psychology unit 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
1
New cards
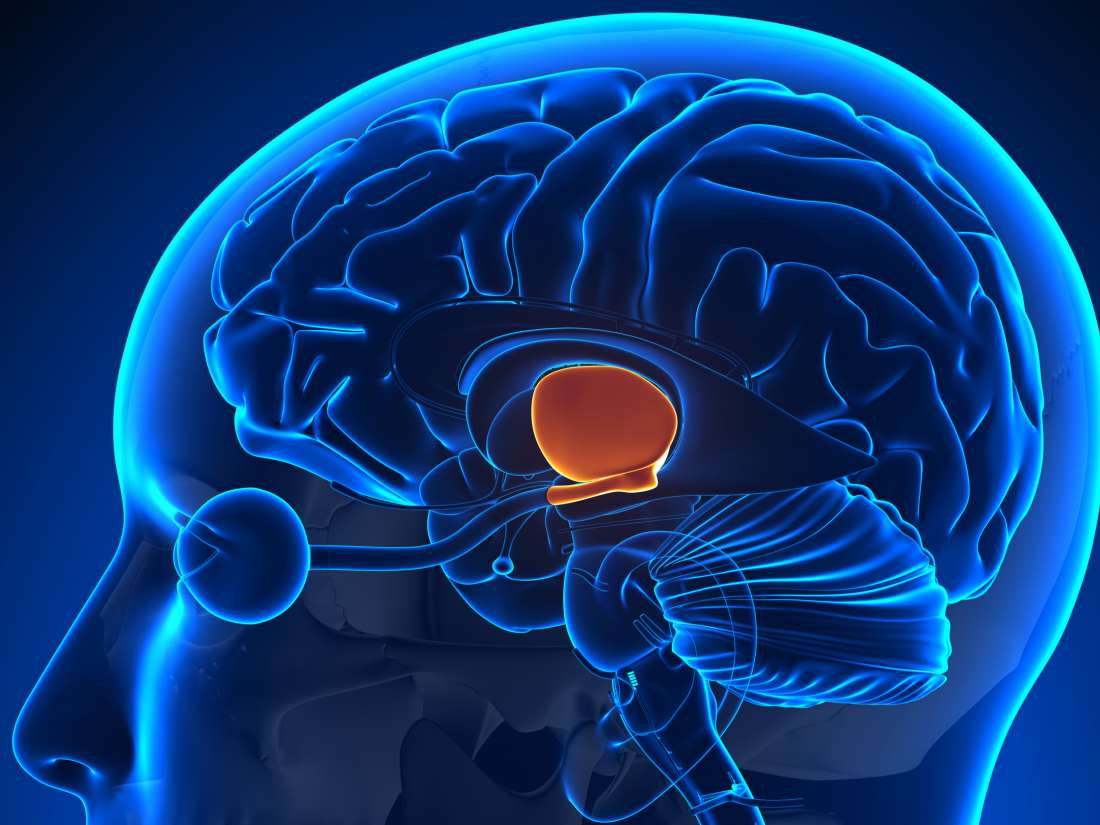
hypothalamus
controls pituitary (master) gland; monitors blood chemistry, controls motivated behaviors; LIMBIC SYSTEM
2
New cards
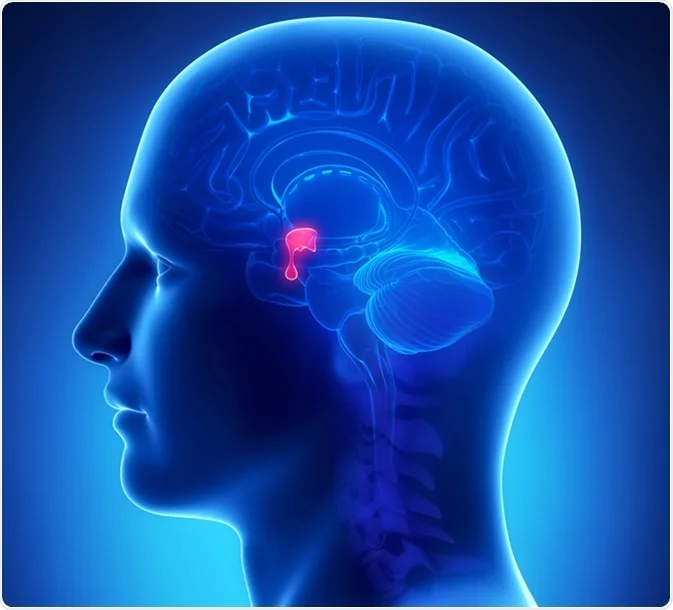
pituitary gland
controls all other glands; releases hormones
3
New cards
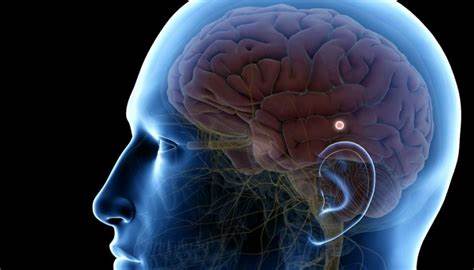
pineal gland
controls sleep and wake patterns
4
New cards
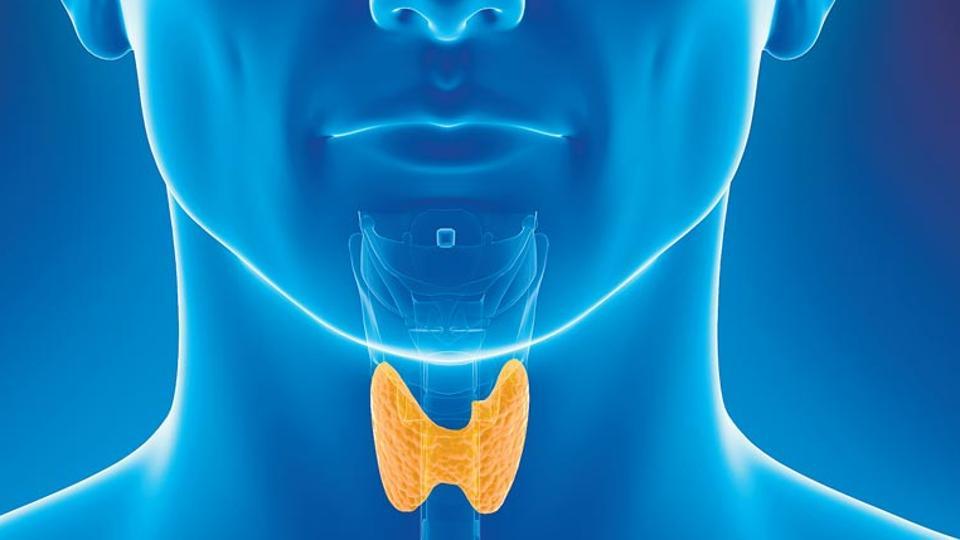
thyroid gland
located near the base of the neck; controls metabolism
5
New cards
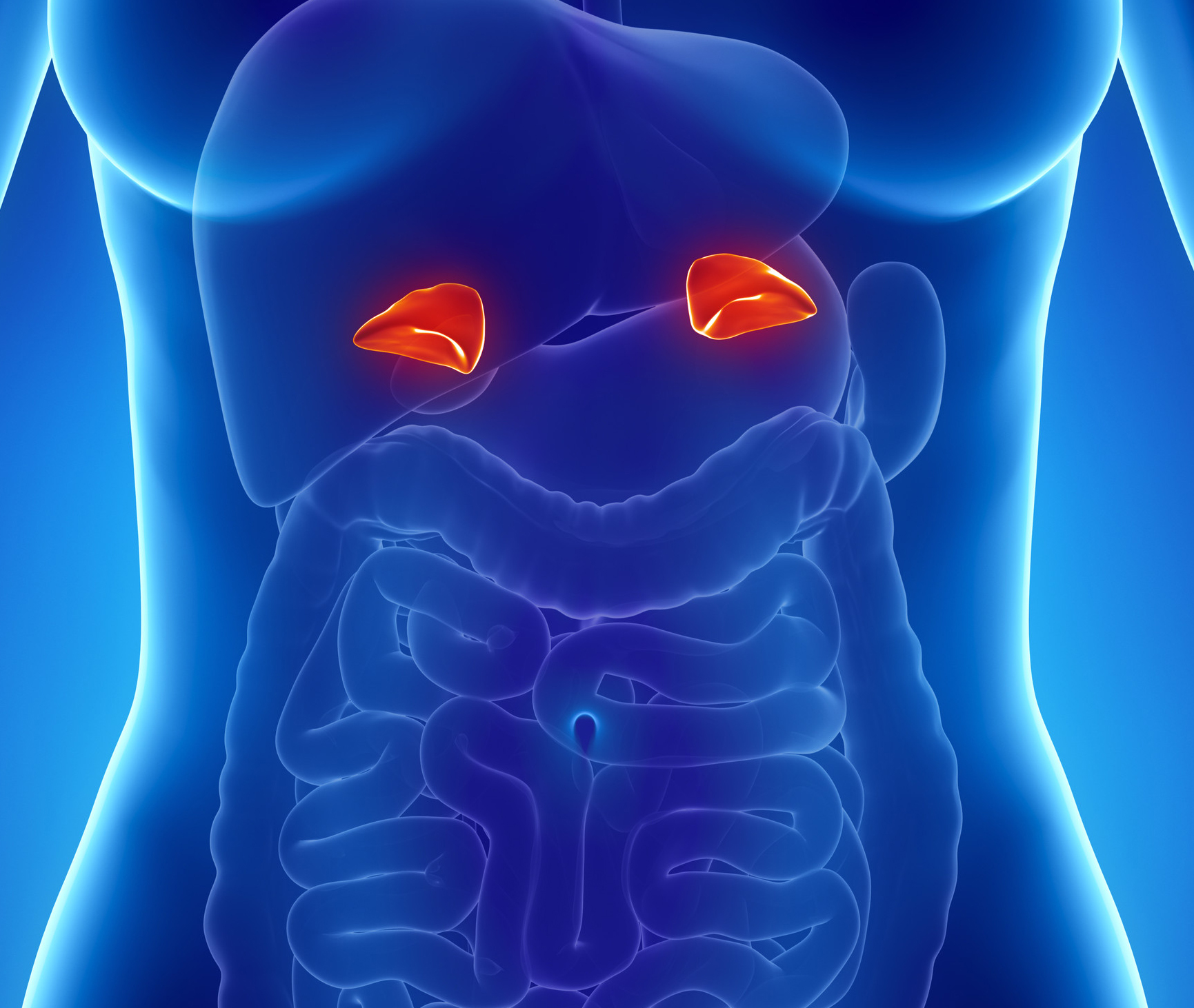
adrenal gland
either pair of complex endocrine glands situated near the kidney; releases adrenaline
6
New cards
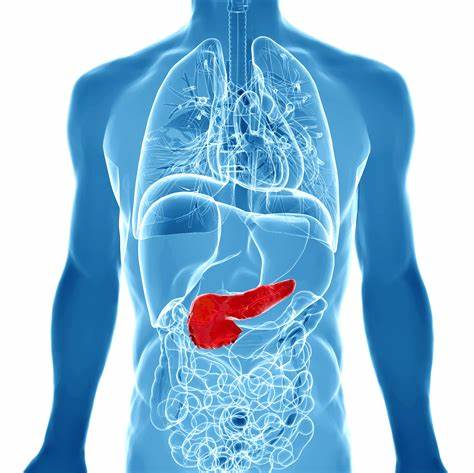
pancreas
