Hearing Science: Cochlear Potentials (OHC Motility)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Electrical Potentials
nature (if unimpeded) always seeks equilibrium
-an unbalanced condition will result in electron flow (this lasts until the atoms are in a balanced state)
The greater the disparity of electrons, the greater the charge...
the greater the potential for electrons to move in the quest for equilibrium
How can the magnitude of the charge be expressed?
as the potential for electron movement or flow
How is the magnitude of the potential expressed?
volts (V)
Volt
a statement of potential electron flow
Ion
an atom or molecule with a net electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons
Cochlear Potentials
a surplus of electons has the potential to flow
-flows into the OHC and IHC
-the microchannels in the stereocilia allows the flow
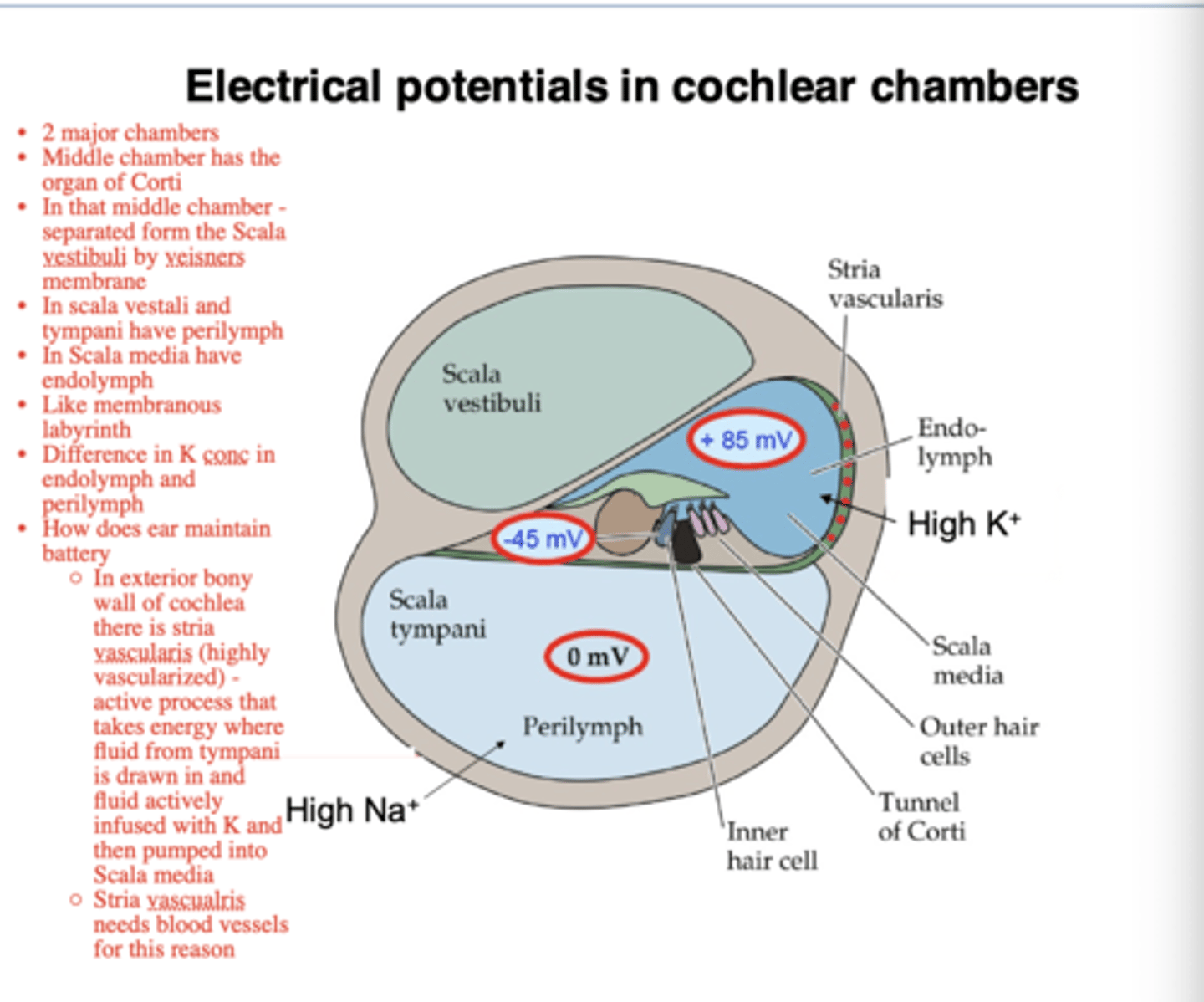
What happens if ion concentrations are different?
potentials occur
What happens if different fluids within the cochlea have different concentrations of ions?
have different electrical charges
What does the rarefaction in the sound waves do to the basilar membrane?
makes the BM go up (stapes footplate moves away from the window)
Endolymph is ____ more positive than perilymph.
