HA exam 2: head, face, neck, and regional lymphatics
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Parotid glands and submandibular glands
2 pairs of salivary glands accessible to examination on the face
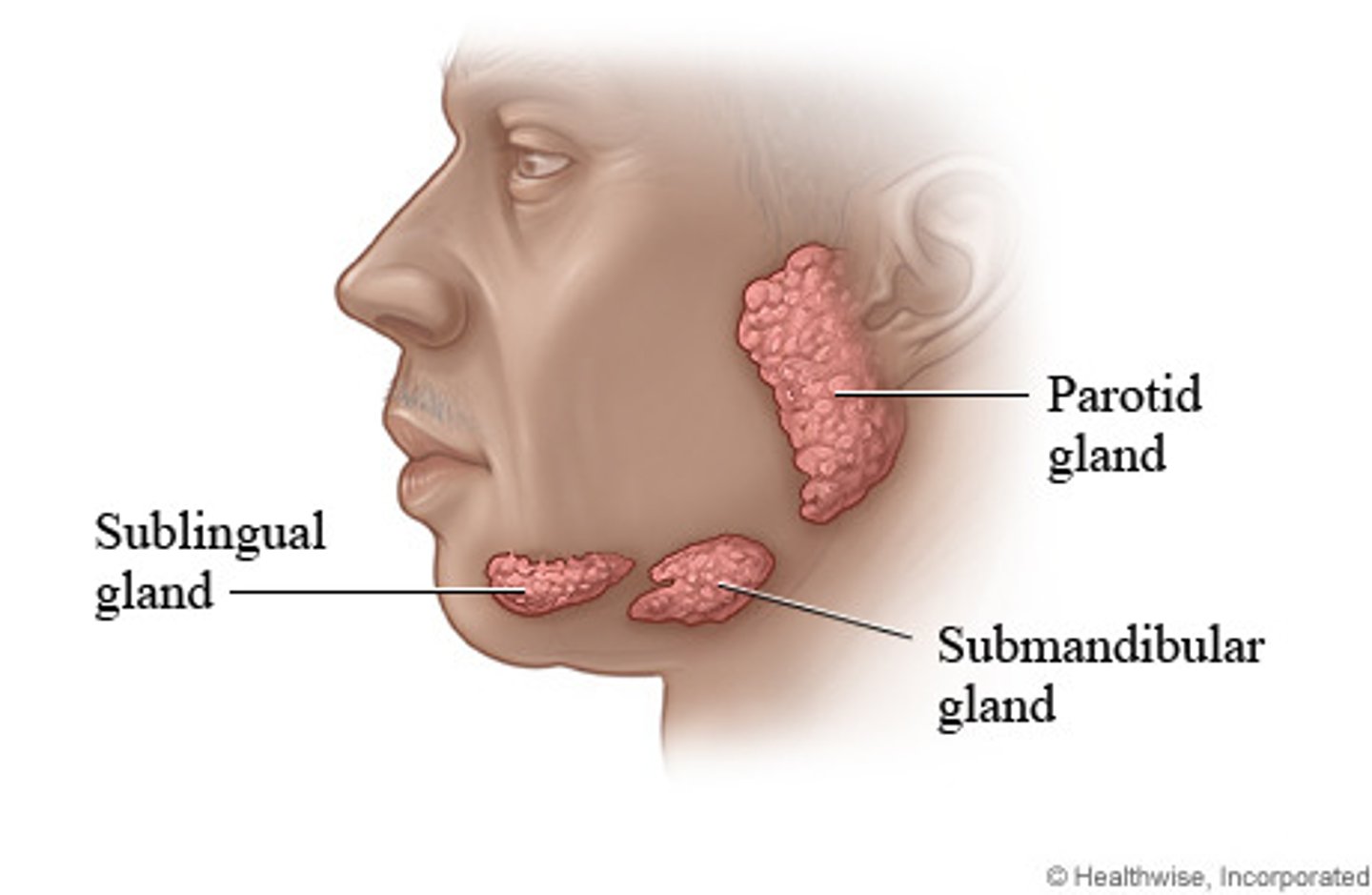
sublingual glands
3rd pair of gland that lies in the floor of the mouth
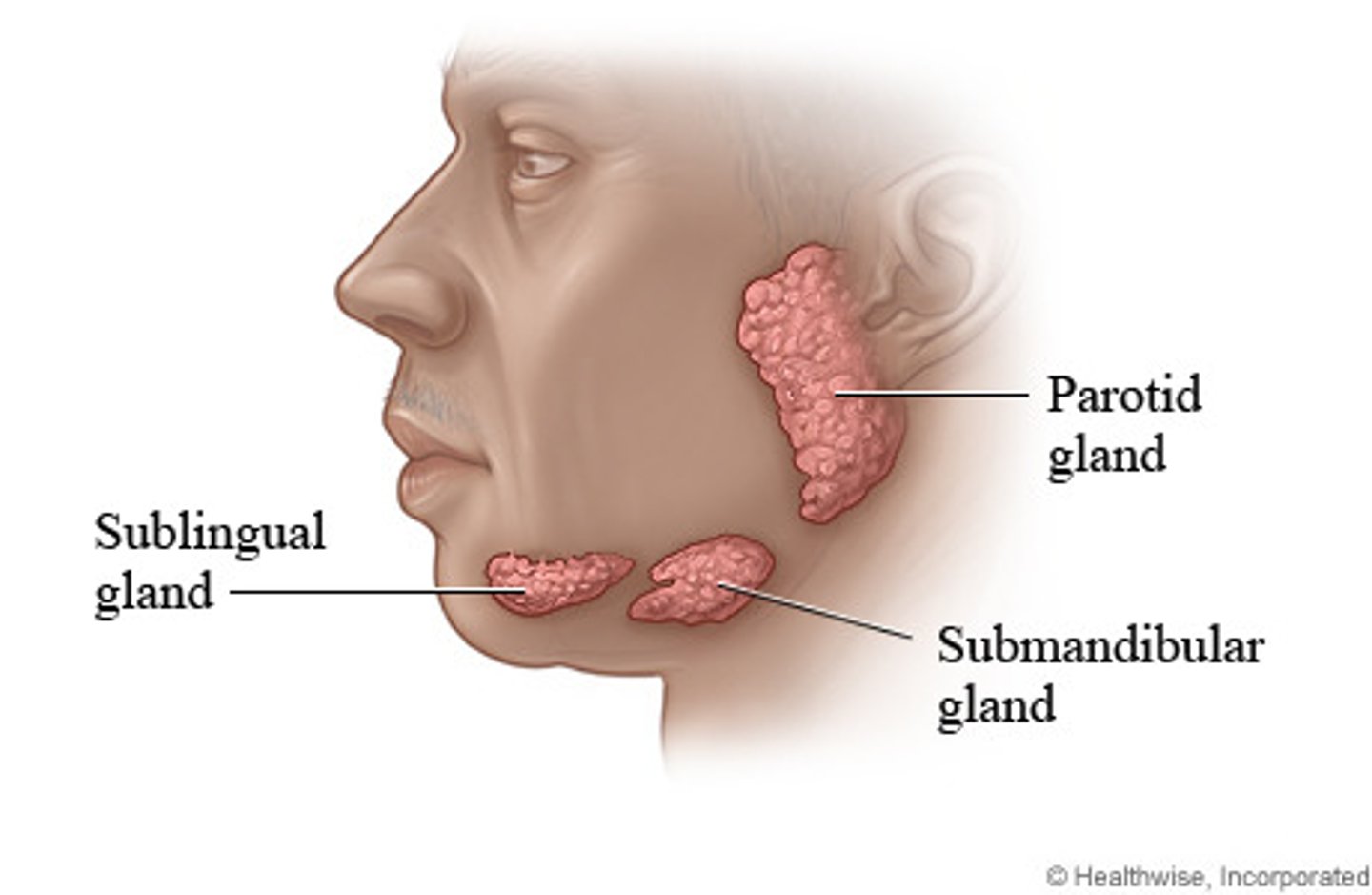
anterior to ear
pulsation for temporal artery is palpable where?