a large elongated exocrine gland located behind the stomach; secretes pancreatic juice and insulin; regulates sugar in the blood
7
New cards
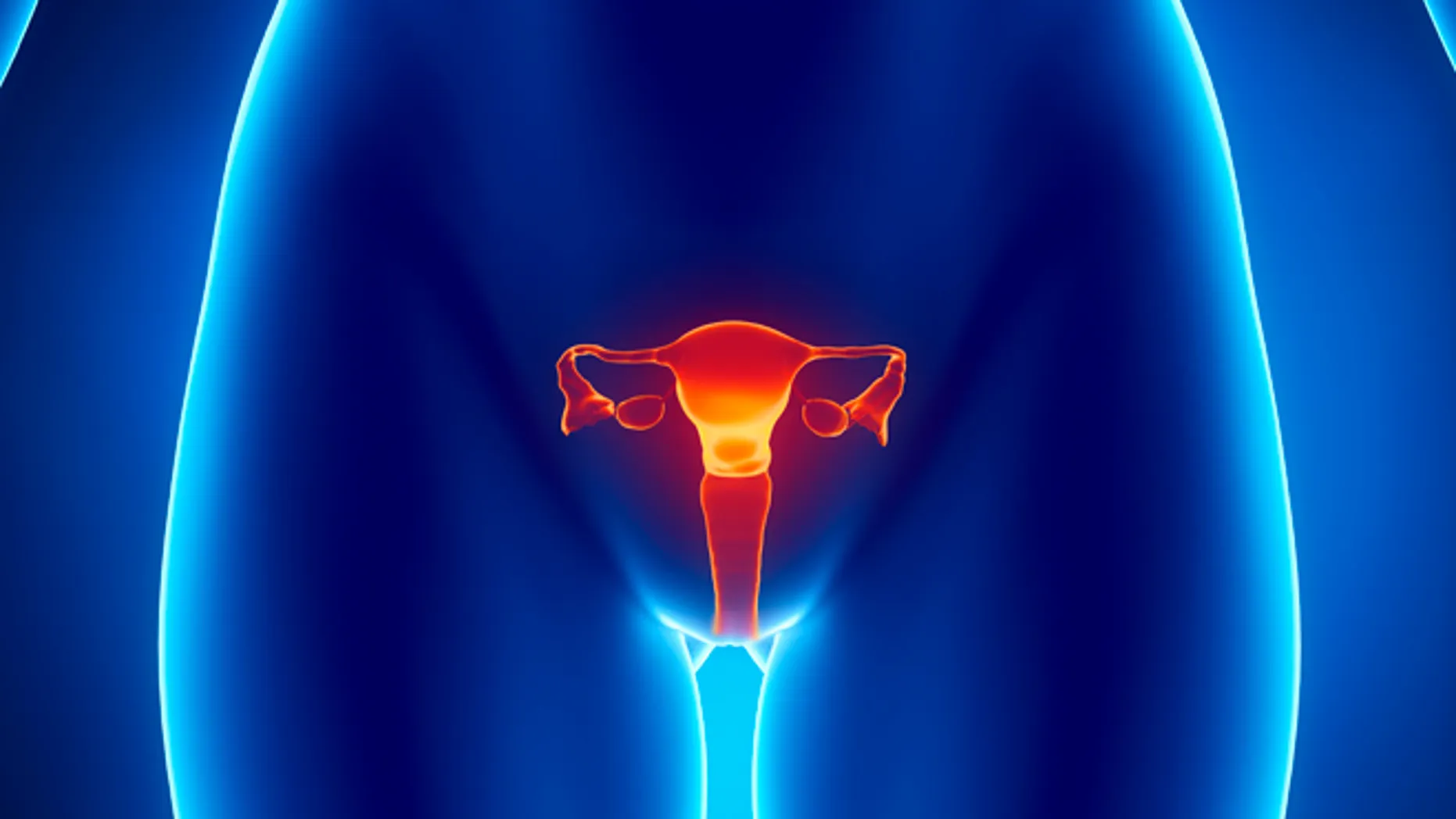
ovary
female sex hormones
8
New cards
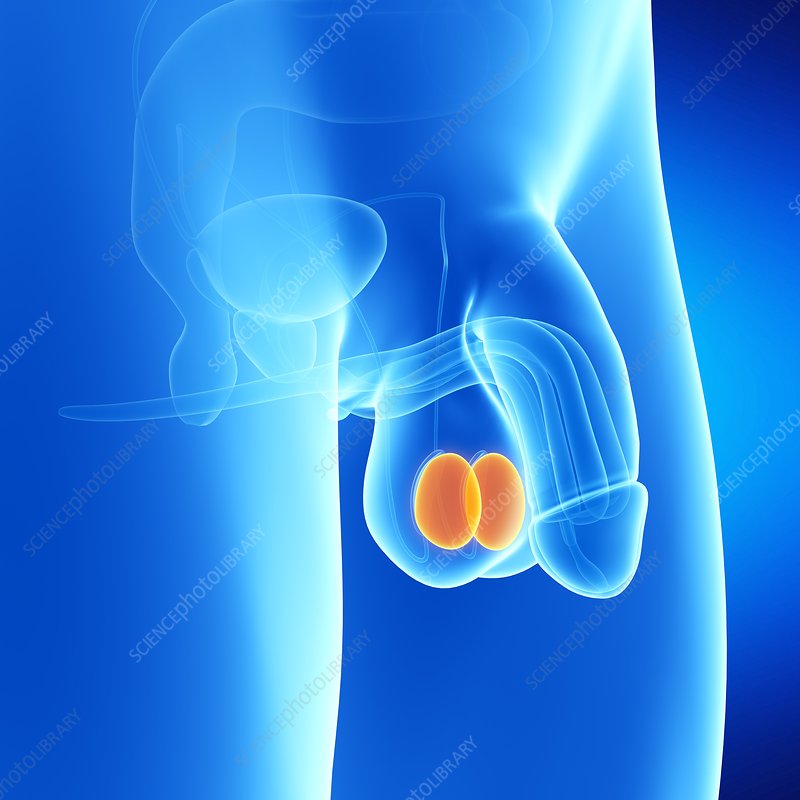
testes
male sex hormones
9
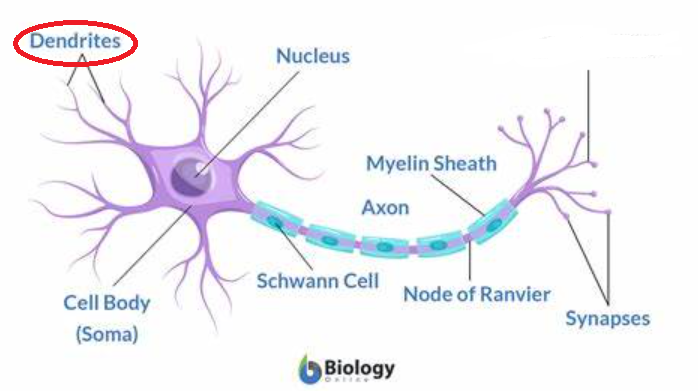
New cards
dendrite
short fiber that conducts toward the cell body of the neuron; stimulated into activity
10
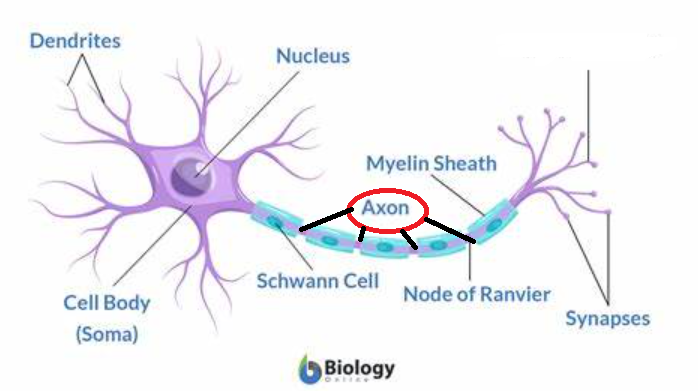
New cards
axon
long nerve fiber that conducts away from the cell body of the neuron; the path of electrical impulse
11
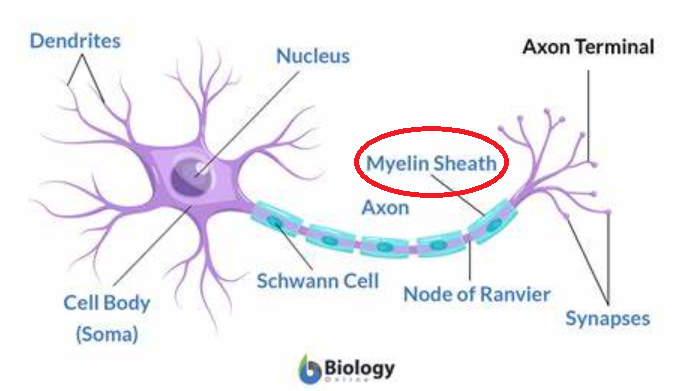
New cards
myelin sheath
fatty tissue that insulates the axon; speeds electrical impulse
12
New cards
axon terminal
end of neuron; releases NT into synapse
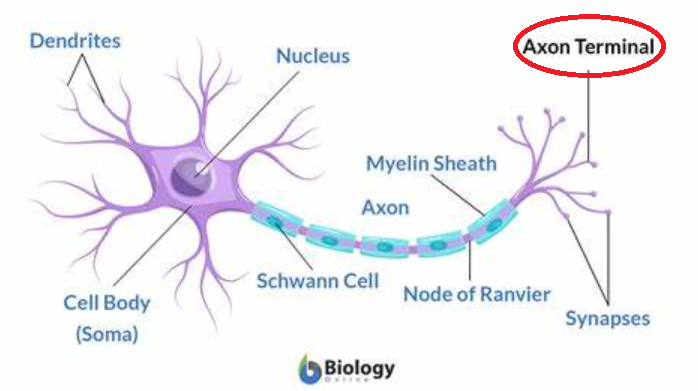
13
New cards
synapse