100 mV
Inner hair cells are about ____ more negative than perilymph.
40 mV
Outer hair cells are about ____ more negative than perilymph.
70 mV
What are the hair cells bathed in?
cortilymph
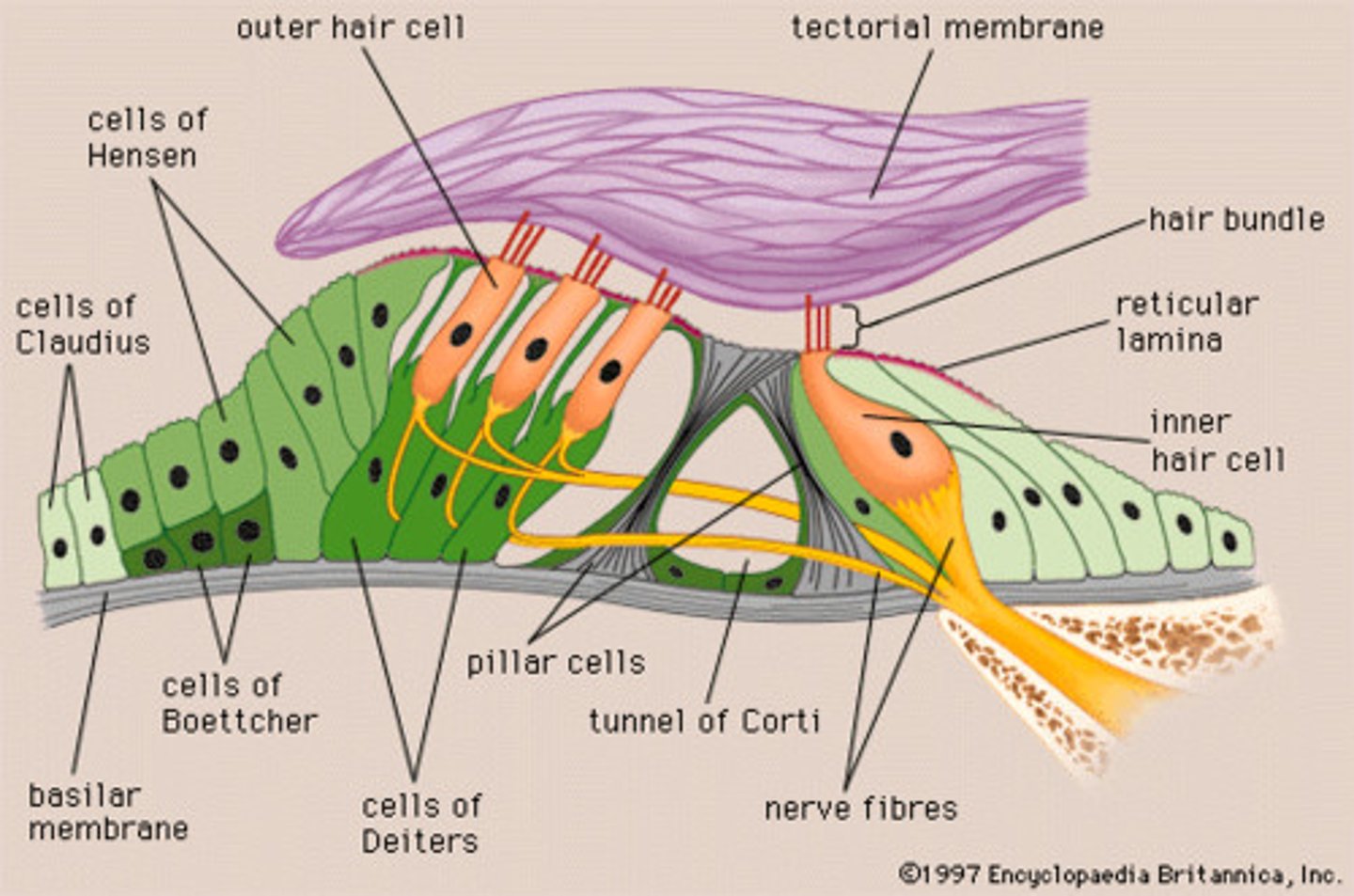
Reticular Lamina
separates the potassium (K+) rich endolymph from the hair cells
There is a ____ potential for ion flow between the endolymph and the inner hair cells.
