Hematology exam 2 review (for finak study more on cell morphology+characteristics)
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
At what structure level is a heme group inserted into each of the four globin chains?
Tertiary 3^0 level
Normal hemoglobin production is dependent on what processes?
adequate iron delivery and supply, adequate synthesis of protoporphyrin, and adequate globin synthesis
What form is the majority of iron mostly stored as in macrophages?
Ferritin
How many atoms of ferric iron can transferrin transport through the plasma so it goes into RBCs?
2
Best description of heme transport
Heme leaves the mitochondria and travels to the cytosol (cytoplasm) to join the globin chains
How to describe the tertiary hemoglobin structure
Helically coiled, third structural level of one globin molecule has primarily alpha helices (NO beta pleats)
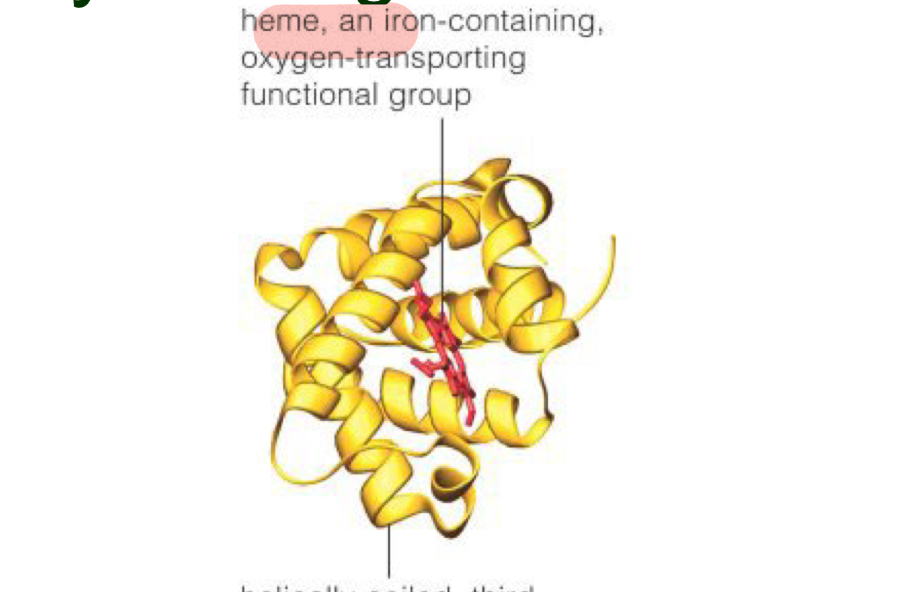
How many polypeptide chains? How many pairs? are associated with the Hgb quarternary level structure?
4 polypeptide chains, 2 pairs
Describe the quarternary structure of a Hgb molecule
spherical, has four heme groups attached to four polypeptide chains, and can carry four molecules of oxygen
Primary structure of Hgb is best described as
A sequence of a chain of amino acids (polypeptide chain)
how is a secondary level Hgb structure formed?
Occurs when the sequence of amino acids are linked by hydrogen bonds
How is the teriarty level of a Hgb molecule formed?
Occurs when certain attractions are present between alpha helices and pleated sheets
What types of hemoglobin accumulation/conditions would shift the oxygen dissociation curve left?
Carboxyhemoglobin and methemoglobin
2,3-BPG/DPG = _____ form = decreased O2 affinity = increased O2 offloading (in ____ ?)
No 2,3-BPG/DPG = ______ form = increased O2 affinity = increased O2 uptake (in ____?)
Tense, tissues
Relaxed, lungs
Bohr effect is phenomenon in which
increased pH (= decreased acidity) causes left shift.
Embryonic Hgbs formed at the first three months after conception are
Portland, Gower I and Gower II
Gower I is made up of what chains?
2 zeta and 2 epsilon
Portland Hgb is made of what globin chains?
2 zeta 2 gamma
Gower II is made up of what chains?
2 alpha 2 epsilon
Glycosylated Hemoglobin
- Hgb can be modified by nonenzymatic binding of various sugars with the globin
- Most common is Hgb A1C – glucose attaches to the N-terminal valine of the β chain
→Older cells typically contain more due to prolonged exposure (4-6% normal)
→ Normally, 4-6% of Hgb A circulates as Hgb A1c, but increases with diabetes (proportional to the mean glucose level over 2-3 months
What is the largest cell in the bone marrow
Megakaryotcytes
Normal range for platelets
150,000-450,000/ul
What is the major growth factor that regulates megakaryocytopoiesis?
thrombopoietin
What doesLD-CFU stand for?
Light Density colony forming units
What happens to the nucleus size as a megakaryocyte matures?
It increases
Fe3+ ferric or ferrous?
Ferric
Which type of megakaryocyte is the largest cell in the bone marrow?
