Module 1: Labor, Delivery, and Recovery and Pediatric Respiratory Alterations
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
A. regular
B. rest
C. progressive
True Labor
-Contractions: (A) - increasing frequency, duration, and intensity
-Pain: does not decrease w/(B)
-Cervix: (C) change in dilation and effacement
A. irregular
B. alleviated
C. no change
False Labor
-Contractions: (A)
-Pain: (B) with rest or change in position
-Cervix: (C)
Questions that help determine if the client is in true labor
-Do you feel like the contractions are getting stronger?
-Does anything you do make the pain better?
-Do the contractions feel the same when lying down?
-How frequent are the contractions?
-Where do you feel the contraction pain most?
coordinated, involuntary, and intermittent
*Learning Outcome: Describe the maternal and fetal responses to labor*
What are three characteristics of contractions?
coordinated contractions
*Learning Outcome: Describe the maternal and fetal responses to labor*
As woman approaches full term, contractions become organized and gradually assume a regular pattern of increasing frequency, duration, and intensity during labor.
involuntary contractions
*Learning Outcome: Describe the maternal and fetal responses to labor*
Uterine contractions are not under conscious control.
The mother can not cause labor.
Walking or other activity may stimulate existing labor contractions; anxiety or stress can diminish them.
intermittent contractions
*Learning Outcome: Describe the maternal and fetal responses to labor*
Labor contractions are not sustained, allowing relaxation of the uterine muscle & resumption of blood flow to & from the placenta to permit gas, nutrient, & waste exchange for the fetus.
effacement
thinning and shortening of the cervix
dilation
opening of the cervix
A. decreases
B. increase
C. decrease
D. between
*Learning Outcome: Describe the maternal and fetal responses to labor*
Cardiovascular Changes
During each uterine contraction, blood flow to the placenta gradually (A), causing a relative increase in the woman's blood volume. Subsequently, this causes an (B) in her blood pressure and a (C) in her pulse. Thus, the mother's vital signs are best assessed (D) contractions.
supine
*Learning Outcome: Describe the maternal and fetal responses to labor*
The mother should be encouraged to rest in positions other than ___ to promote blood return to her heart and thus enhance blood flow to the placenta.
depth and rate of respirations increase
*Learning Outcome: Describe the maternal and fetal responses to labor*
What happens to the mother's respiratory system during labor?
gastric motility decreases
(provide ice chips, clear liquids, or hard candy)
*Learning Outcome: Describe the maternal and fetal responses to labor*
What happens to the mother's gastrointestinal system during labor?
A. decrease
B. fetal
*Learning Outcome: Describe the maternal and fetal responses to labor*
During labor, often times women experience a (A) in sensing a full bladder. This can inhibit (B) descent.
1. clotting factors
2. fibrinolysis
3. venous thrombosis
*Learning Outcome: Describe the maternal and fetal responses to labor*
During labor, women experience an increase in (1) and a decrease in (2), which help protect from hemorrhage. However, it also raises the mother's risk for (3).
intermittently
*Learning Outcome: Describe the maternal and fetal responses to labor*
During strong labor contractions, the maternal blood supply to the placenta stops _____; thus, placental exchange occurs during the interval between contractions.
110-160 bpm
*Learning Outcome: Describe the maternal and fetal responses to labor*
The fetal cardiovascular system reacts quickly to events during labor, with a fetal heart rate of (1).
decreases
*Learning Outcome: Describe the maternal and fetal responses to labor*
As term approaches, production of fetal lung fluid ___ and its absorption increases.
engagement and descent, flexion, internal rotation, extension, external rotation, expulsion
*Learning Outcome: Describe the mechanisms of labor.*
List all six.