the junction between two neurons or between a neuron and a muscle; tiny gaps between dendrites and axon terminals
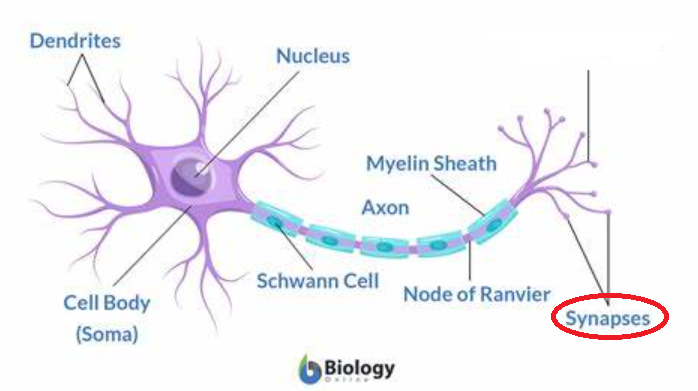
14
New cards
vesicle
tiny, spherical packets with an axon terminal that contain high levels of NT; located in the axon terminal
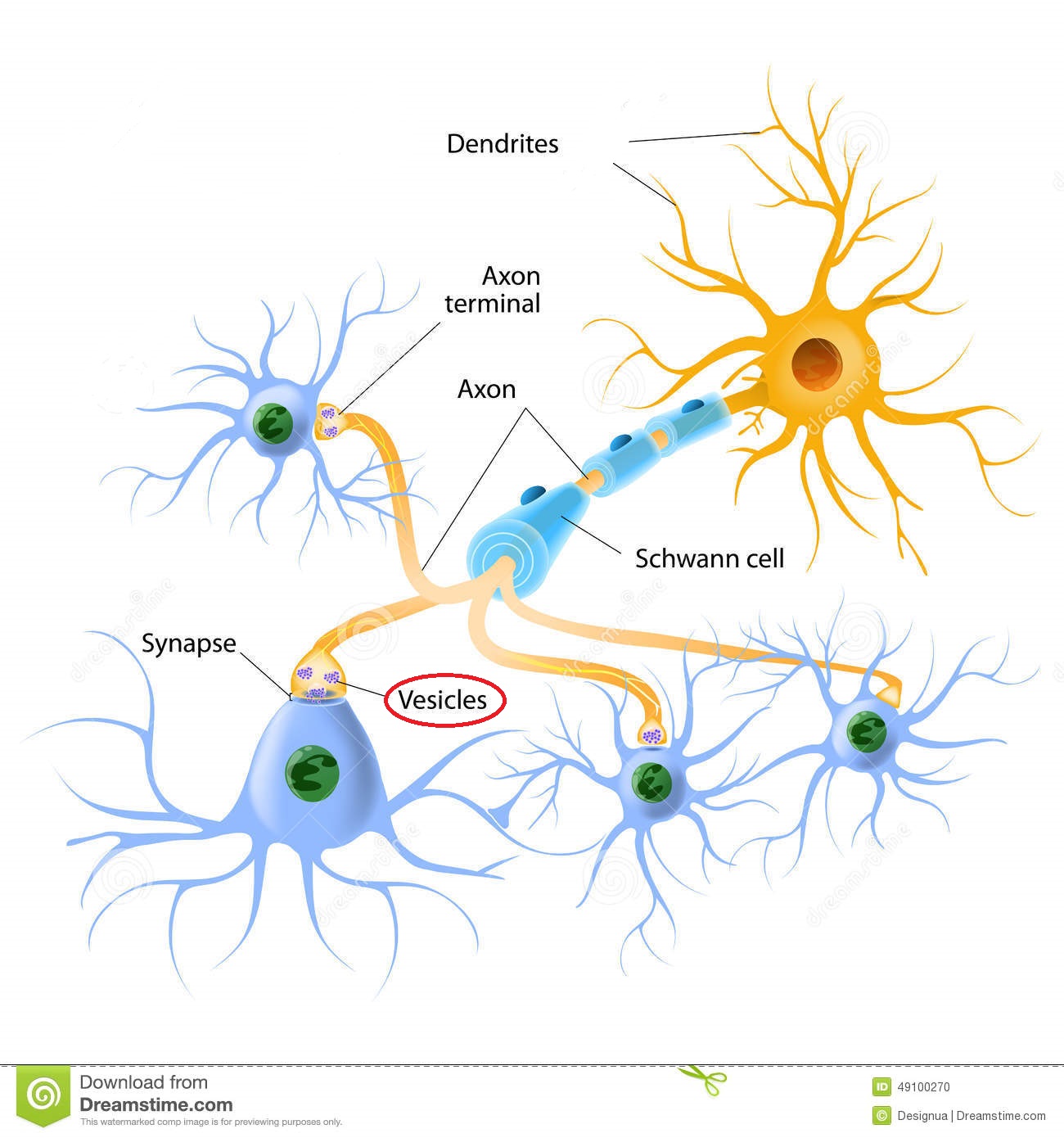
15
New cards
cell body/soma
contains the nucleus
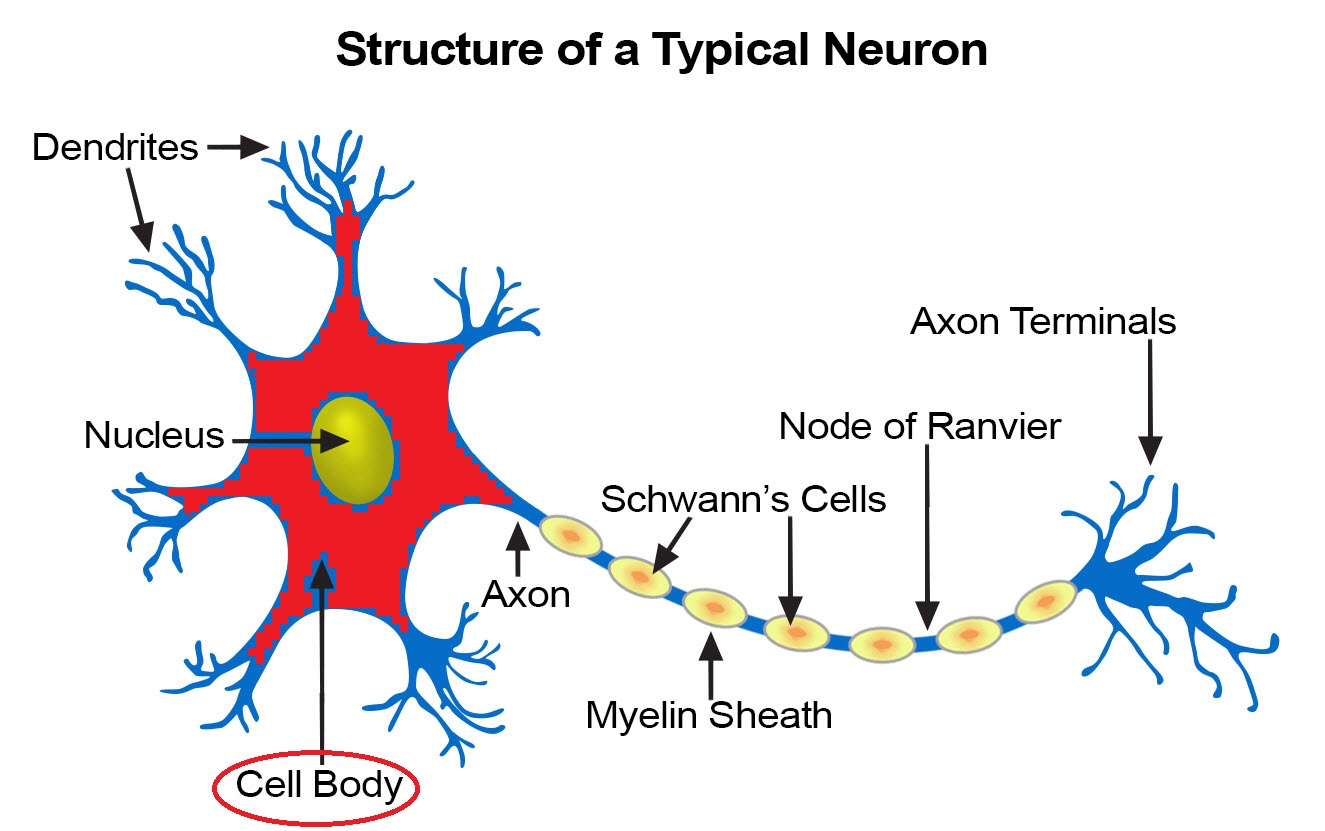
16
New cards
endorphin
blocks pain

17
New cards
dopamine
releases pleasure and rewarding sensations

18
New cards
norepinepherine
regulates stress and blood pressure; promotes alertness; depression

19
New cards
epinephrine
high stress situations; fight or flight; epi-pen

20
New cards
acetylcholine (ACH)
contracts muscles, memory, and learning; alzheimers

21
New cards
serotonin
regulates mood, hunger, and sleep

