Lab Practical 1 A&P
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
divides the body into left and right parts
Sagittal Plane
divides the body into equal right and left sides
midsaggital plane (midline)
divides the body into unequal left and right sides
parasagittal plane
plane divides body vertically into anterior (front) and posterior (back) parts
front (coronal) plane
plane divides body horizontally into superior (top) and inferior (bottom) parts
transverse plane
cuts made diagonally
oblique plane
-protects nervous system
-includes additional cavities: cranial and vertebral cavities
-encases brain and spinal cord
dorsal cavity
contains brain
cranial
contains spinal cord
spinal cavity
houses the internal organs (viscera), and is divided into two subdivisions: thoracic and abdominopelvic
ventral cavity
separates upper and lower ventral cavities
diaphragm
contains heart + lungs
thoracic cavity
fluid filled space that surrounds the lungs.
pleural cavity
located between the pleural cavities and includes the heart, great vessels, esophagus, and trachea.
mediastinum
contains heart
pericardial cavity
any organ below the diaphragm, lining the abdominal pelvic cavity.
peritoneal cavity
contains digestive viscera
abdominal cavity
contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, rectum
pelvic cavity
outer layer lining the thoracic wall
parietal pleural membrane
inner layer on the surface of the lung
visceral pleural membrane
outer layer around the heart within the mediastinum
parietal pericardial membrane
inner layer on the surface of the heart
visceral pericardial membrane
outer layer enclosing the abdominal organs
parietal peritoneal membrane
inner layer on the surface of most abdominal organs
visceral peritoneal membrane
toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above
Superior (cranial)
away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below
inferior (caudal)
front or toward the front of the body
Anterior (ventral)
Toward or at the back of the body; behind
Posterior (dorsal)
toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of
medial
away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of
lateral
Closer to the point of attachment
Proximal
farther away from the point of origin
distal
toward or at the body surface
Superficial (external)
Away from the body surface; more internal
Deep (internal)
Flat surface along which body or structure is cut for anatomical study
plane
-liver and gallbladder
-located in RUQ
What is located in the right hypochondriac region?
ascending colon of large intestine
What is located in the right lumbar region?
cecum, appendix
-located in RLQ
What is located in the right iliac (inguinal) region?
stomach
What is located in the epigastric region?
small intestine, transverse colon of large intestine
What is located in the umbilical region?
urinary bladder
What is located in the hypogastric (pubic) region?
diaphragm
-located in LUQ
what is located in the left hypochondriac region?
descending colon of large intestine
What is located in the left lumbar region?
initial part of sigmoid colon
What is located in the left iliac (inguinal) region?
top: right upper quad, left upper quad bottom: right lower quad, left lower quad
from left to right what is the order of the quadrants?
top: right hypochondriac region, epigastric region, left hypochondriac region
middle: right lumbar region, umbilical region, left lumbar region
bottom: right iliac (inguinal) region, hypogastric (pubic) region, left (inguinal) region
from left to right what is the order of the regions?
provides a sturdy, flat surface to support and steady the microscope
function of the base of the microscope
located at the base; the light from the lamp passes directly upward through the microscope
function of the substage light of the microscope
located at base or arm; the dial allows you to adjust the intensity of the light passing through the specimen
function of light control on the microscope
Supports the slide being viewed, it has a hole in it that allows light to pass through the specimen
Function of stage on a microscope
holds the slide in position while being viewed; it has two adjustment knobs that control the precise movement
function of the mechanical stage on a microscope
focuses light through the specimen; small non-magnifying lense located beneath the stage that concentrates the light of the specimen and may have a knob that raises and lowers to vary the light delivery. best position is close to the inferior surface of the stage
function of the condenser on a microscope
controlled by a lever to adjust the amount of light passing through the condenser; it can be moved to close the diaphragm and improve contrast.