-2 position
+3 position
*Learning Outcome: Describe the mechanisms labor*
When do we typically say the infant is engaged? When do we say it's "crowning", meaning the head is visible and delivery is imminent?
first stage of labor
*Learning Outcome: Describe the stages of labor and their phases in nulliparous and parous women*
-onset of contractions to full dilation of cervix
-Goal: dilate to 10 cm
-contractions are coordinated, progressively stronger, and regular
-Mother is social, excited, anxious
second stage of labor
*Learning Outcome: Describe the stages of labor and their phases in nulliparous and parous women*
-Full dilation to birth
-“Pushing”
-Mother is concentrating on pushing and oblivious to surroundings
third stage of labor
*Learning Outcome: Describe the stages of labor and their phases in nulliparous and parous women*
-Birth of fetus until delivery of placenta
-Takes up to 30 minutes
-fetal engagement often occurs before the beginning of labor in primigravidas, where with multigravidas the fetus often doesn't engage until labor begins
-Mother is excited and relieved after baby’s birth and first cry
Nursing Interventions for Third Stage of Labor
-gather supplies PRN
-assist w/medication administration
-take "family" photo
-documentation
fourth stage of labor
*Learning Outcome: Describe the stages of labor and their phases in nulliparous and parous women*
-2 hrs post-delivery of placenta
-Close monitoring of Mother
Vitals q15min
One-to-one nursing care
-Mother is tired
Latent Phase: beginning of true labor until 3 cm of cervical dilation
Active Phase: 4-7 cm
Nursing Interventions for Fourth Stage of Labor
-frequent patient assessments
-fundal checks w/VS
-ensure patient eats and drinks
-OOB to bathroom
-straight catheterization PRN