Basophilic/ Granular megakaryocyte (MK III)
A mature megakaryocyte should have what characteristics?
All of the choices are correct
________ stimulates production of platelets, ________ activates platelets
Thrombopoietin (TPO), thrombin
Where do granulocytes develop? What type of cells are produced there?
bone marrow; segs, eos, monos, basos
What form is ferrous iron?
Fe2+
Each Hgb molecule consists of
4 globin chains and 4 heme groups, each w/ a center iron molecule (4 iron)
What type of “pocket” does each globin chain contain? What do they contain? Why?
Each globin chain has a hydrophobic “pocket” containing a heme group
→Arrangement prevents the Fe2+ from oxidation into the ferric form (Fe3+)
Heme is produced how?
Protoporhyrin IX + Fe2+
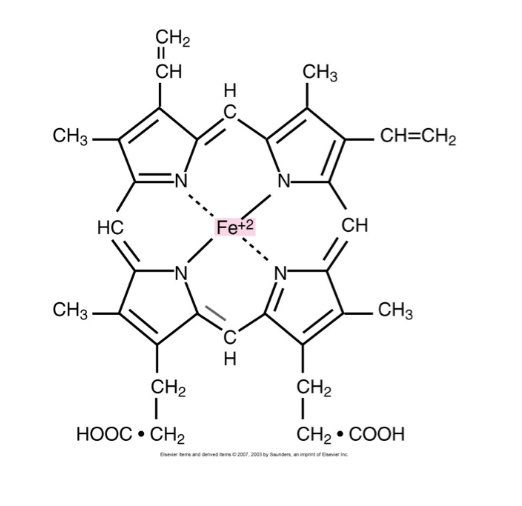
What is each heme iron directly bonded to in the globin chain?
2 histidines of the globin chains
Proximal histidine function
Increases oxygen affinity
Oxygen tension occurs
In tissues
Oxygen affinity occurs
in the RBCs
How is oxygen tension regulated?
Through the oxygen affinity of Hgb
How is oxygen affinity regulated?
modulated by the concentration of phosphates in cell
When tissue is hypoxic
Hgb decreases which reduces oxygen affinity (bc oxygen will move from Hgb into tissue to compensate)
Oxygen dissociation curve
The affinity of Hgb for O2 depends on the partial pressure of O2 (PO2).
graph plots the O2 content of Hgb (% saturation) versus the PO2
A shift to the left on the oxygen dissociation curve would affect oxygen affinity in what way? Where?
Increased oxygen affinity that would occur in the lungs
think left→lungs
What causes a shift left in the oxygen association curve (inc. oxygen affinity)
Decreased CO2, decreased 2,3-DPG, decreased body temp.
increased pH, increased oxygen affinity
Carbon Dioxide Is transported from the tissues to the lungs by what methods?
Dissolution directly into the blood, binding to hemoglobin-carbaminohemoglobin, carried as a bicarbonate ion (~75%)
carbonic anhydrase (CA) function
Catalyses the conversion of CO2 (given up by tissues) and H2O, to produce carbonic acid (H2CO3)
About 90% of the blood CO2 is converted to
Bicarbonate and H+ ions
What type of iron is contained in methemoglobin?
Ferric (Fe3+)
Accumulation of methemoglobin shifts the oxygen dissociation curve-
Left, leading to hypoxia
Leukopoeisis produces and proliferates white blood cells except
Where does leukopoiesis occur?
Lymphocytes, in the bone marrow,lymphnodes,&thymus. “BLT”
Production of neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils is called
Myelopoiesis
Why are mononuclears Not considered granulocytes?
Mononuclears can have very fine granules, but granulocytes all have large noticeable granules and segmented nuclei
The presence or absence of nucleoli indicate what for nuclear characteristics?
Immaturity
Eosinophils contain granules that mostly contain what?
Crystalloid form Major Basic Protein (MBP)
Largest cell in the peripheral blood (p.b)
Monocytes
Primary phagocytes are what types of cells?
Monocytes and neutrophils
Name blood cells that are capable of phagocytosis
Eosinophils, basophils, neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages,
Chemotaxis is best described as
Process of phagocytes movement along gradient of increasing chemotaxis (generated by infection or inflammation)
what cells get to the site of inflammation/infection first?
Segmented neutrophils
Place the following WBCs in order of their phagocytic activity (NOT SPEED)
Eos, Basos, Monos, & Segs
Monos > segs > eos > basos
CFU-L differentiates the lymphoid maturation pathways into what?
B-lymphocyte precursor
T -lymphocyte precursor
Basophilic in hematology refers to
Bluish color (NOT related to whether cell s a basophil!)