function of iris diaphragm on microscope
allows you to make large adjustments to the height of the stage to initially focus your specimen
function of coarse adjustment knob on a microscope
used for precise focusing once the initial coarse adjustment focusing has been completed
function of fine adjustment knob on a microscope
attaches to the nosepiece to support objective lenses; provides for attachment of the eyepieces which have the ocular lenses
function of the head of the microscope
vertical portion of the microscope that connects the base and the head
Function of the arm of a microscope
rotating mechanism of the head; it carries three or four objective lenses and permits positioning of these lenses over the hole in the stage
Function of the Nosepiece of the Microscope
they are attached to the nose piece; scanning is 4x, low power is 10x, high power is 40x; the lenses you use to magnify the specimen
Function of the objective lenses of a microscope
located in the eyepieces at the superior end of the head; have a magnification of 10x
function of the ocular lens(es) of a microscope
Scanning (red): 4x 10 =40
Low Power (yellow): 10x 10=100
High Power (blue): 40x 10=400
Total magnification of a microscope
they are tiny, spherical body is composed of RNA and proteins; floating, free, or attached to a membrane structure (the rough ER) give me a cytoplasm. Actual sides of proteins synthesis.
What are ribosomes and their function?
membranous system of tubules that extends throughout the cytoplasm. Includes rough ER and smooth ER.
-Rough ER provides an area for storage and transport of the proteins made on the ribosomes to other cell areas.
-Smooth ER, which has no function in proteins synthesis is a side of steroid and lipid synthesis, lipid metabolism, and drug detoxification
what is endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and what is its function?
Stack of flattened, sacs with bulbous ends and associated small vesicles; found close to the nucleus.
-Play the role in packaging proteins or other substances for export from the cell or incorporation into the plasma membrane and in packaging lysosomal enzymes
What is the Golgi apparatus and its function?
various sized membranous sacs containing digestive enzymes, including acid hydrolases
-Their function is to digest, worn out cell organelles in foreign substances that enter the cell. They have the capacity of total sell destruction, if ruptured an hour, for this reason, referred to as "suicide sacs"
what are lysosomes and their function?
small lysosome, like membranous sacs containing oxidase enzymes that detoxify, alcohol, free radicals, and other harmful chemicals. They are particularly abundant in liver and kidney cells.
what are peroxisomes and their function?
Rod shaped bodies with a double membrane wall; inner membrane is shaped into folds, or cristae.
-contain enzymes that oxidize foodstuffs to produce cellular energy (ATP)- often referred to as the "powerhouses of the cell"
what is mitochondria and its function?
cylinder bodies that lie at right angles to each other close to the nucleus. Each centriole is composed of nine triplets of microtubules
-They direct the formation of the mitotic spindle during cell division: form the bases of cilia and flagella and in that role are called basal bodies
what are centrioles and their function?
they provide cellular support function in intracellular transport.
-Microfilaments are formed largely of Acton, a contractile protein in our important and sell mobility in muscle cells
-Intermediate filaments are stable elements composed of a variety of proteins and resist. Mechanical forces acting on cells.
-Microtubules form the internal structure of the centrioles and help determine cell shape
what are cytoskeletal elements: microfilaments, intermediate filaments , and microtubules and their function?
interphase
What phase of mitosis is this?
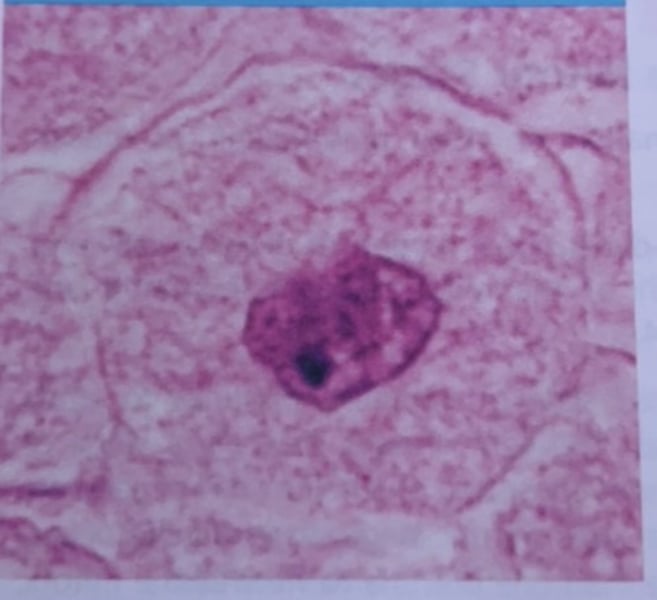
Early Prophase
what phase of mitosis is this?
