The Neuron and Brain
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
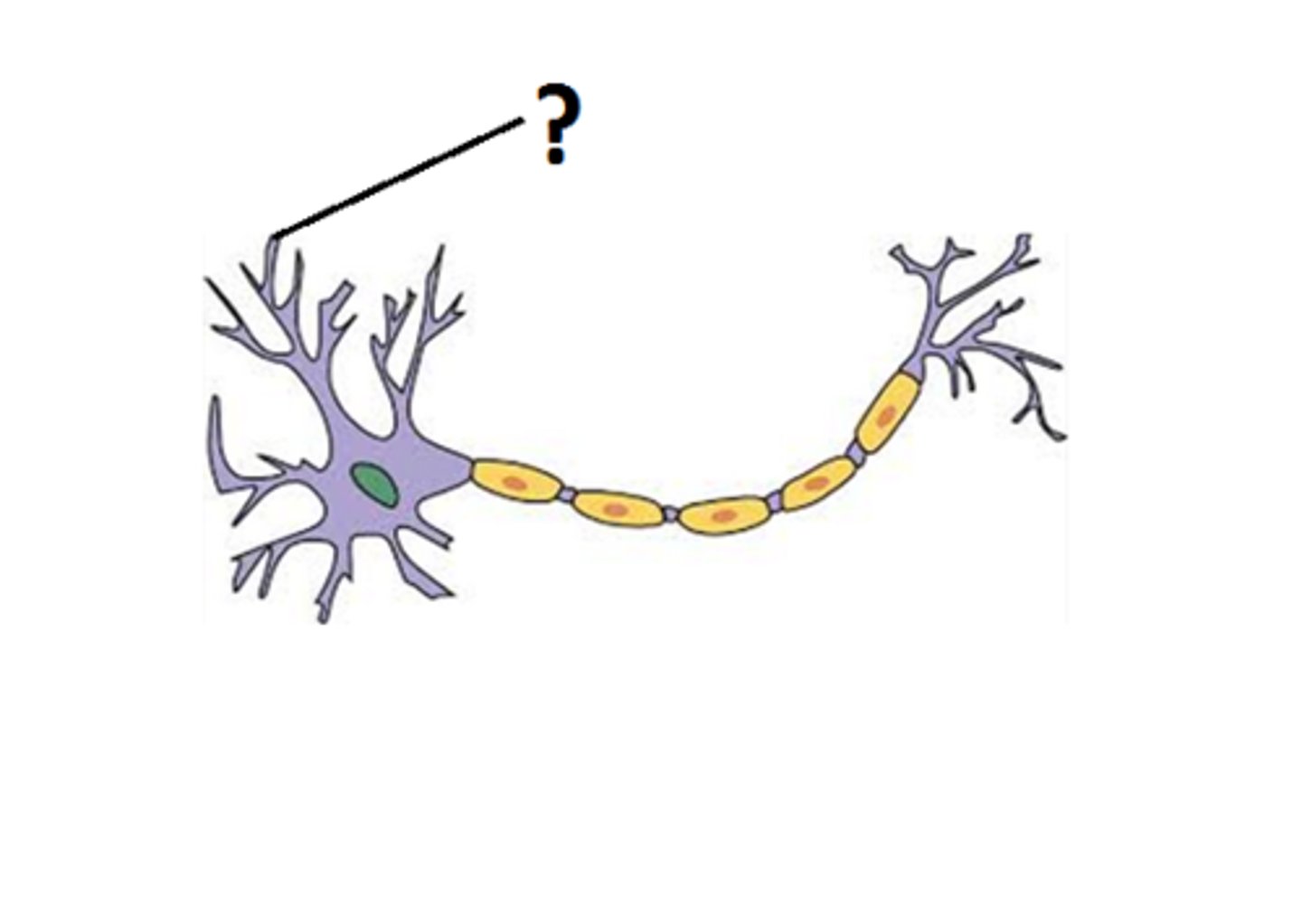
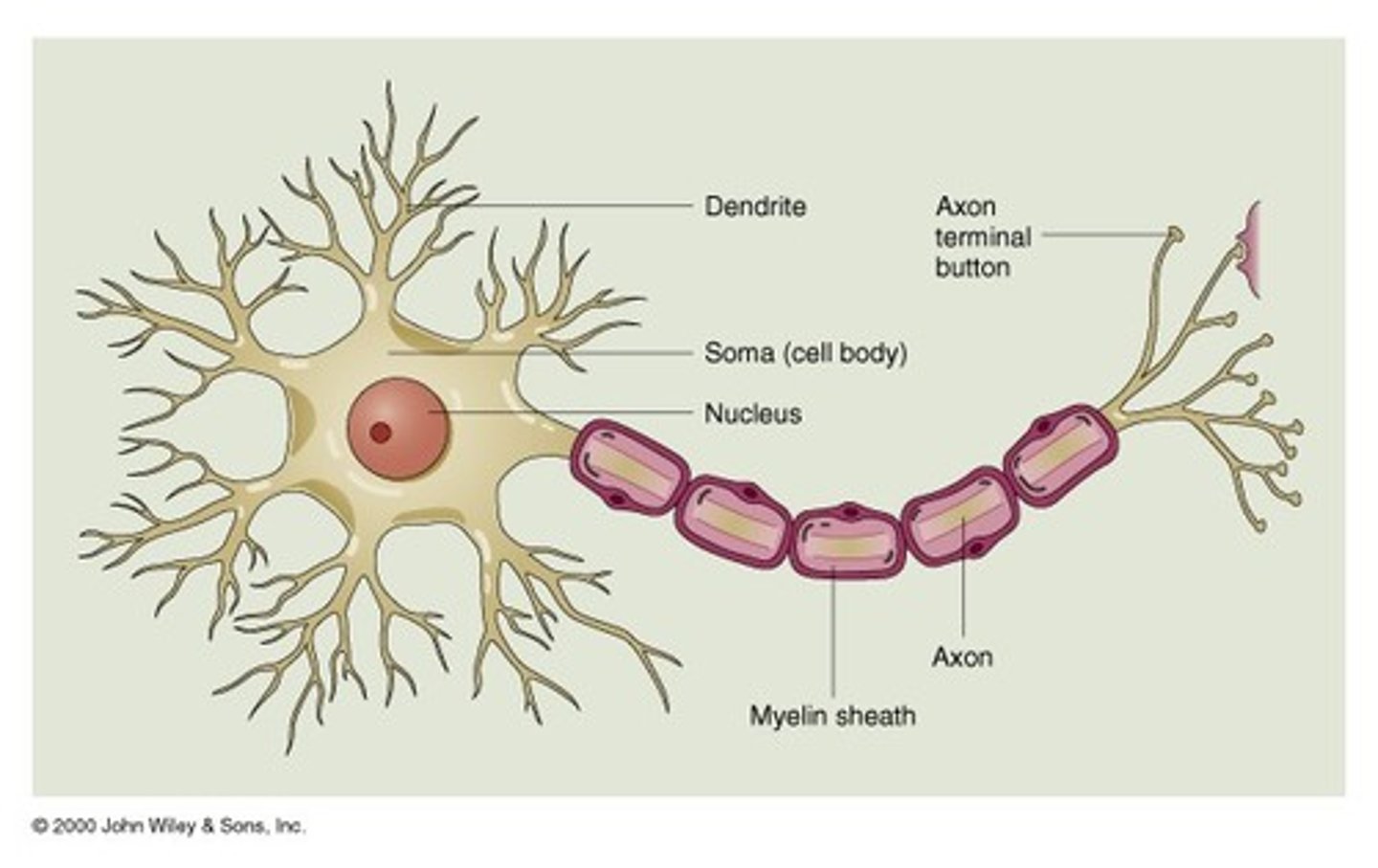
Dendrite
Receives incoming signals and carries them toward the cell body.
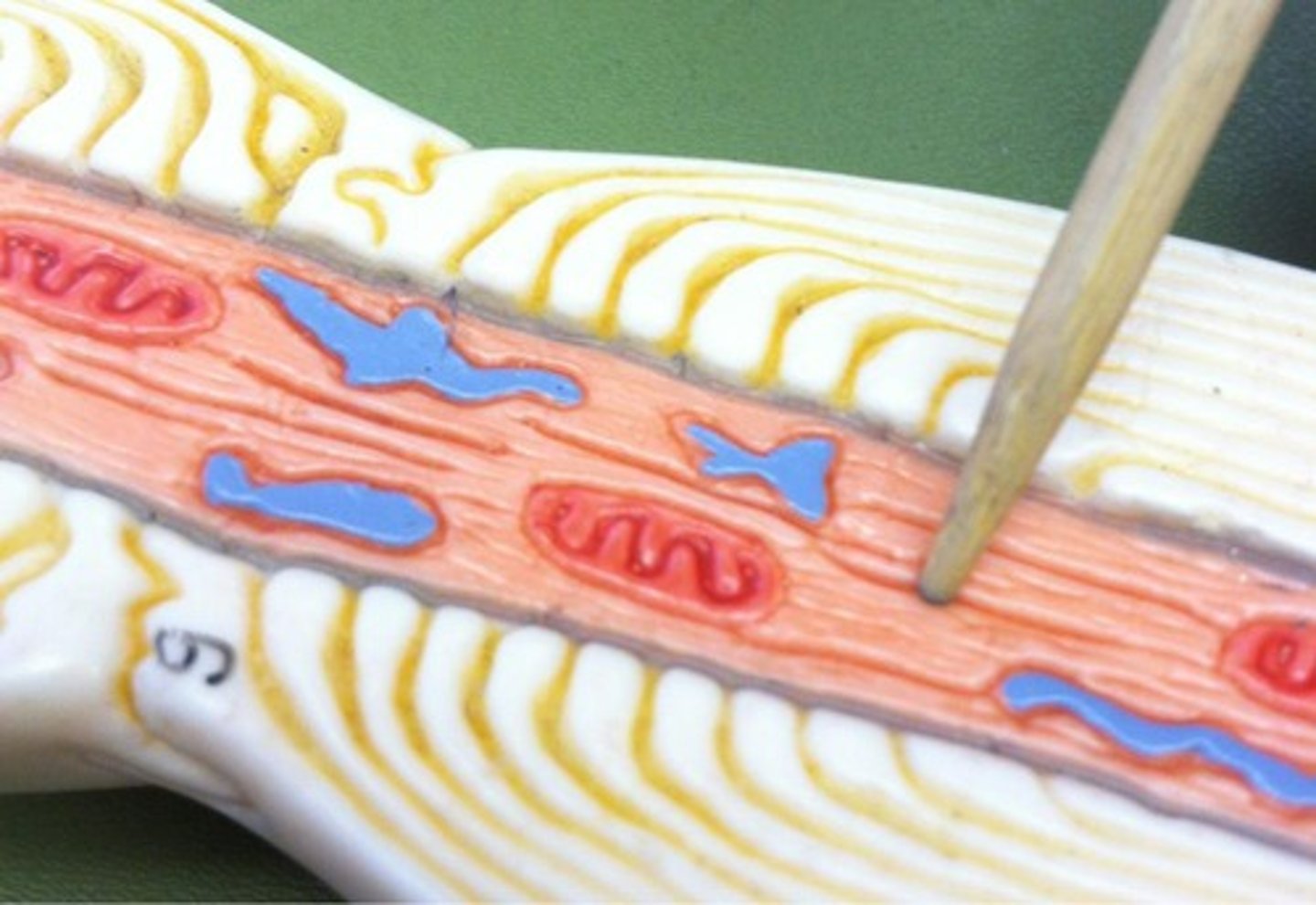
Neurofibrils
Cytoskeletal structures that provide support and help transport substances in neurons.
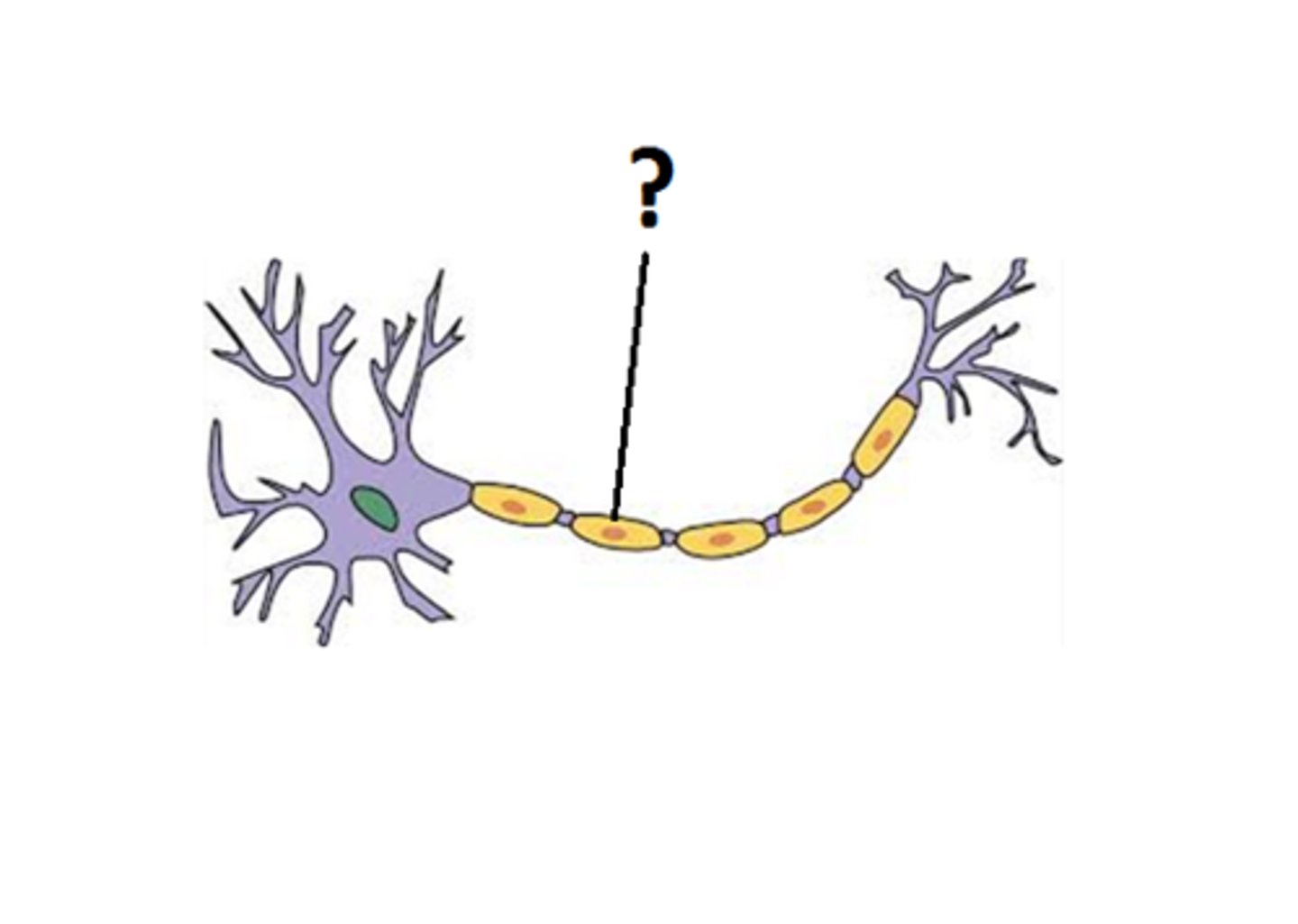
Myelin sheath
Fatty covering around axons that speeds up electrical impulses.
Nissl bodies
Clusters of rough endoplasmic reticulum in neurons; involved in protein synthesis.
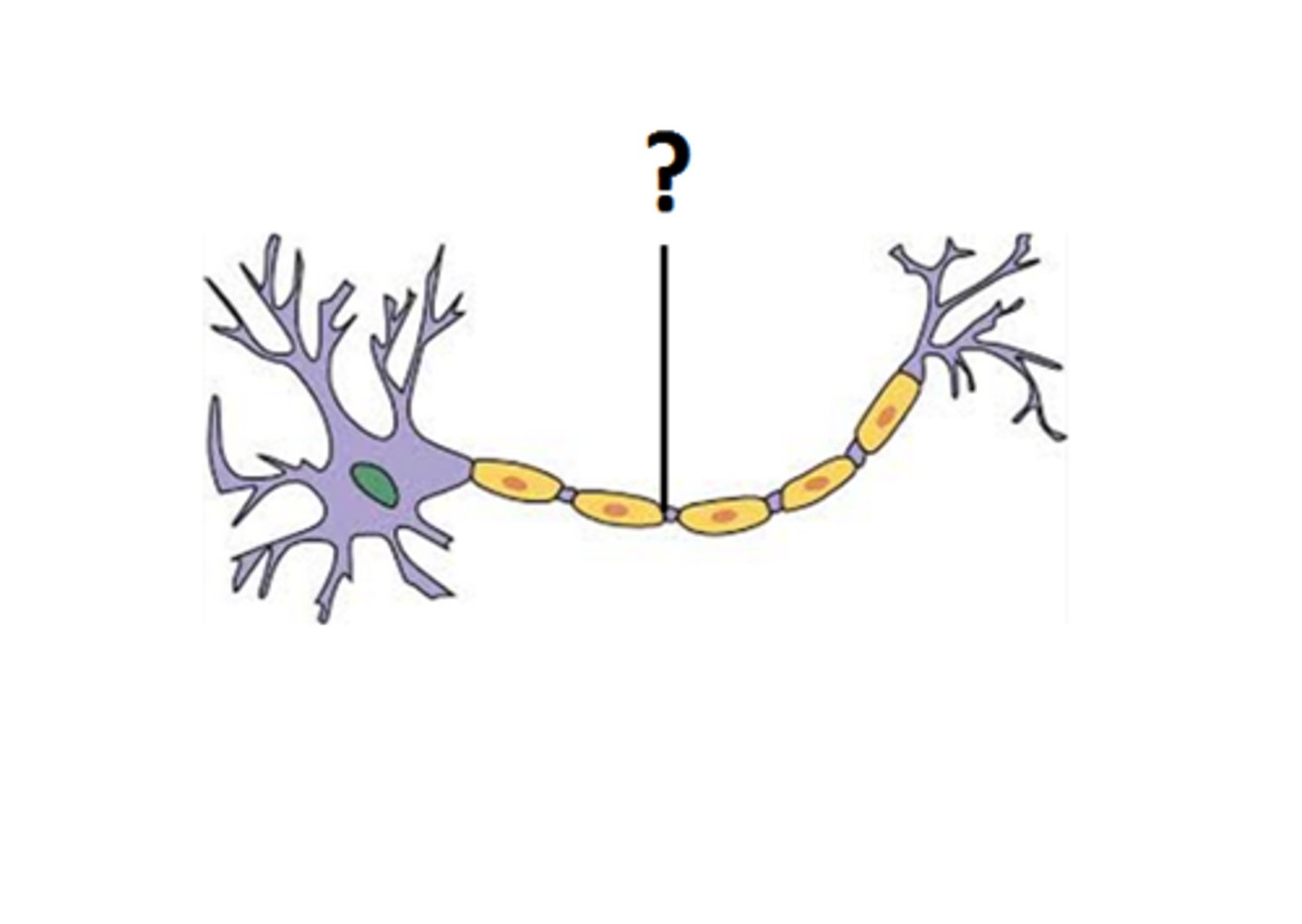
Axon
Long projection that carries impulses away from the neuron's cell body.
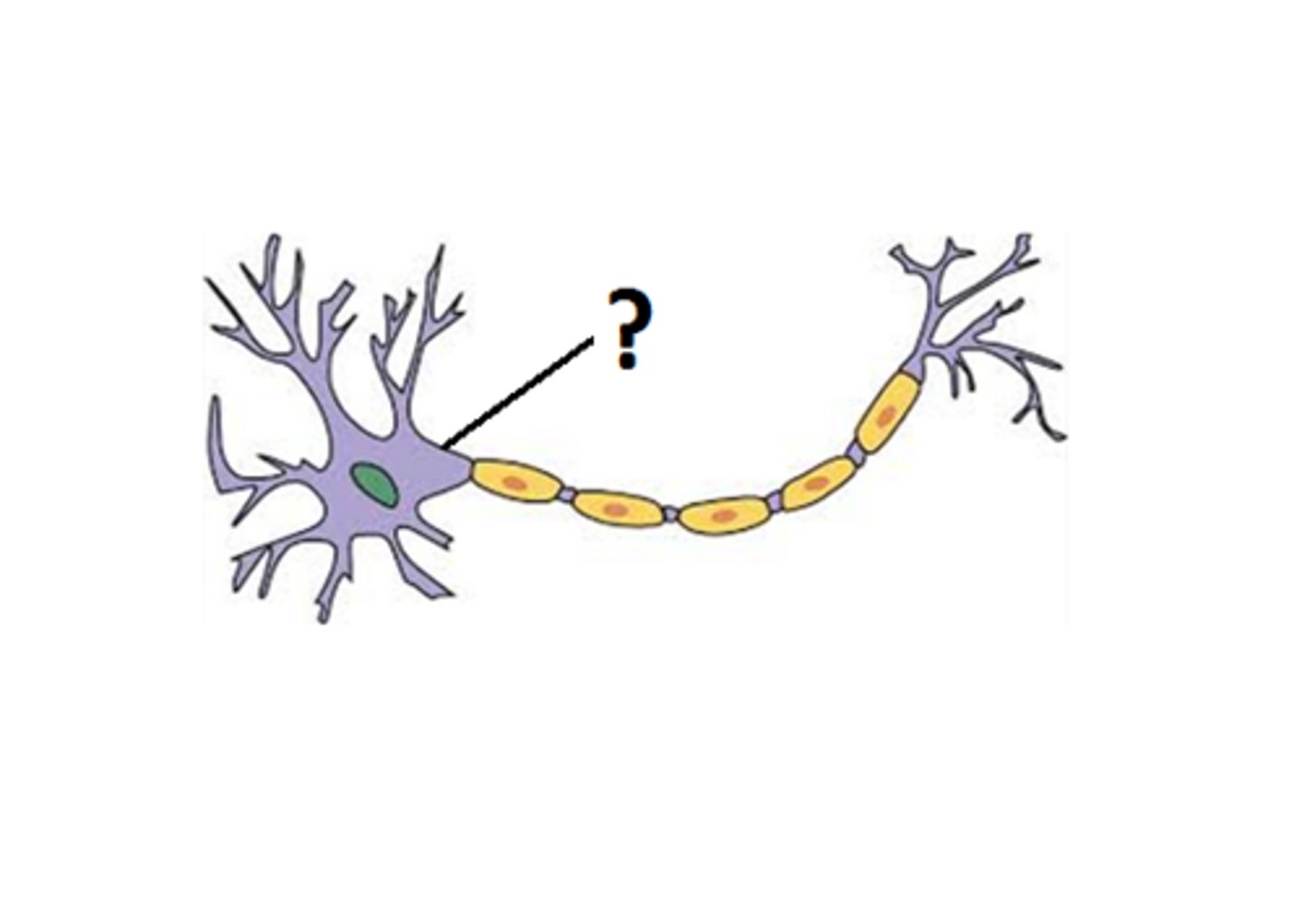
Axon hillock
Cone-shaped area of the cell body where the axon begins; site of action potential initiation.