-140 mV
A small deflection may be insufficient to open what?
the microchannels in the stereocilia
What can cause a small deflection of the stereocilia?
low level sounds (so low level it does not stimulate the nerves)
What happens if there is further deflection of the stereocilia?
open the microchannels
-this allows K+ to flow into the hair cell
What happens when the stereocilia move away from the modiolus (towards the tallest cilia)?
the microchannels open allowing potassium to enter the normally negative hair cell
-this causes the cell to become more positive
-this is called depolarization
What happens when the cilia deflect toward the modiolus?
the hair cell can become more negative as the potassium is pumped out
Cochlear Microphonic
a recording of the fluctuating hair cell polarity (+ to -)
-where the voltage is changing
-mimics the stimulus
Where is the name cochlear microphonic derived from?
the experimental
protocol where the output from the cochlea was sent to a speaker
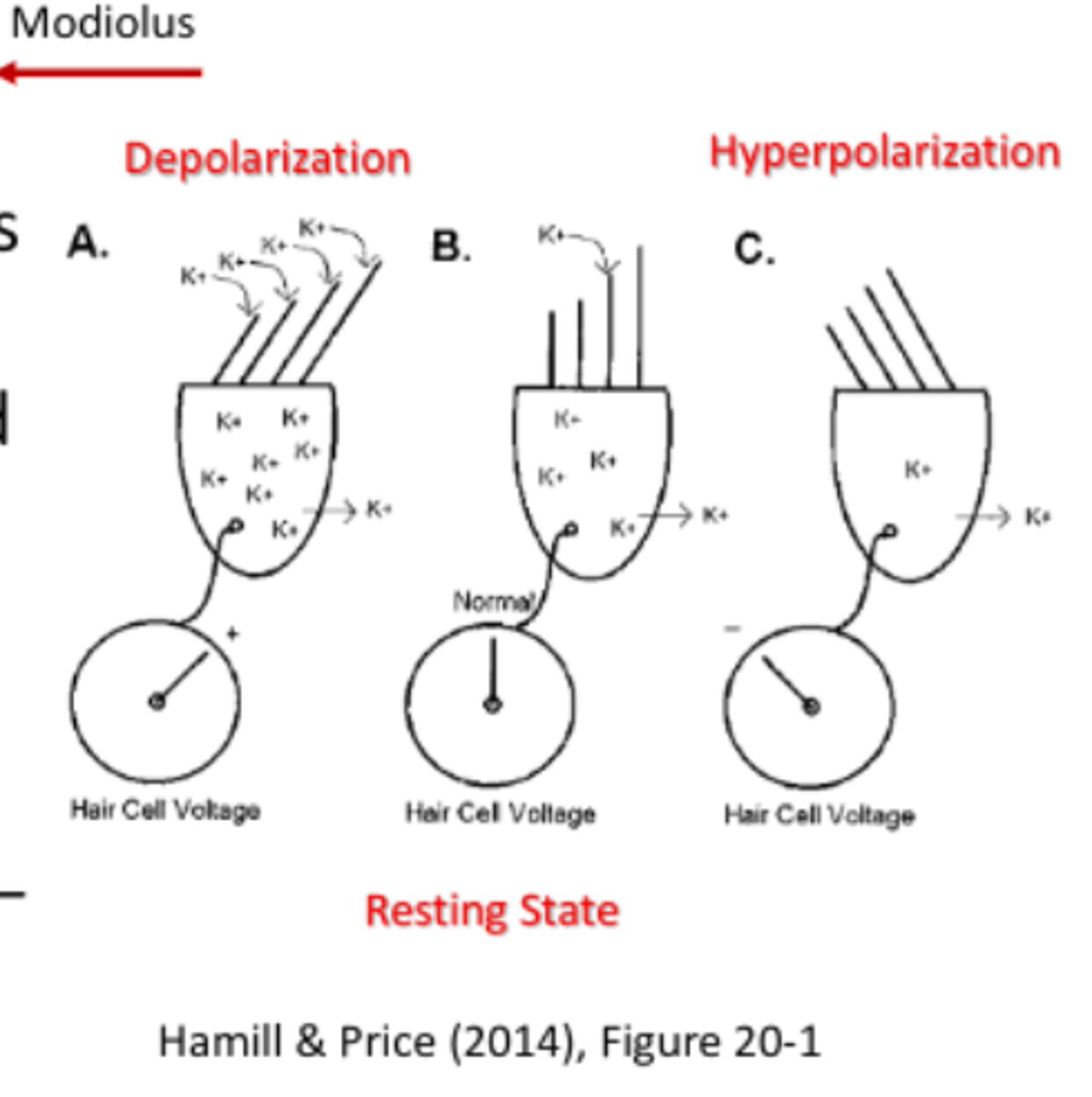
Where is the basilar membrane during the hyperpolarization phase?
