embryology quiz 1
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
subdivisions of embryology
descriptive
comparative
experimental
descriptive embryology
study of the mechanisms of development
comparative embryology
study that compares the development of one species to that of another species
experimental embryology
- study of external factors on development
- only area of embryology with active research
embryon
something that swells in the body
prenatal period
- before birth
- embryonic and fetal periods
embryonic period
0-8 weeks (most during weeks 3-8)
fetal period
8 weeks to birth
postnatal period
- after birth
- infancy, childhood, puberty, adolescence, adulthood
infancy
- 0-1 year
- first 4 weeks = neonatal period
childhood
1-13 years
puberty
girls: 12-15 years
boys: 13-16 years
adolescence
- 12-17 years
- ability to reproduce
adulthood
18-death
ventral
toward the belly
dorsal
toward the back
cranial
toward the head
caudal
toward the tail
rostral
toward the nose
median (midsagittal) plane
equal right and left halves
sagittal plane
right and left sections
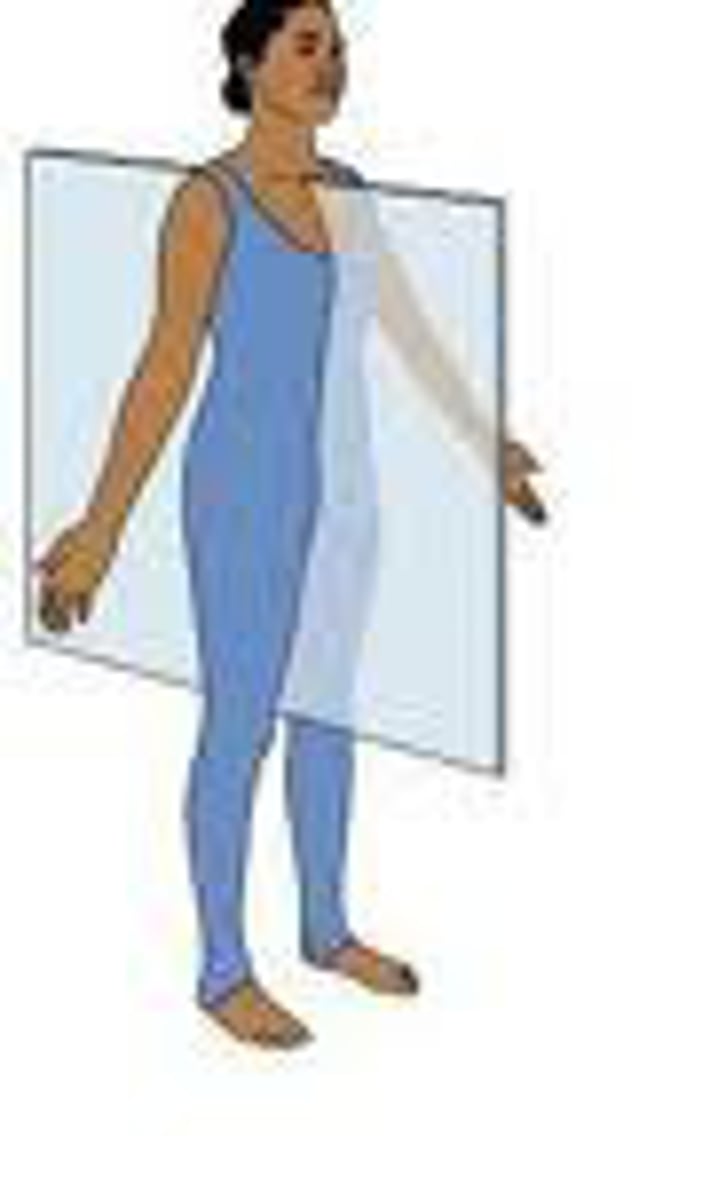
transverse plane (cross section)
top and bottom sections
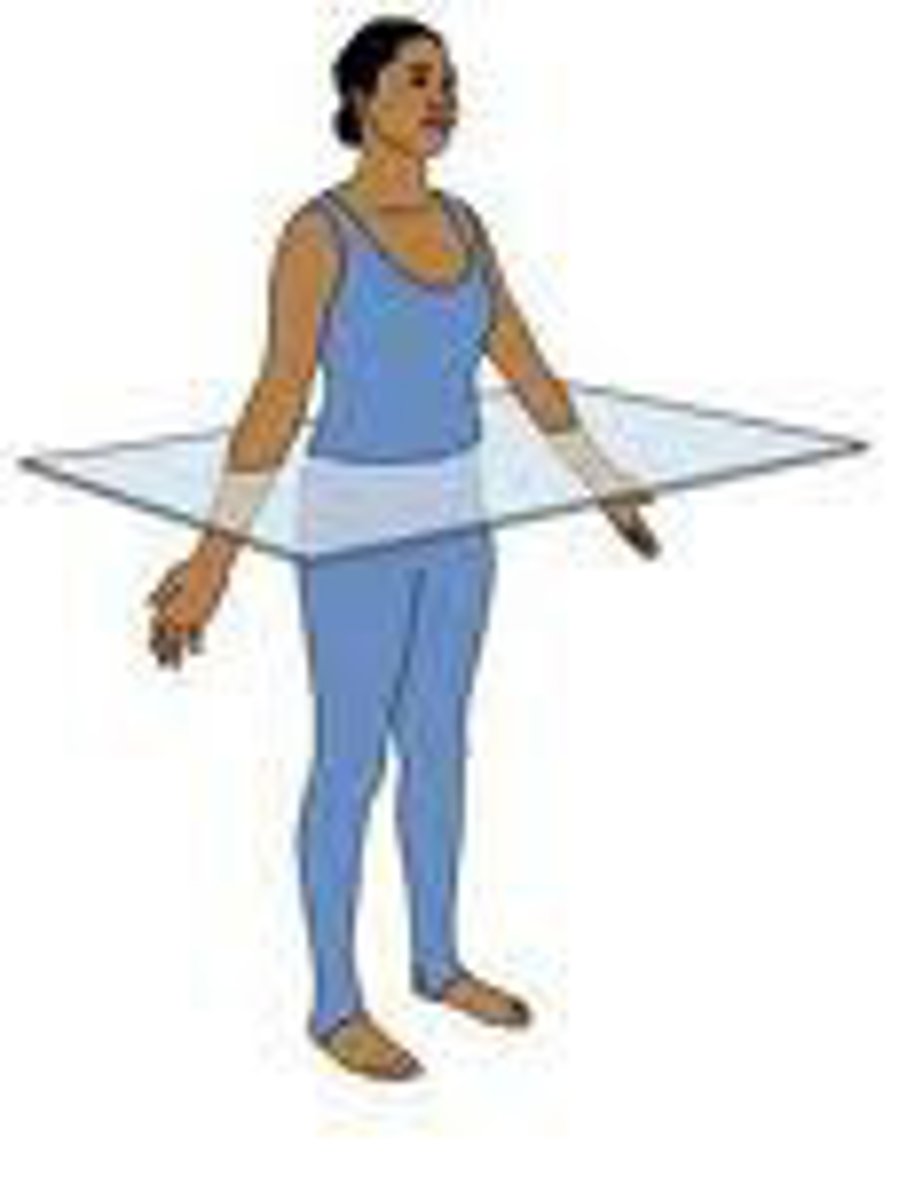
frontal (coronal) plane
- front and back sections
- frontal = body, coronal = head

oblique plane
any section that is not cut on the three main planes of the body
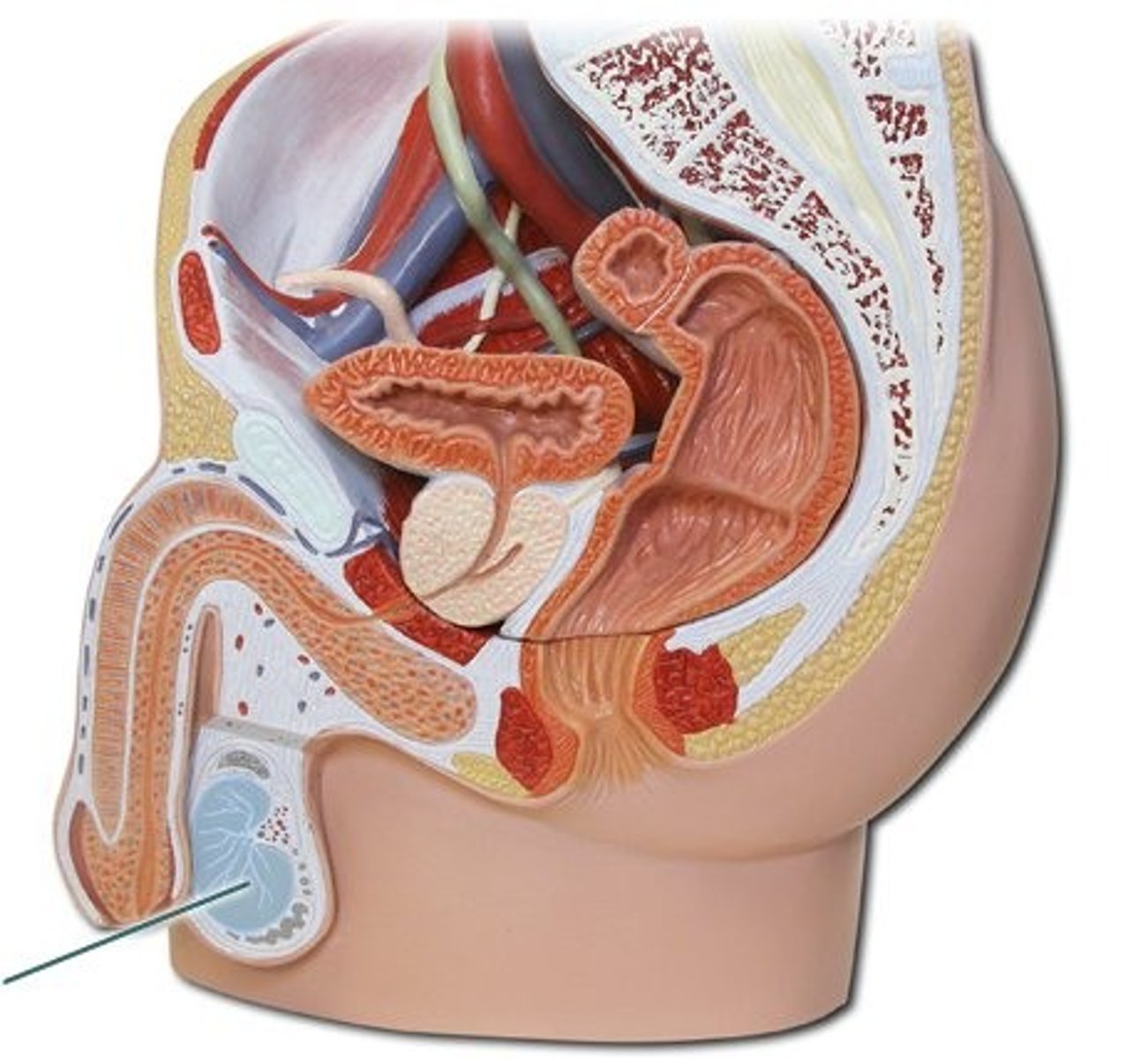
male reproductive system
