Bone Tissues and Anatomy Overview
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
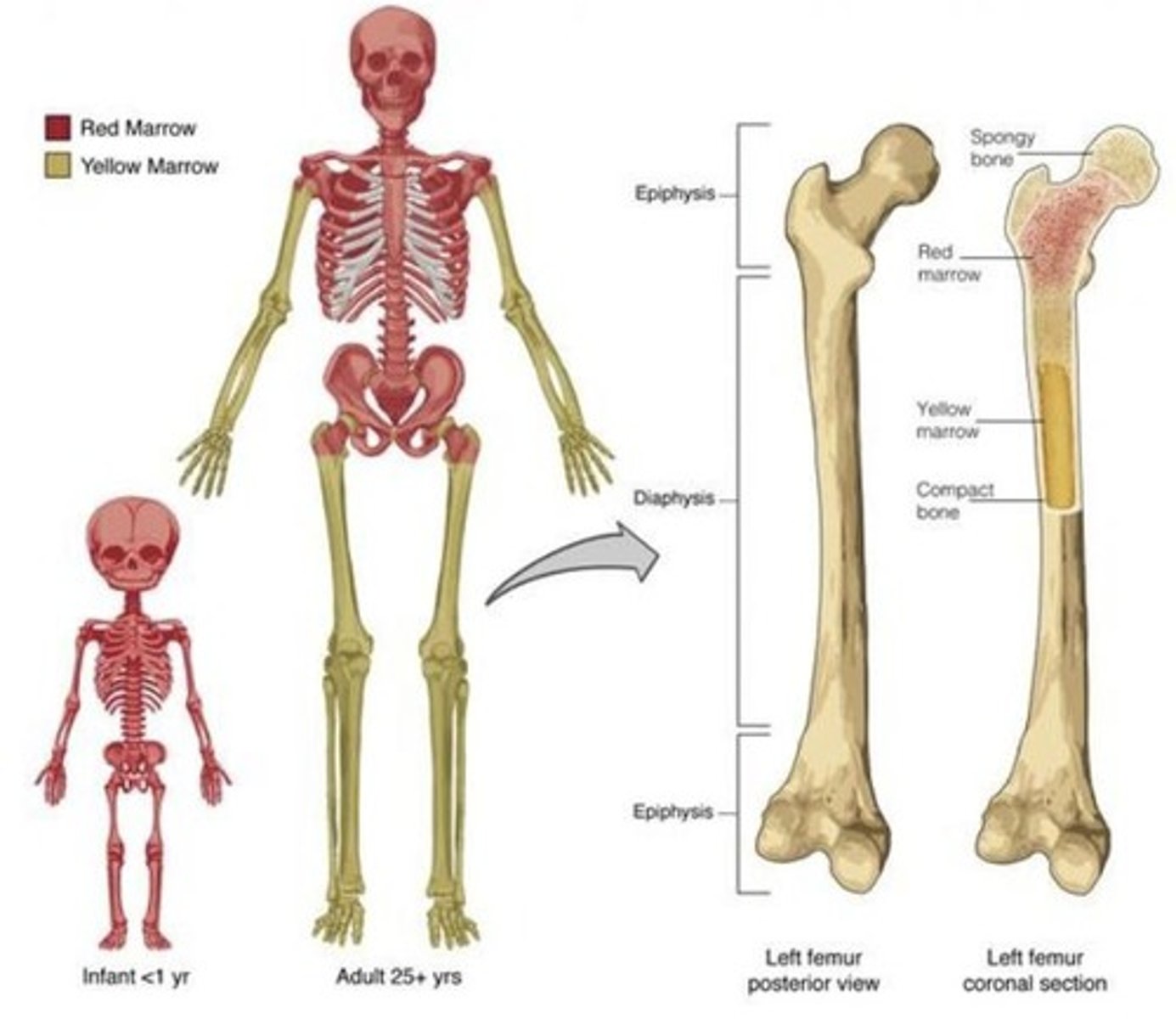
Epiphysis
Ends of long bones, contains articular cartilage.
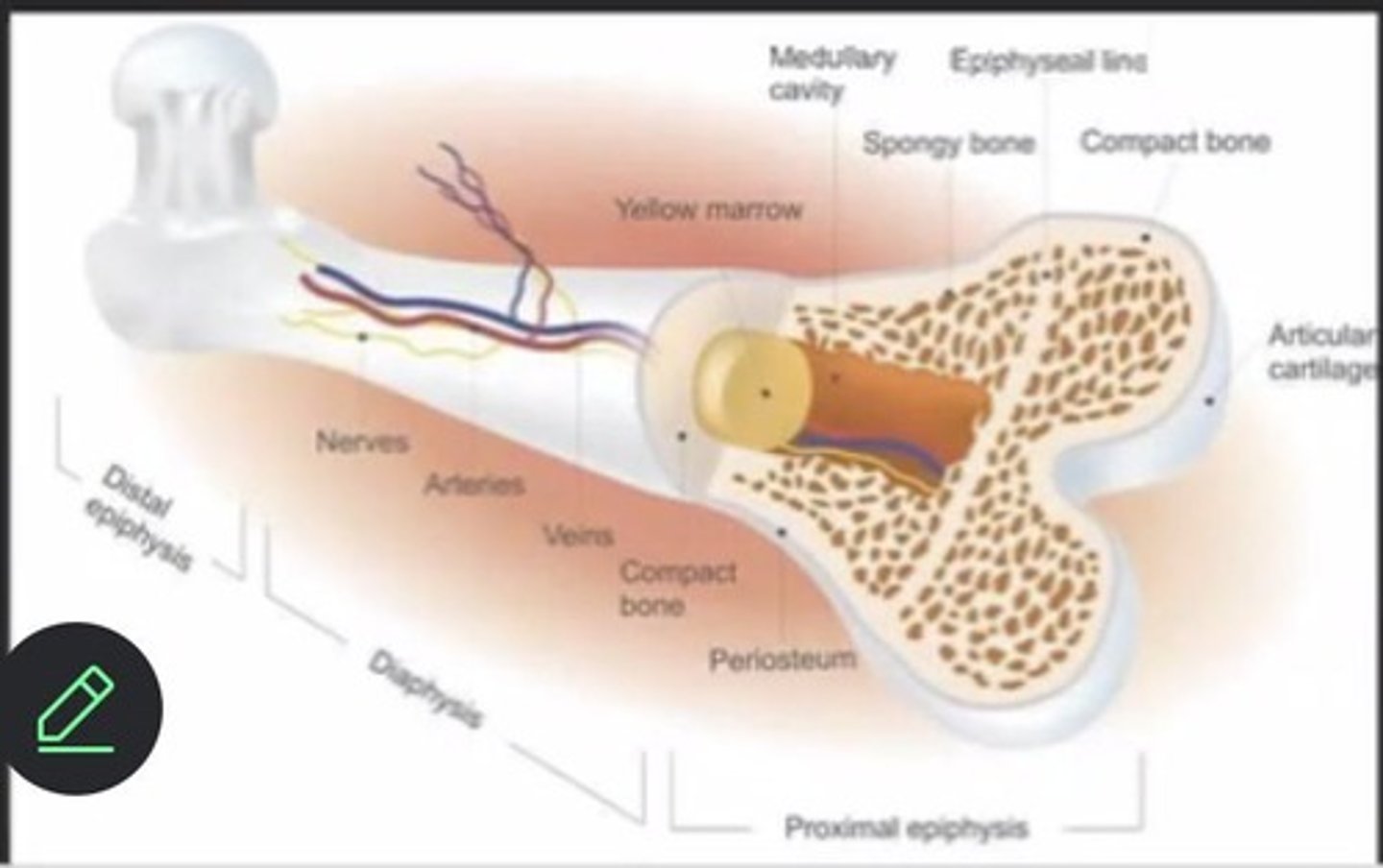
Metaphysis
Growth zone between epiphysis and diaphysis.
Diaphysis
Shaft of the bone, provides diameter.
Proximal Epiphysis
End of bone closest to torso.
Distal Epiphysis
End of bone farthest from torso.
Articular Cartilage
Hyaline cartilage covering bone ends at joints.
