Physiology: Respiratory System
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Pressure - Atmospheric
Atmospheric pressure - 760mmHg or 1atmosphere
Transmural pressure: Inside - outside
Respiratory Pressures
Pleural pressure is 4mmHg below atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure = alveoli pressure
Transpulmonary pressure = alveoli pressure - pleural pressure.
Thoracic cavity expansion - Inspiration at rest
Contraction of the diaphragm:
increases vertical dimension of the thoracic cavity
Elevation of ribs causes sternum to move out, increasing Front- to back dim
Contraction of external intercostal muscles:
Causes elevation of ribs and increase side-side dimension
Thoracic cavity compression (Passive or active)
Passive:
Everything occurs in the opposite direction of inspiration
Active:
Contraction of internal intercostal muscles flattens ribs and sternum, further reducing side-to-side and front-to-back dimensions
Contraction of abdominal muscles forces diaphragm upward, further reducing vertical dimension.
Boyle’s Law
the volume of a given mass of gas varies inversely with the pressure when the temperature is kept constant.
Definitions: Tidal volume, Functional residual capacity
TV: Volume of air breathed in and out of the lung under resting conditions
FRC: Volume of air in the lung after a normal tidal expiration.
Definitions: Total lung capacity, Residual volume
TLC: Volume of air in the lung after maximal inspiration
RV: Volume of air in the lung after a maximal forced expiration
Definitions: Inspiratory Capacity, Inspiratory reserve volume
IC: Maximal volume of air that can be inhaled into the lung above a normal tidal inspiration
IRV: Volume of air that can be inhaled into the lungs above a normal tidal inspiration.
Definitions: Expiratory reserve volume, Vital capacity
ERV: Volume of air that can be exhaled out the lungs from the functional residual capacity (FRC)
