2LE - FCSan
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
1
New cards
Storage Area Network
high-speed, dedicated network of servers and shared storage devices; provides storage consolidation and facilitates centralized data management
2
New cards
Fibre Channel
a high-speed network technology that runs on high-speed optical fiber cables and serial copper cables.
3
New cards
Components of FC SAN
node ports, cables, connectors, and interconnecting devices, SAN management software
4
New cards
Nodes
The end devices, such as hosts, storage arrays, and tape libraries
5
New cards
Two Types of Optical Fiber Cables
Multimode Fiber (MMF) Cable and Single-mode fiber (SMF)
6
New cards
Multimode Fiber (MMF) Cable
carries multiple beams of light projected at different angles simultaneously onto the core of the cable
7
New cards
Modal Dispersion
This collision weakens the signal strength after it travels a certain distance
8
New cards
Single-mode fiber (SMF)
carries a single ray of light projected at the center of the core
9
New cards
Connectors
attached at the end of a cable to enable swift connection and disconnection of the cable to and from a port
10
New cards
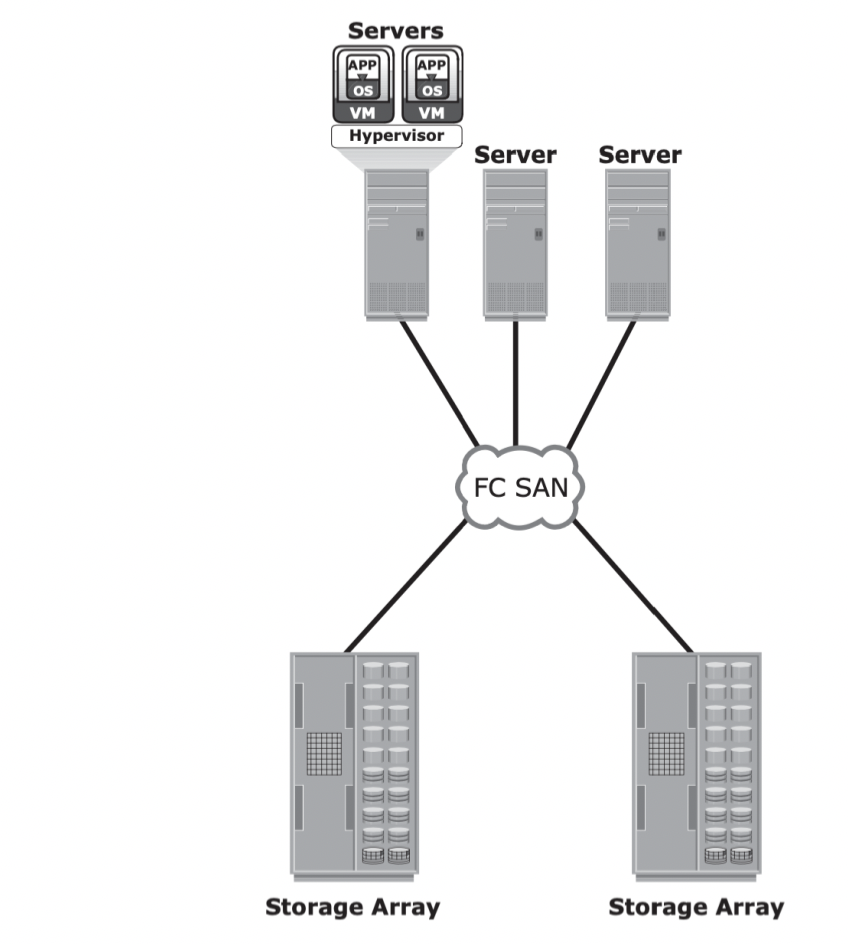
Name this diagram
FC SAN Implementation
11
New cards
Interconnect Devices
Hubs, switches, and directors
12
New cards
Hubs
used as communication devices in FC-AL implementations.
13
New cards
Switches
more intelligent than hubs and directly route data from one physical port to another. Therefore, nodes do not share the bandwidth.
14
New cards
Directors
high-end switches with a higher port count and better fault-tolerance capabilities.
15
New cards
SAN Management Software
manages the interfaces between hosts, interconnect devices, and storage arrays; provides a view of the SAN environment and enables management of various resources from one central console
16
New cards
Fabric
a logical space in which all nodes communicate with one another in a network;
created with a switch or a network of switches
17
New cards
Interswitch Link (ISL)
the link between any two switches
18
New cards
N_Port
end point in the fabric; host port (HBA) or a storage array port connected to a switch in a switched fabric.
19
New cards
E_Port
forms the connection between two FC switches
20
New cards
F_Port
port on a switch that connects an N_Port
21
New cards
G_Port
generic port on a switch that can operate as an E_Port or an F_Port
22
New cards
Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP)
FC SAN uses the *________________* that provides both channel speed for data transfer with low protocol overhead and scalability of network technology.
23
New cards
Fibre Channel Protocol Stack
FC-4 Layer, FC-2 Layer, FC-1 Layer, FC-0 Layer
24
New cards
FC-4 Layer
defines the application interfaces and the way *Upper Layer Protocols* (ULPs) are mapped to the lower FC layers
25
New cards
FC-2 Layer
provides Fibre Channel addressing, structure, and organization of data (frames, sequences, and exchanges)
26
New cards
FC-1 Layer
defines how data is encoded prior to transmission and decoded upon receipt
27
New cards
FC-0 Layer
defines the physical interface, media, and transmission of bits
28
New cards
World Wide Names (WWN)
a 64-bit unique identifier assigned to each device in the FC environment
29
New cards
Zoning
an FC switch function that enables node ports within the fabric to be logically segmented into groups and to communicate with each other within the group
30
New cards
Zone Members
nodes within the SAN that can be included in a zone
31
New cards
Zone Sets
composed of a group of zones that can be activated or deactivated as a single entity in a fabric
32
New cards
Port Zoning
Uses the physical address of switch ports to define zones.
33
New cards
WWN Zoning
Uses World Wide Names to define zones
34
New cards
Mixed Zoning
Combines the qualities of both WWN zoning and port zoning
35
New cards
Mesh Topology
Full Mesh and Partial Mesh
36
New cards
Full Mesh
every switch is connected to every other switch in the topology; a maximum of one ISL or hop is required for host-to-storage traffic
37
New cards
Partial Mesh
several hops or ISLs may be required for the traffic to reach its destination
38
New cards
Core-edge Fabric and Mesh
Two types of topologies
39
New cards
Core-Edge Fabric Topology
has two types of switch tiers--edge tier and core tier
40
New cards
Edge Tier
composed of switches and offers an inexpensive approach to adding more hosts in a fabric
41
New cards
Core Tier
composed of enterprise directors that ensure high fabric availability; all traffic must either traverse this tier or terminate at this tier
42
New cards
Block-level Storage Virtualization
aggregates block storage devices (LUNs) and enables provisioning of virtual storage volumes, independent of the underlying physical storage
43
New cards
Virtual SAN (VSAN)
a logical fabric on an FC SAN, which enables communication among a group of nodes regardless of their physical location in the fabric