Secondary lymphopoiesis occurs where
Spleen, lymph nodes
Plasma cells physical description
Type of lymphocytes with eccentric (off to the side) nucleus
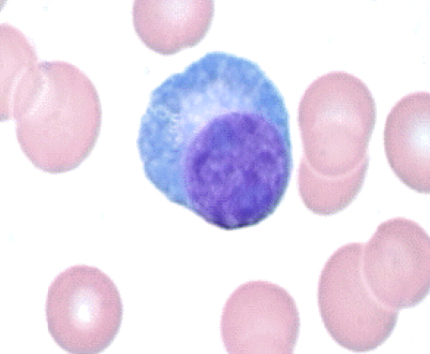
Plasma cell functions
Secrete immunoglobulins and are responsible for antibody production
Helper T cells, other name and function
CD4+ cells, induce other lymph’s to carry out certain functions (ex. Inducing B cells to produce Antibodies)
Delayed hypersensitivity T cells function
Produce chemotactic lymphokines(cytokines produced by lymphs) in response to antigens
Majority of natural killer T cells are, what is their function?
CD56+ or CD16+
Kills tumor/virus infected cells
Cells that confuse lymphocyte identification
Blasts, monocytes, rubricytes/polychromatic normoblasts
Monocyte difference from lymphocytes
Monocyte cytoplasm tends toward blue gray color and have an opaque, “ground glass” appearance
Rubricyte difference from lymphocytes
Rubricyte cytoplasm has a grayish blue appearance, lymph cytoplasm is a clearer blue. Rubricyte chromatin is much denser than lymphocytes’ chromatin
describe an primary/nonspecific/azurophilic neutrophil granule contents
red-purple color, contains: lysosomes, acid hydrolases, myeloperoxidase (MPO), proteases, superoxide, positive for peroxidase
secondary/ specific/ neutrophilic neutrophil granule contents
pale- lavender pink , contain lysozyme, NO peroxidase
tertiary neutrophil granule contents
color is invisible/clear, appears in very late stages, contains lysozymes and gelatinase, NO peroxidase
Lymphocytosis
Above normal range in adults - 4.0 × 10³/ ul
Above normal range in children - 9.0× 10³/ul
Type II atypical lymph’s other name
Aka Downey cells
Downey cells
Classical reactive or atypical lymphs
Indicative of Epstein-Barr virus!
Seen in infectious mononucleosis!!!
Abundant cytoplasm, irregularly shaped, and edges indented by surrounding structures
Fried egg appearance, no nucleoli
Type III atypical lymphocytes are
Largest of the atypical lymphocytes
Immature chromatin with nucleoli
Myelopoiesis refers to the production of which cells?
Neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
What WBCs are classified as granulocytes?
Basophils, Neutrophils, Eosinophils
Rmemorize five main types of WBCs and their prominence in the bone marrow
Neutrophils- 50-70%
Lymph- 18-42%
monos- 2-11%
eos- 1-3%
basophils 0-2%
CFU-GM functions and what it matures into
ILs and CSFs control the stability of cell numbers and their functions
Matures into a myeloblast
CFU-GEMM matures into
CFU-GM
Multi-CSF / IL-3 production is stimulated by what?
Endotoxin released from infection
Source of multi CSF/IL-3
Secreted by marrow fibroblasts , t-lymph’s, macrophages and monocytes
function of G-CSF
Stimulates AND enhances the functional response of neutrophils
Band nucleus traits
Curved band- like nucleus, straight C or S shaped nucleus with no segments
Possess full motility, active adhesion properties and some phagocytic activity
A maturation shift to the left occurs when neutrophil bands are increased in pb in comparison to the number of sets
Segmented neutrophil traits
Comprise 50-70% of total WBC population in normal adult
Cell is completely functional
Should have 2-5 lobes
Maturation shift to the right occurs when there is more than 5 lobes (inc. maturation)
Circulating pool (CP)
Neutrophils circulating in the blood
Marginating pool (MP)
Neutrophils that lie against endothelial lining of blood vessels
diapedesis
Performed by granulocytes, process which they squeeze through tight junctions between endothelial cells of the blood vessels and exit into the tissues. Once in the tissues, they do not return
Eosinophils granule contents
Major Basic Protein
Major basic protein (MBP) are
Granulocytes of eosinophils which is lysine and arginine rich
Functions of eosinophils
Control parasitic infections and dampen allergic/hypersensitivity reactions
which of the following are granulopoiesis regulators?
all of them
which is the most EPO / Erythropoietin sensitive?
CFU-E
function of IL-2
growth factor that produces lymphocytes
what Hgb is never found in adults?
epsilon
which colony stimulating factor is important for myeloid maturation in the bone marrow?
GM-CSF
which neutrophilic stage comes first?
bands
A cell has water soluble, large bluish-black lysosomes that contain heparin and histamine. These granule contents also can overlie the nucleus. What cell is this?
Basophils