Spongy Bone
Loose bone tissue, contains red marrow.
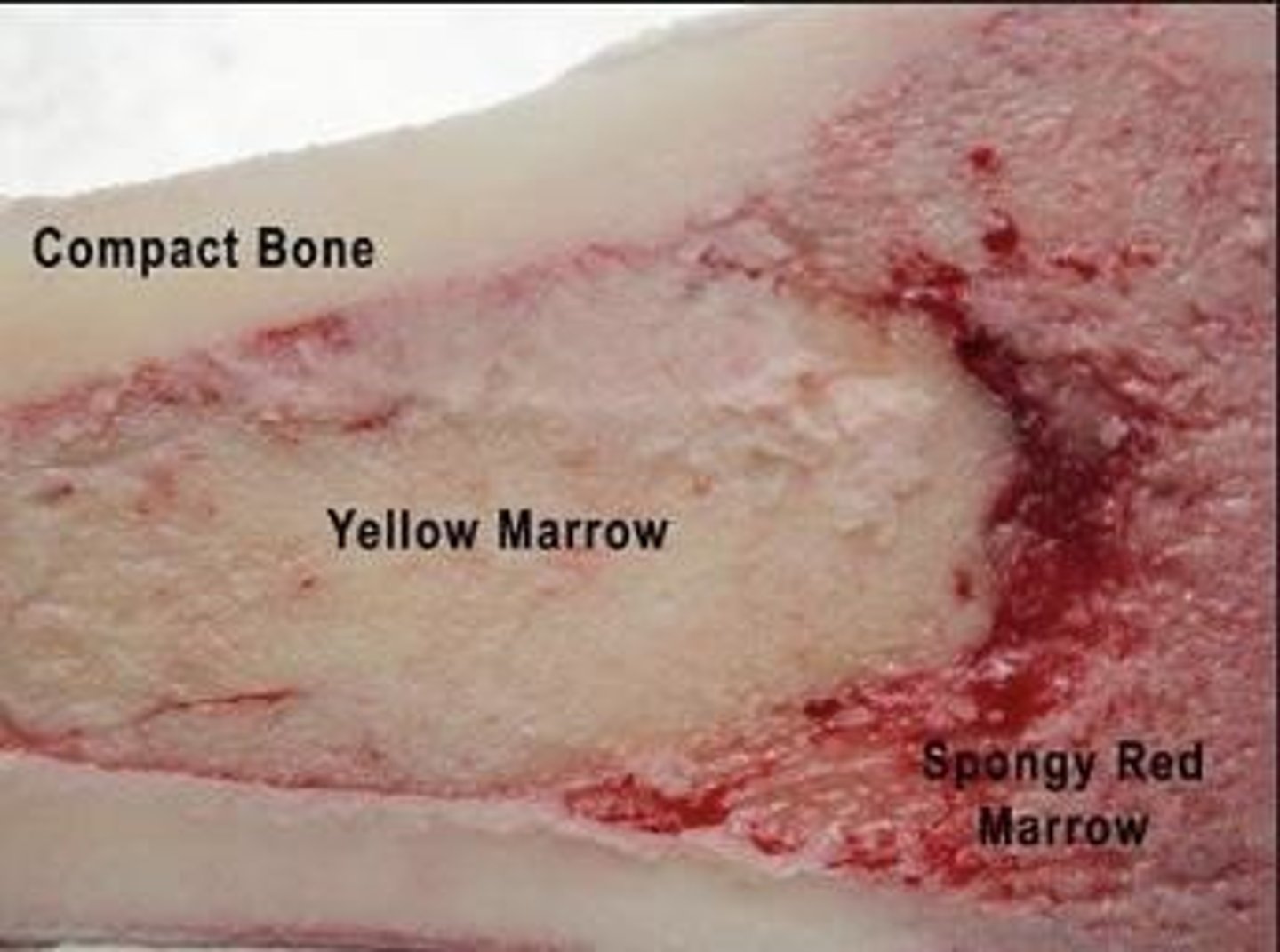
Red Marrow
Site of blood cell production in bones.
Endosteum
Inner surface of bone, aids remodeling.
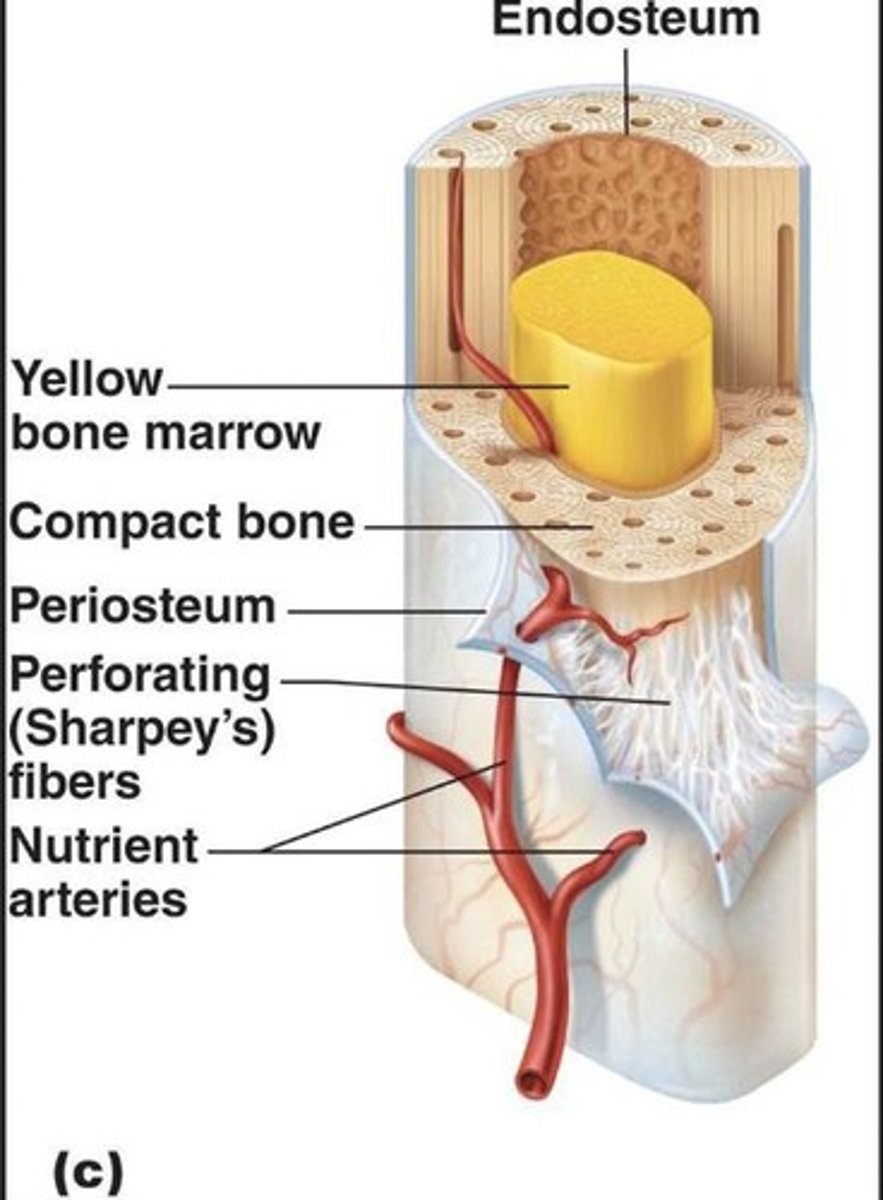
Compact Bone
Dense outer layer of bone structure.
Medullary Cavity
Hollow center of bone, contains yellow marrow.
Yellow Bone Marrow
Fat storage within the medullary cavity.
Periosteum
Outer layer, attachment point for muscles.
Skeletal System
Composed of bones, cartilage, and ligaments.
Bone Functions
Support, protection, movement, electrolyte balance.
Calcium Carbonate
Released to neutralize blood acidity.
Calcium Ions
Primary mineral for electrolyte balance.
Hematopoiesis
Production of blood cells in bone.
Bone Tissue
Connective tissue undergoing mineralization.
Mineralization
Hardening process through calcium phosphate deposition.
