Mitosis
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are the stages of mitosis in order?
interphase
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
telophase
Cytokineisis
What happens in interphase?
DNA replication
cell growth
organelles replicate
protein/ enzymes synthesised
How does the cell look during interphase?
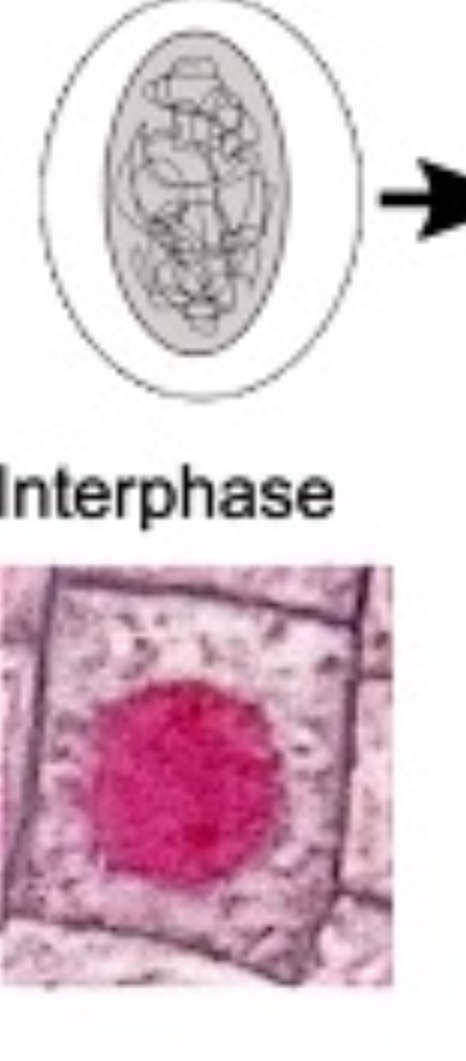
What happens during prophase?
chromosomes : condense, coil, shorten, thicken - becomes visible
centrioles move to poles and spindles
nuclear envelope disintegrates
How does the cell look during prophase?
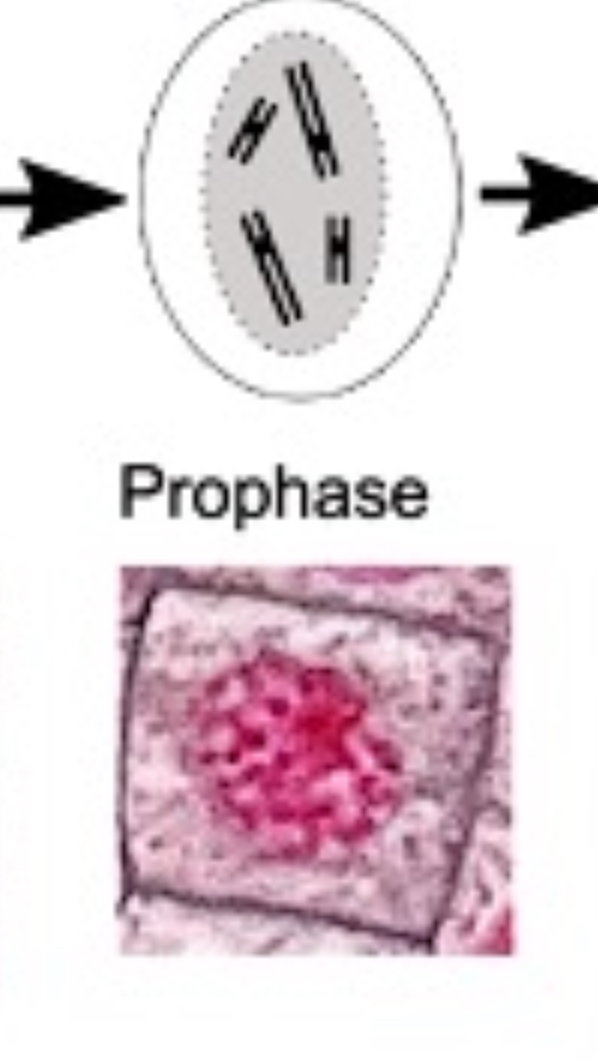
What happens during metaphase?
spindle fibre attaches to centromere
chromosomes align on the equator
How does the cell look during metaphase?