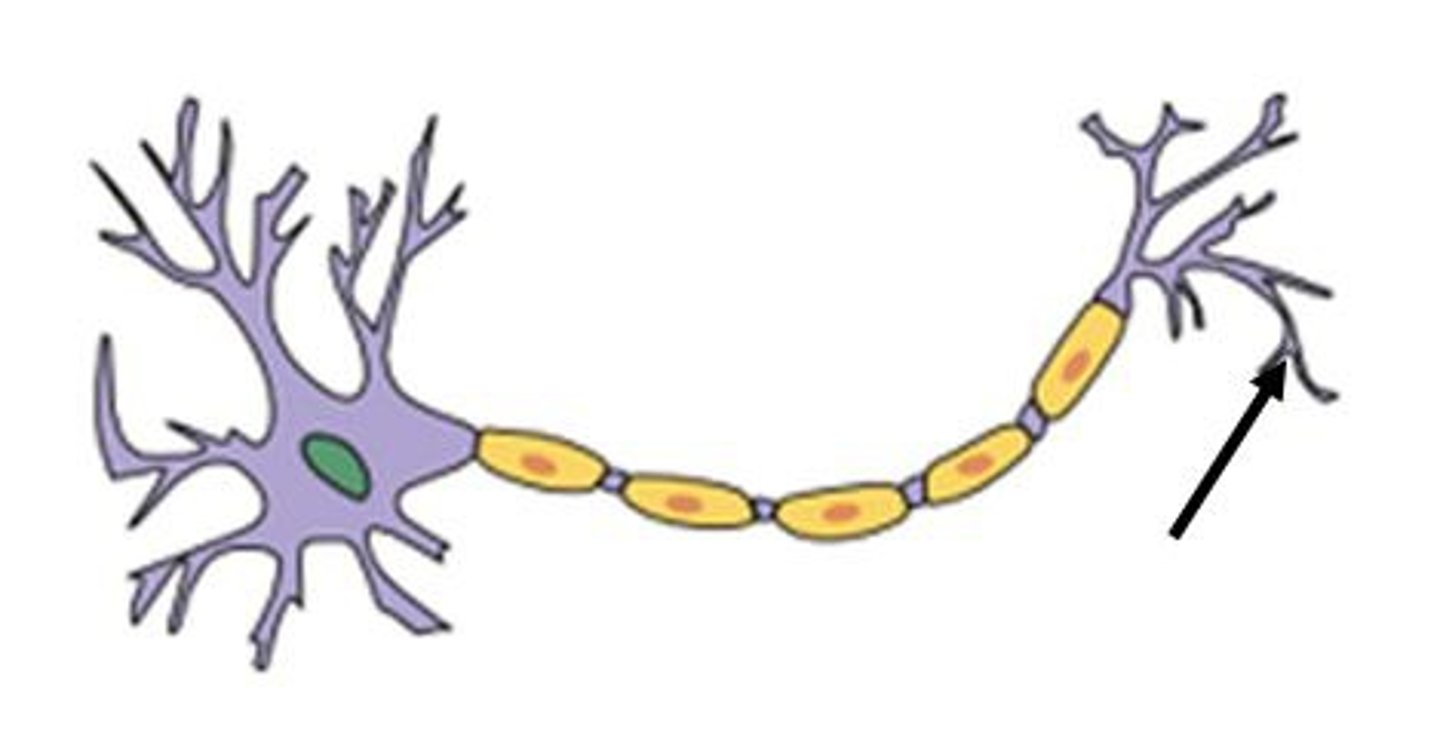
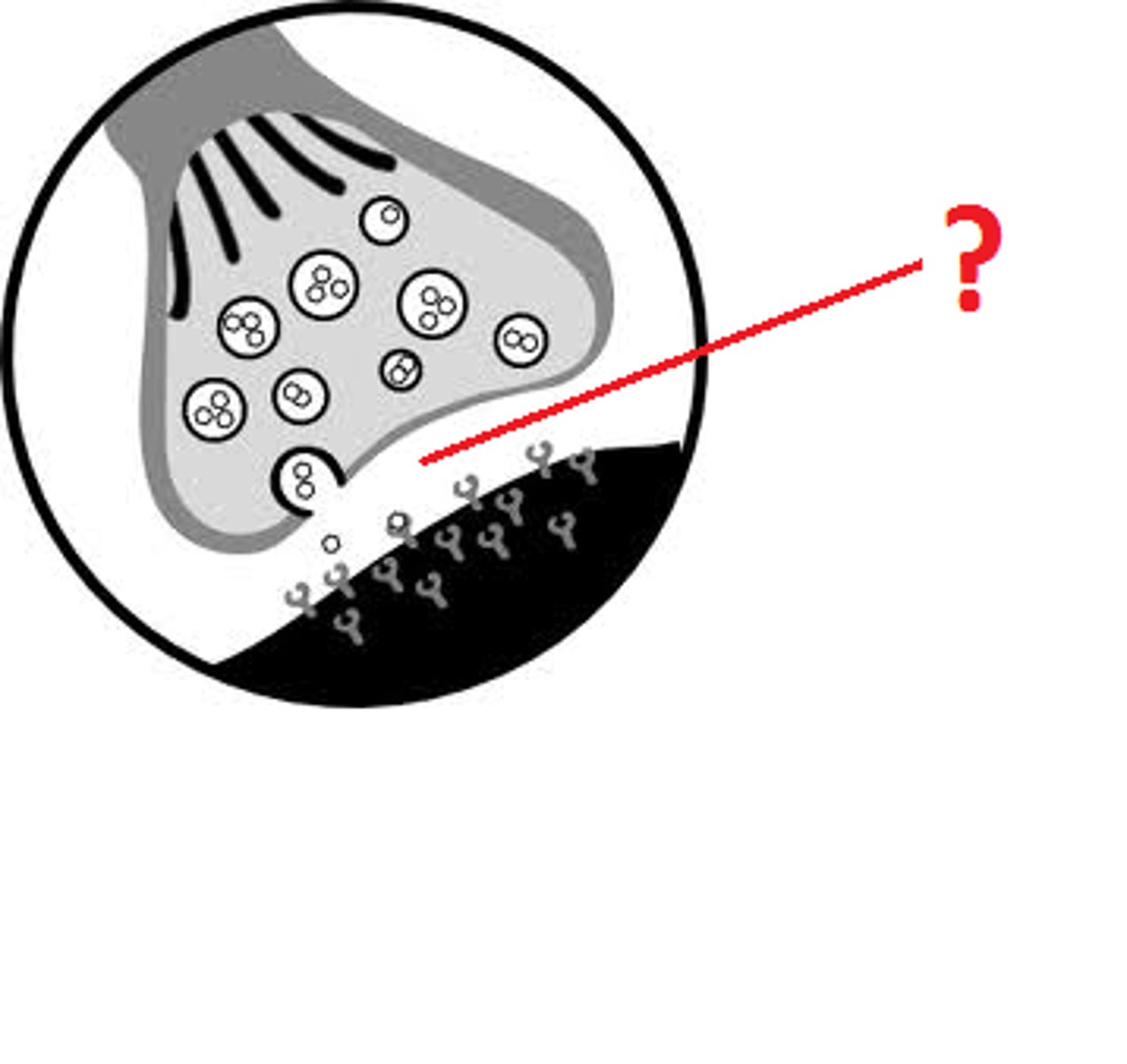
Nerve terminal
Ends of the axon where neurotransmitters are released.
Synaptic cleft
The small gap between the axon terminal and the target cell.
Multipolar neuron
A neuron with many dendrites and one axon; the most common type.
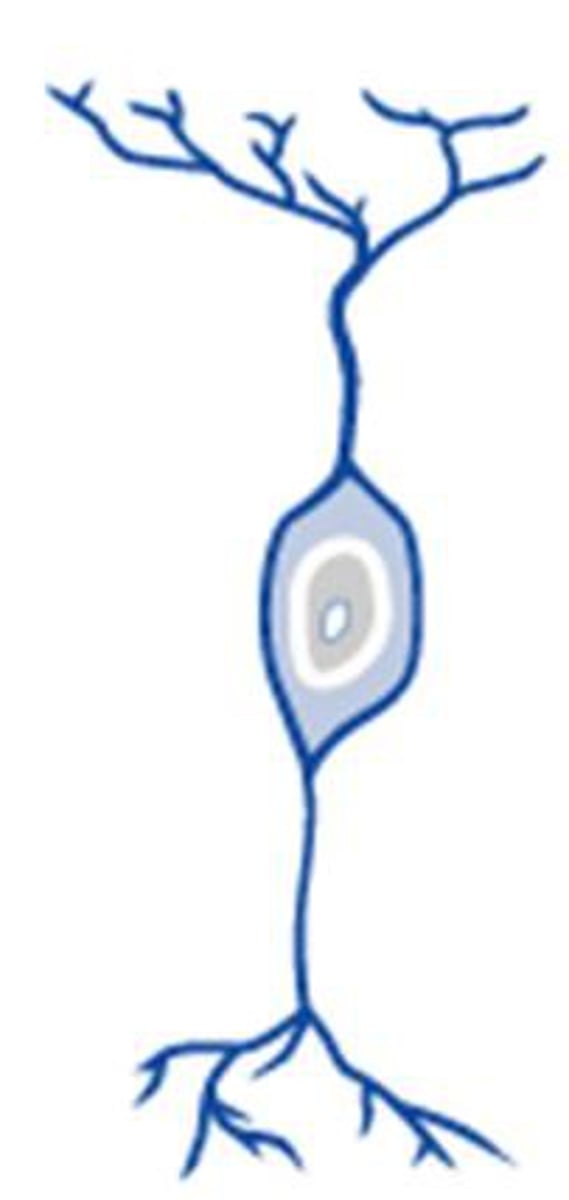
Bipolar neuron
A neuron with one axon and one dendrite; found in sensory organs like the retina.
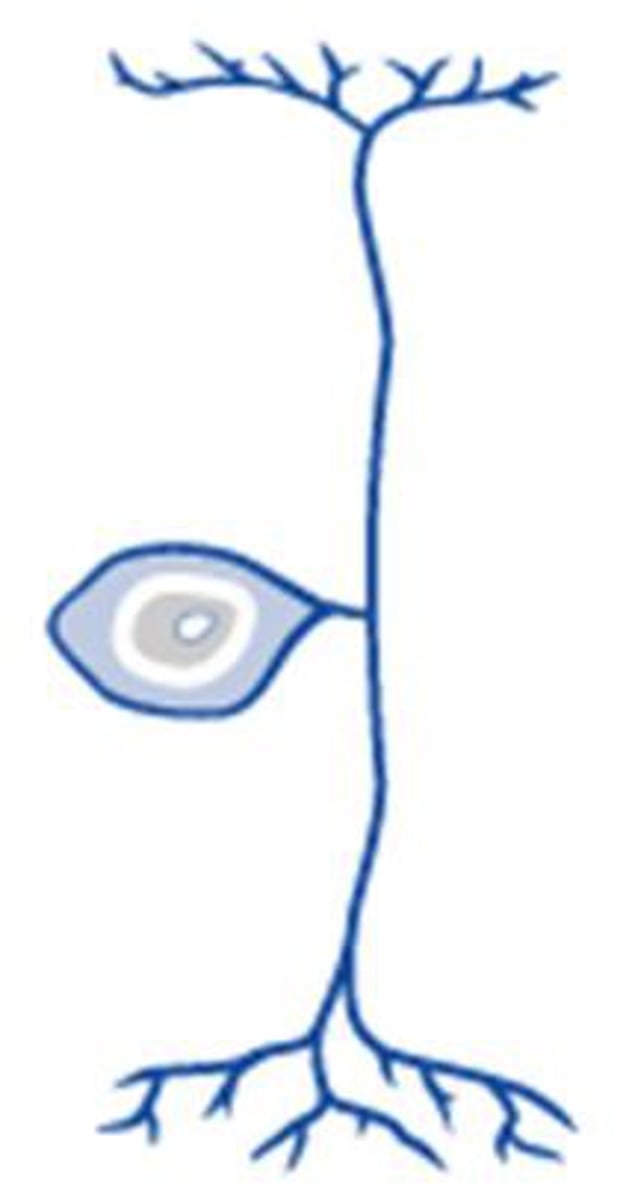
Unipolar neuron
A neuron with one process that splits into peripheral and central branches; common in sensory neurons.
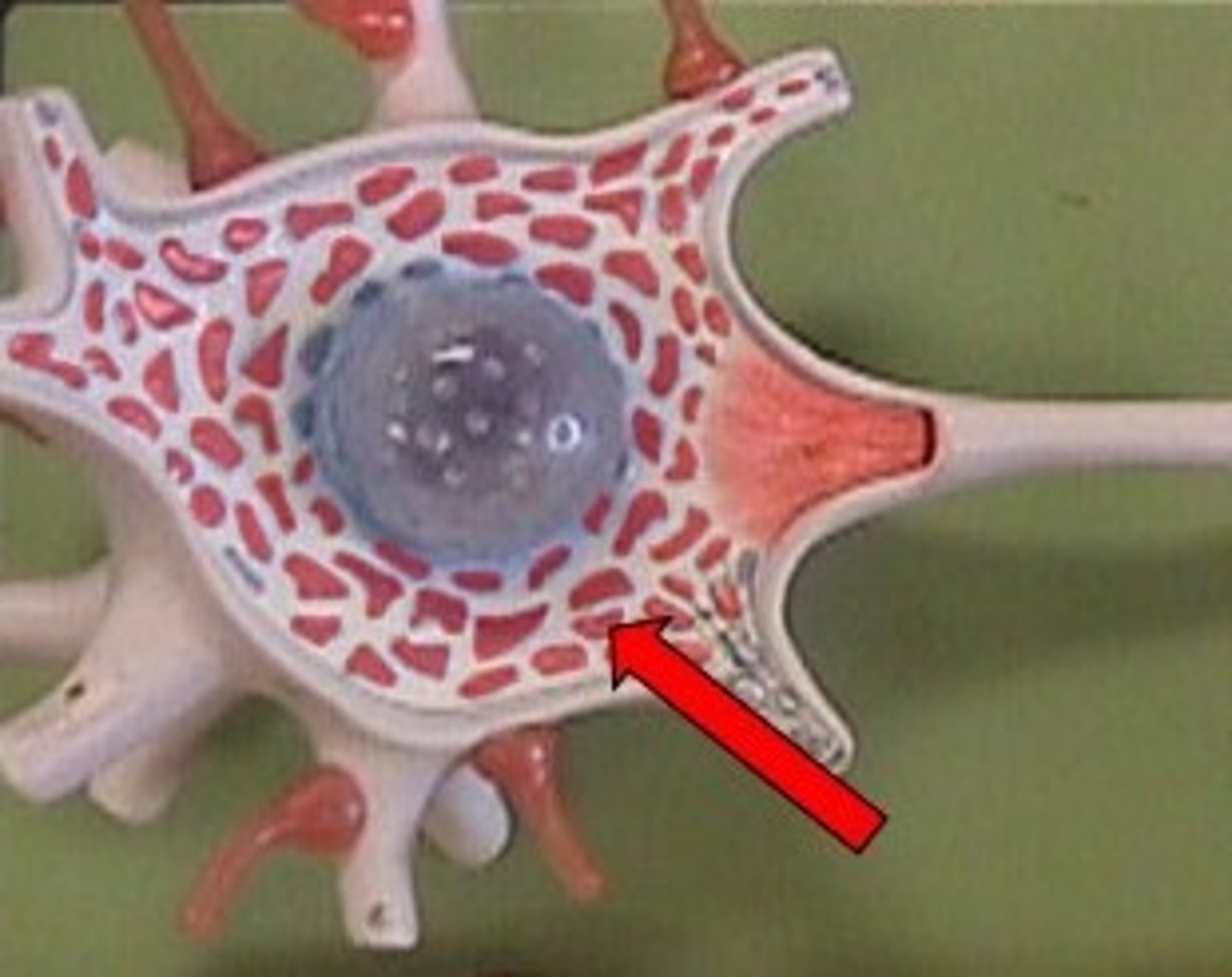
Epineurium
Connective tissue that surrounds the entire nerve.
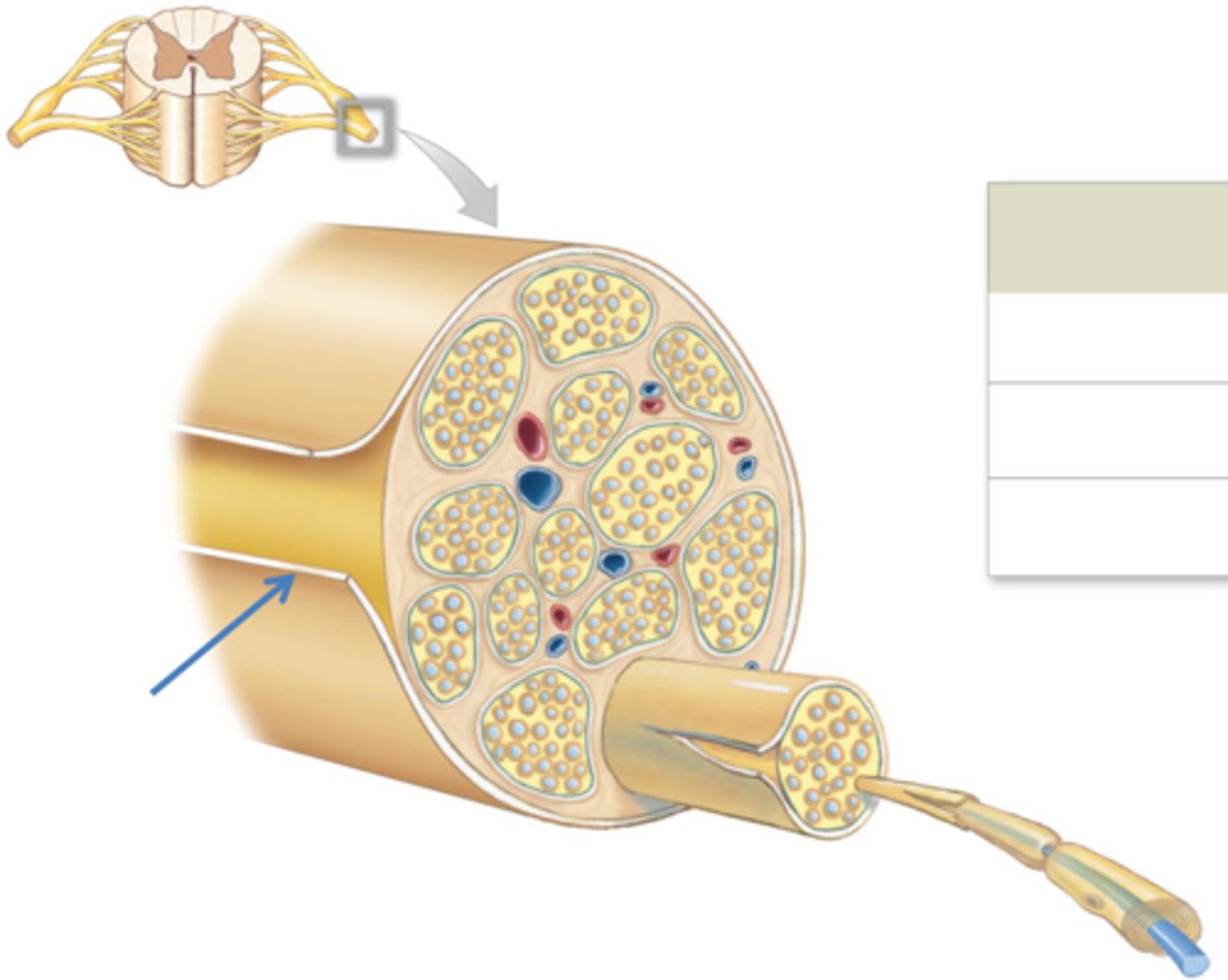
Perineurium
Connective tissue that surrounds a nerve fascicle (bundle of axons).
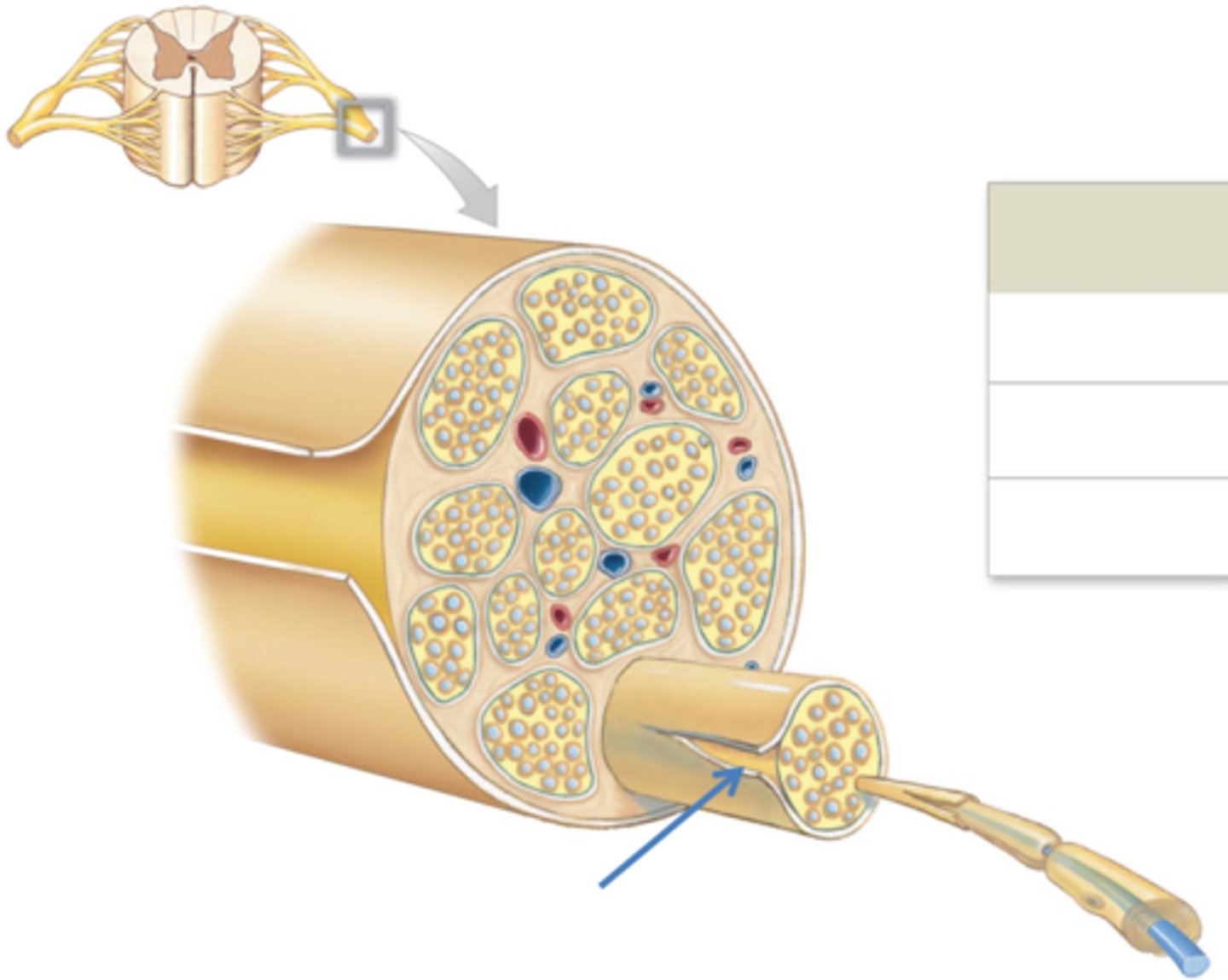
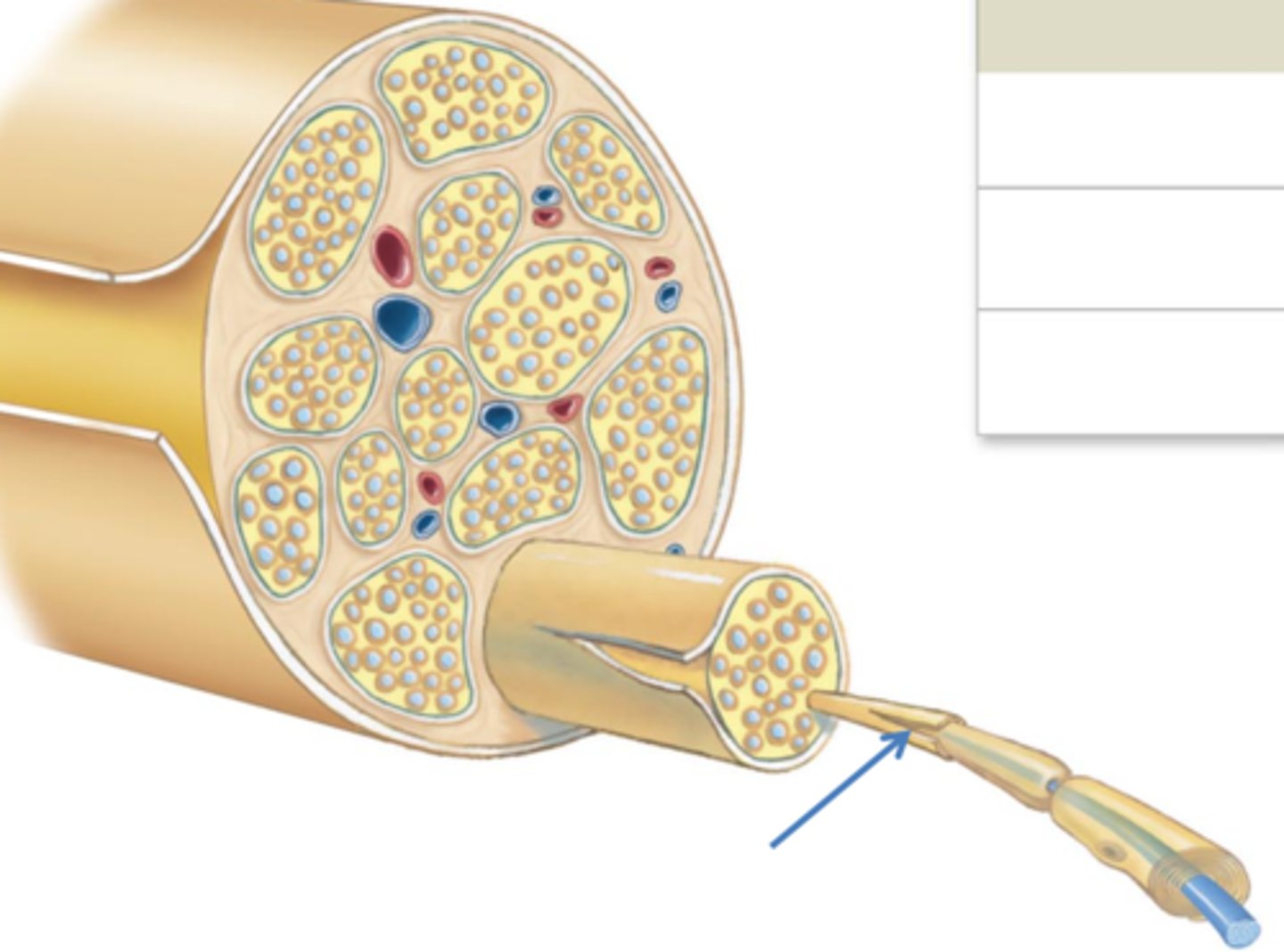
Endoneurium
Connective tissue that surrounds a single axon.
