Epidemiology: Practical Disease Concepts
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
TEST 5/13 (TUESDAY)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is etiology?
the study of causes of disease and their mode of operation
Remember the difference between communicable & non-communicable diseases:
Communicable: Infectious Disease
Non-Communicable: Chronic Disease
What is the definition of acute?
relatively severe disorder with sudden onset and short duration of symptoms
What is the definition of chronic?
less severe but continuous duration, lasting over long periods, if not a lifetime
What is the agent?
the cause of disease
What is the host?
a human or animal that is susceptible to the disease
What is a vehicle (fomite)?
a nonliving intermediate such as clothing, food, or water that conveys the infectious agent from its reservoir to a susceptible host
What is a carrier?
contains, spreads or harbors an infectious organism
can be asymptomatic
What is viability?
the capacity of the pathogen to survive outside the host and to exist or thrive in the environment
What is a zoonotic disease?
disease that can be passed from vertebrate animals to humans or vice versa
Who is patient zero?
refers to a person identified to be the first carrier of a communicable disease in an outbreak of related cases
What is vertical transmission?
Transmission from an individual to their offspring through sperm, placenta, milk, or vaginal fluids
What is horizontal transmission?
Transmission from an individual to a susceptible contemporary. This can involve direct transmission (STDs), a common vehicle (water-borne, food-borne, or blood-borne diseases), airborne pathogens (like tuberculosis), or vector borne pathogens (like malaria)
What is direct transmission?
immediate transfer of an infectious agent from one person to another
What is indirect transmission?
→ an agent is transferred by an intermediate item, organism, means, or process to a host, resulting in disease
Airborne: when droplets or dust particles carry pathogens to a host
Vector-borne: when an arthropod (mosquito, flee, etc.) conveys the infectious agent
Vehicle-borne: an inanimate object (such as water) that conveys an infectious agent to a host
What are the stages of disease?
Stage of Susceptibility
Stage of Presymptomatic Disease
Incubation Period: The time period between an infection by a pathogen and the first symptoms of disease
Latency Period: the time when a disease is present but not symptomatic or detected
Clinical Disease
Stage of Recovery, Disability, or Death
How is disease classified?
Congenital and Hereditary: structural or functional anomalies that occur during intrauterine life. 6% of babies are born with congenital anomalies
Allergies and Inflammatory Diseases: Allergies are a hypersensitivity of immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. Inflammation is a biological response of the body to a harmful stimuli such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants.
Degenerative Diseases: disease in which function or structure of the affected or organs changes for the worse over time. It is often associated with the aging process but it may not be age related.
Metabolic Disease: when abnormal chemical reactions in your body disrupt the ability to process and break down food for energy
Cancer: a group of many diseases characterized by uncontrolled cell growth or the loss of a cell’s ability to perform apoptosis
What are reportable diseases?
The WHO provides a list of internationally recognized diagnostic classifications for general epidemiologic and health management purposes, called the ICD (International Classification of Disease).
The WHO uses death certificates, hospital records, and other sources to compare statistics among member states.
The CDC also has a national reporting system. It is not mandatory to report nationally but it is mandatory to report to the state. Each state has different requirements. The requirements also change year to year to reflect the emergence of new pathogens or the decline in incidence of certain diseases
What is needed for a disease to be on a state’s list?
Causes serious morbidity or death
Has the potential to spread
Can be controlled with appropriate intervention
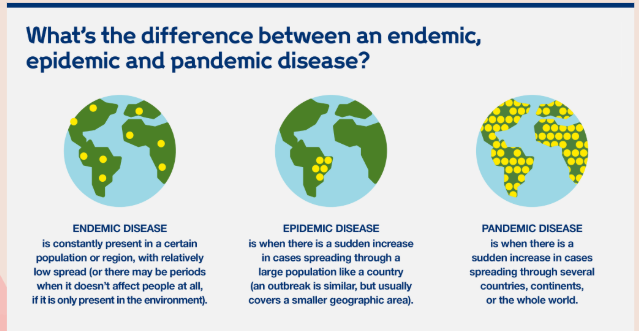
What is the difference between endemic, epidemic, & pandemic?
→
What is primary prevention?
preventing a disease or disorder before it happens. Health promotion, health education, and health protection are primary prevention.
Active requires behavior change of the individual
Ex. begin exercising, stop smoking, immunizations, etc.
Passive primary does not require behavior change
Ex. eating vitamin-enriched foods, drinking fluoridated water)
What is secondary prevention?
aimed at health screening and detection to identify disease
What is tertiary prevention?
limiting disabilities by providing rehabilitation when a disease, injury, or disorder has already occurred and caused damage
How do vaccines work?
imitating an infection to engage the body’s natural defenses
A single dose of vaccine only provides partial immunity
Live attenuated vaccines give more protection than non-live attenuated vaccines, however, all of them usually require multiple doses and/or a booster to restore protection
What is the difference between an antibody and antigen?
All vaccines have an active ingredient called an antigen. An antigen is a substance that causes the immune system to begin producing antibodies
Antibodies are proteins produced by white blood cells to identify and neutralize foreign substances.
The antigen is either:
Weakened or killed virus or bacteria
Bits of the exterior surface or genetic material of a virus or bacteria
Bacterial toxin treated to make it non-toxic
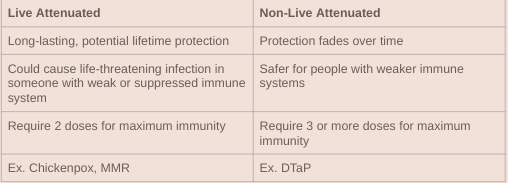
Explain the difference between live attenuated and non-live attenuated immunizations:
→
Explain the difference between active & passive immunity:
Active - exposed to disease whether naturally or vaccine-induced
*Active immunity takes longer to build but lasts longer
Passive - provided from another human or animal
Ex. babies are passed antibodies from their mother during the final months of pregnancy
immediate but fades quicker
What is herd immunity?
The notion that if the herd (a population or group) is mostly protected from a disease by immunity, the chance that a major epidemic will occur is limited. Herd immunity provides barriers to prevent direct transmission through a population