thyroid
endocrine gland is found in
detect and eliminate foreign substances from body
lymphatics
more prominent
in the aging adult, facial bones and orbits appear
headache
leading cause of acute pain and lost productivity
Tension type headache
most common type of headache
migraine
2nd most common type of headache
episodic and chronic
headaches can be
behind browbone and/or cheekbones
sinus headache pain is
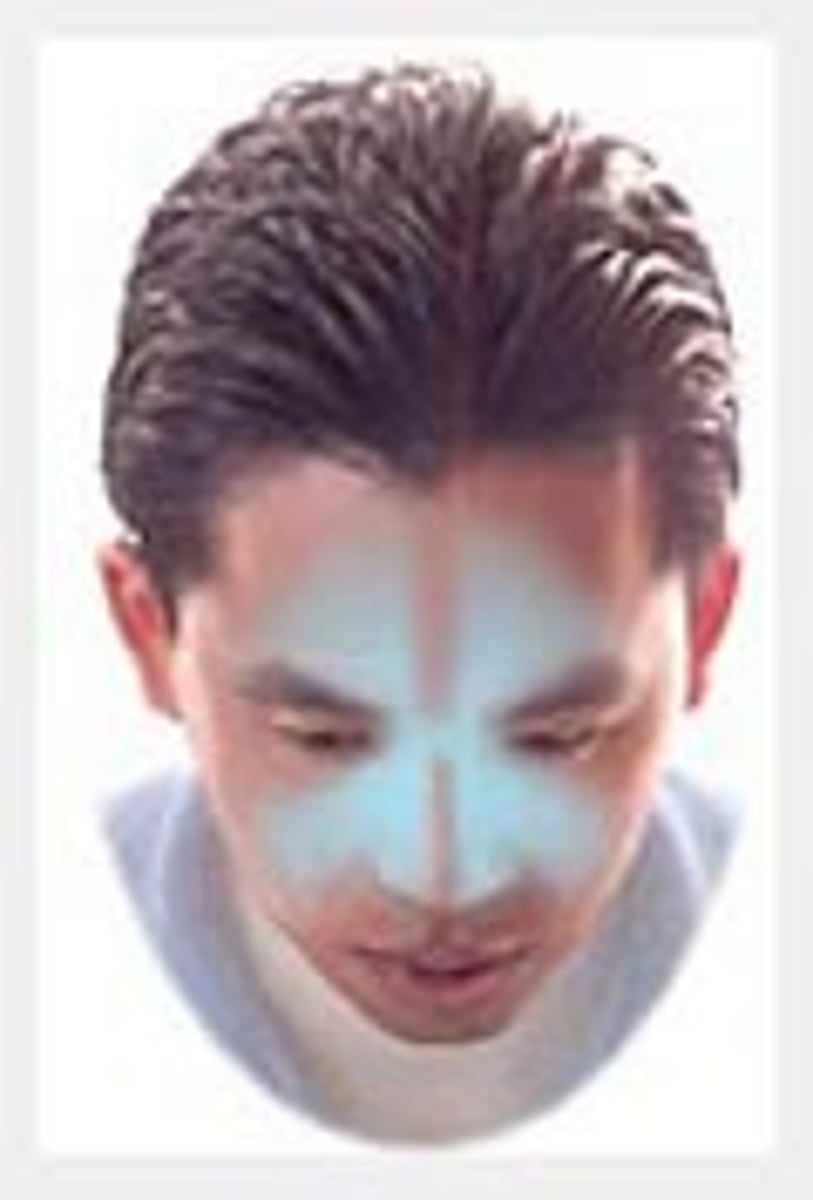

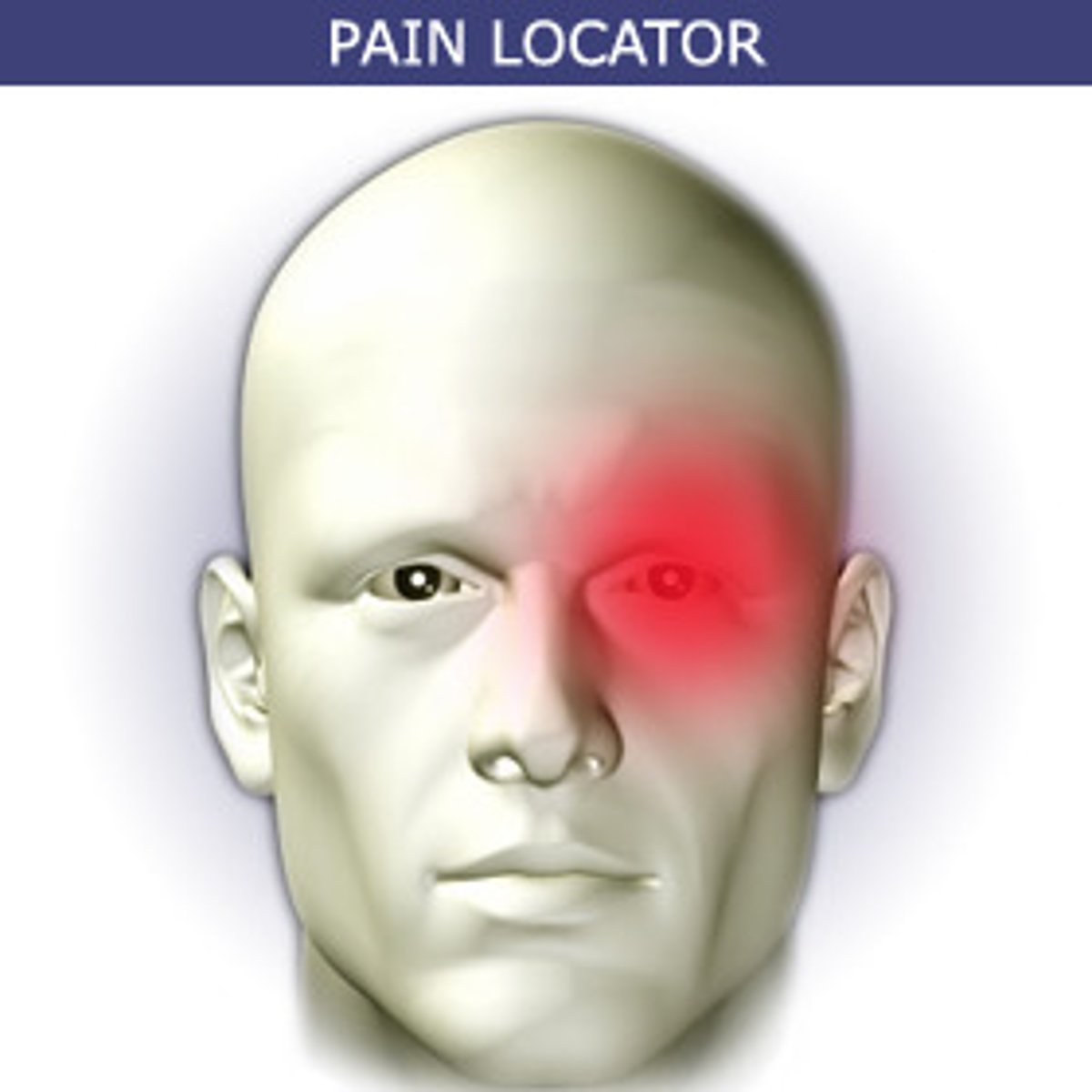
in and around one eye
cluster headache pain is
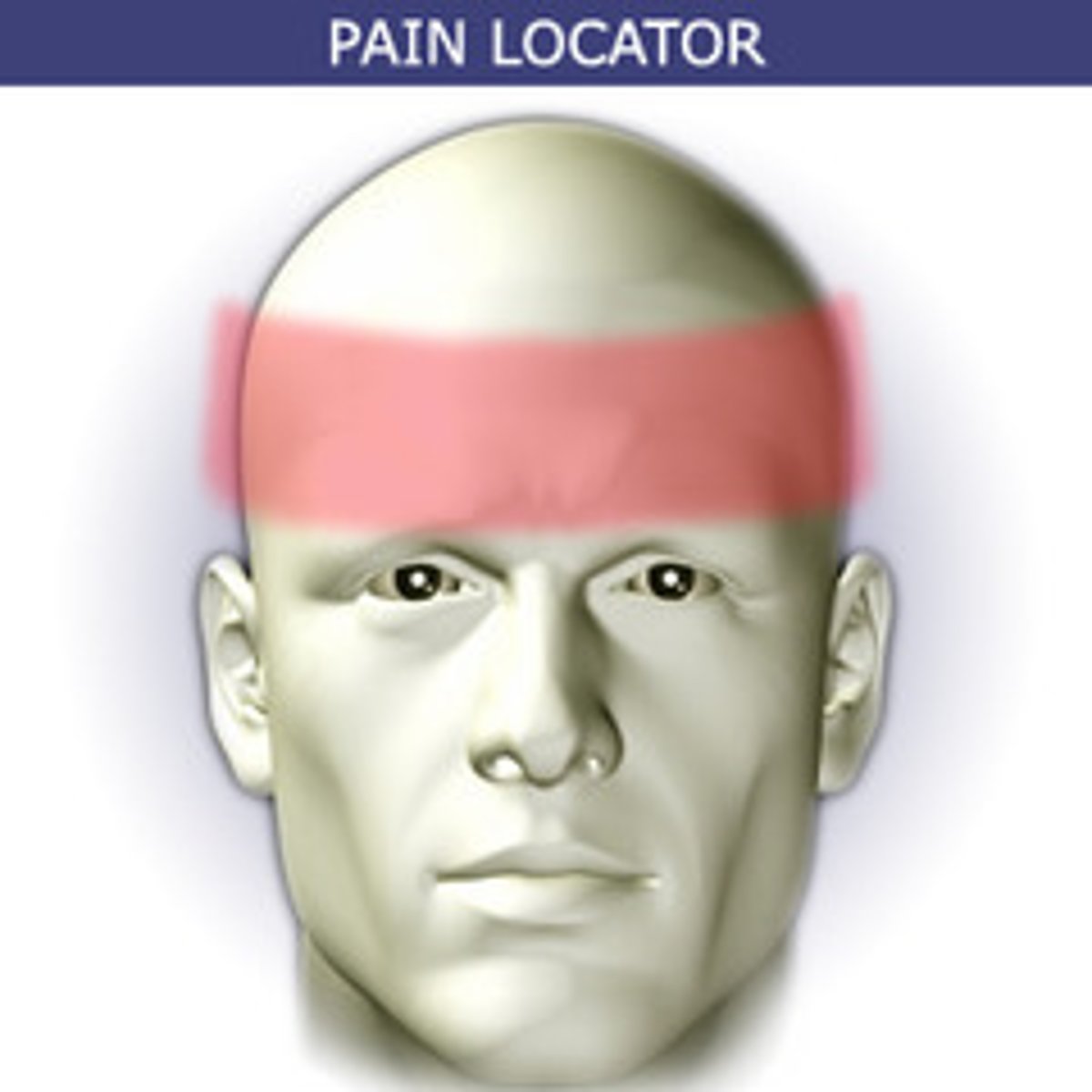
like a band squeezing the head
tension headache pain is
pain, nausea and visual changes are typical of classic form