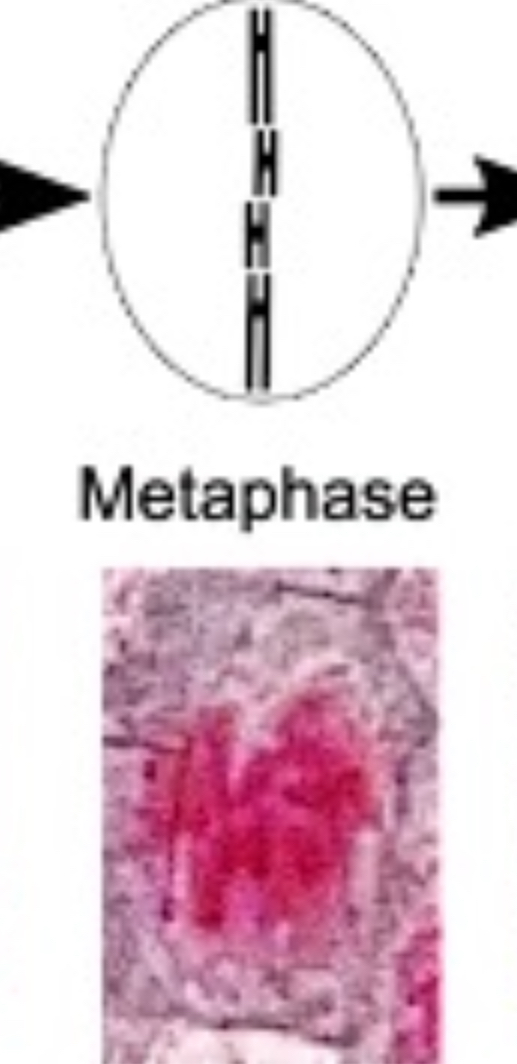
What happens during anaphase?
spindle fibres shorten - centromeres separate
now separated chromatids pull to opposite poles by centromere
How does the cell look during anaphase ?
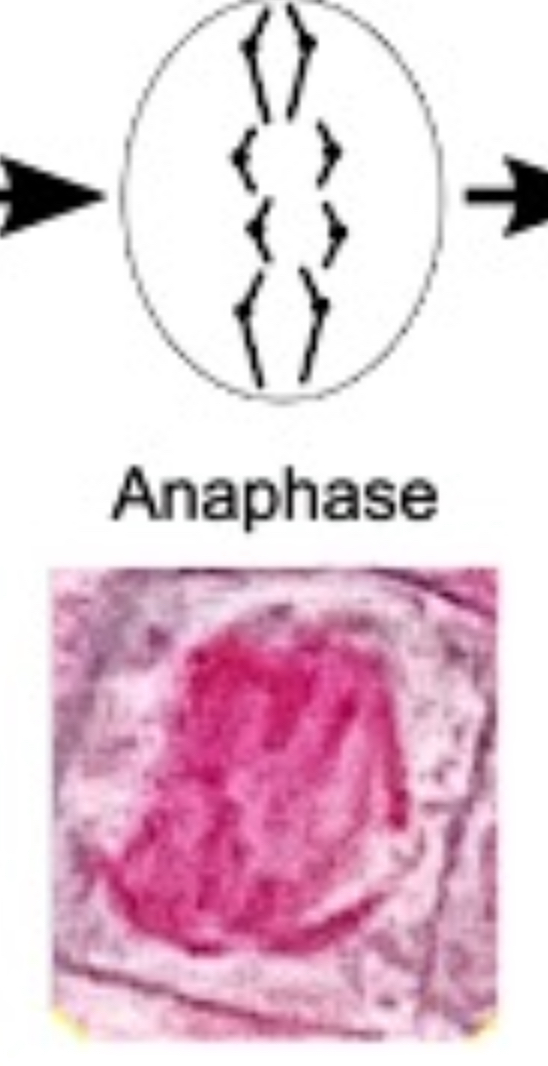
What happens during telophase?
chromosomes uncoil and lengthen
spindle fibres break down
nuclear envelope reforms
nucleolus reappears
How does the cell look during telophase?