-coordinate w/baby RN regarding infant assessment and medications, infant feeding, voids/stools
powers, passage, passenger, psychological response
Describe the four Ps of labor, which are all interrelated to promote or inhibit a vaginal birth.
uterine contractions, maternal pushing
What are the two "powers" of labor?
uterine contractions
-coordinated, involuntary, intermittent
-propel the baby downwards, causing cervical effacement (thinning and shortening) and dilation (opening)
-start in uterine fundus and spreads downward toward cervix
Decreased blood flow to uterus and placenta
What happens if contractions are too frequent or strong?
Cervix may not dilate effectively enough for delivery of the baby
What happens if contractions or infrequent or too weak?
Braxton hicks
uterine contractions that begin before the first stage of labor begins
maternal pushing efforts
Ferguson reflex
-urge to push or bear down
-occurs when cervix is fully dilated (10 cm) and fetal head is fully engaged, causing stretching of vaginal tissue
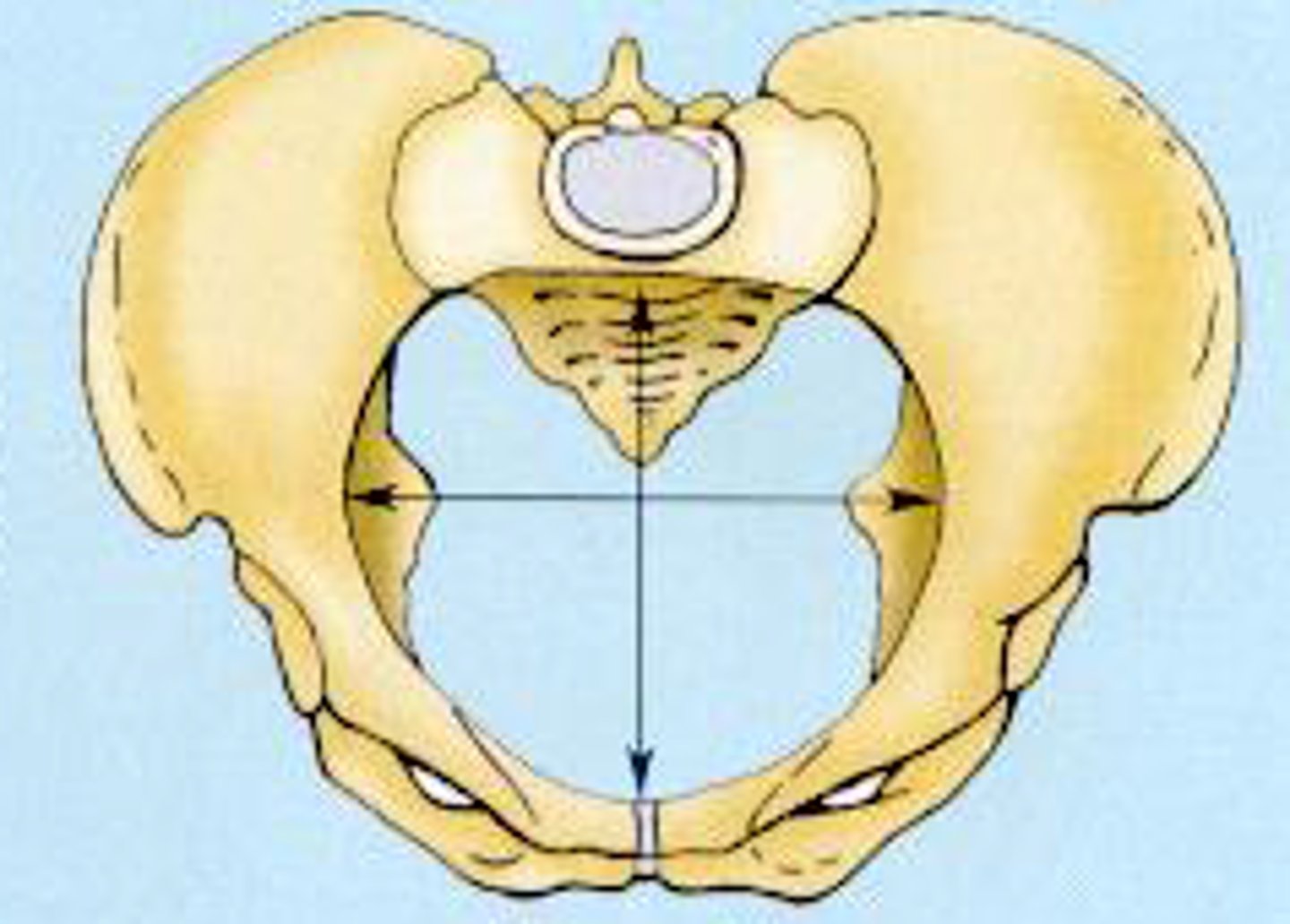
maternal pelvis and its soft tissues
Passage:
What's the birth canal composed of?
gynecoid pelvis
most favorable pelvis for successful labor.
Passenger
Fetus and Placenta
-fetal size
-fetal lie: 99% of pregnancies have a longitudinal lie
-fetal attitude
-fetal presentation
fetal attitude of flexion
-with the head, arms, and legs flexed tightly against the trunk
-babies like to be swaddled because it reminds them of this position
fetal attitude of extension
fetal presentation
determined by fetal part to *first* enter pelvis
1. cephalic & vertex - when it's the head
2. breech - when it's the foot
*Frank (butt) = most common
*single footling
*complete
3. shoulder