migraine headache
Coarse facial features, exophthalmos, changes in skin color or pigmentation, or abnormal swellings
abnormal facial structures
Head position is centered in midline, and accessory neck muscles should be symmetric; Head should be held erect and still
head and neck symmetry
location, size, shape, delimitation, mobility, consistency, and tenderness
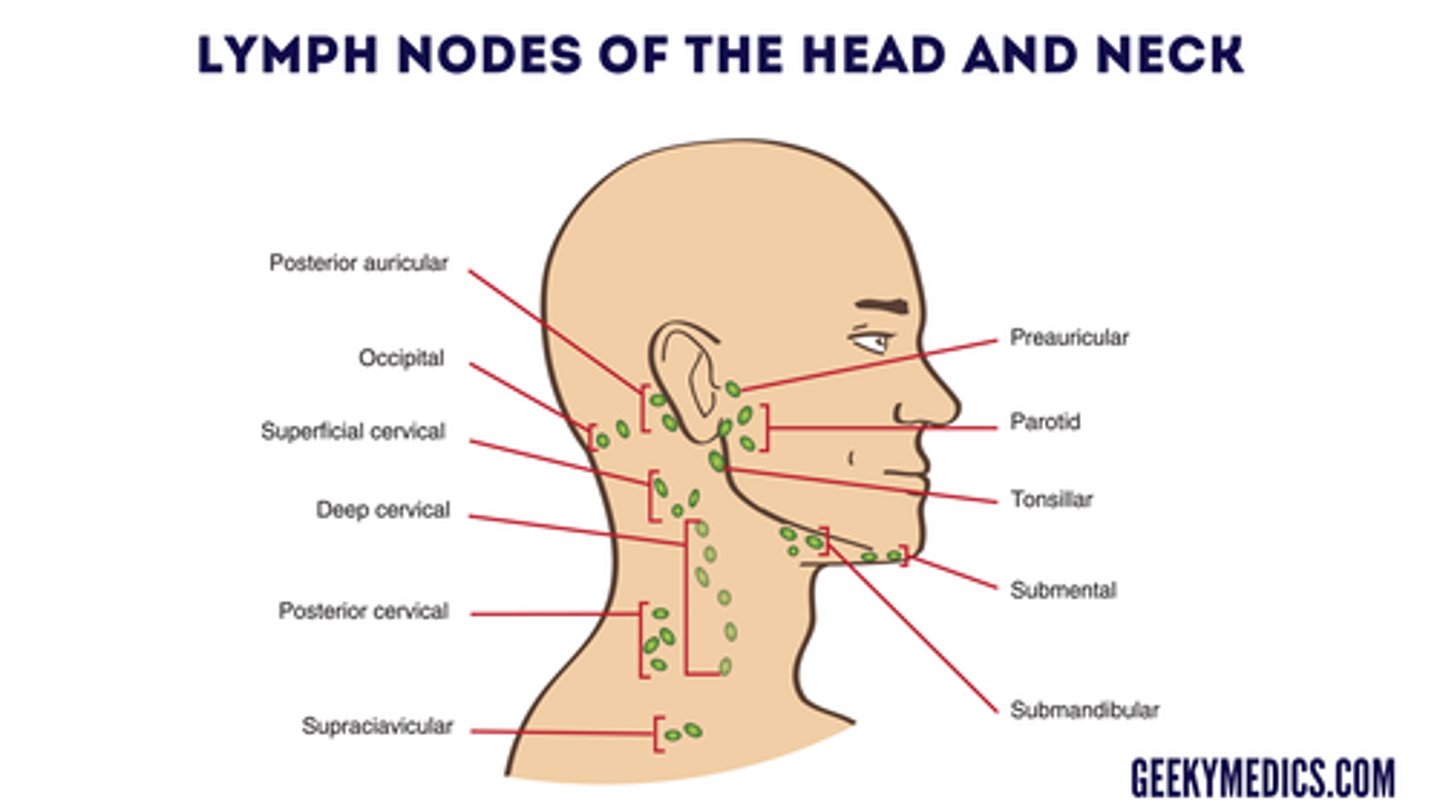
when palpating nodes, note
a gentle circular motion of finger pads
examine lymph nodes using
preauricular, posterior auricular, occipital, submental, submandibular, tonsillar (parotid), superficial cervical, deep cervical, posterior cervical (along the trapezius muscle), and supraclavicular.