BM movement in the direction of the scala tympani produces hyperpolarization
Where is the basilar membrane during the depolarization pahse?
BM movement toward scala vestibuli (the excitatory phase which causes depolarization)
Cochlear Microphonic (CM)
voltage changes following along with the changes in the ear
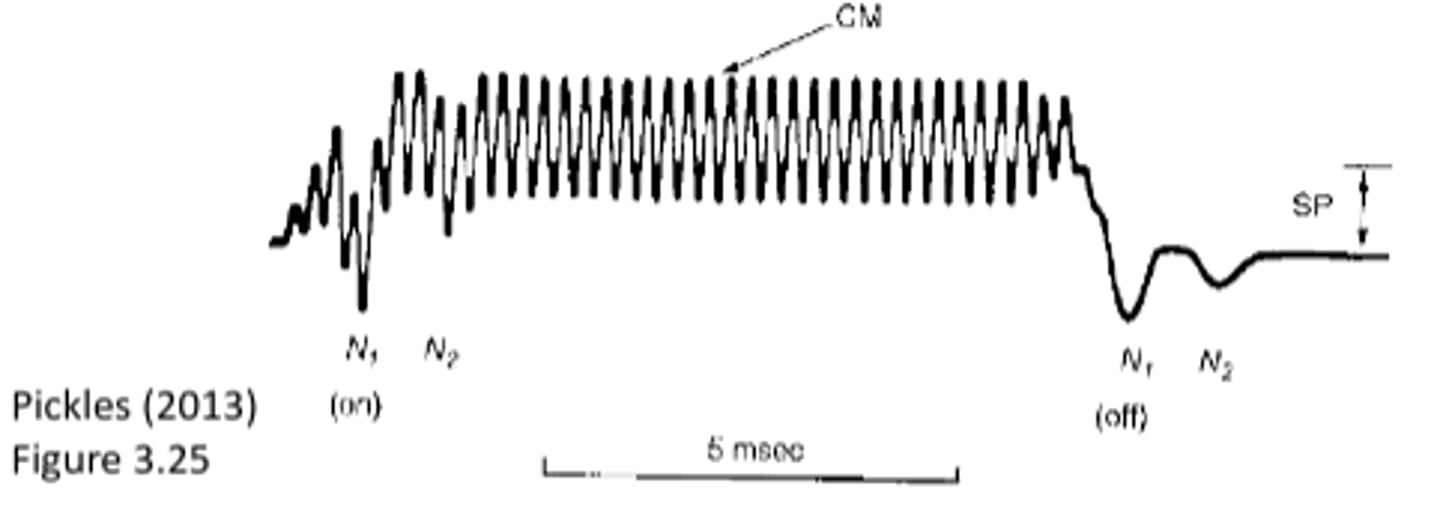
Summating Potential (SP)
the change in voltage
-when a sound is presented to a cochlea, the hair cells are firing, positive and negative voltages are occurring, and the overall average of voltage is the SP (positive/negative voltage across time)
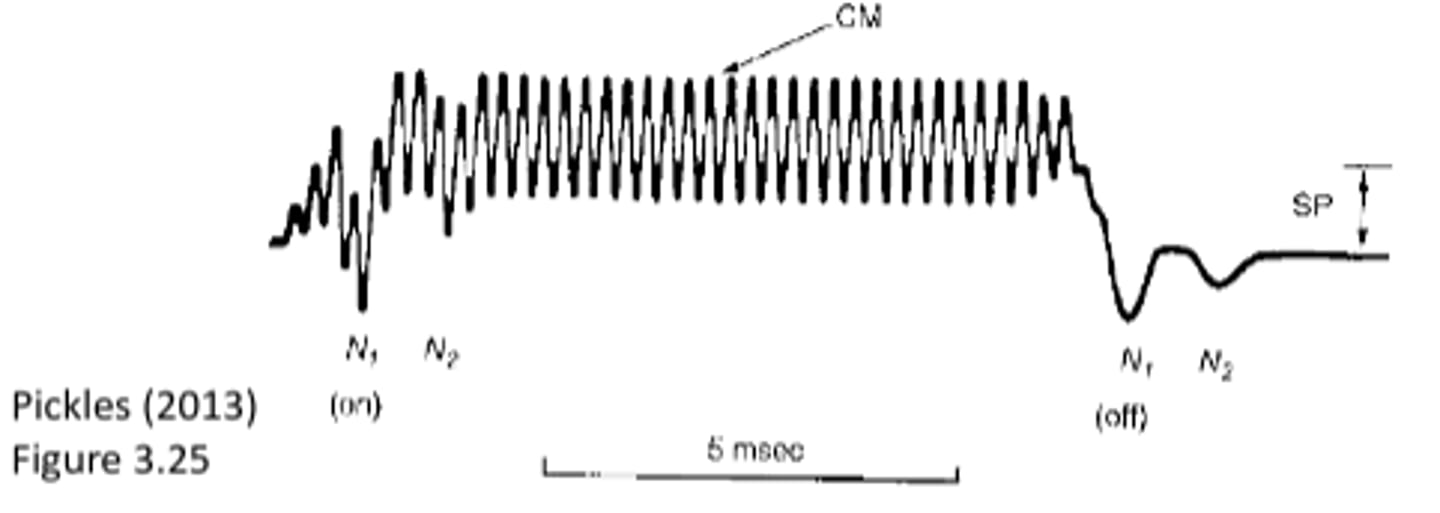
In response to sound...
the IHCs and OHCs experience alternating current changes (CM)
When is the hair cell more positive on average?
during stimulation
OHC Mechano-Electrical-Transduction (MET) and Prestin Conformational Change
excite = open channels
inhibit = close channels
When the OHC are in depolarization...
prestin is narrow
When the OHC are in hyperpolarization...
prestin is wide
Prestin
motor protein of outer hair cells
Conformation
the way in which something is formed or shaped
Excitatory Phase
basilar membrane goes up
Inhibitory Phase
basilar membrane goes down
What happens when the stereocilia of the OHC are moved away from the modiolus?
the channels at the top of the stereocilia may open
-This will allow for the flow of potassium (K+) and calcium (Ca+) ions to flow into the stereocilia and into the OHC. This will initiate the depolarization (increase in voltage) of the OHC. This causes the prestin molecules
to become narrower and results in OHC contraction.
What happens when the stereocilia move towards the modiolus?
the channels on top of the stereocilia will close
