PBL Finals Trimester 1 Combot
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms

What are the black lines?
Intermediate filament (keratin) (in a keratinocyte cell)
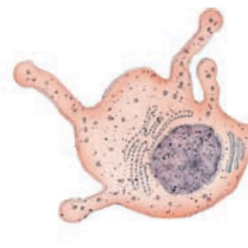
What are the dots?
Melanin granules (in a melanocyte)
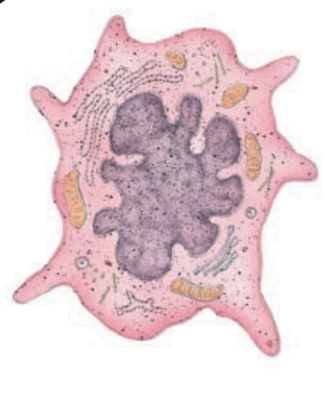
What is this?
langerhans cell
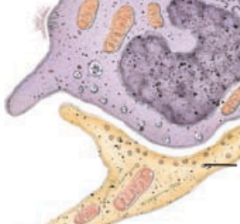
black line is pointing to?
Merkel (tactile) disc
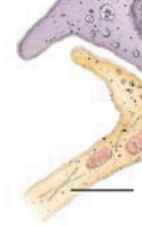
black line is pointing to?
sensory neuron of a merkel cell
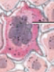
What type of cell is this
langerhans cell
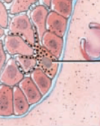
What type of cell is this? the one the black line is pointing to?
Melanocyte
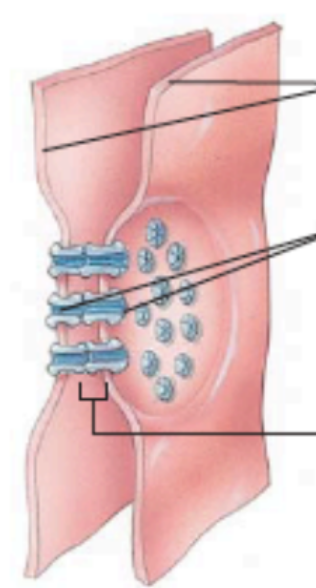
What is this?
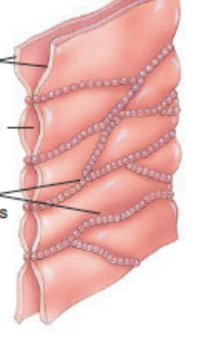
gap junction
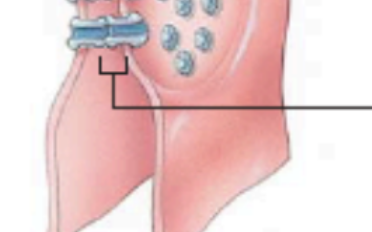
what is the line pointing to?
gap between cells
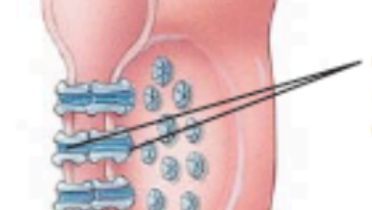
What is the lines pointing to? (photo of gap junction)
connexons (composed of connexins)
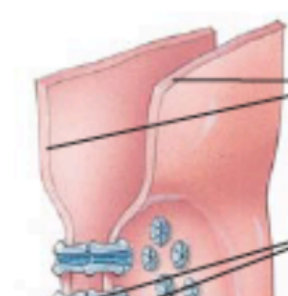
what are the top lines pointing to? (in a gap junction)
adjacent plasma membranes
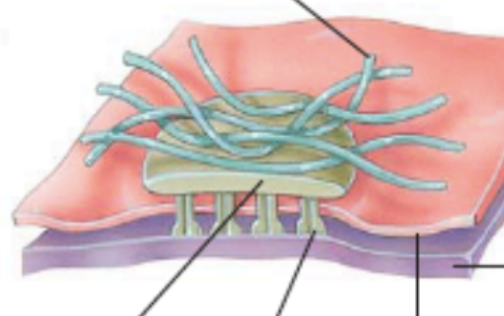
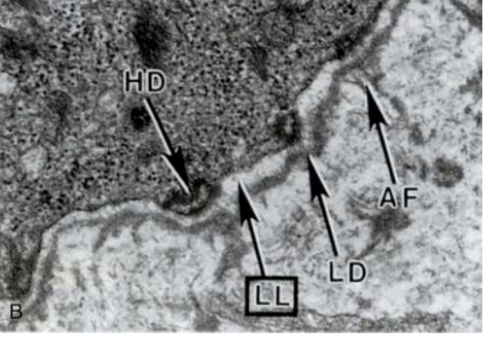
what is this overall photo of?
hemidesmosome
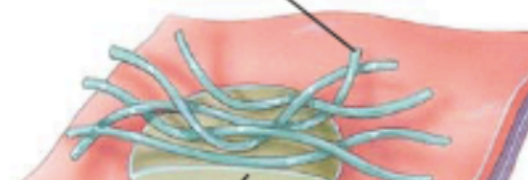
what is this blue part of a hemidesmosome?
intermediate filament (keratin)
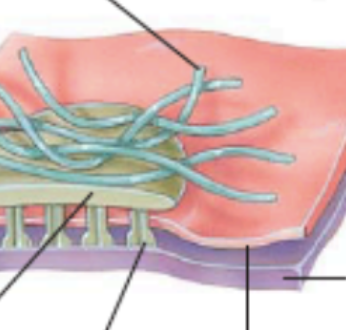
what is the pink layer and what is the purple layer (hemidesmosome)
pink = plasma membrane; purple = basement membrane
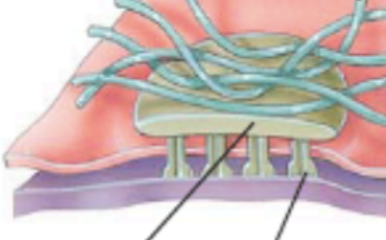
What are the two lines pointing to? (hemidesmosome)
top = plaque; bottom = transmembrane glycoprotein (integrin) in extracellular space
what is this?
tight junctions
what are the lines pointing to?
strands of transmembrane proteins
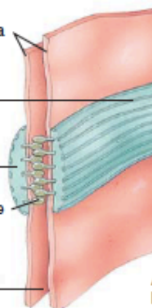
what is this?
adherens junction
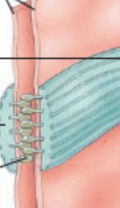
what do the blue and green represent on this adherens junction?
blue = plaque; green = transmembrane glycoprotein (cadherin)
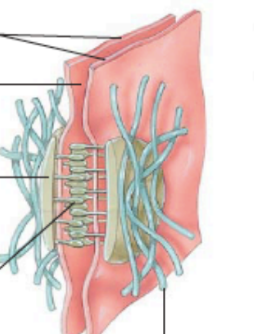
what is this photo of?
desmosome
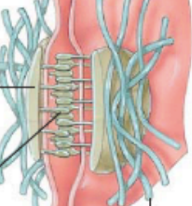
What are the blue lines?
intermediate filaments (keratin)
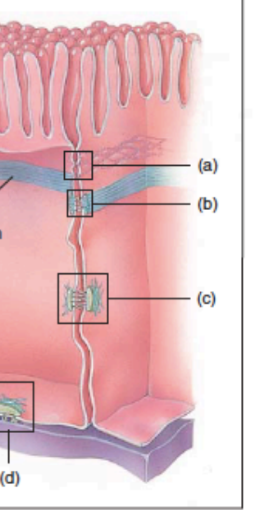
What is the thick blue line?
adhesion belt
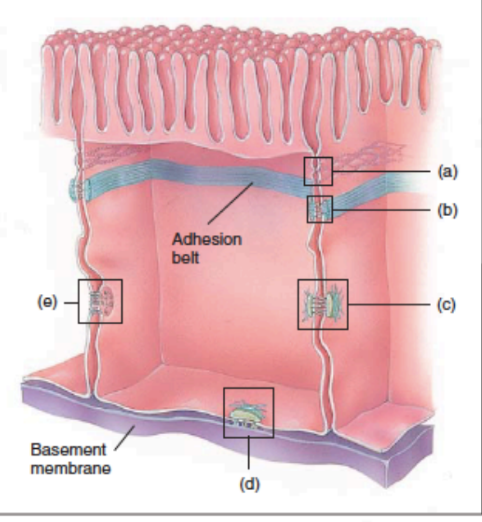
in this photo, what is a,b,c,d,e?