Bone (Organ)
Group of tissues including osseous tissue.
Bone (Tissue)
Group of cells with extracellular matrix.
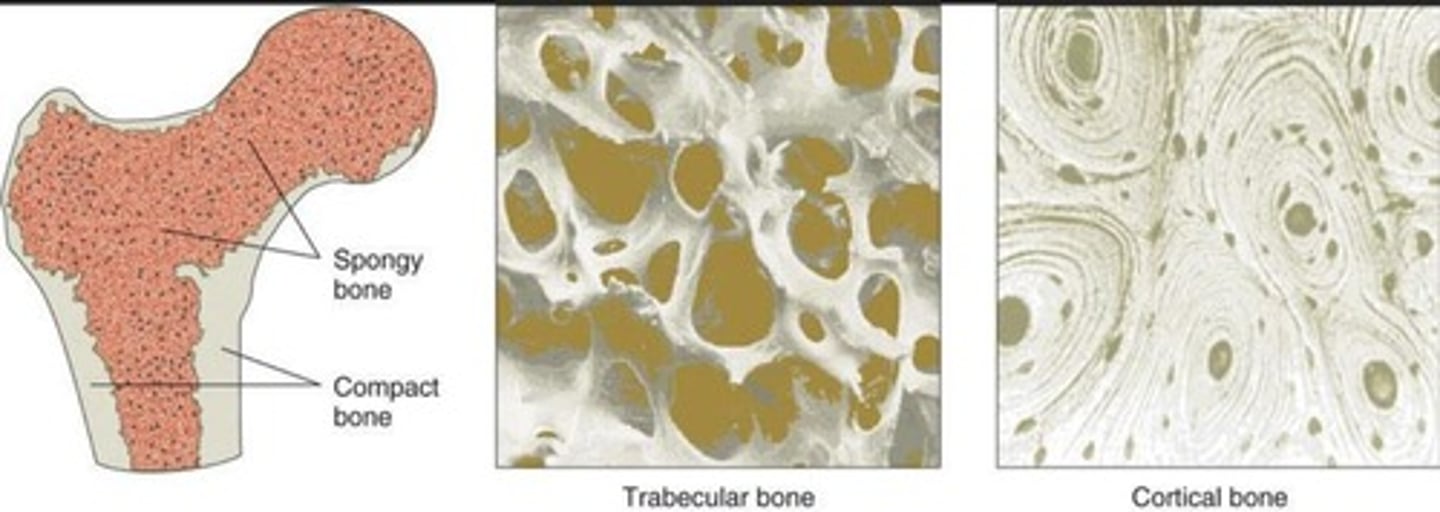
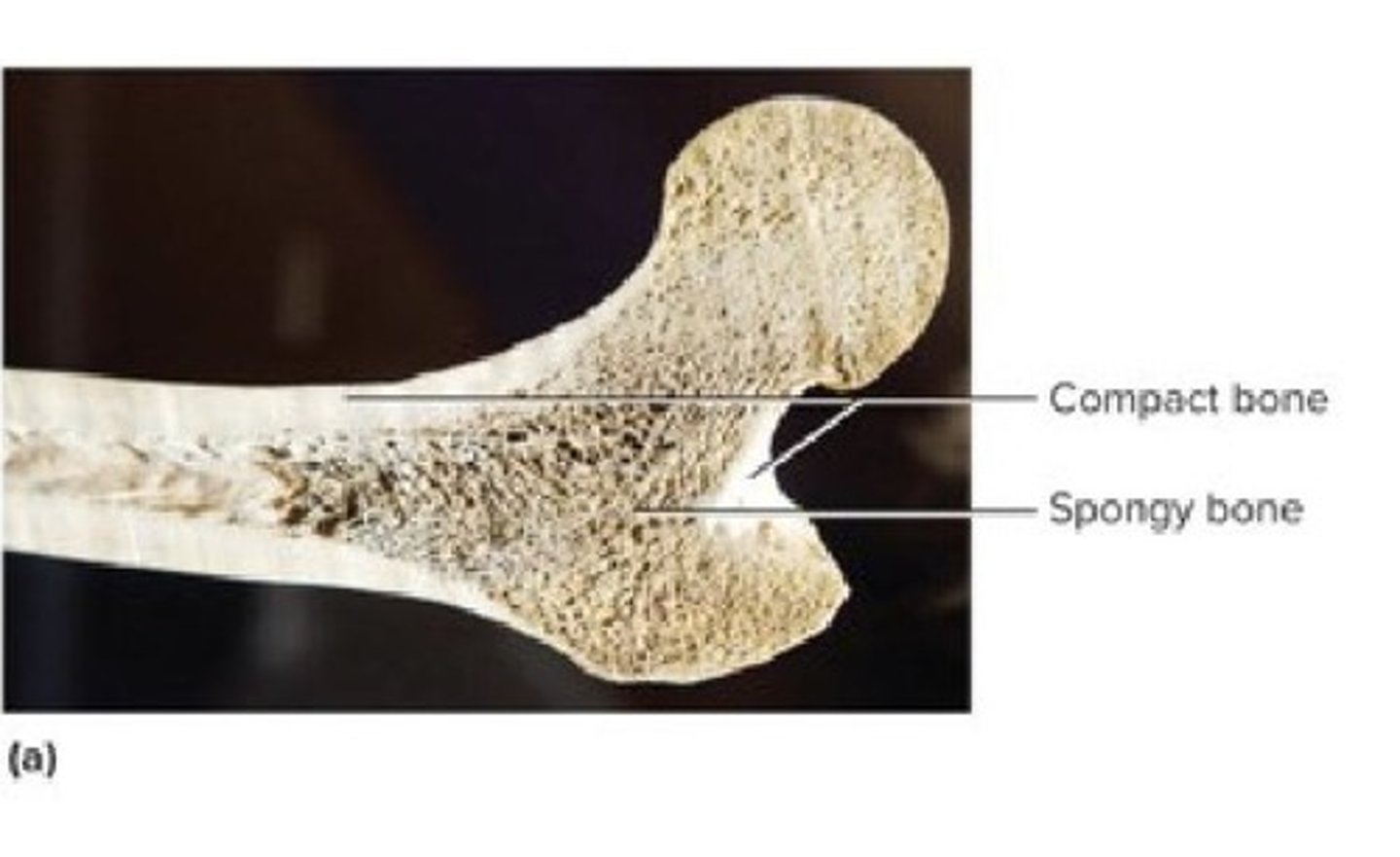
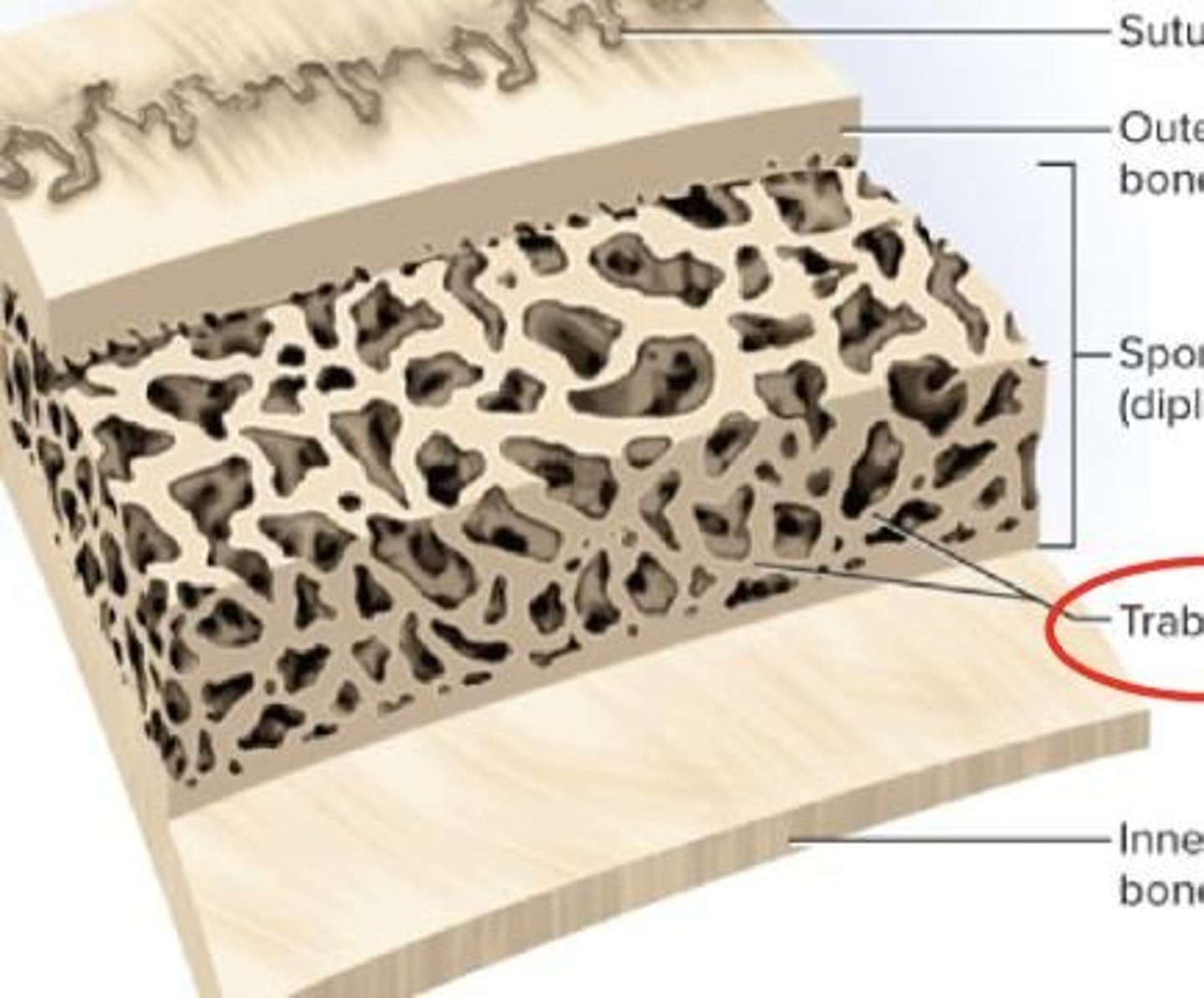
Compact vs. Spongy Bone
Compact is dense; spongy is loose and flexible.