- produce and deliver male gametes, sperm cells
- external system
- made up of testis, epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct, urethra
testis
- primary sex organ
- where sperm cells are developed and where testosterone is produced
- located in scrotum
- contains inactive sperm cells
primary sex organ
where sex cells are produced
where hormones are produced
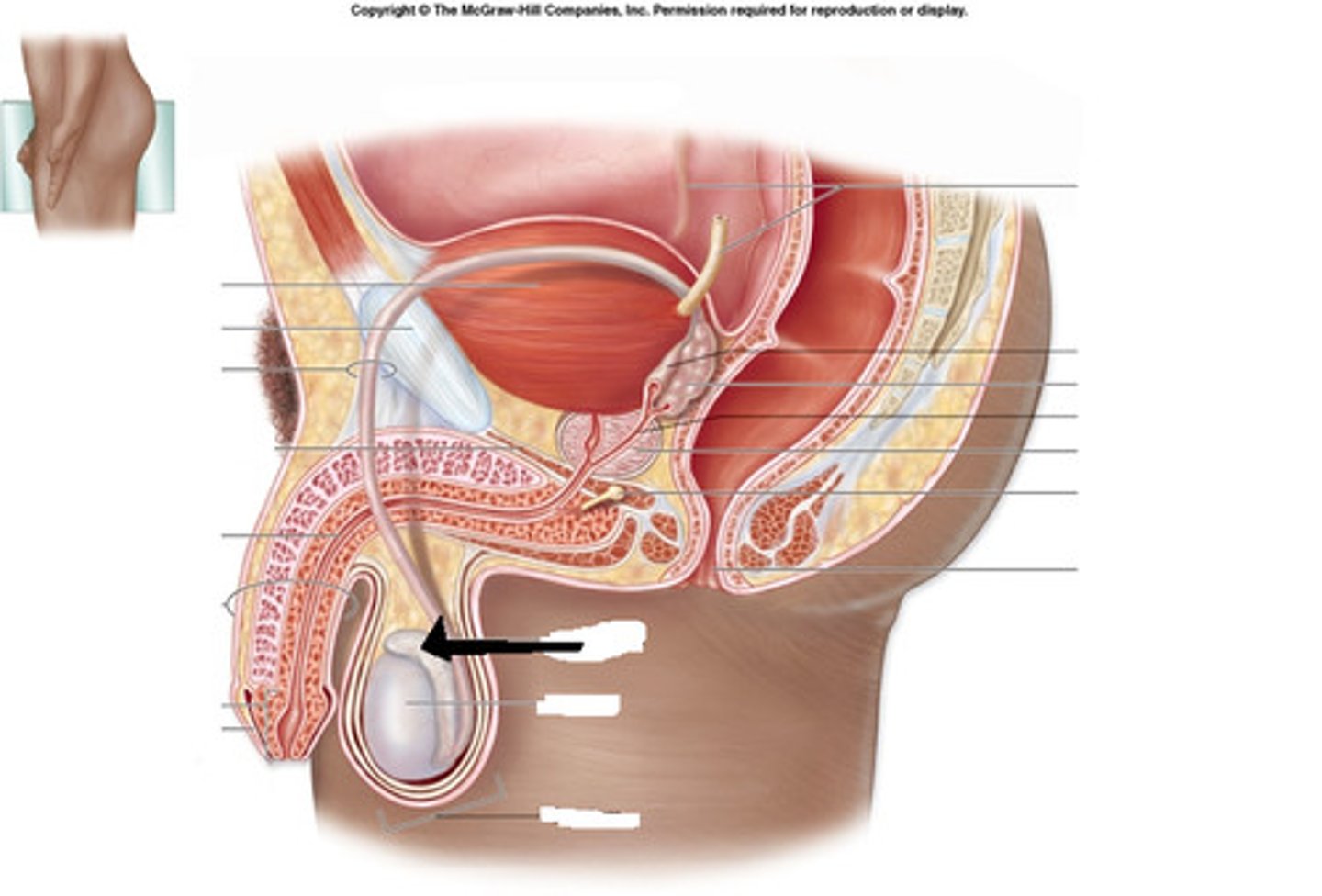
epididymis
- primary site of storage and activation of sperm cells
- sperm cells can spend up to 3 weeks here
- located in superior posterior aspect of scrotum
- made up of head, body, and tail
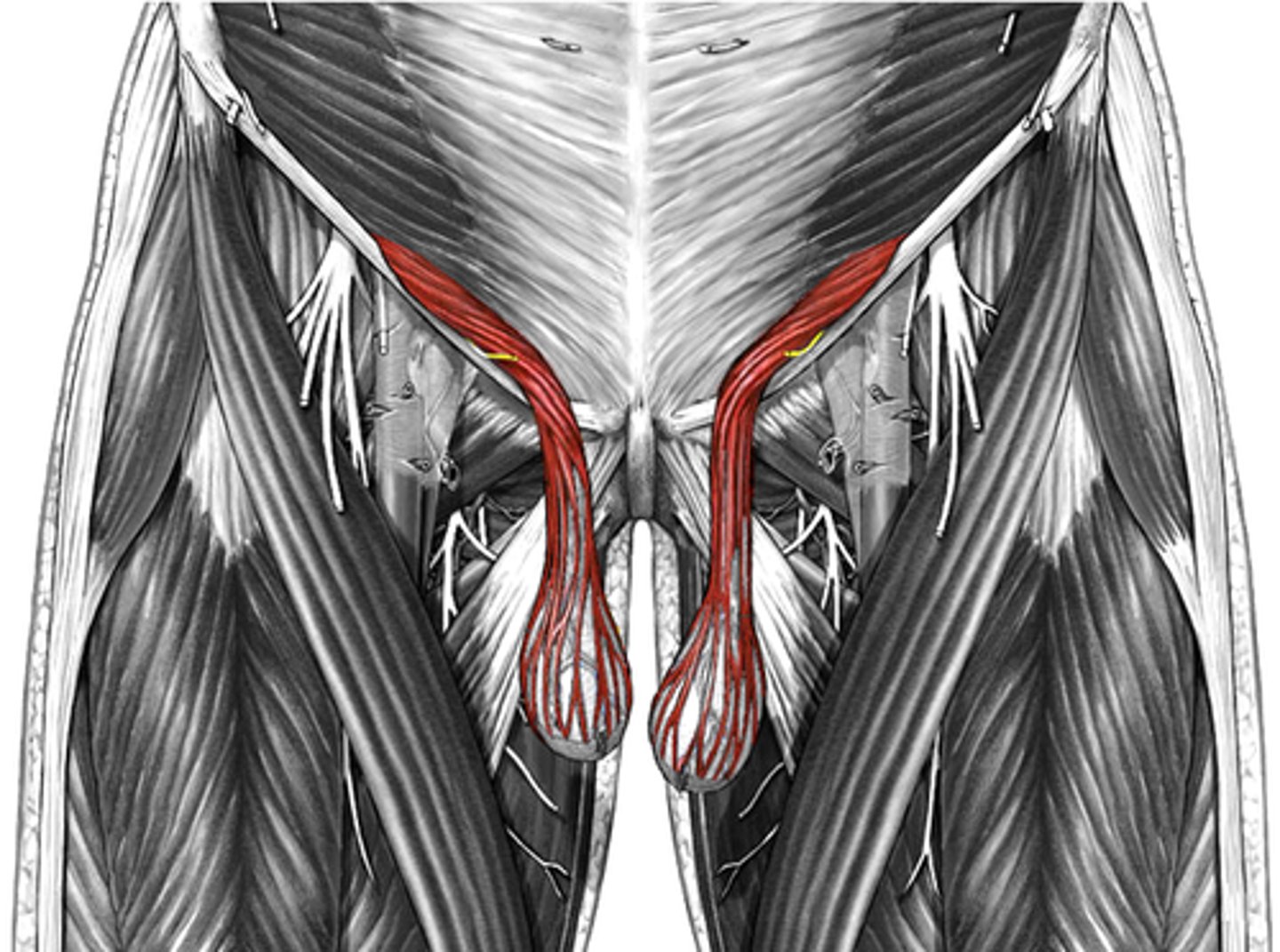
cremaster muscle
elevates or suspends testes to control temp
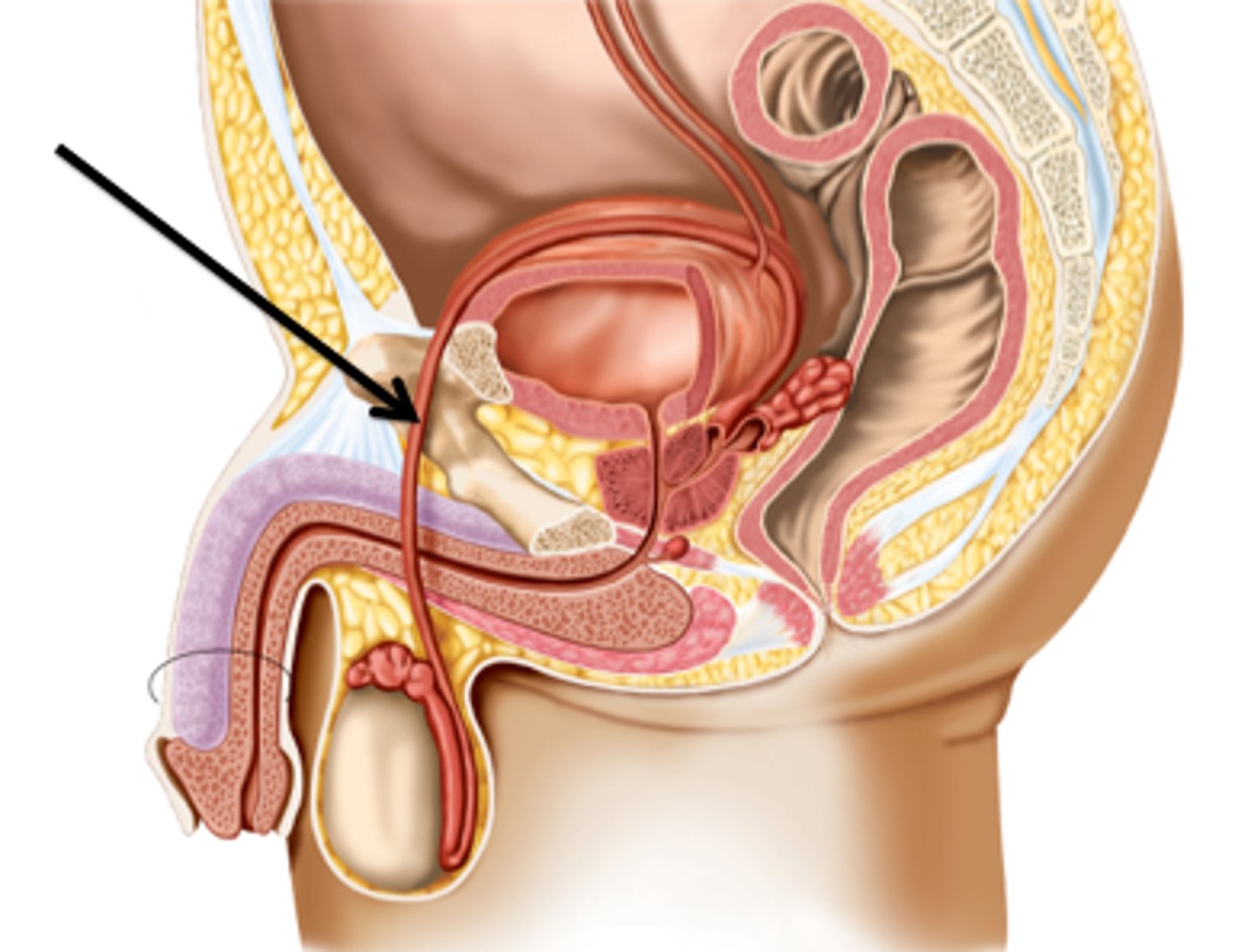
ductus (vas) deferens
- muscular tube that transports the sperm cells from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct
- passes from epididymis through spermatic cord, through the inguinal canal and to the posterior aspect of the urinary bladder, then joins with duct of seminal vesicle to form the ejaculatory duct
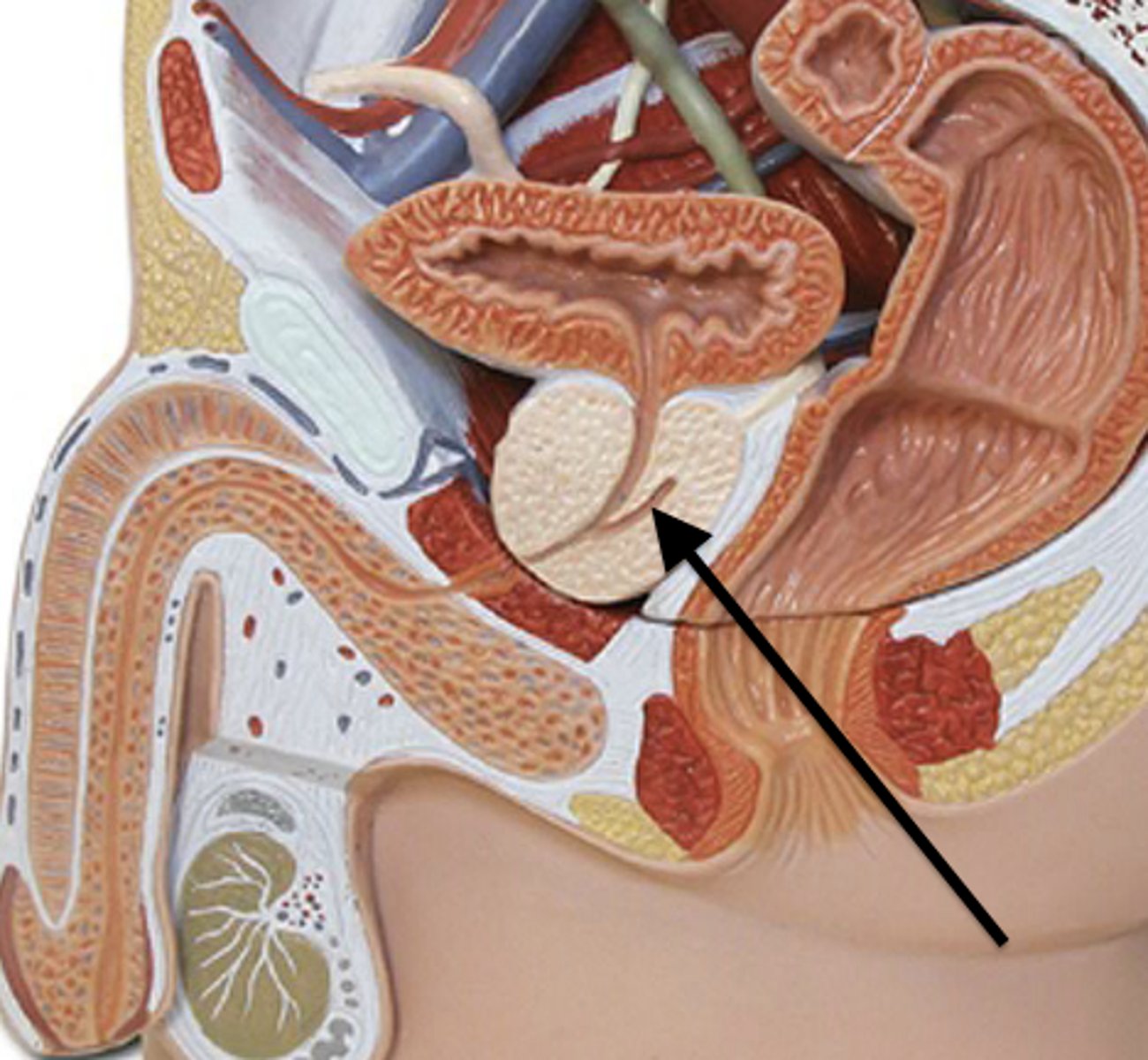
ejaculatory duct
- short duct that forms the union of the ductus deferens and the duct of the seminal vesicle
- passes through the prostate gland to empty into the prostatic urethra
seminal vesicles
- secretory glands that add an alkaline fluid to the seminal fluid
- located on the posterior aspect of the urinary bladder
