Respiratory substrates & quotients (RQ)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What are respiratory substrates?
Any organic structures that can be used in respiration to produce ATP
Which substrates produce more ATP when respired?
Substrates with more H atoms per unit mass
Carbohydrates
15.8 kJ g⁻¹
Lipids
39.4 kJ g⁻¹
Proteins
17.0 kJ g⁻¹
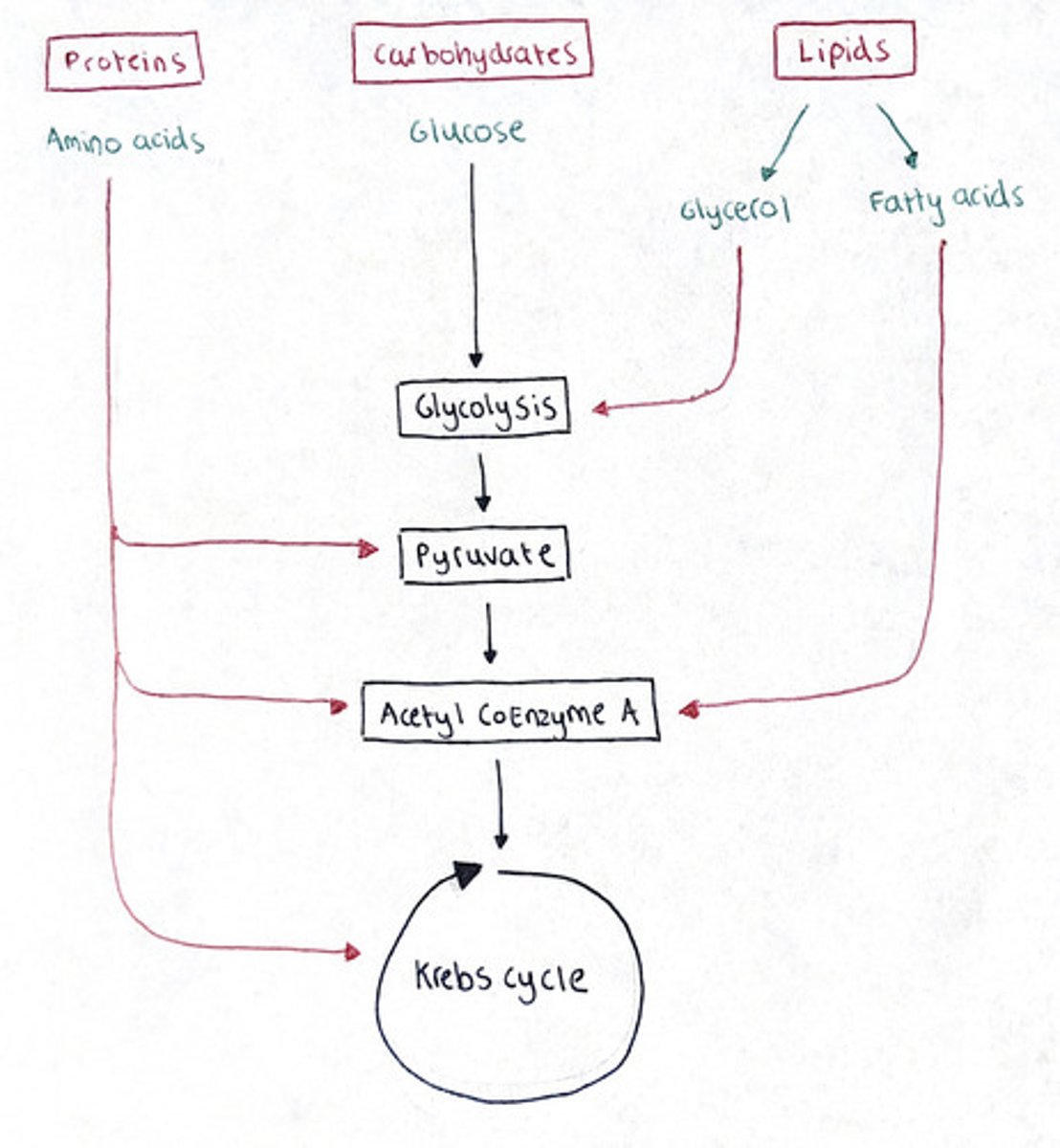
Respiratory substrates in Aerobic Respiration
Carbohydrates = Glycogen/starch forms glucose
Lipids = Fatty acids break down into 2x Acetyl CoA, then enter the Krebs cycle
Proteins = Proteins break down into amino acids, which are deaminated into pyruvate or Acetyl CoA
What is the Respiratory Quotient?
The ratio of the volumes of oxygen consumed and carbon dioxide given of in respiration
RQ equation
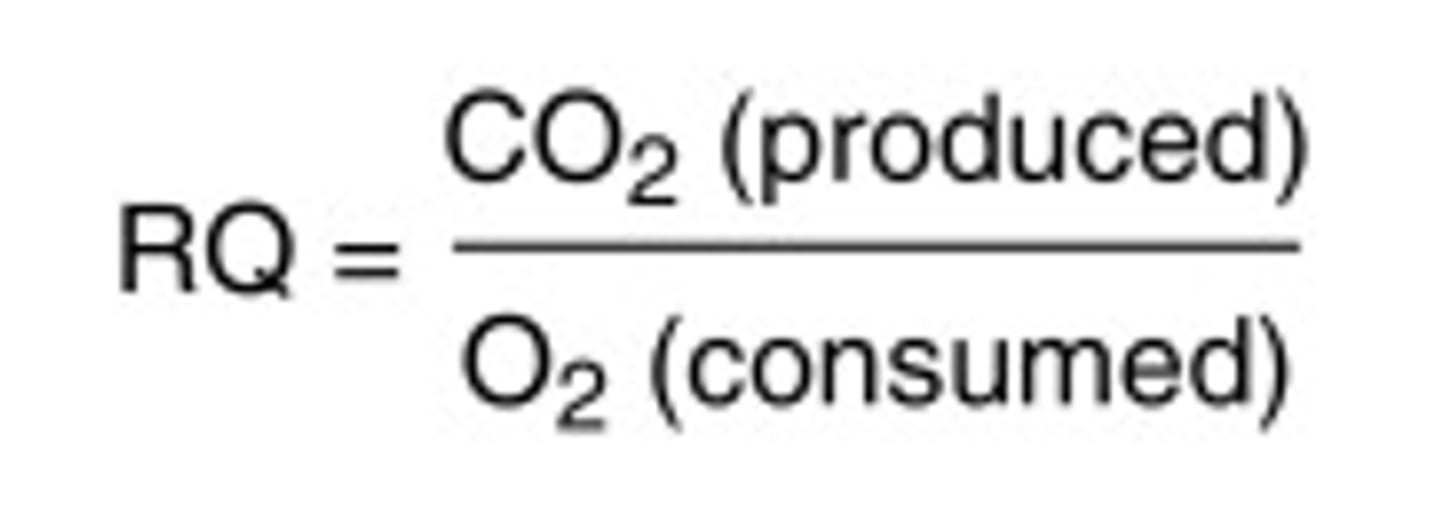
Q1) C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O
Volumes aren't given here but we do have number of molecules
6CO₂ released / 6O₂ consumed
6/6
1
What's the RQ of carbohydrates?
1
What's the RQ of proteins?
0.9
What's the RQ of lipids?
0.7
Why is the RQ different to the volume of energy produced?
Lipids and proteins RQ value is lower as more oxygen is needed to oxidise them, in comparison to carbohydrates.