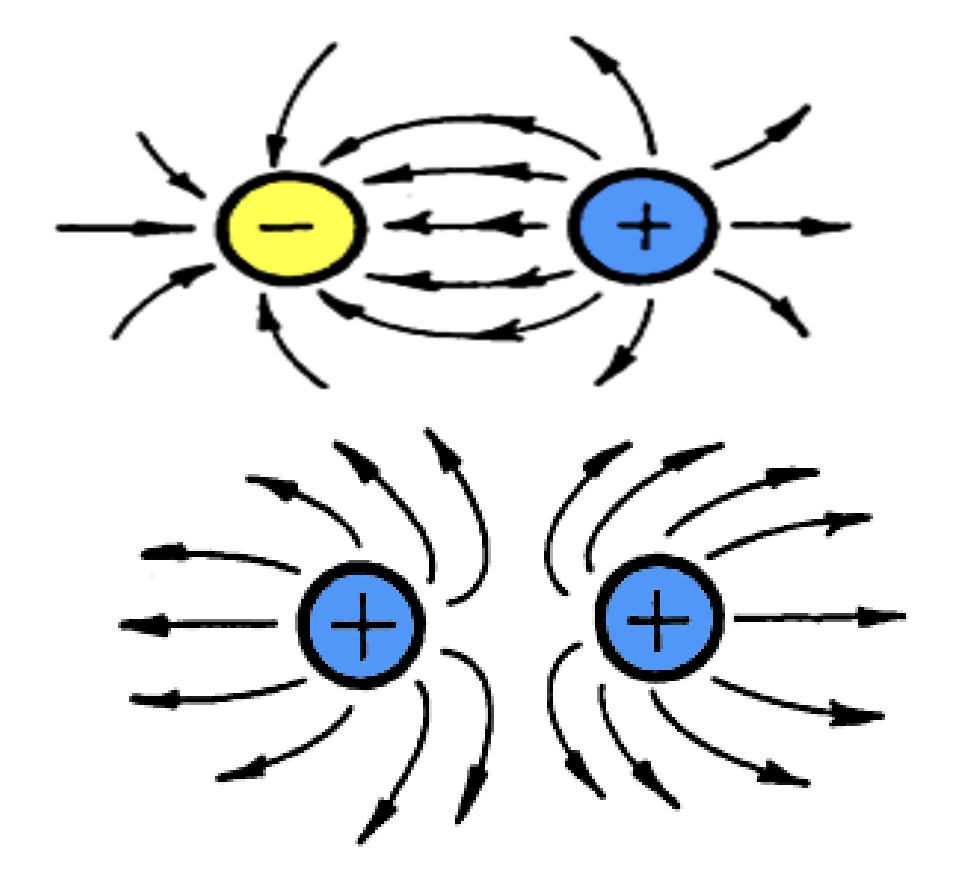
1st Law of Electrostatics
different charges attract, same repel
2nd Law of Electrostatics
electrons travelon outside of a conductor (wire)
3rd Law of Electrostatics
electric charges are concentrated on the sharpest curvature of a conductor
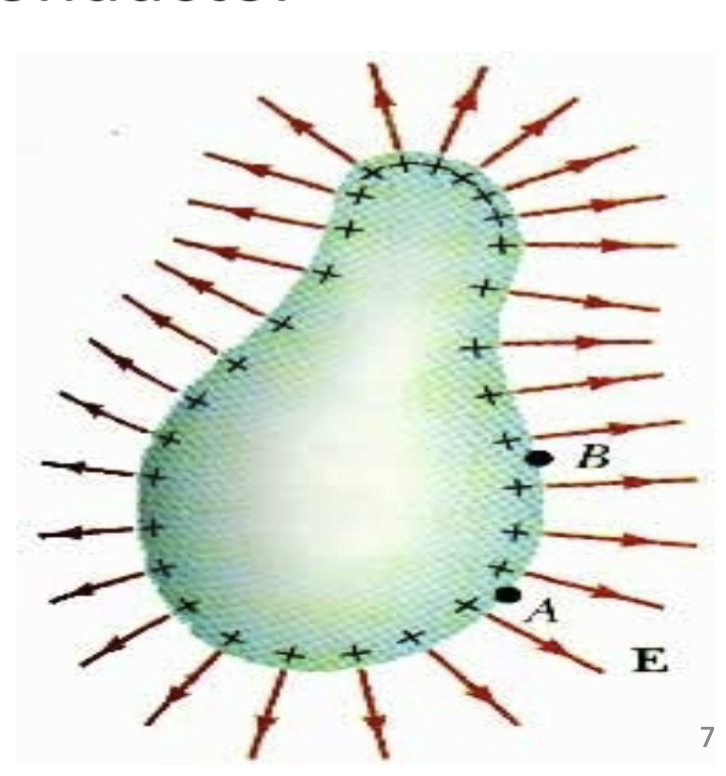
4th Law of Electrostatics
Electrostatic force is:
Directly proportional to the product of charges
Inversely proportional to the square of the distance
Coulomb’s law is…
EF = k(Q1Q2)/d2
An object that’s electrically charged has the…
potential energy to do work
Measure x-ray energy in…
volts/kilovoltage potential (kVp)
electrodynamics is…
study of electricity in motion
What is currents?