order to palpate lymph nodes in
twisted and prominent
temporal arteries in the aging adult may look
mild rhythmic tremor
In some aging adults, a _____ of head may be normal
ROM and position changes slowly
Maintain patient safety by indicating patient perform
potential for dizziness
peforming ROM and position changes slowly minimizes ___ in a patient
Hematoma in one sternomastoid muscle; head tilt to one side and limited neck ROM to opposite side
Congenital torticollis; results in
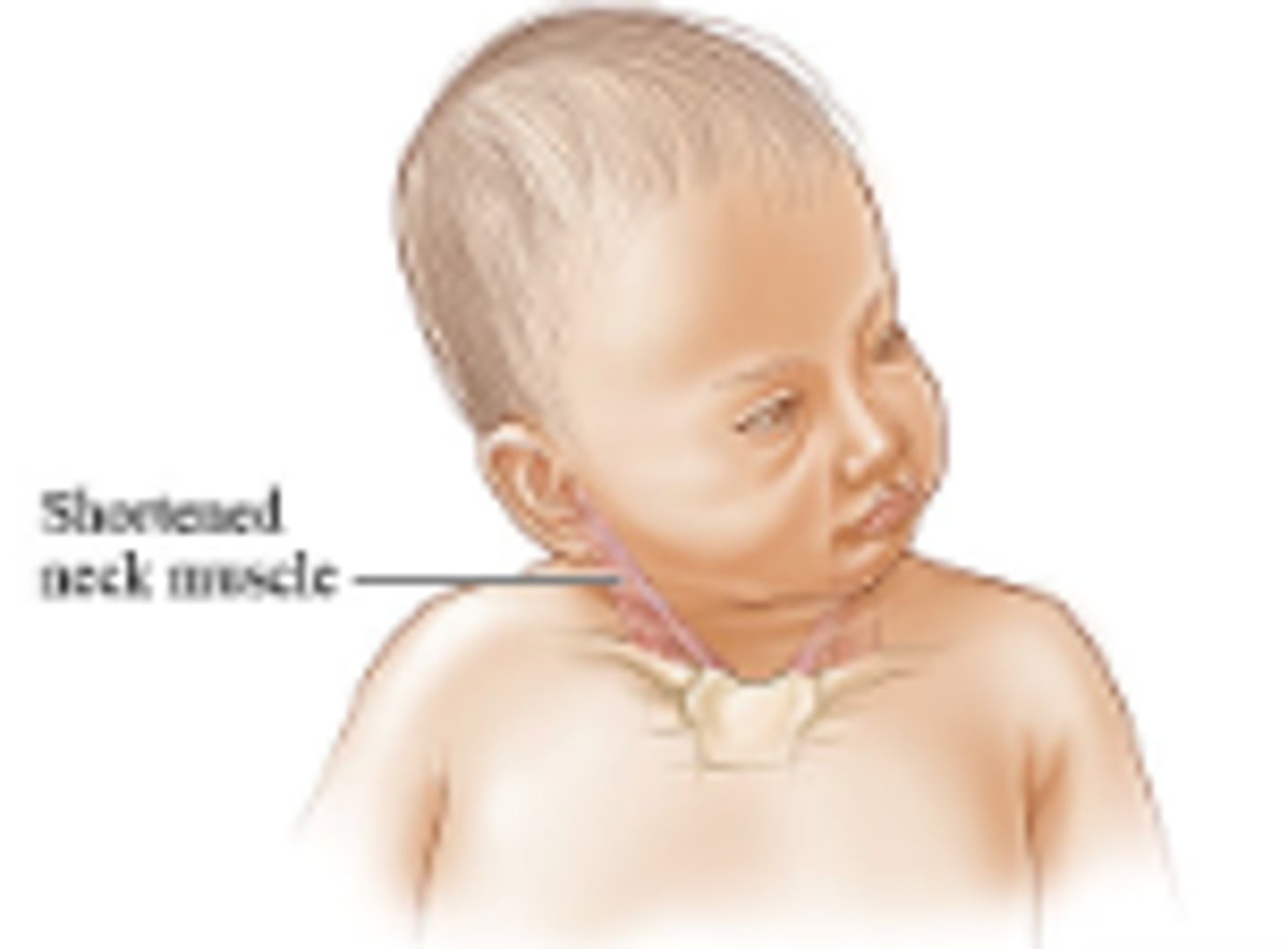