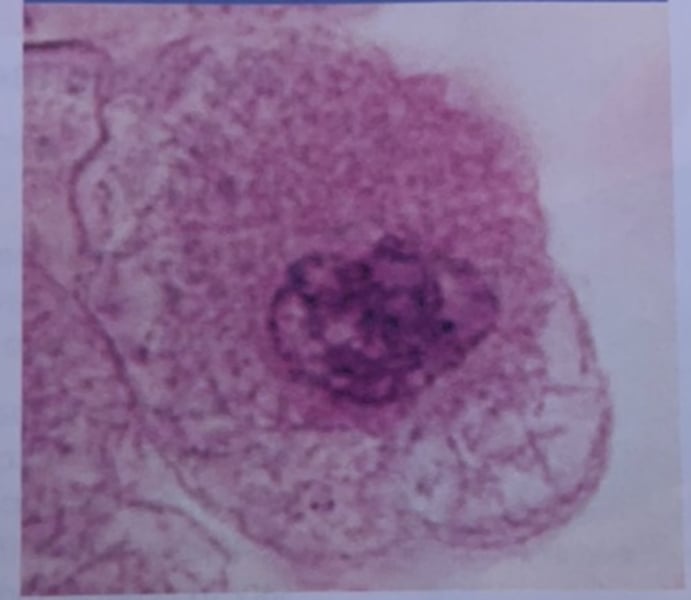
late prophase
What phase of mitosis is this?
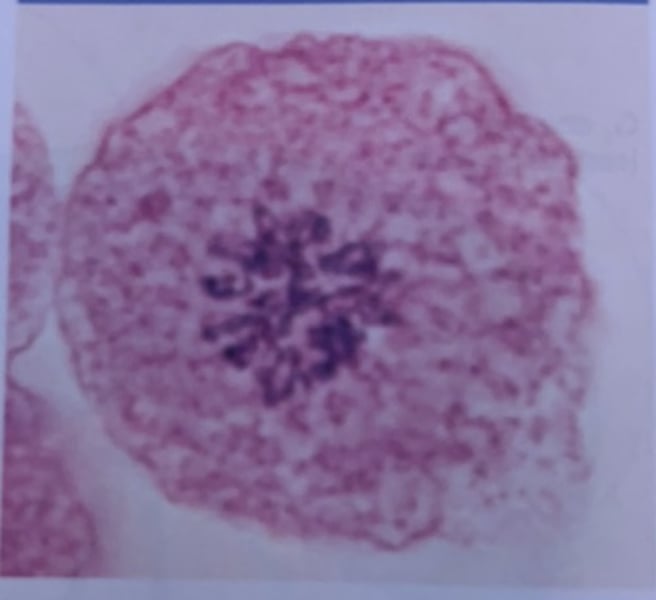
metaphase
What phase of mitosis is this?
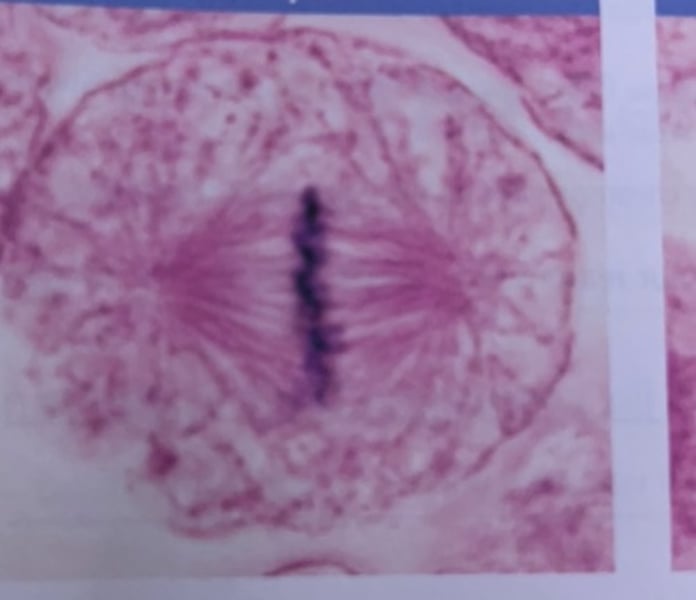
anaphase
what phase of mitosis is this?