the flow of electricity or electrons
how to measure currents?
amperage (A)/ mAs
conductor vs insulator
allows electrons to flow vs inhibits electron flow
Ex of conductors…
metal, gold, copper, silver, water
Ex of insulators…
wood, rubber
semiconductors are…
conduct or insulate under certain conditions, like silicon
superconductor is…
for allowing electron flow without resistance like titanium
circuit
allows electron flow from a generated source through multiple parts and back to source again
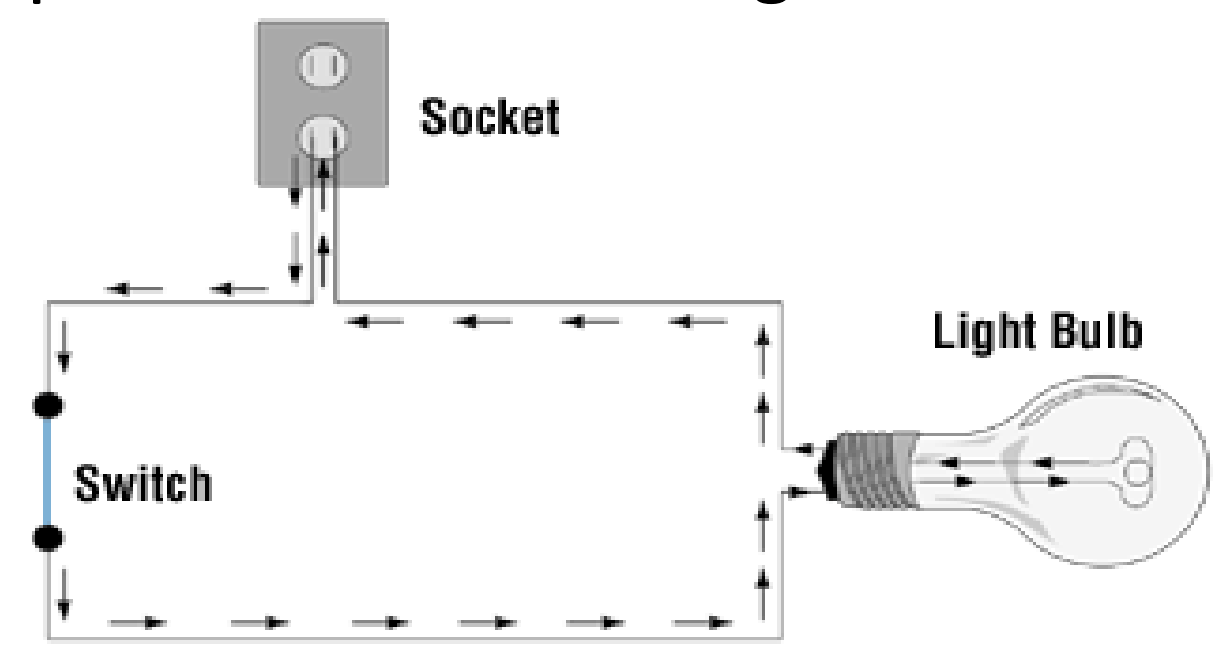
Ammeter
measures electron flow
3 Parts of a Circuit
current
potential differences
resistances
Current is measured in…
amperes (A)
Potential differences is measured in…
volts (V)
Resistances (R) is measured in…
ohms (Ω)
What is resistance?