a = tight junction
b = adherens junction
c = desmosome
d = hemidesmosome
e = gap junction
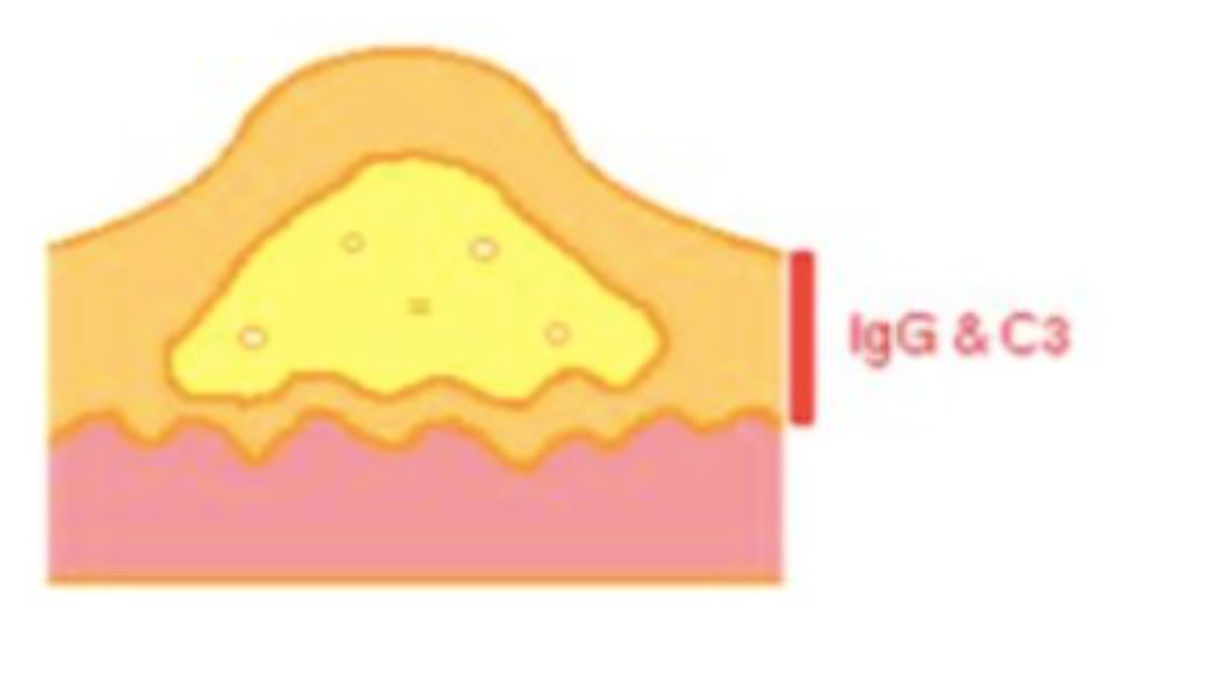
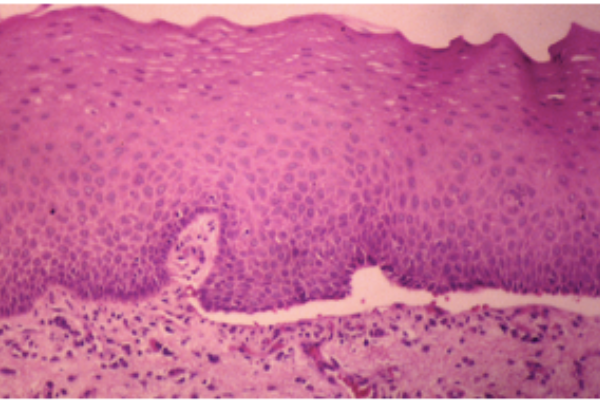
Which disease: blister within the epidermis; floor lined by basal csel acantholytic slcel ni blister fluid; intercellular igG &C3 by direct immunofluorescence
pemphigus vulgaris
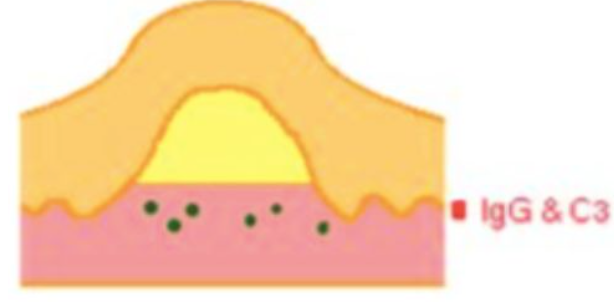
Which disease? subepidermal blister; eosinophil infiltrate underlying dermis basement membrane IgG &C 3 by direct immunofluorescence
pemphigoid
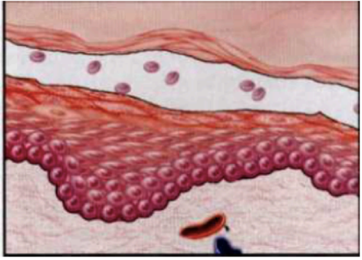
what kind of blister
Subcorneal (stratum corneum forms the roof of the bulla) (such as in PF)
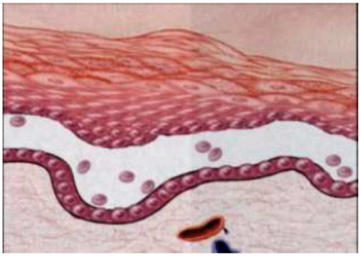
what kind of blister
suprabasal (such as in PV)
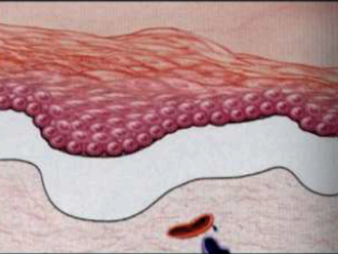
what kind of blister
subepidermal (such as in pemphigoid or dermatitis herpetiformis)
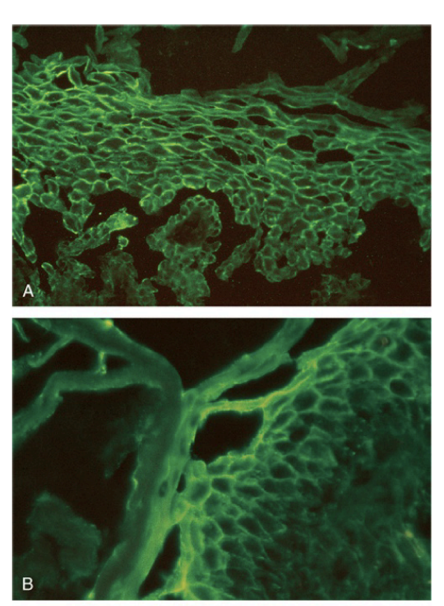
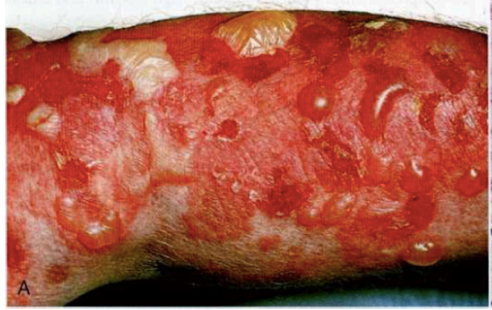
What disease is shown?
pemphigus vulgaris
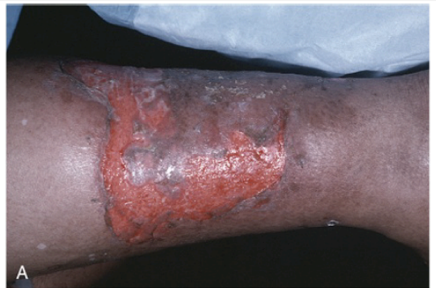
what is this?
pemphigus vulgaris
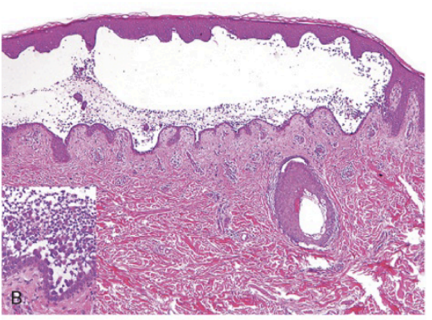
this is a histological slide of:
pemphigus vulgaris
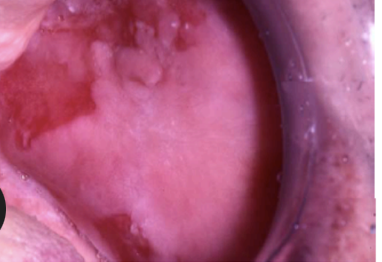
PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS
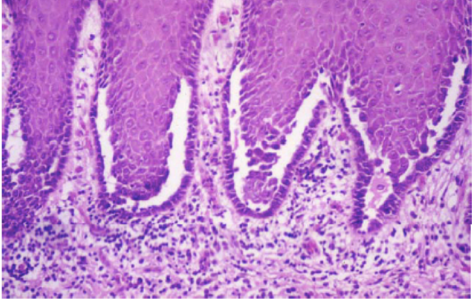
pemphigus vulgaris
pemphigoid
pemphigoid
pemphigus vulgaris
pemphigoid
pemphigoid
pemphigus vulgaris
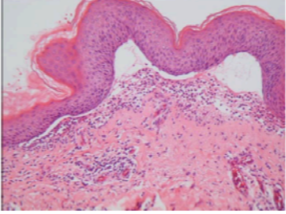
this shows
blister
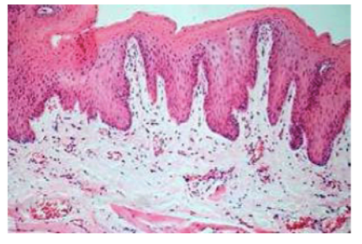
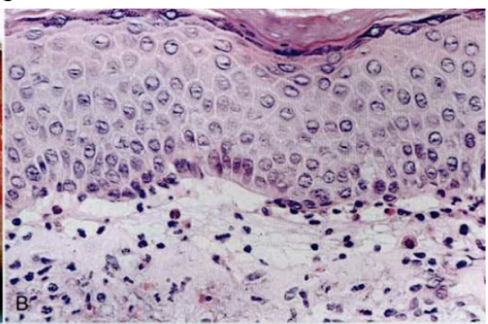
this shows
normal skin histology
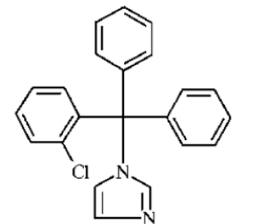
Mycelex
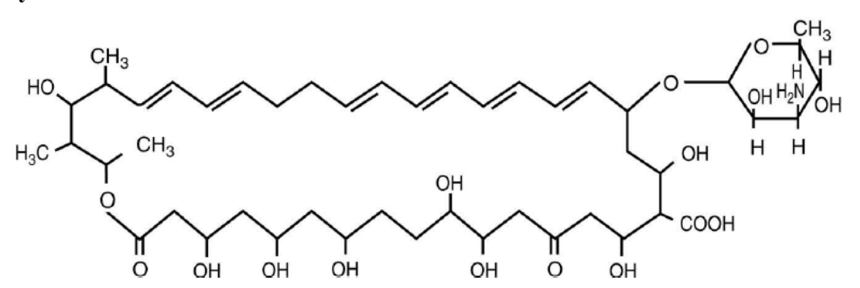
Nystatin
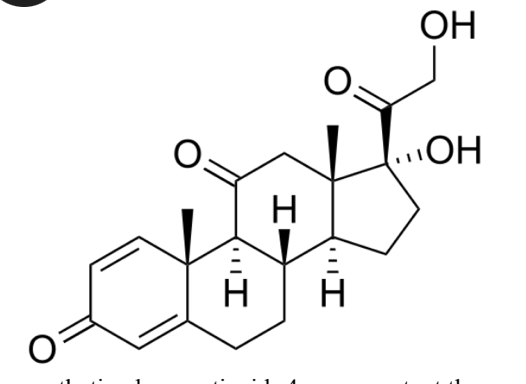
prednisone
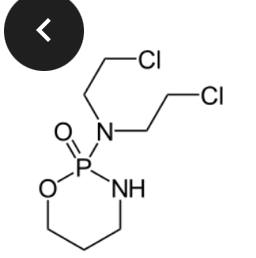
cyclophosphamide
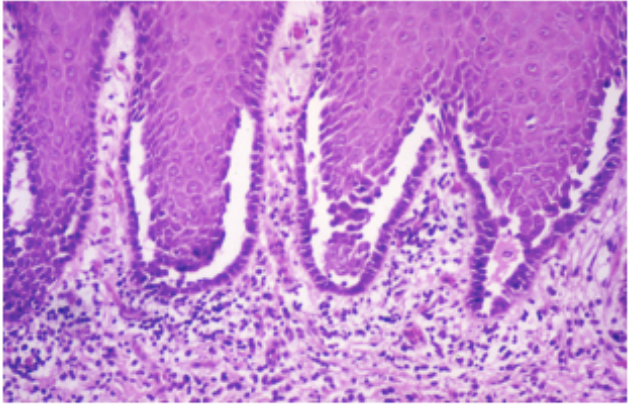
pemphiGUS
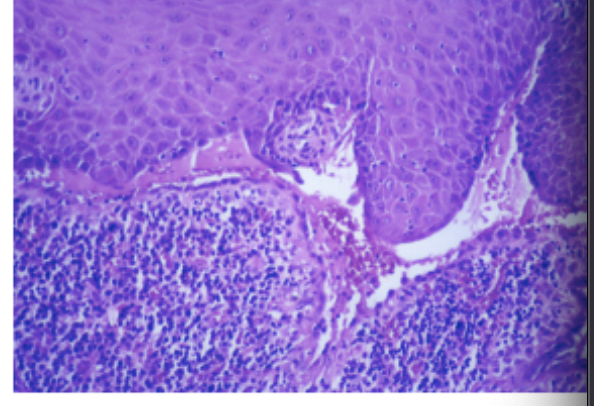
pemphigoid
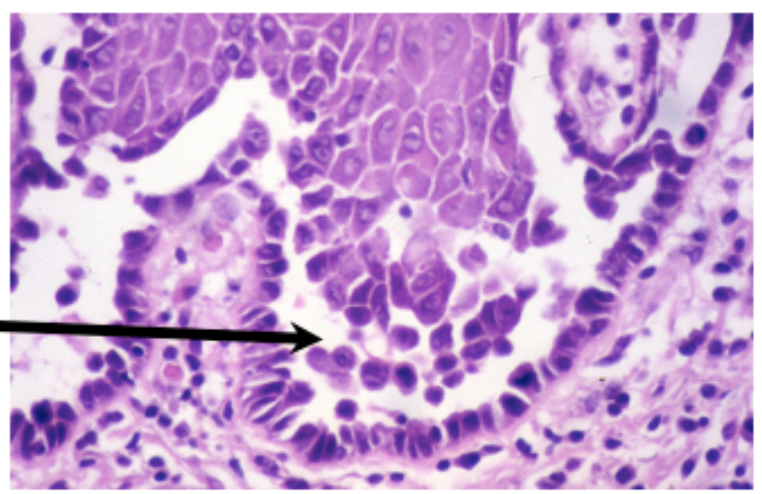
What cells?
