Dissolution, Diffusion, and Osmotic Controlled Modified Release Systems
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
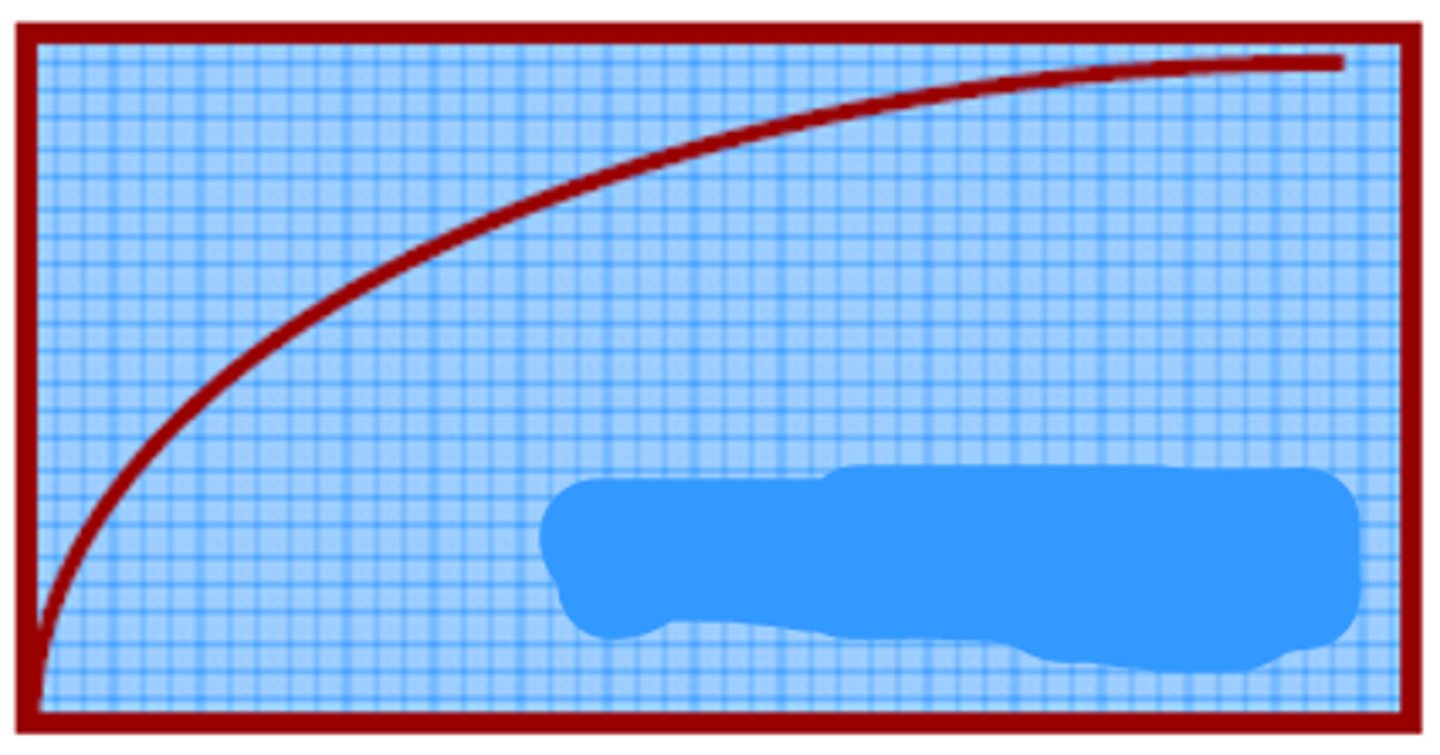
First order ER
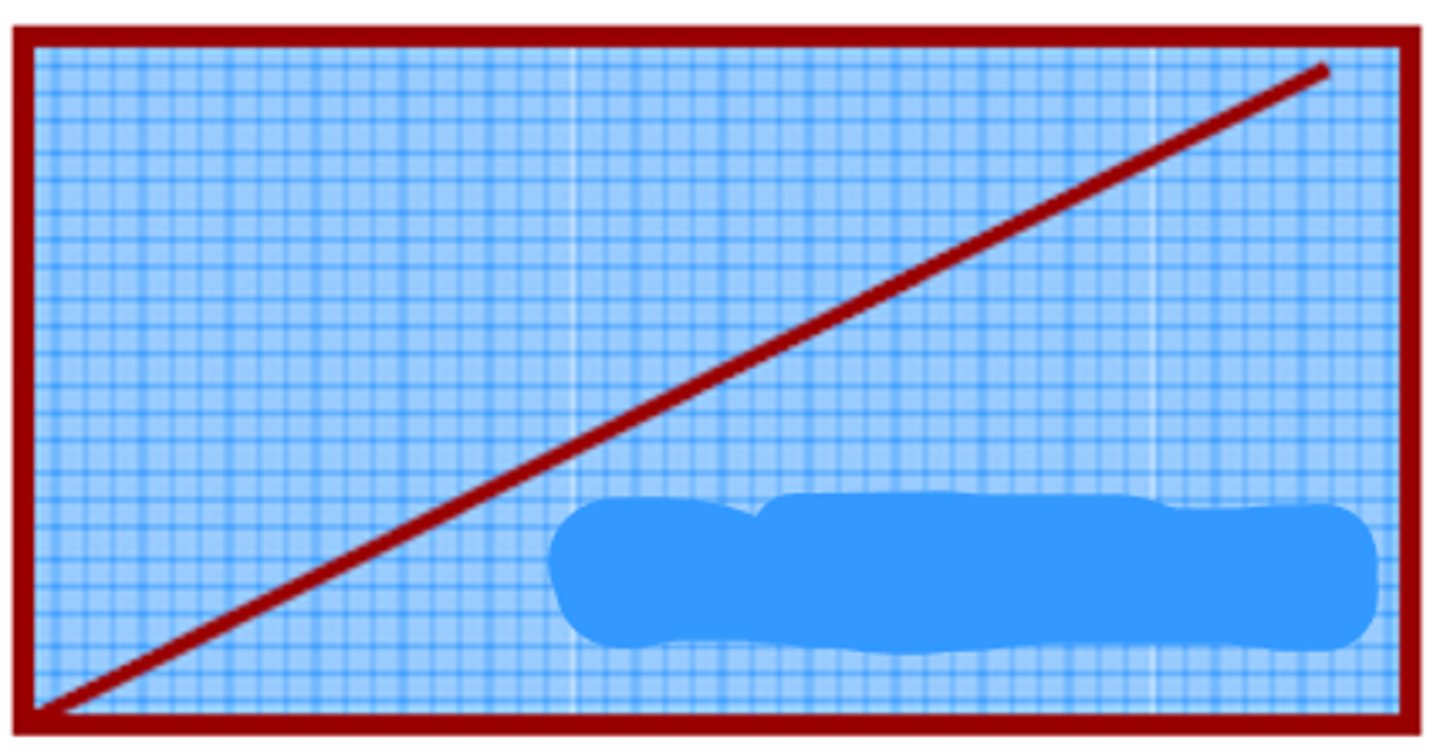
Zero order ER
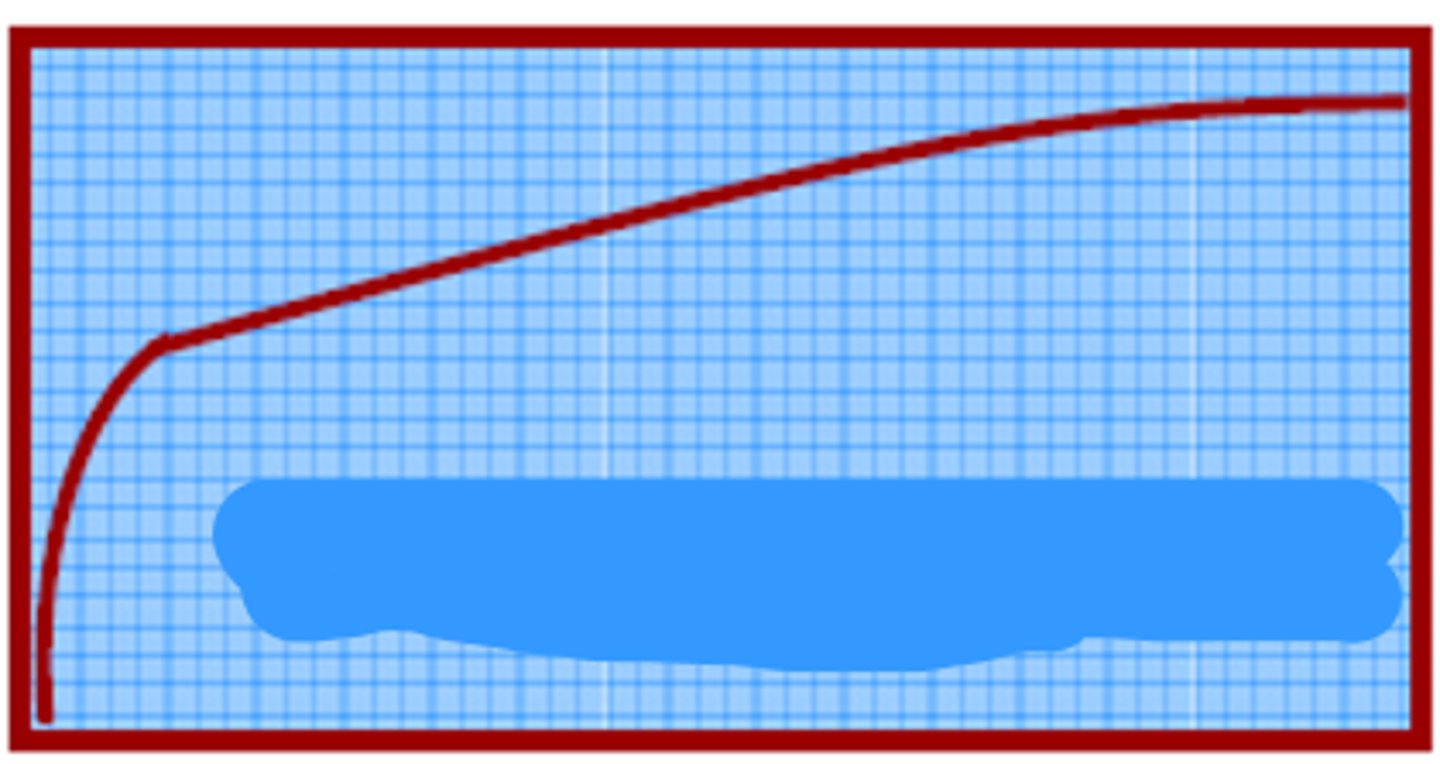
Ascending
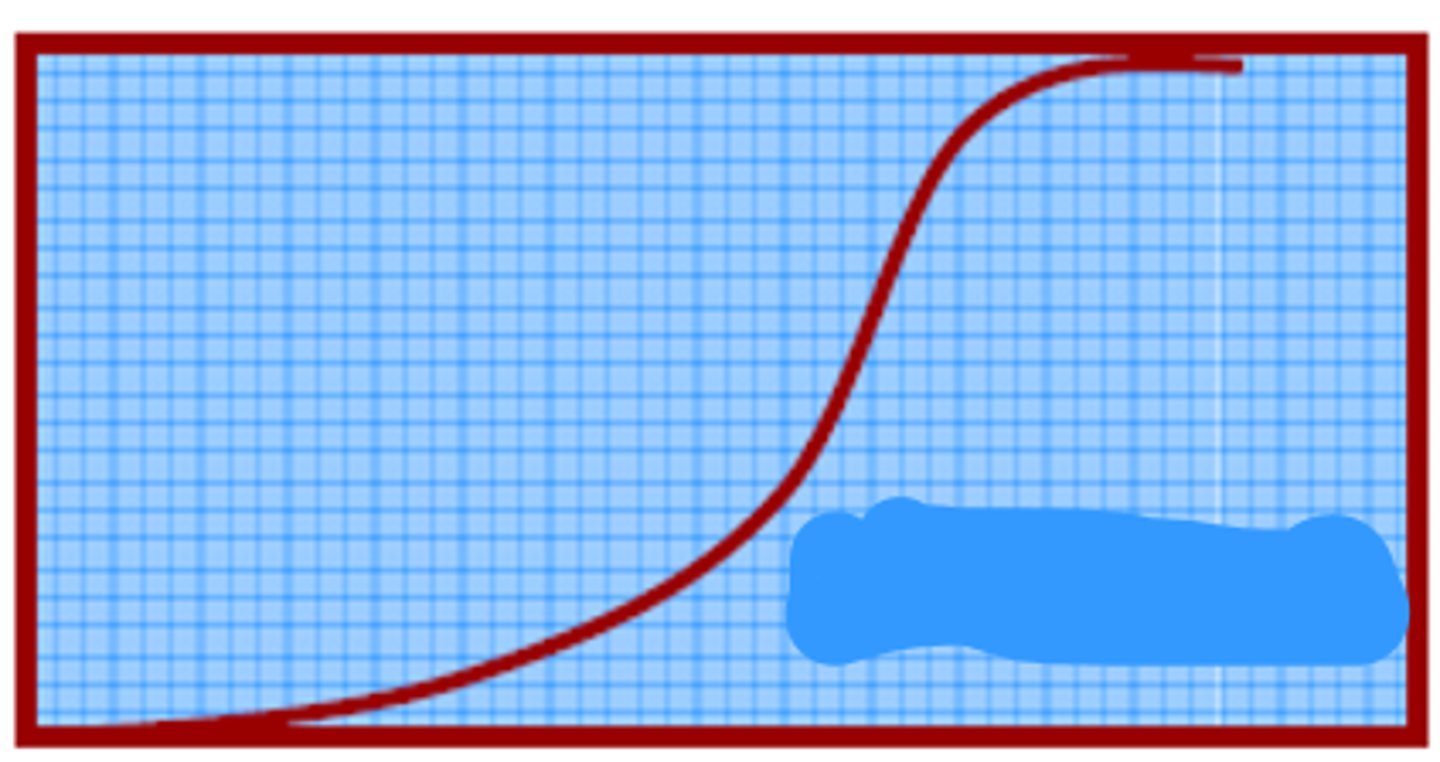
Loading + sustained
Pulsatile

Delayed + sustained

Enteric
Intestinal
Leaky enteric
What is the core matrix of a dissolution-controlled MR system?
Water-soluble polymers
What type of matrix system is a dissolution-controlled MR system?
Hydrophilic matrix system
How is drug release controlled in a hydrophilic matrix system (dissolution-controlled)?
