Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is complex regional pain syndrome?
A complex of systems that include extreme pain, joint stiffness, diffuse edema, trophic skin changes, and vascular instability
What is CRPS caused by?
painful lesion, predisposition to condition, abnormal sympathetic reflex
What can be events that precede CRPS?
Fracture, sprain, surgery, immobilization of the limb, spinal cord injury, stroke, infection skin or joint, injections, venipuncture, burn, frostbite
CRPS Type 1
no known peripheral nerve injury
Classic reflex sympathetic dystrophy
pain out of proportion to injury
autonomic dysfunction
trophic changes
functional impairment
CRPS Type II
Involves peripheral nerve injury → typically median or sciatic nerve
classic causalgia
similar signs and symptoms as Type 1
Precipitating event with CRPS Type 1 and CRPS Type 2
CRPS 1: Sometimes
CRPS 2: Yes
Single peripheral nerve involvement with CRPS Type 1 and Type 2
CRPS Type 1: Sometimes
CRPS Type 2: Yes
Physiologic changes in affected limb CRPS Type 1 and Type 2
CRPS Type 1: Yes
CRPS Type 2: No
Cardinal signs of CRPS Type 1
spontaneous pain, swelling, different skin temperatures
Cardinal signs of CRPS Type 2
Burning pain, allodynia, hyperalgesia
Progression of CRPS Type 1 and Type 2
CRPS Type 1 progresses
CRPS Type 2 sometimes progresses
Bone atrophy CRPS Type 1 and Type 2
CRPS Type 1: Yes
CRPS Type 2: No
Types of pain associated with CRPS
Allodynia, hyperalgia, hyperpathia
Allodynia
Painful response to a normally innocuous stimulus
Hyperalgia
increased sensitivity to pain
Hyperpathia
stimuli evoke exaggerated levels of pain
How does pain present in CRPS?
Abnormal sympathetic reflex arc, meaning the processing of pain is not normal. Most common and universal complain associated with CRPS. It is disproportionate to injury. There can be burning, throbbing, deep aching, cramping, flashing hot/cold, or increased pressure
CRPS Joint stiffness characteristics
There will be joint thickening and palmar nodules. It will exceed the expected response and occur rapidly and increases. The client will typically be in protective posturing that will lead to contractures.
CRPS Edema Characteristics
Can be extreme in nature, and is initially soft and relieved by retrograde massage. Brawny edema will localize to dorsal hand.
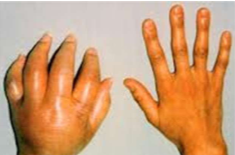
Stage 1
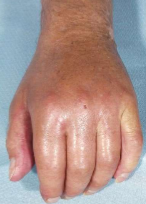
Stage 2
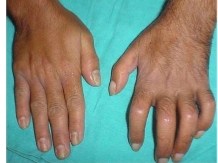
stage 3
Autonomic changes with CRPS
Vasoconstriction which can lead to blue, sweaty, and cold limbs
Vasodilation which can lead to red, dry, and hot hands
Trophic changes for CRPS
Skin becomes tight and shiny, possibly goose bumps, Pencil pointing of fingertips. Abnormal hair growth and texture, fingernail changes, atrophy of soft tissues
What motor dysfunctions can occur with CRPS?
Tremor, dystonia, increased tone, spasms, and loss of strength/endurence
True or False: CRPS can affect bone density
True, bone demineralization can occur
True or false: CRPS cannot affect skin color
False, CRPS can affect skin color
What vasomotor change can occur with CRPS?
temperature alteration
What sudomotor change can occur with CRPS?
hyperhidrosis
Acronym to remember characteristics of CRPS
STAMP
sensory, trophic, autonomic, motor, pain
Stage 1 CRPS
Acute
Within weeks of injury
Swollen, red, and burning; increased diaphoresis; pain near site of injury; limb hot and sweating; protective posturing
Bone demineralization within 3-5 weeks
Soft, pitting swelling edema
Stage 2 of CRPS
Dystrophic
Cool and diaphoretic, pain throughout limb, bone atrophy on x-ray; skin becomes glossy and shiny; disuse develops; limb cool and sweaty
Within months of injury
Edema becomes hard and brawny
Stage 3 CRPS
Atrophic
Pale and shiny, atrophy of muscle and bone, pain may be constant
years after injury, also may resolve
Extreme stiffness
Periarticular thickening/joint enlargement
Contractures, nonfunctioning limb
CRPS Medical Interventions
pharmacologic agents
stellate ganglion blocks
sympatholytic drugs
sympathectomy
Assessing CRPS
Absolutely necessary and non-provocative testing
Monitor circulatory and sympathetic changes
Observation at rest and during activity
Pain assessment
What are we assessing with active ROM in CRPS? What should we be careful of?
Joint tightness versus musculotendinous limitation
Intrinsic versus extrinsic tightness
We should be careful of pain during testing
What should be used assessing sensibility during CRPS?
Monofilaments and two-point discrimination
What should we assess when looking at skin temperature with CRPS?
To see if the skin is hot or cold to determine what stage the CRPS is in
How can we measure the quality of edema?
Figure of eight, circumferential measurement (be mindful with pain, and volumeter with warm water
What should be the goal of OT for CRPS?
management of pain and other symptoms, maximize motion, restore function. We should be a cheerleader for our clients to encourage functional use of the limb
How can pain be managed for CRPS?
For cold limbs → superficial heat modalities (hot packs or fluidotherapy at 98 degrees
For warm limbs —> cryotherapy
Ultrasound
TENs
How can edema be managed with CRPS?
simple elevation, gentle pain-free AROM, pulsed electrotherapy, pneumatic compression, manual edema mobilization, compression garments, retrograde massage
How can retrograde massage be used for CRPS?
Massage distal to proximal to increase blood and lymph flow. It is performed during stage 1. Prior to and after therapeutic exercise.
Can sensory issues be managed with CRPS?
For hypersensitive clients, desensitization for 5 to 6 times a day is important. The stimuli must be mildly irritating. Start outside sensitive areas and work toward hypersensitive area. Protect hypersensitive areas between sessions
What interventions can be used to treat vasomotor changes?
Generalized aerobic exercise routine, avoid caffeine and alcohol, self management for cold, cyanotic limbs, electro therapy for circulation, temperature biofeedback
Mirror therapy for CRPS
Done 5 minutes 2 times a day, working up to 15 minutes/day
Remove jewelry and watches
quiet area, same time of day, same location
progress to making one change at a time,
progress to practice with distractions
Move from exercises to activities
Stress loading for CRPS
3 to 5 minutes 3 times a day working up to 10 minutes
Compressive active exercises
follow with distraction techniques
aquatic therapy can also be utilized
When should a continuous passive motion orthotic be utlized?
as a last ditch effort, to increase tissue nutrition, used periodically, only within comfort range, supplemental
What position should a static orthosis be in for CRPS?
Intrinsic plus
Why should orthotic be used for CRPS?
To manage contractures. No more than 2 orthotics should be used per client.
What is the purpose of improving functional activities for CRPS?
To improve self-care, IADLs, work skills, craft activities, start simple and move to more difficult tasks, and to reinforce confidence
What stage of CRPS should strengthening begin?
Stage 3, however if they can tolerate it in earlier stages, start it sooner
Why is strengthening important for CRPS?
to prevent weakness, to build endurance, and to provide stimulation for work
What patient education tools can be used for CRPS?
joint protection, energy conservation, assistive devices, encourage participation in a support group, psychosocial issues, home programs