intrauterine malposition
Congenital torticollis is probably due to
iodine deficiency
Simple diffuse goiter (SDG) is due to
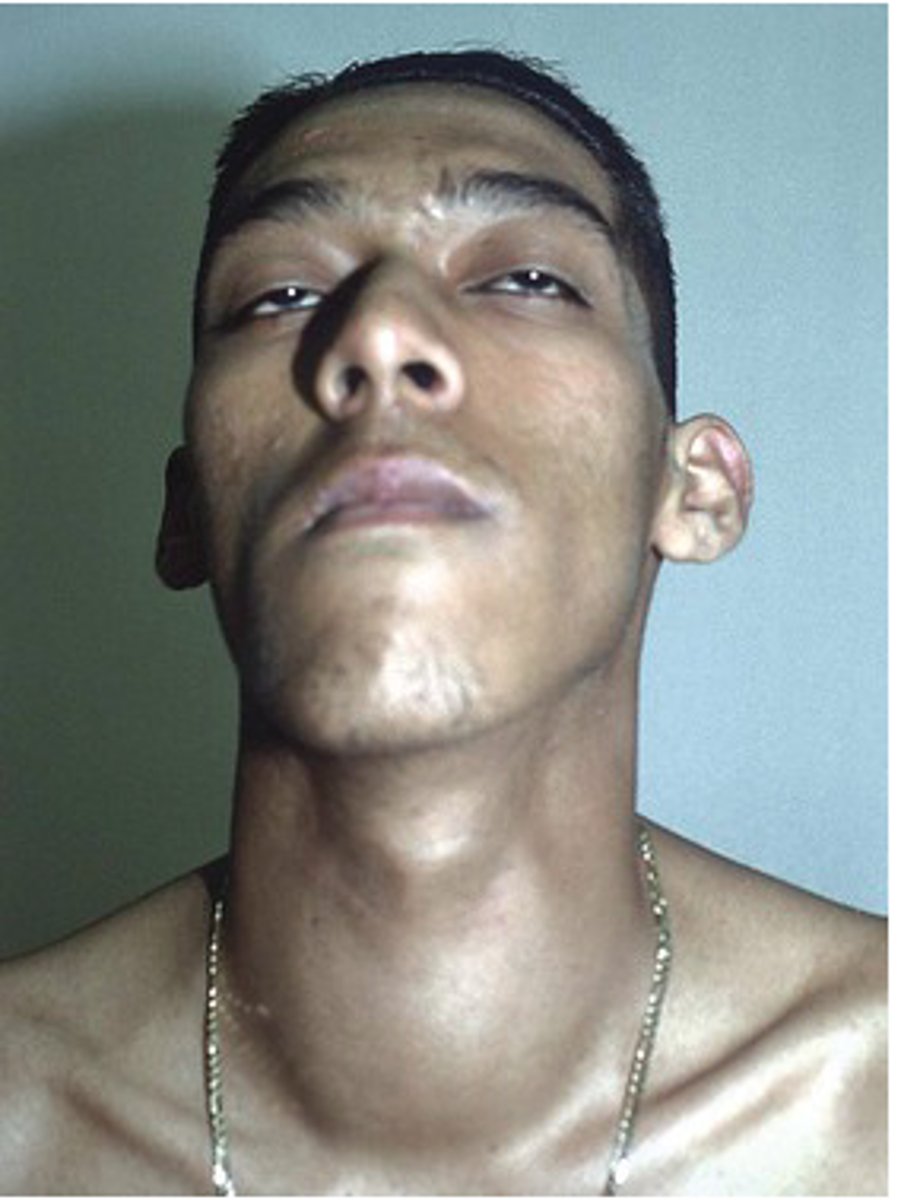
chronic enlargement of the thyroid gland
simple diffuse goiter (SDG) results in
inflammation or multinodular goiter (rather than a neoplasm [tumor]; however, suspect any rapidly enlarging or firm nodule)
Thyroid—multinodular goiter (MNG) (multiple modules) usually indicates
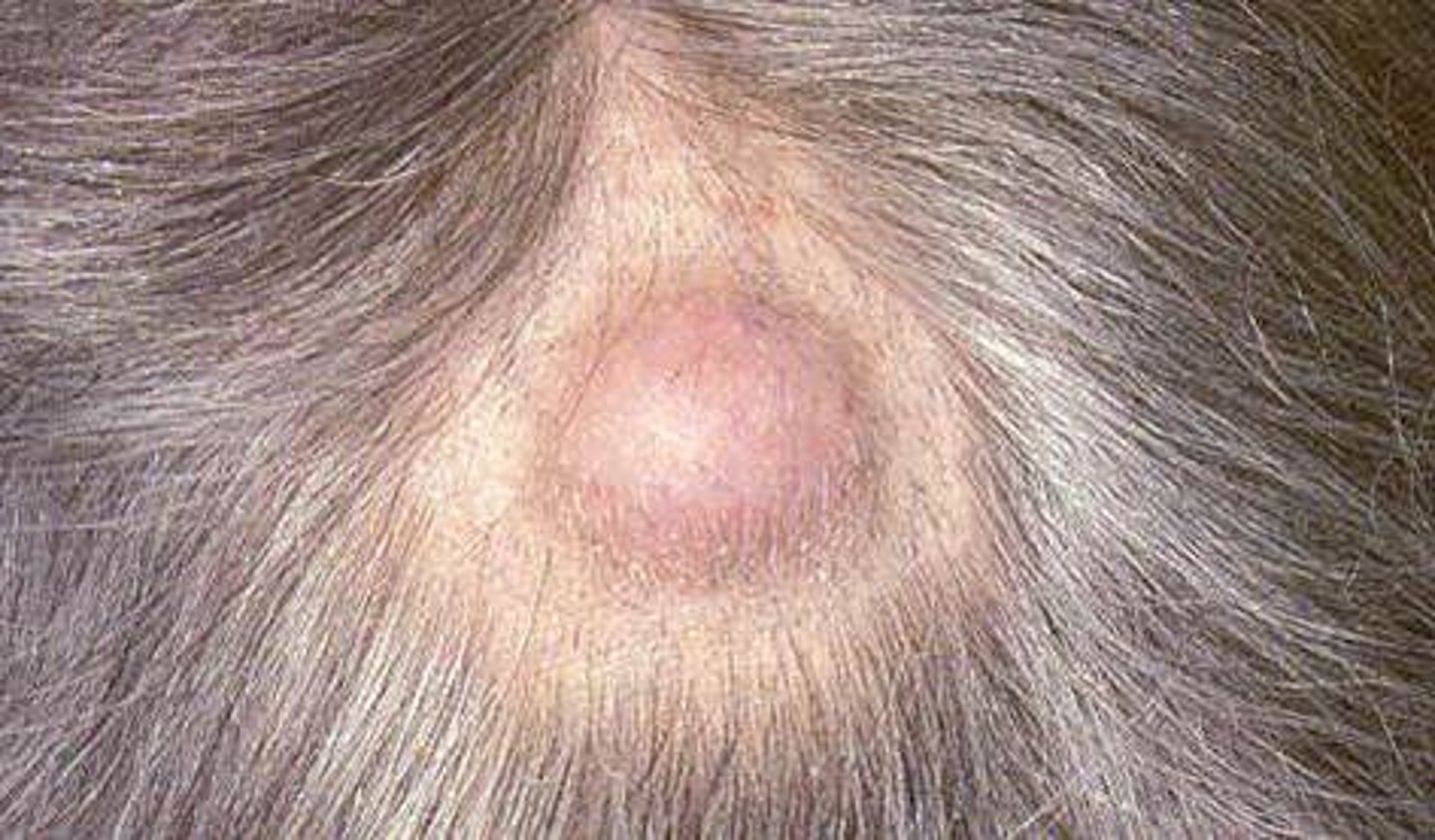