VC: Vital capacity: Volume of air that can exhaled out the lungs from TLC during a non-forced manoeuvre.
Helium dilution
lung volume can be determined from the gas dilution
C1 x V1 = C2 x V2
C1 x V1 = C2 x (V1 + FRC)
FRC = (C1 x V1/C2 ) - V1
Airway resistance
Causes a loss of enegery due to the air molecules colliding itch the liminal surface of the airway.
Lumen radius is therefore. Critical determinant of resistance
Small change in adius procedure a large change in resistance

Airway resistance in the lungs
Determines by the number and the size of airways
Resistance is greatest in the more proximally located towards the trachea
The distal airways (towards the periphery) have very little resistance due to large cumulative cross-sectional area and are often referred to as the ‘silent zone’
Airway resistance - smooth muscle contraction
Bronchoconstriction increases airway resistance and makes breathing more difficult,
From a 5 mm readout to a 1mm radius, there is a 600 fold increase in resistance.
Airway resistance - asthma
contraction of the airway smooth muscle in diseases like asthma occurs due to release of histamine (allergic cascade) which binds to the histamine - 1 receptors. (Causes inflammation and mucus production)
Parasympathetic nerve stimulation releases acetylcholine that binds to muscarinic - 2 receptors on the muscle cell and induces contraction
Bronchocontraiction
produced by parasympathetic nerve stimulation
Blocked by atropine
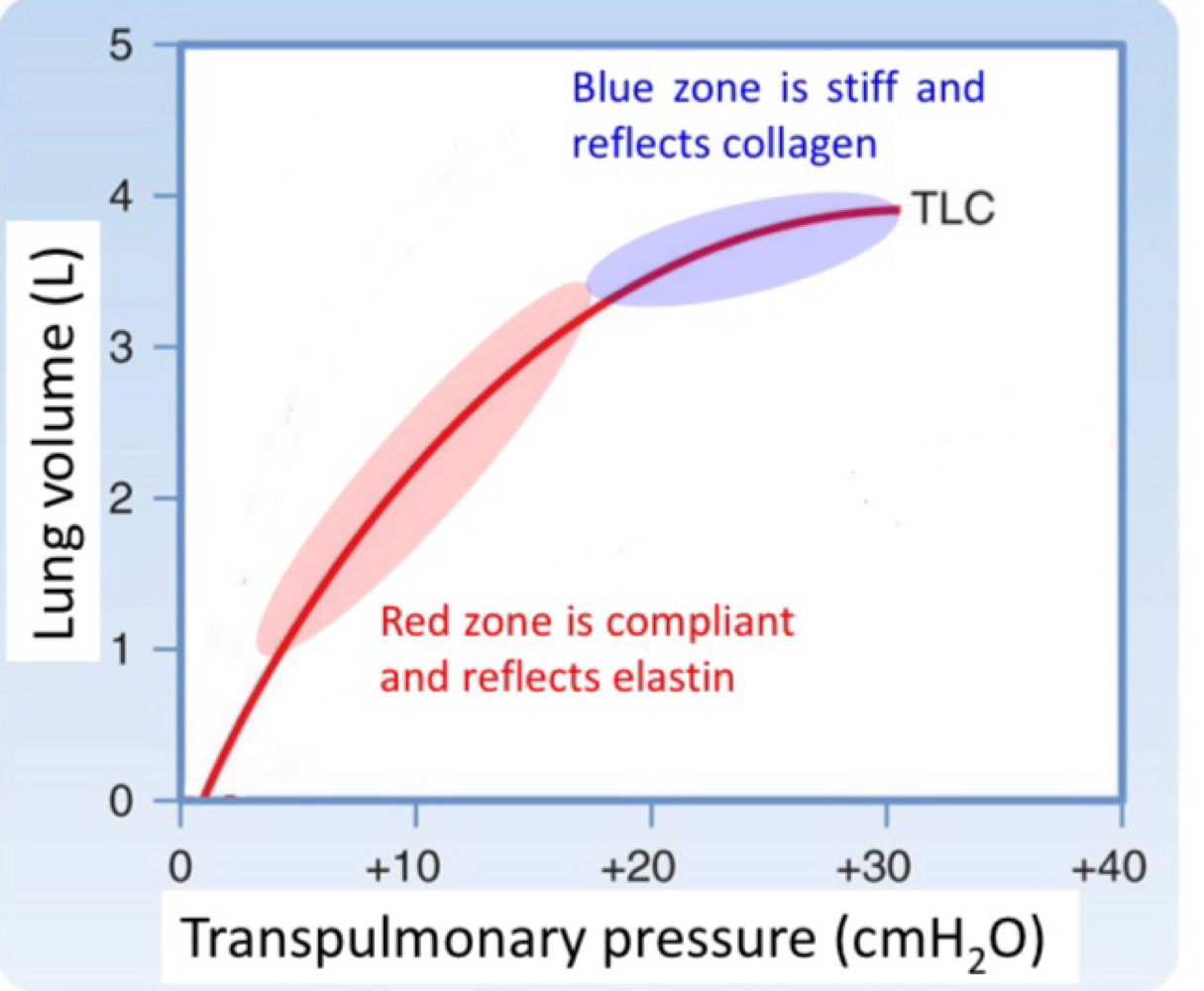
Lung compliance - Pressure-volume curve
compliance determines how easy it is to inflate the lung
Volume change per pressure (L/cmH2O)
Lung is more compliant at lower lung volumes and become stiff towards total lung capacity
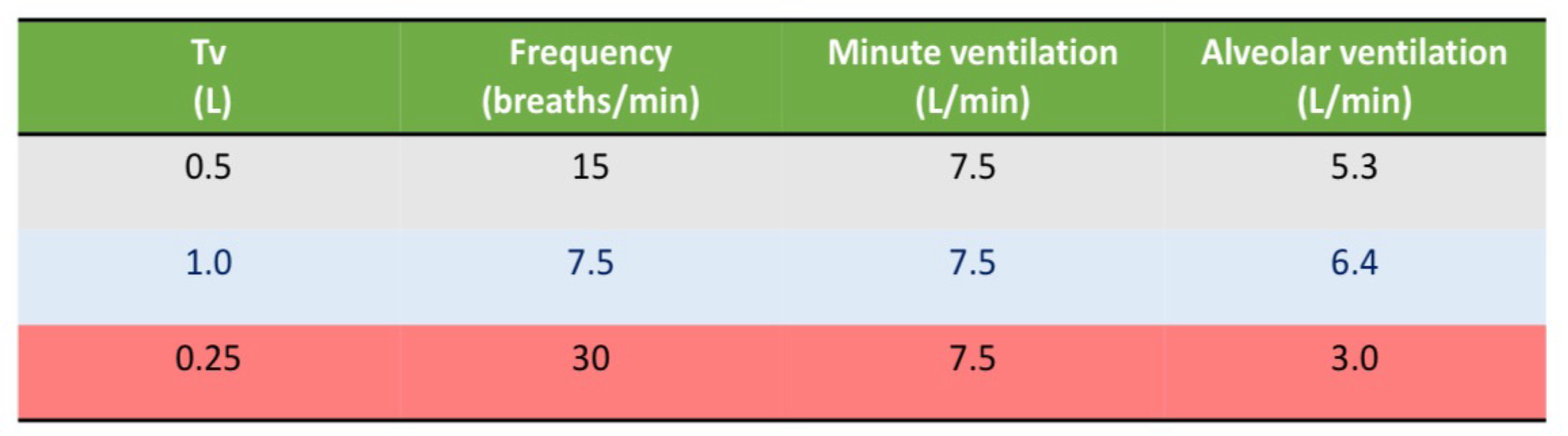
Ventilation - Minute versus alveolar
Approximated at 0.5L per breath and 15 breaths/min
Minute ventilation = tidal volume x breathing frequency
0.5 × 15 = 7.5L/min
Alveolar ventilation = (tidal volume - dead space volume) x breathing frequency.