anything that opposes or hinders electron flow
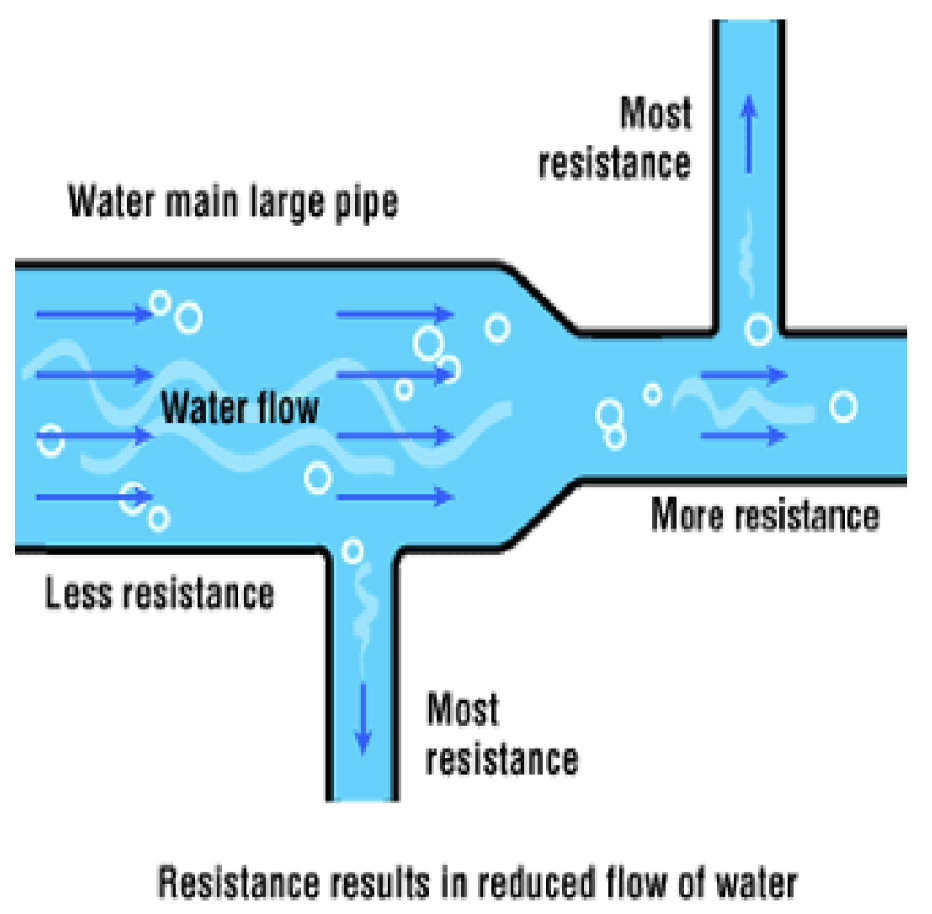
What 4 aspects influence Resistance (R)?
length of conductor
cross-section of wire
material wire is composed of
wire temp
Ohm’s law =
Voltage (V) = Current (I) x Resistance (R)
Power is…
work done per unit of time, measured in watts (W)
Power (P) =
Current (I) x Voltage (V) OR I2 x Resistance (R)
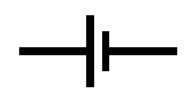
What electrical symbol is this?
single cell


What electrical symbol is this?
battery
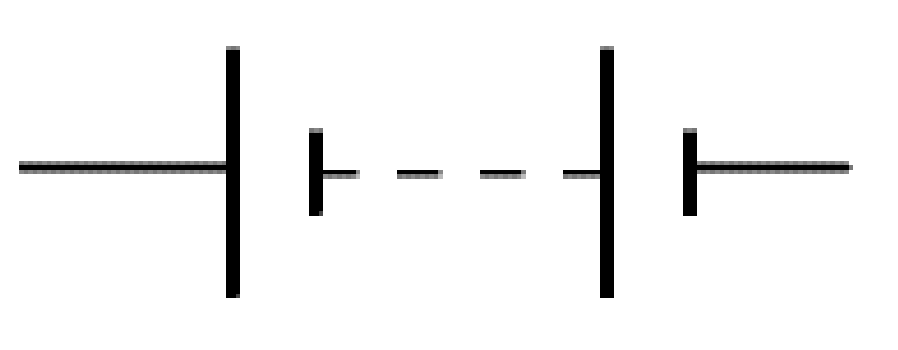
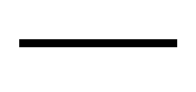
What electrical symbol is this?