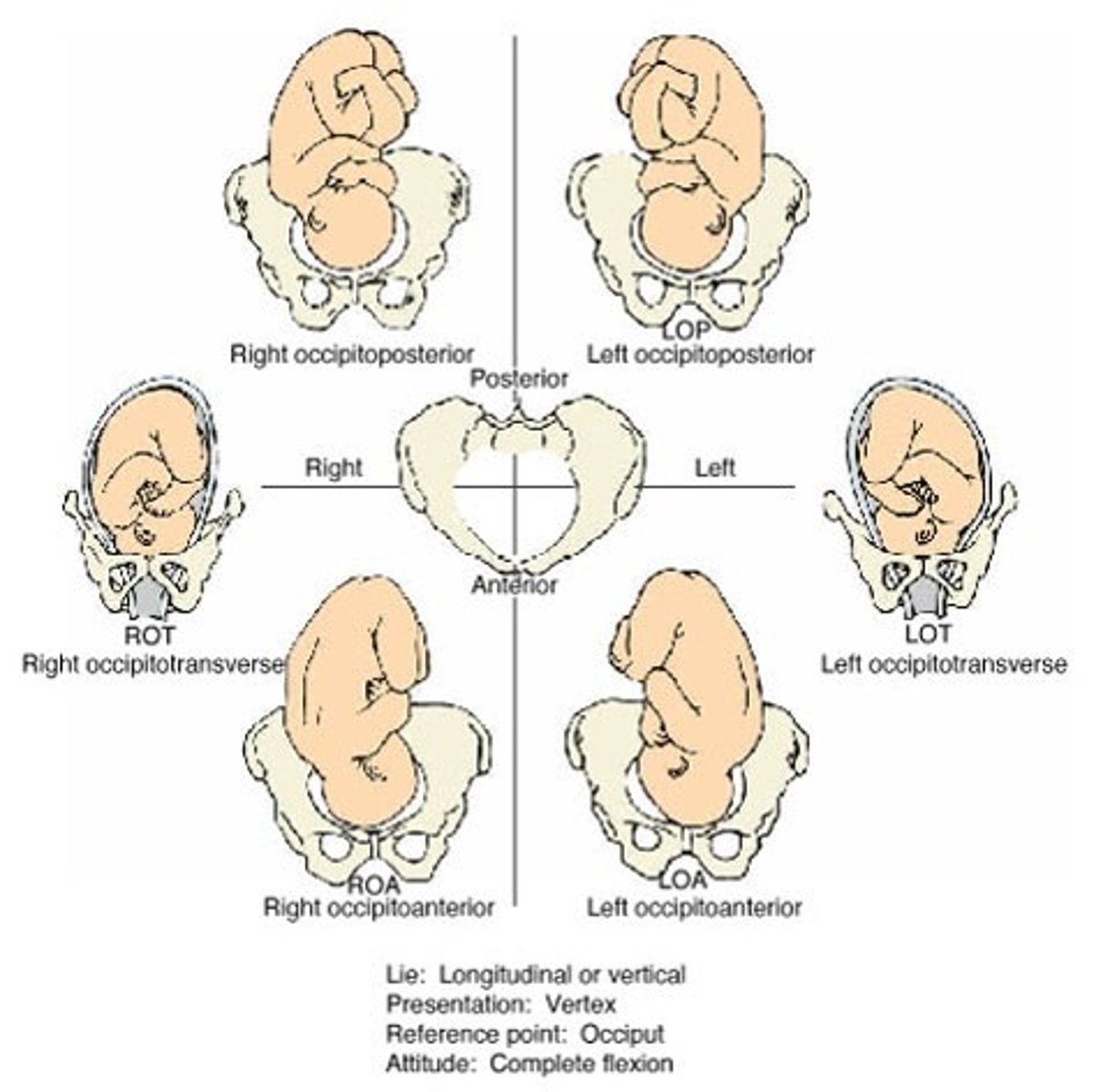
fetal position
-Location of a fixed point, typically occipital bone, and maternal pelvis
-Denoted using a three-letter abbreviation
1. Right (R) or Left (L) of maternal pelvis
2. Fixed point
e.g. occipital bone (O)
3. Anterior (A), posterior (P), transverse (T)
psychological response
-High levels of maternal stress → release of catecholamines → decrease ability of uterus to contract, reduced blood flow to fetus
-Goal is to make mother feel as good about the labor as possible
maternal position
-Frequent changes in position
Relieve fatigue
Increase comfort
Improve circulation
-Laboring woman should be encouraged to find positions most comfortable to her
A. ambulation
B. back
C. ROT or LOT
D. squat
E. all fours
How Nurse Can Facilitate Cardinal Movements of Labor
-Encourage (A) in labor if appropriate
-Avoid having laboring patient lying on her (B)
-For fetus in an (C) position, have mother lie on the side of the fetal small parts to facilitate rotation
-For a large fetus, have the mother (D) to facilitate descent
-For a posterior (OP, LOP, ROP) fetus (which is more painful for back), put mother on (E)
unique nature of pain during birth
-It's part of a normal process
-Woman has several months to prepare
-Has a foreseeable end
A catecholamines
B. placenta
C. hypoxic
*Learning Outcome: Describe the impact of pain on the laboring woman and fetus.*
Pain and anxiety escalate mother's already high metabolic rate by increasing the production of (A) (epinephrine and norepinephrine), cortisol, and glucagon. These result in maternal respiratory and metabolic changes, which reduce blood flow to the uterus and (B). Good placental blood flow must be restored, otherwise it may become (C) and shift to an anaerobic metabolism.
