862: compensatory vs restorative movement and neuro movement diagnoses
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Medical diagnosis
Based on the patients signs and symptoms and results of a standardized set of tests and measures
Movement diagnosis
Based on the patient primary movement system signs and symptoms, the results of a standardized set of tests and measures, and movement analysis
Movement pattern coordination deficit
Primary movement fault/impairment: poor timing and sequencing of either intersegmental movements or of postural responses relative to balance demands
Key finding for movement pattern coordination deficit
Performance typically improves with practice and instruction
Force production deficit
Primary movement fault/impairment: weakness
Key findings for force production deficit
Unable to generate sufficient force to overcome effect of gravity or fatigue with repetition
Sensory detection deficit
Primary movement fault/impairment: inability to execute intersegmental movement due to moderate-severe loss joint position sense or protective sensation, vision, and/or the vestibular system
Key findings for sensory detection deficit
Worse with eyes closed as they can no longer compensate
Limited improvement with practice
Sensory selection and weighting deficit
Primary movement fault/impairment: decreased ability to screen for and attend to appropriate sensory cues for postural orientation and postural stability
Issues with sensory processing which my impact steady state, anticipatory and reactive postural control as well as limb movement
Key findings for sensorry selection and weighting deficit
Difficulty making transitions from one sensory environment to another
Dizziness
Postural vertical deficit
Primary movement fault/impairment: inaccurate perception of vertical orientation with resistance of correction to COM alignment
Key findings of postural vertical deficit
Resists correction of COM alignment
Fearful/agitated when COM is corrected
May have disregard or neglect of involved extremity
Fractioned movement deficit
Primary movement fault/impairment: inability to fractionate movement
Key findings of fractioned movement deficit
Non fractioned movement
Moderate to severe hyperexcitability/hypertonicity
Unable to generate quick movements
Dysmetria
Primary movement fault/impairment: inability to grade forces appropriately for distance and speed of a task/movement
Key findings for dysmetria
Notable under or overshooting of targets
Abnormal rhythm and incoordination that does not improve with practice
Excessive postural sway
Hypokinesia
Primary movement fault/impairment: slowness in initiating and executing movement. Usually associated with small amplitude movement and may be associated with stopping of ongoing movement
Key findings of hypokinesia
Difficulty initiating movement
Delayed timing of postural adjustments
Lack of preparatory movements
Cognitive deficit
Primary movement fault/impairment: impaired motor control related to lack of arousal, attention, or ability to apply meaning to situation that is appropriate for age
Key findings for cognitive deficit
Difficulty initiating movement
Delayed timing of postural adjustments
Lack of preparatory movements
Compensatory
Neuro plasticity used to form new connections
Therapeutic interventions used to discover new ways of accomplishing a task
Restorative
Neuroplasticity used to relearn and restore damaged functions
Trying to regain normal movement
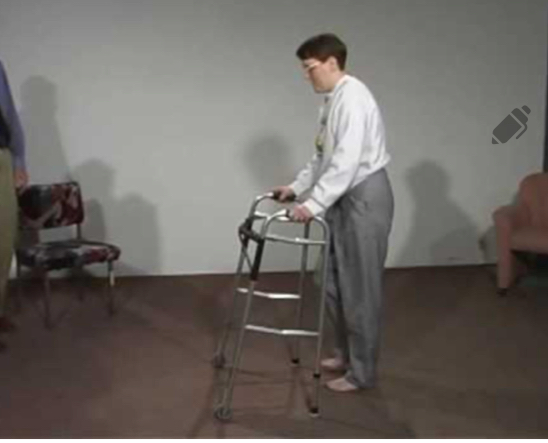
Force production deficit

Fractionated movement
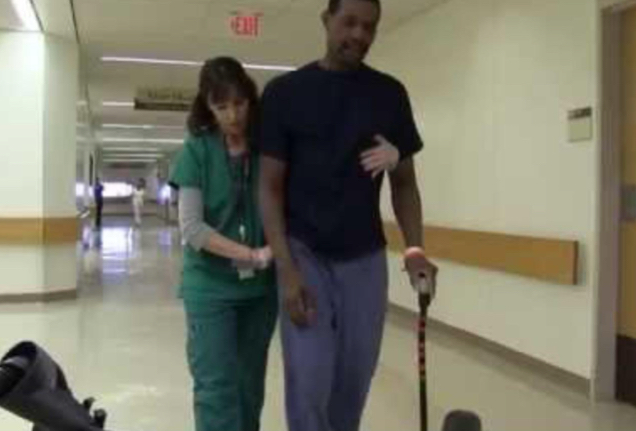
Force production deficit