connecting wire
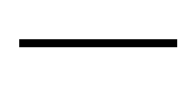

What electrical symbol is this?
resistor

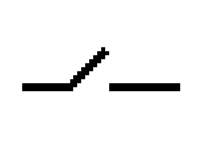
What electrical symbol is this?
switch (open)
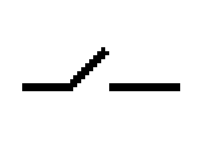
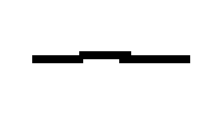
What electrical symbol is this?
switch (closed)
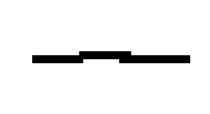
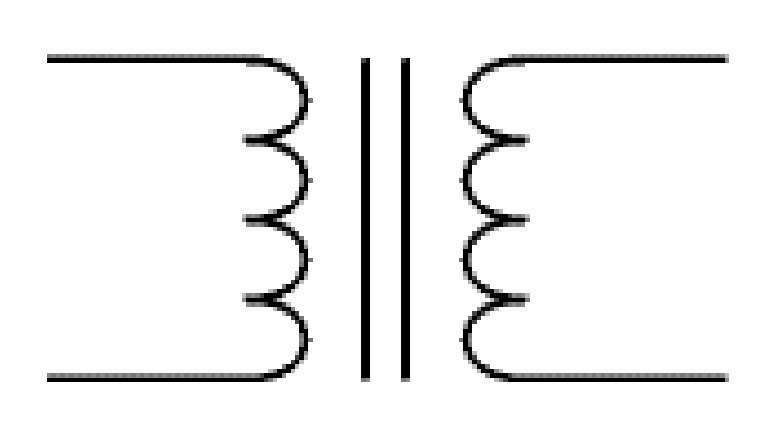
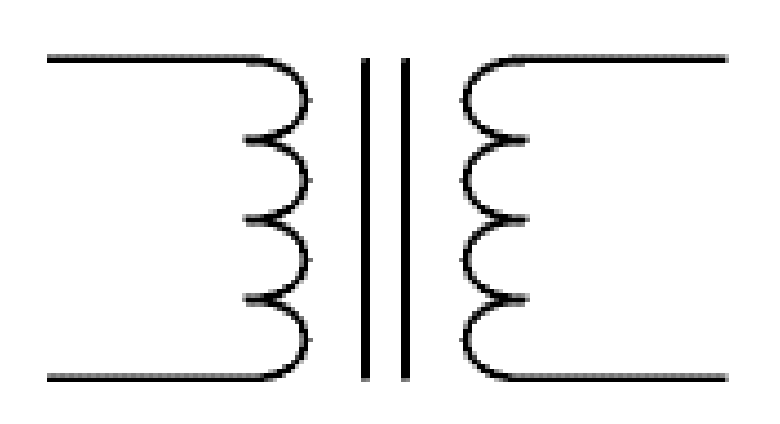
What electrical symbol is this?
transformer

2 types of circuits
series
parallel


Series vs Parallel Circuits - difference in path?
Series has 1 path of electron flow vs Parallel has 2+


Series vs Parallel Circuits - difference in interruption reaction?