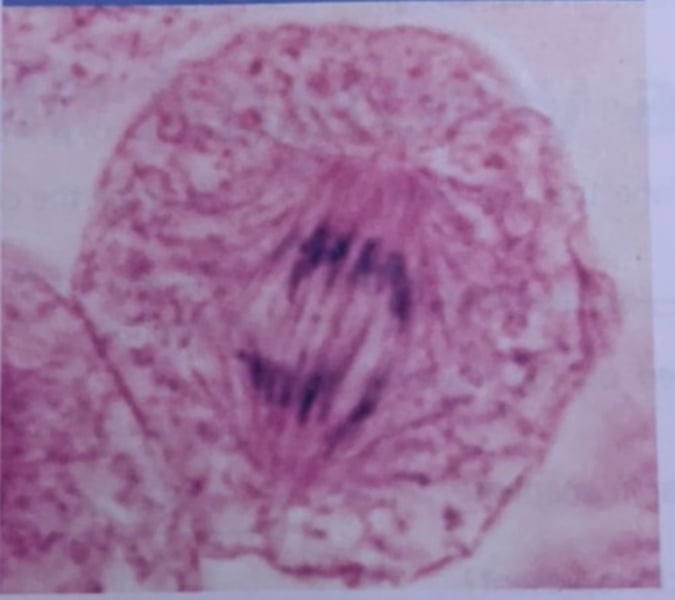
telophase and cytokinesis
what phase of mitosis is this?
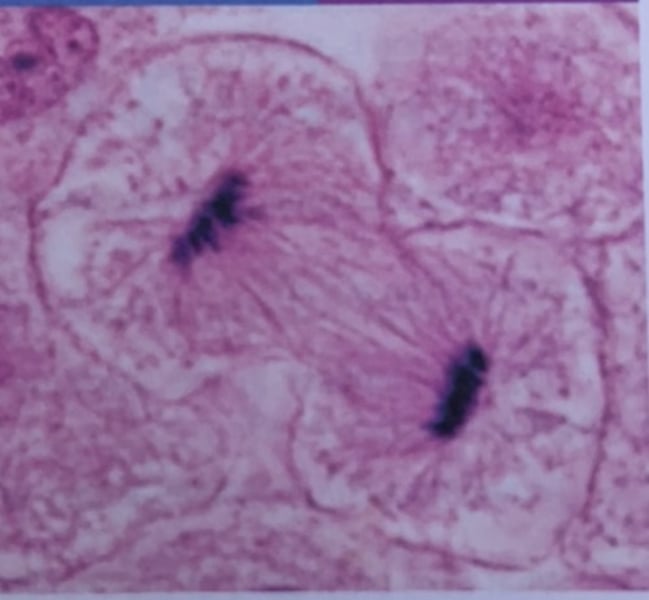
methylene blue solution and potassium permanganate solution
What chemicals were used on the plates for diffusion?
A compound microscope can receive higher levels of magnification compared to a simple microscope. Compound means you look through two lenses.
What's the difference between a compound microscope and a simple microscope?
When you have the object in focus with one objective. It will be visible on all objectives with just a minor adjustment from the fine adjustment knob
what does parfocal mean?
the high molecular weight leads to slower diffusion.
Why did one chemical diffuse more than the other?
*comparing methylene blue and potassium permanganate
it contains more non-penetrating solute particles than the interior of the cell
What does it mean if a cell is hypertonic?
it contains fewer non-penetrating solute particles than the interior of the cell
What does it mean if a cell is hypotonic?
it contains a concentration of non-penetrating solutes (proteins or some ions) equal to that in the cells (same solute/water concentration)
What does it mean if a cell is isotonic?
-simple columnar epithelium
function: absorption, secretion of mucous, enzymes, and other substances
location: most of the digestive tract (stomach to rectum), gallbladder, and excretory ducts of some glands.
What tissue is this? What is its function and where is it located?