Tribacular
Another term for trabecular bone.
Compact Bone
75% of skeleton, provides protection.
Spongy Bone
25% of skeleton, absorbs shock.
Diploe
Spongy bone in cranial bones.
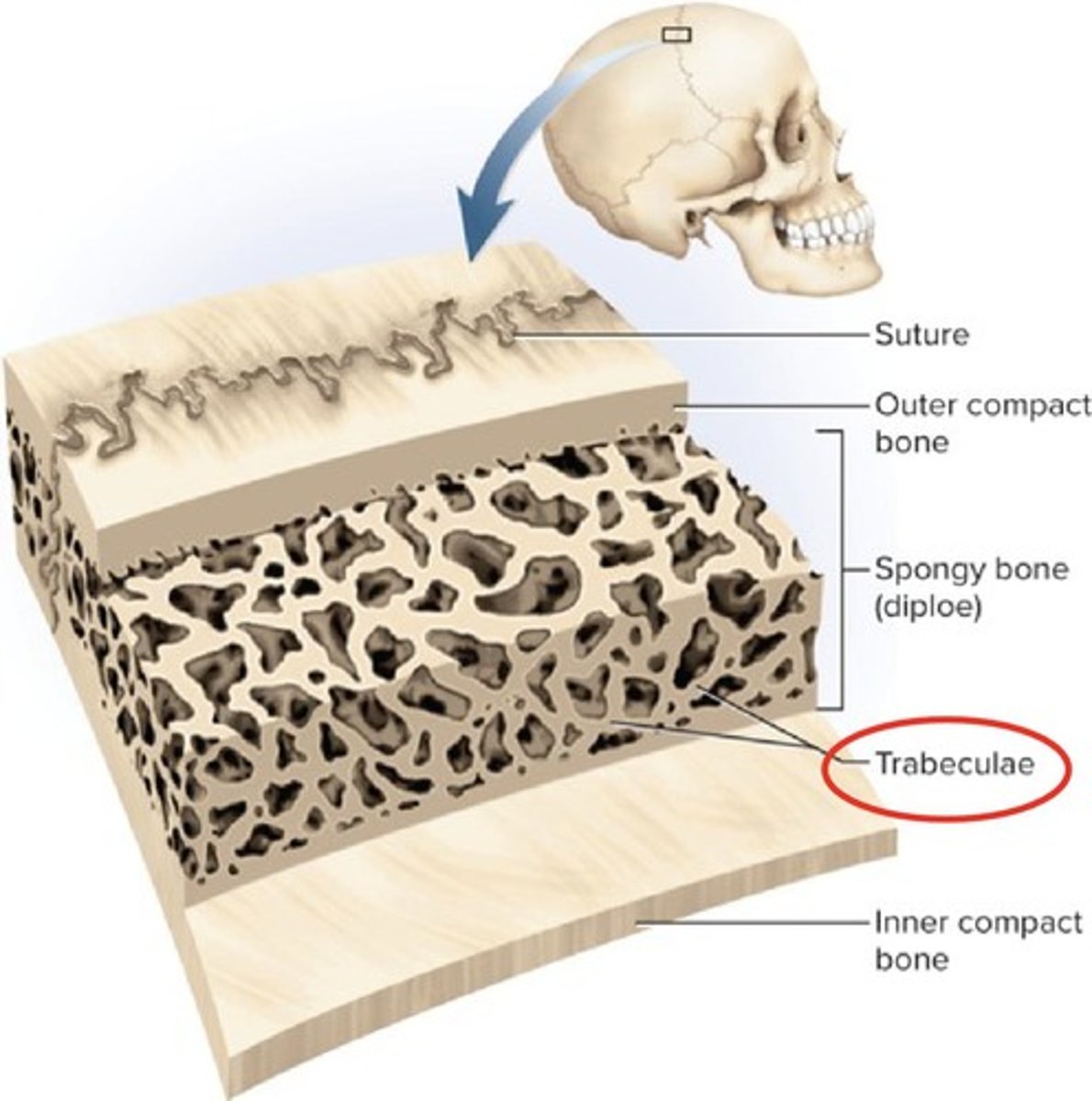
Red Bone Marrow
Produces red blood cells in bones.
Trabeculae
Thin bony structures in spongy bone.
Mechanical Stress Distribution
Aligns stress lines to resist forces.
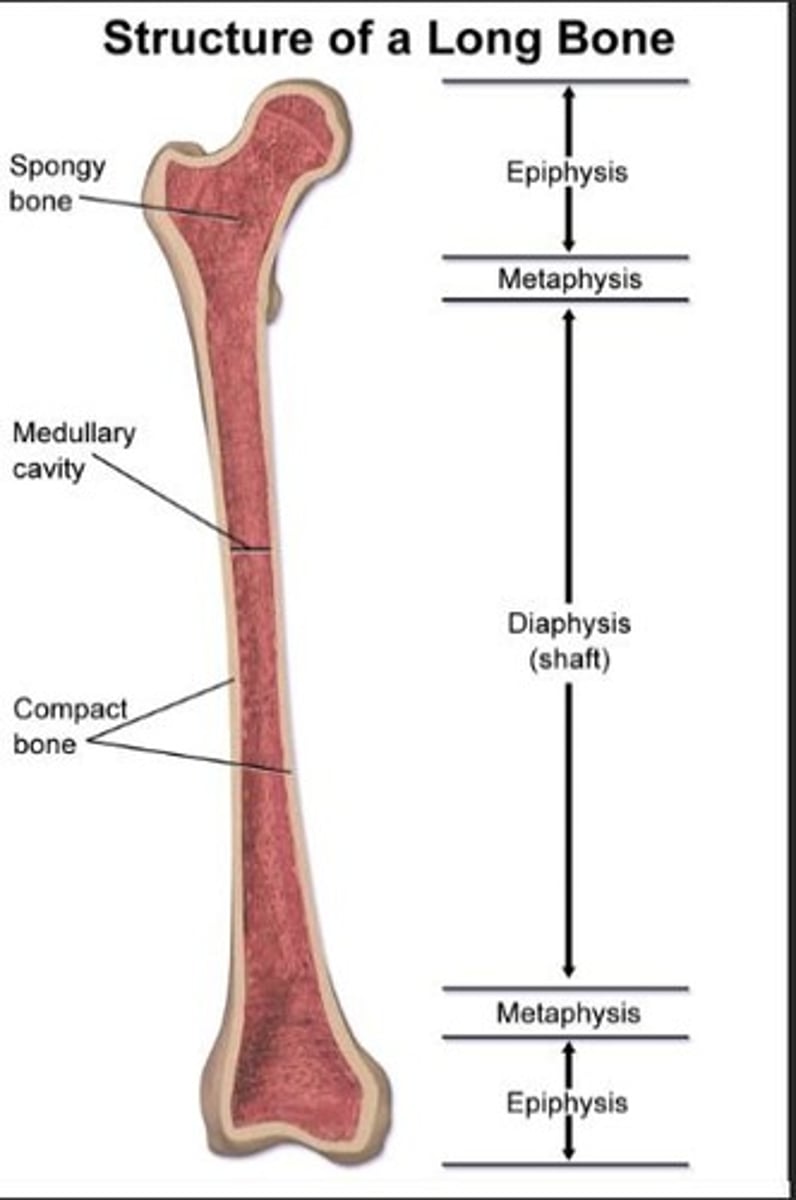
Diaphysis
Long shaft of a long bone.