psychological effects of pain on the laboring woman
*Learning Outcome: Describe the impact of pain on the laboring woman and fetus.*
-difficult to interact w/infant
-unpleasant memories of birth
A. anxiety
B. lungs
C. overdose
D. self-administered
E. dizziness
*Learning Outcome: Identify the benefits, risks, and side effects for the pregnant woman and fetus of pharmacologic pain control methods in labor*
Nitrous Oxide
-Tasteless odorless gas, most used in US
-Helps reduce (A), improves feelings of well-being
-Clears body through (B)
-Minimal risk for (C)
Must be (D) and woman has to hold mask herself
Delivery stops when she is not inhaling
-Educate mother on potential side effects
(E), nausea, vomiting, dysphoria
A. perception
B. placenta
C. drug use
D. injectable
*Learning Outcome: Identify the benefits, risks, and side effects for the pregnant woman and fetus of pharmacologic pain control methods in labor*
Opioids
-Reduces perception of pain without loss of (A)
-Are distributed throughout the body and can pass the (B)
-assess mother for history of (C)
-(D): fentanyl, butorphanol, and nalbuphine
Timing is very important
Can cause respiratory depression
Assess mother for history of drug use
A. respiratory depression
B. beginning
C. agonist and antagonist
Opioids: Teaching & Nursing Considerations
-May cause (A) in newborn
-Usually given IV in small, frequent doses
-Start injection at (B) of contraction when blood flow to placenta is reduced to limit transfer to fetus
-Avoid combining opioid (C) drugs
-After delivery, monitor the infant's vitals (Respirations!!) (<30 min)
naloxone
opioid antagonist; opioid antidote; MOA is shorter so must observe for recurrent RDS
meperidine
most common for intrapartum pain control
adjunctive medications
*Learning Outcome: Identify the benefits, risks, and side effects for the pregnant woman and fetus of pharmacologic pain control methods in labor*
-Reduce nausea w/opioid drugs and reduce anxiety to promote rest
-Common drugs: promethazine and metoclopramide
A. baseline data
B. IV fluid
C. position
D. spinal headaches
Nursing Care - “Blocks”
-Always obtain (A)
-Preload of (B) for “blocks” to prevent maternal hypotension
-Assists patient to appropriate (C) and maintain throughout procedure
-Continue monitoring VS of both mother and fetus
-Assess for (D) and other common side effects
spinal headaches
Mother can't sit up because of intense pressure, lights are very irritable; require procedure
pudendal and paracervical blocks
*Learning Outcome: Identify the benefits, risks, and side effects for the pregnant woman and fetus of pharmacologic pain control methods in labor*
What are two regional anesthesia methods?