22
New cards
GABA
helps you relax

23
New cards
glutamate
thinking, learning, and memory; need just the right amount

24
New cards
medulla oblongata
lower or hindmost part of the brain; continuous with spinal cord; life sustaining functions
25
New cards
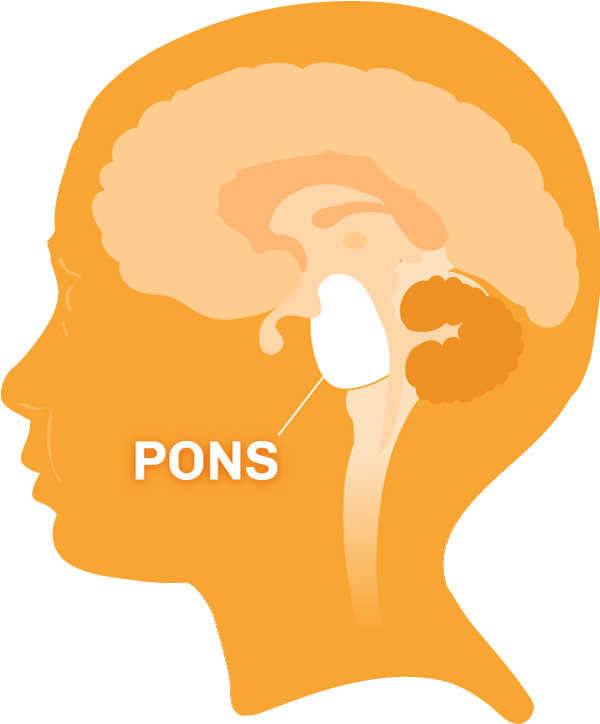
pons
facial movements; left to right side of the brain
26
New cards
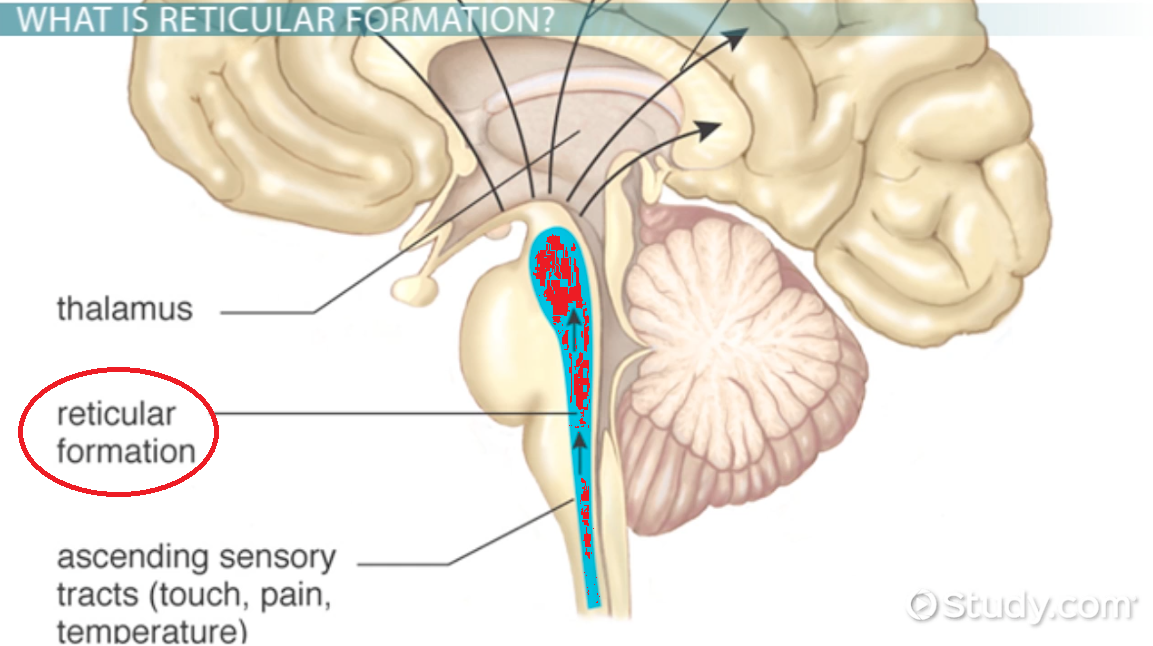
reticular formation
within medulla and pons; controls arousal, alertness, and wakefulness
27
New cards
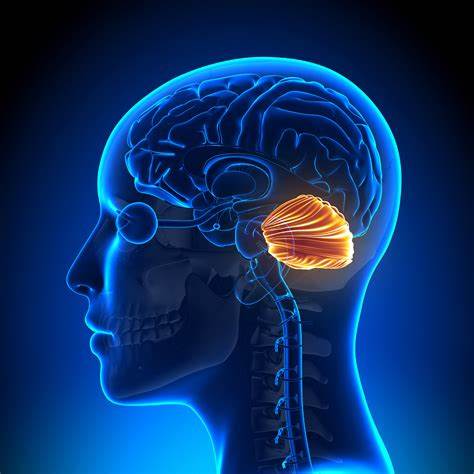
cerebellum
rear of the brain stem; coordinates voluntary movement, balance, non verbal learning and memory
28
New cards
thalamus
top of brainstem; receives info from all senses except smell; the info goes to cerebellum and medulla
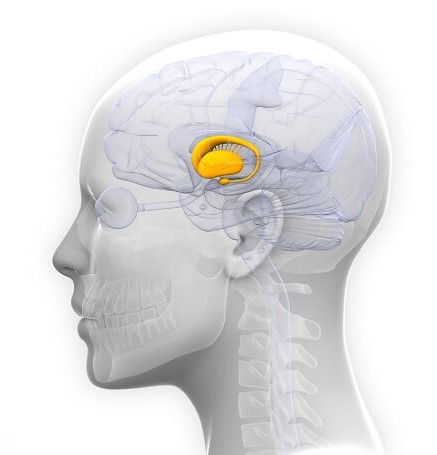
29
