Pathophysiology
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
Do RBC have a nucleus
NO
Osmolarity vs Osmolalily
miliosmoles/L vs miliosmoles/kg
Normal Na+ range in the body
136-145 mmol/L
Normal K+ body levels
3.5-5.0 mEq/L
Normal Ca+ body levels
9.0-10.5 mg/dL
Normal Mg+ body levels
1.3-2.1 mEq/L
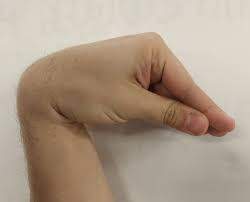
Trousseau sign
Sign of hypocalcemia when a blood pressure cuff is inflated and there is palmar flexion.
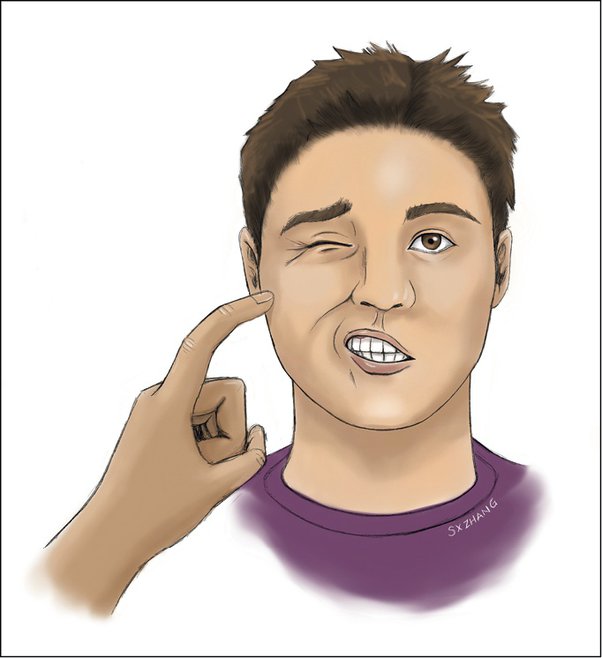
Chvostek's sign
Involuntary twitching of facial muscles that occurs when the facial nerve is tapped, indicating hypocalcemia
Type 1 Hypersensitivity
Immediate, IgE, anaphlactic
Type 2 Hypersensitivity
Quick onset, antibody-resistant cytotoxicity, IgG, associated with blood, penicillin, etc.
Type 3 Hypersensitivity
Slow onset, Immune complex disease, specific disorders
Type 4 Hypersensitivity
Onset a few days, sensitive T-cells release lymphokines, ex: poison ivy, jewelry, etc.
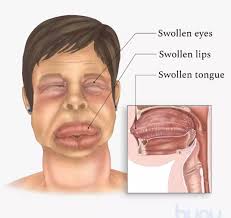
Angioedema
Severe type of hypersensitivity type 1, usually caused by NSAIDs & ACEI
Anaphylaxis
Rapid, life-threatening, type 1 severe hypersensitivity, use epinepherane
Angioedema vs Anaphylaxis
Symptoms vs systemic
Usually paired together
Common 3 drugs for anaphylaxis
Antihistamines, Corticosteroids, Albuterol
What are the 5 antibody types (can be given through plasma as immunoglobulin)
IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, IgM
five cardinal symptoms of inflammation
Warmth, redness/hyperpigmentation, swelling, pain, and decreased function.
Where are B and T immune cells produced
Thymus and bone marrow
emetogenic
a substance that can induce nausea and vomiting
Infiltration and extravasation
IV fluids or medications leaking from the vein into surrounding tissue
immune-related adverse events (irAEs)
Adverse events related to immunotherapy.
immunotherapy
Drugs activate immune system to attack cancer cells
nadir
When bone marrow suppression is the greatest and the patient is at highest risk for complications.
neutropenia
Decreased numbers of neutrophil white blood cells, leading to immunosuppression.
primary tumor
The original cancer cells and tumor.
thrombocytopenia
Decreased numbers of platelets, leading to impaired clotting and bleeding.
vesicants
Drugs that can cause severe tissue damage to surrounding tissue if they escape into subcutaneous tissue.