A. anticipated
B. start
C. q15min
D. bladder
E. depressed
*Learning Outcome: Identify the benefits, risks, and side effects for the pregnant woman and fetus of pharmacologic pain control methods in labor*
Medication Administration Principles
-Explain (A) (but not guaranteed) results
-Push IV bolus slowly at (B) of contraction
-DOCUMENT response, pain level
-Reassess periodically
-Monitor VS, FHR, contraction pattern (C)
-Monitor (D) for distention, retention (especially post-regional anesthesia)
-Decrease environmental stimuli
-Document time elapse between last drug administration and birth on birth record
-Assess for (E) neonate, especially if delivered at peak action time
A. maternal hypotension
B. fetal monitoring
C. maternal bladder
*Learning Outcome: Identify the benefits, risks, and side effects for the pregnant woman and fetus of pharmacologic pain control methods in labor*
Things to Remember
-The nurse has an important role in monitoring for (A) during and after the initiation of an epidural, spinal block, or CSE block.
-The nurse should continue (B) during and after the initiation of an epidural, spinal block, or CSE block.
-The nurse should monitor the (C) for distention after the initiation of an epidural, spinal block, or CSE block.
*Learning Outcome: Compare and contrast pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic pain management options*
-massage
-mental stimulation
-breathing
-adjust the environment for comfort that's conducive to relaxation
thermostat, warm blankets sock, small electric fan or hand fan
-reduce distractions
don't stand in front of her focal point; delay assessments until after contraction
-reduce irritating stimulants
-check for bladder distention hourly (min. q2h)
-encourage changing positions regularly
-back rub or firm, constant sacral pressure
physical examination of infants
*Learning Outcome: Describe the general sequence of the physical examination of an infant, a young child, a school-age child, and an adolescent.*
-Performed in parents’ arms
-Auscultate heart, lungs, then abdomen
-Uncomfortable procedures done last
Tympanic membranes
Elicitation of Moro reflex
Abduction of hips
physical examination of toddlers
*Learning Outcome: Describe the general sequence of the physical examination of an infant, a young child, a school-age child, and an adolescent.*
-Order is flexible
-Least to most invasive procedures
physical examination of preschoolers
*Learning Outcome: Describe the general sequence of the physical examination of an infant, a young child, a school-age child, and an adolescent.*
head-to-toe; least invasive to most invasive
physical examination of school-aged child
*Learning Outcome: Describe the general sequence of the physical examination of an infant, a young child, a school-age child, and an adolescent.*
Head to toe; examine genitals last
physical examination of adolescent
*Learning Outcome: Describe the general sequence of the physical examination of an infant, a young child, a school-age child, and an adolescent.*
allow for privacy; parent absent
differences in pulmonary system between children and adults
-lack of or insufficient surfactant
-smaller airways and undeveloped cartilage
-obligatory nose breather (infants)
-less well-developed intercostal muscles
-brief periods of apnea common (newborn)
-increased metabolic needs
-Eustachian tubes are relatively horizontal
-tonsillar tissue enlargement
-more flexible larynx, susceptible to spasm
-abdominal breathers
surfactant
-Prevents alveolar collapse
-Kills pathogens and modulates immune responses
more easily obstructed by mucous and foreign bodies
Since children have smaller airways and undeveloped cartilage, their airways are ___.
retractions
Since children have less well-developed intercostal muscles, ____ are common in infants w/respiratory distress.
increased respiratory
Since children have increased metabolic needs, they require more oxygen and have ___ ___ rates.