New cards
amygdala
top of brainstem; influences aggression and fear; activated by emotions
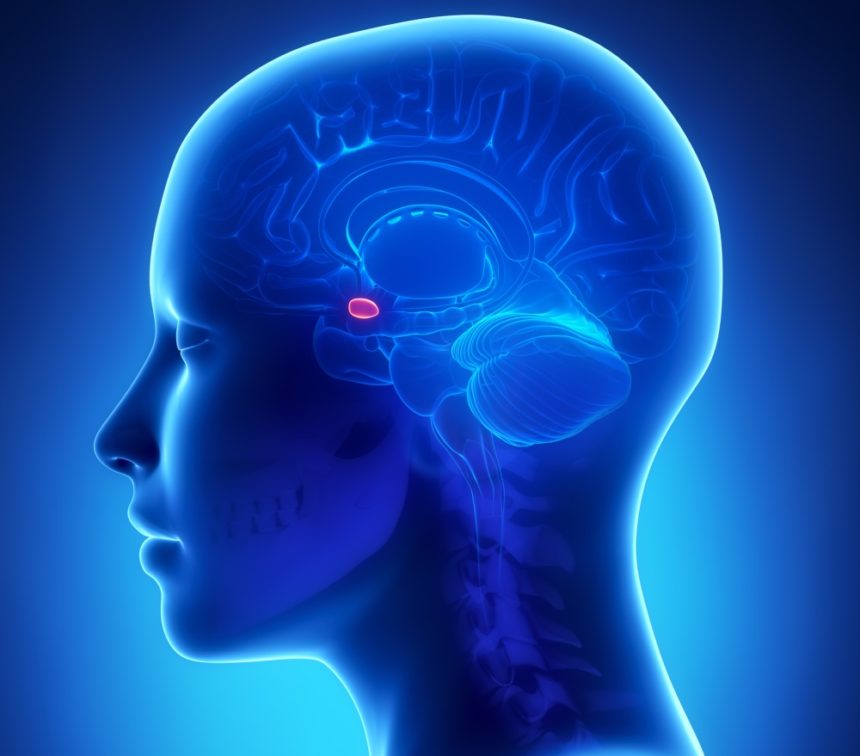
30
New cards
hippocampus
top pf brainstem; keeps track of memories
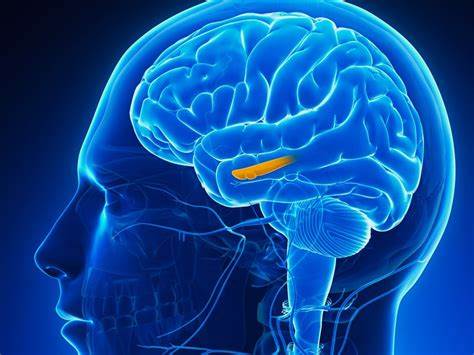
31
New cards
occipital lobe
very back of the skull towards the bottom; vision center
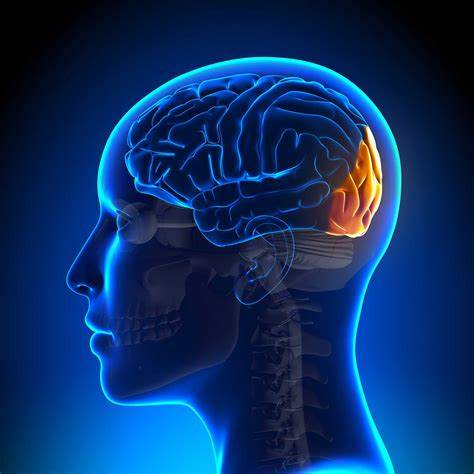
32
New cards
parietal lobe
top rear area of the skull; sensory cortex (sense of touch)
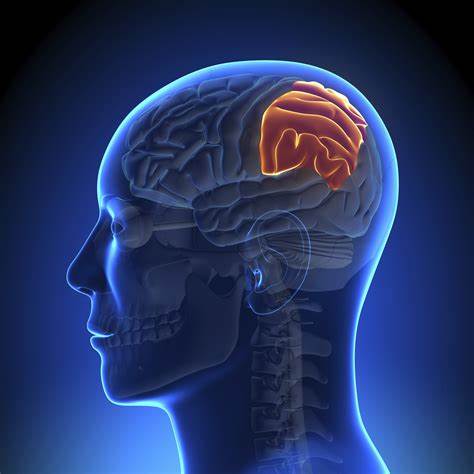
33
New cards
temporal lobe
side area, by the temples; earing
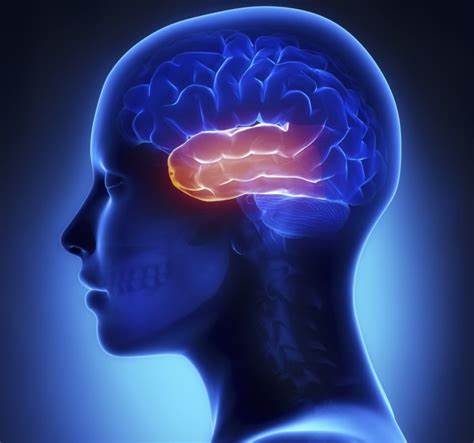
34
New cards
frontal lobe
front area, speaking and motor activities, planning, judging, problem solving
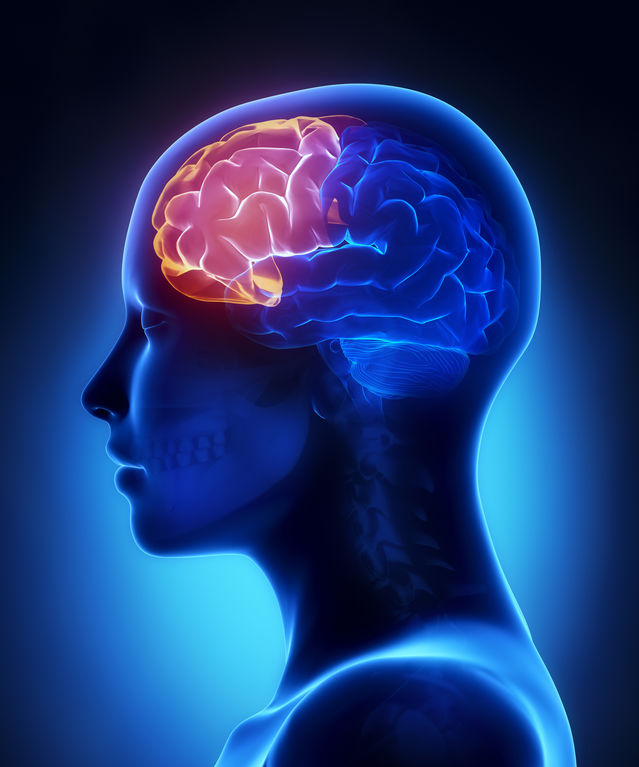
35
New cards
corpus callosum
connects the hemispheres
36
New cards
left hemisphere