- Polymer matrix swells
- Drug diffusion takes place across the viscous gel layer
- Polymer gel layer erodes upon an increase in polymer mobility
How is soluble drug released from a hydrophilic matrix system (dissolution-controlled)?
Diffusion through the gel layer
How is insoluble drug released from a hydrophilic matrix system (dissolution-controlled)?
Gel erosion
What are the advantages to a hydrophilic matrix system?
- Accommodates high and low drug loading
- Suitable for compounds with a wide range of properties
- Excipients are generally cheap and GRAS
- Comparatively simple manufacturing
What are the disadvantages to hydrophilic matrix systems?
- Only possible as single-unit systems
- Need optimal rate-controlling polymers
- Drug release dependent on two processes, diffusion and erosion
What are the examples of polymers used in hydrophilic matrix systems?
- Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC)
- Hydroxypropylcellulose (HPC)
- Polyethylene oxide
What are the components of a hydrophilic matrix delivery system?
- Active drug
- Hydrophilic polymer
- Diluent
- Lubricant/glidant
- Solubilizers and pH modifiers if needed
How does polymer concentration impact drug release of a hydrophilic matrix system?
Drug release rate decreases as polymer concentration increases
Q
Fraction of drug released in time t
Amount of drug released per unit area of the matrix
k
Rate constant
n
Diffusional exponent indicative of the drug release mechanism, 0.5 < x < 1
Power-Law equation
Q = kt^n
Diffusion-controlled MR system
Water-insoluble polymer comprises the matrix OR the membrane
What are the steps for a phobic matrix system?
- Aqueous medium ingress into the core and dissolves the drug
- Drug diffuses out through capillary network
- Matrix remains intact as it traverses GI tract
For what drugs are hydrophobic matrix systems not suitable?
Sparingly soluble drugs
For what systems are hydrophobic matrix systems suitable?
Both single-unit and multi-unit systems
What factors affect drug release rate from hydrophobic matrix systems?