Force production deficit
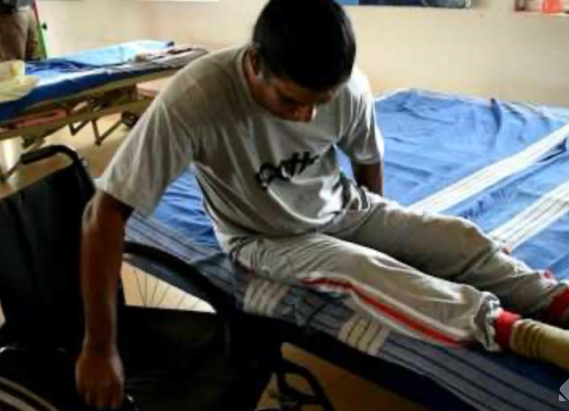

Fractionated movement
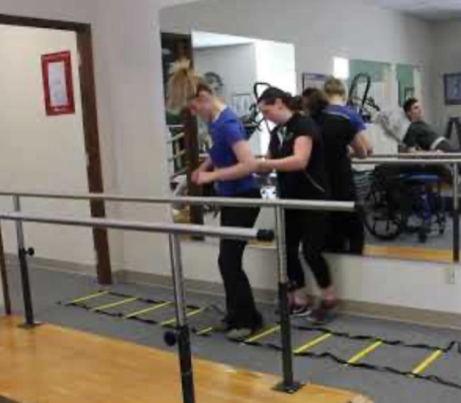

Sensory detection

Force production deficit
Sensory selection and weighting
Force production deficit
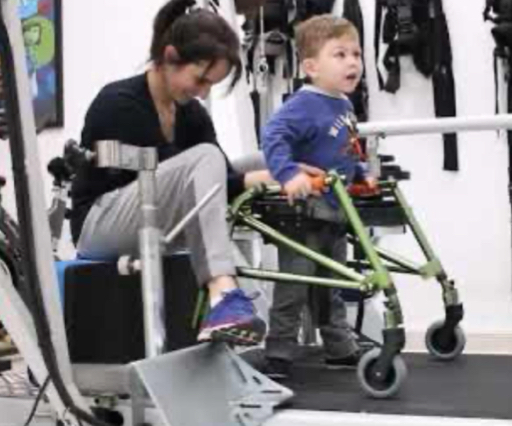

Movement pattern coordination
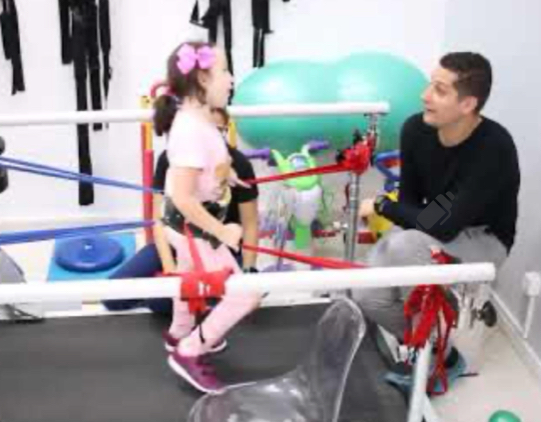

Fractionated movement and dysmetria

Dysmetria
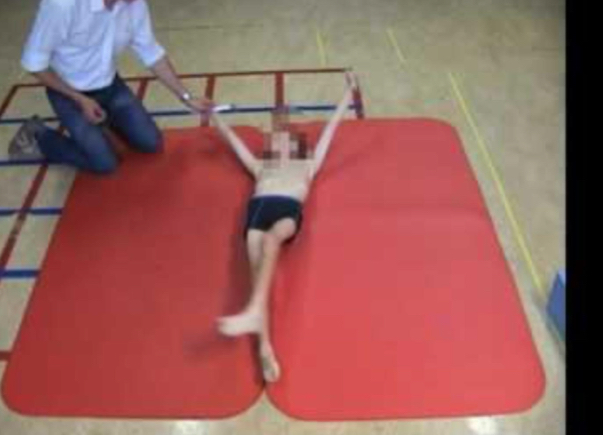

Dysmetria