controls the right side of the body; math and logic
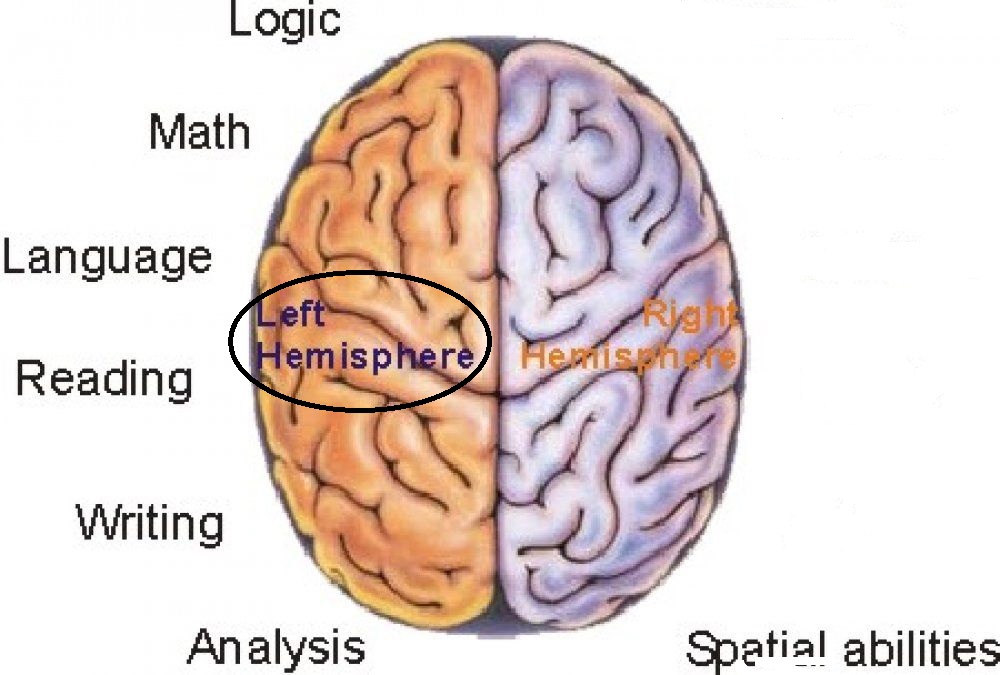
37
New cards
right hemisphere
controls the left side of the body; creativity, music, art
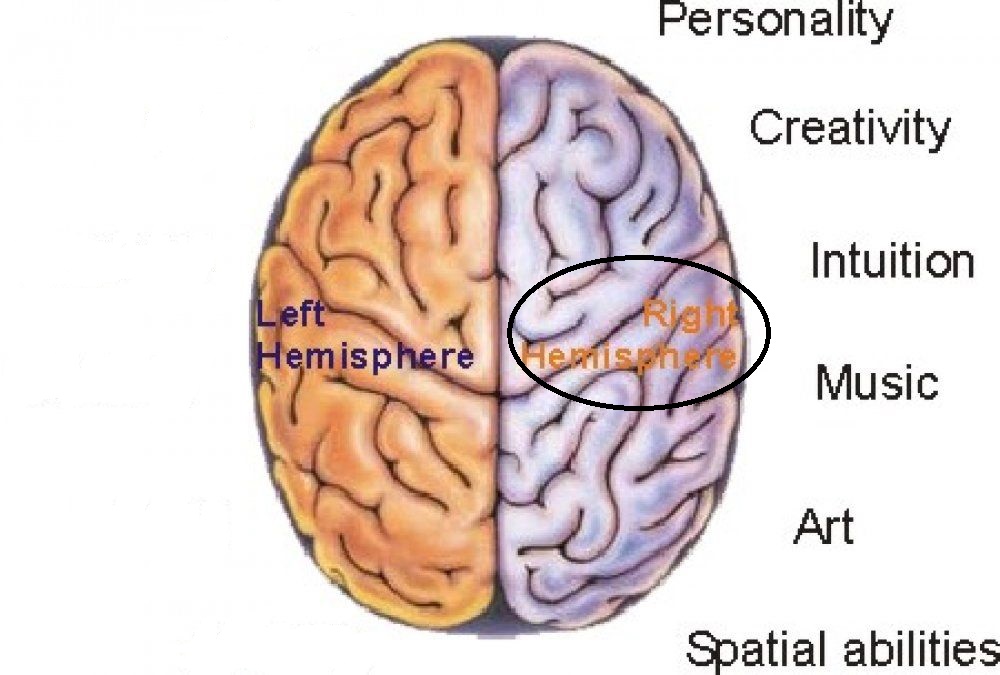
38
New cards
aphasia
loss of impairment to understand language or express oneself through language due to injury or illness
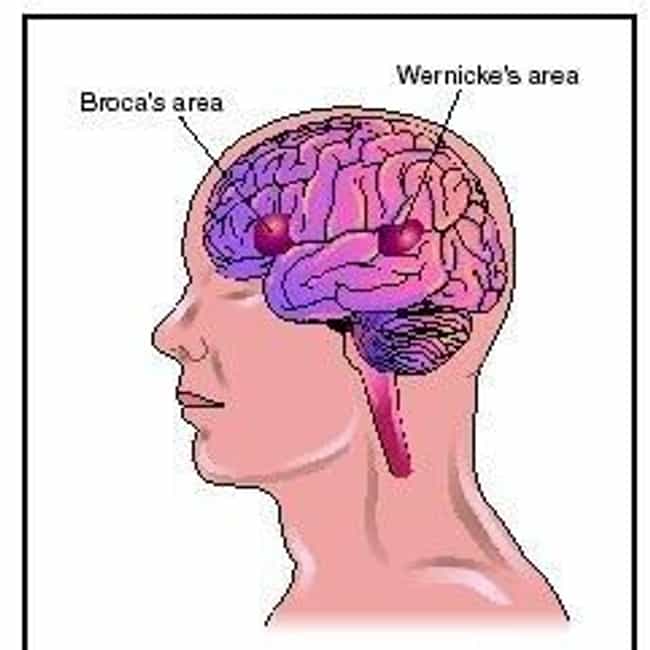
39
New cards
types of neurons
sensory (afferent)
motor (efferent)
motor (efferent)
40
New cards
interneurons
communicate and intervene between sensory inputs and motor outputs; billions of these
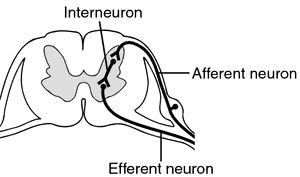
41
New cards
reflex
an automatic instinctive unlearned reaction to a stimulus; occurs at spinal cord; message doesn't travel to the brain for it to happen
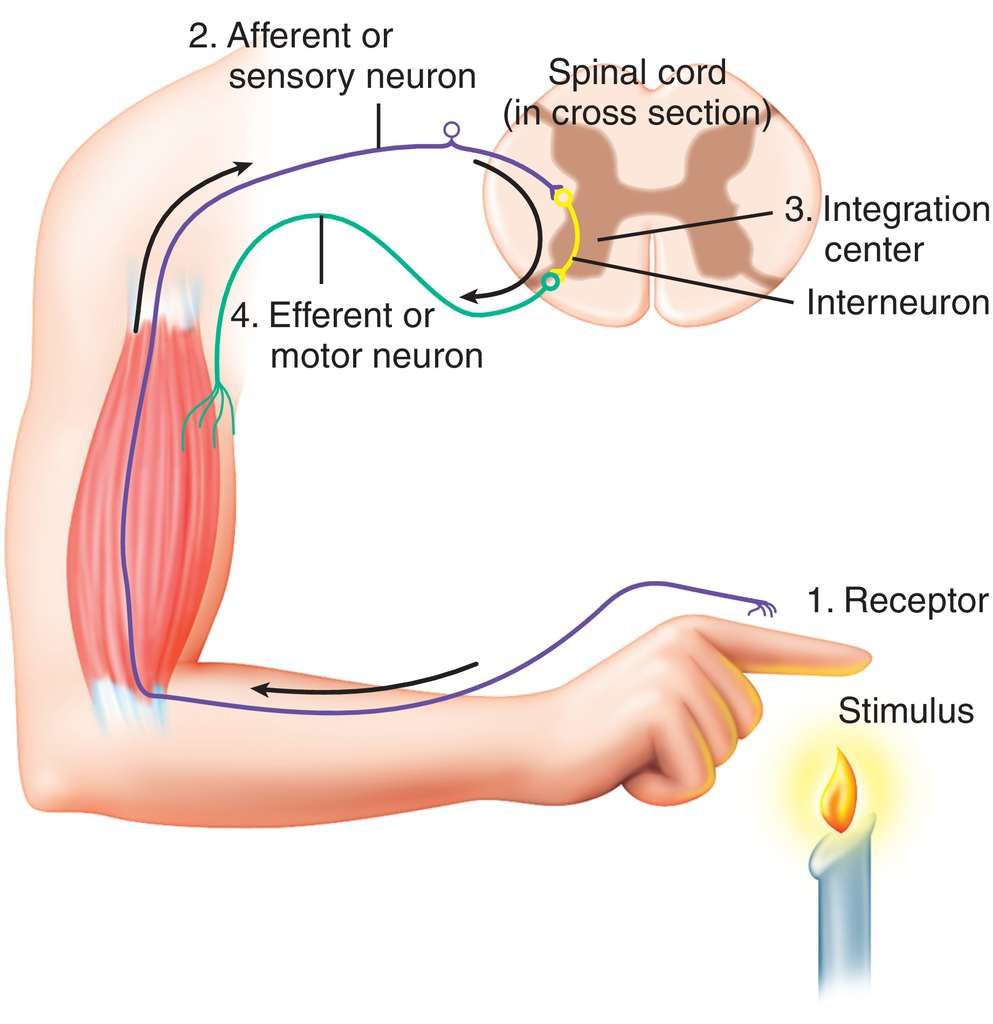
42
New cards
