Biology Unit 3 Topic 4: Cellular Energy
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
atp
molecule that organisms use as source of energy to perform work
by coupling exergonic and endergonic reactions
kinetic energy
energy associated w/ motion
potential energy
stored energy
free energy
determines the likelihood of reactions in organisms
find the amt of energy available to do work
exergonic reaction
chemical reactions that release energy
endergonic reaction
chemical reactions that absorb energy
catabolic pathway
metabolic pathways that release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds
anabolic pathways
metabolic pathways that consume energy to build complicated molecules from simpler compounds
entropy
measure of disorder or dispersal of energy and matter in a system
energy
the ability to do work
organisms need to survive and function
activation energy
smallest amt. of energy needed to start a chemical reaction
laws of thermodynamics
study of energy transformations in matter and applies to the universe
1st law of thermodynamics
energy cannot be created or destroyed
2nd law of thermodynamics
energy can only be transferred or transformed
how does the structure of atp allow for the molecule to store and release energy
breaking of the bond between 2nd and 3rd phosphate in atp → organisms obtain energy
released when released phosphate group moves to another molecule to give energy
how do enzymes affect activation energy
by lowering it
create a flow chart that traces the flow of energy through your body
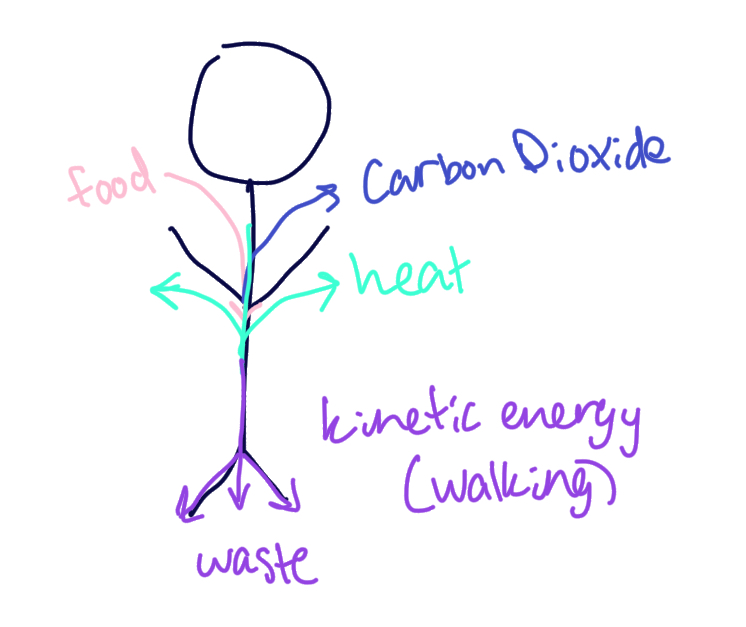
what products increase entropy of you and your surroundings
solid or liquid reactants form gaseous products
solid reactants form liquid products