Benign growth that presents as smooth, fluctuant swelling on scalp
Pilar cyst (Wen)
mumps, blockage of duct, abscess, or tumor
Parotid gland enlargement (rapid painful enlargement) seen in response to
goiter, eyelid retraction, and exophthalmos
thyroid disorder: graves disease (appearance)
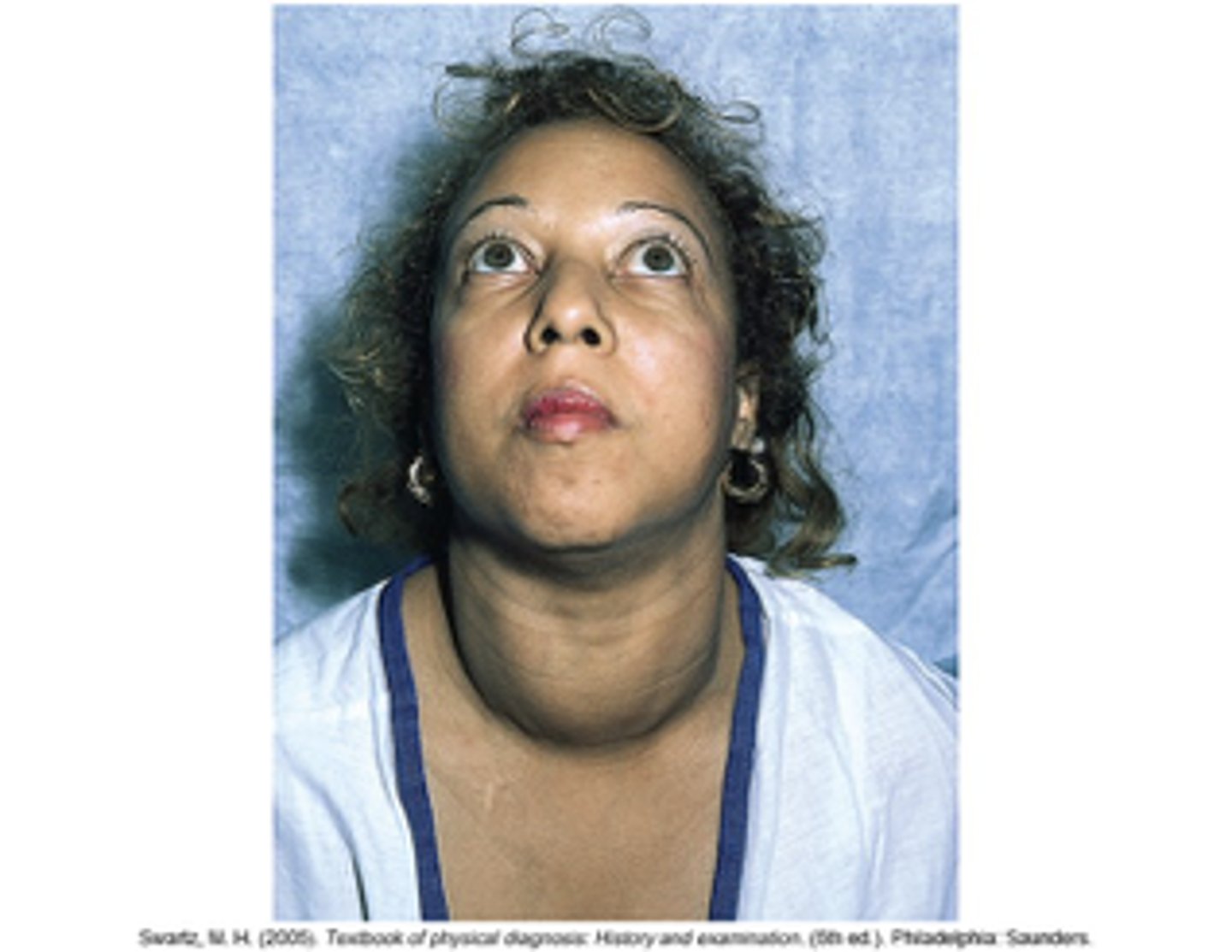
Puffy edematous face; Periorbital edema, coarse facial features, hair and eyebrows
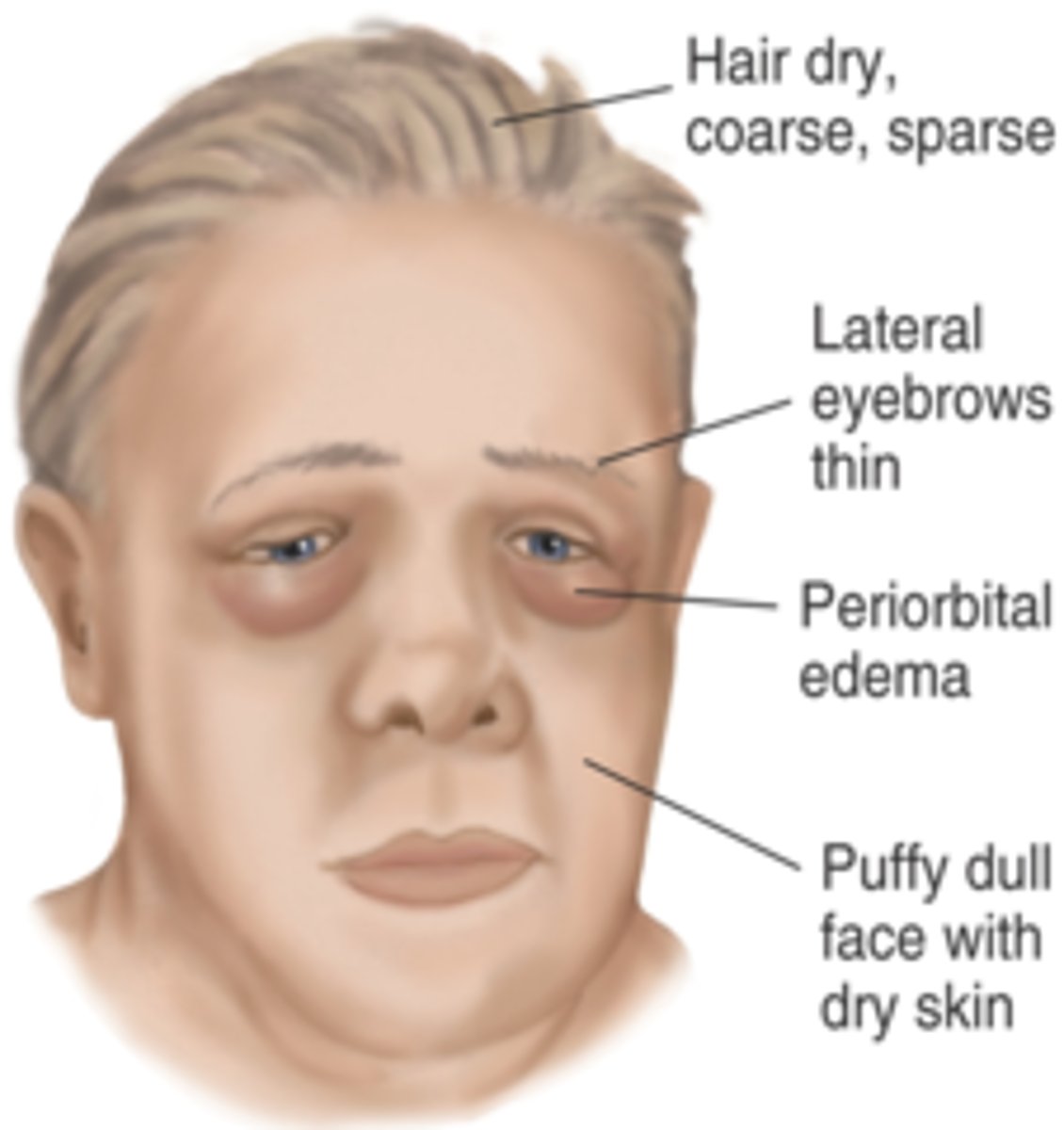
Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidism (appearance)