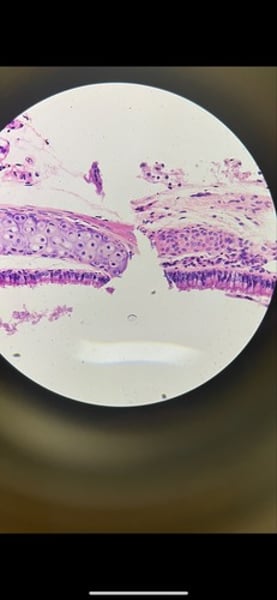
simple cuboidal epithelium
Function: secretion and absorption
Location: kidney tubules; ducts and secretory portions of small glands: ovary surface
What tissue is this? What is its function and where is it located?
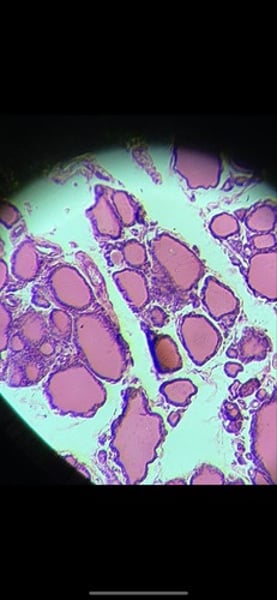
-transitional epithelium
function: stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine
location: lines the ureters, urinary bladder, and part of the urethra
What tissue is this? What is its function and where is it located?
-simple squamous epithelium
function: allows materials to pass by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important; secretes lubricating substances in serosae
location: kidney glomeruli; air sacs of lungs; lining of heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels: lining of ventral body cavity (serosae)
What tissue is this? What is its function and where is it located?
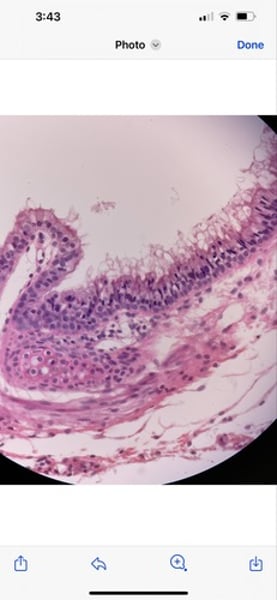
-ciliated epithelium
function: moves particles or fluid over the epithelial surface
location: trachea, bronchial tubes, and nasal cavities
What tissue is this? What is its function and where is is located?
-Areolar connective tissue
function: wraps and cushions organs; plays important role in inflammation; holds and conveys tissue fluids
location: widely distributed under epithelia of body; surrounds capillaries; packages organs
What tissue is this? What is its function and where is it located?
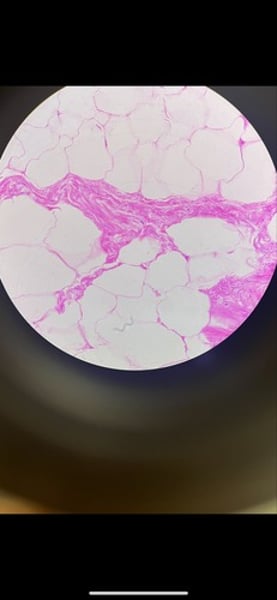
-adipose connective tissue (fat)
function: provides reserve fuel; insulates against heat loss; supports and protects organs
location: under skin; around kidneys and eyeballs; within abdomen; in breasts
What tissue is this? What is its function and where is it located
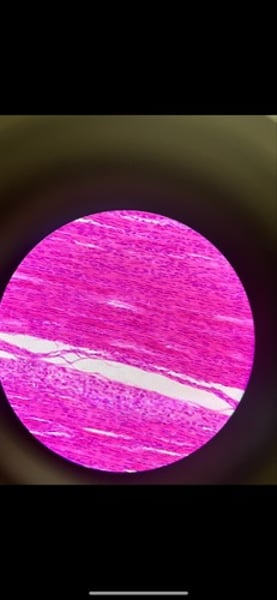
-tendon: dense regular (white elastic) or dense fibrous connective tissue
function: attached muscles to bones or to other muscles; attached bones to bones; withstands great tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction
location: tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses
What tissue is this? What is its function and where is is located?