Tzanck cells (multinucleated giant cells or macrophages) found in HSV, Varicella, Cytomegalovirus, and pemphigus
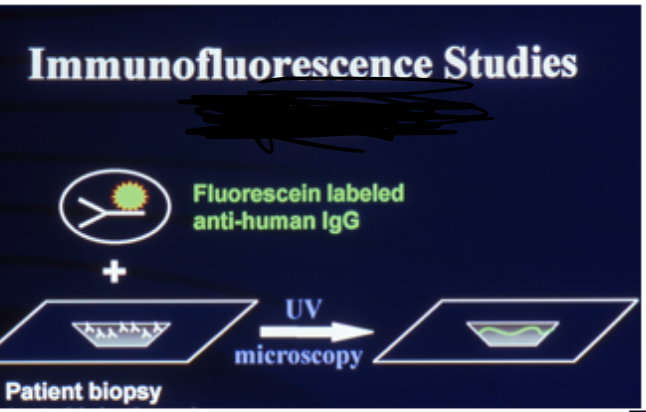
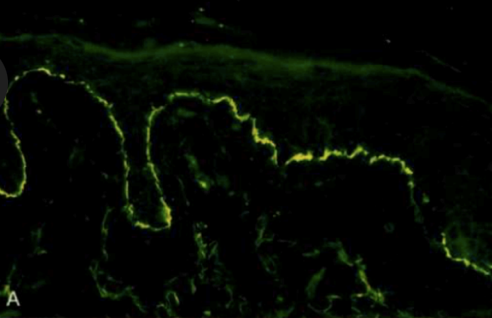
What type of immunofluorescence?
Direct (also be able to label other parts)
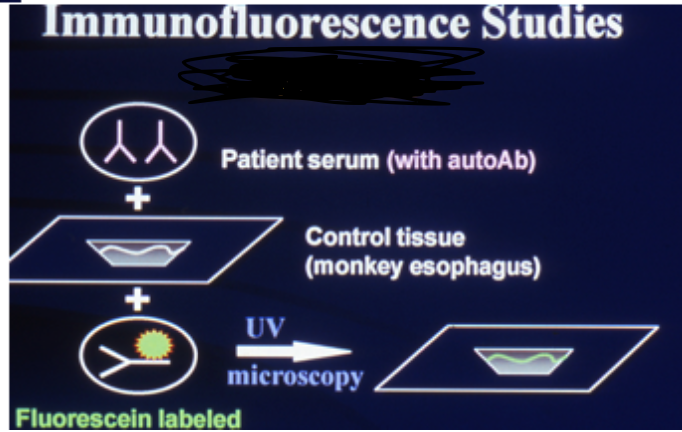
What type of immunofluorescence?
Indirect (also be able to label other parts)
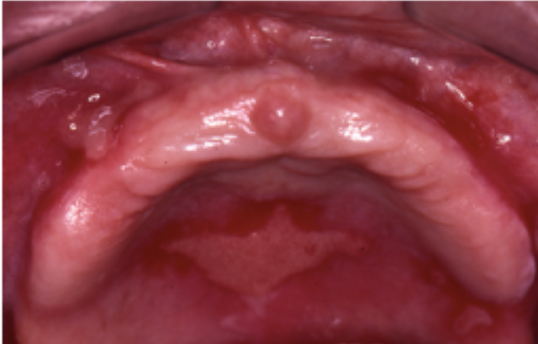