ear infections
Since children's Eustachian tubes are relatively horizontal, their tubes get clogged easily w/fluid, leading to
allergic rhinitis
Inflammatory disorder of nasal mucosa
-Seasonal, recurrent, and triggered by specific allergies
-Usually a family history
-Some children have symptoms year round
rhinorrhea
Clear nasal discharge, "runny nose"
paroxysmal sneezing
uncontrollable type of sneezing not controlled by specific allergies
allergic salute
rubbing nose in response to nasal discharge
allergic shiners
dark circles under eyes
Environmental Modifications for Allergic Rhinitis: pollen and dust
-wash sheets weekly in hot water
-no wool or down blankets
-dust-proof covers on pillows and mattresses
-replace carpet w/wood or tile
-no drapes or blinds; use curtains or shades
-air filters and cleaners, use air conditioner
-household humidity at 40-50%
-multilayer vacuum bags
-clean w/dust-attracting rags/towels
Environmental Modifications for Allergic Rhinitis: Mold
-clean w/mold inhibitor
-dry shoes thoroughly
-moisture remover in closets
-avoid basements
-no rubber or inner-spring mattresses
-use air conditioner
-humidity below 50%, use a dehumidifier
-house ventilation
-limit # of indoor plants
Environmental Modifications for Allergic Rhinitis: Dander
-keep pets outside of bedrooms, remove carpets
-house ventilation
-air cleaners
-dust covers on mattresses and pillow cases
-frequent vacuuming
-air purifier
antihistamines
inhibit allergic reactions of inflammation, redness, and itching caused by the release of histamine
intranasal corticosteroids
-i.e. fluticasone, mometasone
-reduce inflammation
leukotriene inhibitors
-i.e. montelukast
-behavior changes may occur in children
-can make children tired, so have them take in the evening
immunotherapy (allergy shots)
-monitor child closely for 20-30 minutes after injection
A. acute
B. area of involvement
C. time of year
D. viral
General Aspects of Respiratory Infections
-Respiratory infections account for most (A) illnesses in children
-Described according to the (B)
Upper airway = stridors
Lower airway = wheezing, coarse
-(C) determines likelihood of certain illnesses
-Respiratory tract is subject to a wide variety of infective organisms
(D) infections highest during toddler and preschool years