- Surface area of matrix system
- Pore structure of the polymer matrix
- Excipients and surfactants
- Compression force
- Drug loading
- Drug solubility
What is the equation for drug release from hydrophilic matrix systems?
Power-Law equation
What is the equation for drug release from hydrophobic matrix systems?
Higuchi equation
D
Diffusion coefficient of drug
A
Total amount of drug in unit volume of matrix
Cs
Solubility of drug in matrix
Higuchi equation
Q = [2DACst]^1/2
What polymers are used for hydrophobic reservoir systems?
Water-insoluble polymers (not waxes)
How thick are hydrophobic reservoir system films?
50-150 micrometers
What are the polymers used in hydrophobic reservoir systems?
- Ethylcellulose
- Polymethacrylates with quaternary ammonia groups
For what drugs are hydrophobic reservoir systems suitable?
Both good and poor aqueous solubility
What are the examples of drugs available as hydrophilic matrix systems?
- Morphine sulfate SR
- Carbidopa and levodopa (Sinemet CR)
What is the example of a drug available as a hydrophobic matrix system?
Diltiazem hydrochloride (Cardiazem LA)
What are the components of hydrophobic matrix systems?
- Hydrophobic polymers (ethylcellulose)
- Some waxes (carnauba wax, PED monostearate)
What are the examples drugs available as hydrophobic reservoir systems?
- Dextroamphetamine sulfate (Dexedrine)
- Metoprolol succinate ER (Toprol XL)
Eudragit RL
Water-insoluble polymethacrylate with high water permeability
Eudragil RS
Water-insoluble polymethacrylate with low water permeability
Biphasic release
Initial dose is released promptly and the remaining medication is released gradually over a prolonged period through an ethylcellulose coating
What is the equation for drug release from hydrophobic reservoir systems?
Fick's First Law of Diffusion
Fick's First Law of Diffusion
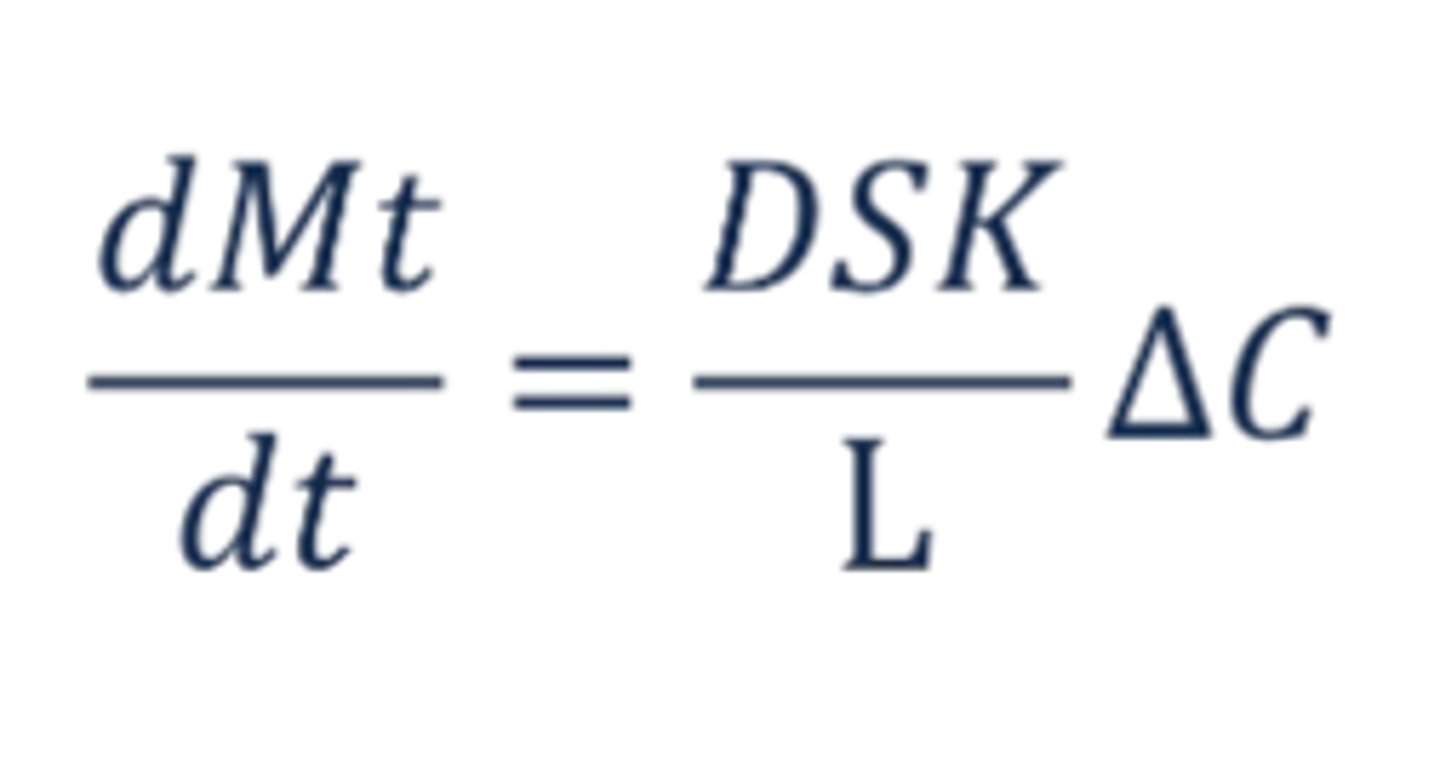
Mt
Total amount of drug released at time t
S
Effective membrane or barrier surface area for drug diffusion
K
Partition coefficient of drug between barrier membrane and external aqueous plases
L
Diffusional pathlength (thickness of film)
deltaC
Drug concentration gradient between the solubility in the reservoir system and the drug concentration in the external aqueous medium
What routes should be considered for abuse-deterrent formulations?
- Ingestion (oral)
- Injection (parenteral)
- Insufflation (nasal)
- Smoking (inhalation)
How does Hysingla ER achieve its abuse-deterrent properties?
Hydrophobic matrix system