Medullary Cavity
Hollow space containing bone marrow.
Epiphysis
Enlarged ends of long bones.
Metaphysis
Region where diaphysis meets epiphysis.
Growth Plate
Cartilage allowing longitudinal bone growth.
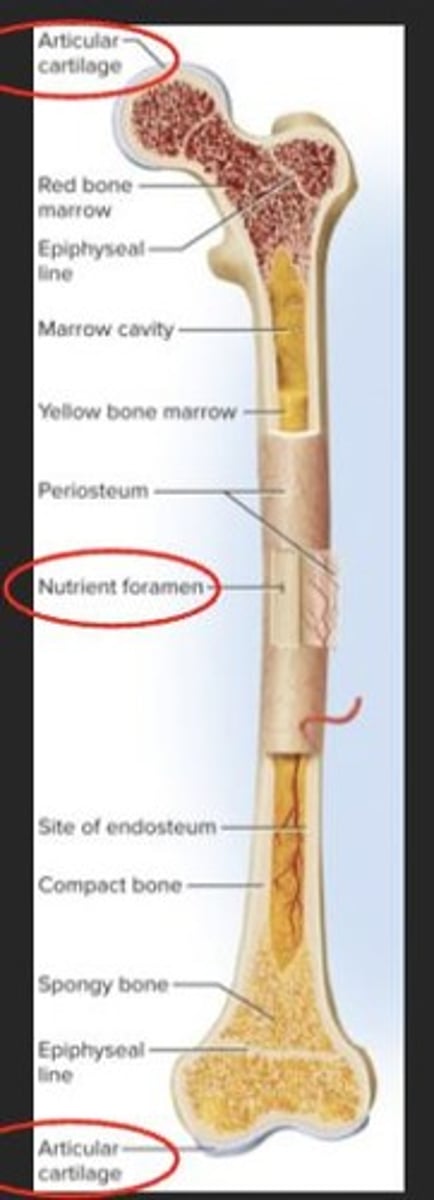
Articular Cartilage
Covers joint surfaces for smooth movement.
Nutrient Foramina
Holes allowing blood vessels and nerves access.
Yellow Bone Marrow
Stores lipids and fat in bones.
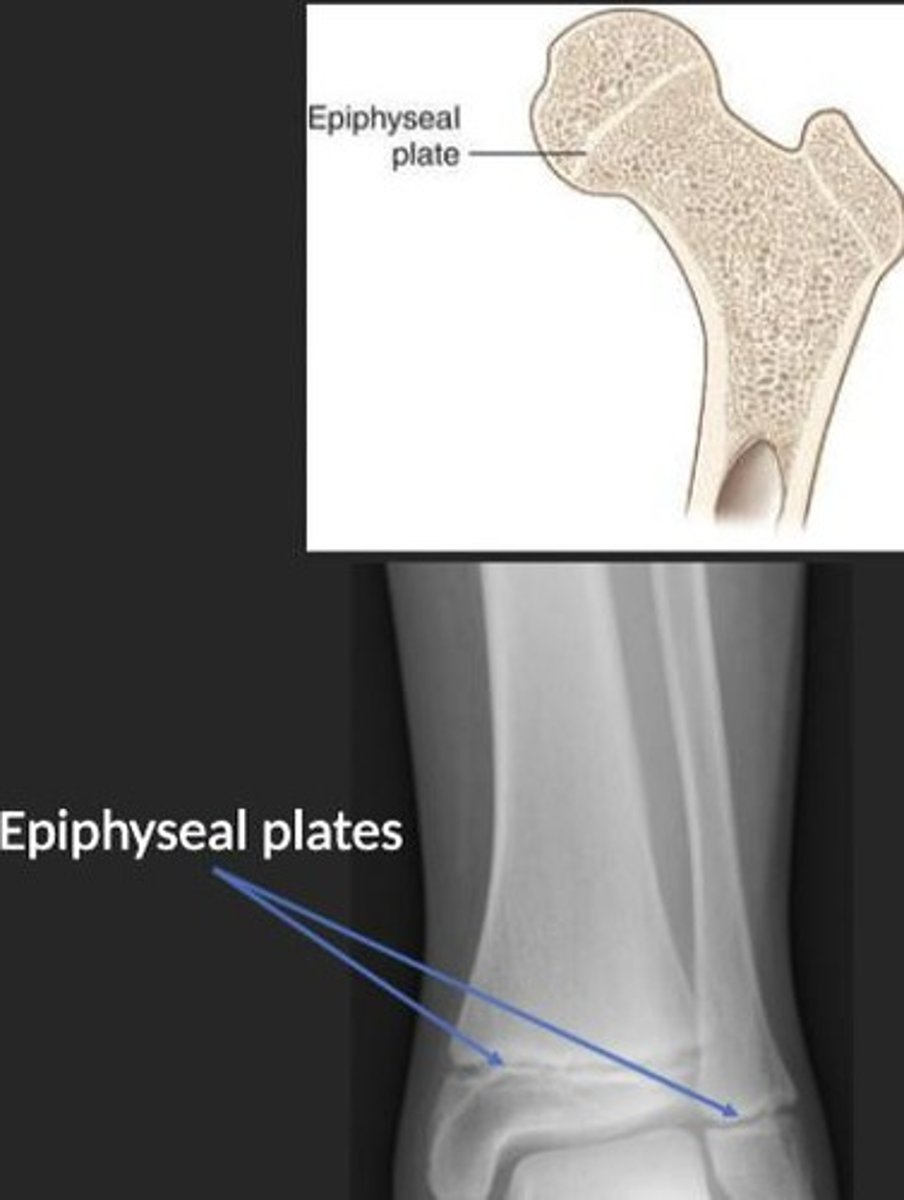
Epiphyseal Plate
Cartilage area enabling bone lengthening.
Epiphyseal Line
Scar left after growth plate closure.
Periosteum
Connective tissue covering outer bone surface.
