Ortho Oncology
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PA Blume Guess Lecturer
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Over 40 (think metastatic), Under 20
Common populations for Bone cancers
Destructive lesion
Metastatic cancer is the most common reasons for a _______________ in adults
Breast, lung, thyroid, renal, prostate
Common carcinomas that spread through the bone
vertebral bodies (MOST COMMON), pelvis, proximal limb girdle
Common sites of metastatic lesions
proximal femur
What is a common site of fracture secondary to metastasis?
Lytic/destructive (lung, thyroid, renal), Blastic/Sclerotic (breast, prostate)
Types of metastatic lesions
pain/ache in the affected limb with movement/loading
Mechanical pain of cancer
pain at night, that often wakes patient up
Tumorigenic pain
Metastatic hypercalcemia
“Bones, stones, growns, thrones, and psychiatric overtones” due to paraneoplastic syndromes (80%) OR osteolytic lesions (20%)
Diffuse tenderness over affected limb, Limited ROM depending on location/pain levels, Neurologic deficits (tumor compressing the spine)
Common exam findings for metastatic bone cancer
8-30%
Pathological fracture is the presentation for _______ of patients with metastatic bone cancer
Xrays, CT chest/abd/pelvis, CT guided core needle biopsy (for bone lesions), PET or bone scans
Imaging workup for patient with a single bone lesion and NO diagnosis of cancer
CBC with diff, ESR, CRP, CMP (Ca, phosphate, LFT, ALP), SPEP/UPEP (multiple myeloma), PSA (prostate), UA (renal)
Lab workup for patient with a single bone lesion and NO diagnosis of cancer
Xrays (AP/lateral)
Most important imaging 🏆 in bone tumors AND best overall depiction of aggressiveness
Pain control, maintenance of independence
Goal of treatment in metastatic disease
Radiation (if none previously and good for pain control), Bisphosphonates (usually IV pamidronate)
Non-op treatment for metastatic bone lesion
Stabilize fractures (IMN/plating to improve QOL), Post-op radiation (unless dying rn or previous radiation)
Operative treatment for metastatic bone lesion
48 months (thyroid), 40 months (prostate), 24 months (breast), variable but as short as 6 months (kidney), 6 months (lung)
Prognosis for metastatic bone lesions
Lipoma
A benign tumor located in the soft tissues that can be fatty, intramuscular, or extramuscular (common in sedentary men 40-60 y/o)
mobile, painless, palpable
Physical findings for lipoma
symptomatic, rapid growth
When do you surgically treat lipomas
Sarcoma
A malignant tumor that arises from transformed cells of mesenchymal origin (AKA connective tissue) that commonly metastasizes to the lung
painless rapidly growing mass
Physical findings for Sarcoma
MRI with contrast 🏆 , CBC, CMP, ESR/CRP
Workup plain for sarcomas
MRI
The dominant imaging modality for soft tissue tumors (good for fat, water, edema, calcifications - but will be disrupted by air and metal) GET WITH AND WITHOUT GADOLINIUM
Water
What is bright on a T2
Fat
What is bright on a T1
STIR
What type of MRI is best for detecting tumor tissue, water and edema
Heterogenous, Ill defined borders, surrounding edema
How do sarcomas look on MRI
Wide excisions, radiation to prevent reoccurence, NO chemo (unless lung metastasis)
Treatment of Sarcomas
Multiple Myeloma
A neoplastic proliferation of plasma cells that results in osteoclastic stimulation (most common primary bone malignancy in adults - 2x in african americans, males, 40+)
Pancytopenia (anemia), Hypercalcemia, renal failure, Bence-Jones Proteins on UPEP
Lab markers for multiple myeloma - CRAB
Chemo, Bisphosphonates (reduce fracture incidence), operative ONLY for fracture stabilization
48 y/o male presents to the clinic for elbow pain and fatigue. He states that his arm just hurts DEEP. Basic labs reveal an elevated creat, hypercalcemia, low Hgb, low Hct, and low RBCs. X-rays reveal punched out lesions. What is your treatment plan?