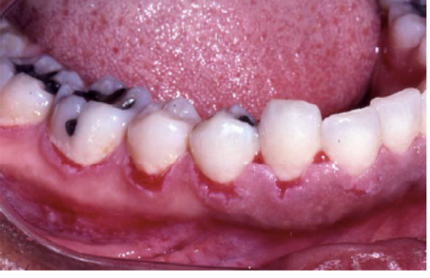
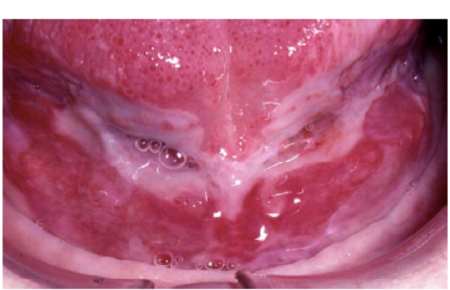
Cicatricial pemphigoid
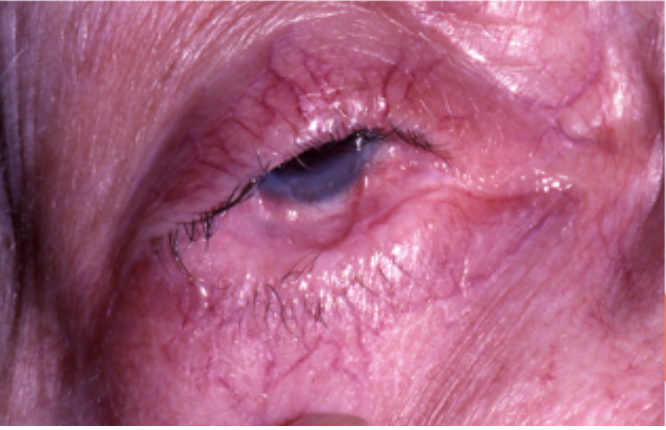
Cicatricial pemphigoid
Cicatricial pemphigoid
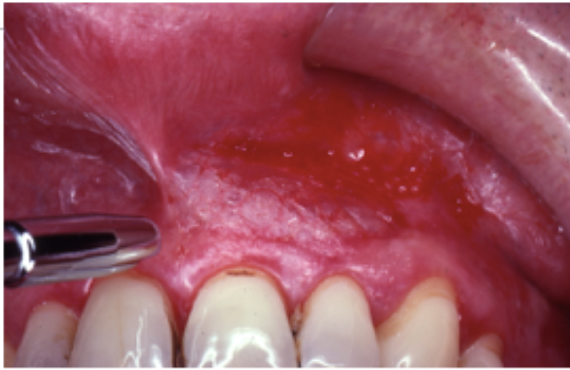
Cicatricial pemphigoid
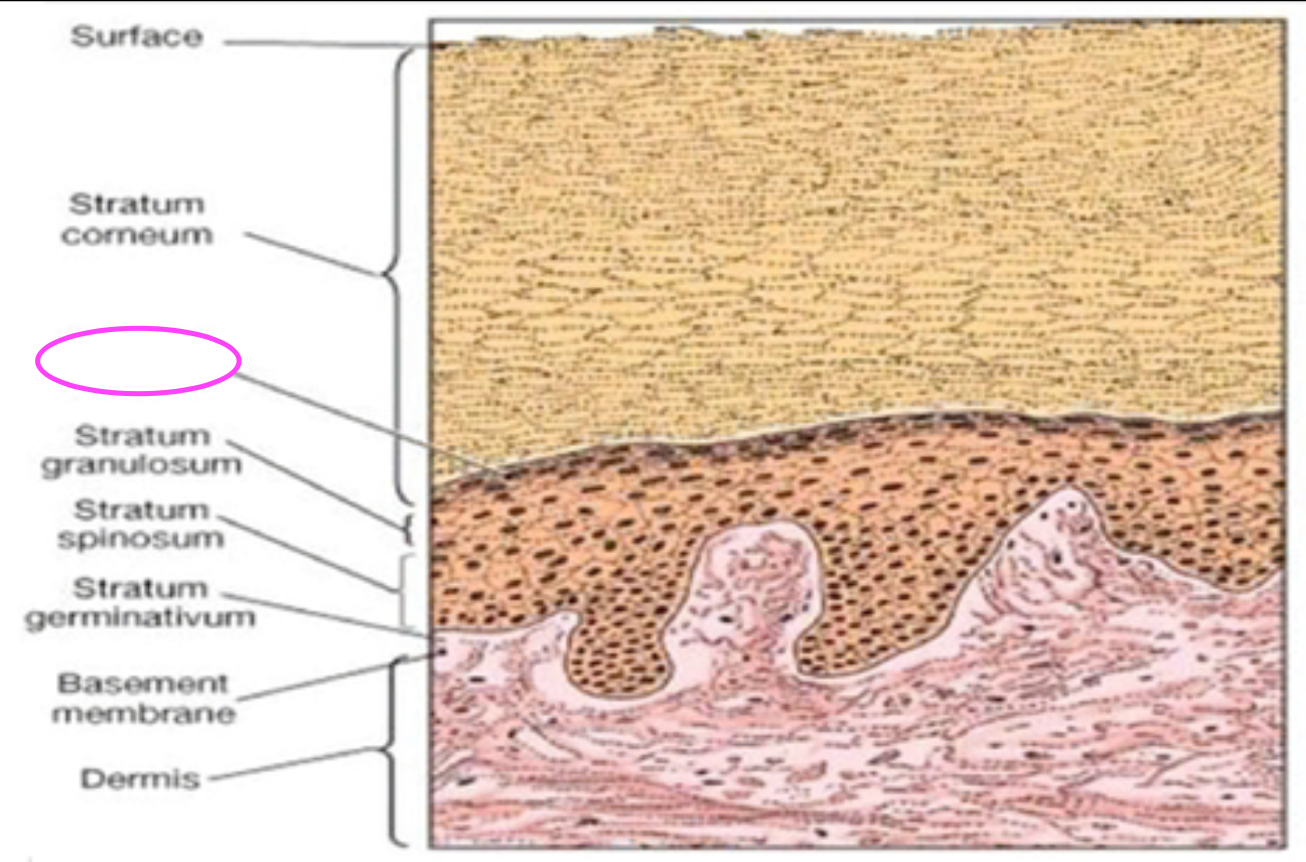
Fill in blank
Stratum lucidum
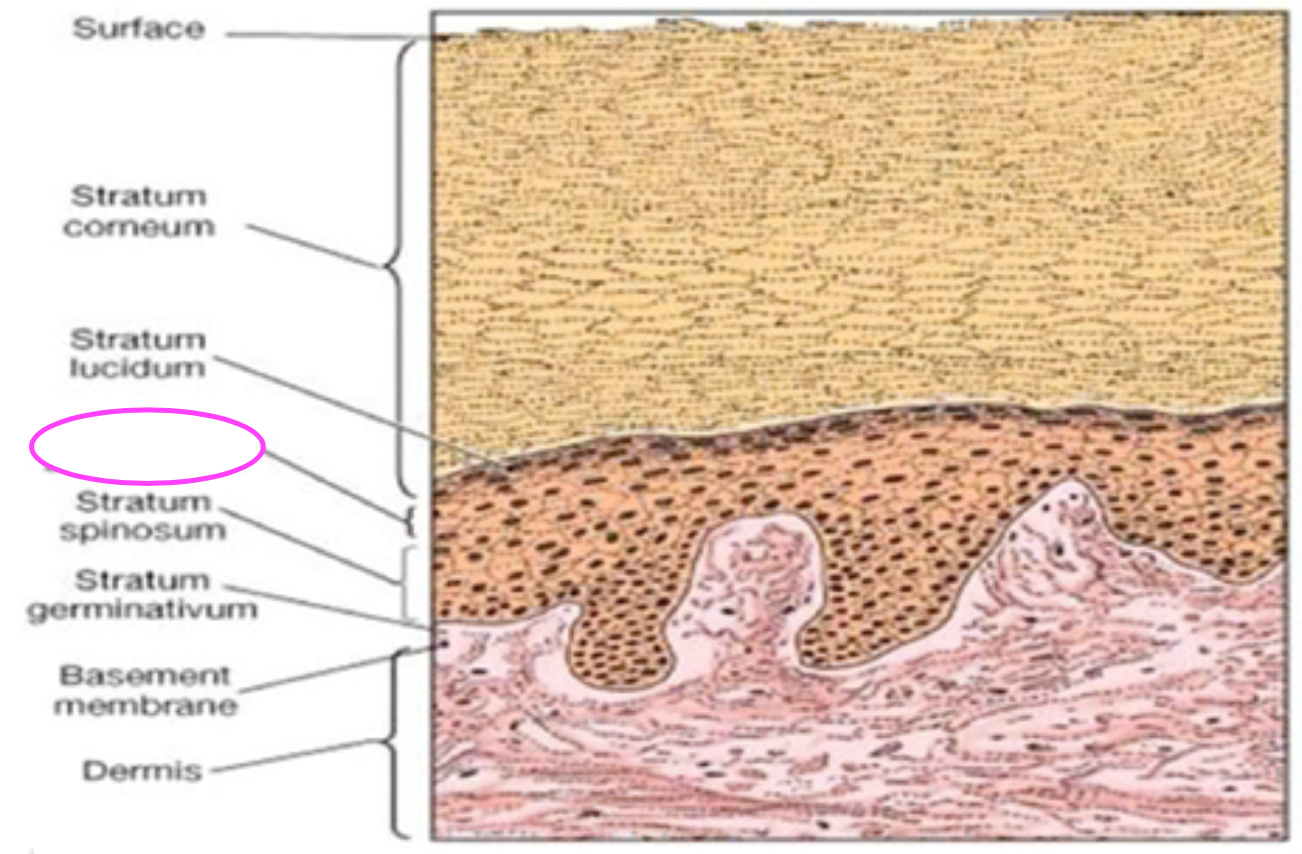
Stratum granulosum