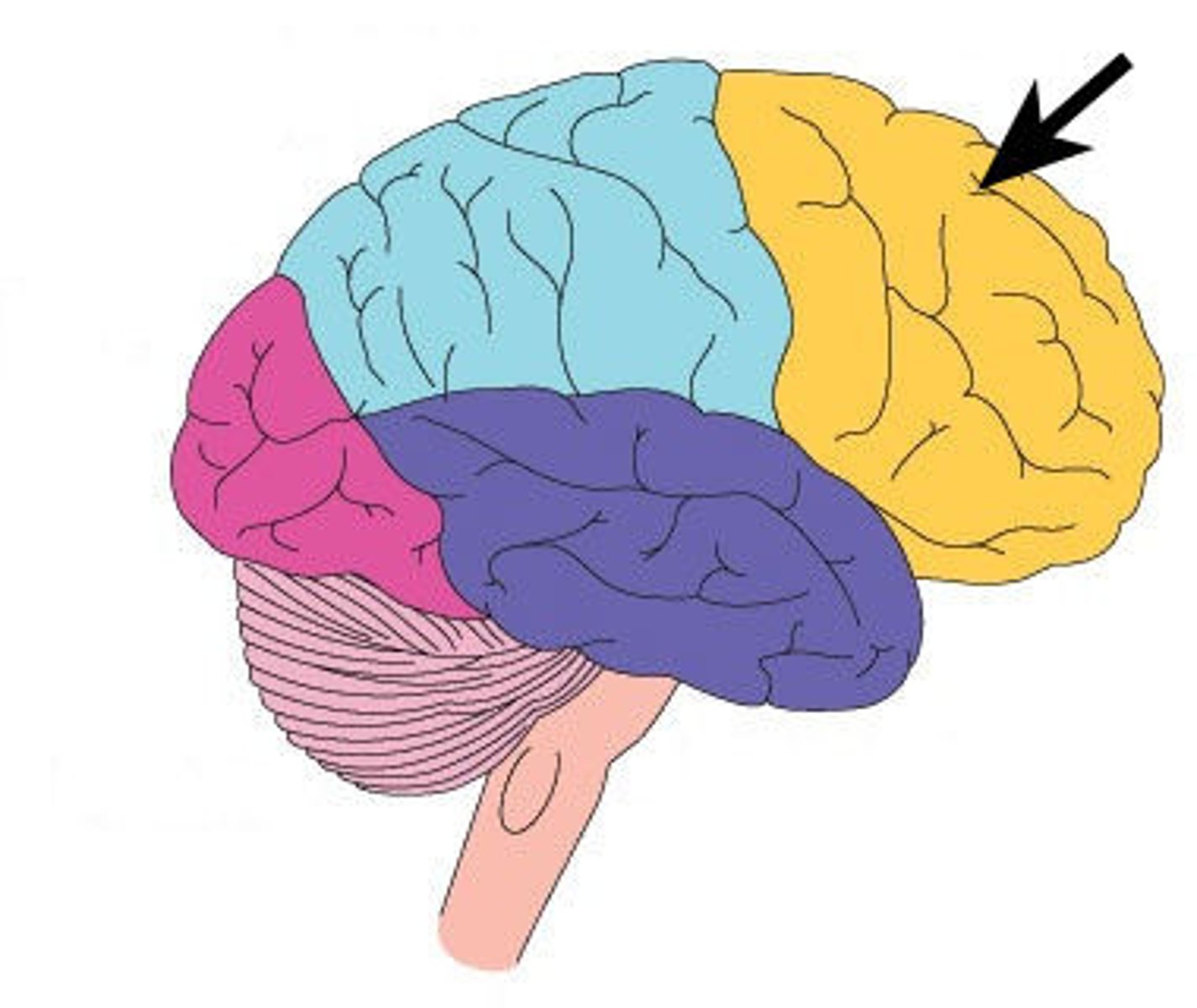
Frontal lobe
Controls voluntary movement, decision-making, and personality.
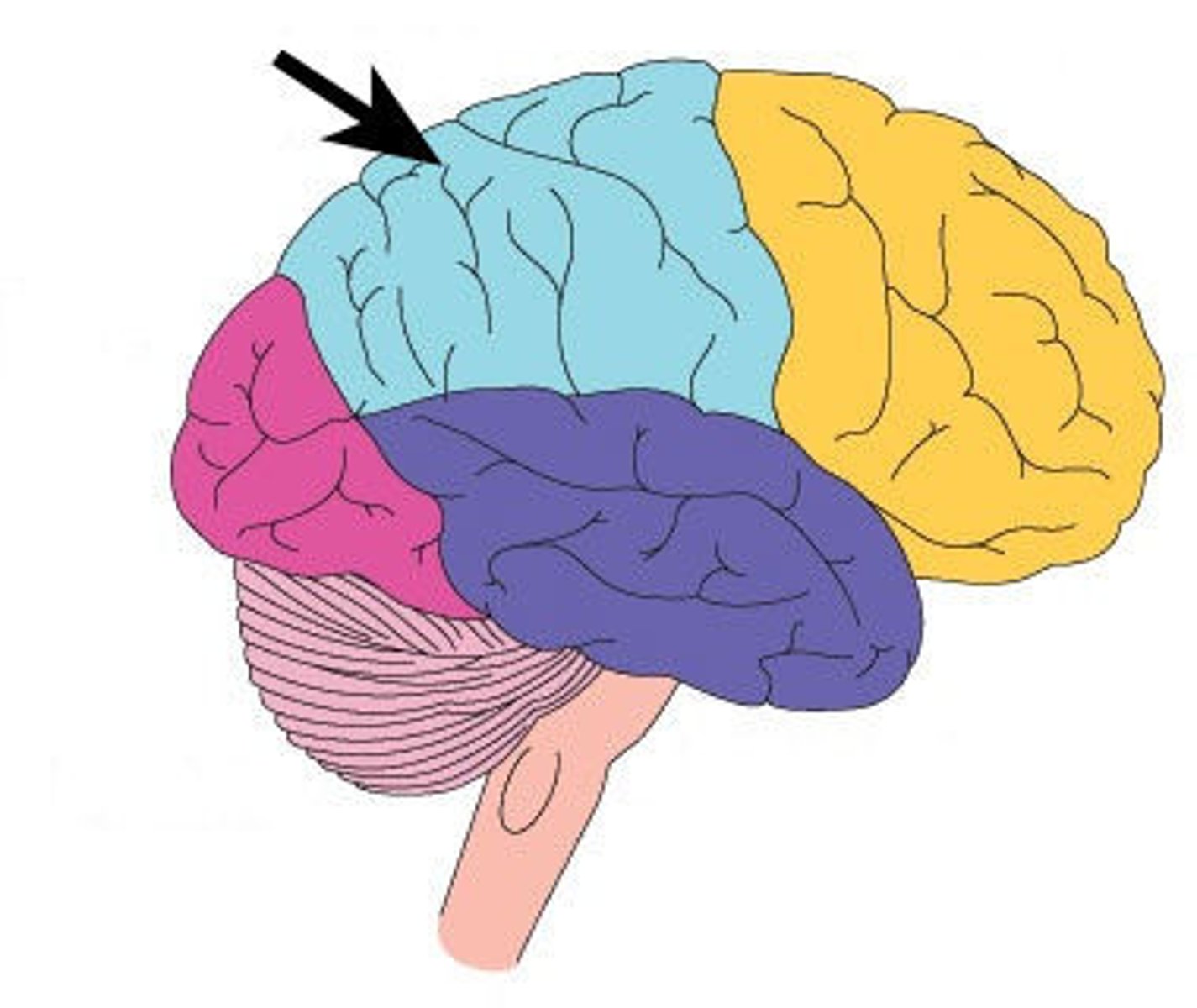
Precentral gyrus
Primary motor cortex; initiates voluntary muscle movements.
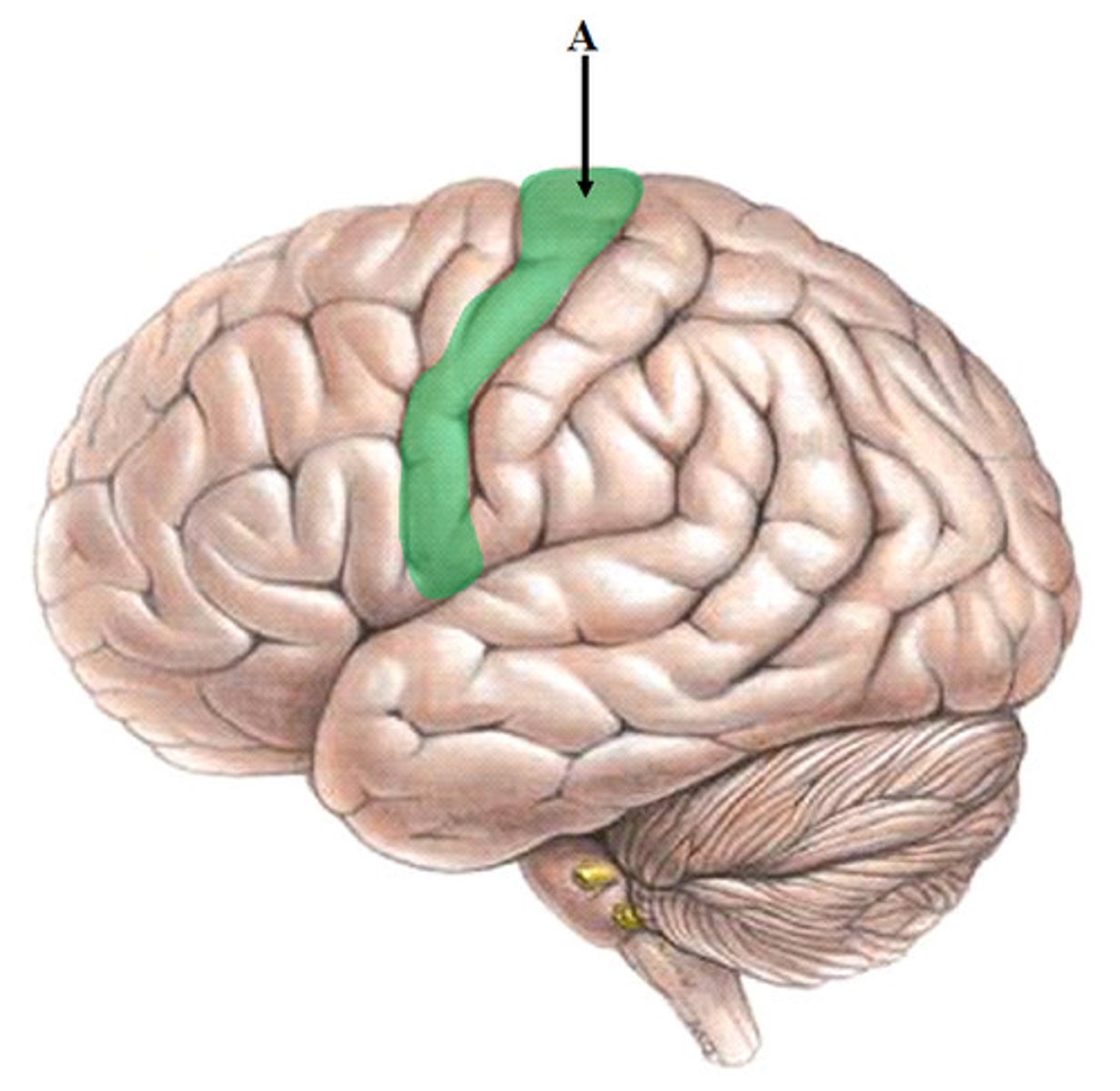
Central sulcus
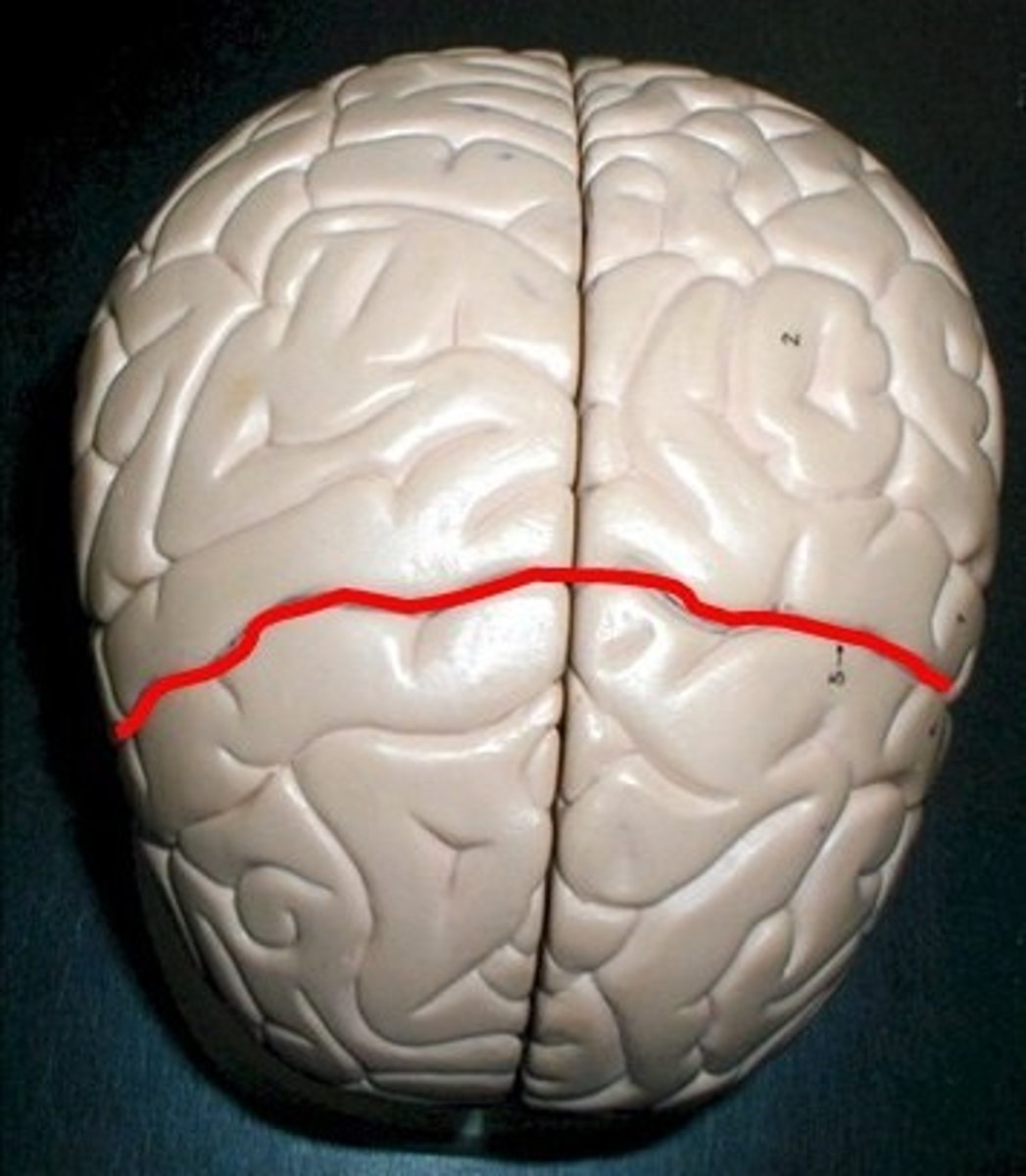
Groove separating frontal and parietal lobes.
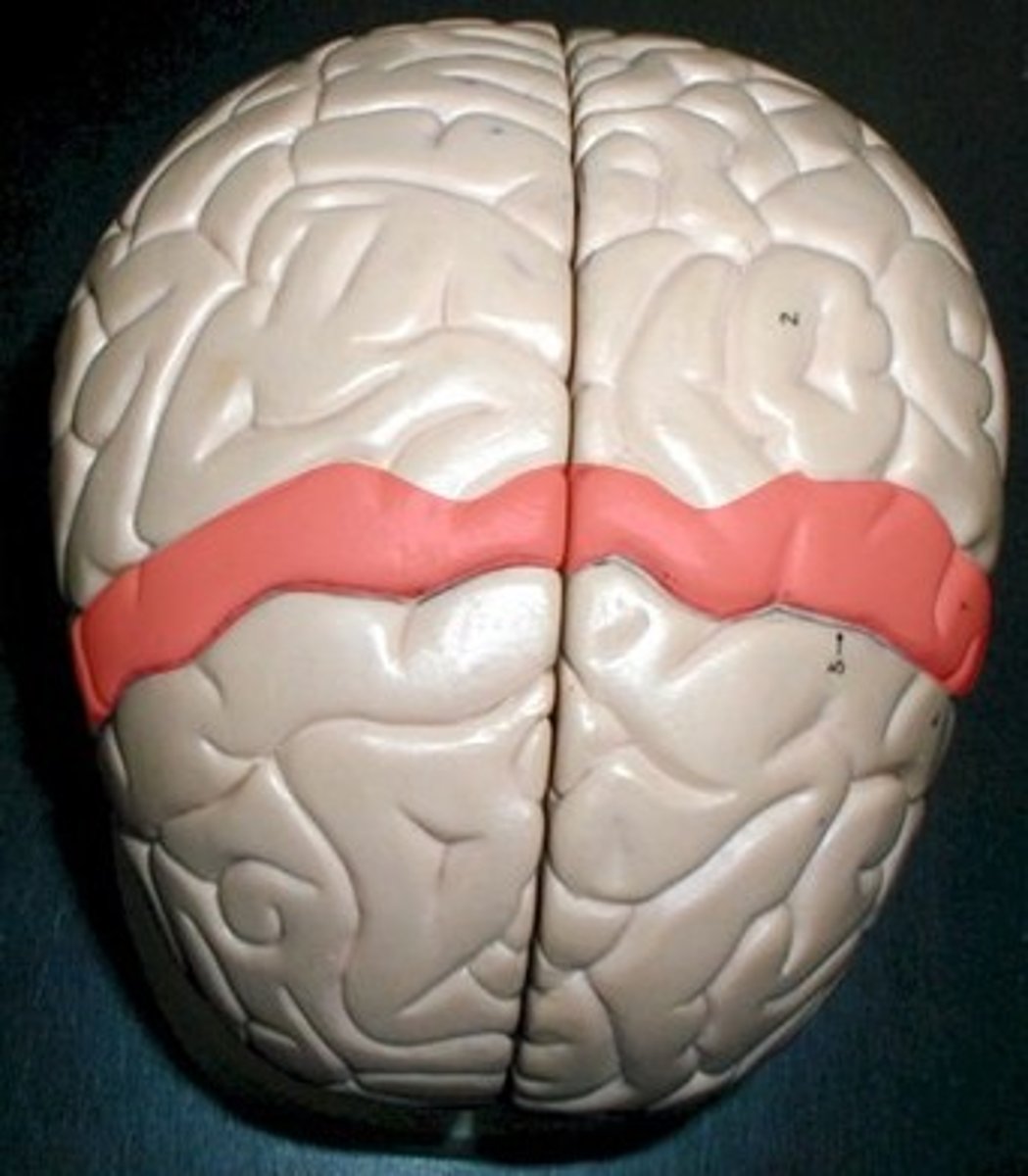
Postcentral gyrus
Primary somatosensory cortex; processes touch and pressure.
Parietal lobe
Processes sensory information like touch, pressure, and temperature.
Occipital lobe
Processes visual information.
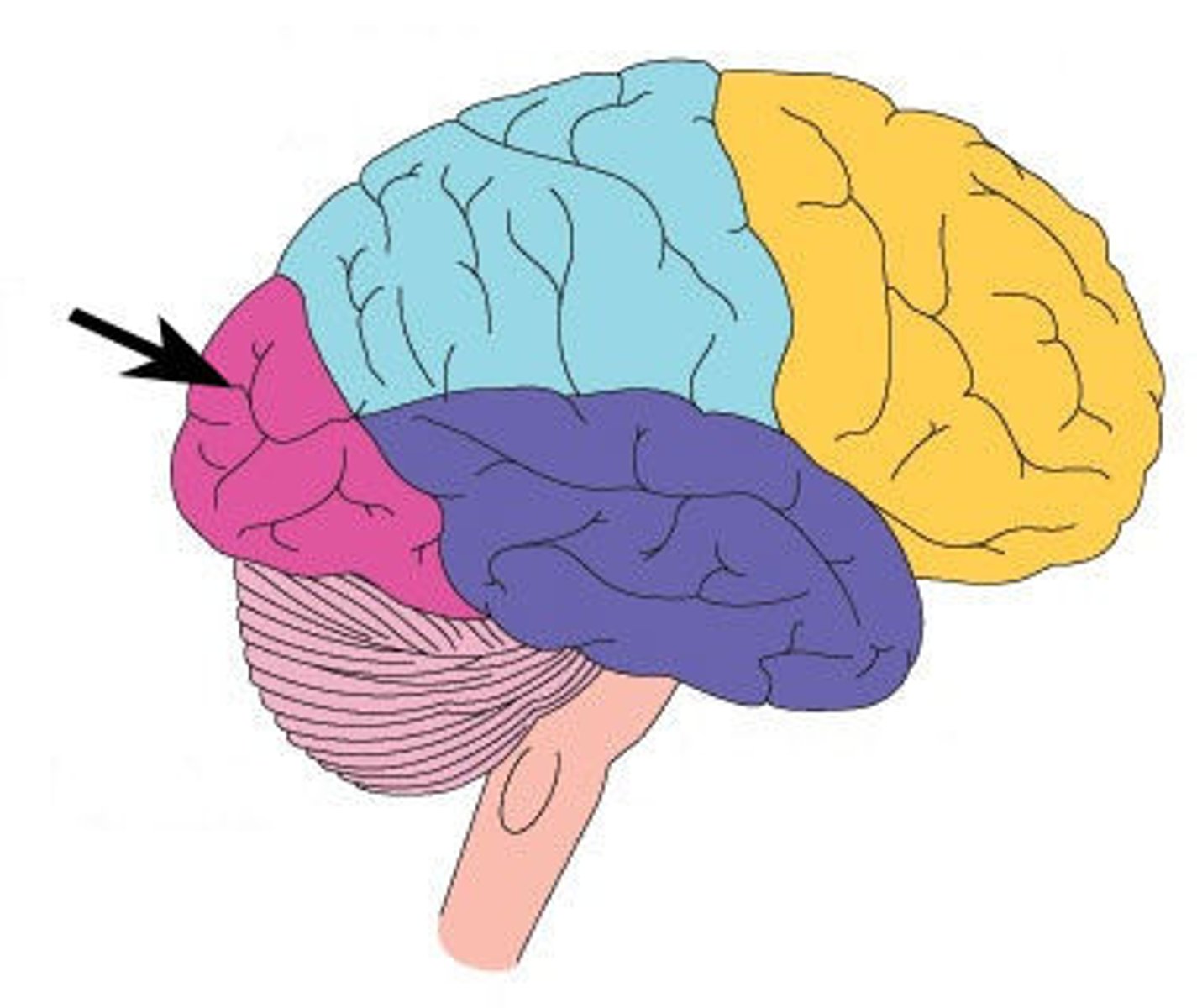
Temporal lobe
Processes auditory and olfactory information.
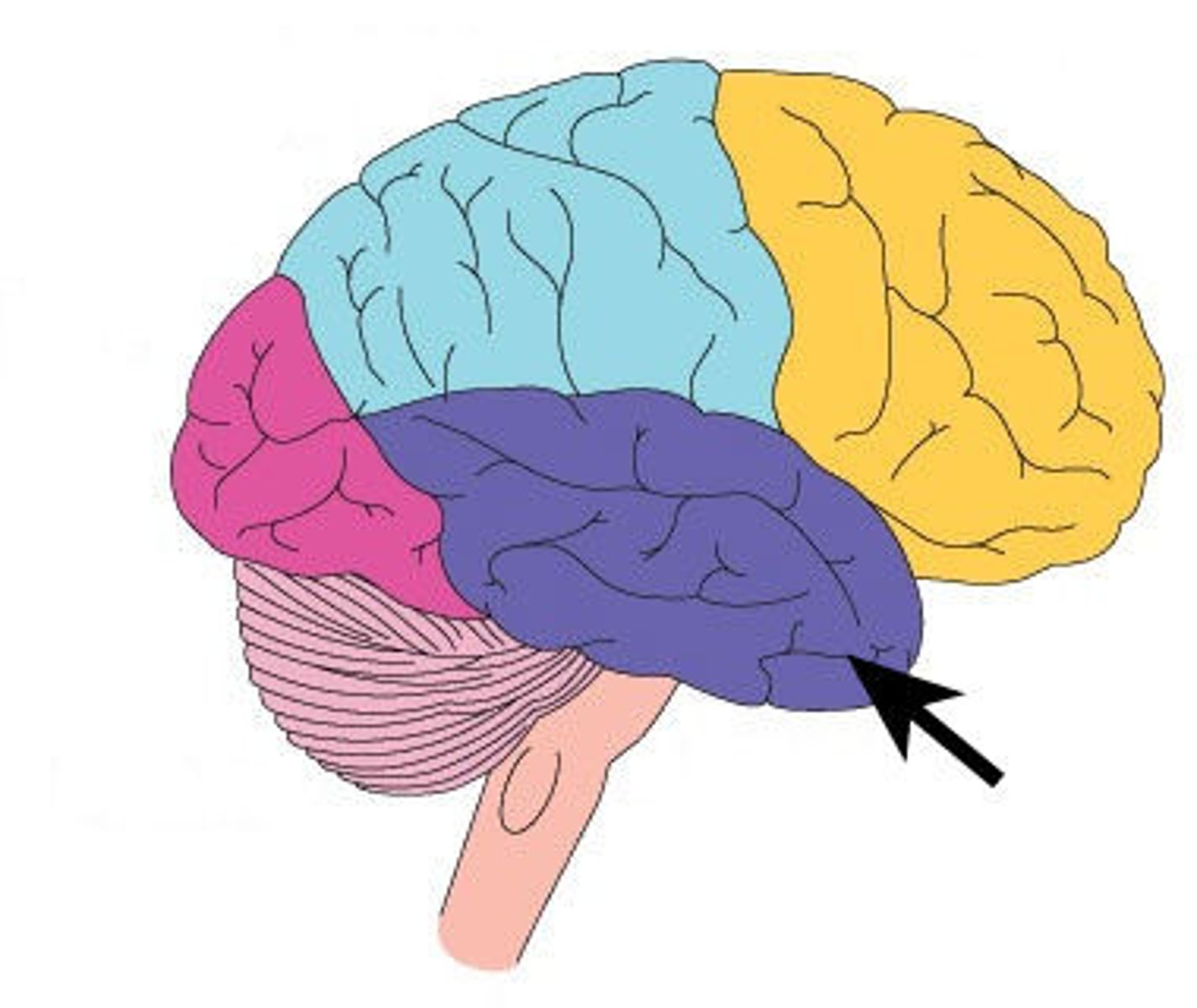
Transverse fissure
Deep groove that separates cerebrum from cerebellum.