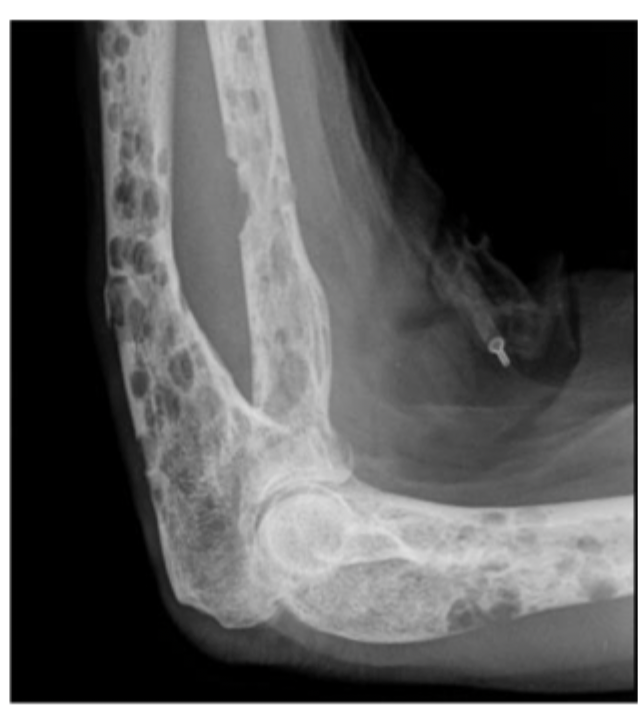
Renal failure (shortest survival rate)
Bad signs for Multiple Myeloma
Osteosarcoma
Most common malignant bone tumor in kids that typically arises as solitary lesions within the fastest growing areas of the long bones of children (like during a growth spurt)
Distal femur, proximal tibia, proximal humerus
Common spots for Osteosarcoma - tbh can be anywhere
X-rays (periosteal destructive lesions), MRI (evaluate extent of bone damage and soft tissue involvement), Head/chest/ABD/pelvis CT, Core needle biopsy, CBC, CMP (ALP, Ca)
8 y/o male presents to the clinic for leg pain that wakes him up at night and is worse with weight bearing. His mother reports that he’s lost weight over the last few weeks. You note a palpable mass on his hip. What do you want to order?
Neoadjunvant and adjuvant Chemo, Surgical resection with wide margins (limb salvation or amputation)
8 y/o male presents to the clinic for leg pain that wakes him up at night and is worse with weight bearing. His mother reports that he’s lost weight over the last few weeks. You note a palpable mass on his hip. Xrays reveal blastic and destructive lesions, an onion skin looking effect. What is your treatment plan?
onion skin, hair on end/sunburst, codman’s triangle
Signs of a periosteal reaction in osteosarcoma X-rays
Ewing’s Sarcoma
A small round blue cell sarcoma that is most commonly found in patients 5-25 ( 🥈 most common bone tumor in children)
Pelvis, distal femur, proximal tibia, femoral diaphysis, proximal humerus
Common locations for Ewings
Xray (moth eaten-appearance 🦋 ), MRI (soft tissue involvement), Bone scan (hot lesion 🔥), CT chest/abd/pelvis, ESR, CBC (anemia, leukocytosis), bone marrow biopsy required
8 y/o male presents to the clinic for leg pain that wakes him up at night and is worse with weight bearing. His mother reports that he’s lost weight over the last few weeks. You note a palpable mass on his hip and an antalgic gait on physical exam. Vitals are stable with the exception of a fever. What do you want to order?
Neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemo (doxorubicin, methotrexate), surgery with wide dissection (amputation, limb salvage), radiation can be used on large tumor
8 y/o male presents to the clinic for leg pain that wakes him up at night and is worse with weight bearing. His mother reports that he’s lost weight over the last few weeks. You note a palpable mass on his hip and an antalgic gait on physical exam. Xrays reveal a moth eaten appearance of the distal femur, WBCs up, ESR Up. Biopsy is positive for Ewings. What is your treatment plan?