-Chronic is having difficulty with oxygen requirements for 3-6 months
respiratory infections of the upper airway
-acute nasopharyngitis
-acute pharyngitis
-tonsillitis
-influenza
-COVID
-otitis media
-Croup Syndromes
hoarseness, barking or brassy cough, stridor, respiratory distress
Name four symptoms of Croup Syndromes.
A. loose cough
B. steroids
C. humidified
Treatment of Mild Croup
-expect (A) in a couple of days; this will last for at least 2 weeks
-oral or inhaled (B)
-(C) air
1. stridor
2. epinephrine
Treatment of Moderate Croup
-mild (1)
- +/- racemic (2) nebulizer (monitor for rebound)
hospital admission
What's the treatment for severe croup?
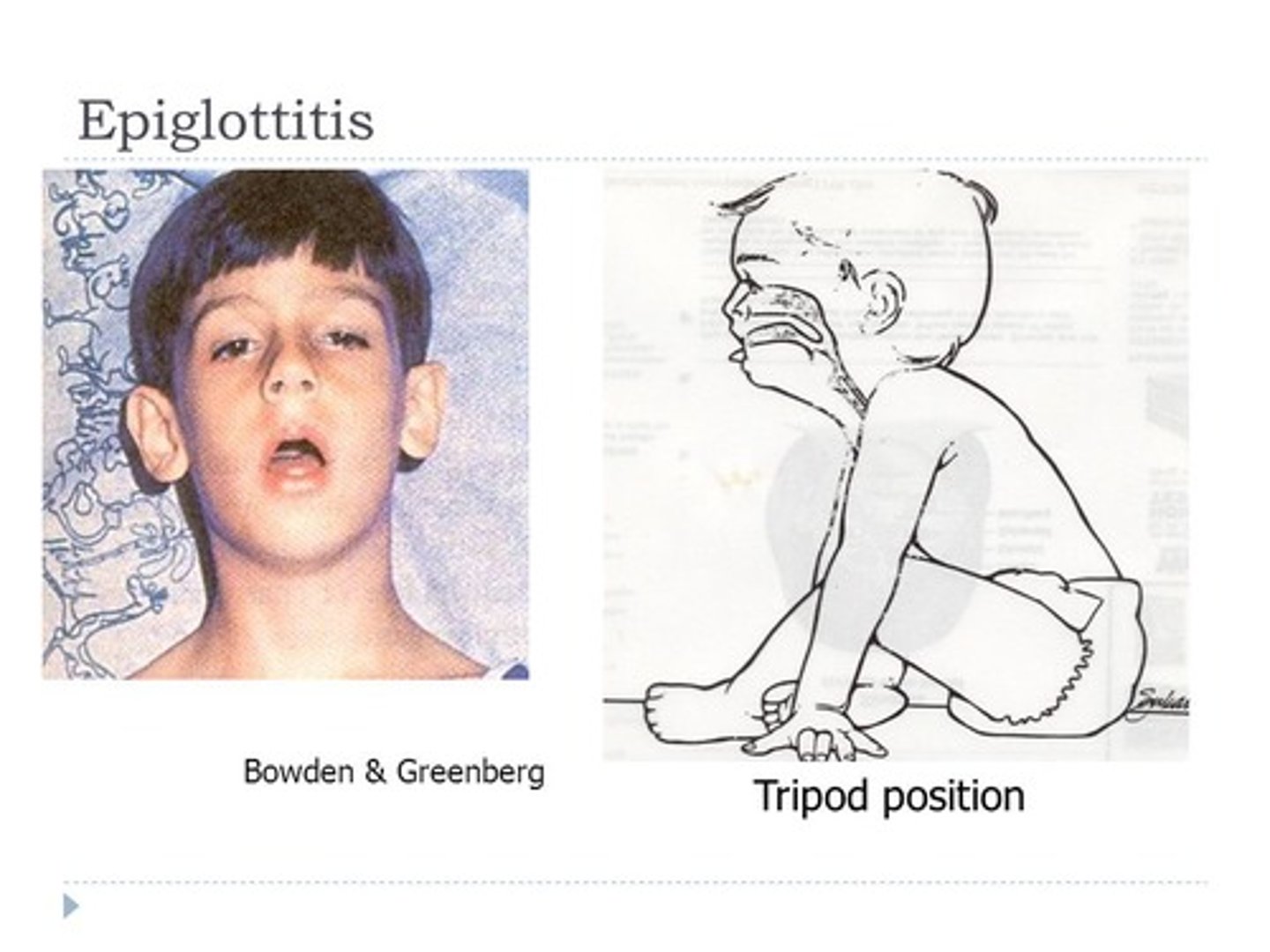
epiglottitis
-acute, life-threatening edema, inflammation of epiglottis and epiglottic folds
-usually HIB (H. influenzae)
-immunization has decreased incidence (get immunization history)
tripod position
An upright position in which the patient leans forward onto two arms stretched forward and thrusts the head and chin forward; suggests epiglottitis
intubation first; followed by throat and blood cultures, antipyretics, IV antibiotics
Describe the treatment of epiglottitis.
acute nasopharyngitis
common cold
acute pharyngitis
sore throat
tonsillitis
"strep throat"
S/S: difficulty opening mouth and swallowing, Trismus, muffled voice, pooling saliva
tonsillectomy
-surgical removal of tonsils
-place child on abdomen to facilitate drainage of secretions
bronchi and bronchioles
What does the lower airway consist of?
bronchitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia
Name three respiratory infections.
The airway becomes obstructed from swelling of the bronchiole walls.
What happens during bronchiolitis?
Risk Factors of Bronchiolitis
-preemies and newborns
-infants w/chronic lung disease, heart disease
-immunocompromised
-dehydration
-formula-fed
-exposure to second-hand smoke
Clinical Manifestations of Bronchiolitis
-low grade fever
-tachypnea prolonged expiratory phase (wheezing if lower airway involved)
-respiratory distress
-rhinorrhea
-cough
A. normal
B. feeding
C. at home
Mild Bronchiolitis
Assessment/Indicators
-(A) O2
-moderate tachypnea
-minimal respiratory distress
-alert, awake, (B) well
Treatment: supportive care (C)