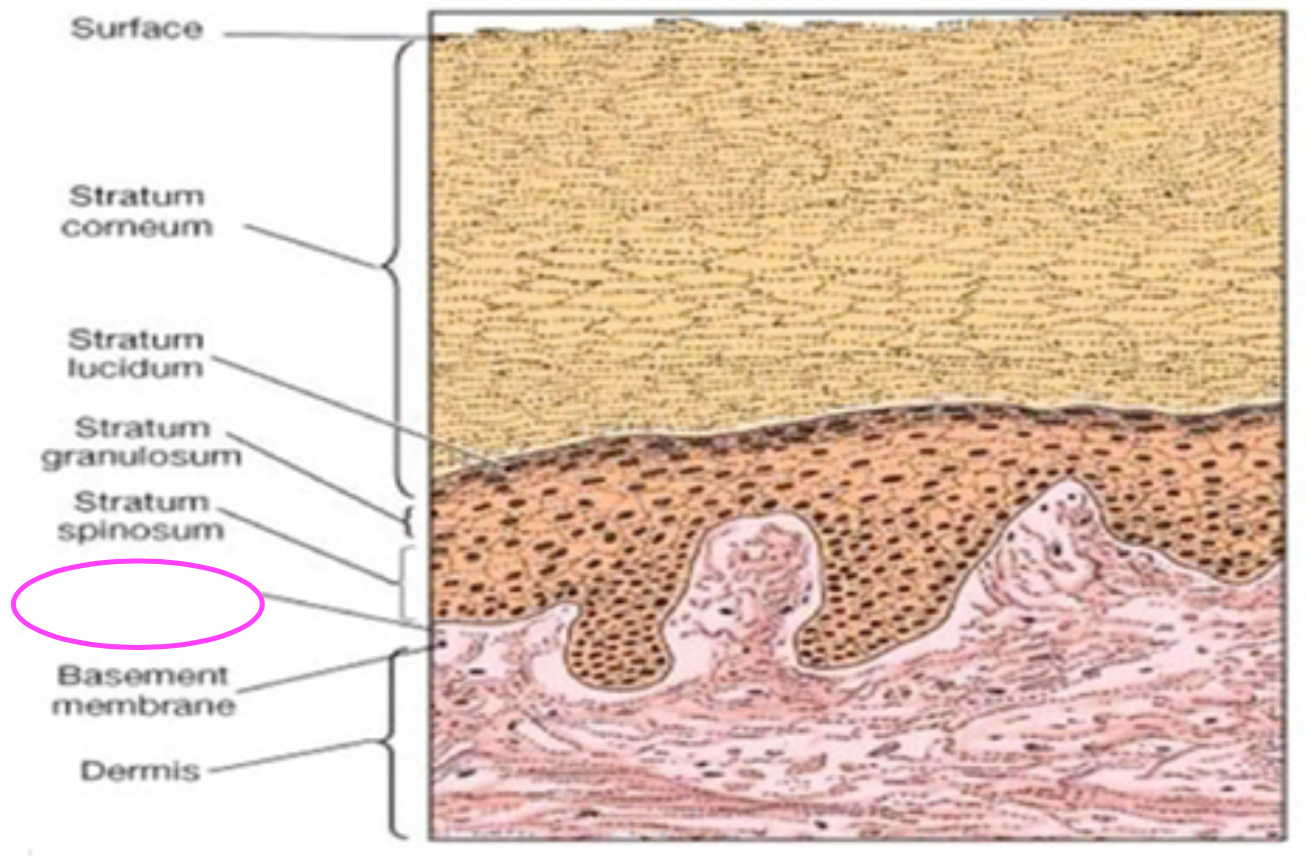
Stratum germinativum
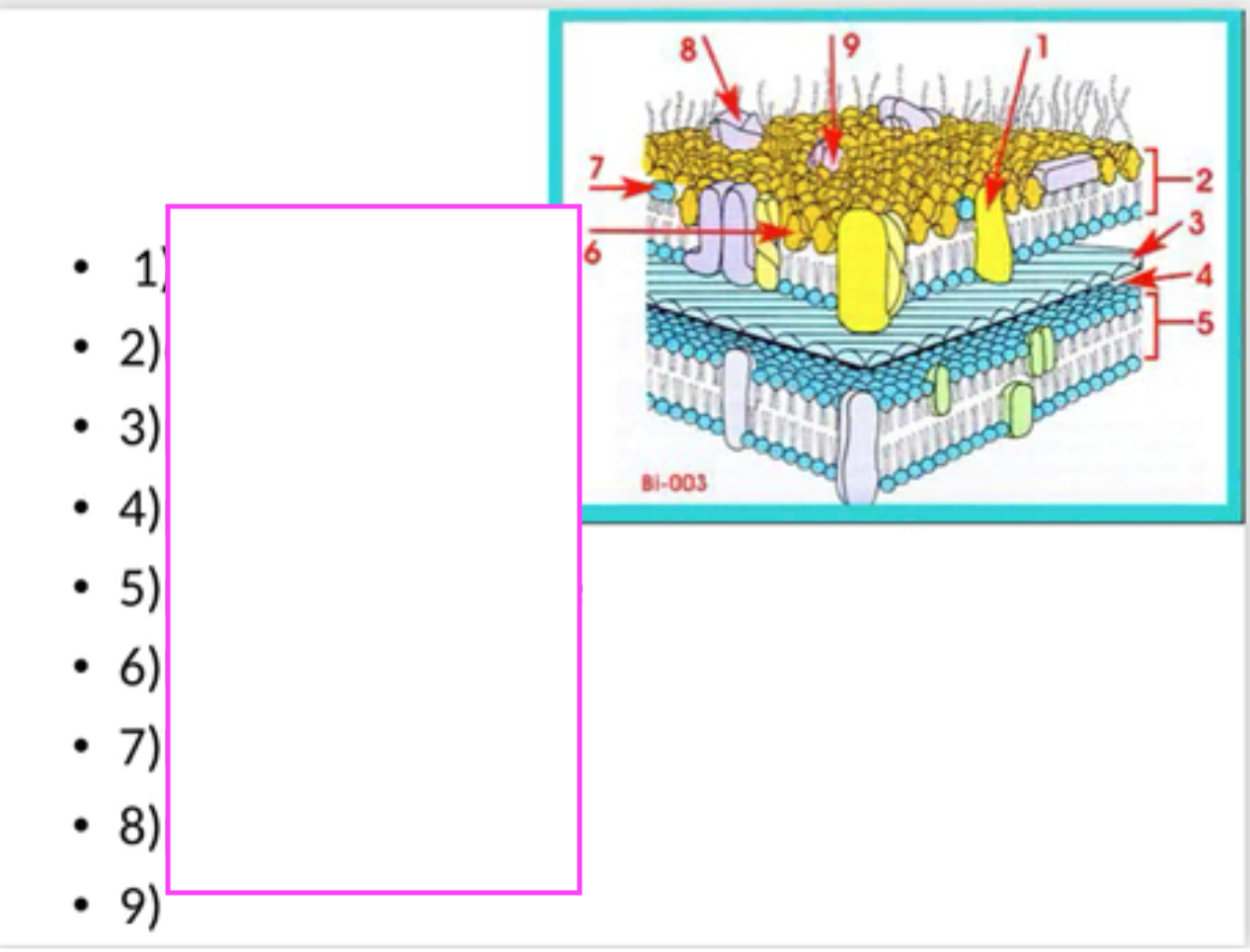
Fill in blanks #1-8
1: lipoprotein______ 2: outer membrane_____ 3: peptidoglycan_____ 4: periplasmic space_____5: plasma membrane _____6: LPS _____7: Lipid A_____ 8: porin
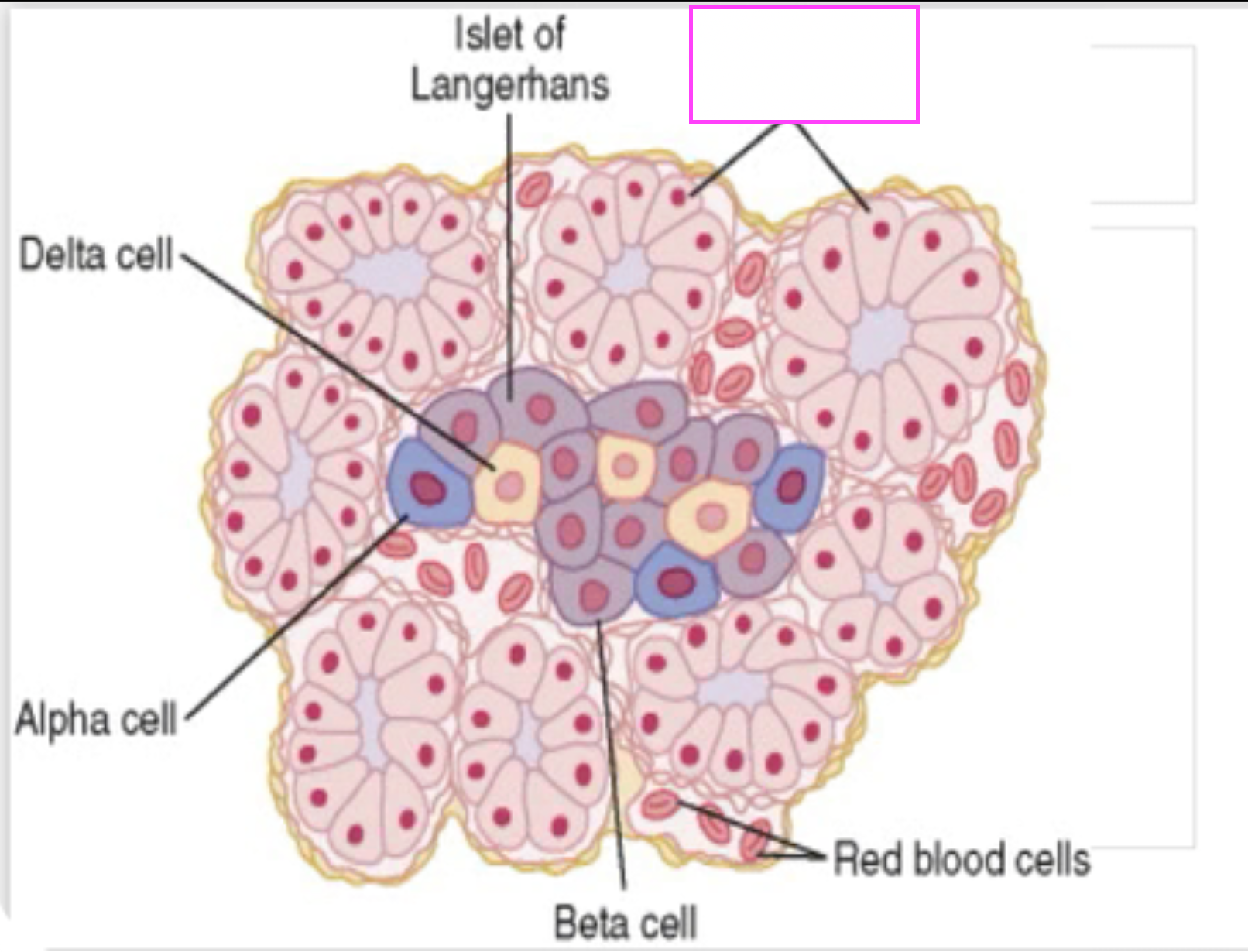
fill in blank
pancreatic acini
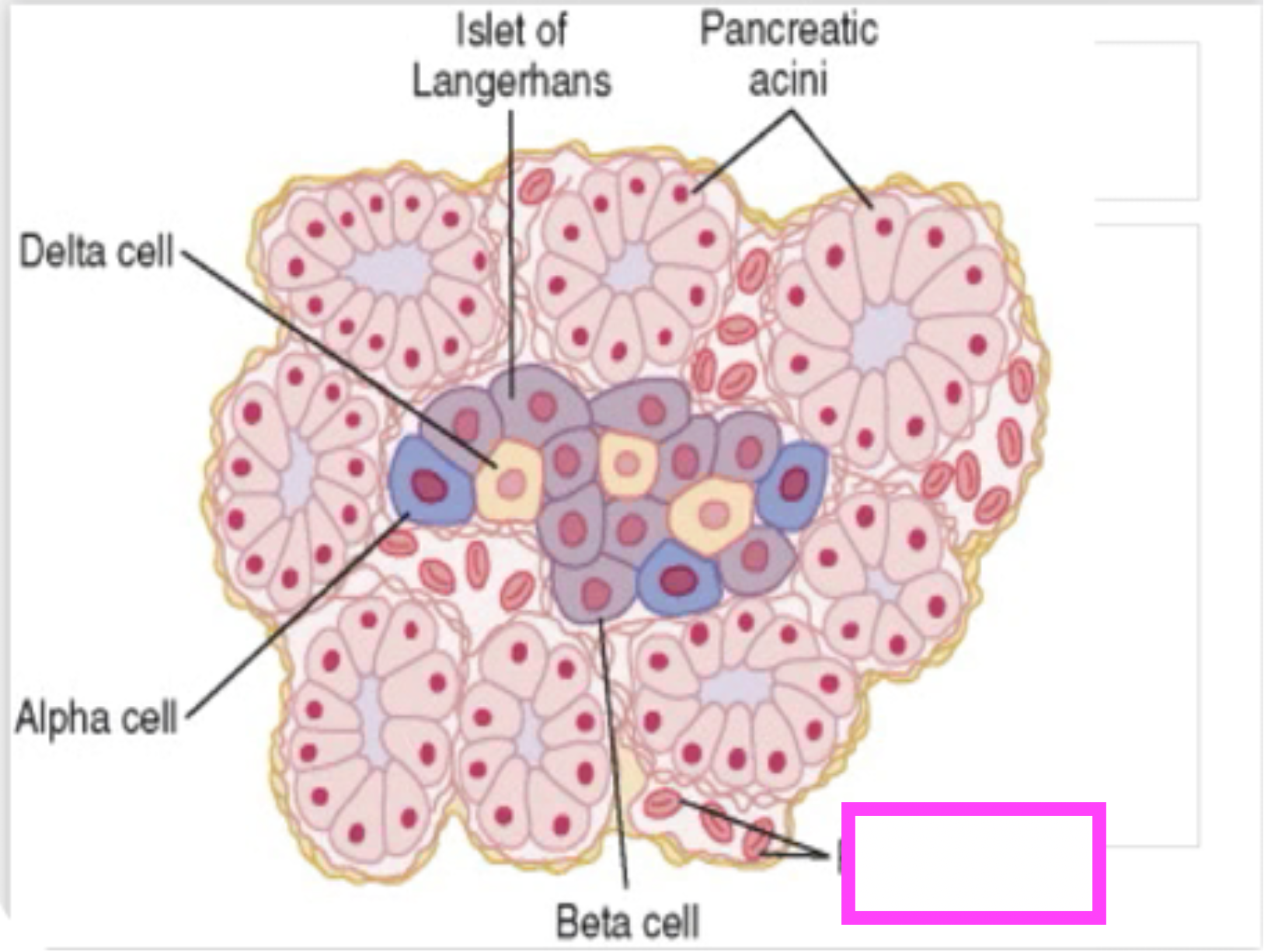
red blood cells
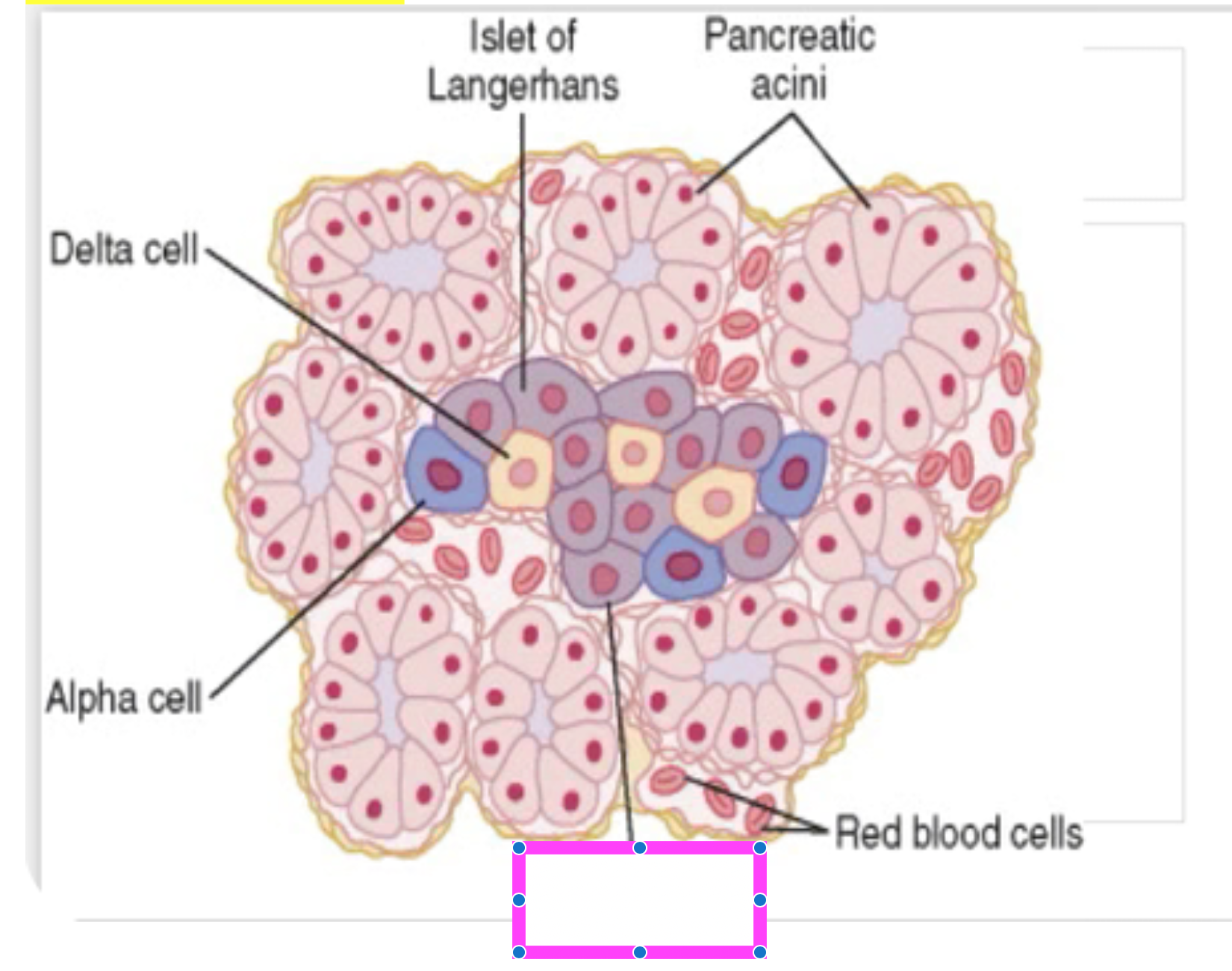