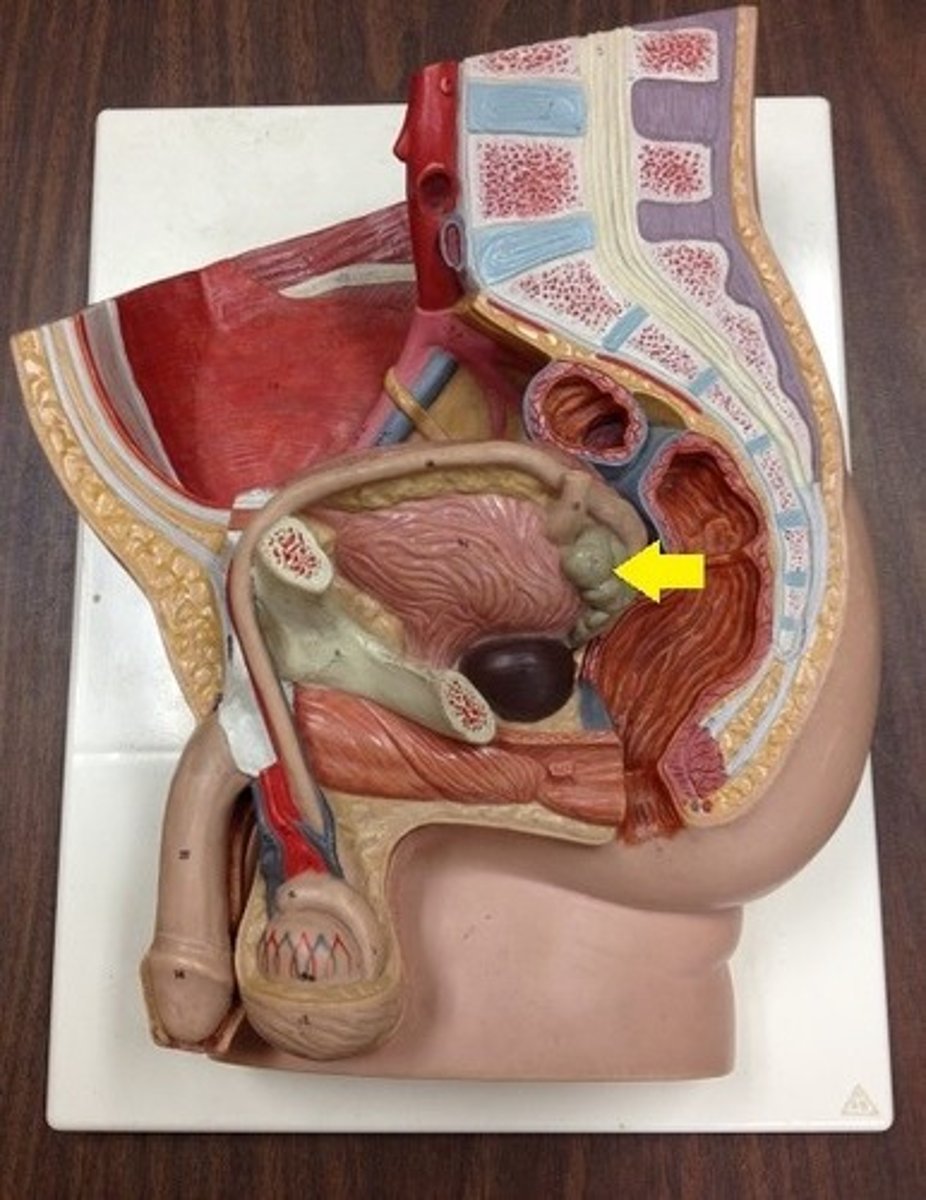
male urethra
prostatic urethra
membranous urethra
penile urethra
prostatic urethra
passes through the prostate gland and represents the union of the reproductive and urinary systems
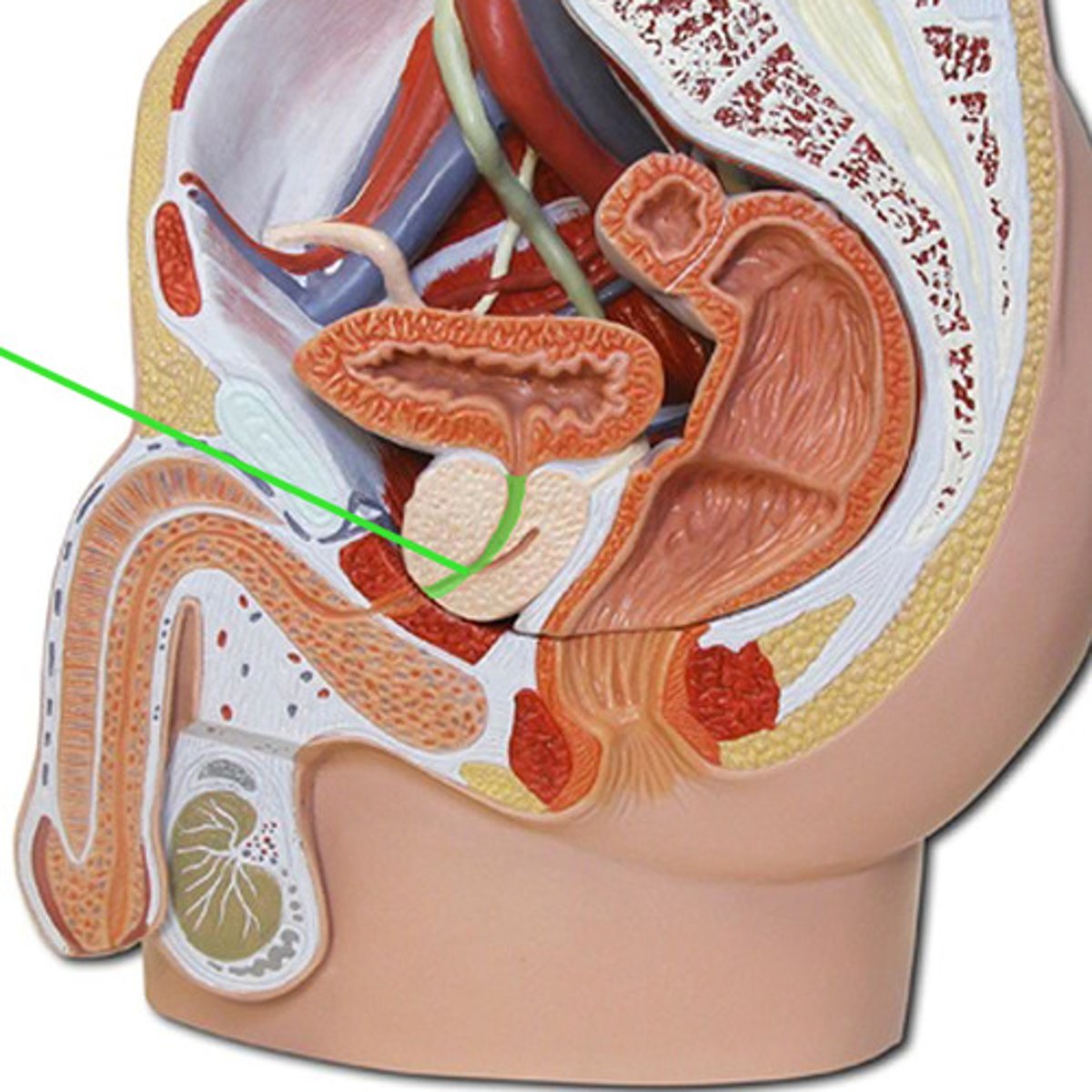
membranous urethra
passes through the pelvic diaphragm
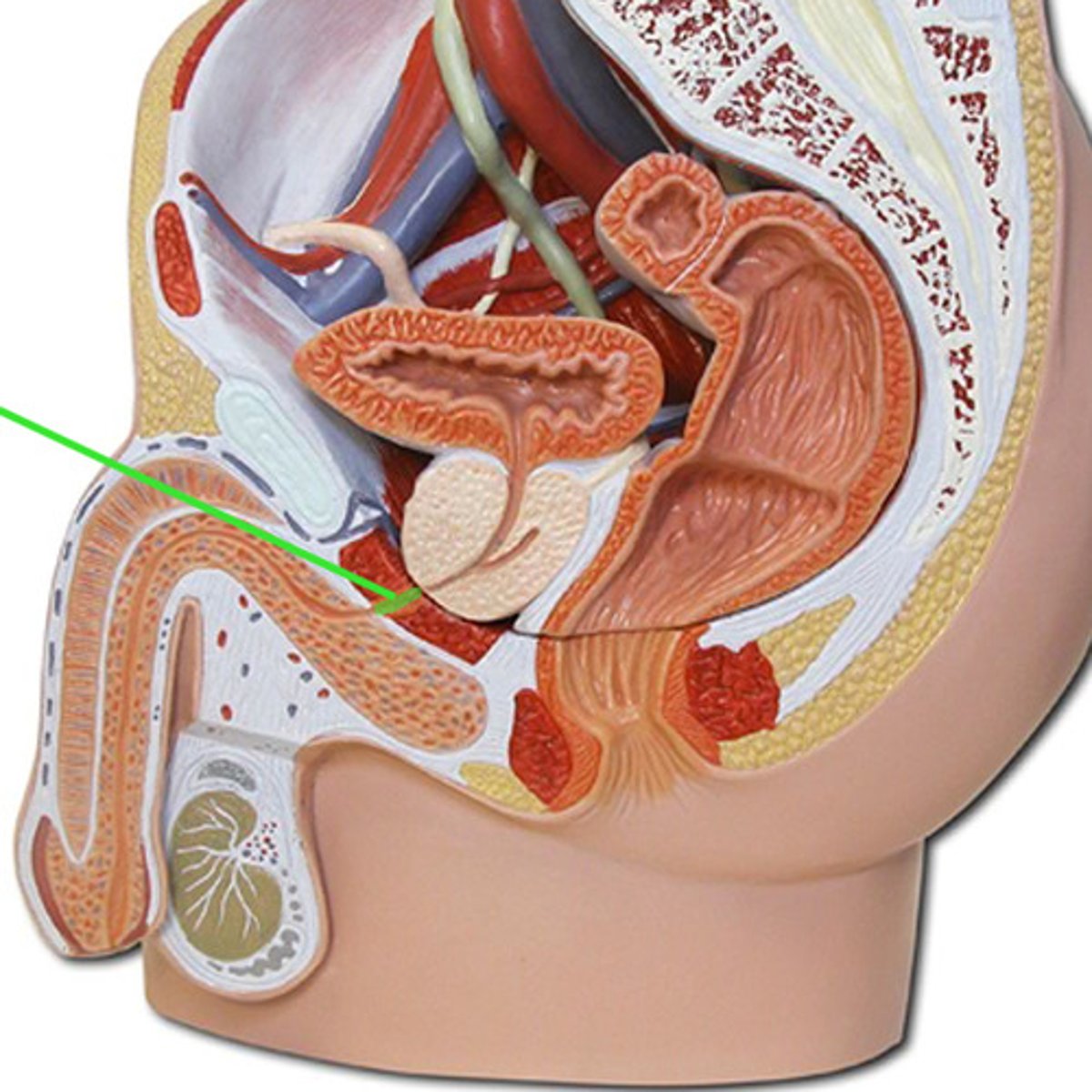
penile urethra
passes through the penis
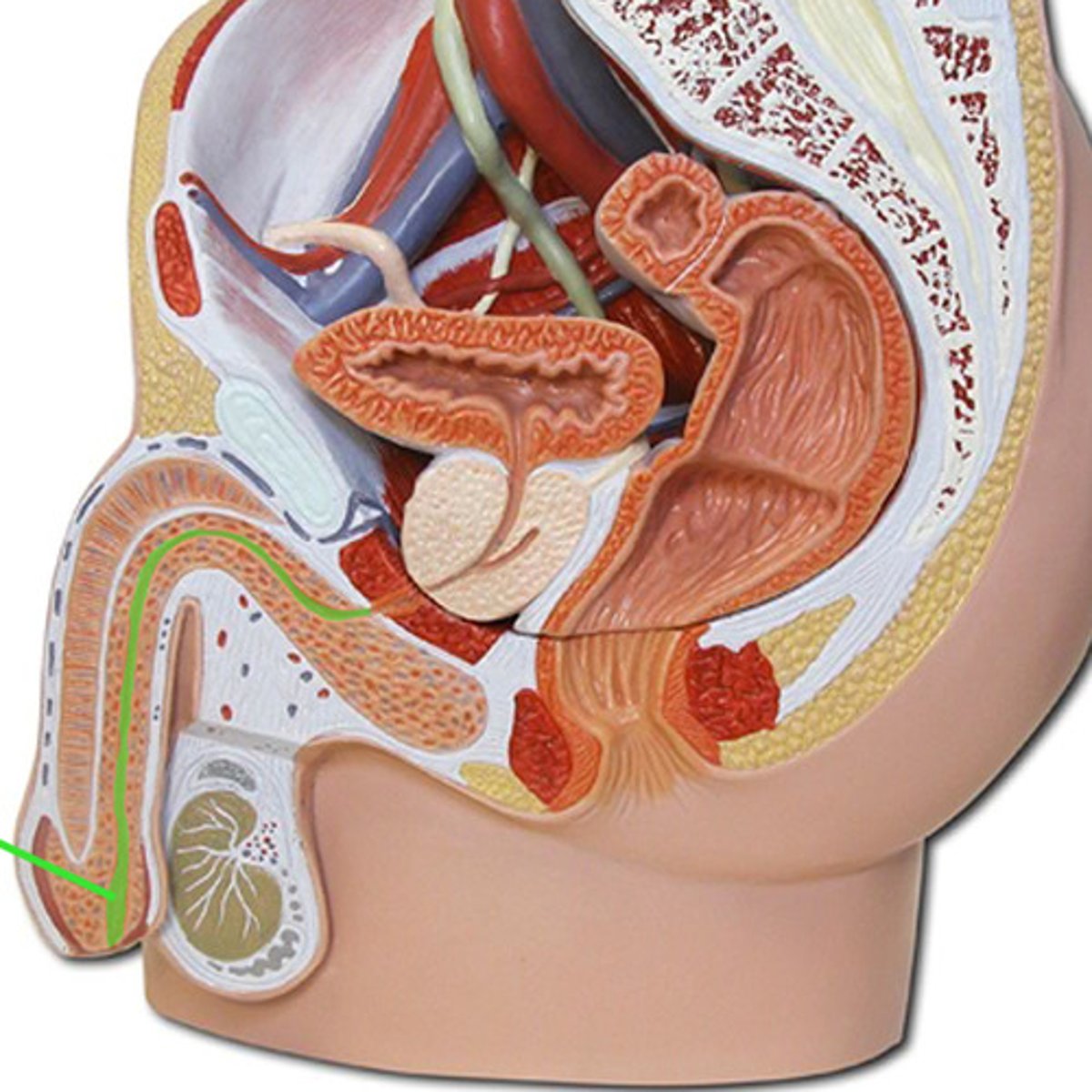
prostate gland
- adds fructose sugar to the seminal fluid
- located at the base of the urinary bladder
- part of the urethra and ejaculatory duct run through it
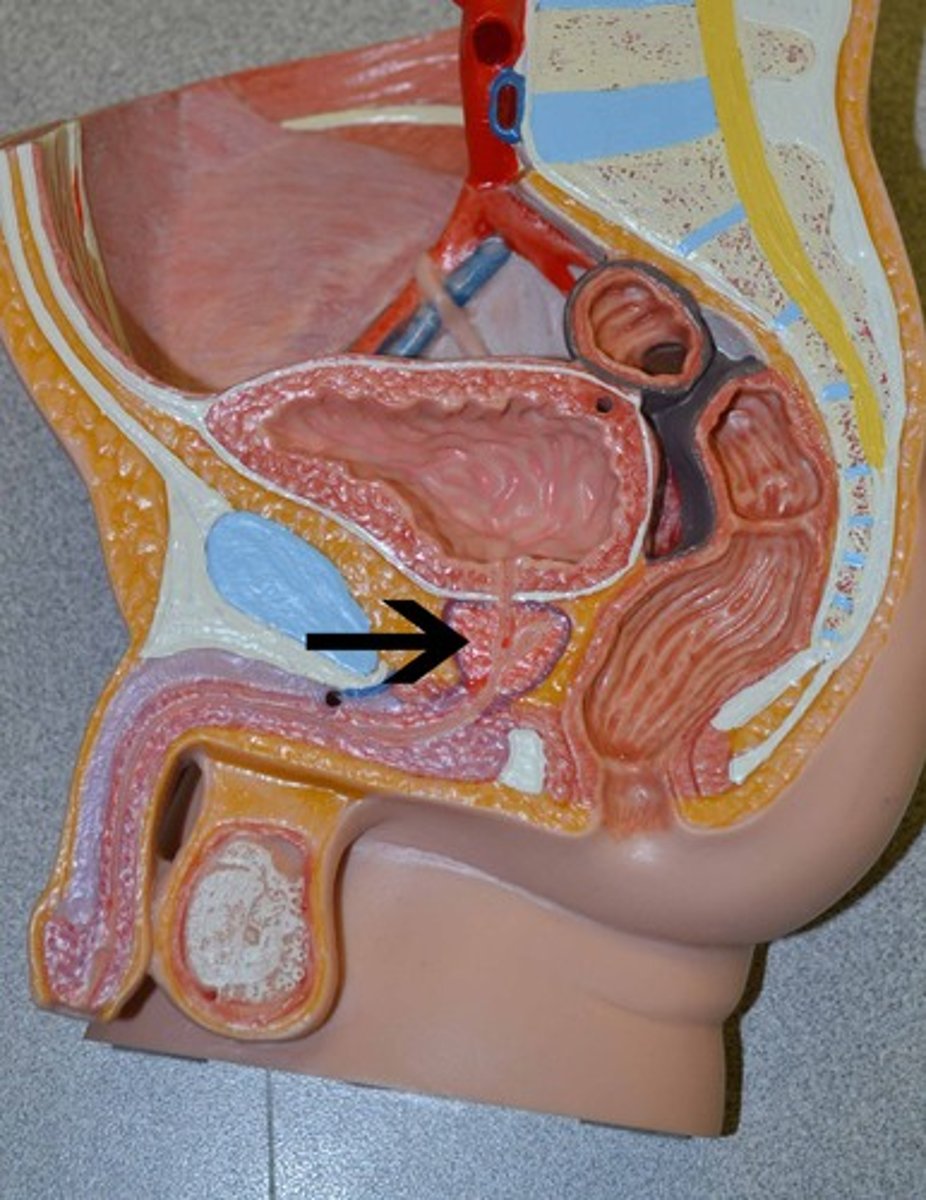
bulbourethral gland
- small gland at base of penis
- secretes lubricating fluid, which passes through penile urethra
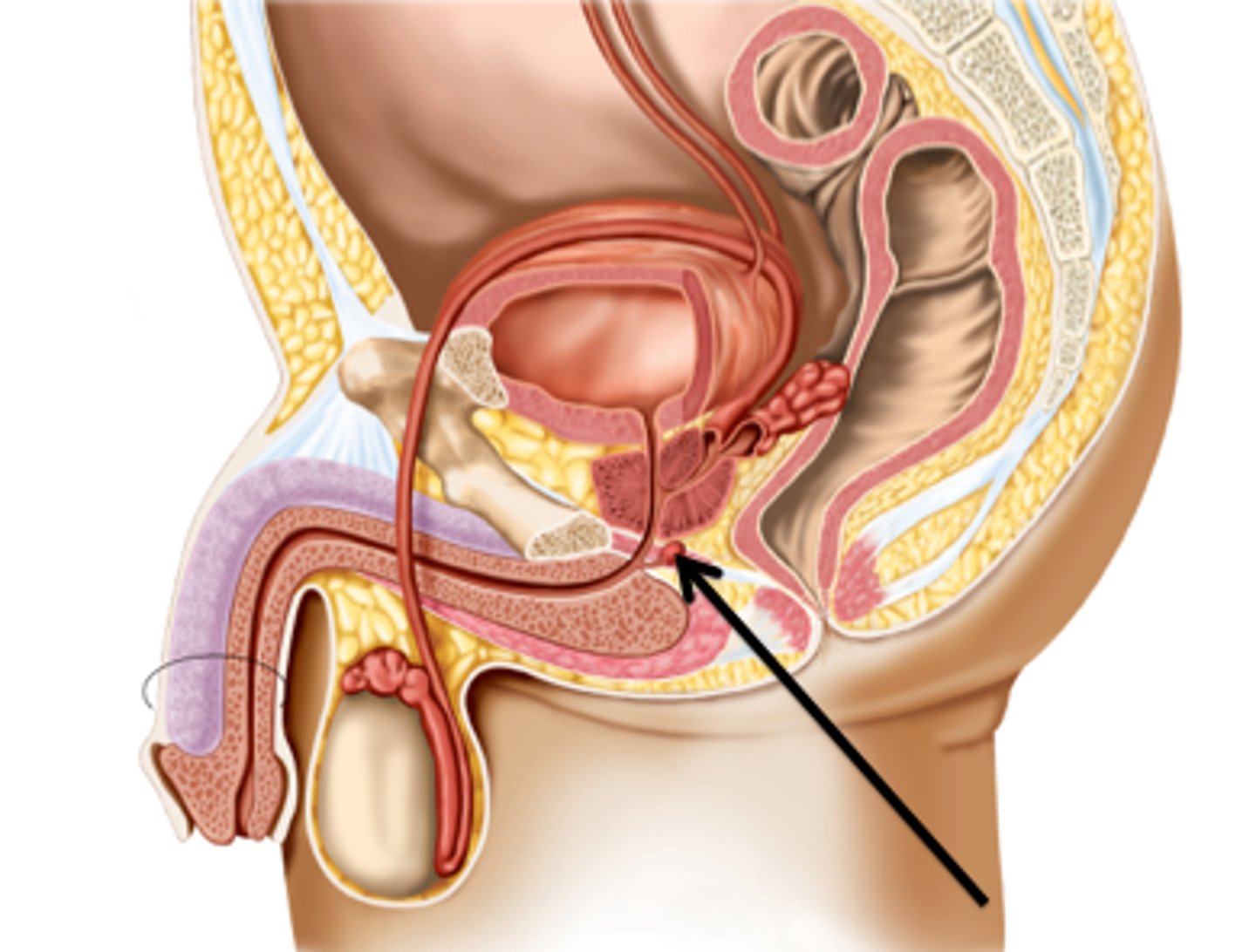
mitosis
- produces two daughter cells identical to the parent cells
- everyday cell division
- 2n cell divides into two 2n cells
meiosis
- produces cells with 1/2 of genetic material of the - parents
- 2n cell divides into two 1n cells
- how sperm and egg cells are made
- only occurs in testis and ovary
diploid cell
- 2n
- 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs
haploid cell
- 1n
- 23 chromosomes
- only sperm and egg cells in humans
spermatogenesis
formation of sperm cells
seminiferous tubules
small convoluted tubules in the testes where spermatogenesis takes place
spermiogenesis phases
golgi phase