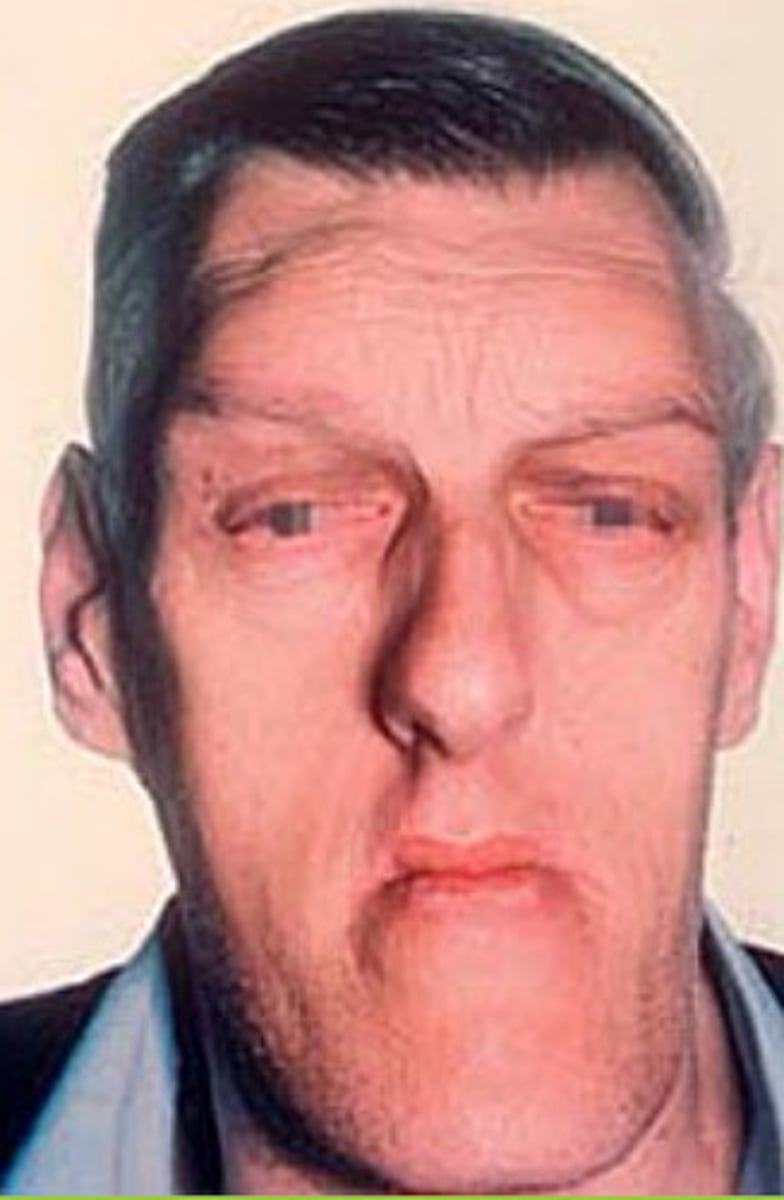
Elongated head, massive face, overgrowth of nose, lower jaw, heavy eyebrow ridge, coarse facial features
Acromegaly face
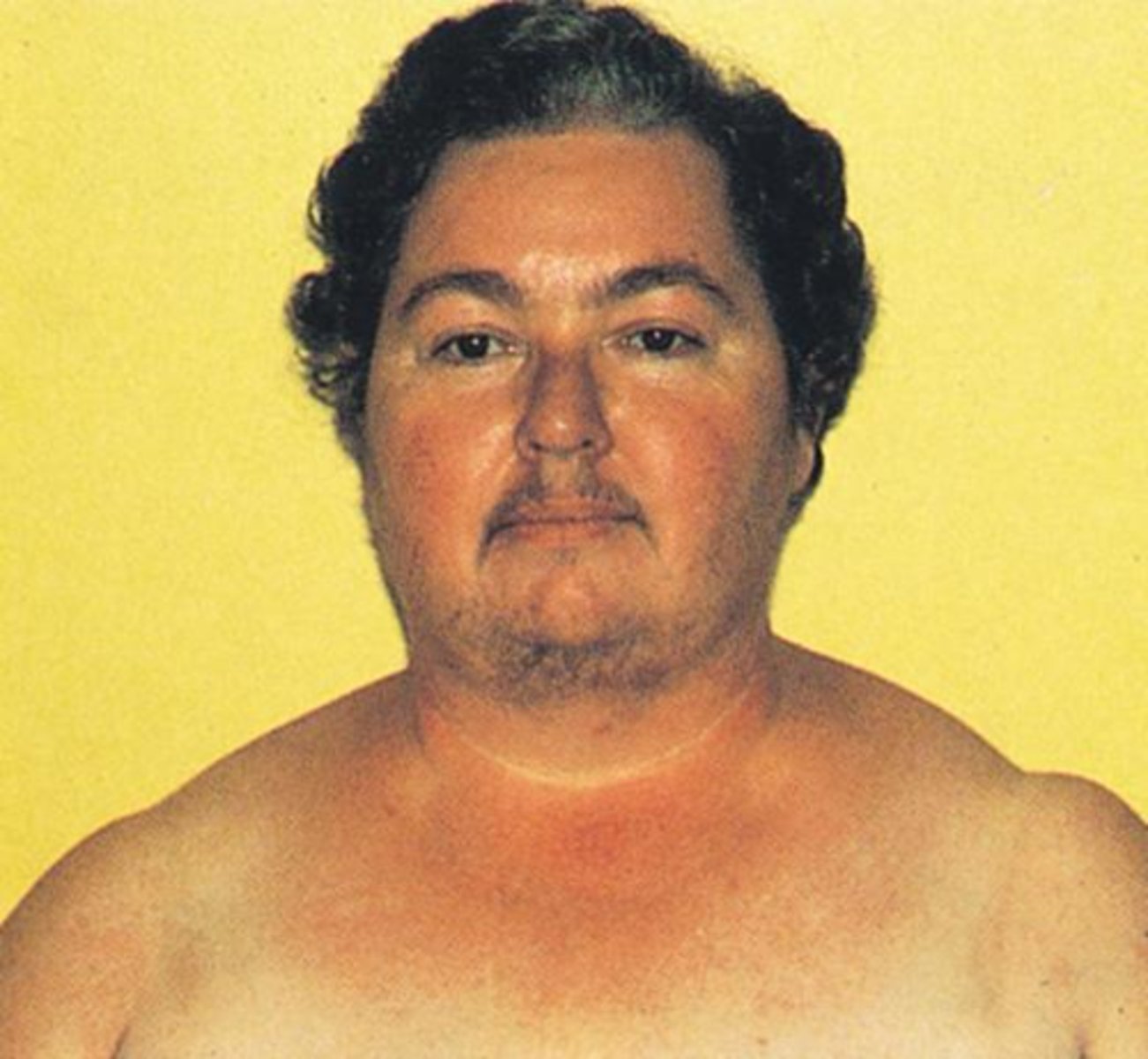
Classic "moonlike" face, red cheeks, and hirsutism
Cushing syndrome face

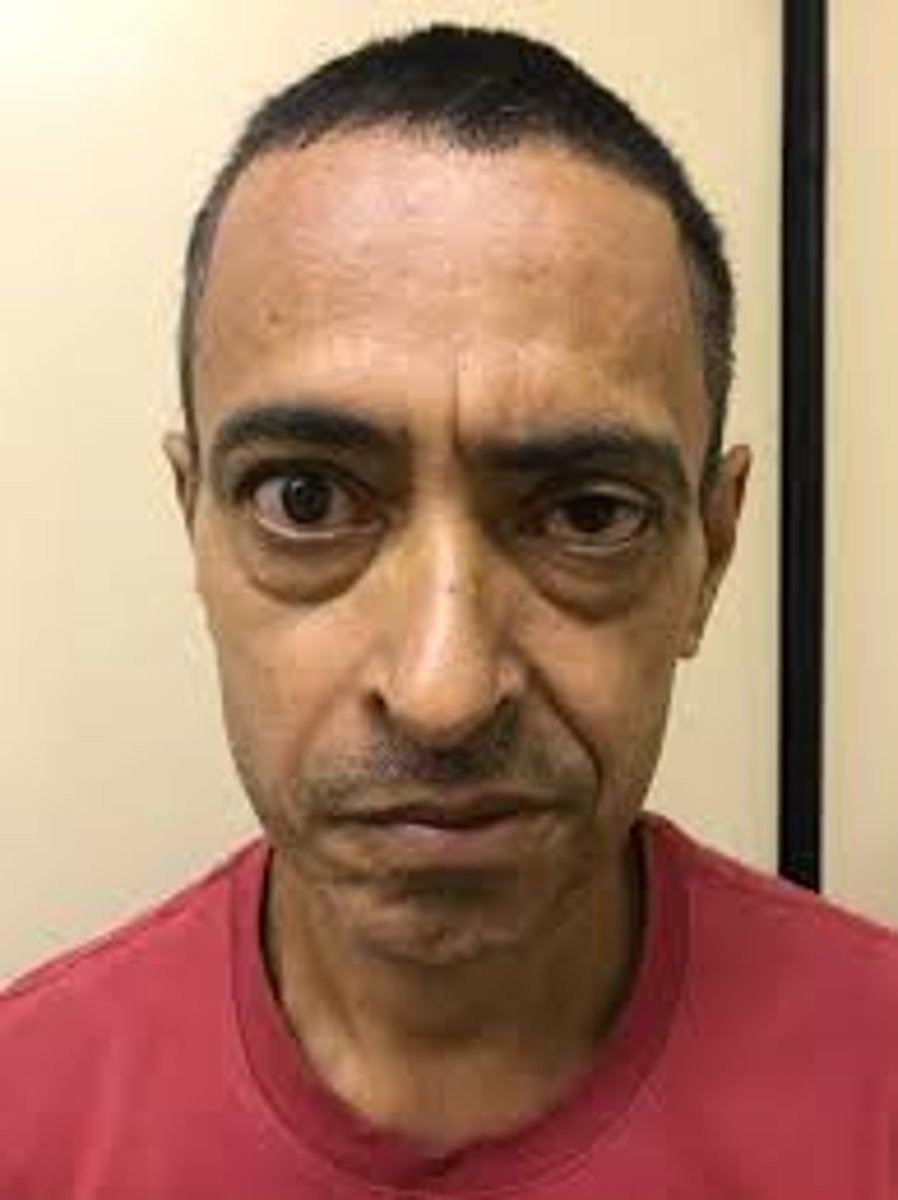
Paralysis on one side of the face as a result of LMN lesion
Bell palsy face
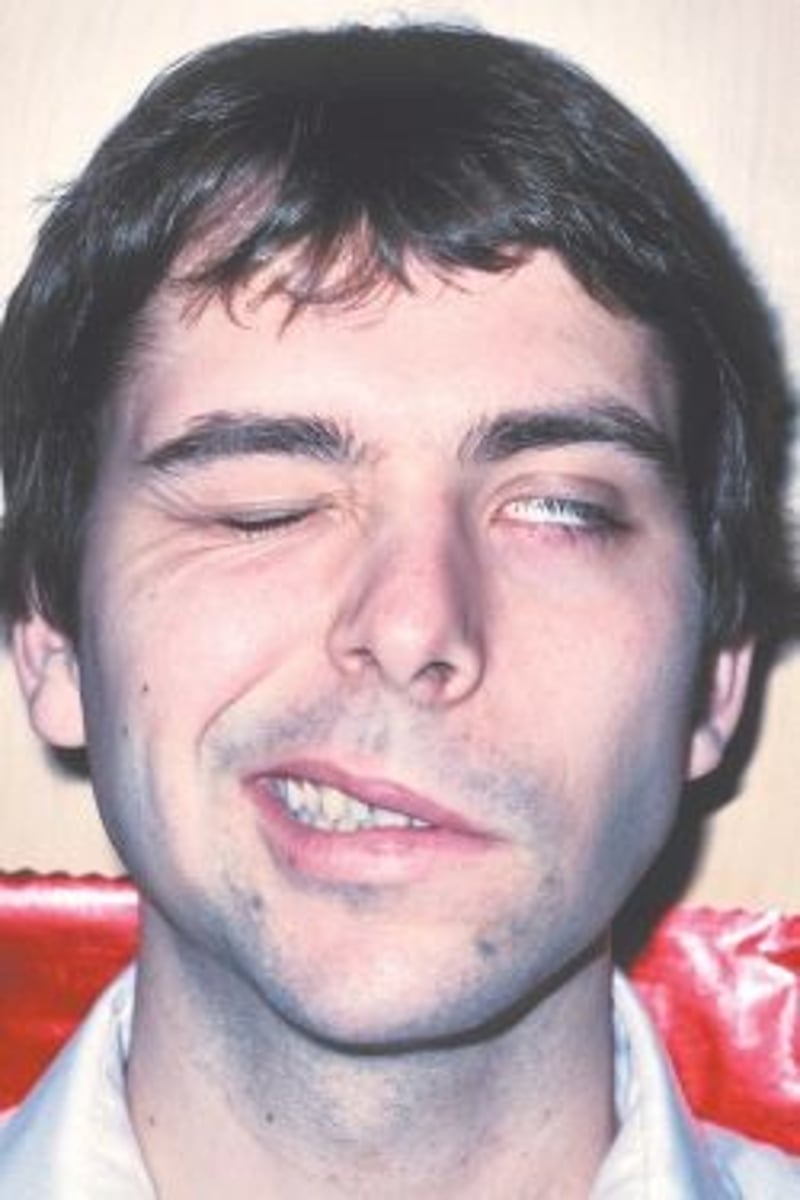
stroke or brain attack
UMN (upper motor neuron) lesion leading to paralysis of lower facial muscles may be caused by
Classic "masklike" appearance, elevated eyebrows, staring gaze, oily skin and drooling due to dopamine deficiency
Parkinson syndrome

Sunken eyes, hollow cheeks, and defeated expression that accompanies chronic wasting diseases
Cachectic appearance
temporal artery and temporomandibular join (TMJ) joint
when palpating the skin, palpate
bruit
if enlarged, auscultate thyroid for ____
blowing, swooshing sound heard through a stethoscope when an artery is partially occluded
bruit