beta cells
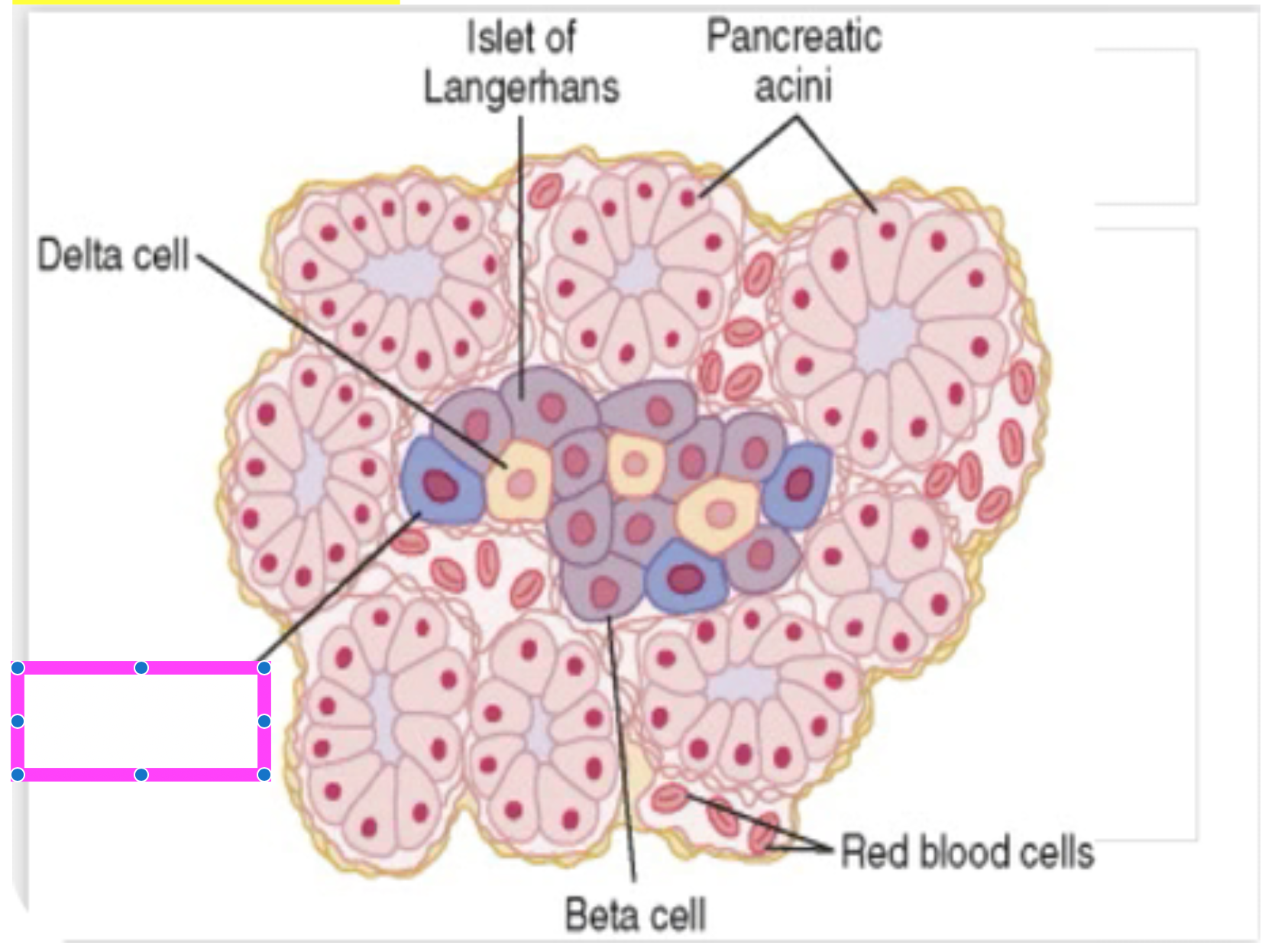
alpha cell
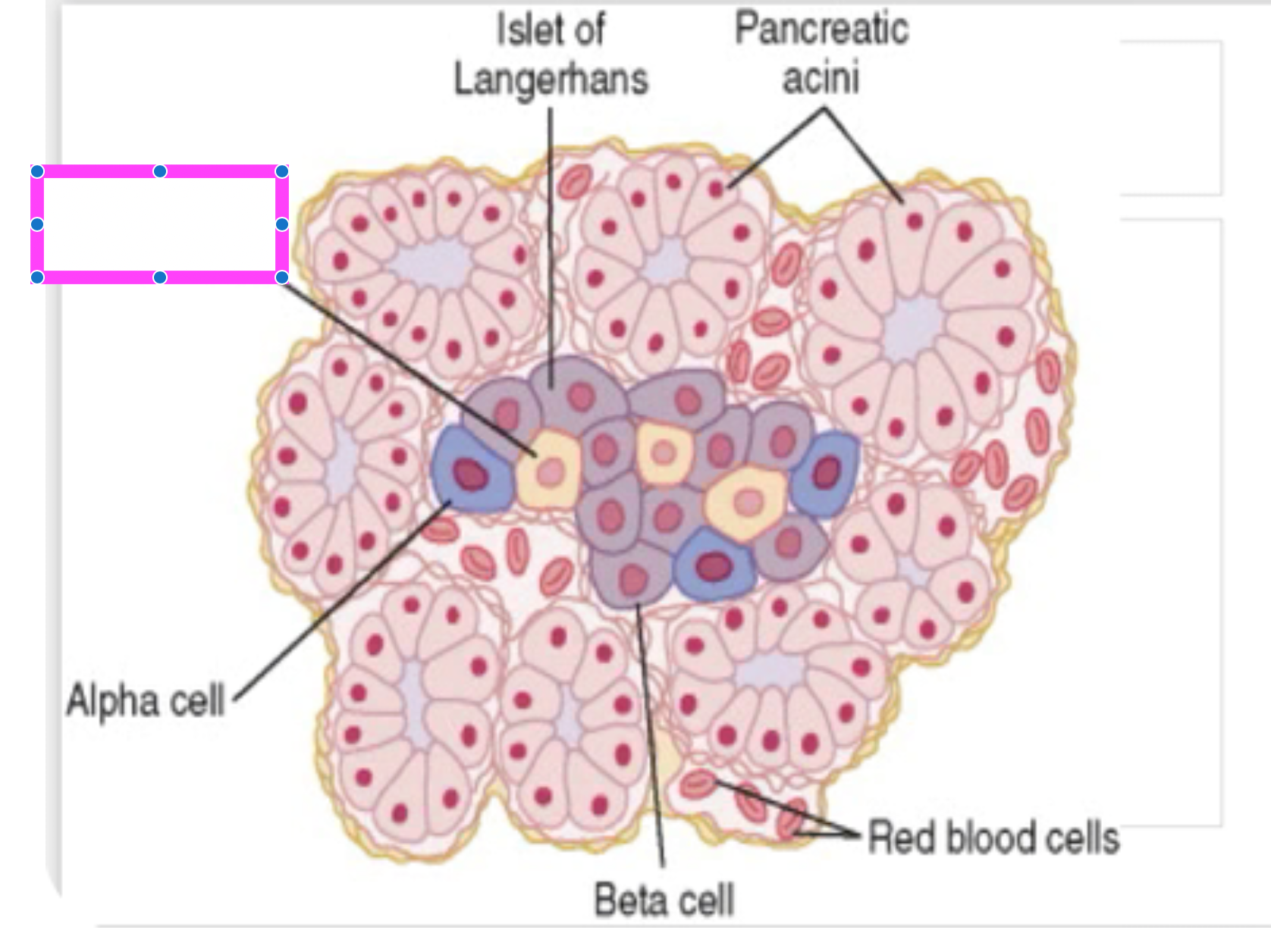
delta cell
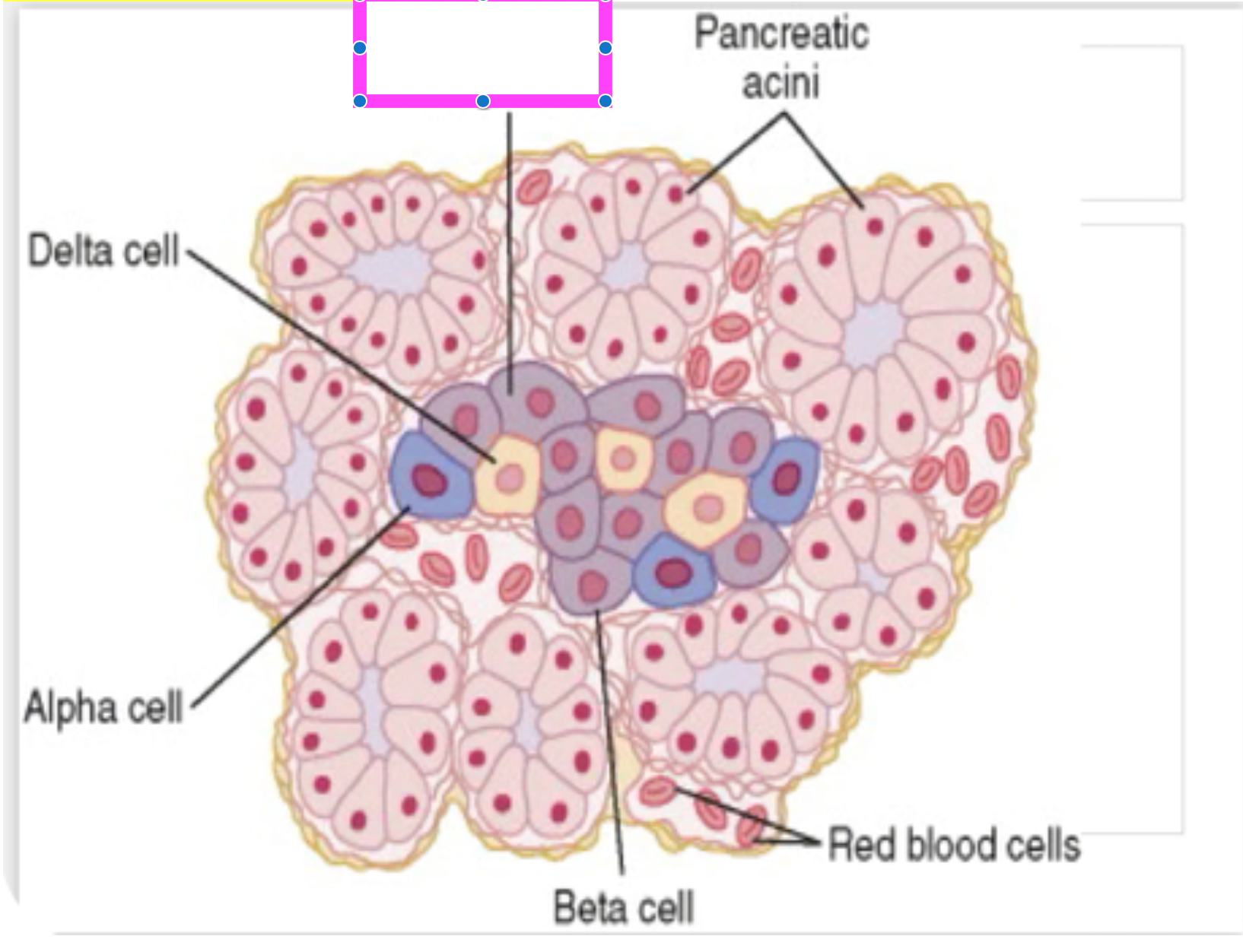
islet of langerhans
Which type of alveolar cells produce surfactant? (type I or type II)
Type II
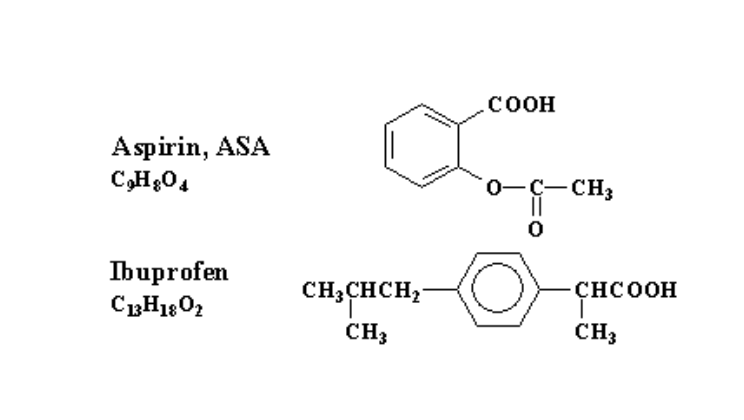
Which drug here contains a carboxylic acid group?
Both
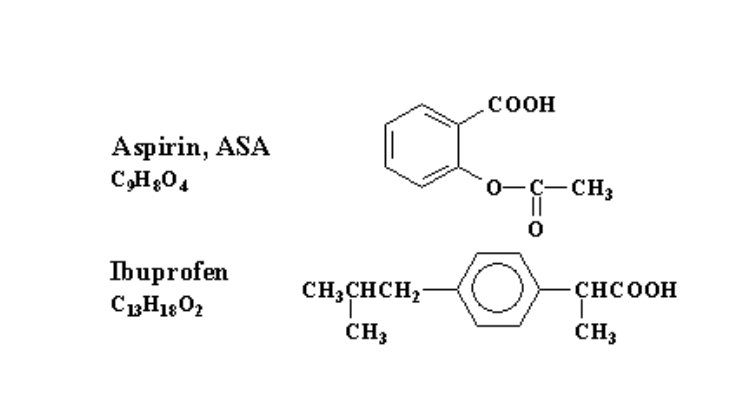