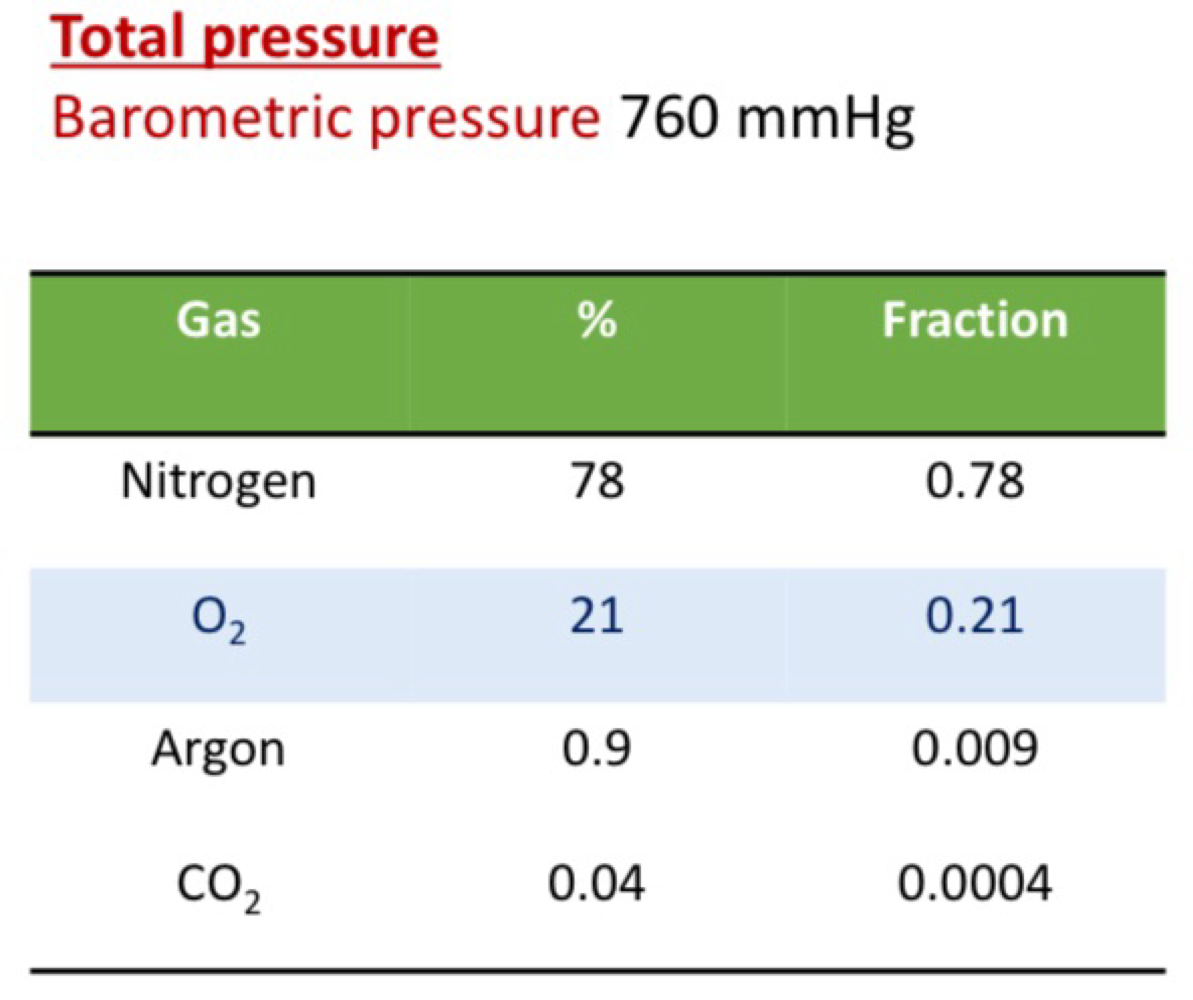
Partial Pressure of O2
Pressure total = PN + PO2 + Pargon + PCO2
PO2 in the atmosphere = barometric pressure x 0.21
760mmHg x 0.21 = 160mmHg
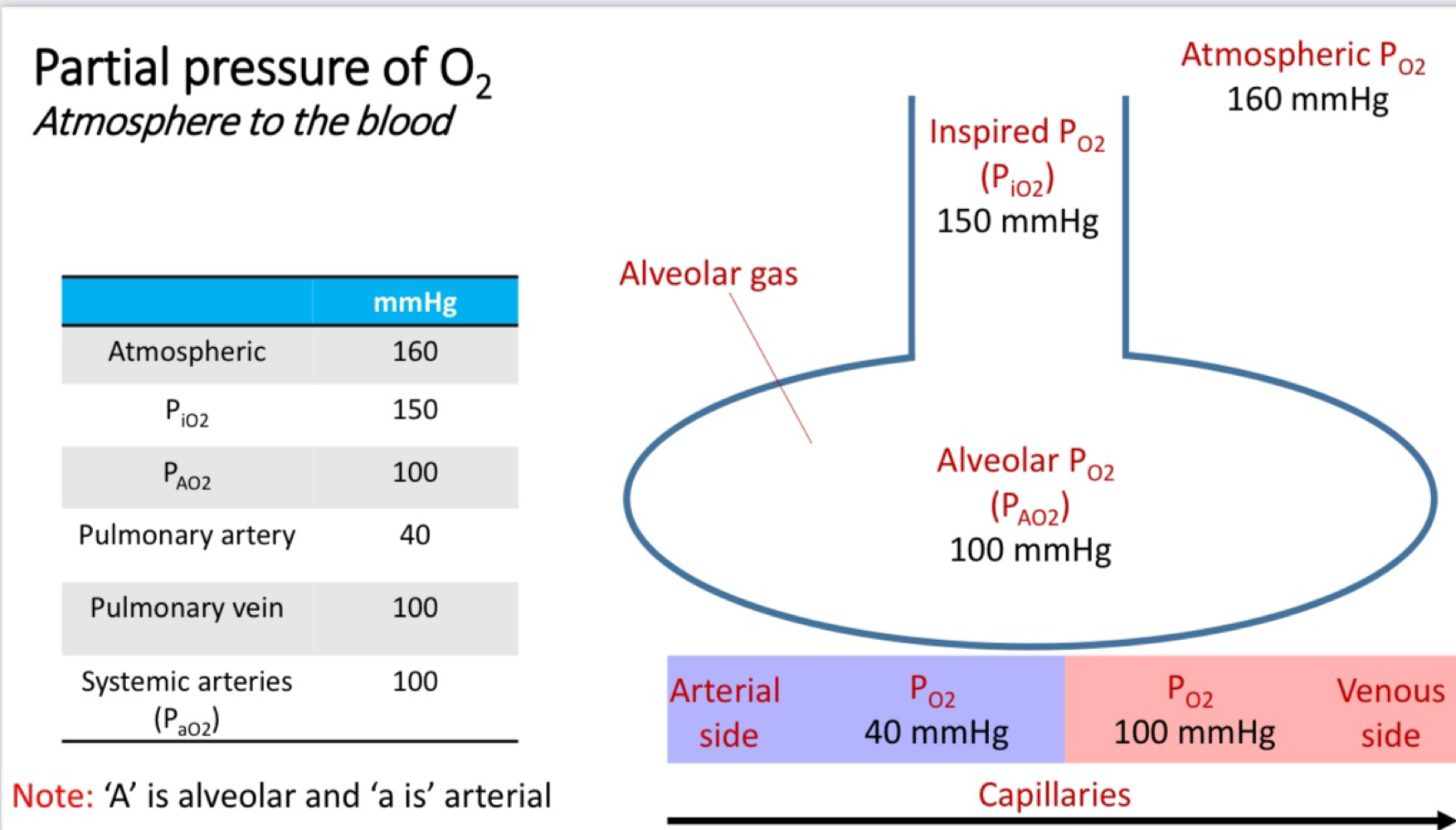
Partial pressure of 02 - atmosphere to the blood
Air that enters the lung is humidified - water vapour exerts. Partial pressure