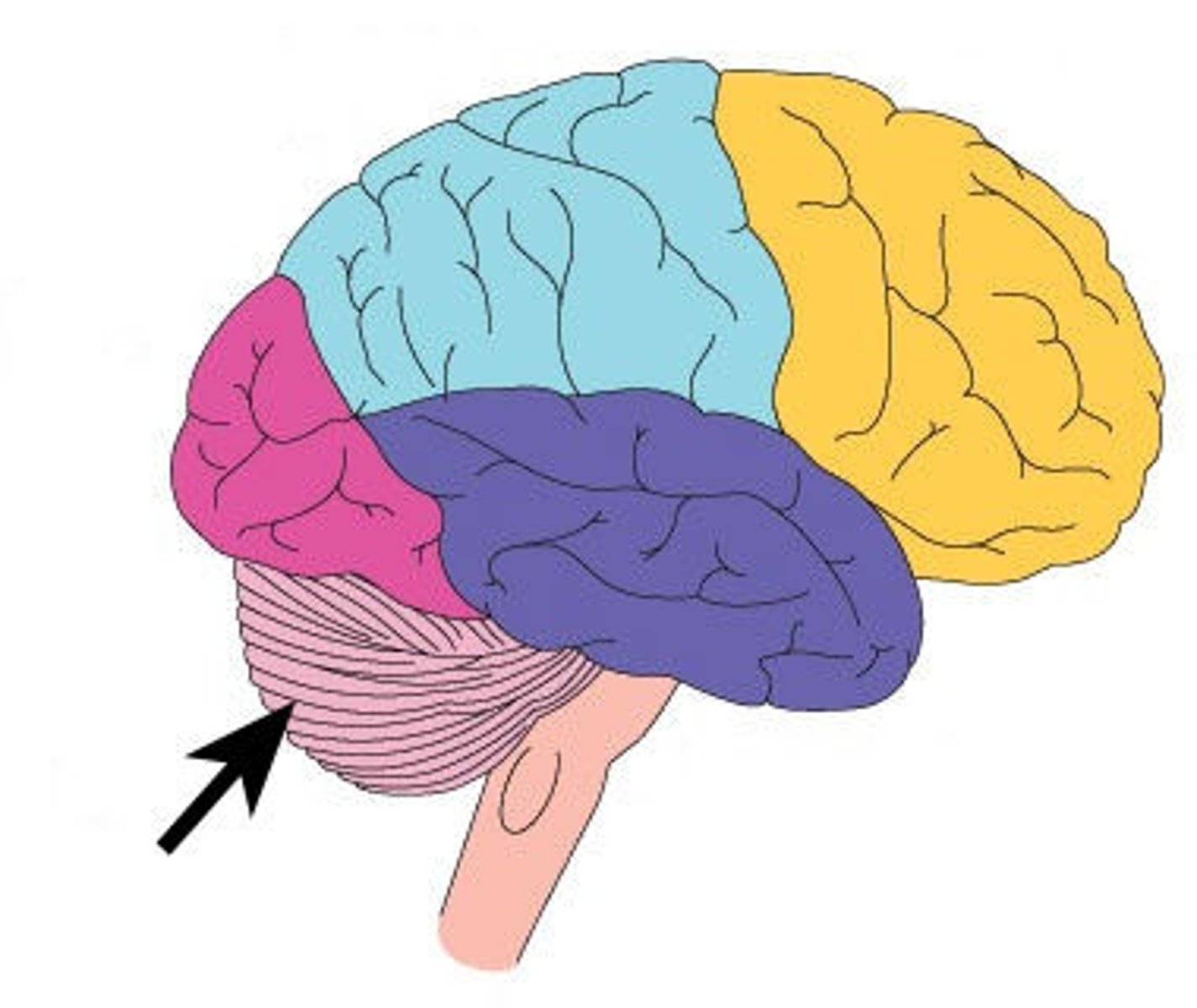
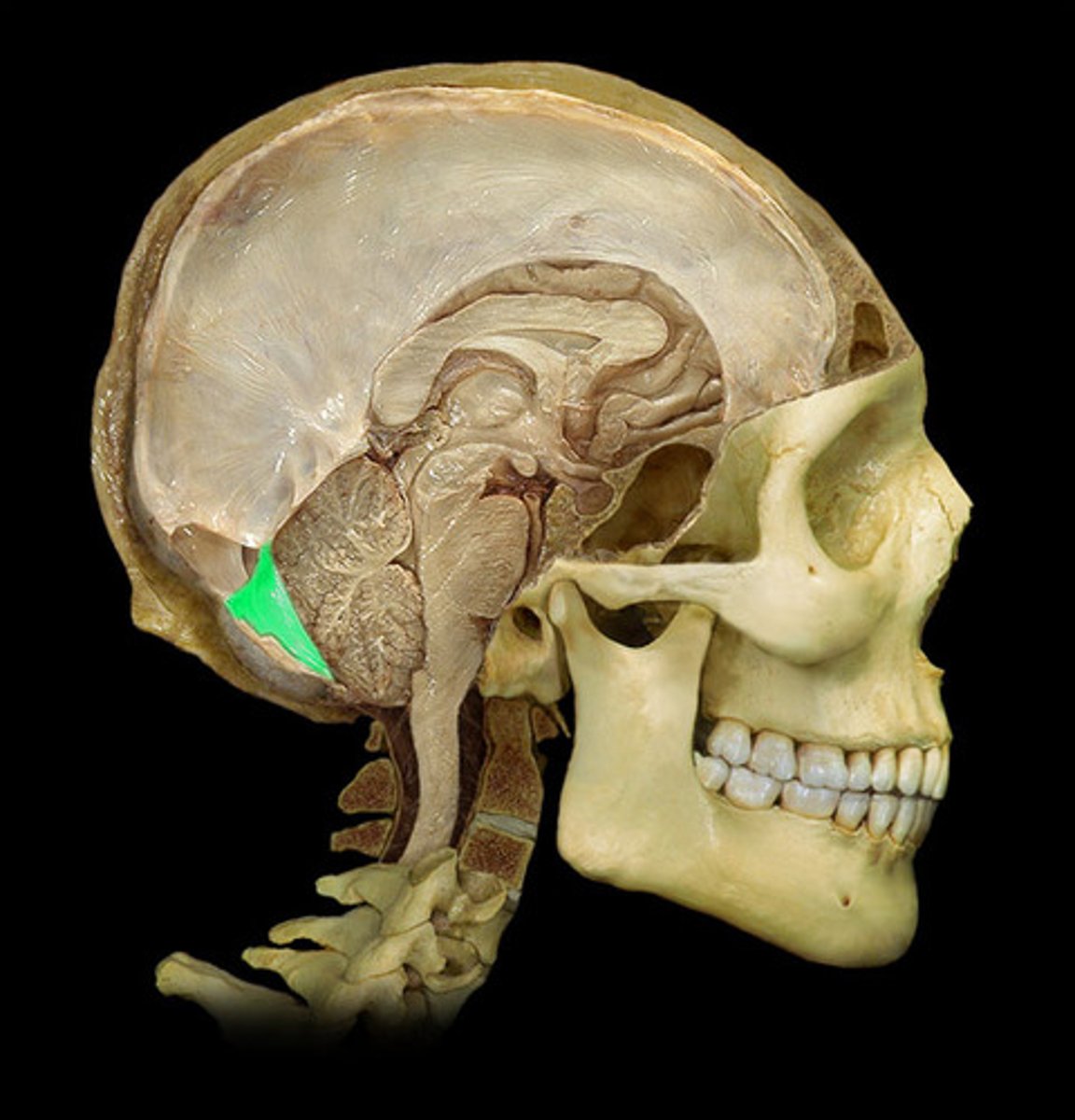
Cerebellum
Coordinates movement and balance.
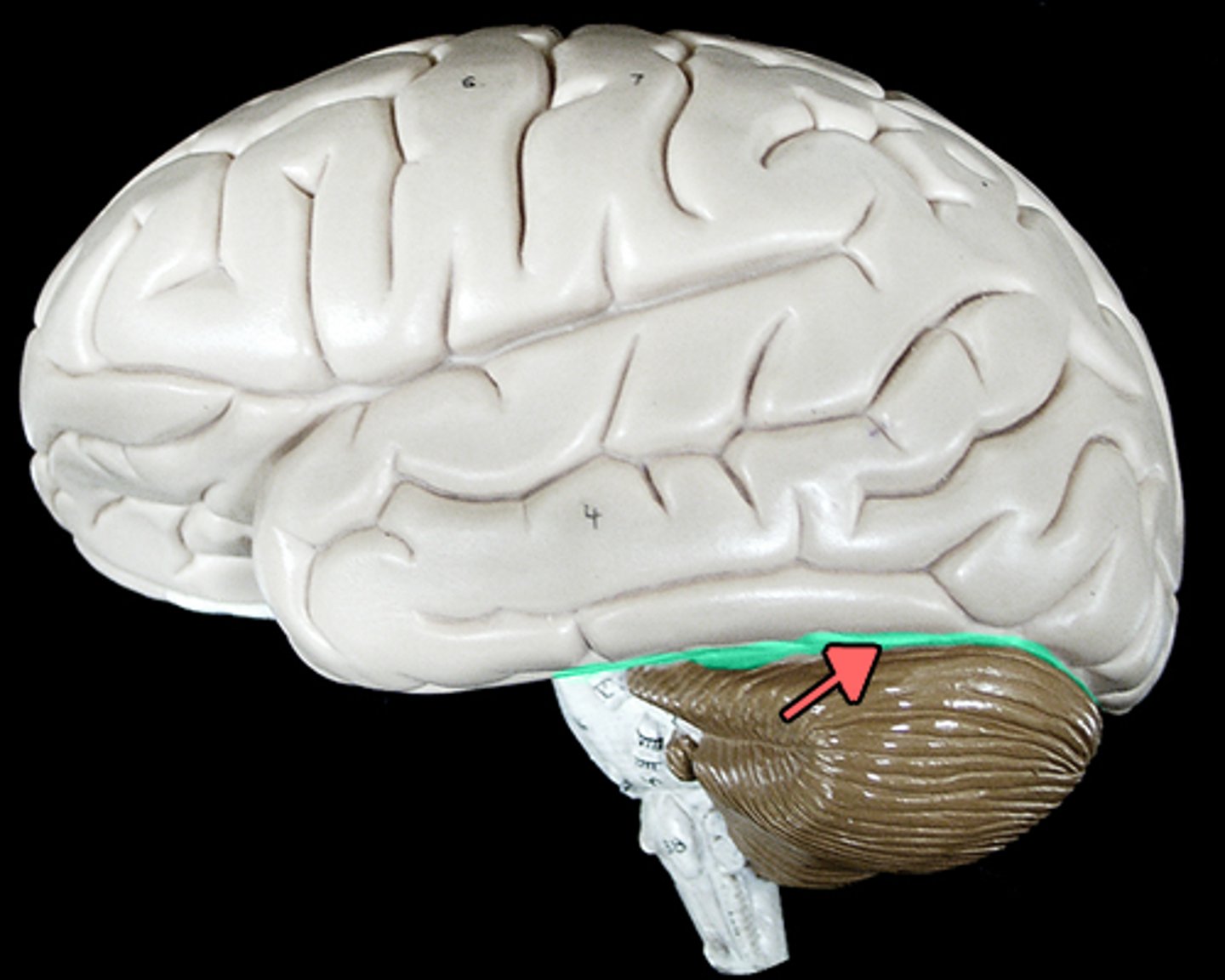
Pons
Part of the brainstem that connects the medulla to higher brain structures; helps control breathing.
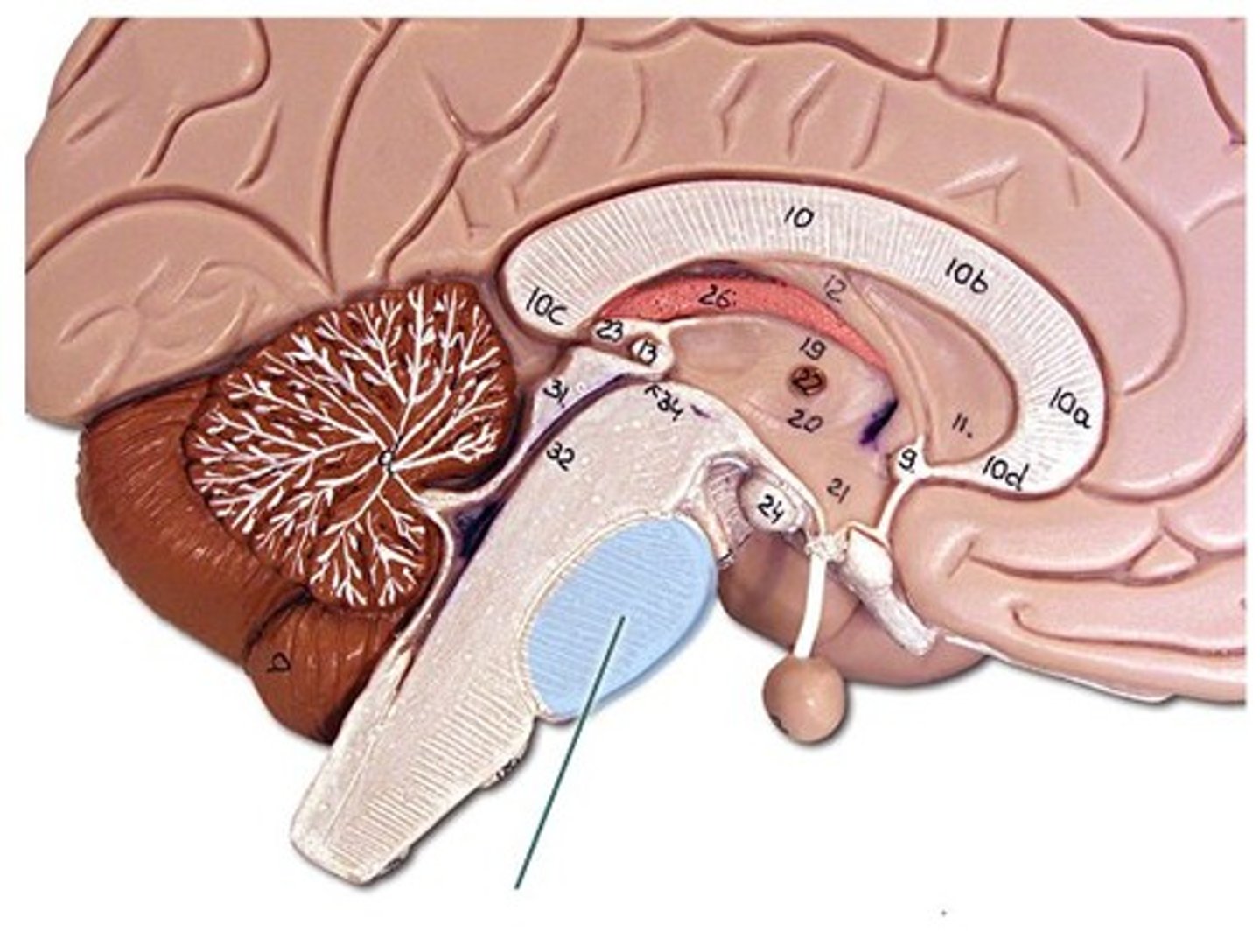
Medulla
Controls vital autonomic functions such as heartbeat and respiration.
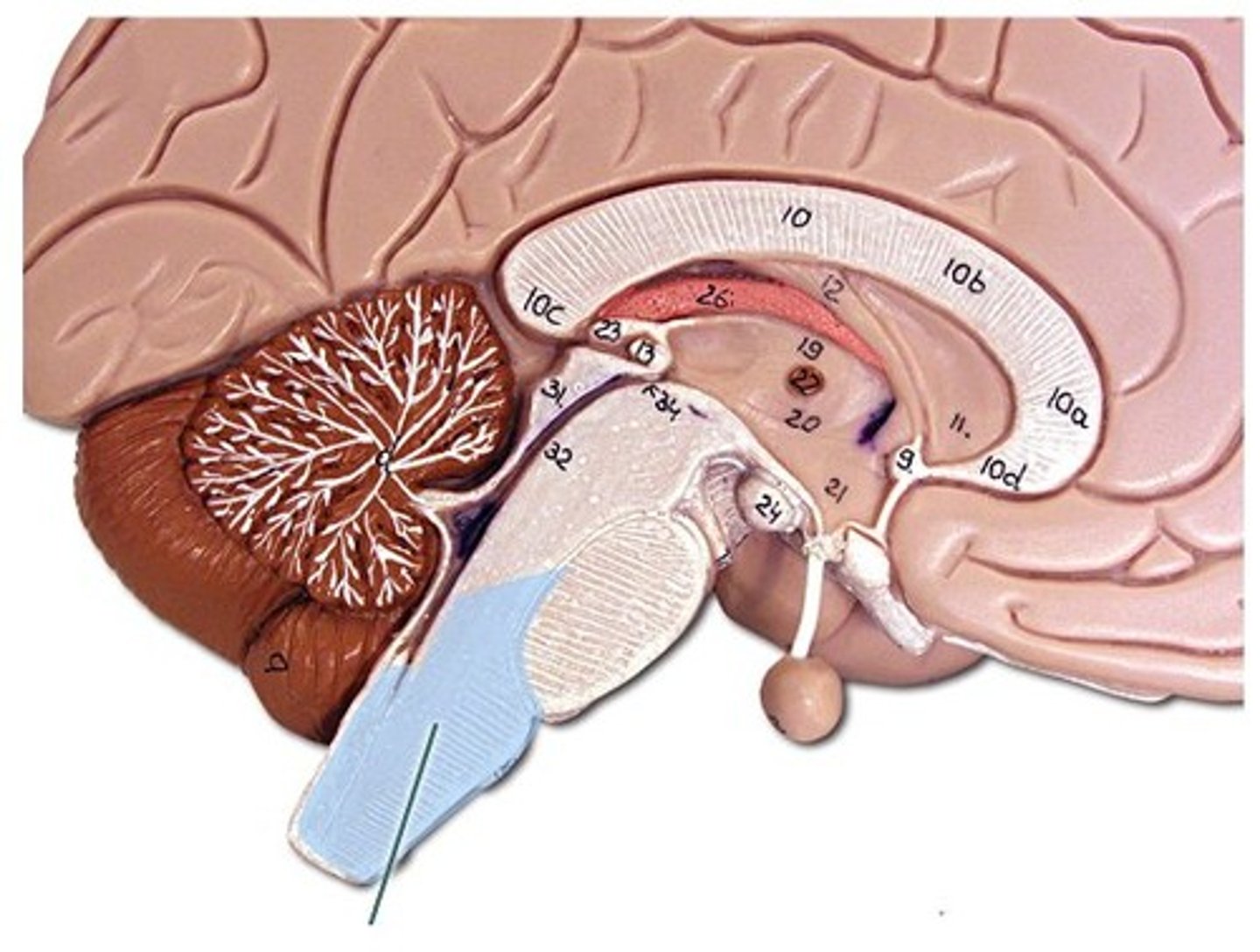
Longitudinal fissure
Deep groove dividing the left and right cerebral hemispheres.
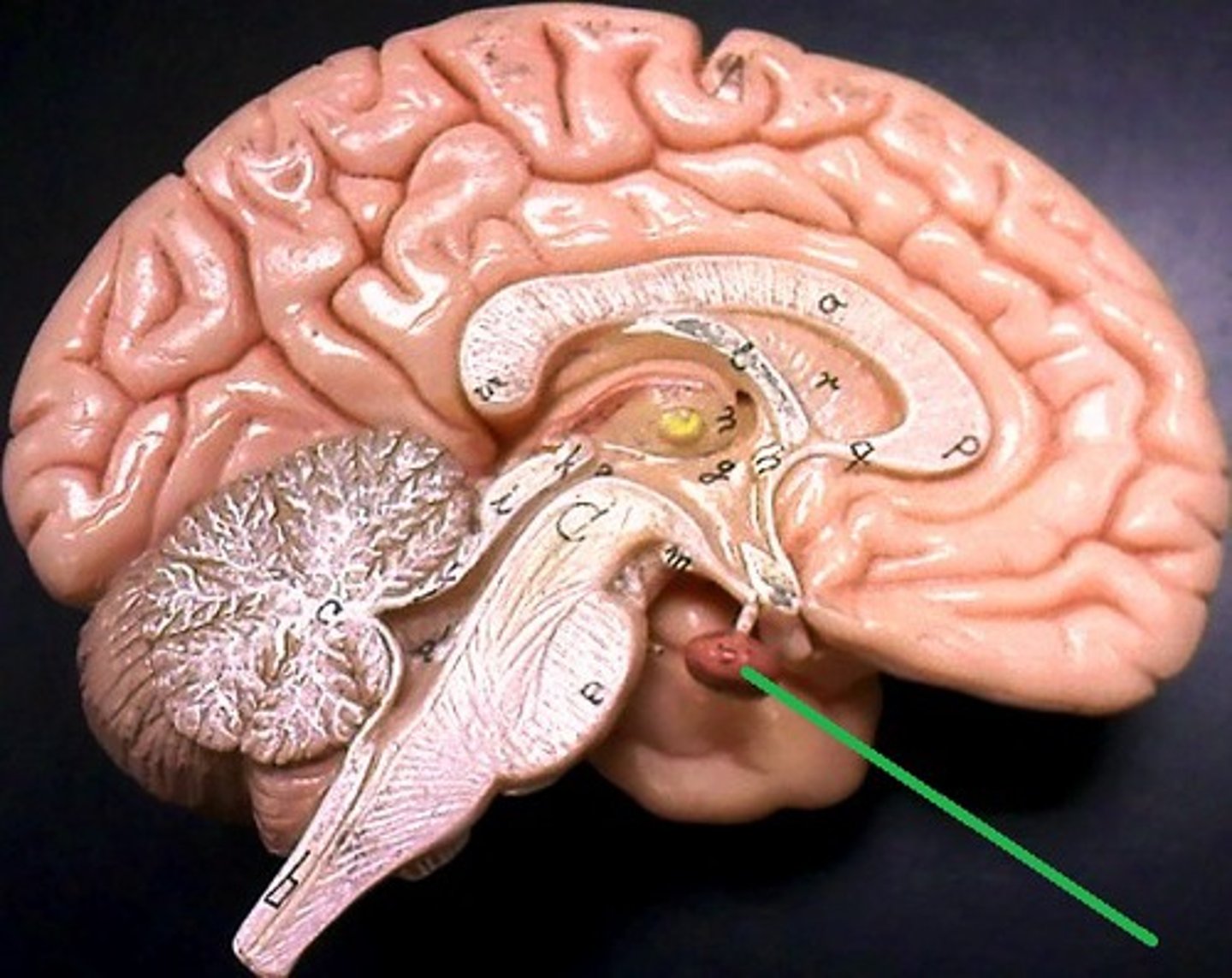
Pituitary gland
Endocrine gland that secretes hormones; controlled by the hypothalamus.
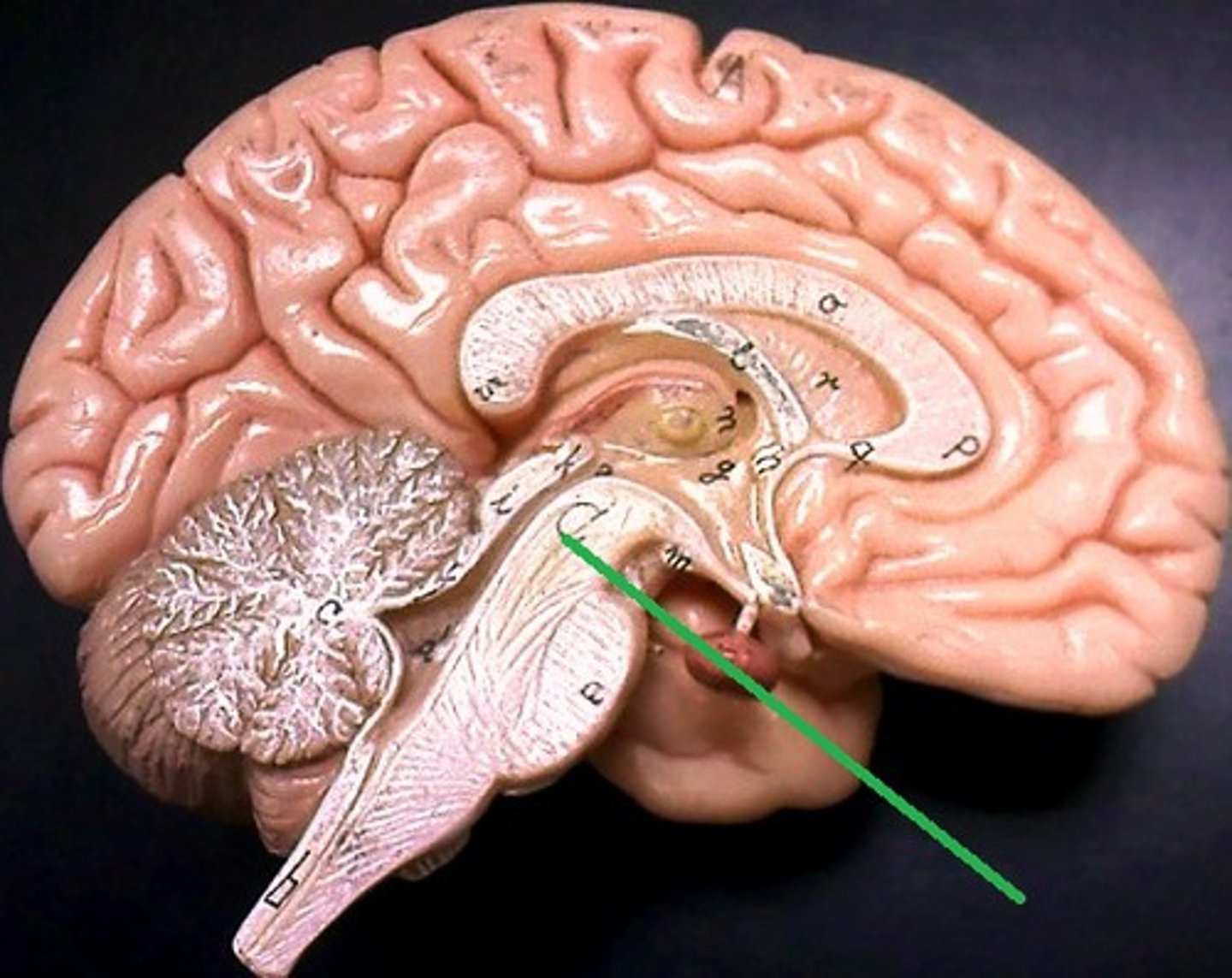
Cerebral peduncle
Part of the midbrain; contains motor tracts from the cerebrum to the pons.