Another word for cancer
maliganancy
Cell regulation (4 parts)
Cell growth, replication, differentiation, and function
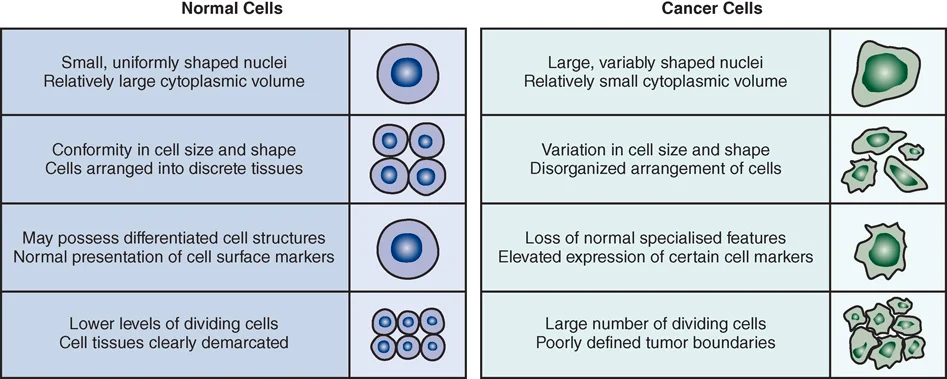
Difference between normal cells and cancer cells (4)
Nuclei size, conformity, cell structures, dividing rate
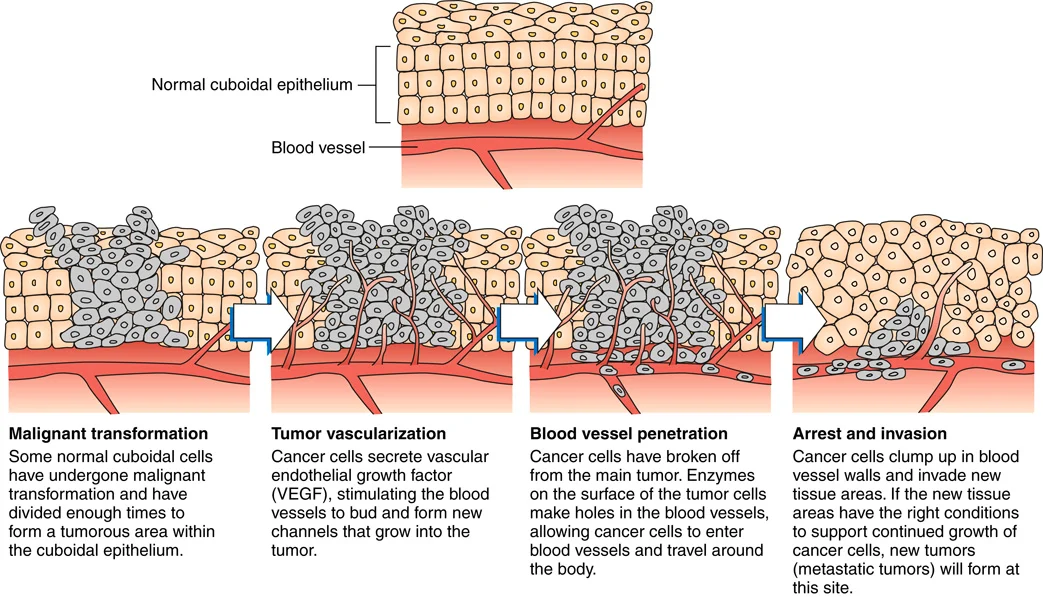
4 steps of metastasis
transformation, vascularization, penetration, invasion
Adeno-
epithelial glands
Chondro-
Cartilage
Fibro-
Fibrous connective tissue
Gilo-
Glial cells (brain)
Hemangio-
Blood vessel
Leiomyo-
Smooth muscle
Rhabdo-
Skeletal muscle
Squamous
Epithelial layer of skin, mucus membranes, and organ lining
Top 3 deadly cancers
Lung, breast/prostate, colon
Top 3 common new cases of cancer