Partial pressure of H2O at 37º is 47mmH
PiO2 = (barometric pressure - 47mmHg) x 0.21
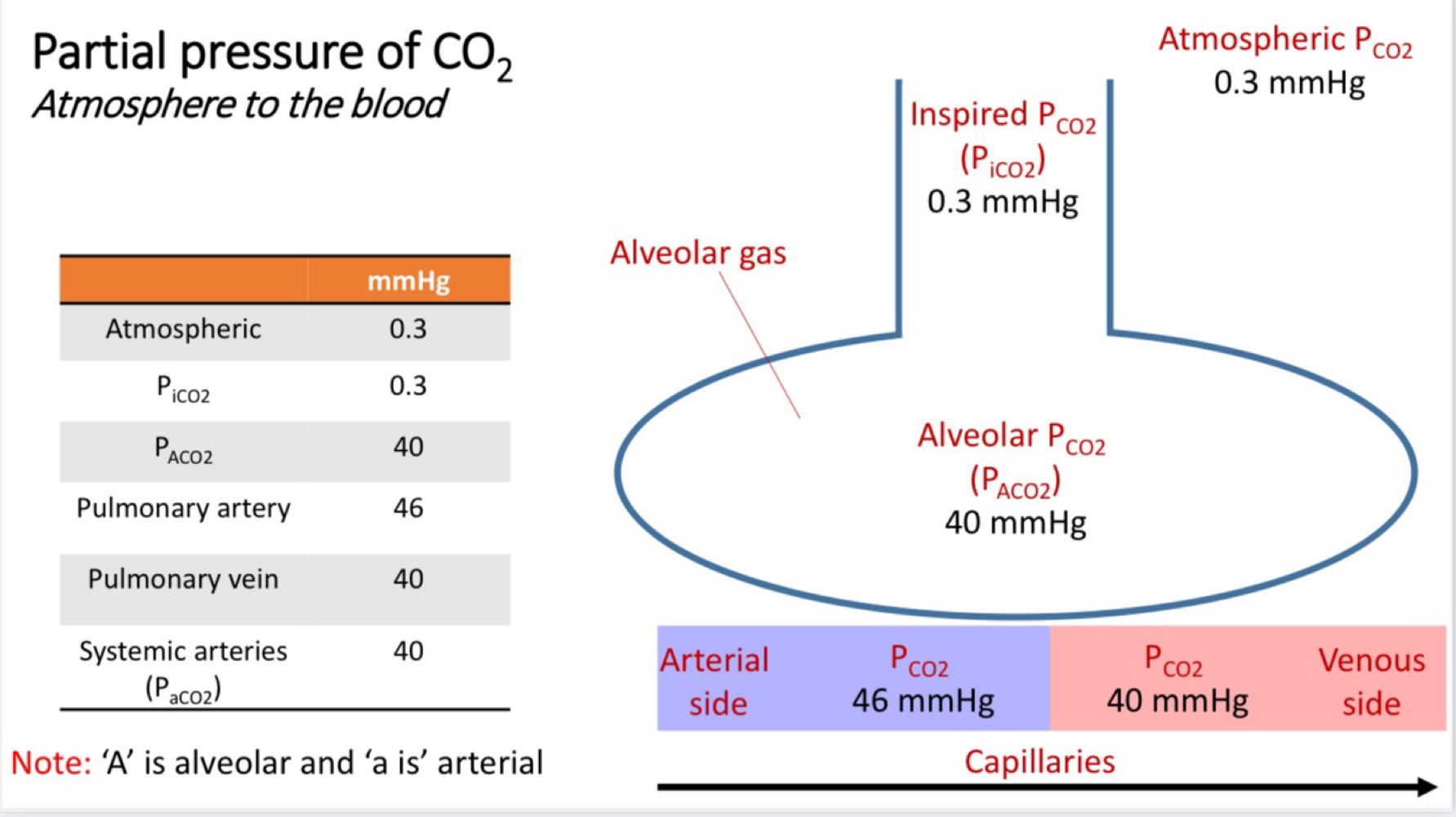
Partial Pressure of CO2 - Atmosphere to the blood
Alveolar gas equation
PAO2 = PiO2 - PACO2/R
R = the respiratory exchange ration which relates the amount of CO2 produced to amount of O2 utilised.