in a Series, electron flow stops if any part is interrupted vs in a Parallel, electrons can flow through other branches of circuit

Series circuit is rep by…
Rt = R1 + R2 + R3… or sub R with V, while Amperage remains constant in circuit
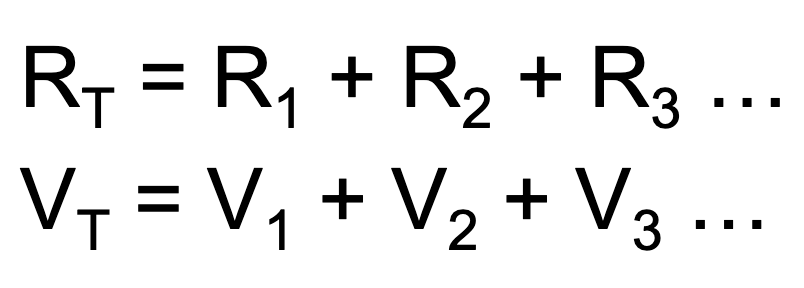
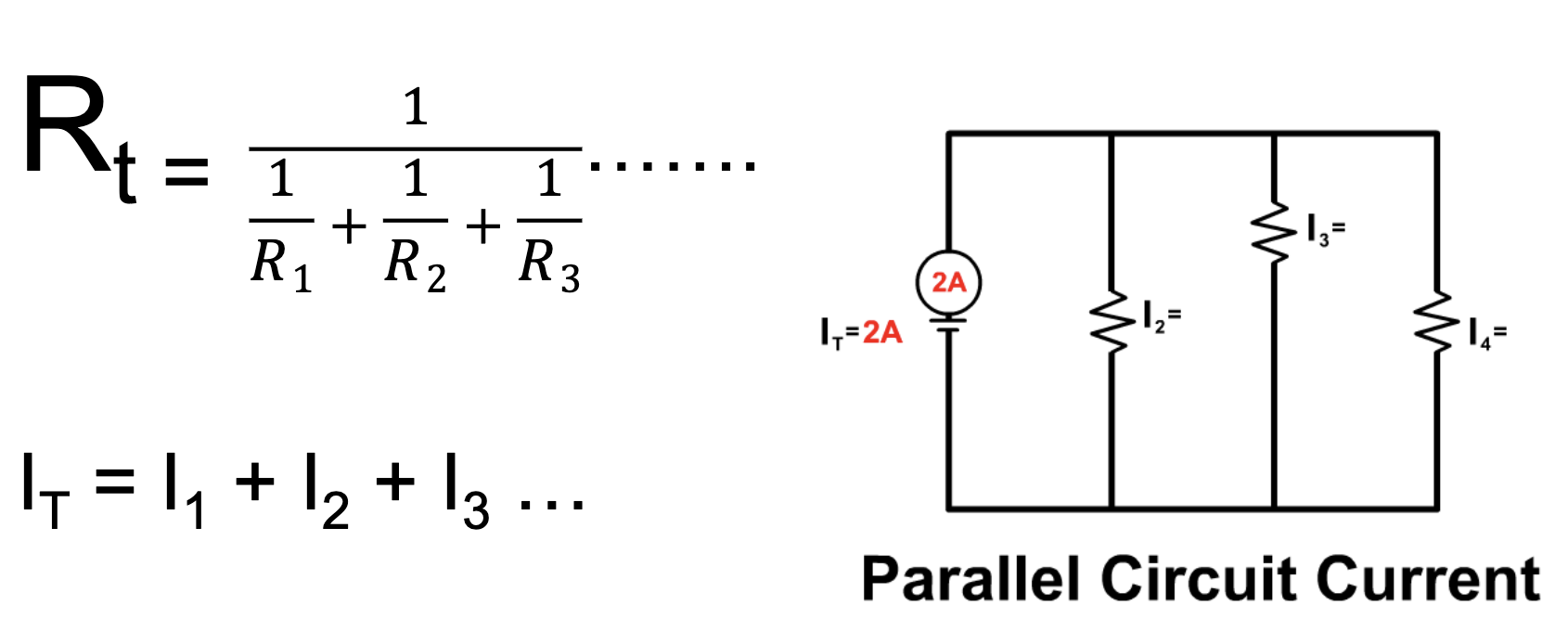
Parallel circuit is rep by…