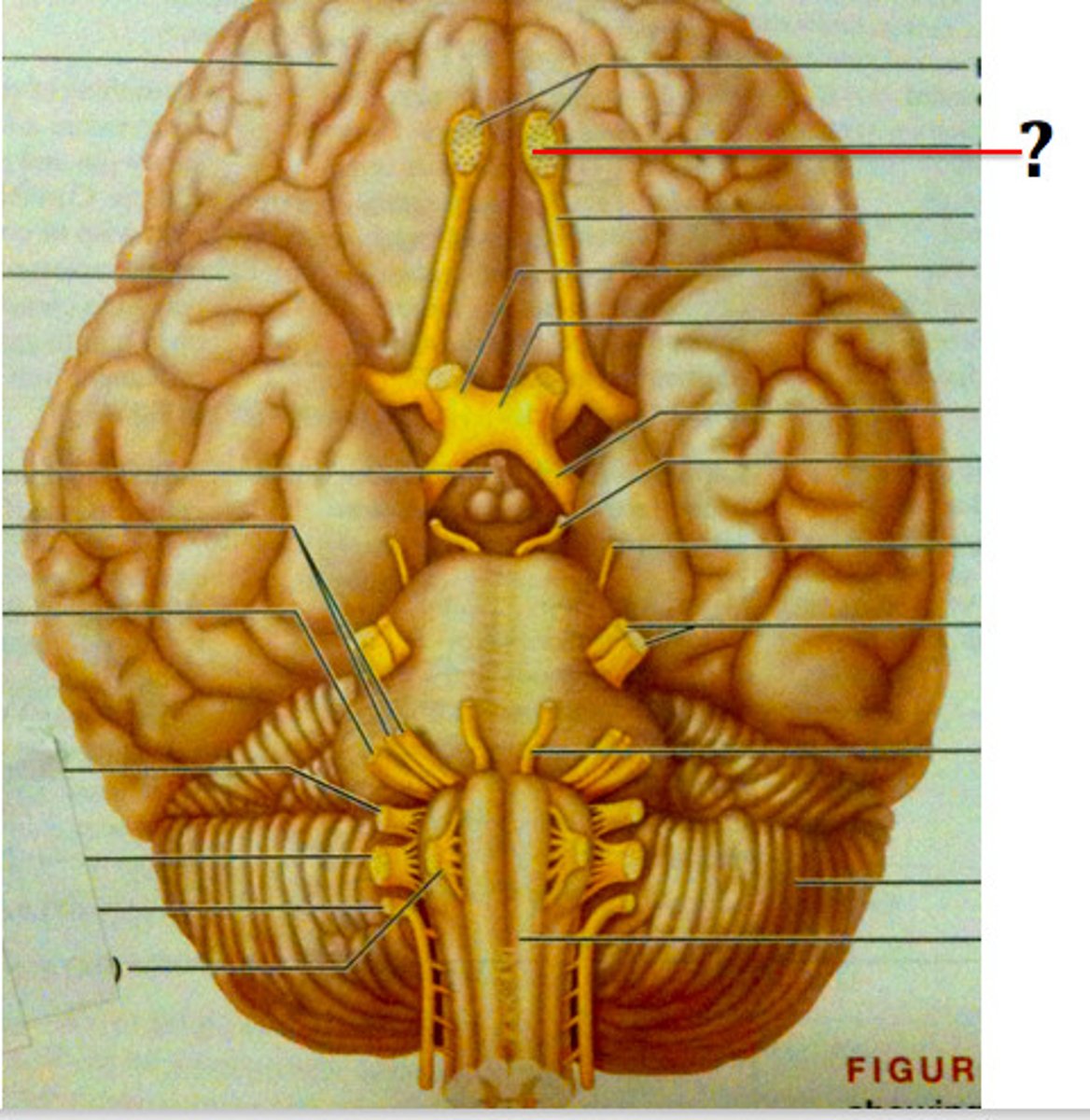
Olfactory bulb
Receives smell input from olfactory receptors.
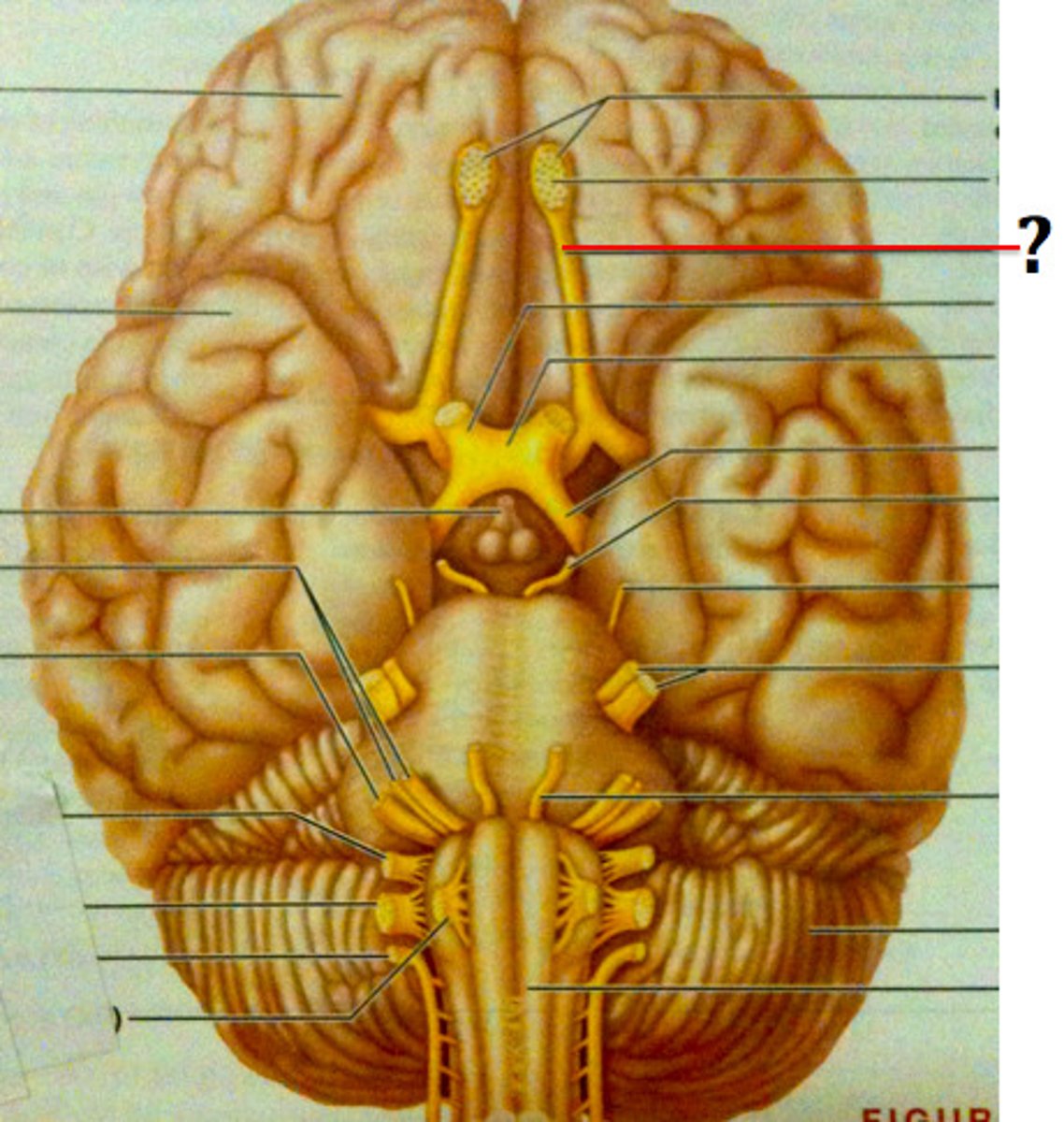
Olfactory tract
Pathway that carries smell signals to the brain.
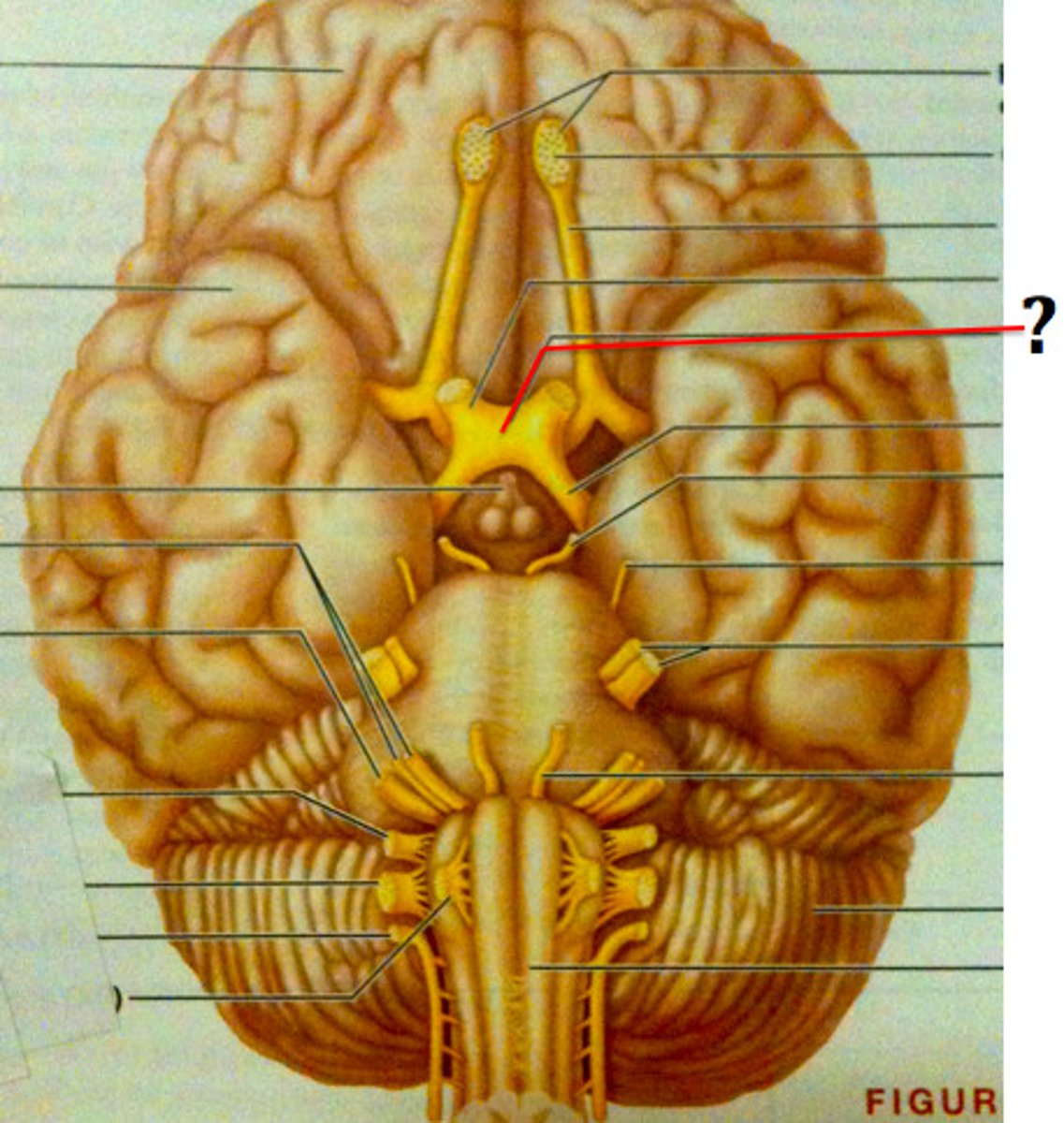
Optic chiasma
Crossing of optic nerves from both eyes.
Optic nerve
Carries visual information from the retina to the brain.
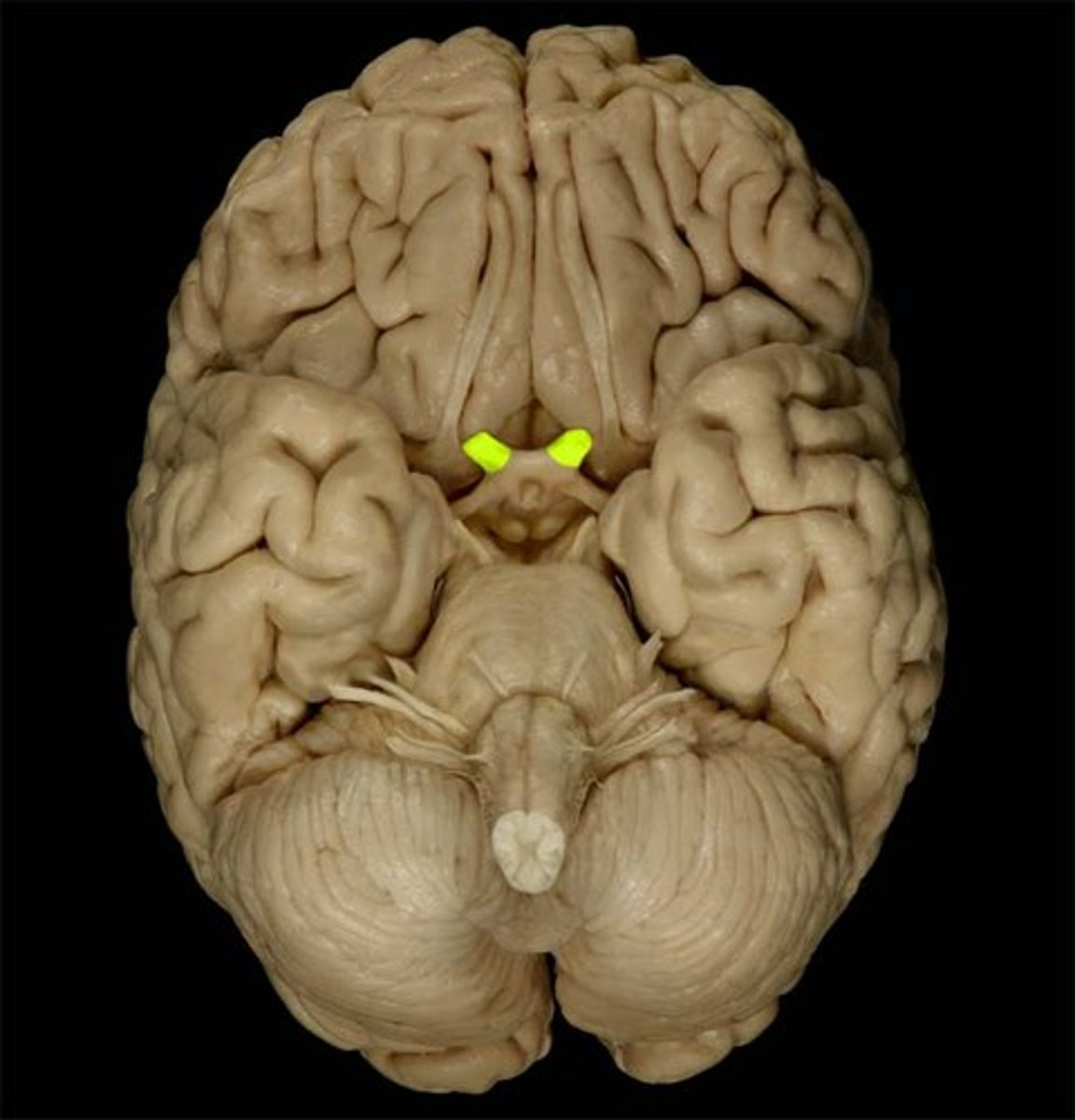
Optic tract
Pathway for visual information from the optic chiasma to the brain.
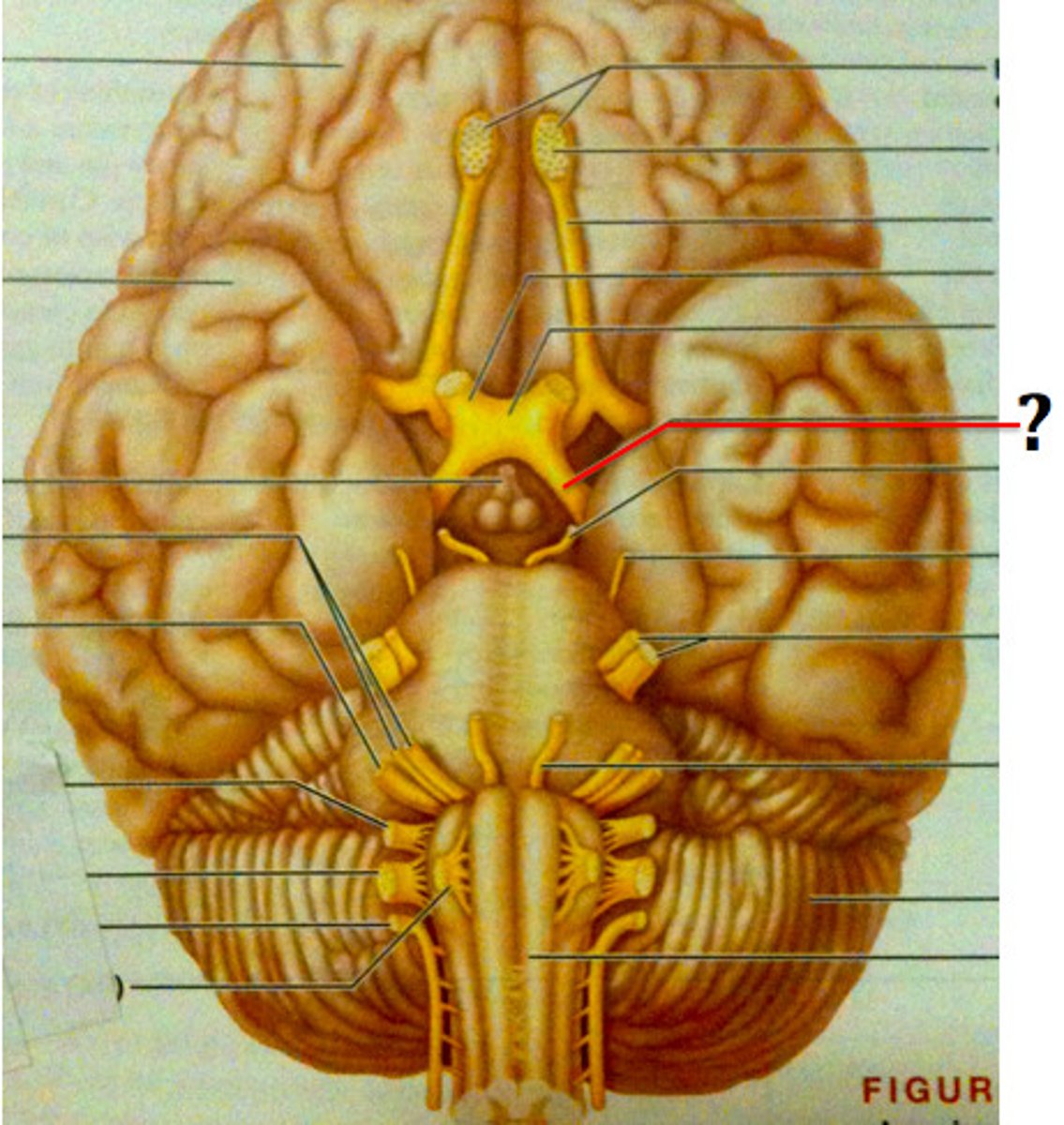
Mammillary body
Part of the hypothalamus involved in memory and smell.
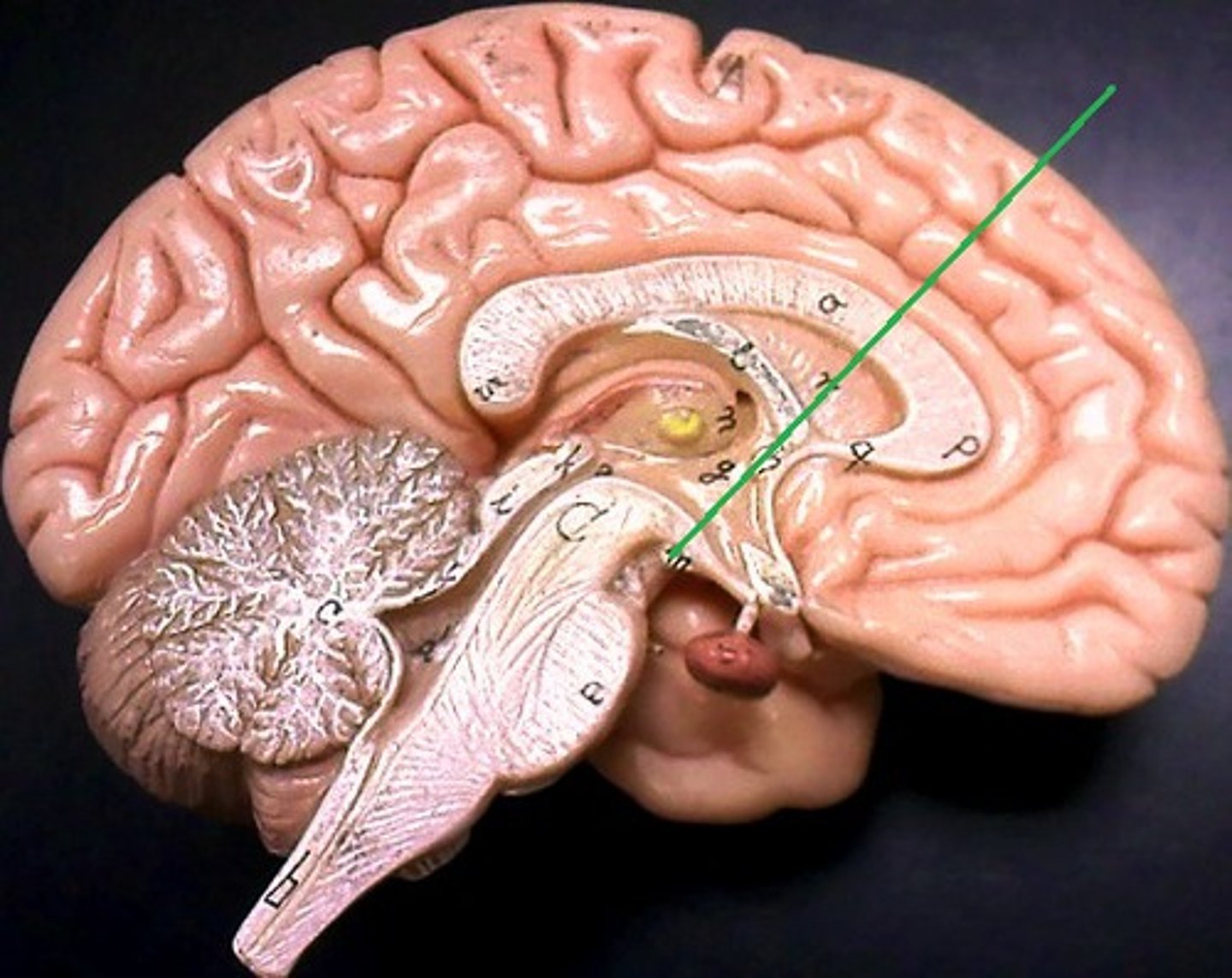
Fornix
Fiber tract that connects parts of the limbic system.
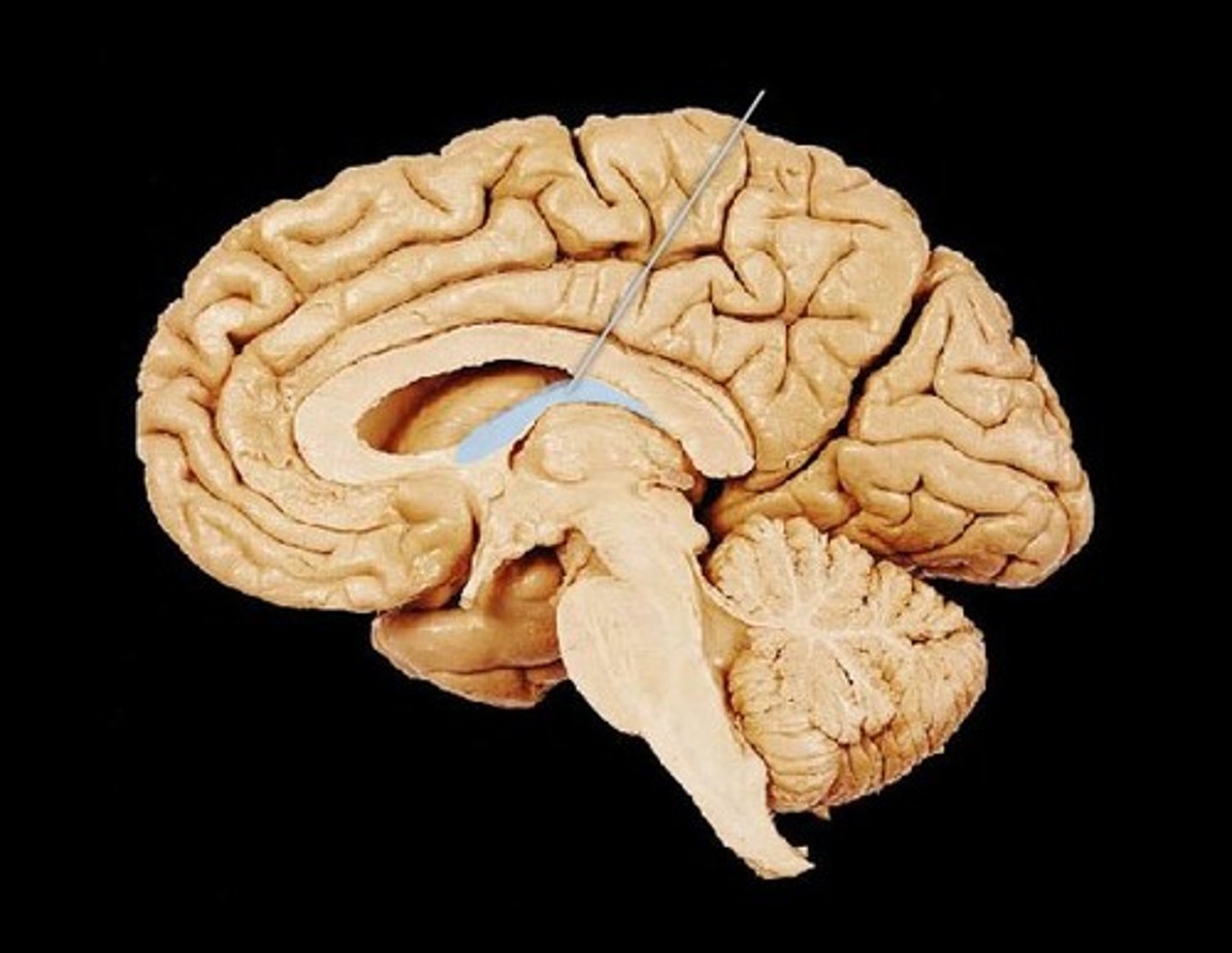
Pineal gland
Secretes melatonin and regulates circadian rhythms.