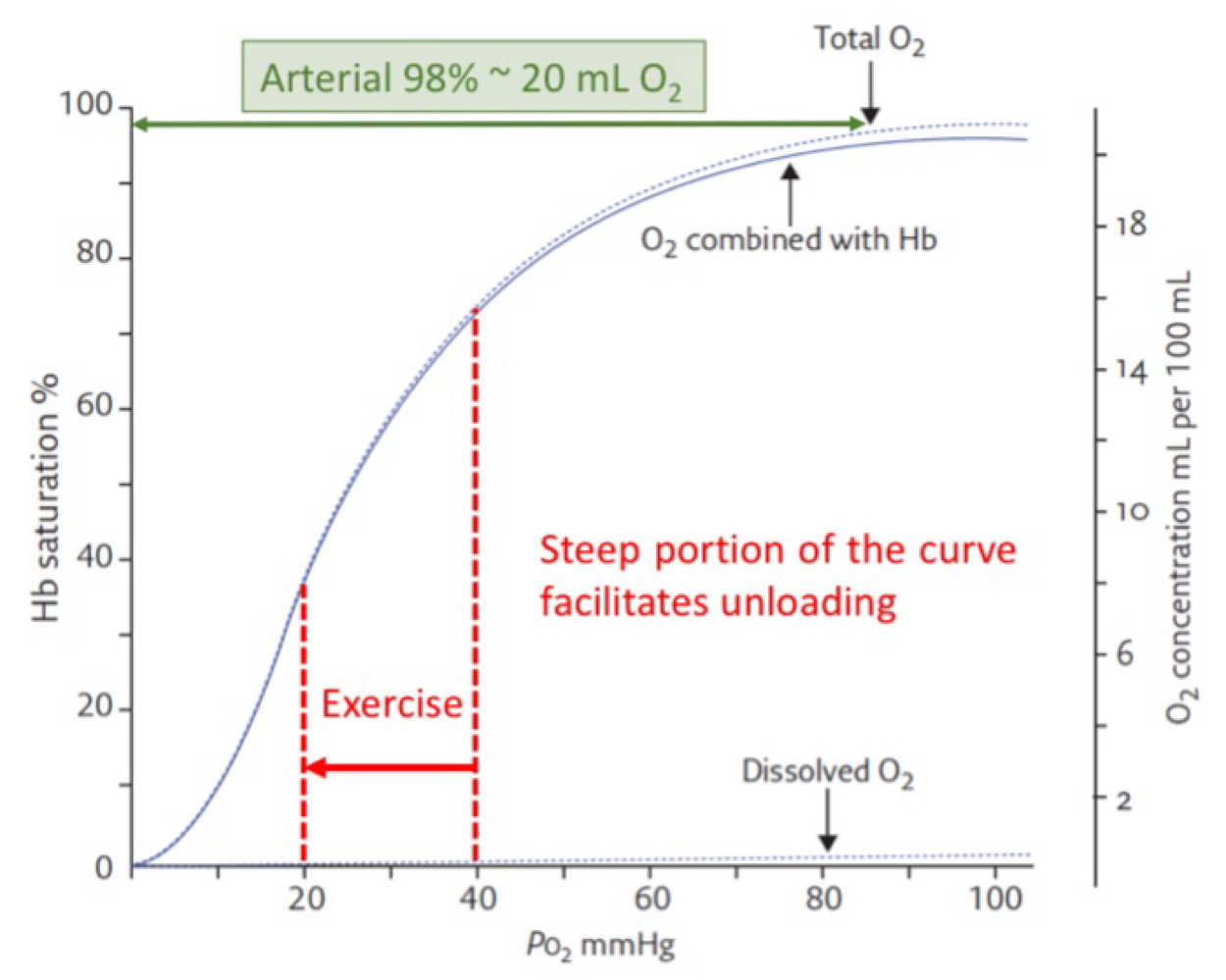
Oxygen-hemoglobin Dissociation curve
% Hemoglobin saturation = sites bound with O2 / Total binding sites
Automatic control of breathing - medulla
Dorsal respiratory group (DRG) contains neurons that stimulate inspiration
Ventral respiratory gourd (VRG) are neurons that