40% for pelvis lesions, 15% with metastasis
Prognosis for Ewing’s
Non-ossifying fibroma
A benign fibrogenic lesion ( 🥇 most common benign bone tumor in children (5-15)) that is related to dysfunctional ossification and is usually incidentally found unless a fracture is present
Metaphyseal, 80% lower extremities
Common sites for Non-ossifying fibroma
Bubbly 🧋 lytic lesion with a scleoritic rim, cortex may be expanded and thin,
Xray findings for Non-ossifying fibroma
Non-op (resolves spontaneously), If there’s a fracture fix the fracture, Curettage and bone grafting if you need to fill the lesion’s void
Treatment for Non-ossifying fibroma
Osteoid Osteoma
Benign abnormal cells that develop in the bone (less than 1.5 cm) that causes reactive osteoid bone to form around it (self limited and pain is unrelated to activity)
Male (3x), 5-25 y/o
Patient Population for Osteoid Osteoma
Diaphysis or metaphysis of tibia and femur (50%), proximal femur, hip joint, scaphoid, proximal phalanx
Common locations for Osteoid Osteoma
X-rays, CT (study of choice 🏆 ), Bone scan ( 🔥 )
17 y/o male presents to the clinic for progressively worsening leg pain. He says that he’s take ibuprofen for the pain. On physical exam you note erythematous, swollen, tender tibia. What you want to order?
joint effusion, atrophy, painless swelling, contracture, limp, muscle atrophy
Physical findings for osteoid osteoma near a joint
Postural scoliosis, paravertebral muscle spasms
Physical findings for osteoid osteoma associated scoliosis
Observation, NSAIDs ( 🥇 First line)
17 y/o male presents to the clinic for progressively worsening leg pain. He says that he’s take ibuprofen for the pain. On physical exam you note erythematous, swollen, tender tibia. Xrays reveal intensely reactive bone around a radiolucent nidus (less than 1.5 cm). CT reveals a nidus with scleoritic rim. What is your 1st line treatment plan?
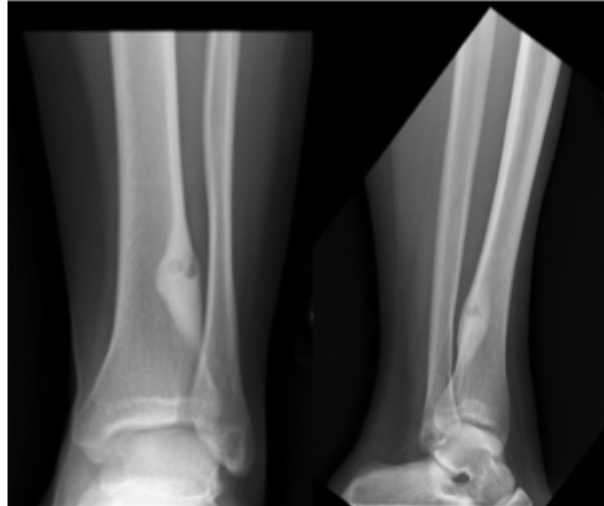
percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (under CT guidance - Call Jankly our IR bestie), Surgical resection with curettage
17 y/o male presents to the clinic for progressively worsening leg pain. He says that he’s take ibuprofen for the pain. On physical exam you note erythematous, swollen, tender tibia. Xrays reveal intensely reactive bone around a radiolucent nidus (less than 1.5 cm). CT reveals a nidus with scleoritic rim. What is your operative treatment plan?
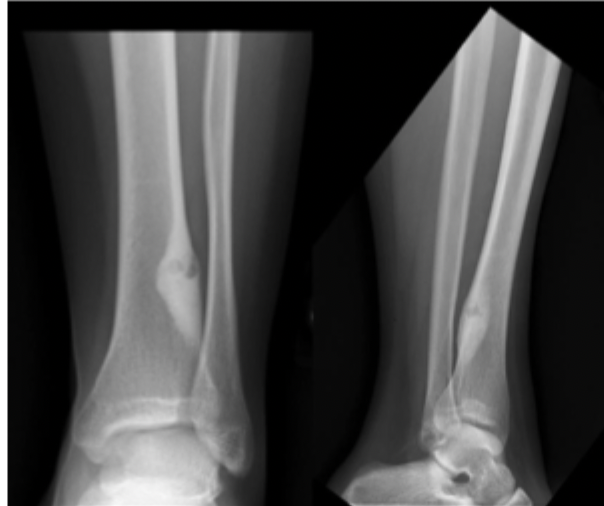
Pain typically resolves in ~ 3 years, Lesions spontaneously resolve in 5-7 years, In the spine early resection leads to resolution of scoliosis in kids under 11 y/o
Prognosis of Osteoid Osteoma