acrosomal phase
maturation phase
golgi phase of spermiogenesis
golgi body forms acrosomal vesicle and centrioles migrate toward nucleus
acrosomal stage of spermiogenesis
acrosomal vesicle grows to cover anterior half of nucleus, nucleus condenses and mitochondria aggregate around the forming flagella
maturation phase of spermiogenesis
residual cytoplasm is lost and sperm cell is released into lumen of tubule
leydig cells
- makes and secretes testosterone
- found outside seminiferous tubules, next to capillaries
- directly affected by LH
- diploid
spermatagonia cells
- diploid cells, 23 pairs (46) chromosomes
- found in periphery of each tubule
- can either undergo mitosis and form more cells or enter into the development of mature sperm cells (primary spermatocytes)
primary spermatocyte
- diploid cell in the testis that undergoes meiosis I to form two secondary spermatocytes
- dark staining nucleus
- located more towards lumen in tubules
secondary spermatocytes
- haploid cells resulting from the first meiotic division of spermatogenesis from primary spermatocytes
- undergo meiosis II to form 4 spermatids
- under influence of FSH
- round shaped cell
spermatids
- 23 chromosomes
- products of meiotic division from secondary spermatocyte
- haploid
spermiogenesis
transformation of spermatids to mature sperm
sertoli cells (sustentacular cells)
- storage, scavenging, protection
- diploid
hypothalamus