are inactive during quite breathing, but active during forced breathing
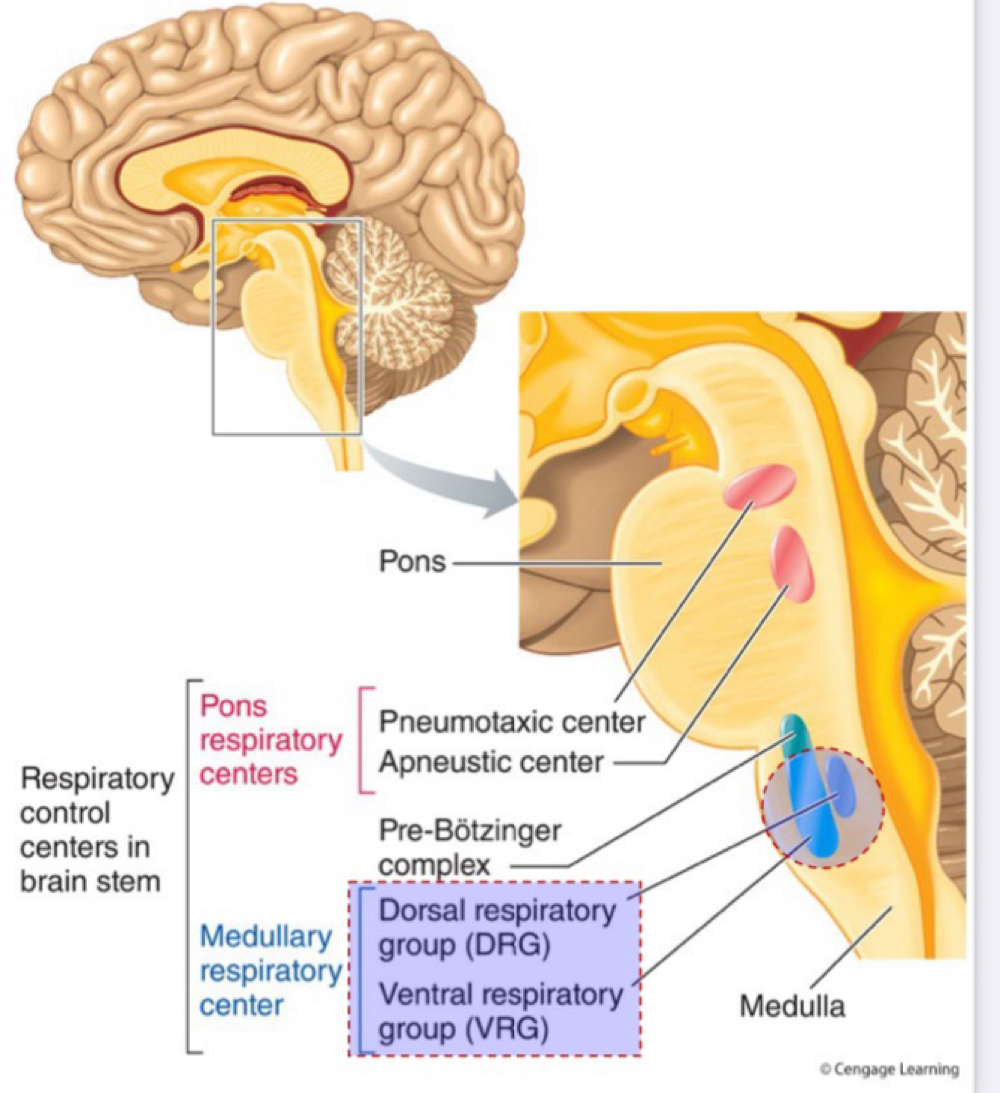
Automatic control of breathing - Pons
Pneumotaxic centre sends neural impulses to the DRG to halt inspiration
Apneustic centre sends neural impulses to the Inspiratory from getting switched off.