Prostate/breast, lung, colon
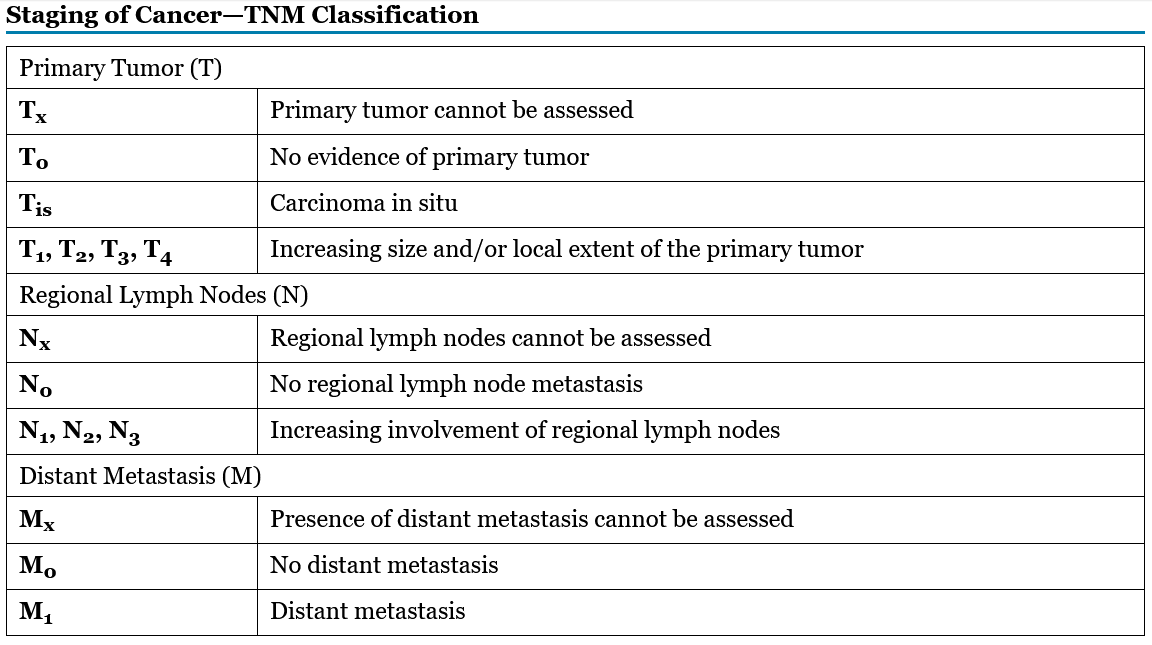
Tumor, node, and metastasis (TNM) system
Grades for cancers
Grading the cancer tumor itself
Gx, G1, G2, G3, G4

7 Warning signs of cancer “CAUTION”
Changes in bowel or bladder habits, A sore that does not heal, Unusual bleeding or discharge, Thickening or lump in the breast or elsewhere, Indigestion or difficulty swallowing, Obvious change in a wart or mole, and Nagging cough or hoarseness

Types of cancer surguries
Prophylactic surgery (prevention), Diagnostic surgery, Curative surgery, Debulking surgery, Palliative surgery (pain relief), Reconstructive or restorative surgery
What happens to skin up to 1 year after radiation therapy?