secretes releasing factors (RF) to the anterior pituitary for FSH and LH
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
stimulates the seminferous tubules to produce sperm cells
luteinizing hormone (LH)
- stimulates interstitial cells of Leydig cells to produce testosterone
- causes follicle cells to transform into luteal cells
inhibin
- inhibitory effect on anterior pituitary and hypothalamus
- secreted in the testis
testosterone
- has an inhibitory effect on anterior pituitary and hypothalamus, creating a negative feedback loop
- secreted by leydig cells in the testes
female reproductive system
- implantation of the embryo and fetus
- internal system
- made up of the ovary, uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina
ovaries
- primary sex organ in females
- where egg cells are stored and developed, also where estrogen and progesterone are produced
- located on either side of the uterus, inferior and posterior to uterine tubes
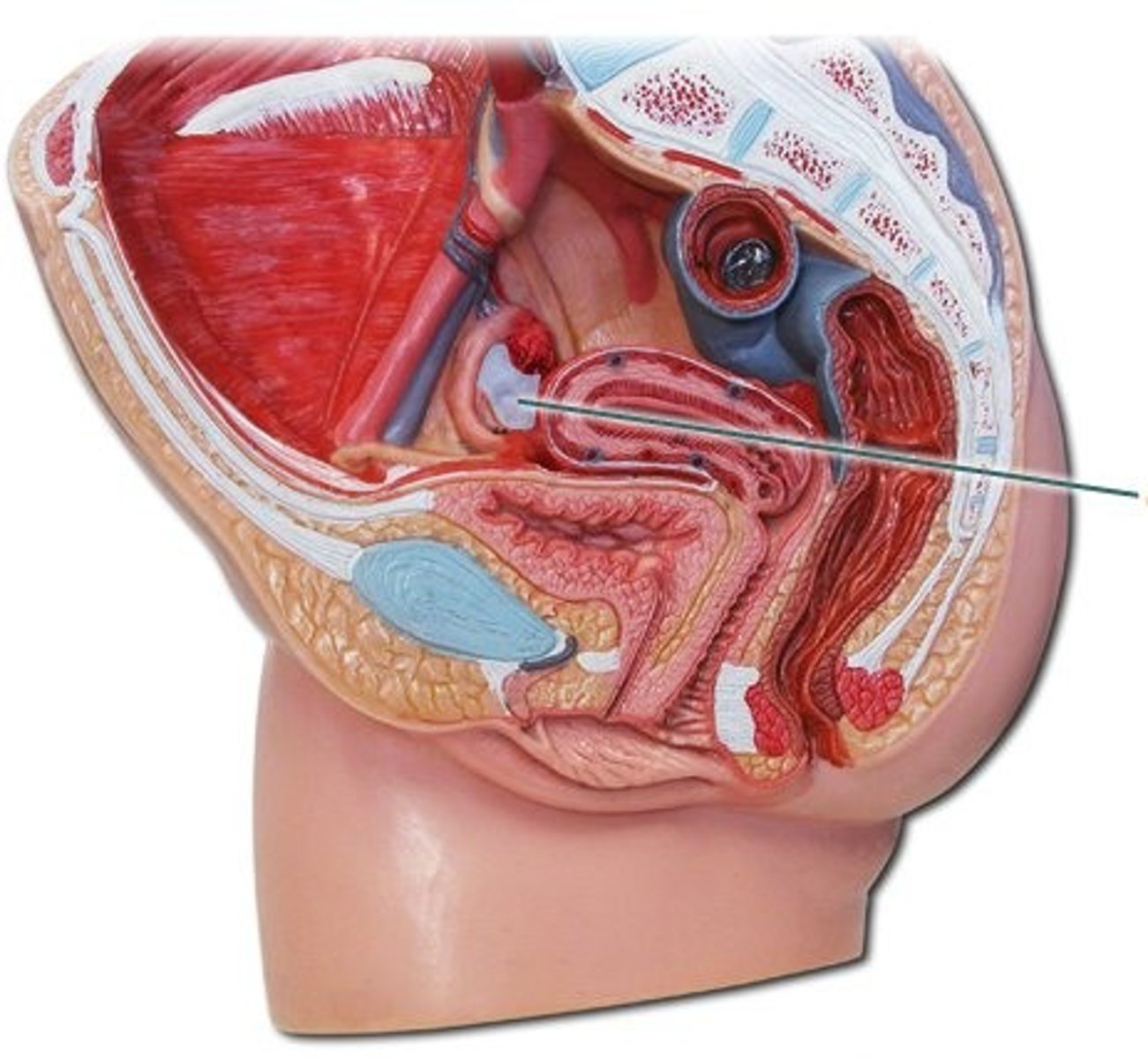
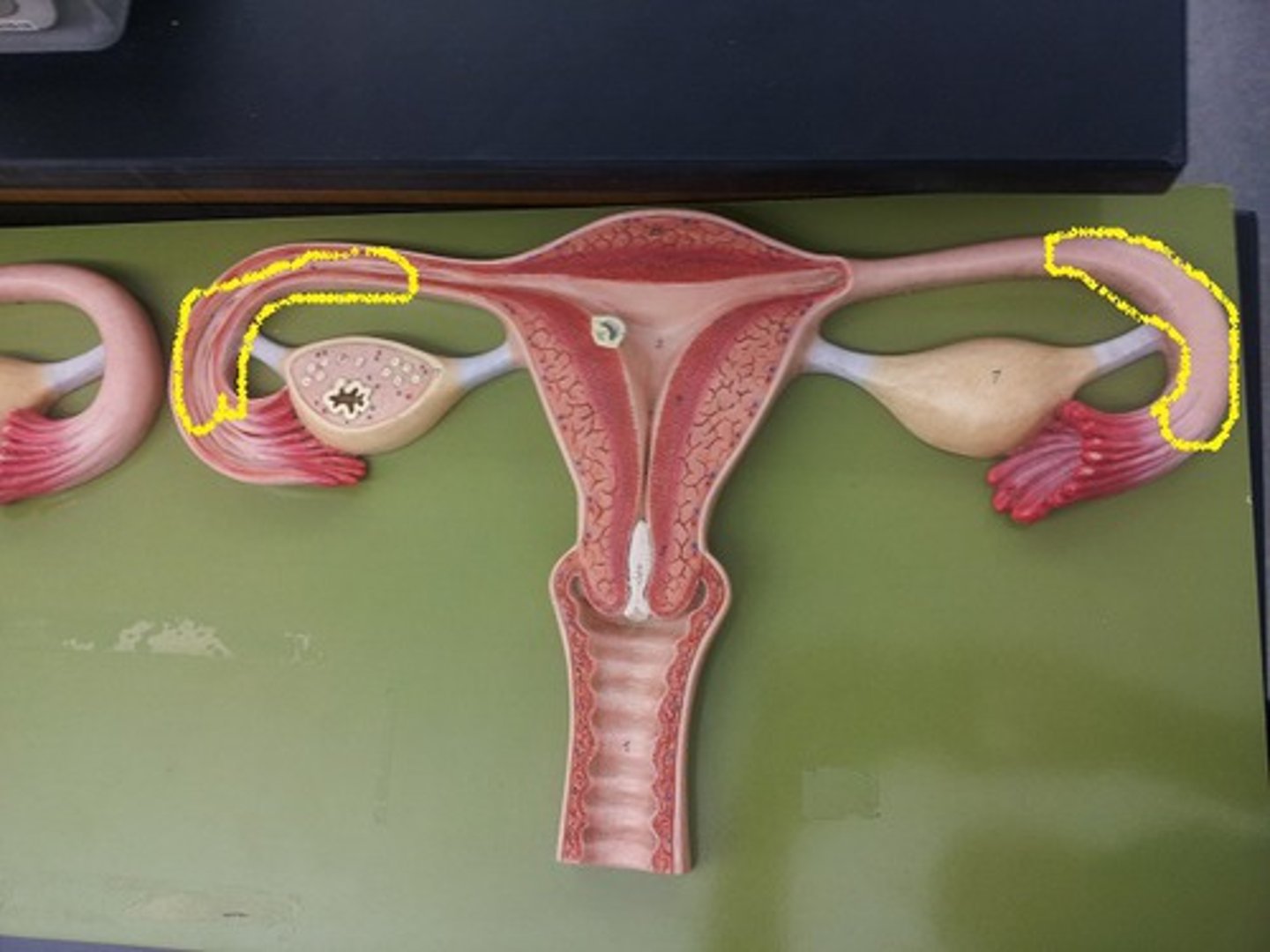
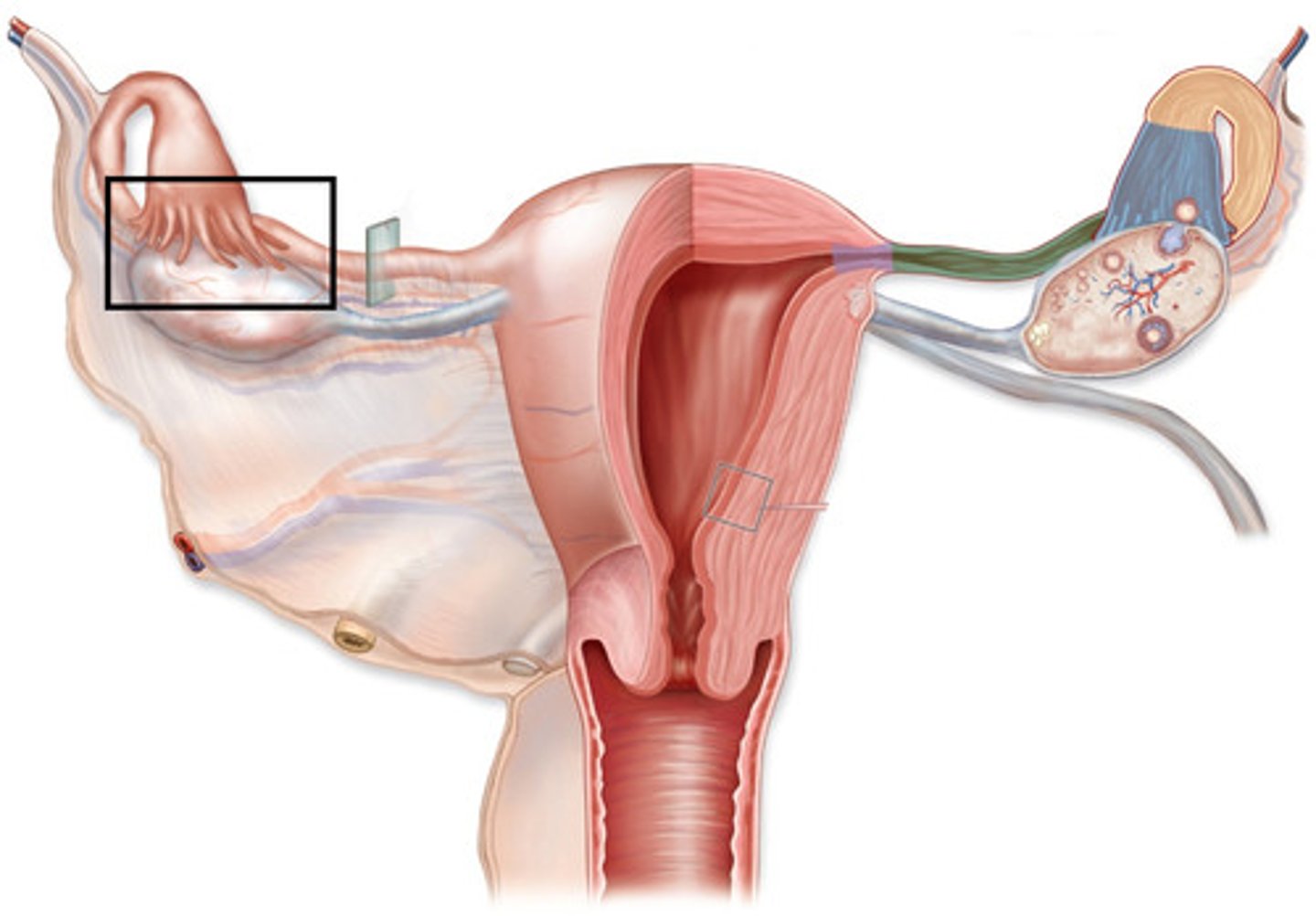
uterine tubes
- provides a passageway from the ovary to the uterus for the egg cell and is the site of fertilization
- extend from the lateral surface of the uterus and cover the superior aspect of the ovary
- muscular tubes that can be divided into an isthmus, ampulla, and infundibulum
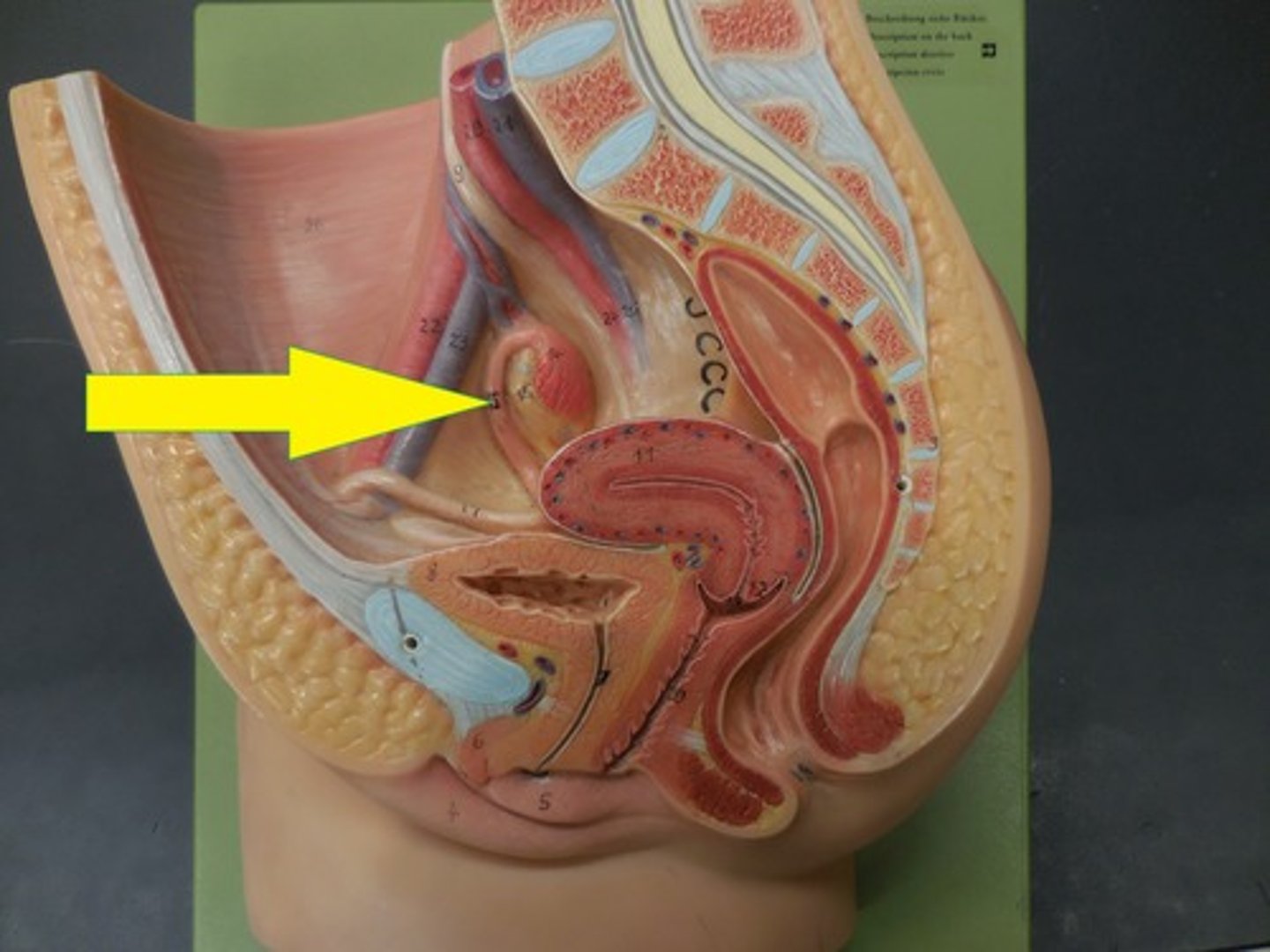
uterus
- site of implantation and where the embryo/fetus develops