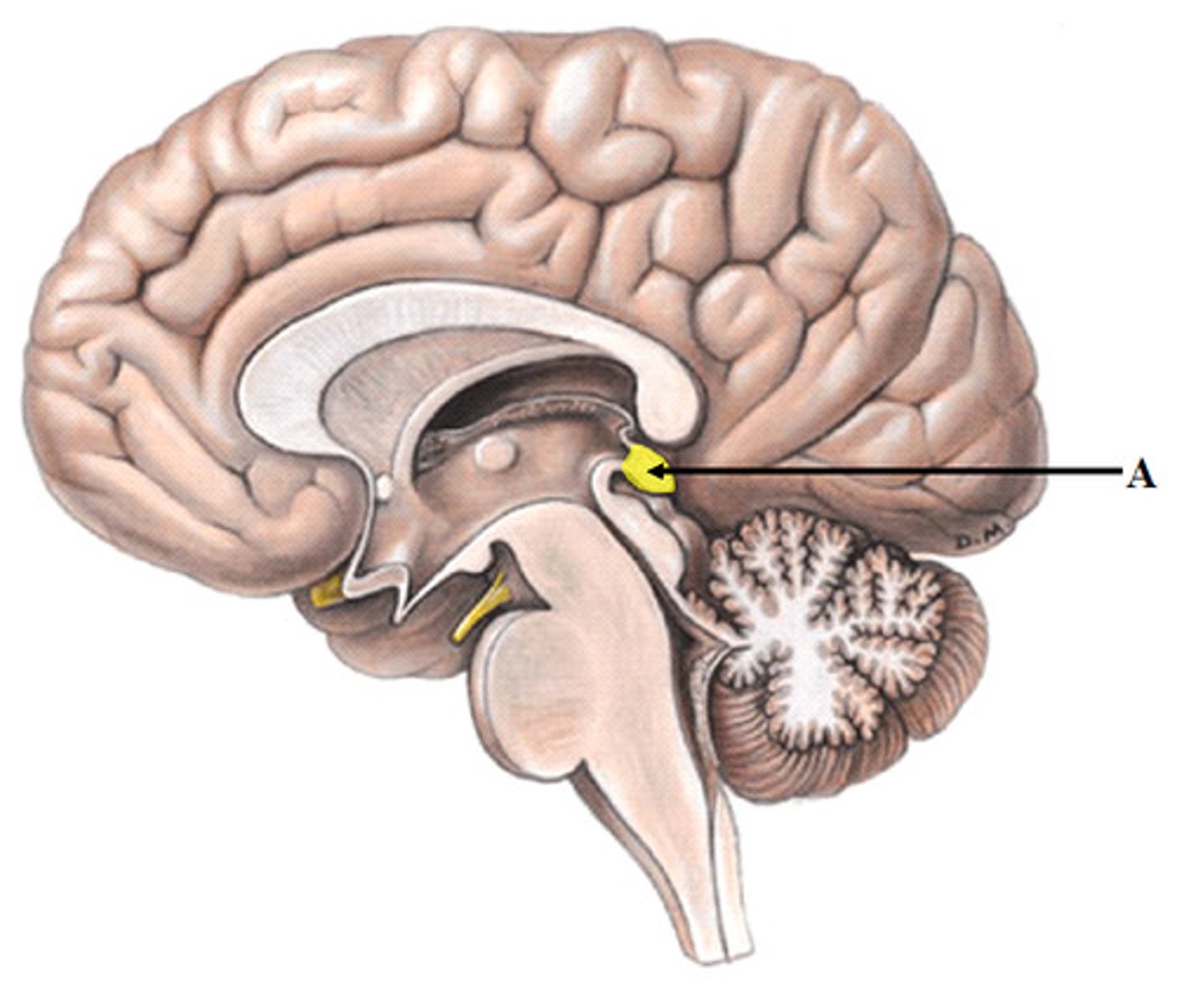
Corpora quadrigemina
Four mounds on the midbrain involved in visual and auditory reflexes.
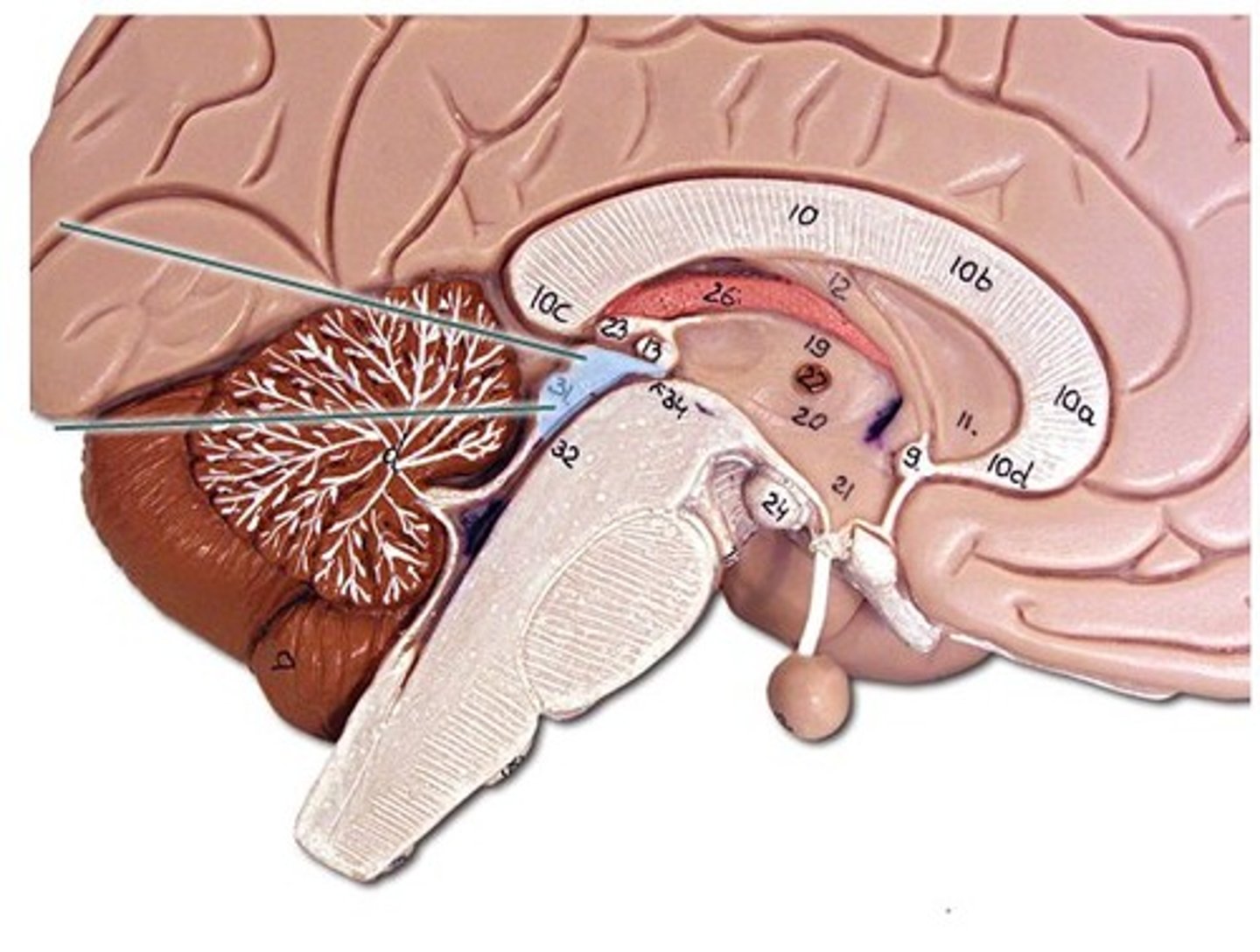
Fourth ventricle
CSF-filled space between brainstem and cerebellum.
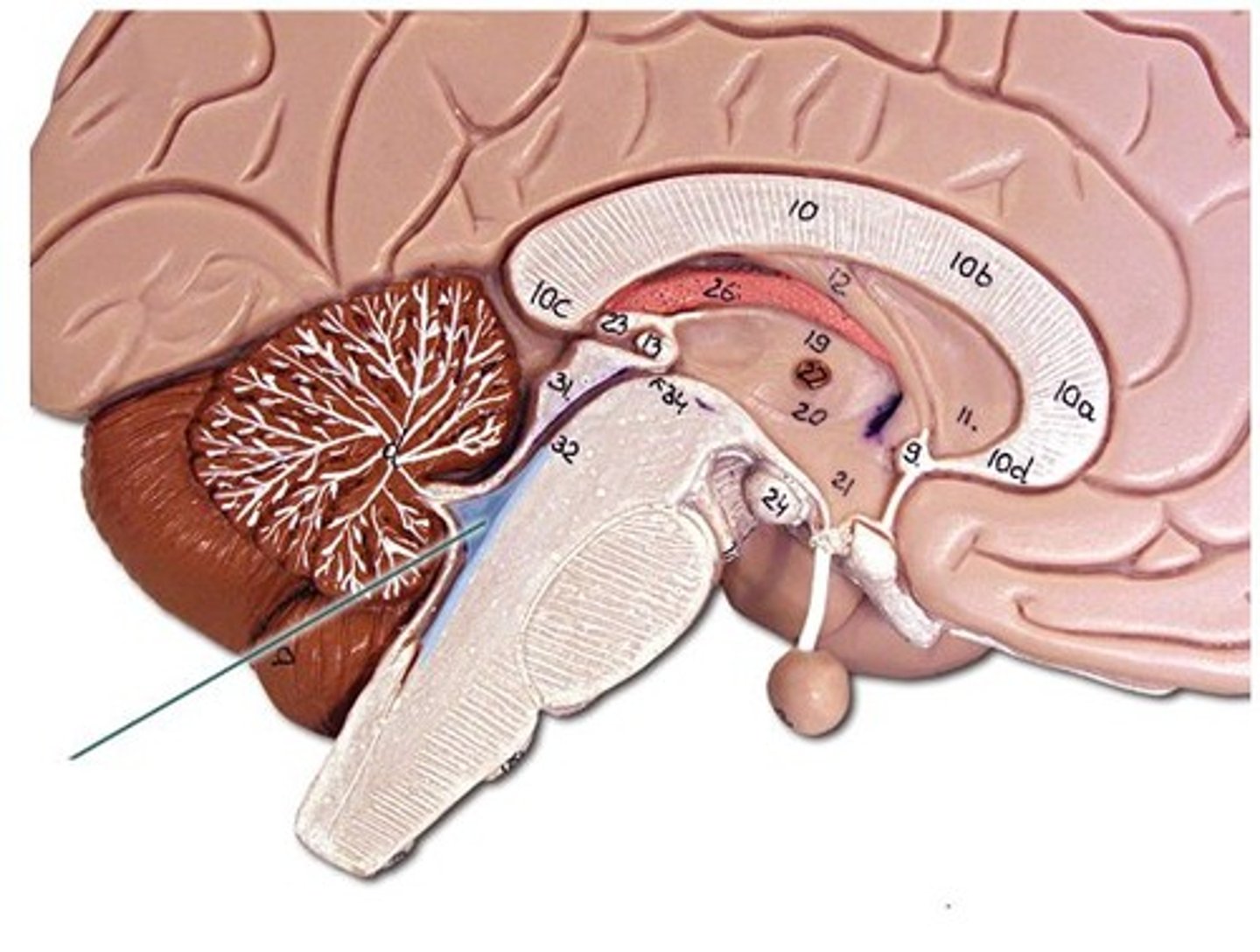
Thalamus
Relay station for sensory information going to the cortex.
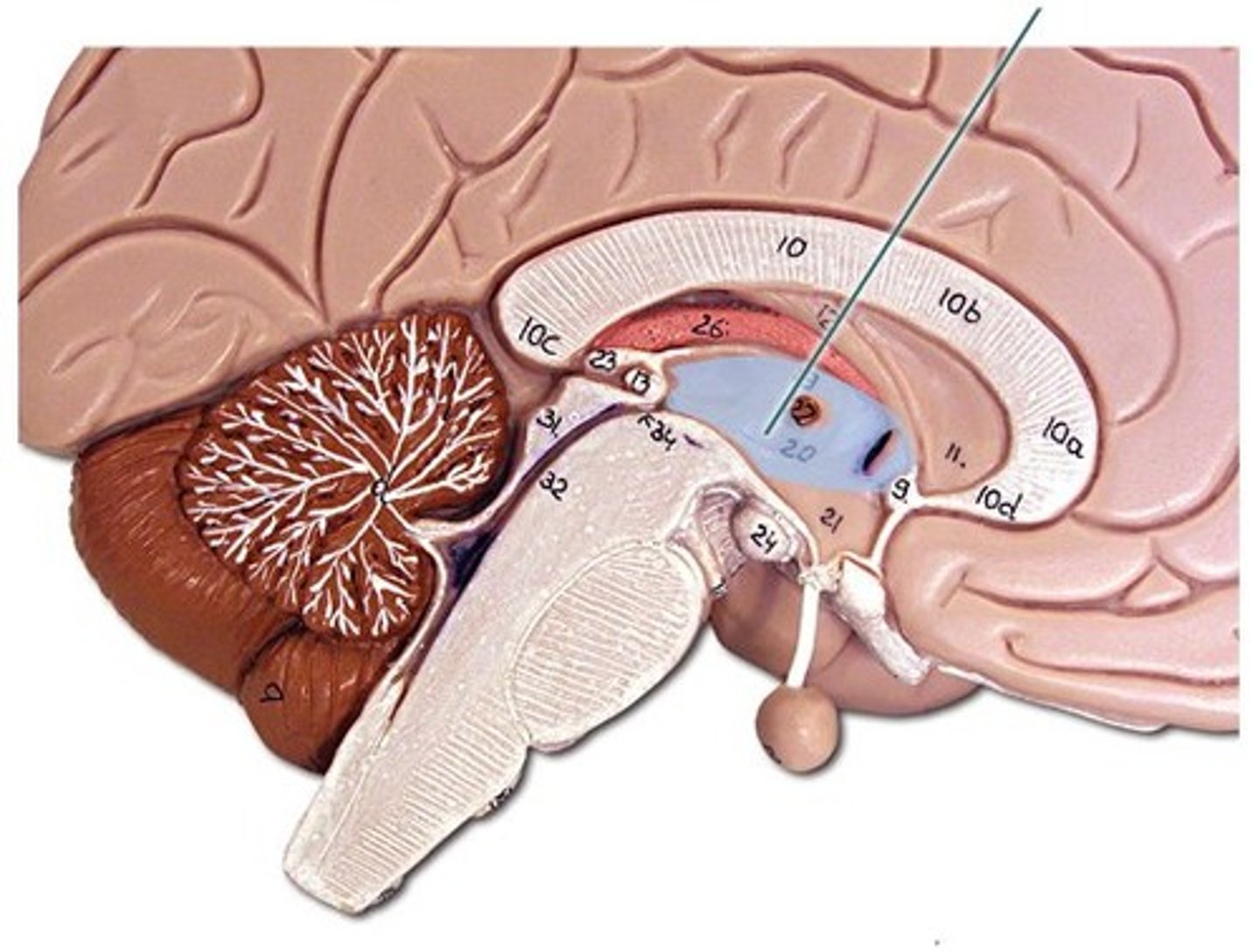
Hypothalamus
Controls autonomic functions and links the nervous system to the endocrine system.
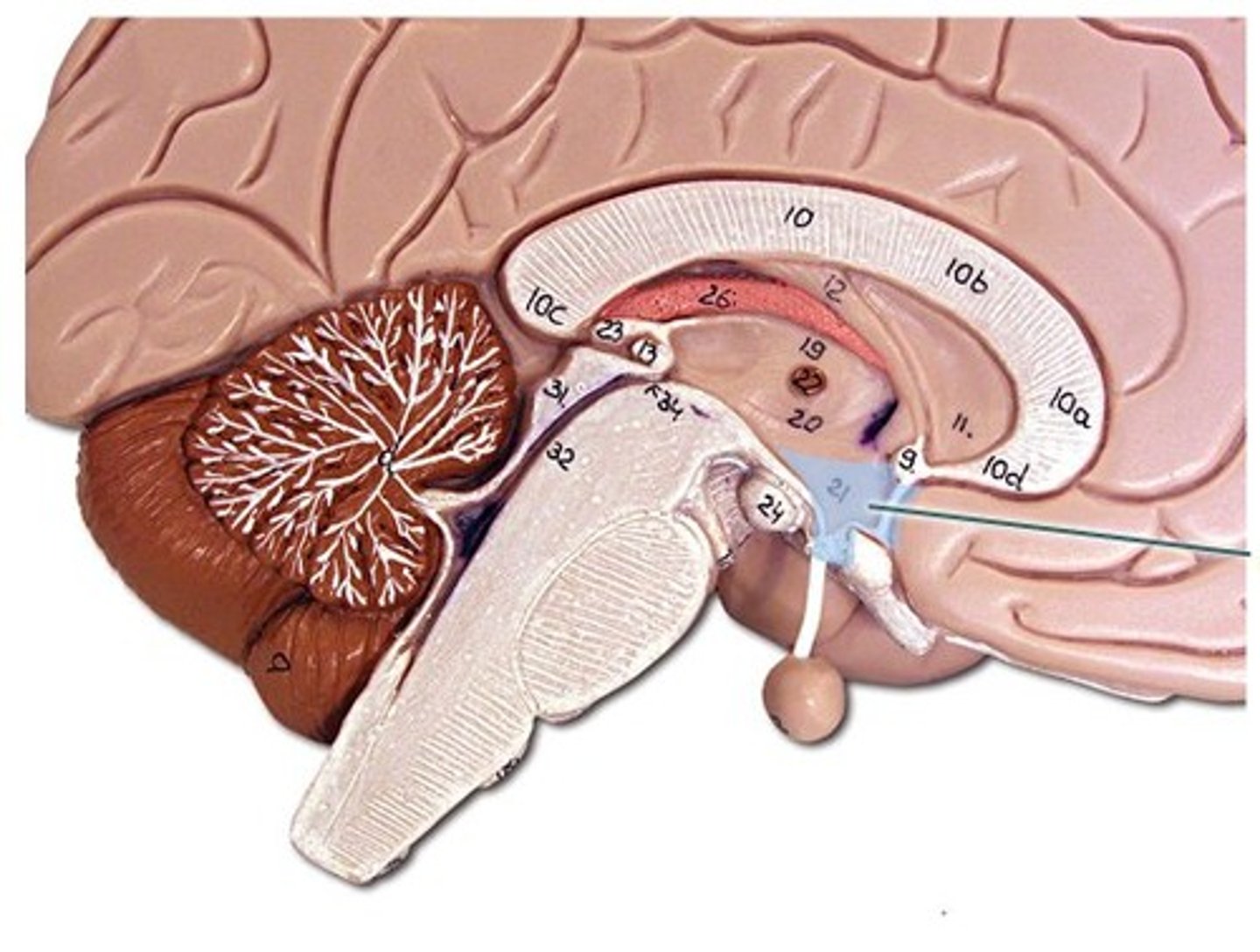
Anterior commissure
Bundle of nerve fibers connecting the two temporal lobes.
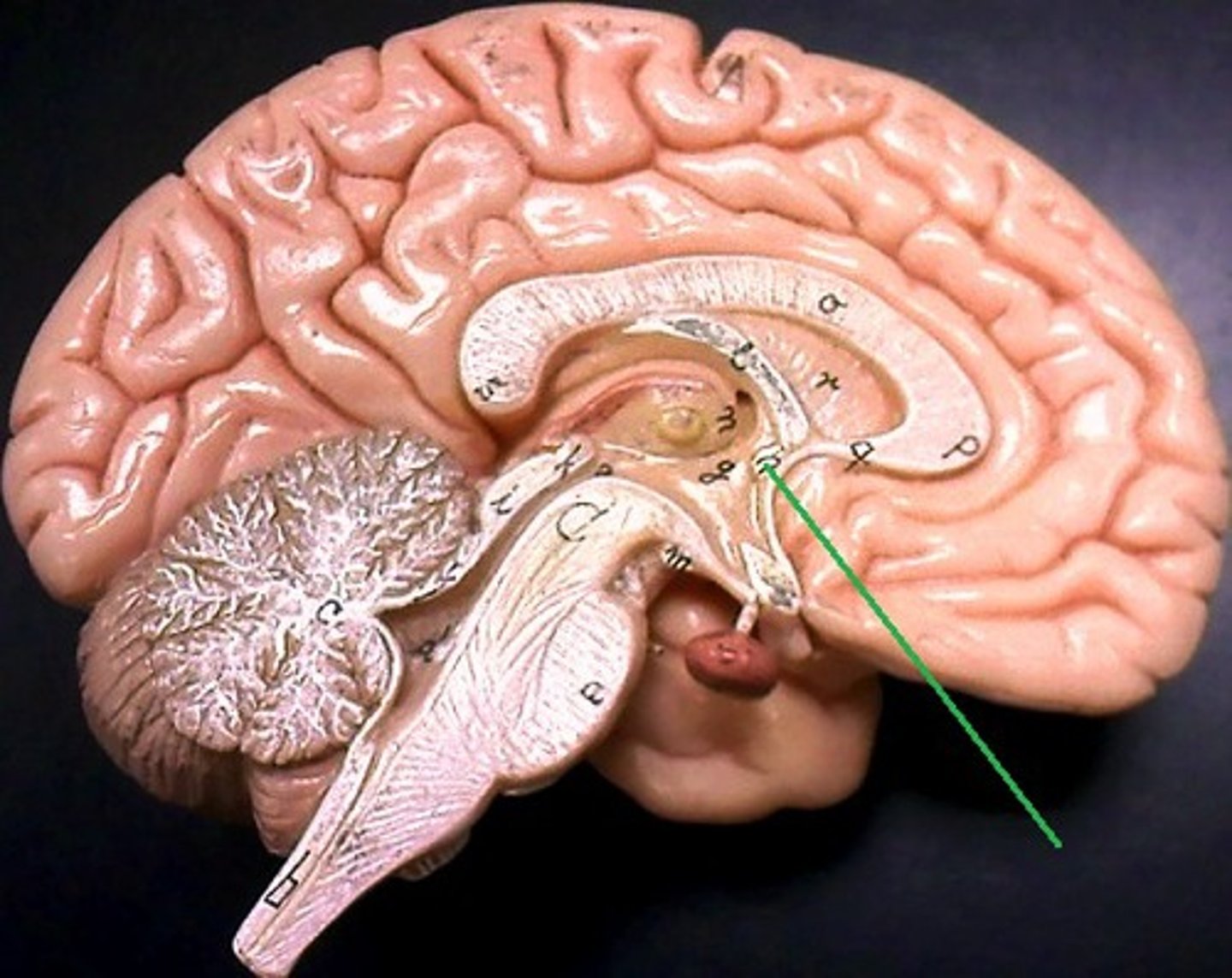
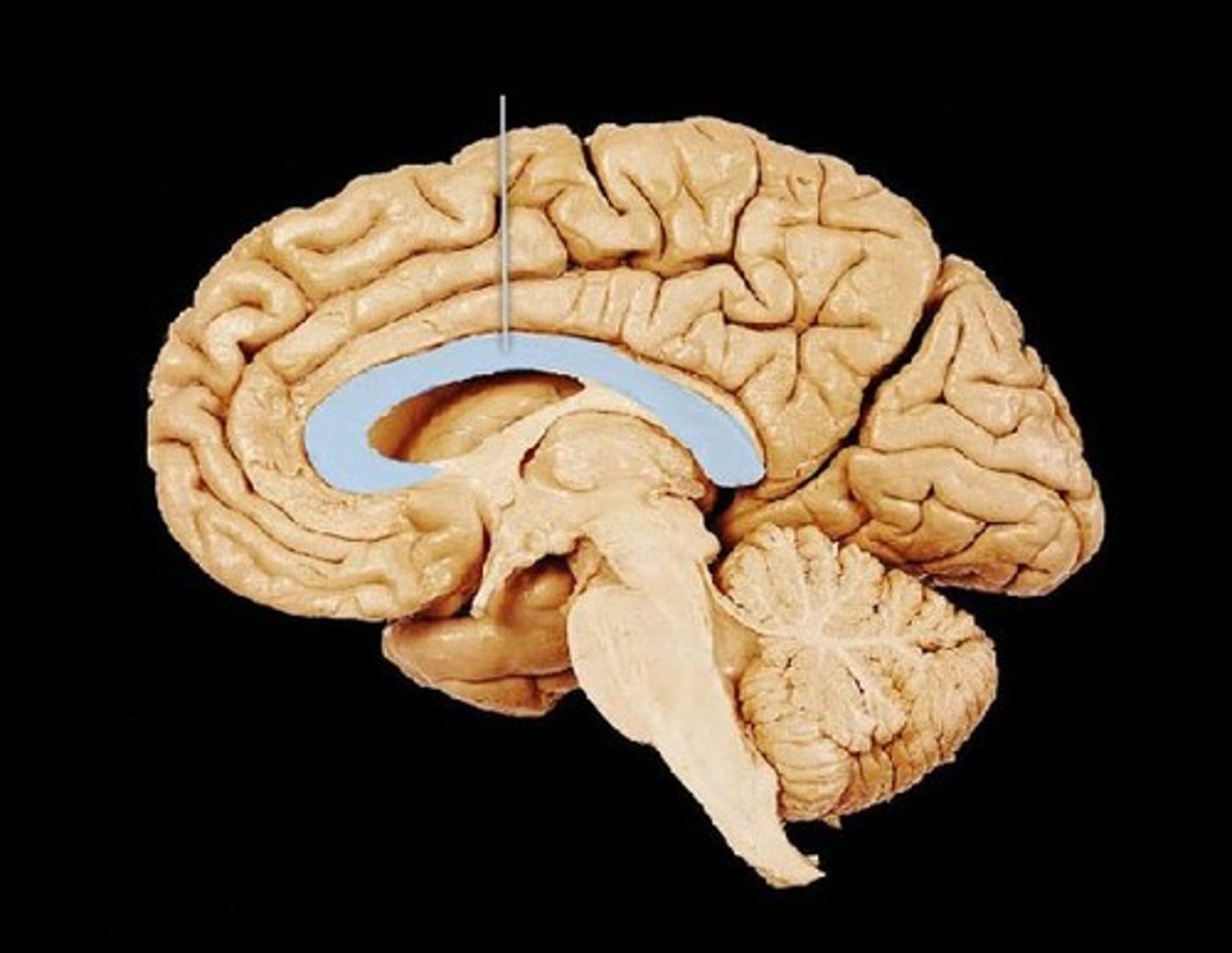
Corpus callosum
Large bundle of nerve fibers connecting the two cerebral hemispheres.