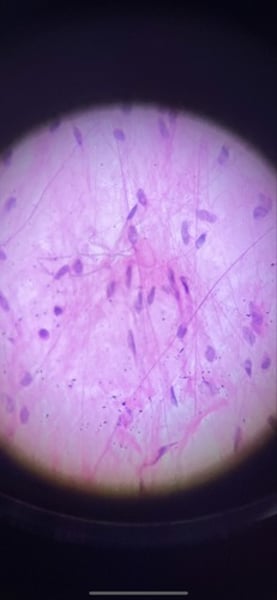
-nerve tissue
function: neurons transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors (muscles and glands); supporting cells support and proved neurons
location: brain, spinal cord, and nerves
What tissue is this? What is its function and where is it located?
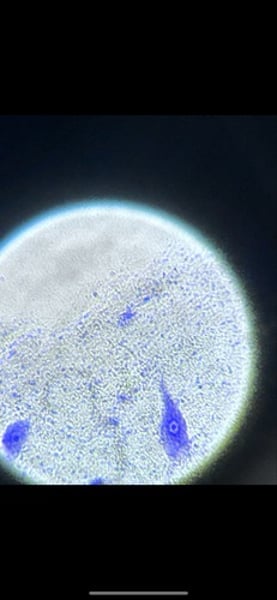
-human skeletal muscle
function: voluntary movement; locomotion; manipulation of the environment; facial expression; voluntary control
location: in skeletal muscles attached to bones or occasionally to skin
What tissue is this? what is its function and where is it located?
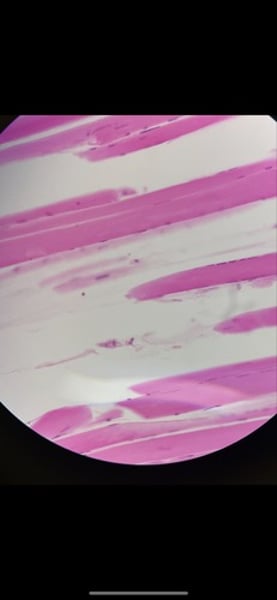
-fibrocartilage
function: tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock
location: intervertebral discs; pubic symphysis; discs of knee joint
What tissue is this? what is its function and where is it located?
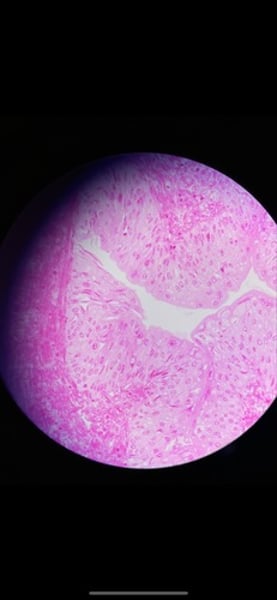
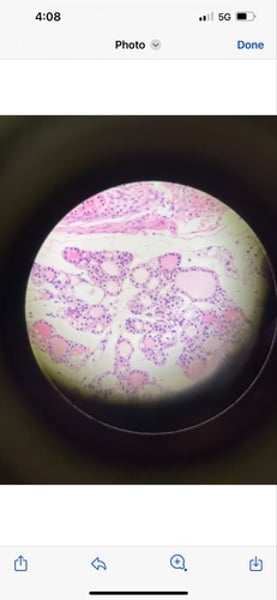
-human hyaline cartilage
function: supports and reinforces; serves as resilient cushion; resists comprehensive stress
location: forms most of embryonic skeleton; covers the ends of long bones in joint cavities; forms coastal cartilages of the ribs; cartilage of the nose, trachea, and larynx
What tissue is this? What is its function and where is it located?
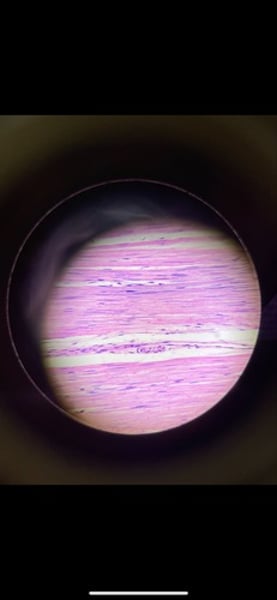
-smooth muscle tissue
function: propels substances (foodstuffs, urine) or a baby along internal passageways; involuntary control
location: mostly in the walls of hollow organs
What tissue is this? What is its function and where is it located?