-This causes OHC hyperpolarization (decrease in voltage) which causes prestin molecules to become wider resulting in OHC elongation.
Why do we want the OHC to contract during low level sounds?
stimulates the inner hair cells (we want this because it is how the signal gets to the brain from the cochlea)
-afferent goes to the brain (sensory nerves)
Steps for the Auditroy Nerve Fiber
1. Basilar Membrane moves up
2. Stereocilia defelction
3. Receptor Current (voltage goes up)
4. OHC contraction
Step One
the traveling wave causes the basilar membrane to move towards the scala vestibuli
Step Two
this upward motion causes rotation of the organ of Corti about the foot of the inner pillar (IP), movement of the reticular lamina (RL) toward the modiolus (left) and shear of the RL relative to the tectorial membrane (TM) that deflects the stereocilia in the excitatory direction (green arrow, away from the modiolus)
-reticular lamina moves towards the modiolus
Step Three
this deflection of the outer hair cell stereocilia opens mechano-electrical- transduction channels, which increases the receptor current driven into the OHC (blue arrow)
Step Four
OHC depolarization causes conformational changes in individual prestin molecules that sum to induce a reduction in OHC length. The OHC contraction pulls the BM upward toward the RL, which amplifies BM motion when the pull on the BM in the correct phase
-The RL moves down in the OHC region and up in the IHC region. The RL pivoting and resulting fluid flow in the sub-tectorial space may provide an additional mechanism by which OHC motility may enhance the mechanical drive to IHC stereocilia
For low level sounds, if the outer hair cells do NOT contract and expand...
the inner hair cells will not be stimulated and no signal will be sent to the brain