Lateral ventricle
CSF-filled chamber in each cerebral hemisphere.
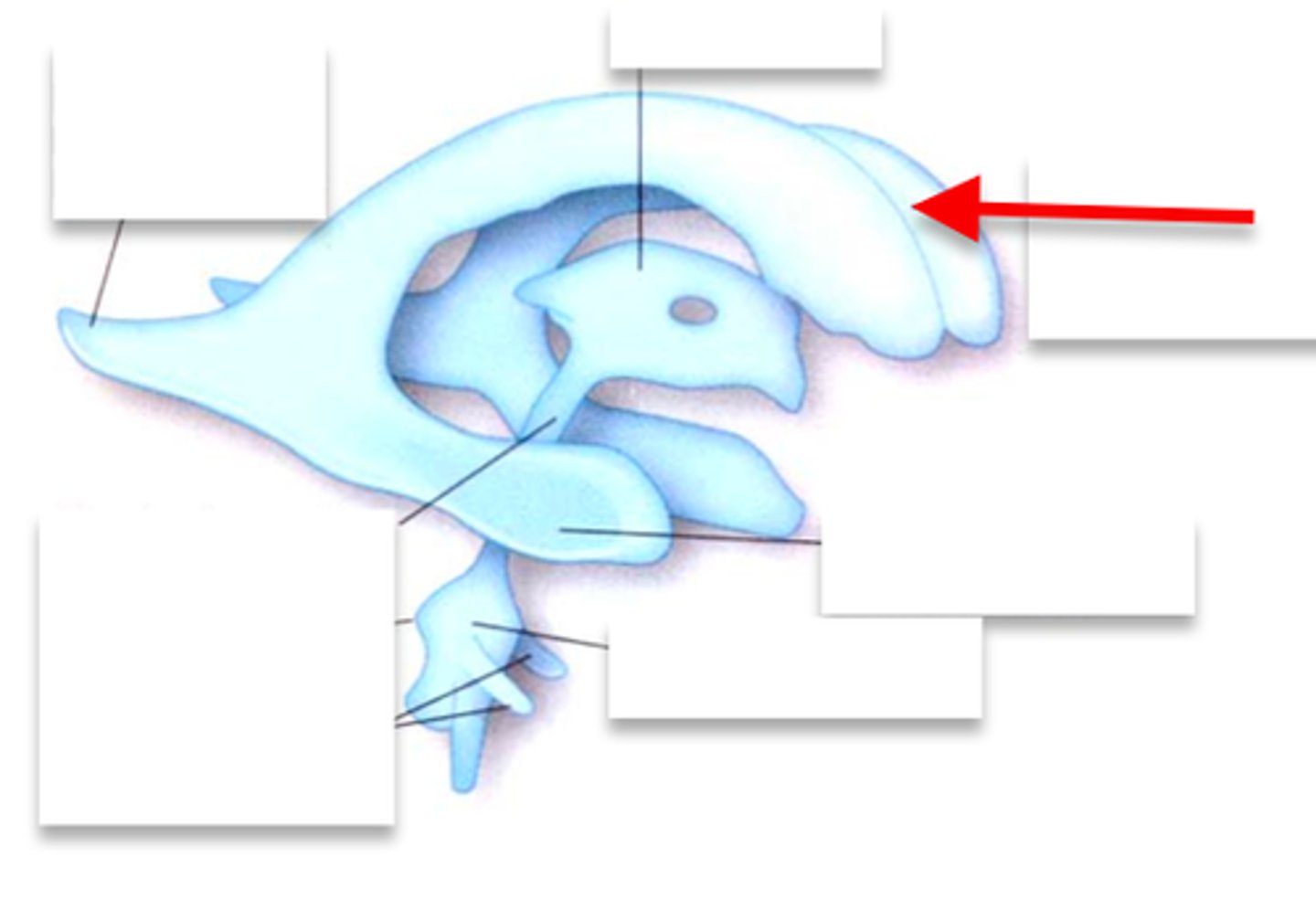
Septum pellucidum
Thin membrane that separates the lateral ventricles.
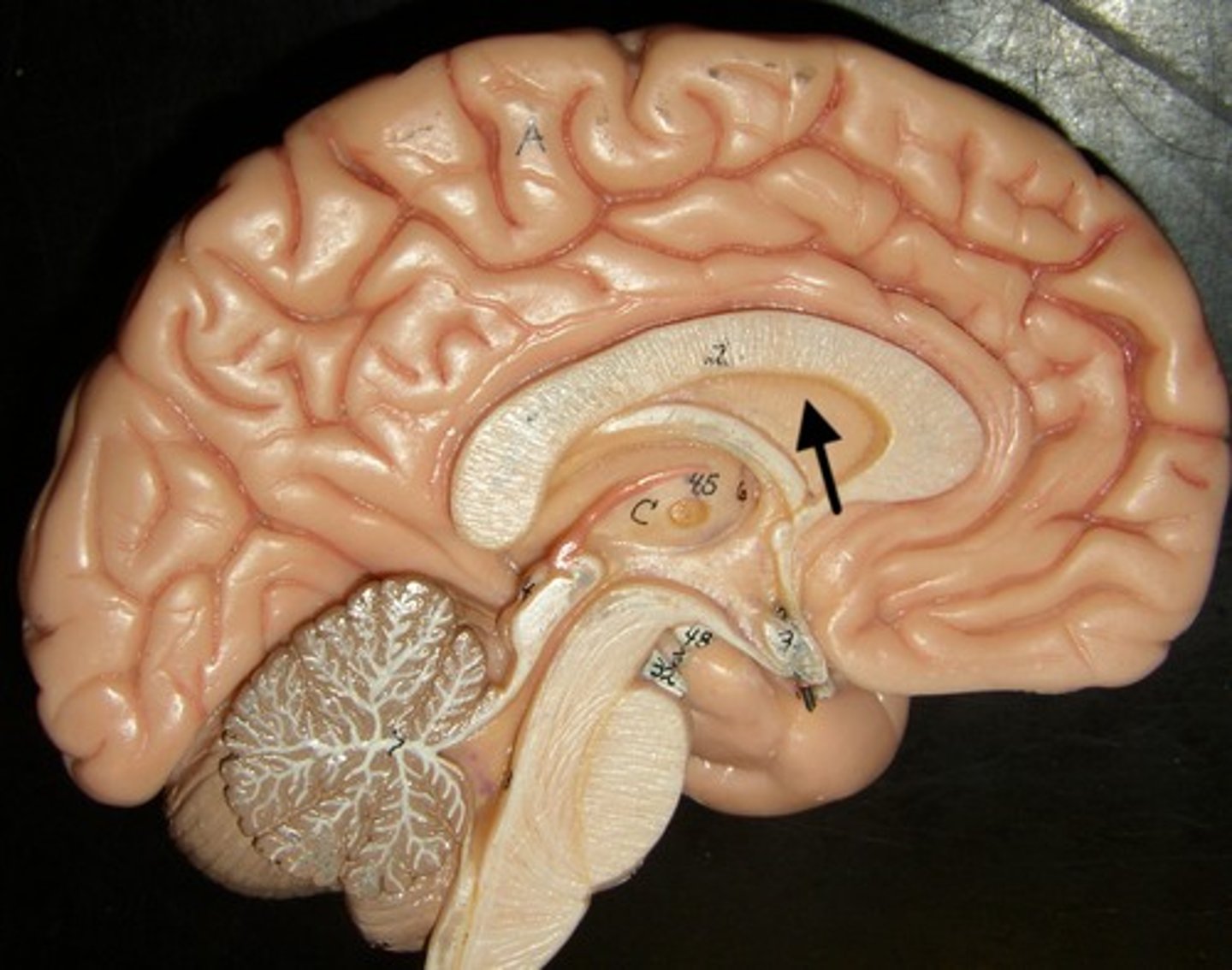
Choroid plexus
Produces cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside ventricles.
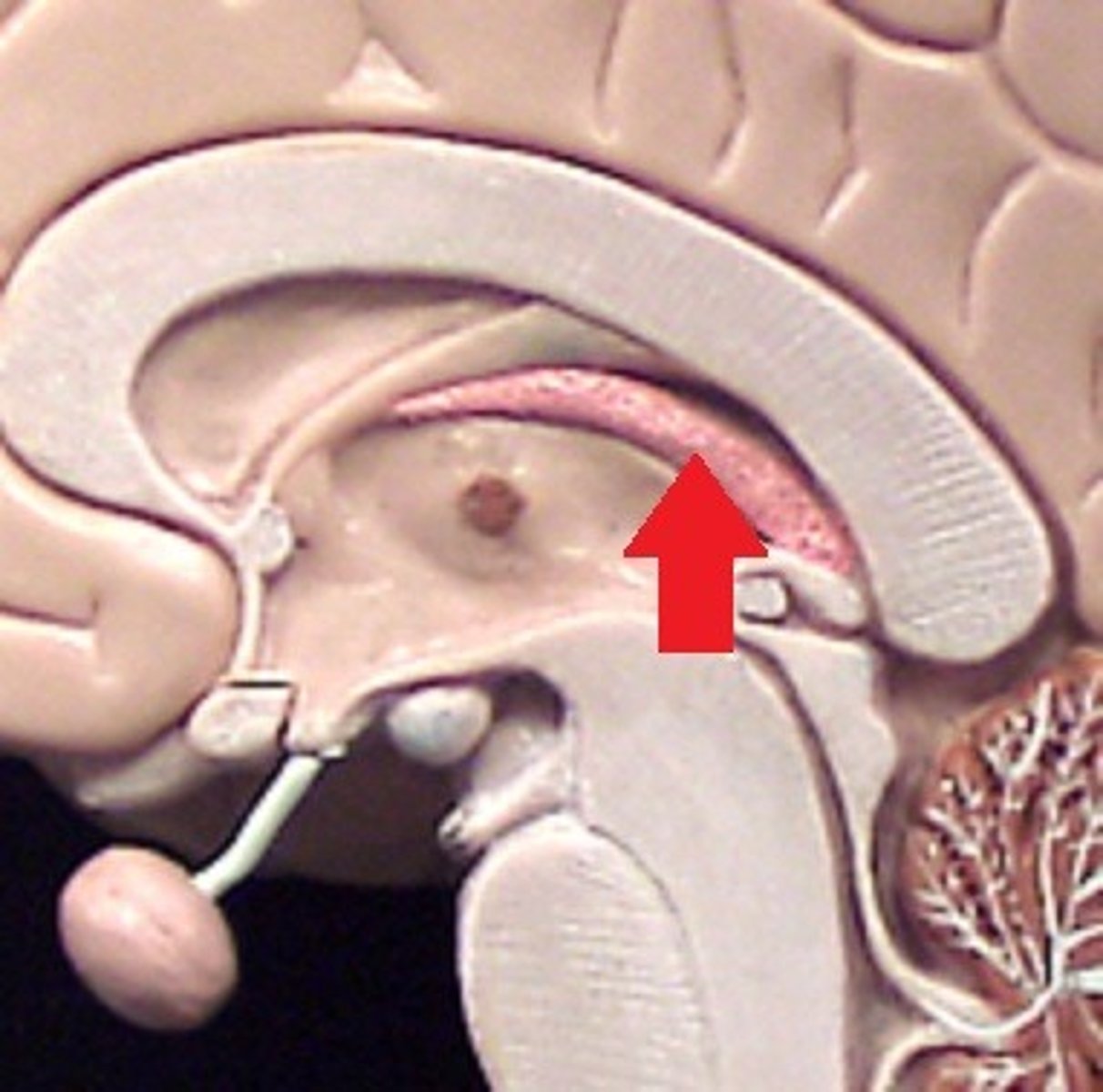
Cerebral aqueduct
Narrow canal that connects the third and fourth ventricles.
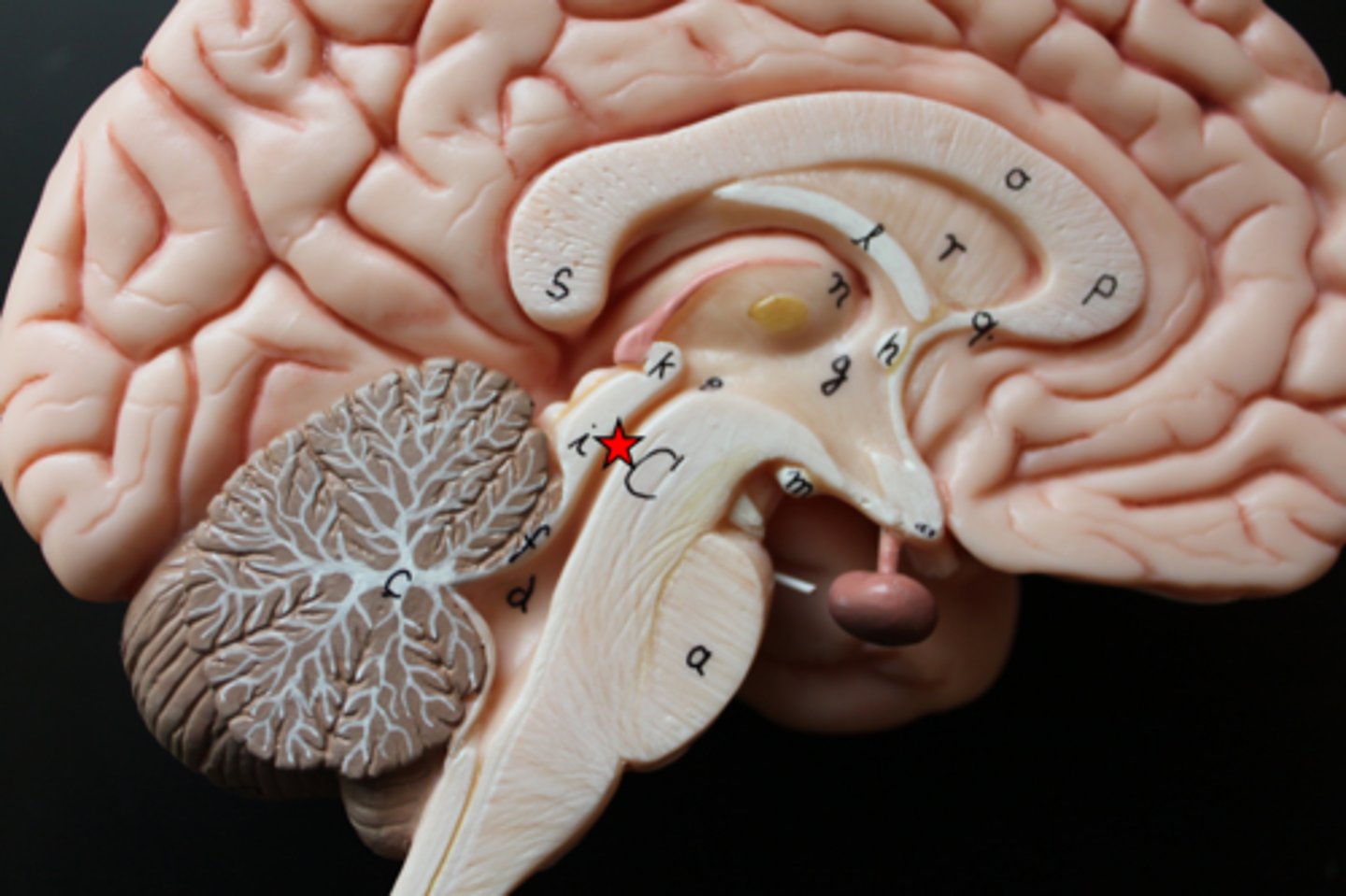
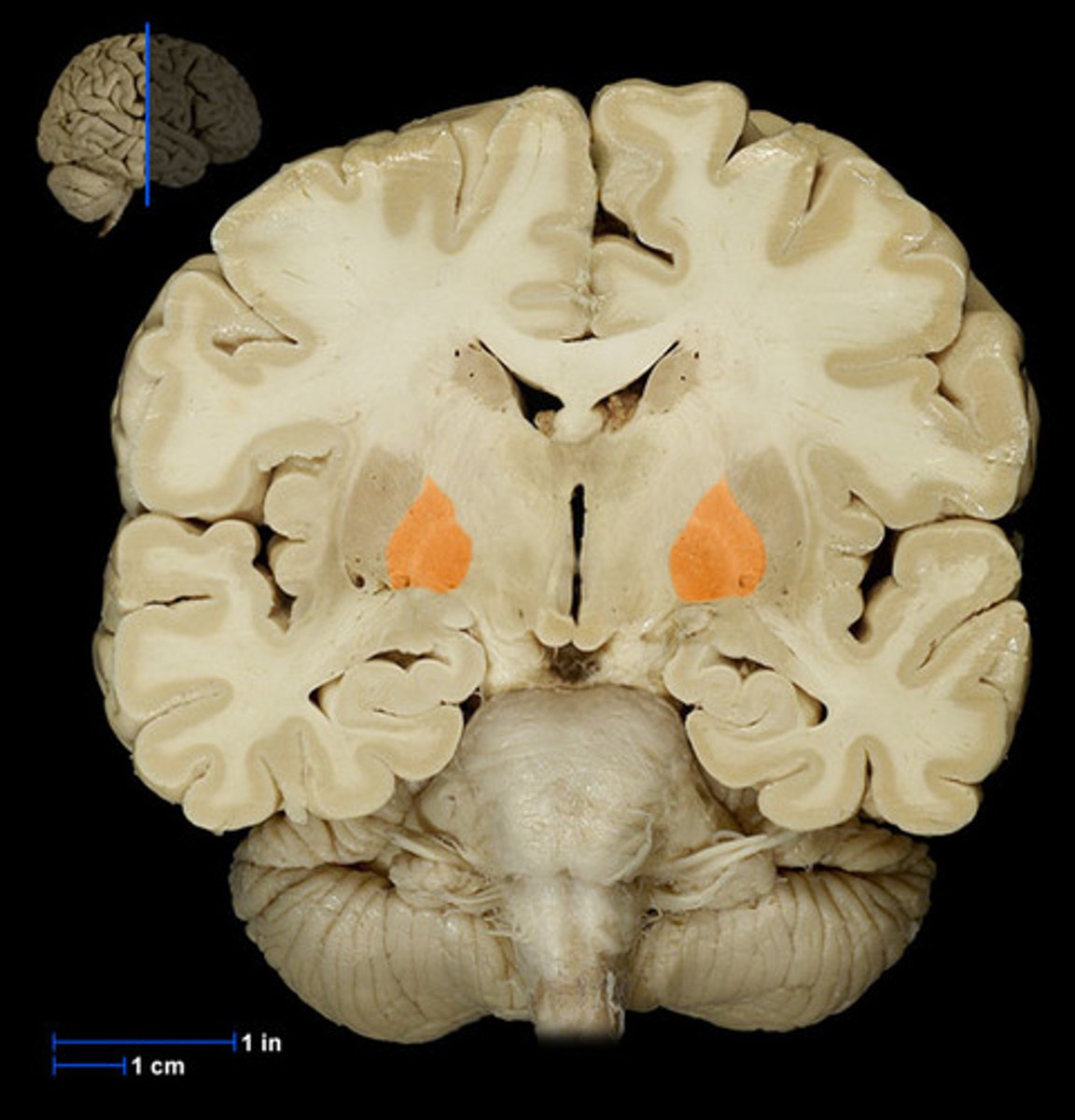
Caudate nucleus
Part of the basal ganglia involved in learning and movement regulation.
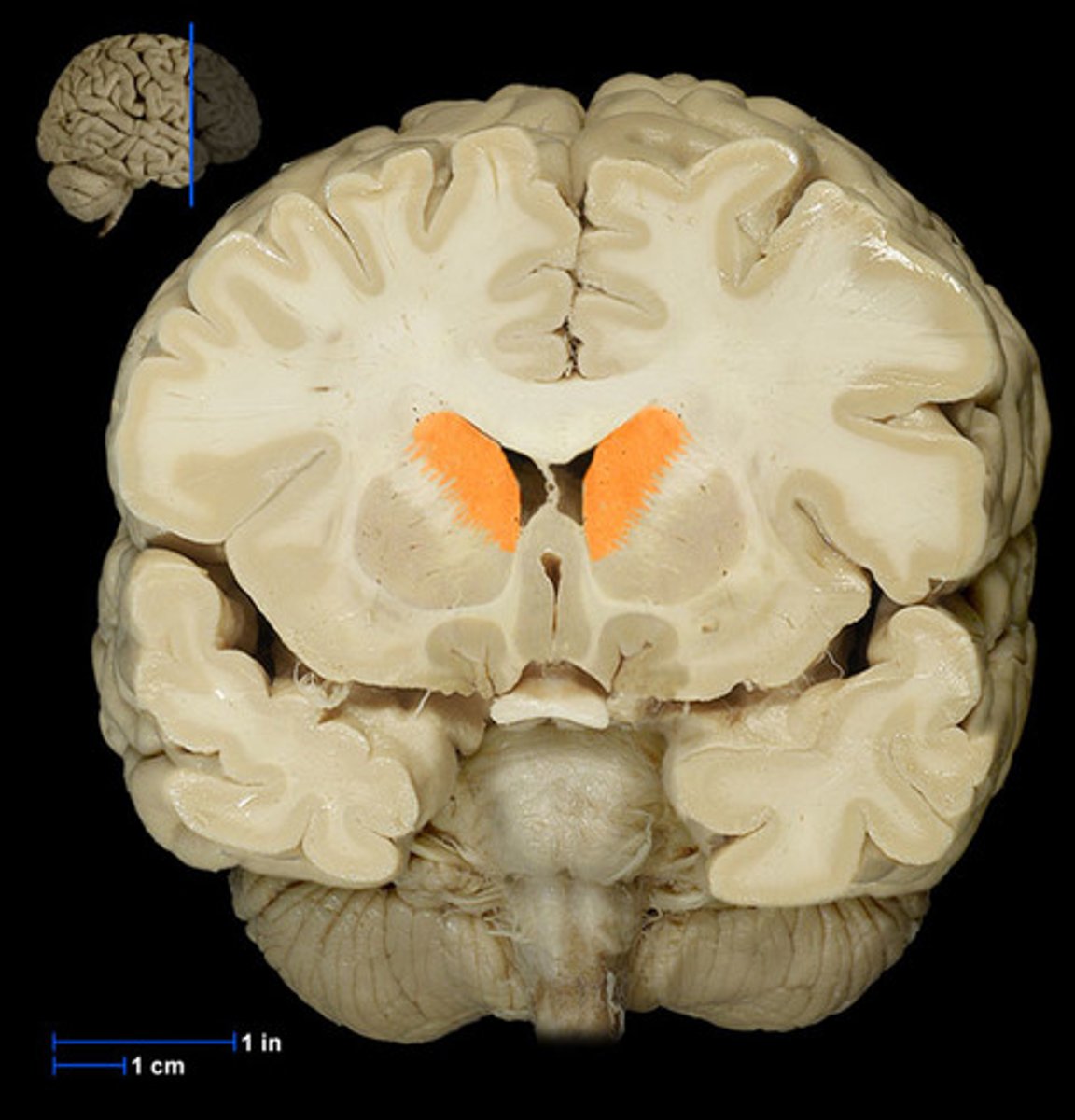
Putamen
Part of the basal ganglia that helps regulate movement.