Voluntary Control of Breathing - Motor cortex
Directly modifies respiratory muscle contraction
breath hold
Deliberately hyperventilate
Blowing up balloon
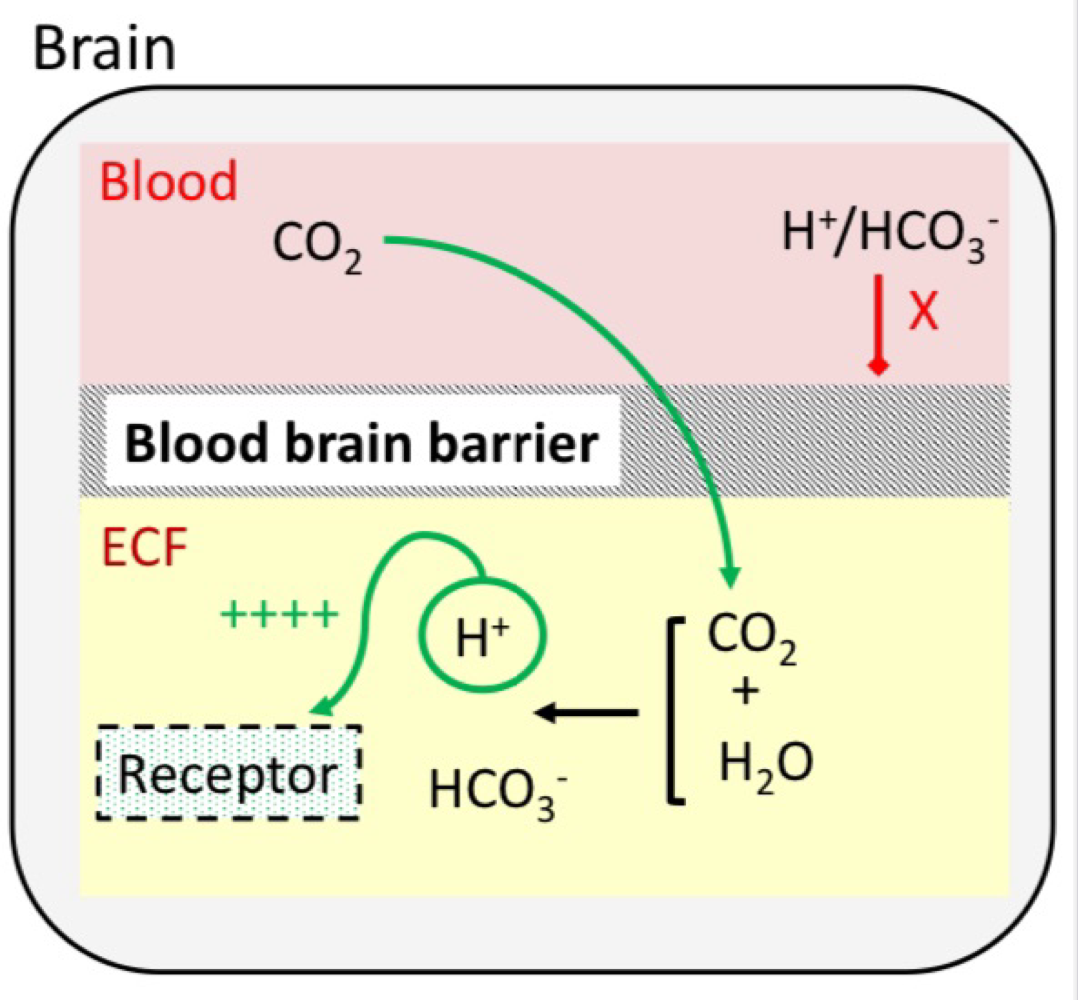
Chemoreceptors - Central
Detects changes in H+ in extracellular fluid within the brain
H+/HCO3- can’t pass through the blood brain barrier but CO2 can → decreasing pH
Contributes 80% of the overall response to an increase in PaCO2
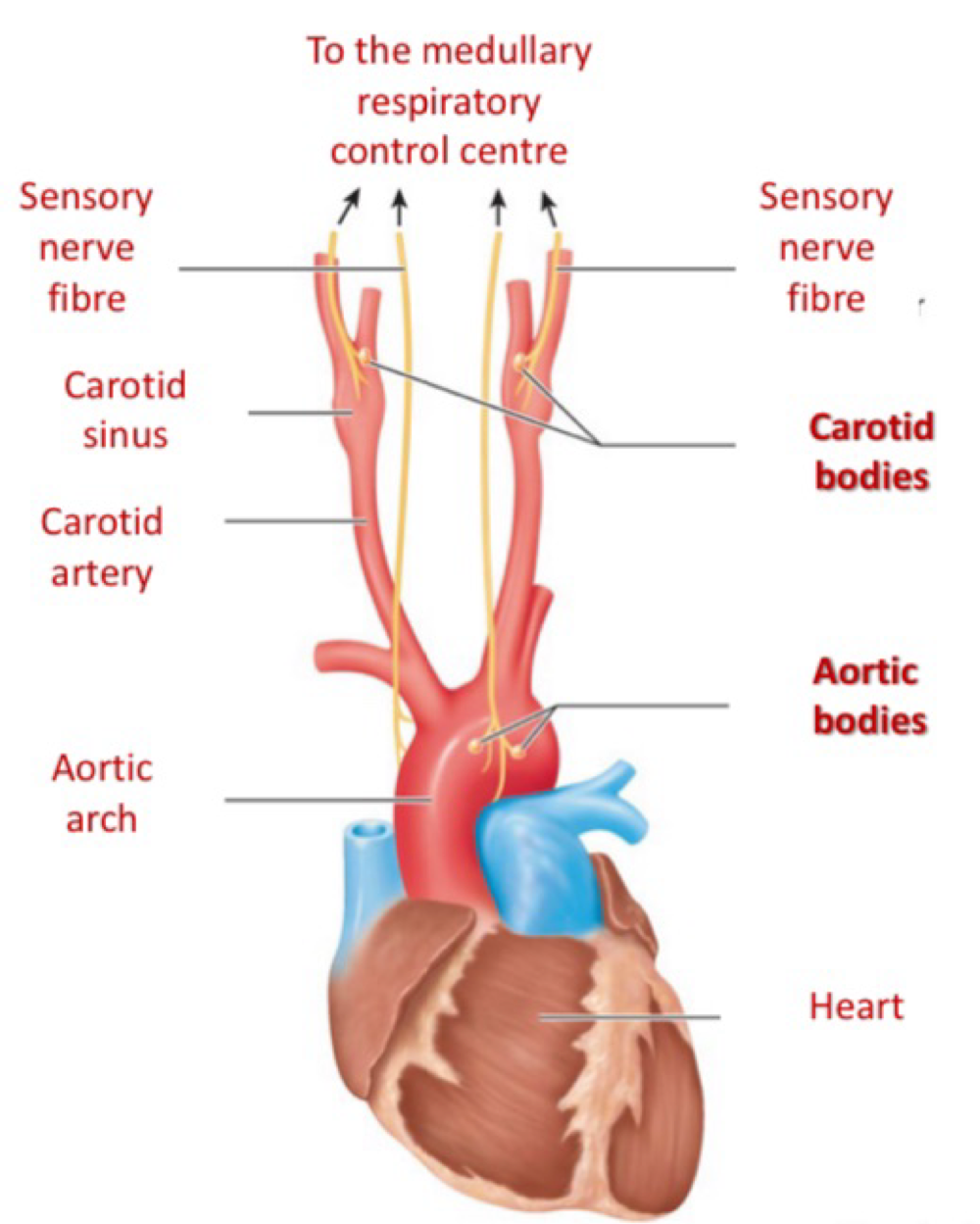
Chemoreceptors - Peripheral