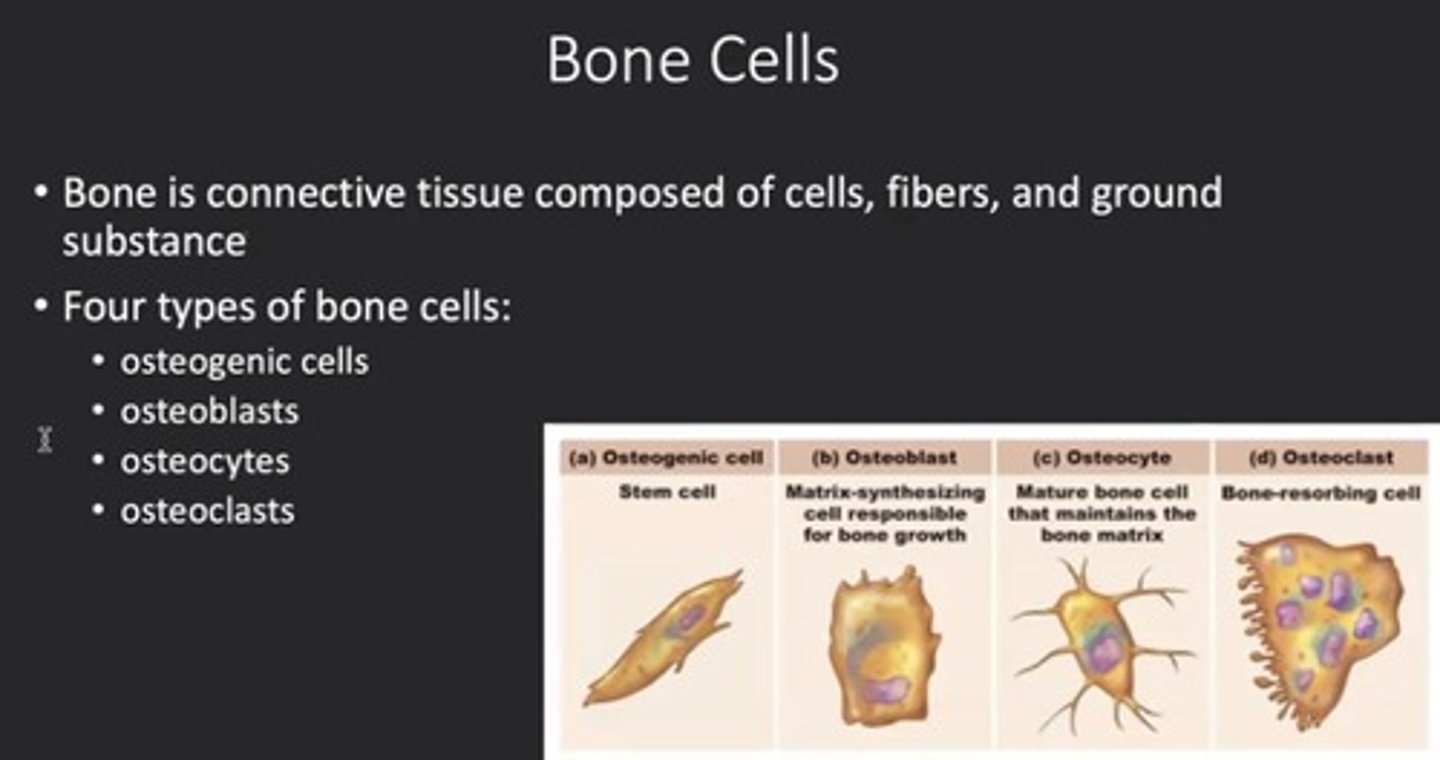
Osteogenic Cells
Stem cells that develop into osteoblasts.
Perforating Fibers
Collagen fibers connecting periosteum to bone.
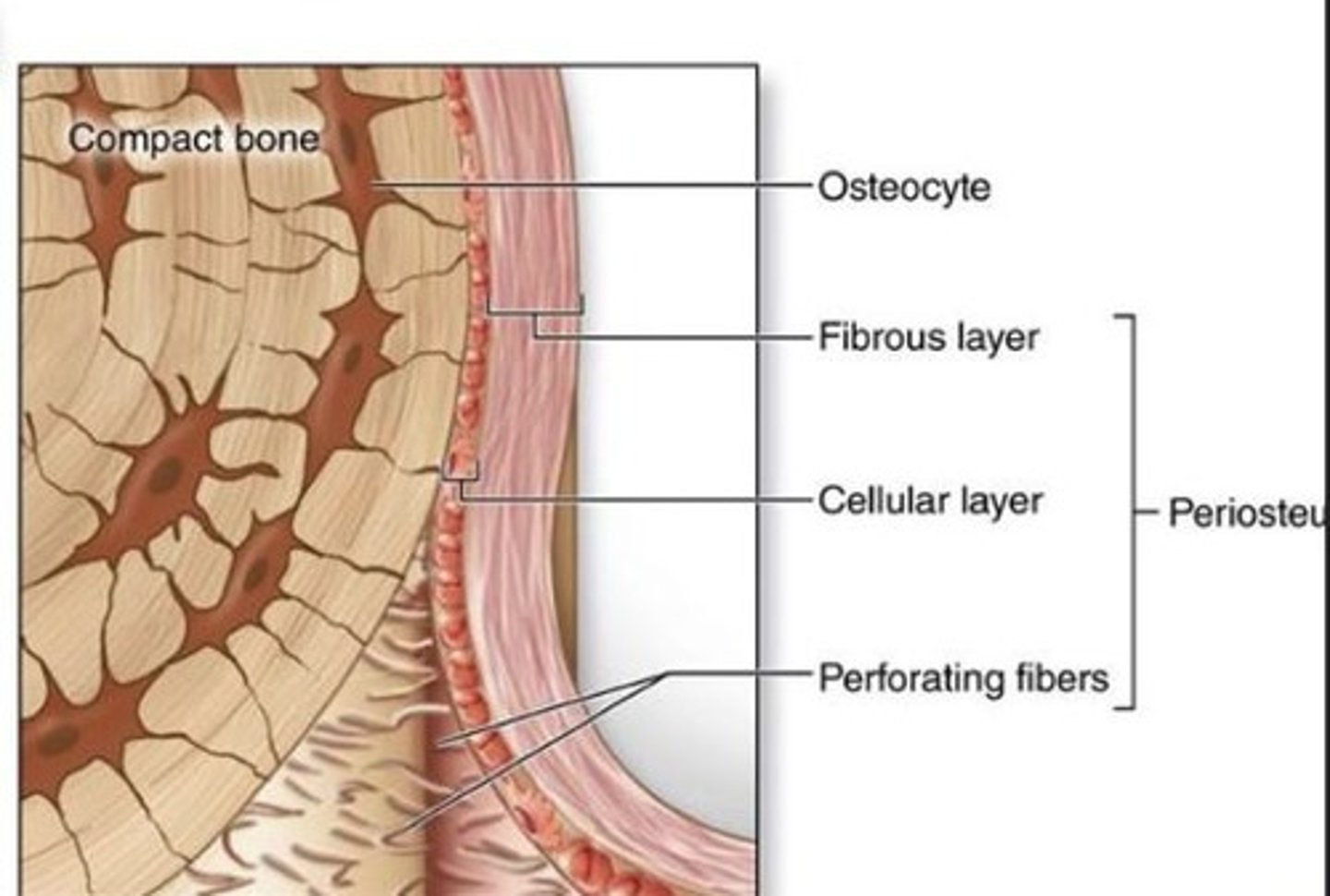
Endosteum
Inner lining of the medullary cavity.
Compact Bone
Lines marrow cavity and canals for blood vessels.
Spongy Bone
Covers honeycombed surfaces of bones.
Osteogenic Cells
Stem cells that produce osteoblasts.
Osteoblasts
Bone builders that create bone matrix.
Osteocytes
Maintenance cells managing bone matrix.