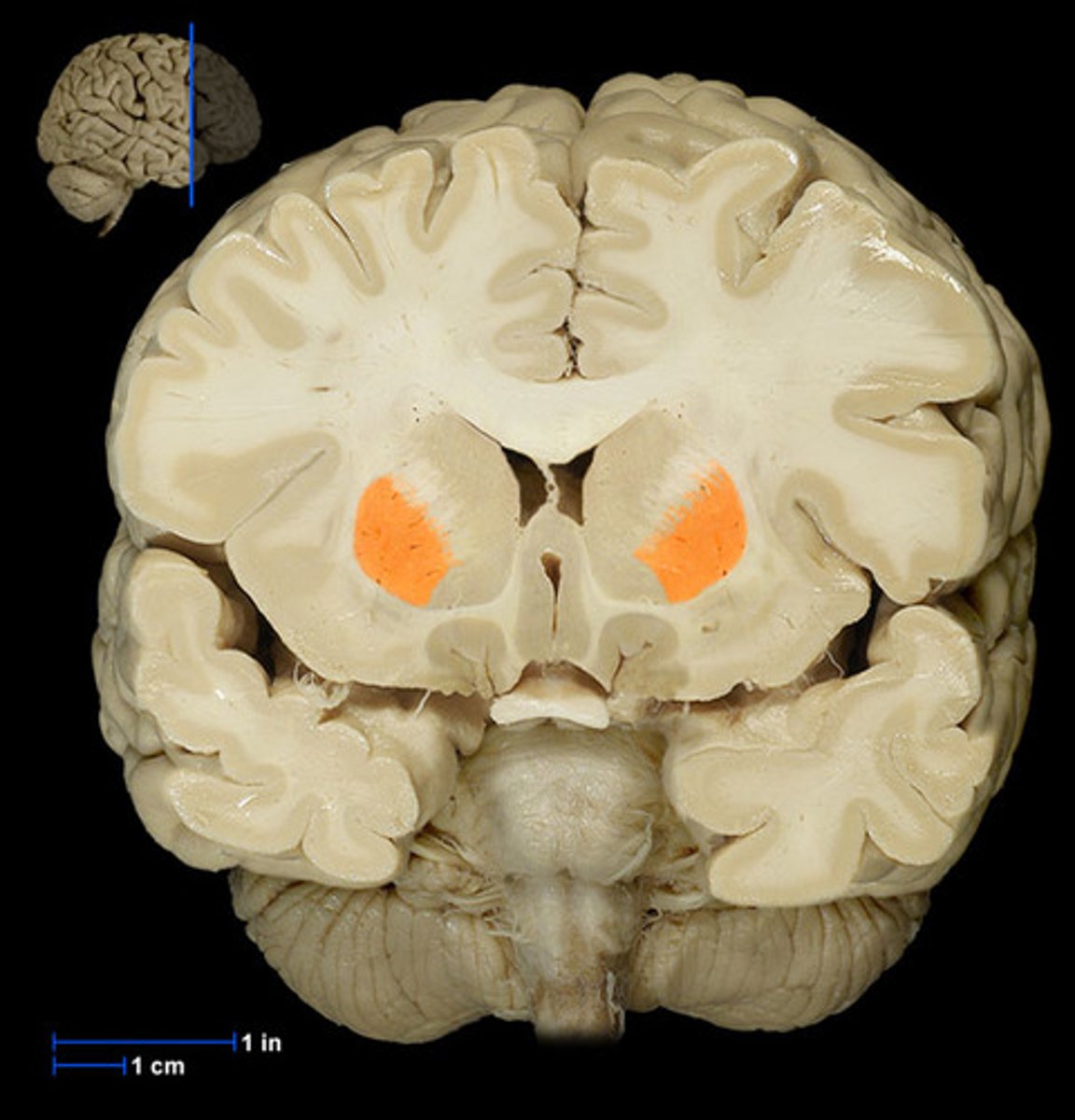
Globus pallidus
Part of the basal ganglia that helps control voluntary movement.
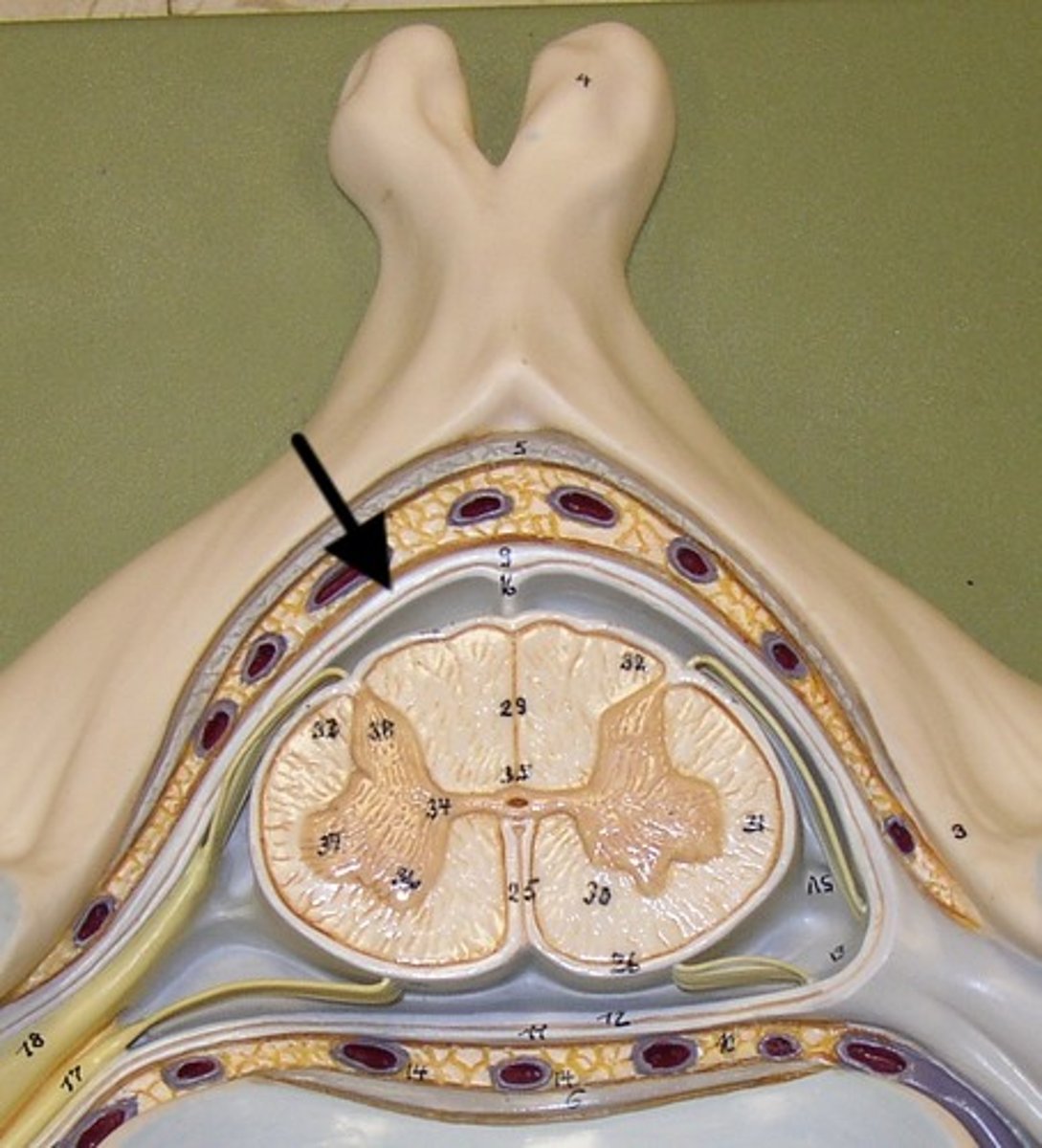
Dura mater
Tough outermost meningeal layer protecting the brain.
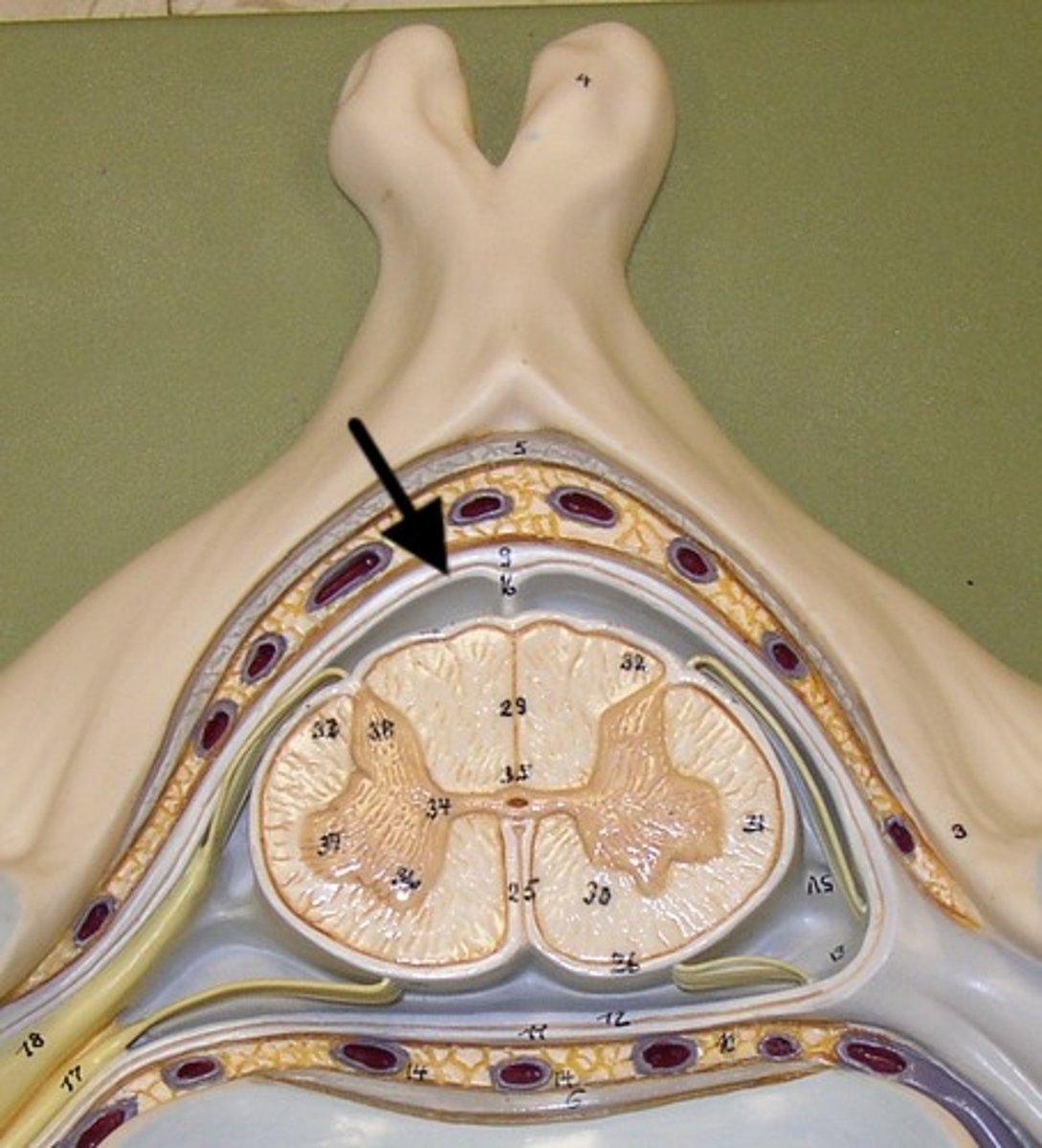
Arachnoid mater
Middle meningeal layer; web-like appearance.
Pia mater
Thin inner layer of meninges that clings to the brain surface.
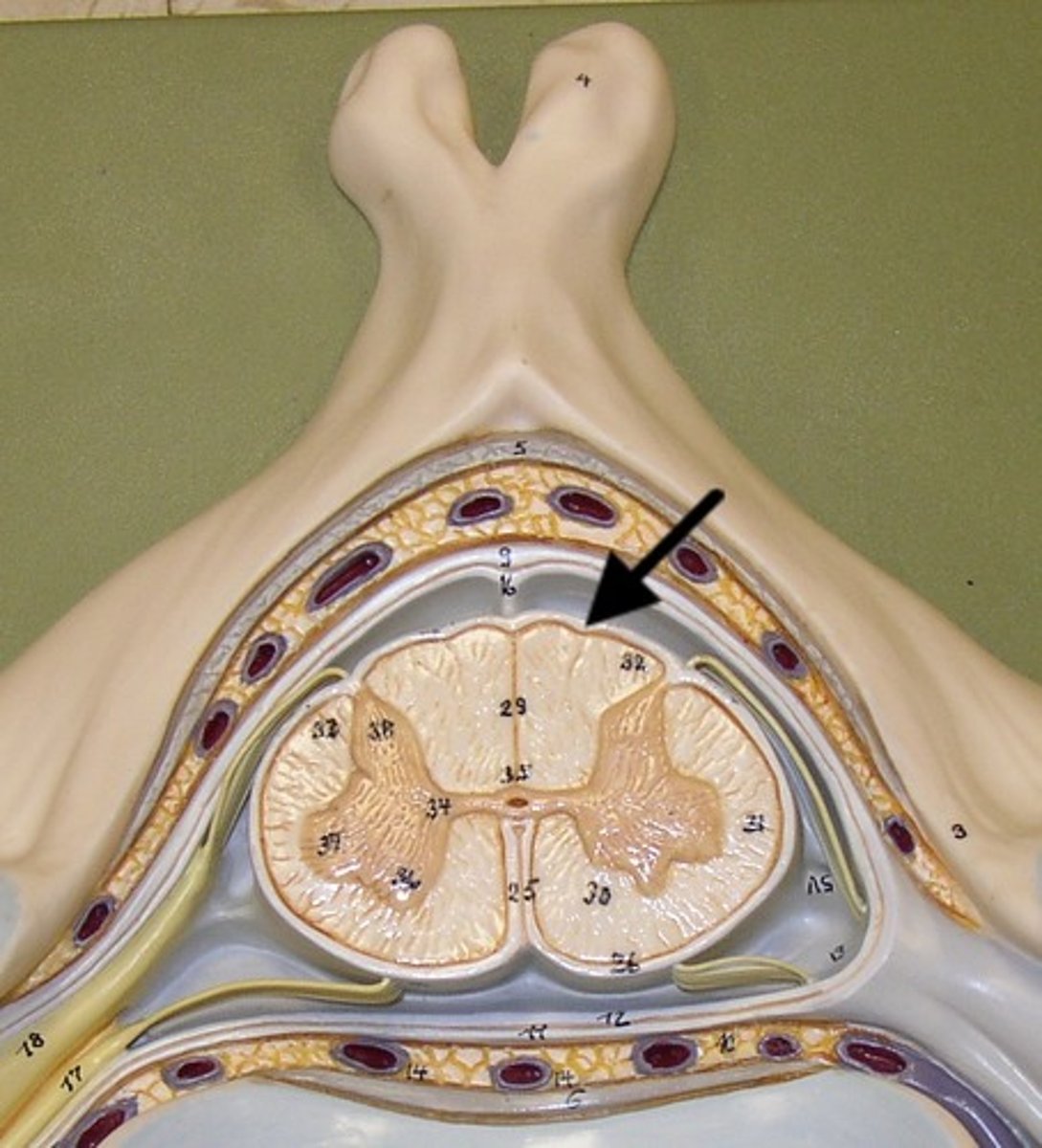
Subdural space
Space between dura mater and arachnoid mater.
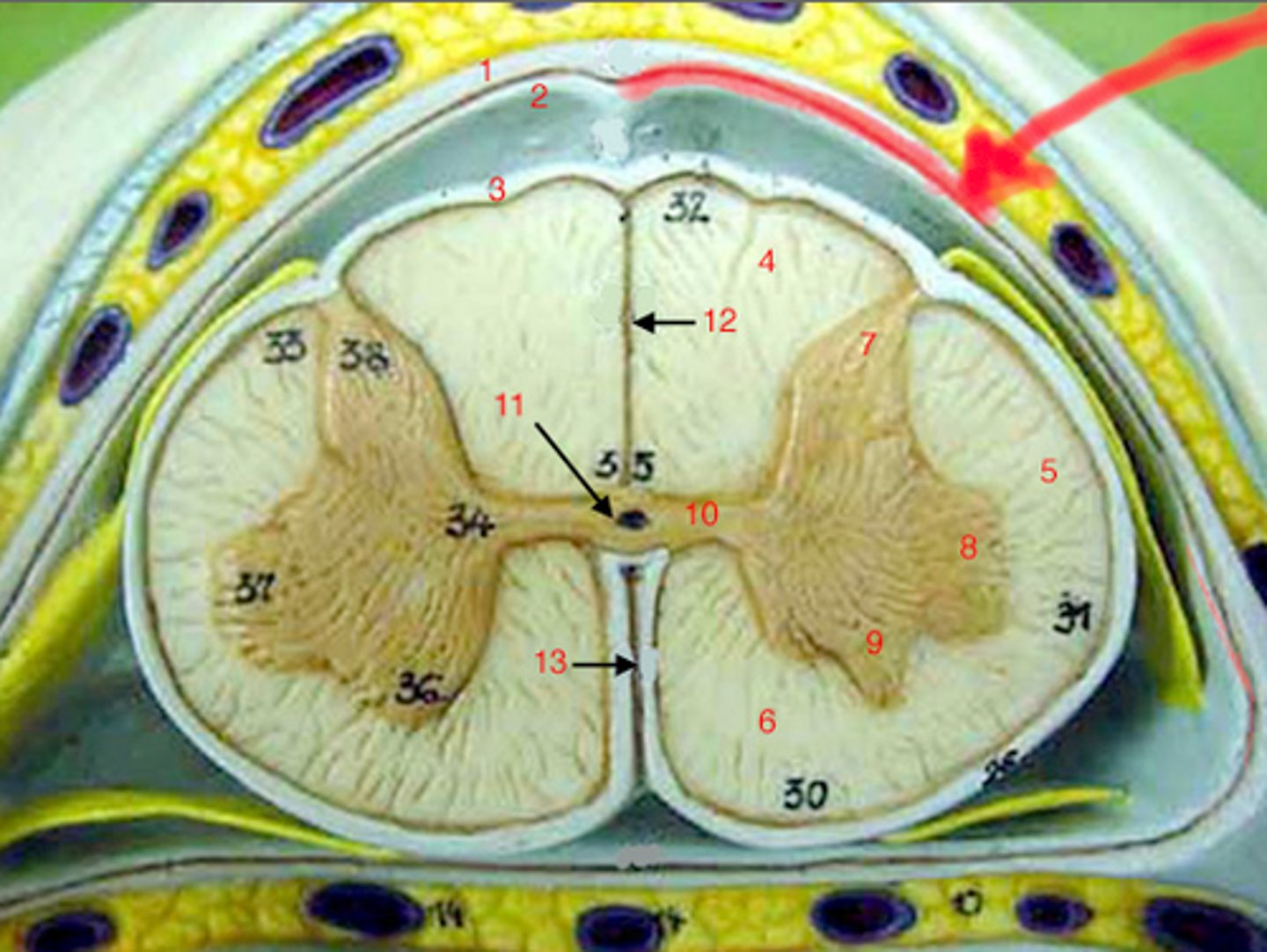
Subarachnoid space
Contains cerebrospinal fluid; located between arachnoid and pia mater.
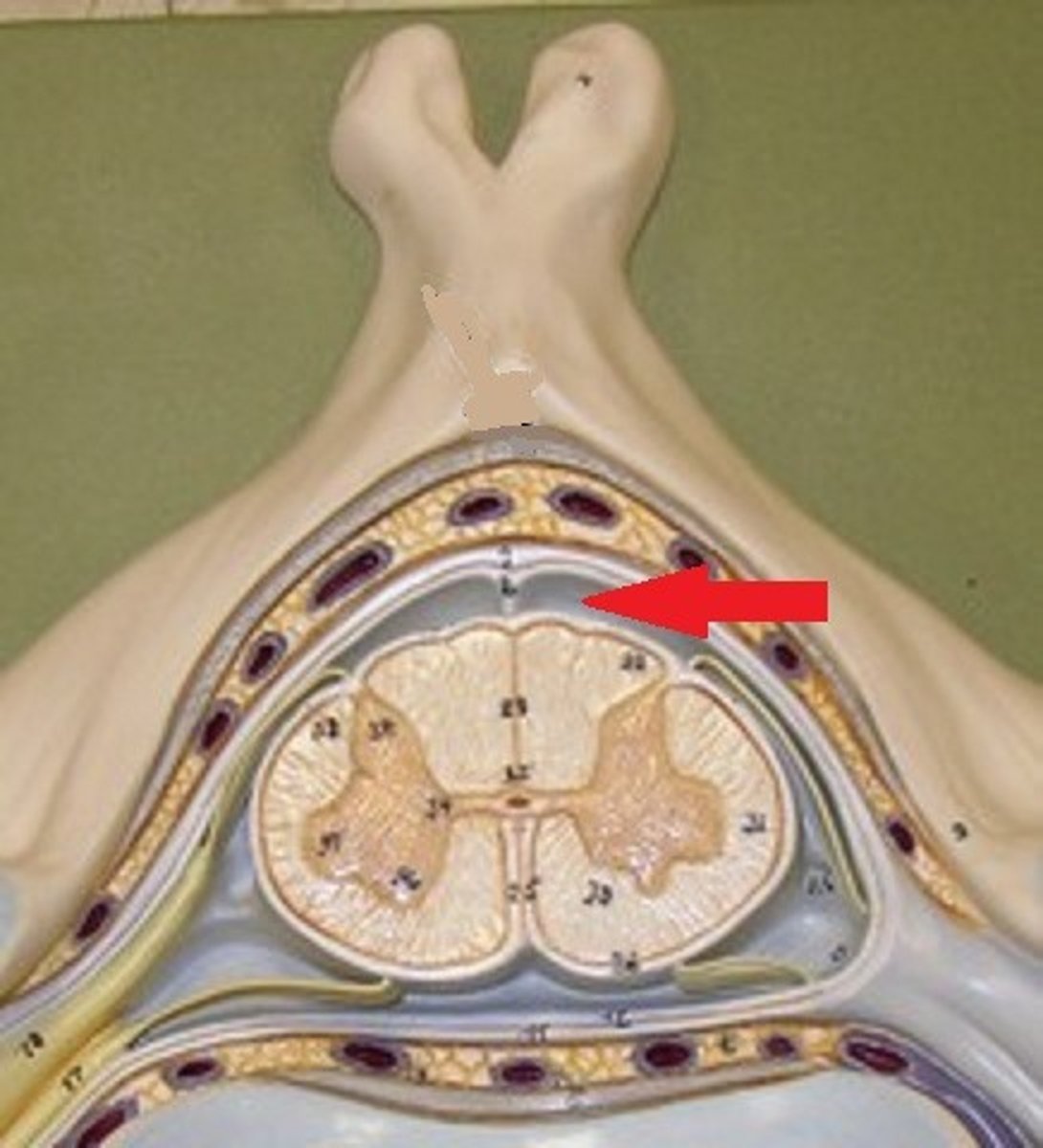
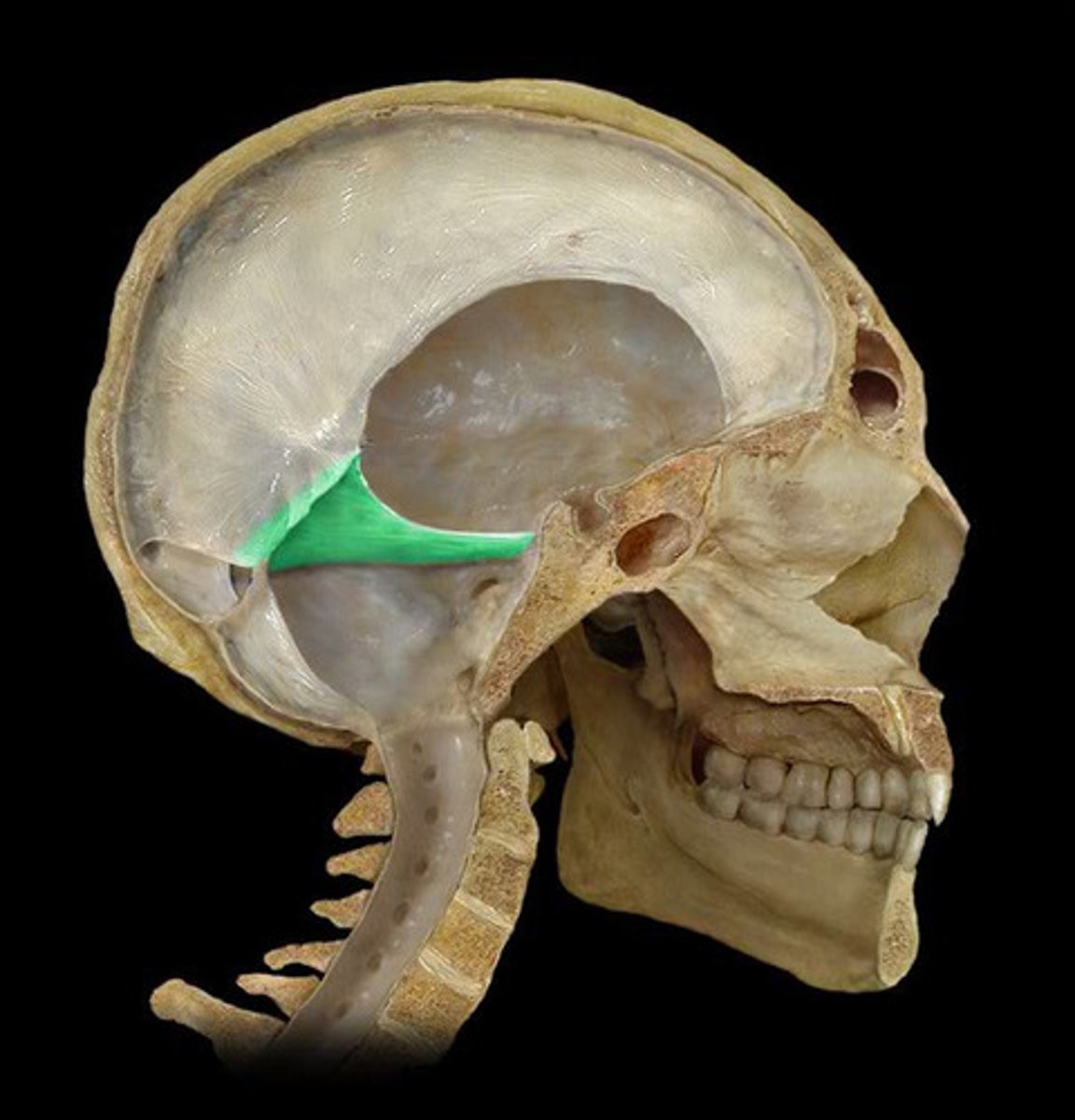
Falx cerebri
Dura mater fold that separates the cerebral hemispheres.
Falx cerebelli
Dura mater fold that separates cerebellar hemispheres.
Tentorium cerebelli
Dura mater fold between cerebrum and cerebellum.