Located in the aortic and carotid oldies
Detects changes in O2 , CO2 and H+
Oxygen: Not activated until PaO2 falls below 60mmHg
Carbon dioxide: weakly responsive
Arterial H+: Highly responsive
Contributes 20% of overall response to an increase in PaCO2
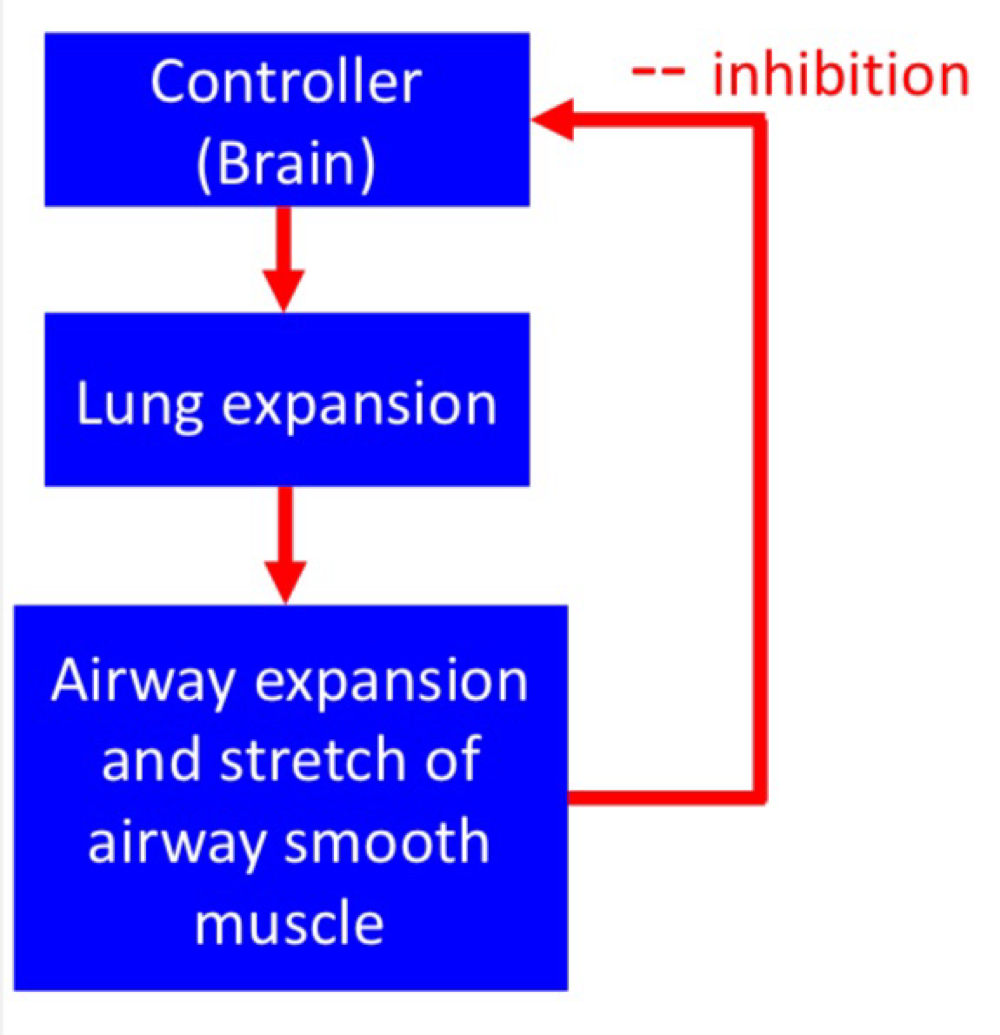
Hering - Breuer Reflex - Stretch receptor
Respond to stretch
Receptors located in the airway smooth muscle
Inhibits Inspiratory drive (negative feedback) and prevents overinflation