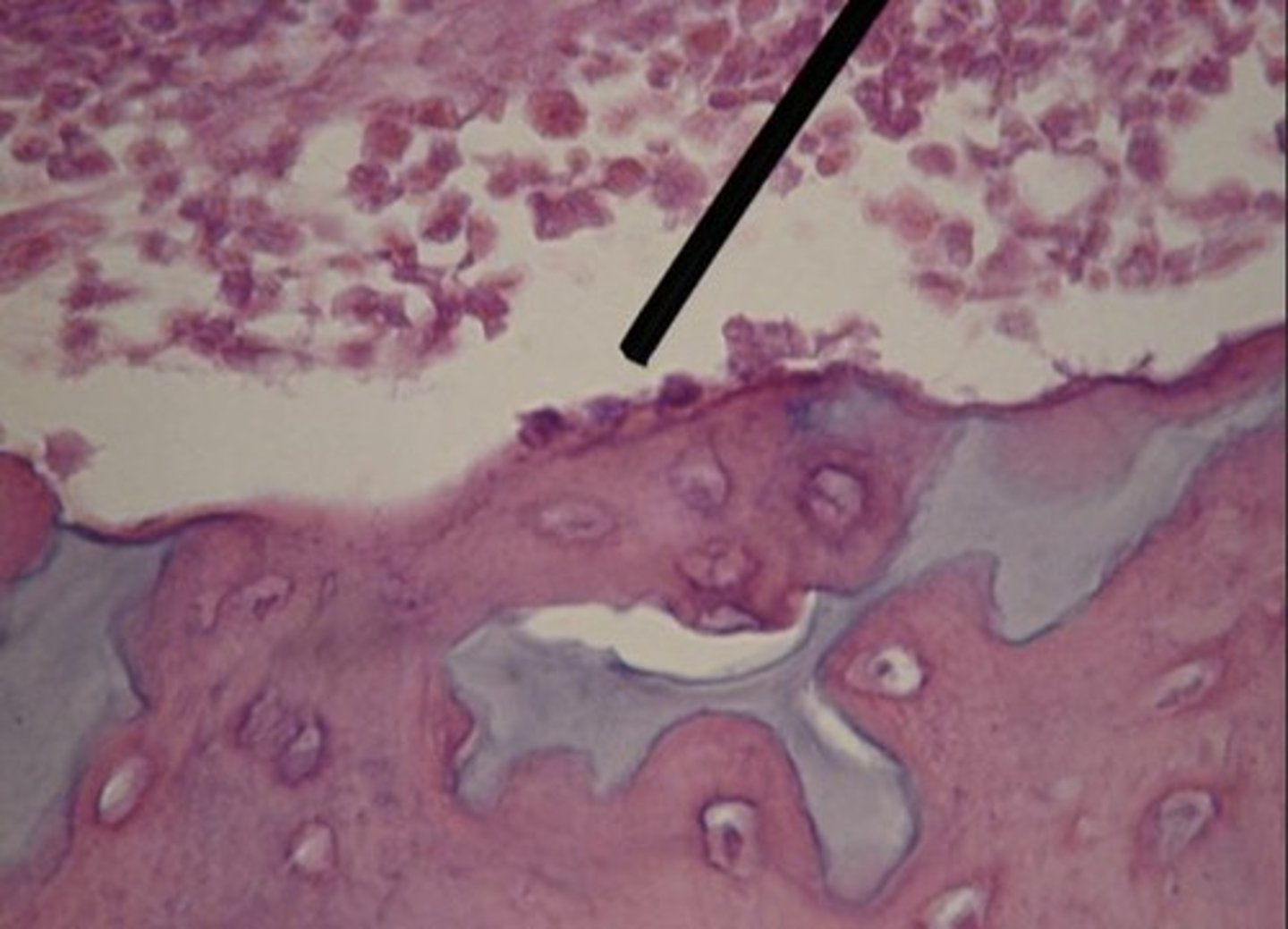
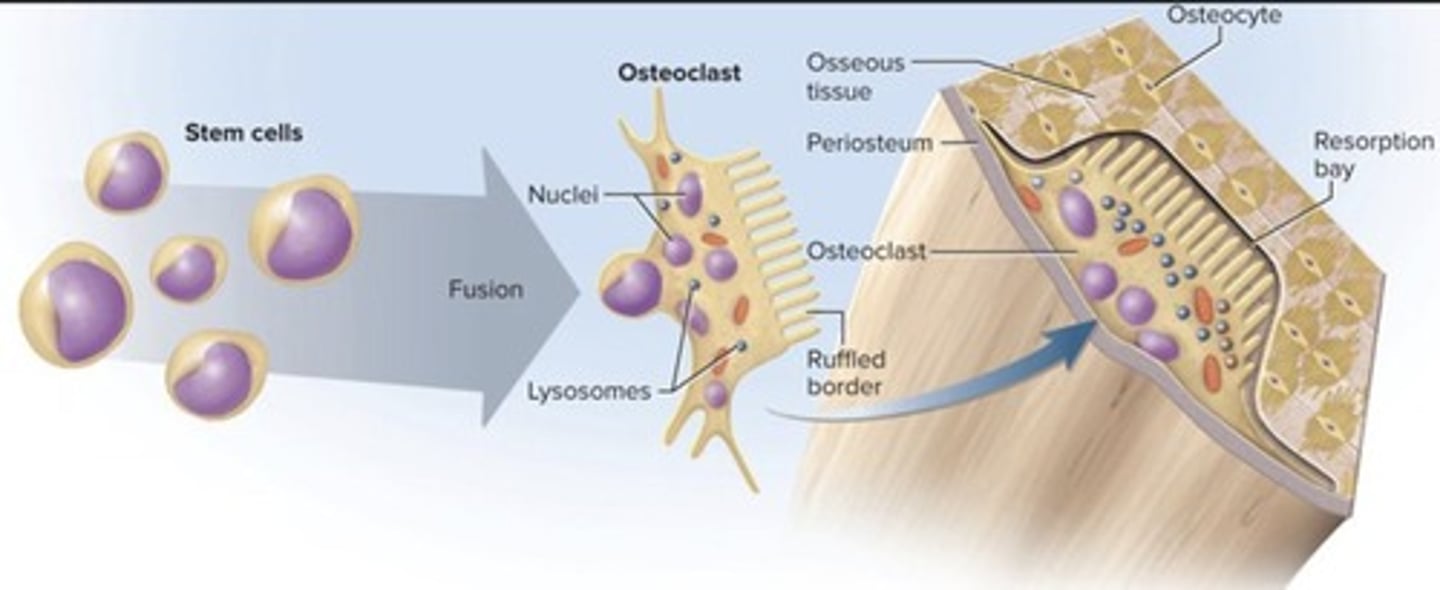
Osteoclasts
Cells that dissolve bone matrix.
Medullary Cavity
Hollow center of long bones.
Yellow Bone Marrow
Adipose tissue in long bones of adults.
Red Bone Marrow
Produces blood cells in specific adult locations.
Hypothermia
Condition where yellow marrow can revert to red.
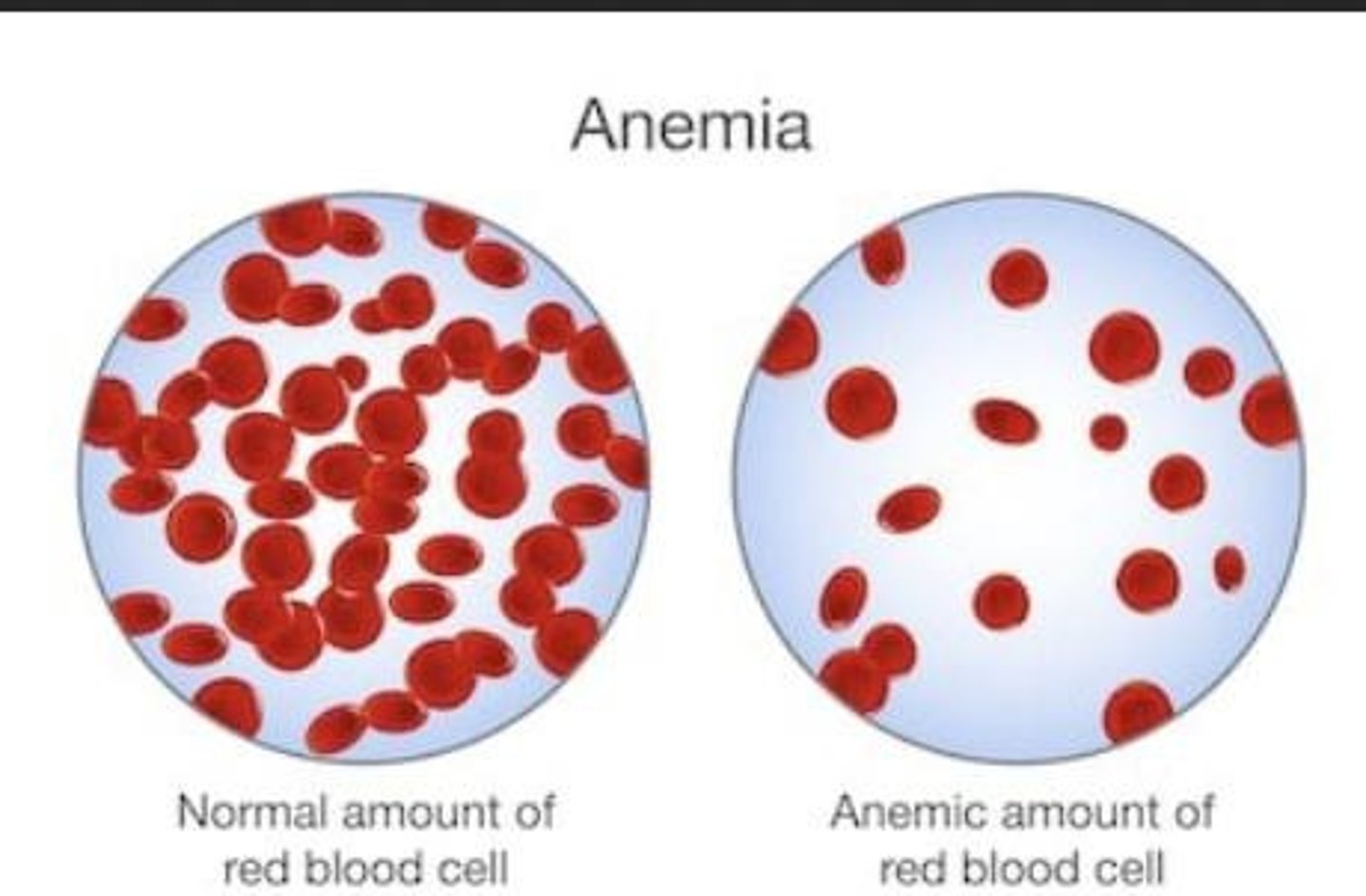
Anemic
Condition of low red blood cell count.