glial cell
not considered neuron but they do a lot to support the neuron; ex) myelin sheath
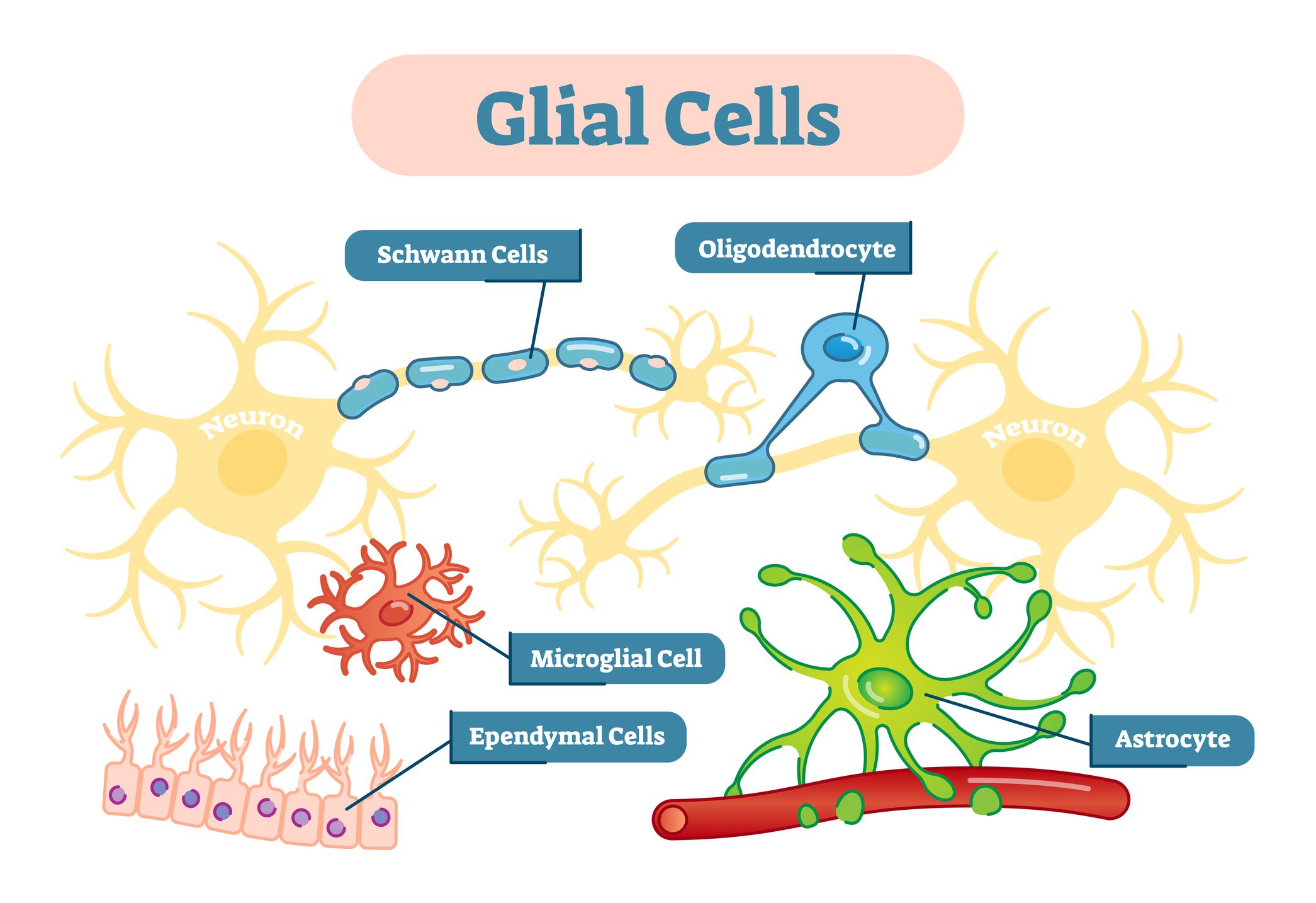
43
New cards
neural communication
neurons are either excited or inhibited (all or nothing)
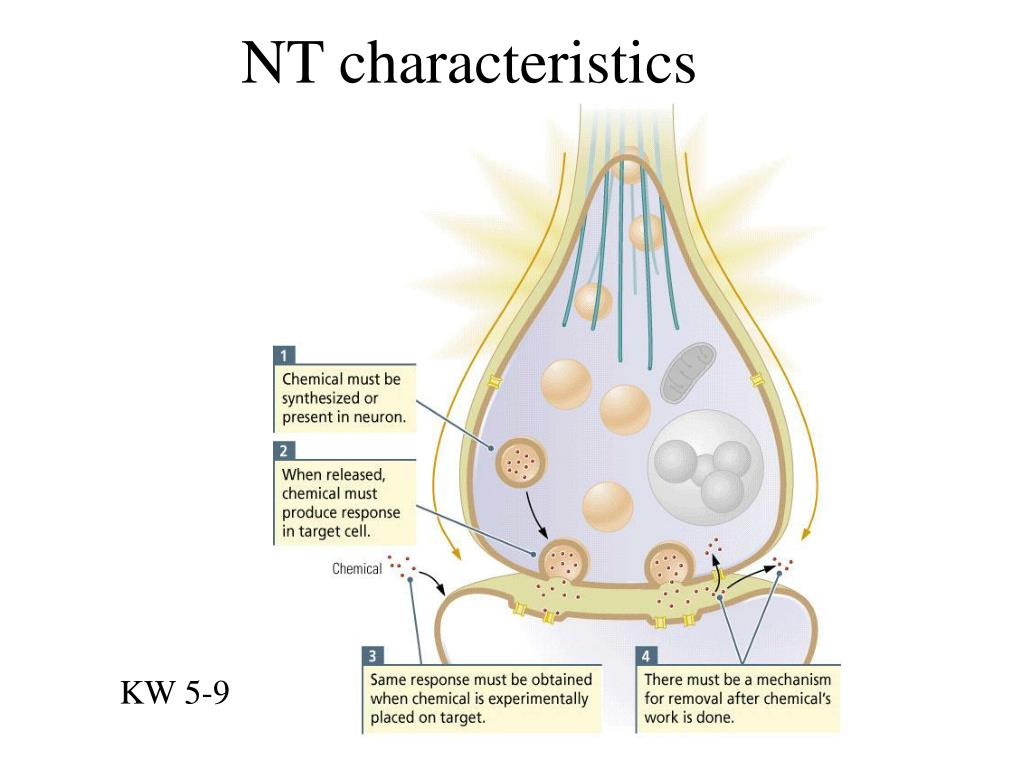
44
New cards
"excited neuron"
action potential traveled down the axon and is propagated by the opening and closing of sodium, and potassium "gates"

45
New cards
CT
head traumas and fractures; x-ray photos
46
New cards
PET
emission; active/inactive parts of the brain
47
New cards
MRI
magnetic; soft tissue in your brain and blood flow
48
New cards
EEG
electrical waves; detects seizures
49
New cards
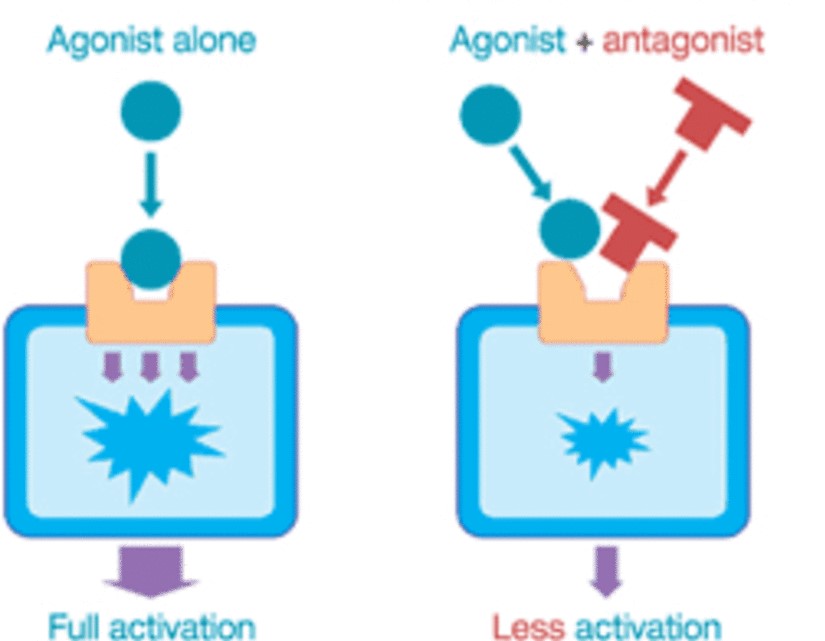
agonist
molecule that mimics the effects of a NT or blocks the reuptake of a NT so the effects are prolonged
50
New cards