Which drug here contains an ester group?
Aspirin
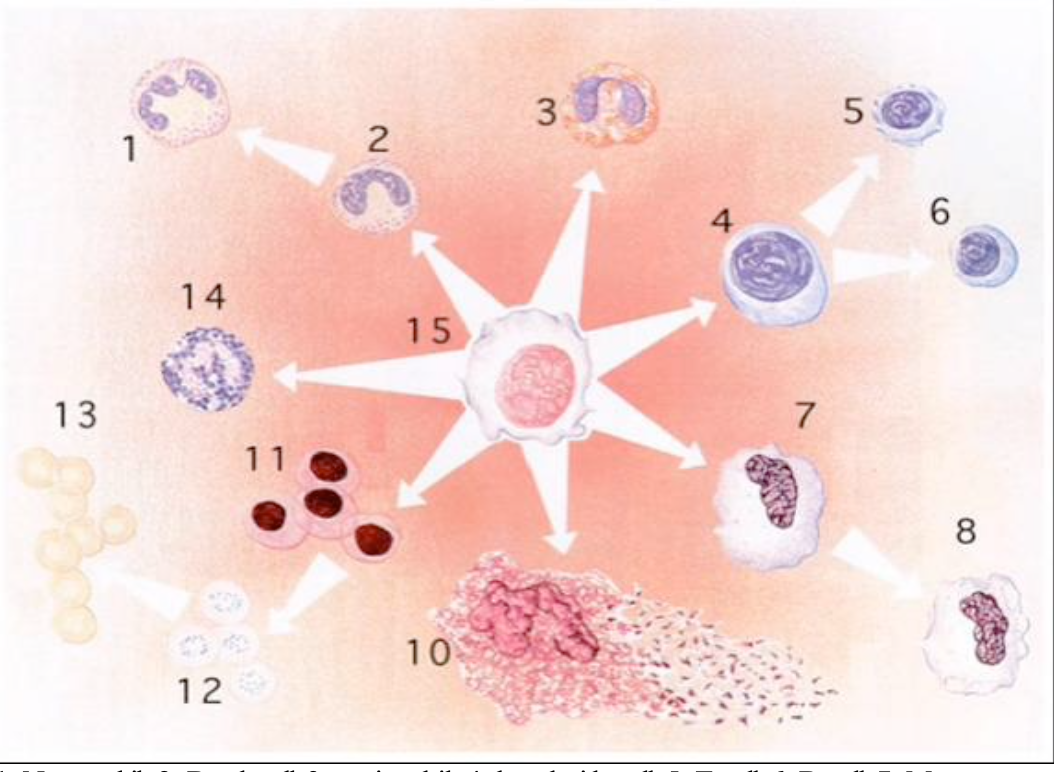
Label #1-15
1- neutrophil
2- band cell
3- eosinophil
4- lymphoid cell
5- T cell
6- B cell
7- Monocyte
8- Macrophage
9- none
10- megakaryocyte
11- proerythrocyte
12- reticulocyte
13- erythrocyte
14- basophil
15- pluripotent stem cell
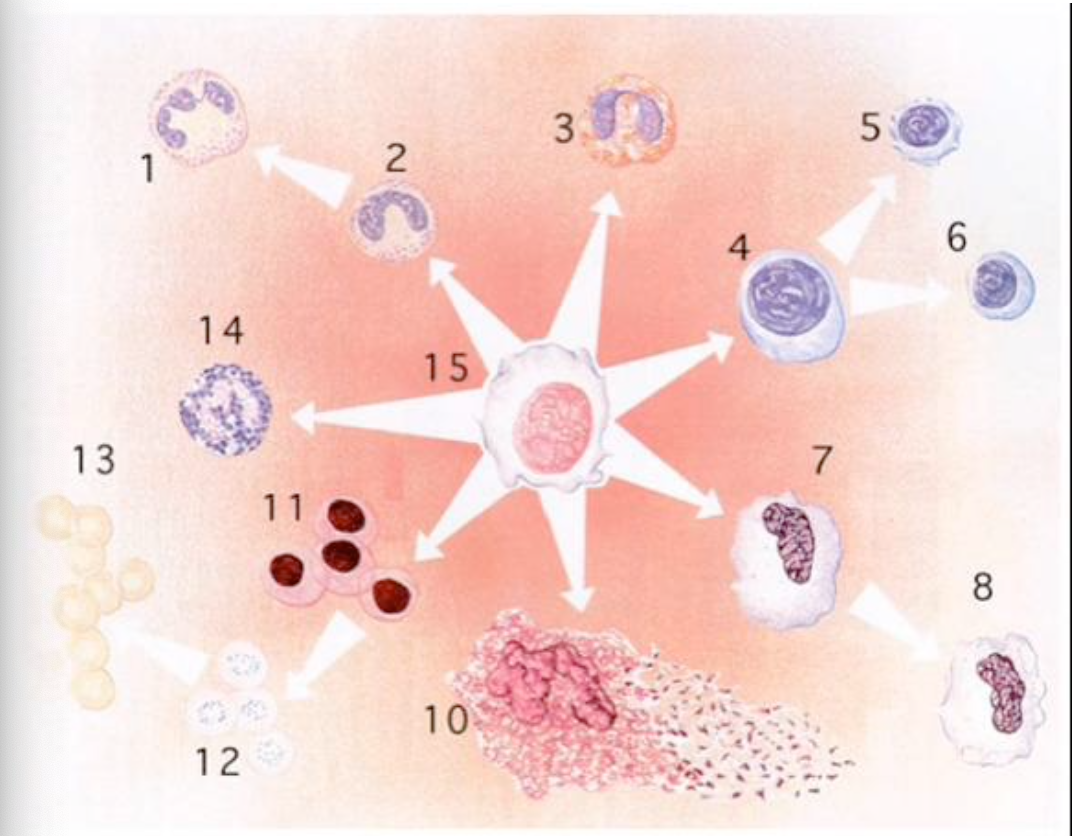
T or F: RBC’s contain a nucleus
false
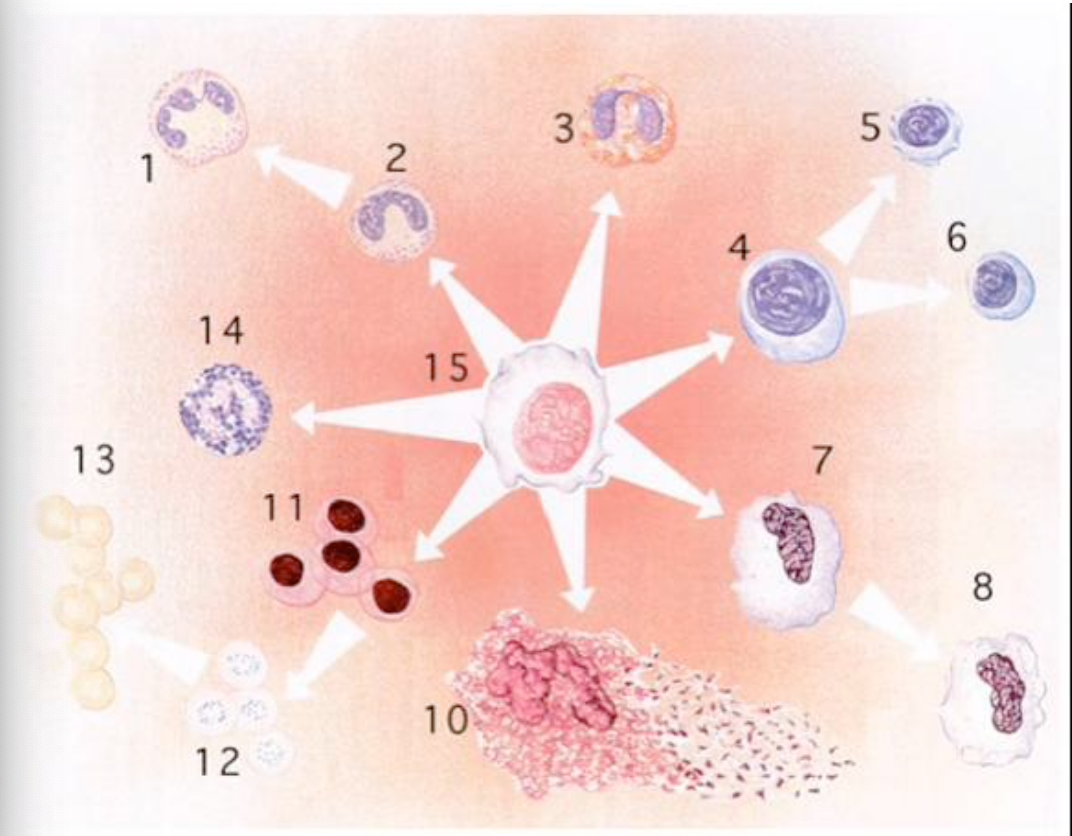