- muscular organ in female pelvis
- divided into the cervix, isthmus, body, and fundus
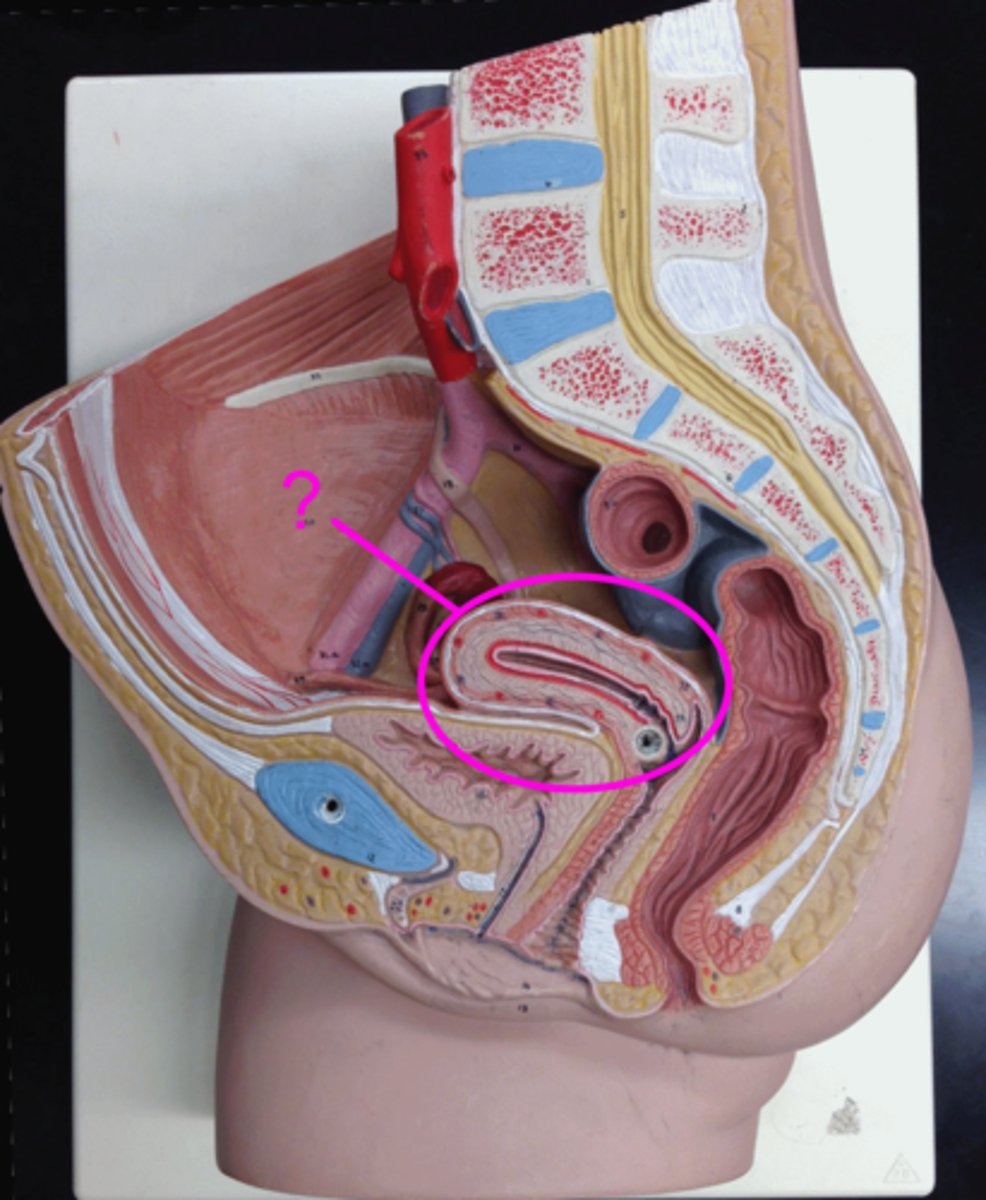
vagina
muscular tube that serves as the site of introduction of sperm into the female reproductive system and as the birth canal
fornix
- site of union of the vagina and uterus
- found in vagina
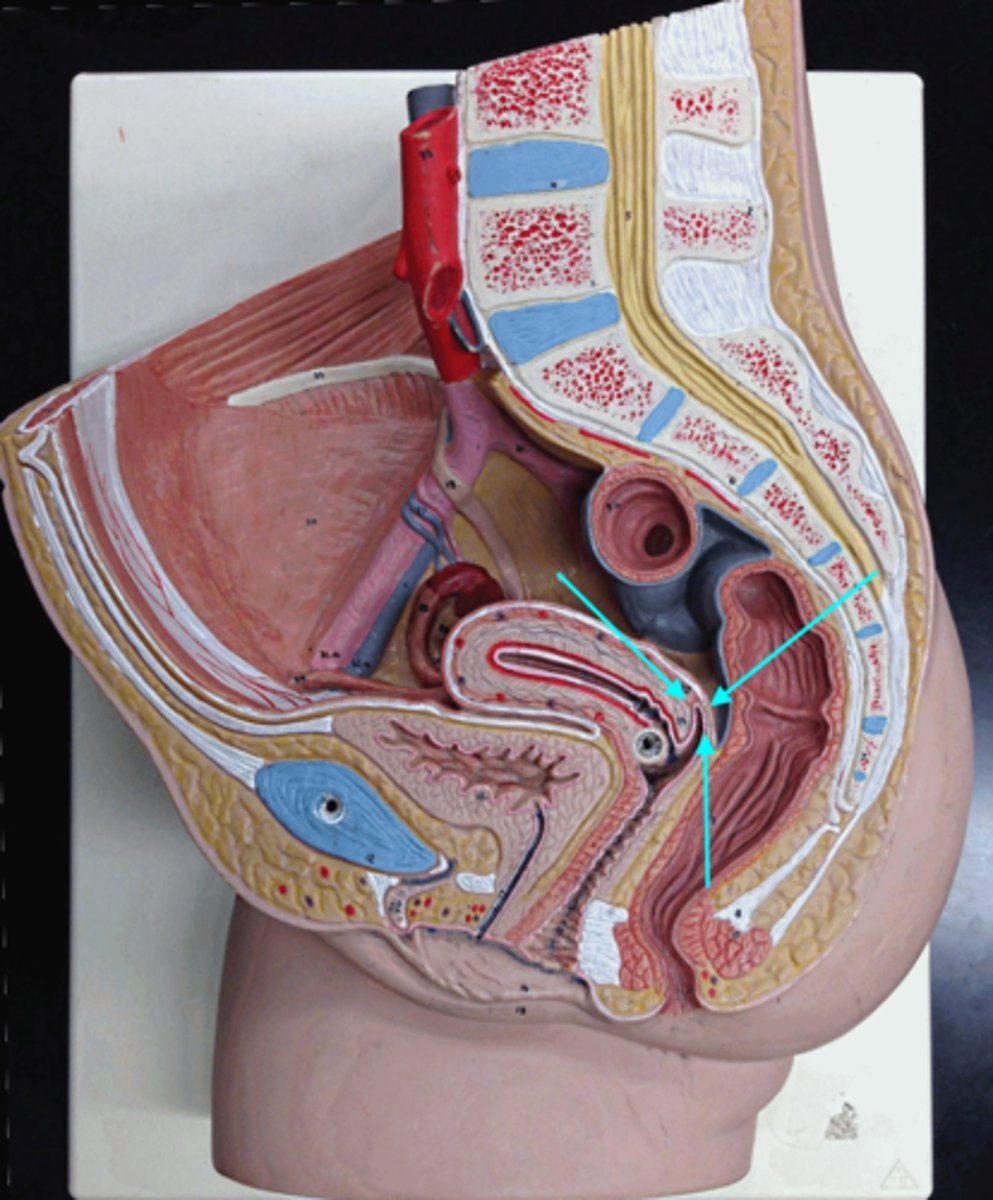
isthmus
- narrowed (long) region between the body and cervix
- attaches directly to the uterus
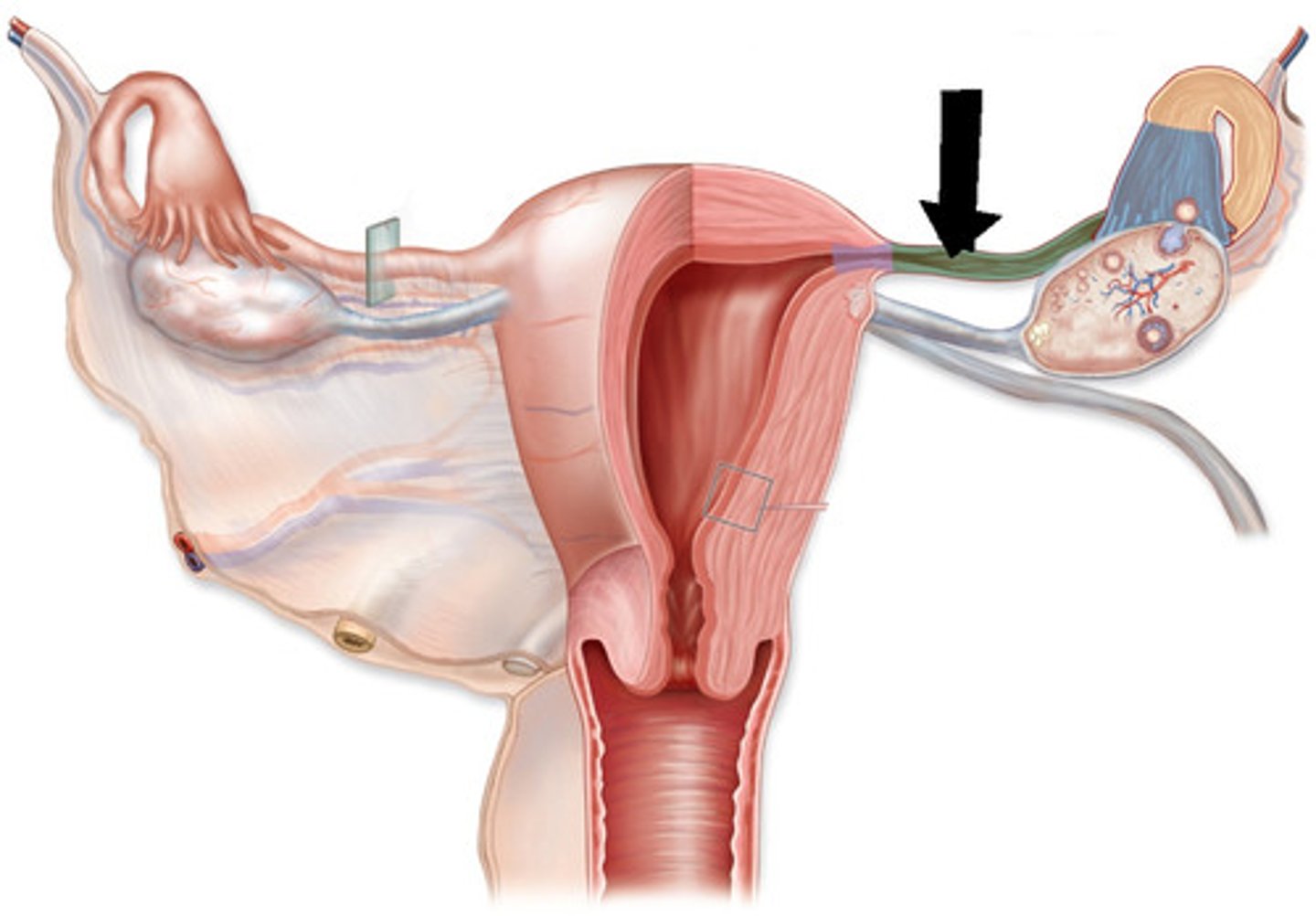
ampulla
site of fertilization (most common)
infundibulum
funnel-shaped opening that is the distal end of each uterine tube
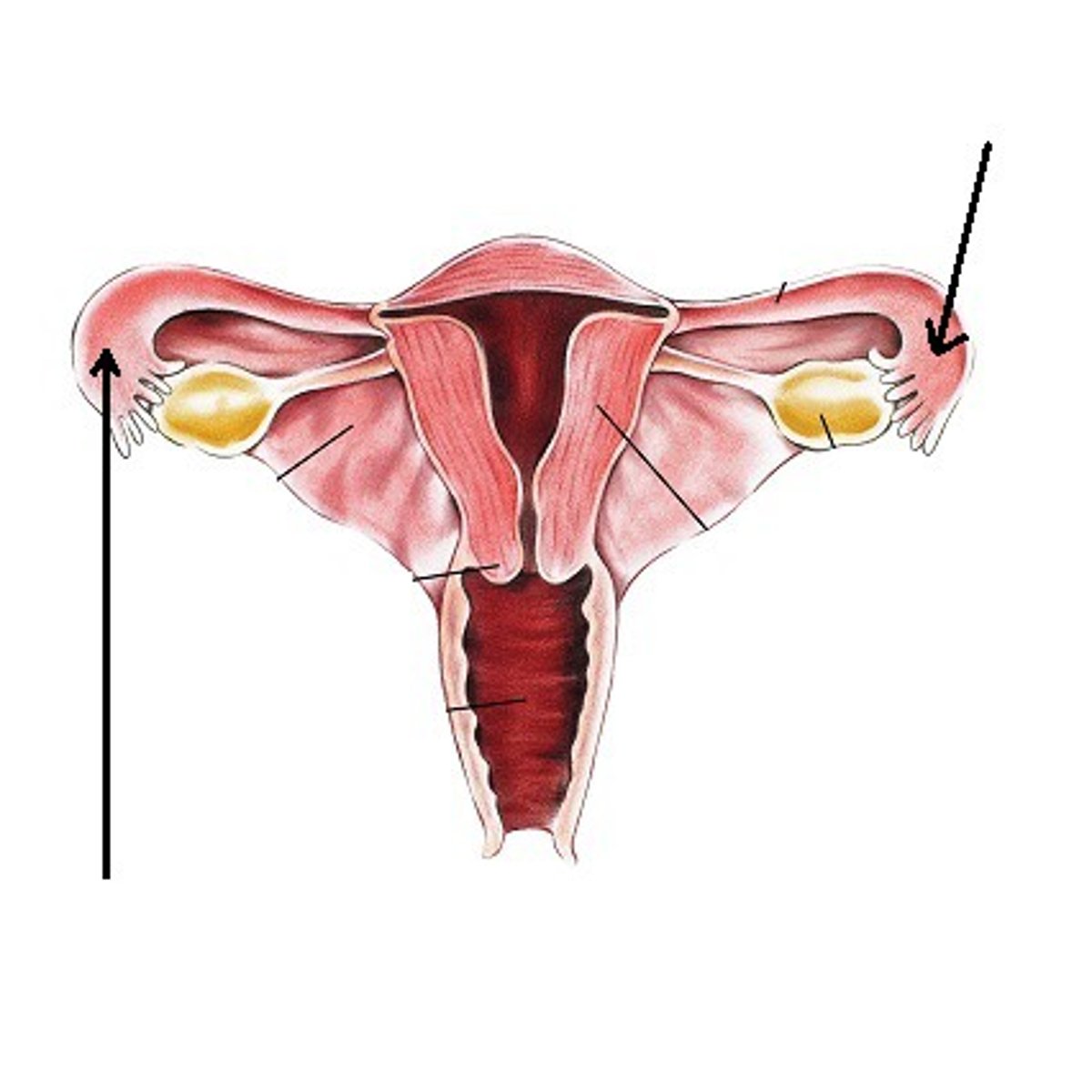
fimbria
- finger-like projection at the free end of the uterine tube
- attached to infundibulum
fundus
any part of the uterus that is above the uterine tubes
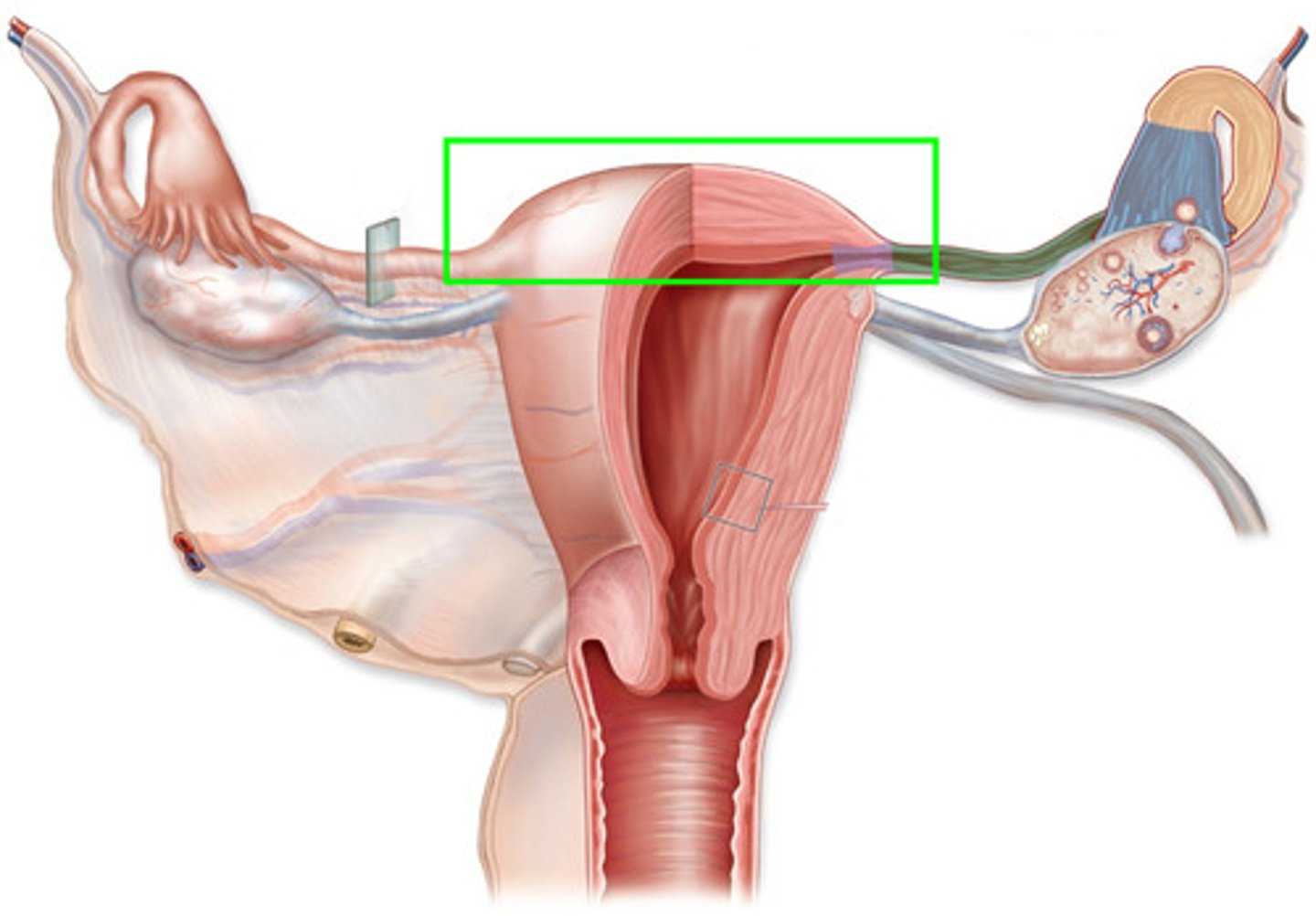
uterus wall
endometrium
myometrium
perimetrium
endometrium
- inner layer
- undergoes the monthly cycle
- where the baby develops
- made up of 3 layers
myometrium
middle layer
smooth muscle
perimetrium
outer layer of connective tissue
cervix
opening of the uterus into the vagina
endometrium layers
basal layer
spongy layer
compact layer
basal layer of endometrium
- nonfunctional outer layer
- helps regenerate functional layer
- straight arteries
spongy layer of endometrium
- functional layer
- bodies of glands
compact layer of endometrium
- functional layer