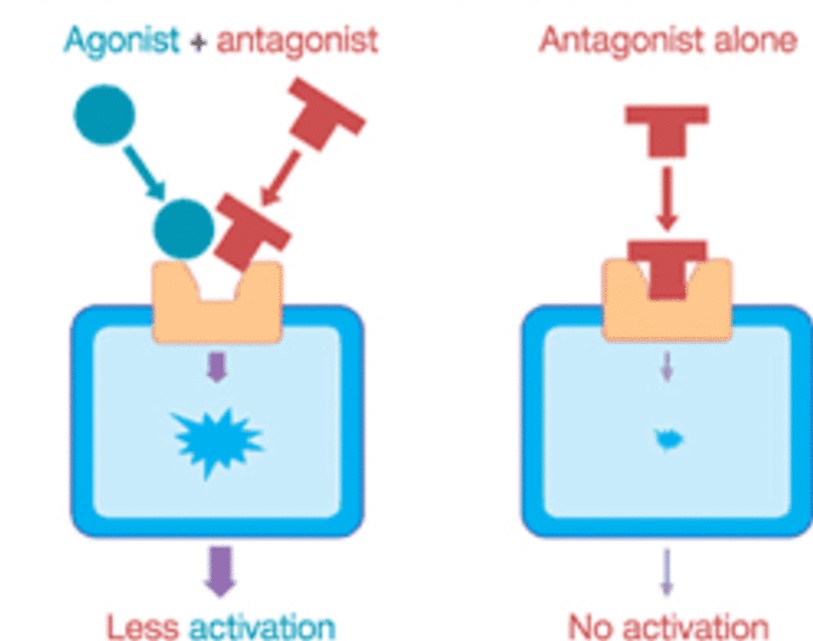
antagonist
molecule that inhibits a NT release; stops the action of the NT
51
New cards
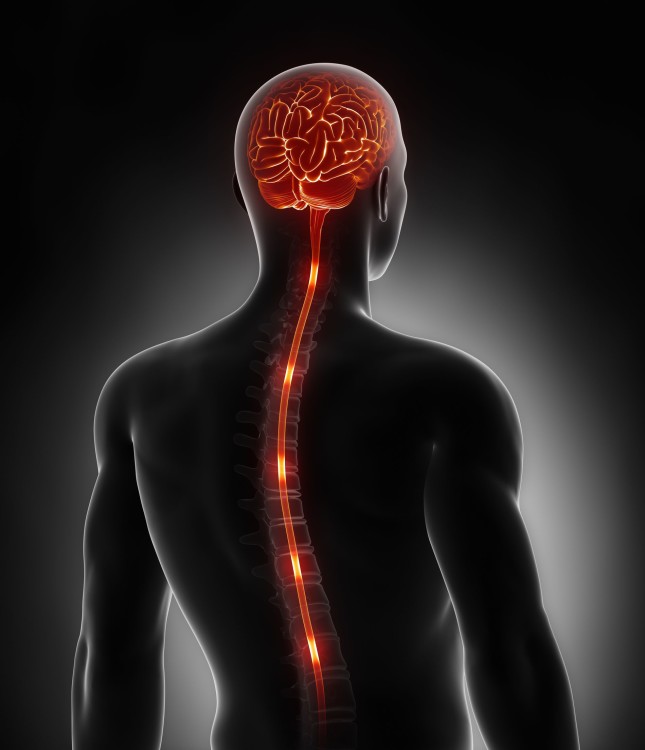
central nervous system
the portion of the vertebrate nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord
52
New cards
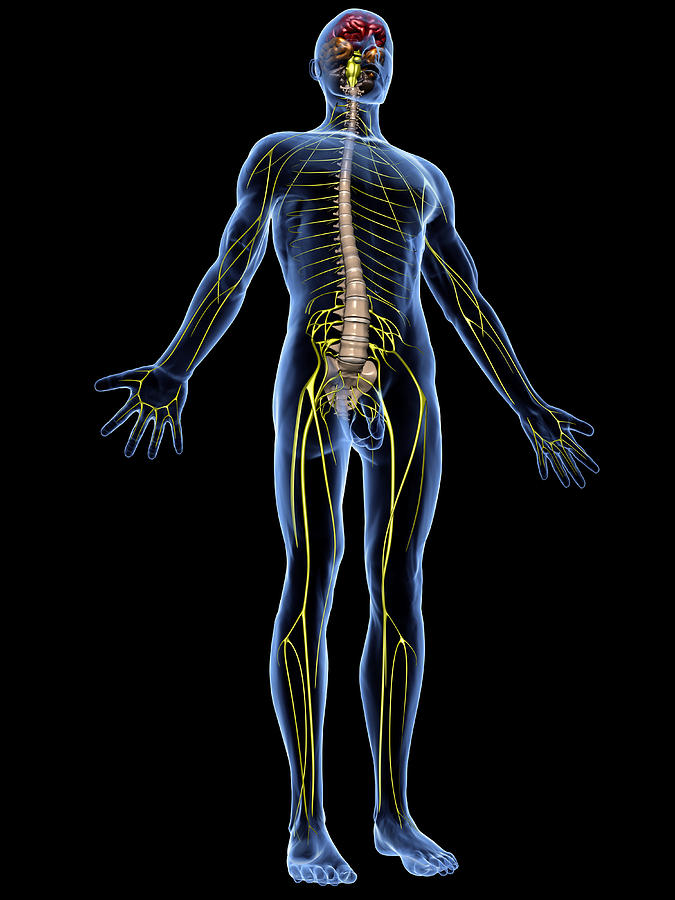
peripheral nervous system
the section of the nervous system lying outside the brain and spinal cord
53
New cards
somatic
controls sense organs and voluntary muscles
54
New cards
autonomic
automatic bodily responses
55
New cards
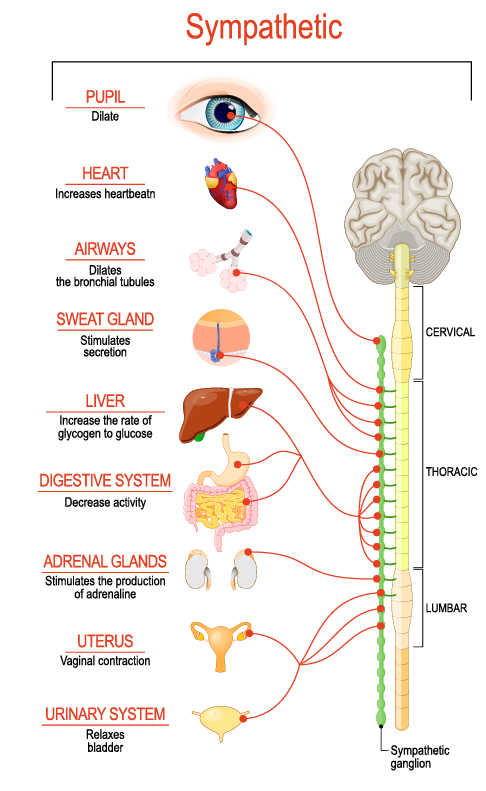
sympathetic nervous system
network of nerves that initiate the fight or flight; heightened
56
New cards
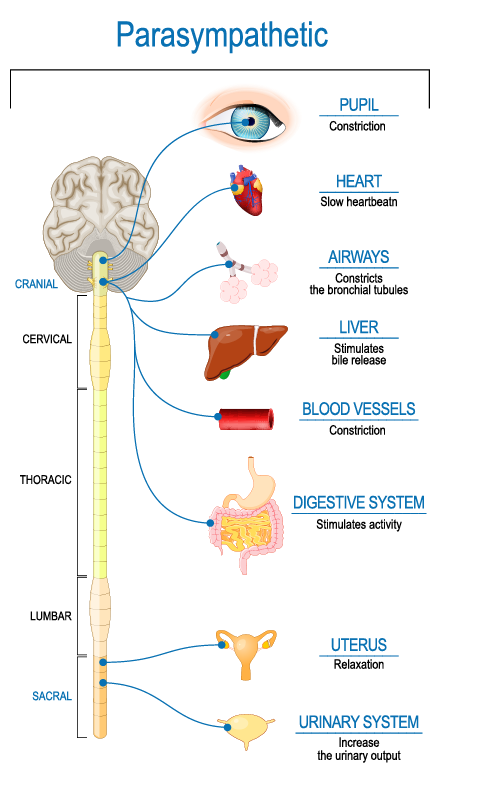
parasympathetic nervous system
regulates rest and digest functions; relaxed