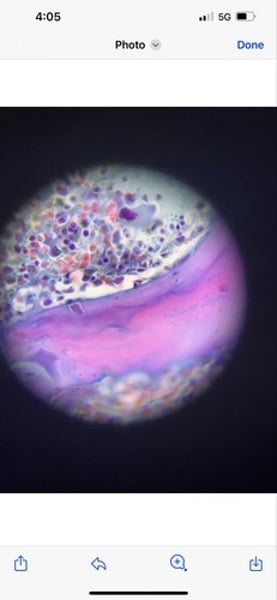
-mammal elastic cartilage
function: maintains the shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility
location: supports the external way (auricle); epiglottis
What tissue is this? What is its function and where is it located?
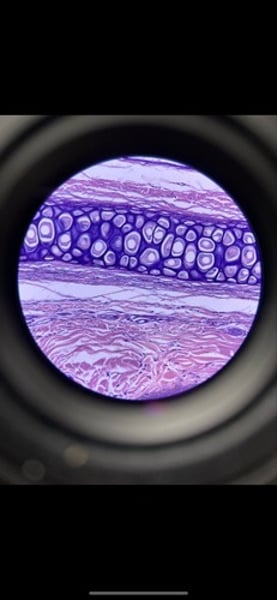
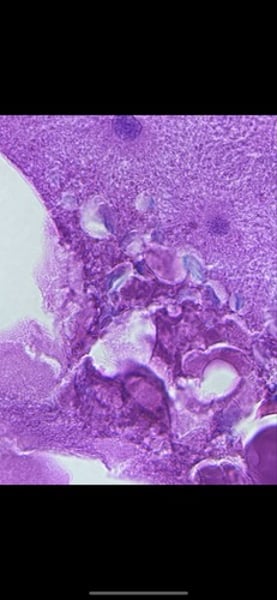
-whitefish (animal)
function: movement and phases of mitosis
-define the phase of mitosis the slide is in
What tissue is this? What is its function and where is it located?
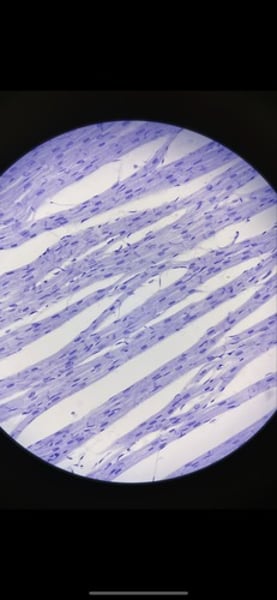
-cardiac muscle
function: as it's contracts, cardiac muscle propels blood into the circulation; involuntary control
location: the walls of the heart
What tissue is this? What is its function and where is it located?
-mammal bone
function: bone supports and protects (by enclosing); provides levers for the muscles at act on; stores calcium and other minerals and fat; marrow inside bones is the site of blood cell formation
What tissue is this? What is its function and where is it located?
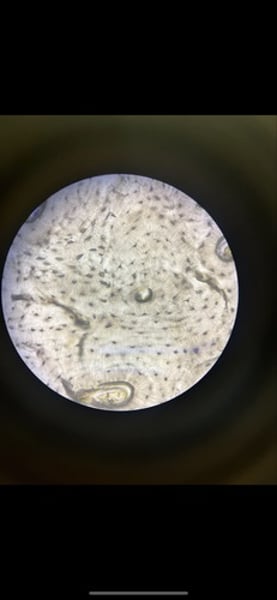
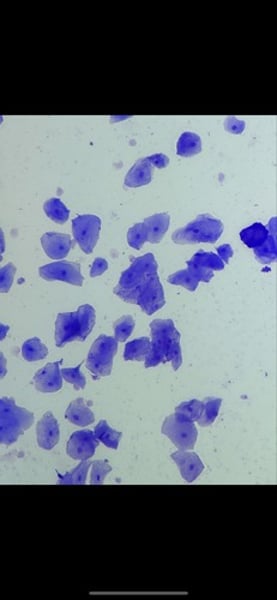
-human blood smear
function: transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances
location: contained within blood vessels
What tissue is this? what is its function and where it located?