- epithelia
- opening
uterine cycle
approximately 28 days (23-35)
menstrual phase
proliferative phase
secretory phase
ischemic phase
menstrual phase of the uterine cycle
- days 1-5
- estrogen and progesterone at lowest
- spongy and compact layers lost
proliferative phase of the uterine cycle
- days 6-14
- estrogen increases
- functional layer rebuilt
secretory phase of the uterine cycle
- days 15-27
- progesterone increases
- glands begin to function
- implantation occurs on day 21
ischemic phase of the uterine cycle
- day 28
- estrogen and progesterone drop quickly
- smooth muscle walls spasm
- menstrual flow begins due to spasm
- spiral artery affected
egg nest
- where eggs are stored in the ovary
- made up of egg cells and one layer of follicle cells
thecal cells
make and secrete estrogen
antrum
- fluid-filled cavity that appears in a secondary follicle (6)
- formation of one marks the development of a mature follicle
zona pellucida
- a thick, transparent coating rich in glycoproteins that surrounds an oocyte
- protects the egg cell
ovarian cycle
- (under FSH) 12 egg nests per month develop into primary follicles
- antrum forms in 6 follicles (secondary follicles)
- one of 6 forms into a mature follicle
- (day 14 - ovulation) mature follicle ruptures and egg cells + corona radiata released
- (under LH) remaining cells in follicle swell, small blood clot formed (corpus hemorrhagicans)
- follicles swell and secrete progesterone (corpus luteum)
