Linguistics Flashcards
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards for a Syntax lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Syntax
The study of how words combine to form phrases and sentences.
What is a Sentence?
1. HIGH-LEVEL UNIT
2. LINEAR STRUCTURE WITH HIERARCHIES
3. SCENARIOS OF MEANING
Sentence
A high-level unit composed of words ordered into larger chunks (phrases).
Clause
Expresses a whole event/situation with a subject and a predicate. A syntactic unit usually smaller than a sentence. NP-VP- structure.
e.g. "The cat sleeps."
"She runs quickly."
Constituent
A component part of a clause that fulfills a function. For example, a noun phrase or verb phrase that can stand alone or be part of a larger structure. They constitute the clause. Constituents can be simple (one word) or complex (more words). They fulfil functions.
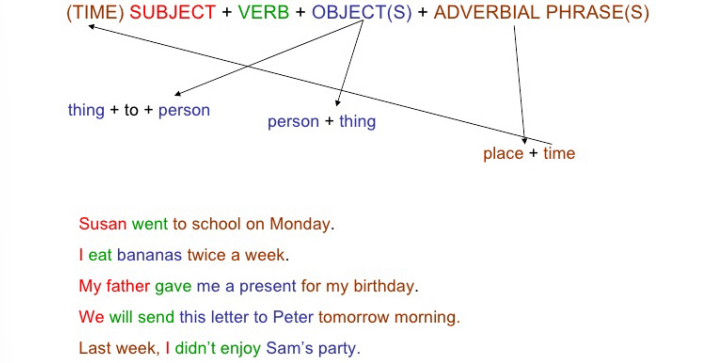
Linear Structure
Sentences string together words one by one creating a linear structure with clear ordering.
Hierarchies
Some elements in a sentence are 'weightier' than others and govern less 'weightier' bits.
Syntactic Creativity
Elements (phrases) in sentences can be expanded and sentences creatively enlarged ad infinitum.(PRODUCTIVITY, RECURSIVENESS).
Syntactic Functions
Functions taken over by phrases in a sentence (e.g., subject, predicate, object).
Form
are word classes and types of phrases. (e.g. noun, verb, adjective)
Function
The role a phrase fulfills in a sentence (e.g., direct object).
Functional Types of Sentences
>> DECLARATIVE
>> INTERROGATIVE
>> EXCLAMATORY
>> IMPERATIVE
Declarative Sentence
makes a statement.
e.g. This is a spectacular canyon.
Interrogative Sentence
asks a question.
e.g. What canyon is this?
Exclamatory Sentence
expresses strong emotion/exclamation
e.g. What a spectacular canyon; if only I could see it!
Imperative Sentence
gives a command.
e.g. Hike that canyon.
Complex Sentence
Formed by combining clauses. dependent + independent clause
e.g. Although it was raining, we decided to hike.
Independent Clause
Also known as a main clause;Can stand alone as a sentence.
e.g. Tom cried..
Dependent Clause
Also known as a subordinate clause. It cannot stand alone as a sentence
e.g. …because it was raining,
TESTING FOR CONSTITUENTS
A number of tests can be used to find out which words belong together and form clause consJtuents.
>> movement
>> pro-noun subsJtuJon
>> question
Movement
A test used to find out which words belong together and form clause constituents.
e.g. Shifting phrases to the front of the sentence.

Pro-noun Substitution
A test used to find out which words belong together and form clause constituents.
e.g. Tom was tired → He was tired
Question
A test used to find out which words belong together and form clause constituents.
e.g. Tom was tired → who was tired? - Tom
Expand
To increase the size or complexity of a constituent.
Add
To include extra constituents with new functions.
Types of Constituents
>> SUBJECT: who/what (doing the acJon)
>> PREDICATE: process/acJon
>> COMPLEMENT: (OBJECT or ATTRIBUTE)
>> OBJECT: who/what (affected by acJon)
>> ATTRIBUTE: characterisJcs of object/person
>> ADVERBIAL: when/where/how etc.
Internal Structure of Phrase
The arrangement and relationships of constituents within a larger linguistic unit, such as a phrase or sentence.
Modifiers
Words or phrases that add detail or clarify other constituents in a sentence.
e.g. adjectives, adverbs, or phrases that enhance meaning.
Types of Phrases
Ex. 1 / NOUN PHRASE
Ex. 2 / ADJECTIVE PHRASE
Ex. 3 / VERB PHRASE
Ex. 4 / ADVERB PHRASE
Ex. 5 / PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE
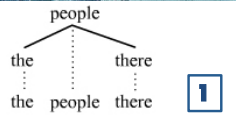
Noun Phrase
Determiner + Head Noun + Postmodifier (Adv.)
Adjective Phrase
Premodifier (Adv.) + Head Adjective + Postmodifier (PP)
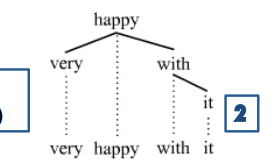
Verb Phrase
Premodifier (Adv.) + Head Verb + Complement (pronoun)
Prepositional Phrase
Headed by a preposition; the preposition is the head.
Auxiliaries
(tense, aspect, modality).
e.g. be (am, is, are, was, were, been, being)
have (has, have, had)
do (do, does, did)
Lexical Functional Grammar
A linguistic theory considering syntax and semantics as parallel, interacting structures.