note: voltage remains constant
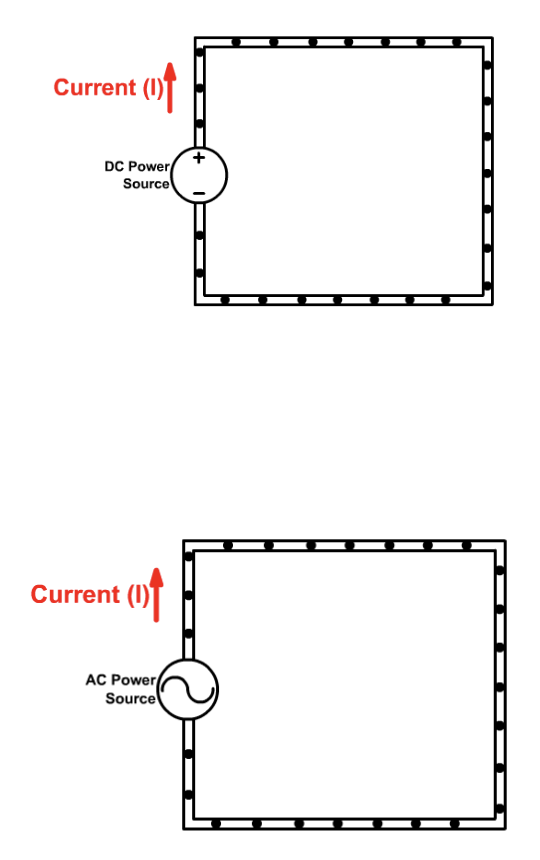
2 types of currents
alternating vs direct
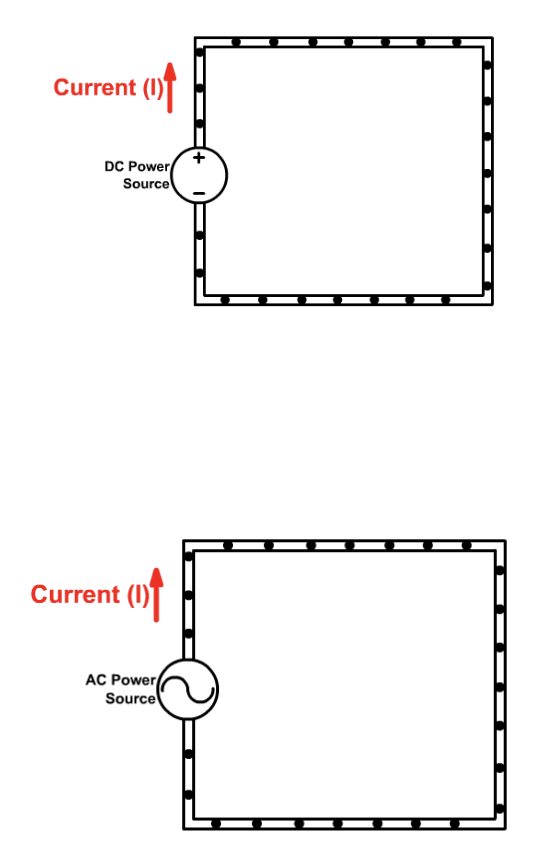
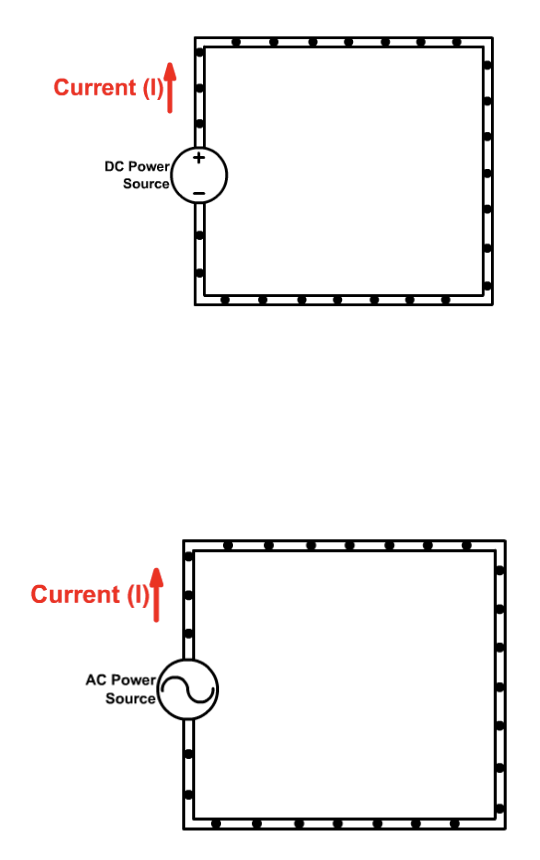
Difference in Alternating vs Direct currents
AC allows electron flow to switch directions (like in an AC generator) vs Direct lets electron flow in one direction (like batteries)