Photosensitivity
Intrathecal drugs
delivers drug directly into CSF
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN)
loss of sensory perception or motor function of peripheral nerves associated with exposure to certain anticancer drugs
Extracellular fluid (ECF)
Consists of plasma and intersititial fluid
Osmosis
Movement of water through a semipermeable membrane
Hypervolemia
Too much water in the body
Insensible water loss
Body water lost from skin, spit, GI, and lungs
Obligatory urine output
Minimum urine needed to excrete in a day to get rid of toxins (400-600mL)
Hypertonic
High solute concentration drawing water out of cellsHy
Hypotonic
Low solute concentration drawing water into cells
RAAS is started by what from low tissue perfusion
Low BP, low blood volume, low O2, low blood sodium
RAAS steps
Renin, angiotensin 1, angiotensin 2
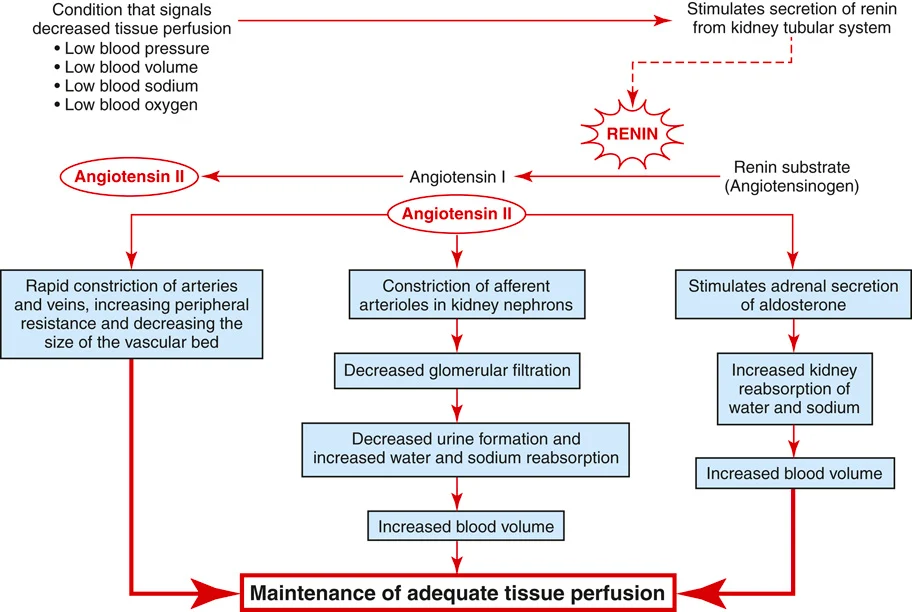
Aldosterone released from adrenal glands
Water and sodium reabsorber. Potassium excretor.
ADH released by pituitary gland
Only retains water
Naturic peptides (NP) on the heart in response to high BP and blood volume
opposite effect of aldosterone
Cyototoxic T cells
Selectivity attacks/destroys non-self cells.
Natural killer cells
Non selectively attacks and kills non-self cells
Regulatory T cell
Regulates balance between offensive and defensive inflammationthe
Helper T cell
Secretes cytokines and lymphokines to enhance immune activity
Memory cell
Remembers an 1 old specific antigen
Plasma cell
Secretes immunoglobulins
B lymphocyte
Uses helper T cells and macrophages to become sensitive to foreign cell proteins
Basophil
Releases histamines, kinins, and heparin in areas with damage
Eosinophil
Releases vasoactive amines during allergic reactions and parasite infestations
Monocyte
Clears dead debris
Macrophage and Neutrophil
Nonspecific indigestion of foreign proteins and microorganisms
Macrophage and Neutrophil difference
Macrophage assists in cell-mediated immunity. Neutrophil is prominent in inflammation/infection
What spleen does for immune system
Antibody producing organ