How does Xtampza ER achieve its abuse-deterrent properties?
Multi-unit system
How does EMBEDA achieve its abuse-deterrent properties?
- Hydrophobic reservoir system
- Antagonist core
What are the diffusion-controlled MR systems?
- Hydrophobic matrix systems
- Hydrophobic reservoir systems
What are the osmosis-controlled MR systems?
- Elementary
- Push-pull
What generates controlled drug release in an elementary osmotic pump?
Osmotic pressure
What generates controlled drug release in a push-pull osmotic system?
Osmotic pressure and hydrostatic pressure generated by the swellable polymer
For what drugs are elementary osmotic pumps suitable?
Sufficiently water-soluble
For what drugs are push-pull osmotic systems suitable?
Poor or good water solubility
What are the components of the active layer of a push-pull osmotic system?
Osmotically-active excipients and drug
What are the components of the push layer of a push-pull osmotic system?
Osmotically-active excipients and water-swellable polymers
What are the examples of drugs available as push-pull osmotic systems?
- Doxazosin mesylate ER (Cardura XL)
- Glipizide (Glucotrol XL)
- Nifedipine (Procardia XL)
What are the key characteristics of an elementary osmotic system?
- Single-layer tablet
- One small orifice
- Drug released as a solution
- Drug must be sufficiently water-soluble
What are the key characteristics of a push-pull osmotic system?
- Bilayer tablet often latitudinally compressed
- Osmotic agent in both layers
- Swellable polymer in one layer
- One or more small orifices
- Drug released as a solution or suspension
Q0
Initial amount of drug in solution (usually zero)
K0
Zero order rate constant
What is the kinetic profile of osmotic systems?
Zero order release
What is the equation for drug release from osmotic systems?
Q = Q0 + K0*t
What are the important points regarding osmotic systems?
- Single-unit systems only
- Lag time of drug release 1-2 hours
- < 25% drug loading
- Requires specialized equipment and complex processes
- "Ghost" tablets remain in stool
What are the examples of drugs available in ion-exchange resin MR systems?
- Methylphenidate HCl (Quillichew ER)
- Amphetamine ER oral suspension (Dyanavel XR)
What is the important characteristics of Quillichew ER?
Can be administered regardless of food
What are the important points of ion-exchange resin MR systems?
- Can be administered regardless of food
- Tailored drug release
- Chewable tablets, ODTs, and suspensions
- Niche applications
- Effective taste masking