T or F: Monocytes can differentiate into macrophages
True
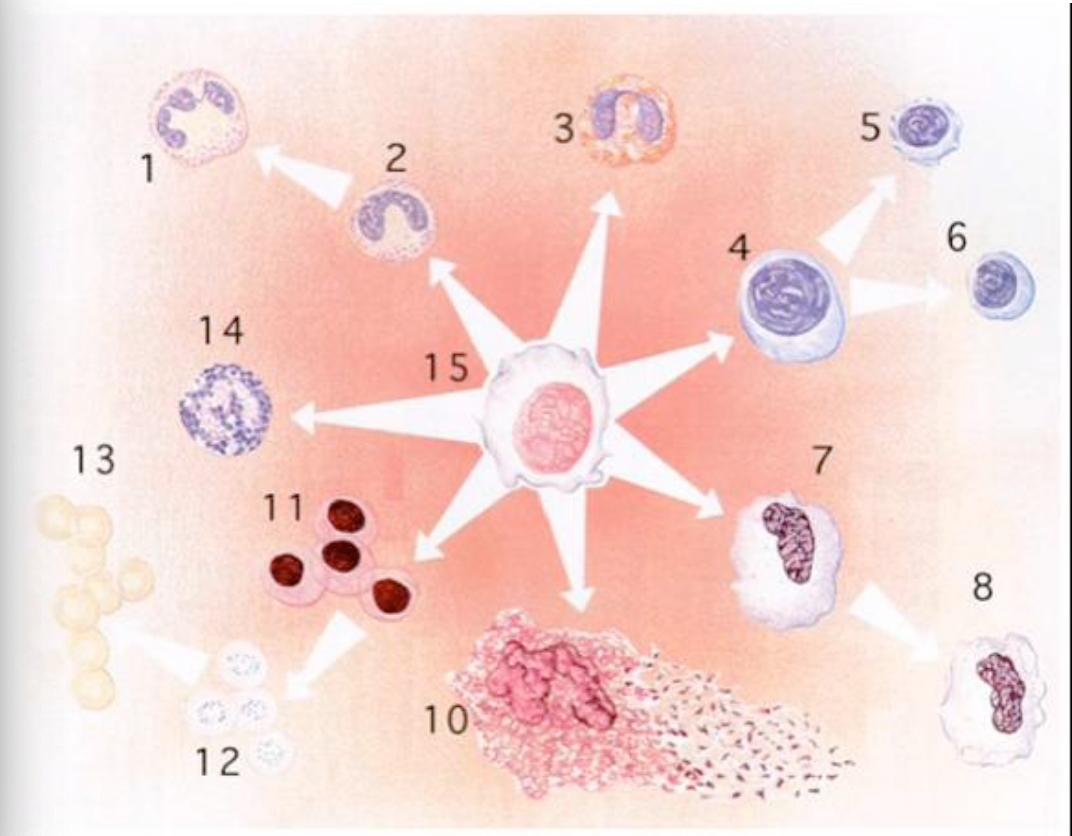
Platelets are derived from which of the following cells?
10- megakaryocytes
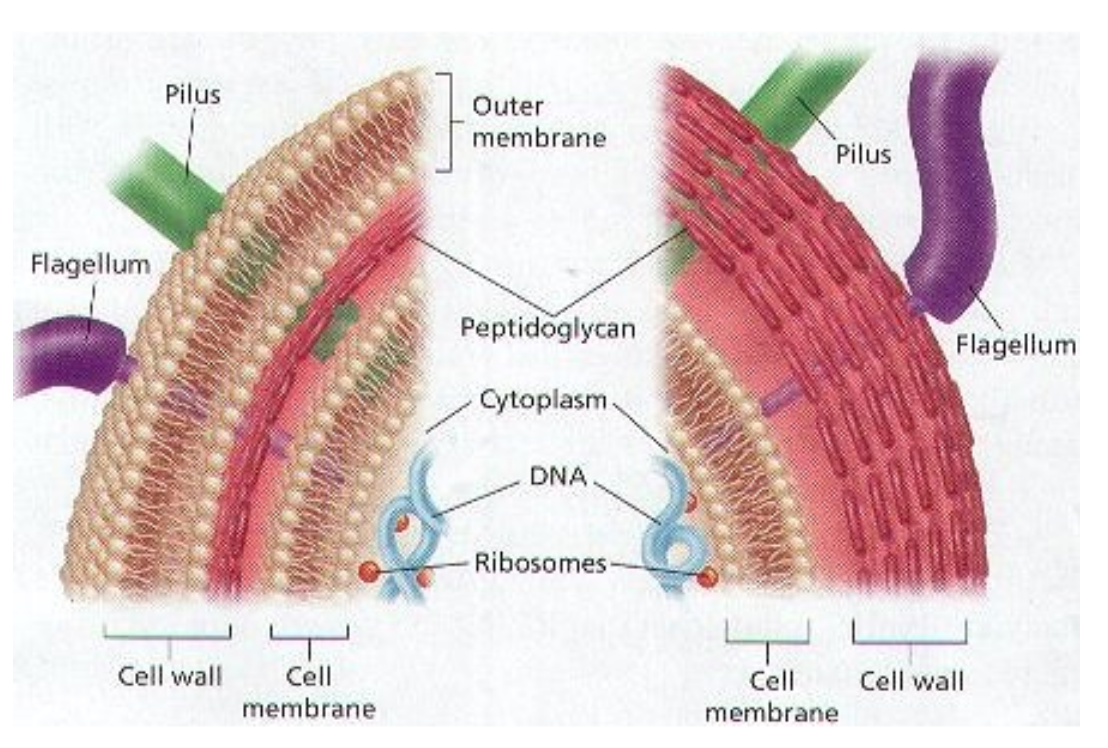
difference between left and right?
left = gram negative
right = gram positive
(note that gram positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer)
E coli is gram (+ or -)
gram negative