Endemic, epidemic, pandemic
Know where and when, in a country contained unexpected increase, crosses country boarders
Wound healing phases (3)
inflammation, proliferation, maturation
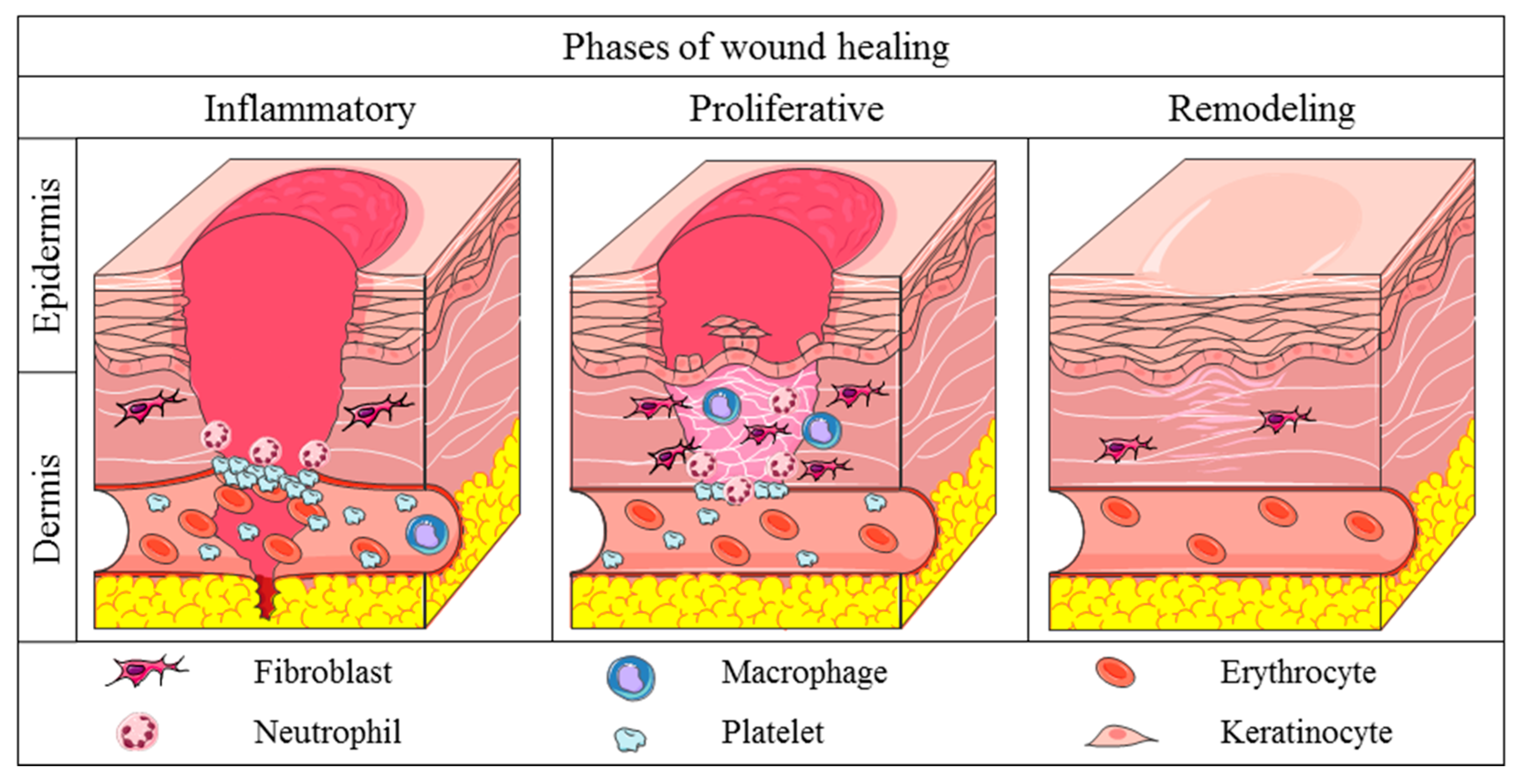
Inflammatory Response stages (3)
Vascular, cell exudate (pus high neutrophils), repair
When is the immune system the healthiest
20-30 years old
endogenous vs exogenous infection
patient infection from patient’s flora or from outside environment
IgA function
tags pathogens for destruction lives in the mucous membranes
IgD function
B-cell antigen receptor
IgE function
allergies. Protects against parasites
IgG function
Long term immunity activates upon second exposure
IgM function
B-lymphocyte forms this upon first interaction with a virus. Has up to 10 binding sites.
What issues would you find in someone with hypo/hypernatremia
Altered cerebral function. muscle weakness/twitching
What issues would you find in someone with hypo/hyperkalemia
Life threatening, cardiovascular, intestinal, mental, and muscle changes.
What issues would you find in someone with hypo/hypercalcemia
Neuromuscular, cardio, skeletal, and intestinal changes
What issues would you find in someone with hypo/hypermagnesemia
cardio, neuromuscular changes.
What cells does HIV target
Cells with CD4 on their membrane (T-cells and dendrocytes) by attaching to them with its gp120 molecule
CD4 function
Attach to and communicate with other immune cells
How does HIV reproduce
going into the cell with its RNA retrovirus (which uses reverse transcriptase to add to the half RNA strand and make a whole active bad DNA)
Why is the PTH hormone released.
Low blood calcium levels.
Why is the hormone calcitonin released
High blood calcium levels.
What part of the body controls temperature.
Hypothalamus
Are babies able to shiver
No
A person who takes salt substitutes are likely to have a high mineral level of what?
Potassium
What drug helps control fever
Antipyretics (most commonly acetaminophen)
Prostaglandin (fever creator) is released by what
hypothalamus
What is malignant hyperthermia
Post surgery fever