Chemistry - Classification of Matter
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
5 Parts of Particle theory (PISAM)
All matter is made of Particles
The particles in a given substance are Identical
There are Spaces between the particles
The particles Attract one another
The particles are Moving
Solid to Gas
Sublimination
Gas to Solid
Deposition
Solid to Liquid
Melting
Liquid to Solid
Freezing
Liquid to Gas
Evaporation
Gas to Liquid
Condensation
Solid
Particles are very close
Strong attraction
Vibration only back and forth
Energy of motion is small compared to forces of attract
Liquid
Particles are close
Particles can slide past each other
Energy of motion is small compared to forces of attraction
Gas
Particles are very far apart
Particles move rapidly
Forces of attraction are almost zero compared to energy of motion
Force of Attraction
The closer the particles are, the stronger the attraction
Energy of Motion
When heat is added to particles, they move more
Elements
A simple substance that cannot be broken down into smaller parts or changed into another substance, it is on the periodic table and has ONE phase (PURE SUBSTANCE) It is made of a single atom
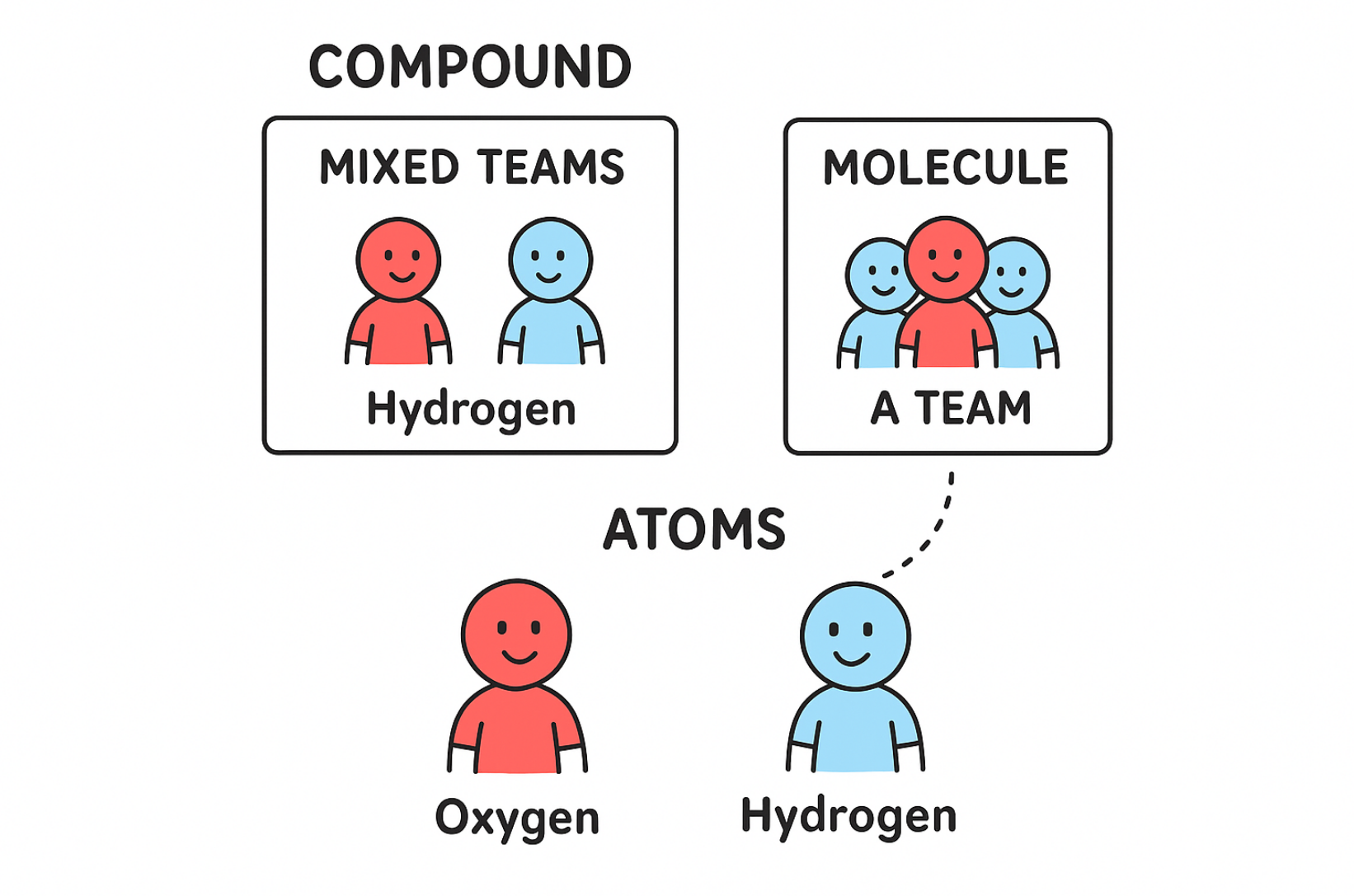
Compounds
a substance made from two or more different elements that have been chemically joined, can be broken down chemically, ONE phase, (PURE SUBSTANCE) a pure substance because it is made up of the same type of particle, but each particle is a molecule that is made of two or more different kinds of atoms bonded together (h20 2 part H 1 part O)
2 Types Of Pure Substances
Elements and Compounds
2 Types of mixtures
Homogenous (Solutions), Heterogeneous (Mechanical)
Pure Substance
All particles are the same in the substance
Homogeneous Mixture (Solution)
A mixture where the ingredients are mixed together so well that you can't see the different parts, looks like one substance (Ex., Kool Aid)
Heterogeneous Mixture (Mechanical)
A mixture where the components are not uniform and can be seen as separate, can see the parts (Ex., soup, pizza)
Solutions
Made up of a solute and a solvent
Solute
A part that dissolves in the solvent
Solvent
What the solute dissolves in
Classification of matter
Is it on the Periodic Table (Element)
Does it have a chemical first and last name (Compound)
Does it have 2 components but one phase (Solution)
Does it have 2 components and 2 phases (Heterogenous)
Exceptions: Some compounds have common names like water, sugar and salt