- if pregnancy occurs, corpus luteum remains for 3 months, if not it degenerates into corpus albicans
luteal cells
- makes and secretes progesterone
- swollen follicle cells
corpus luteum
- empty ovarian follicle that secretes progesterone after release of the egg cell
- forms under the influence of LH
- remains for 3 months if pregnancy, degenerates into corpus albicans
corpus albicans
- the scar tissue that replaces the corpus luteum
- caused by the drop of LH levels in the blood at the end of the 28 day-cycle
- as soon as progesterone production ends, the corpus luteum begins to degenerate and is replaced by this
primary follicle
- an immature ovum enclosed by a single layer of cells
- 12 egg nests per month develop
- under the control of FSH
secondary follicle
- under the control of FSH
- fluid filled antrum forms in 6 follicles
- one forms into a mature follicle
corona radiata
- outer layer of cells surrounding the oocyte
- secreted by follicle cells.
ovulation
day 14
anterior pituitary gland
- under the influence of RFs from hypothalamus, releases FSH, which causes the development of follicles in the ovary, which in turn causes the release of estrogen
- progesterone and estrogen feed back here and hypothalamus to form negative feedback loops
midpiece
where is the mitochondria located in mature sperm?
diploid (2n) cell examples
spermatogonium
sertoli cells
leydic cells
primary spermatocyte