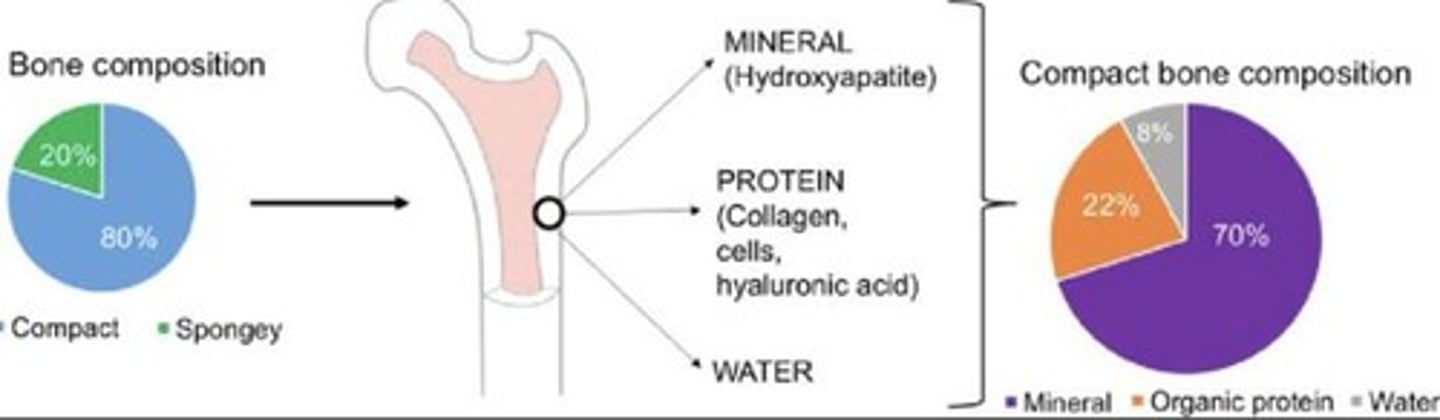
Bone Matrix
Composite material of inorganic and organic components.
Hydroxyapatite
Crystallized calcium phosphate providing bone hardness.
Collagen Fibers
Organic component providing flexibility to bone.
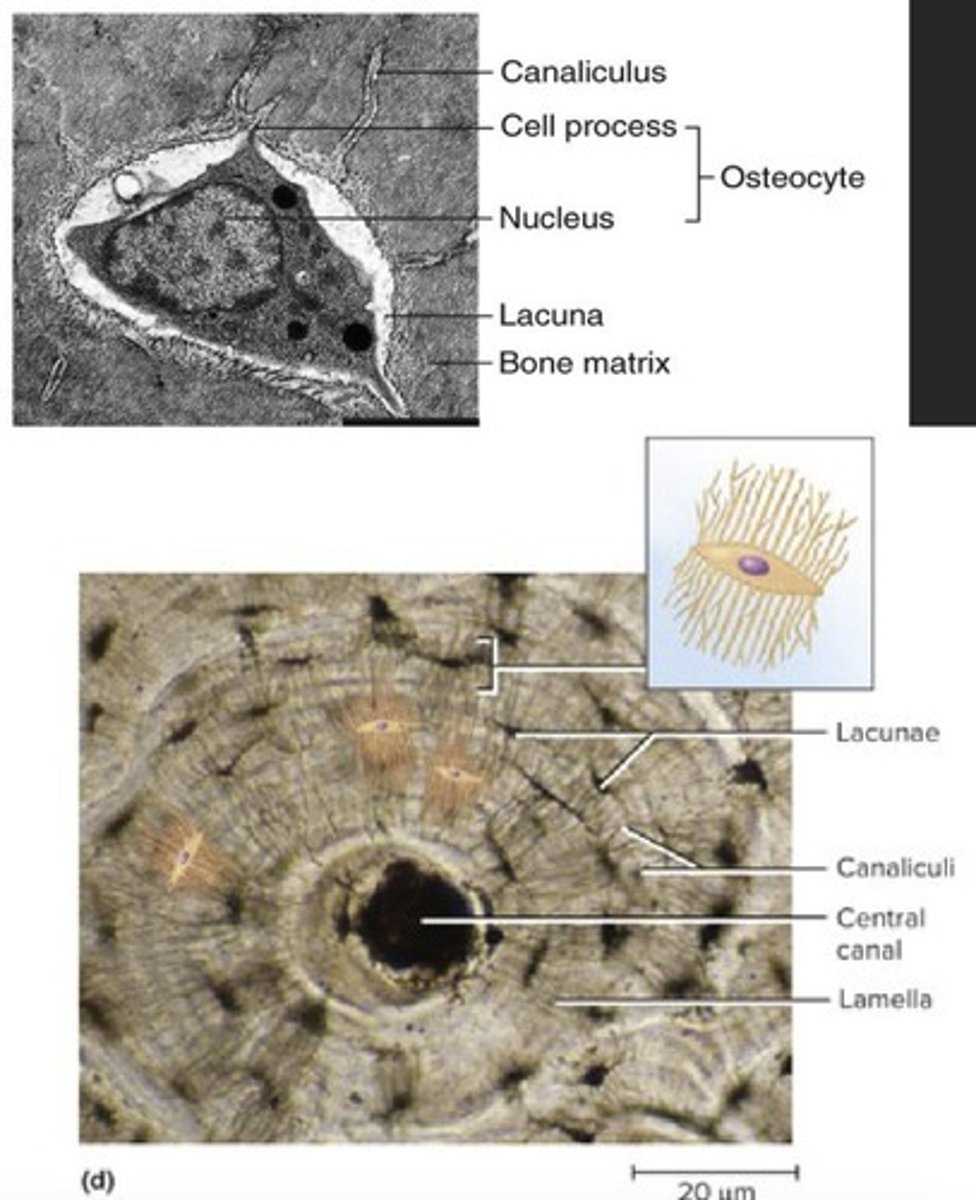
Osteon
Structural unit of compact bone.
Haversian Canal
Central canal for blood vessels and nerves.
Perforating Canals
Connect central canals to periosteum.
Spicules
Small spines in spongy bone structure.
Trabeculae
Plates forming the structure of spongy bone.
Lacunae
Small spaces housing osteocytes in bone.
Canaliculi
Tiny channels for communication between osteocytes.
Bone Remodeling
Process of growth, repair, and reshaping of bone.