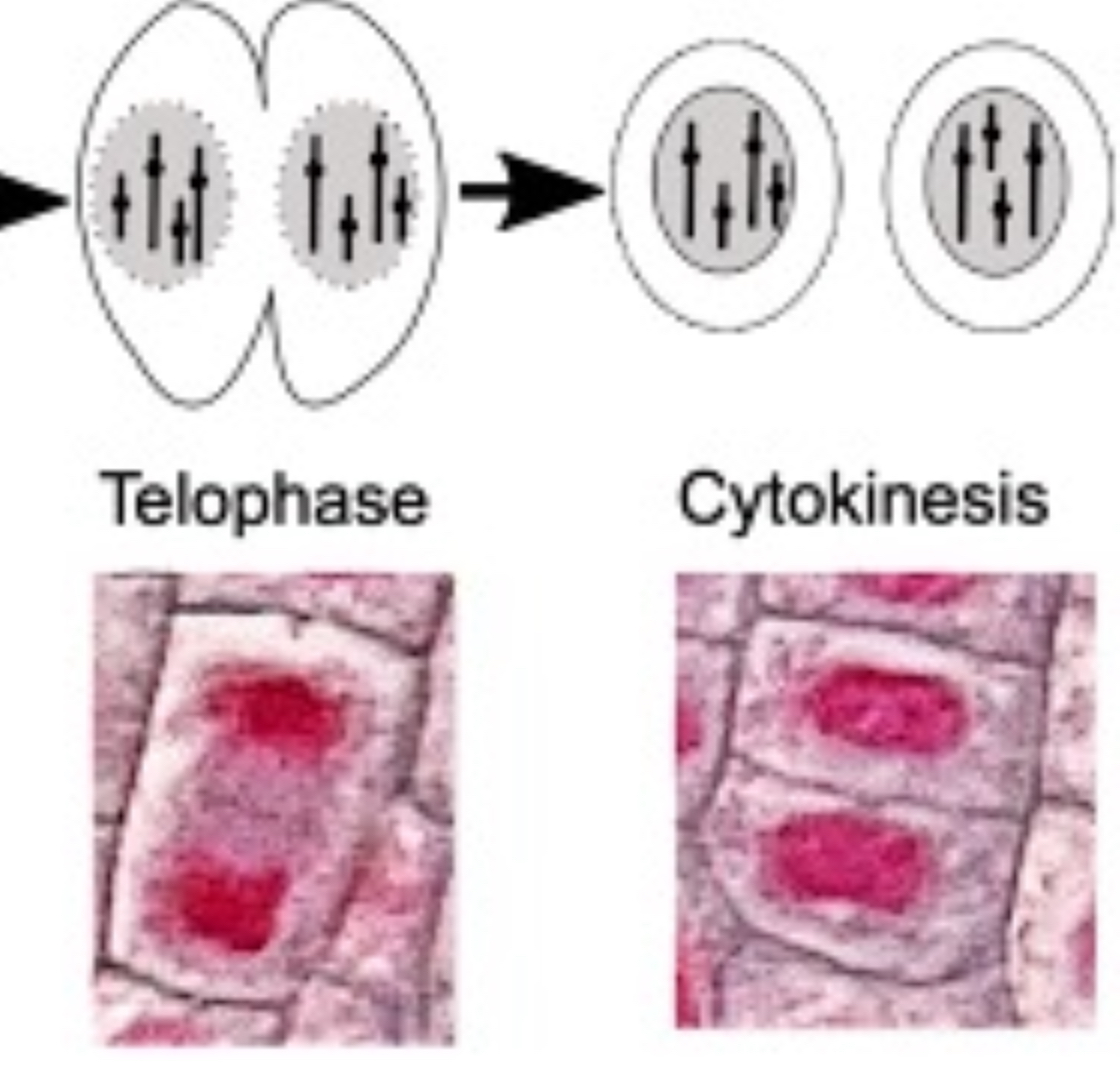
What happens during cytokinesis?
cytoplasm divide making 2 cells
What does haploid mean?
23 chromosomes in total [n]
What does diploid mean?
46 chromosomes in total [2n]
What does ploidy level mean?
number of complete sets of chromosomes in an organism
What does polyploid mean?
organisms with more than 2 complete sets of chromosomes
what does homologous mean?
matching pair of chromosomes
What are the uses of mitosis?
growth
asexual reproduction
repair
How are the chromosome number affected in mitosis?
same as parent cell
exact replica - genetic stability
How is mitosis useful for growth?
replace dead cells
repair tissues - producing new cells
How is mitosis used in asexual reproduction?
no genetic variation - unicellular organisms
What happens if genes are damaged?
uncontrollable mitosis
unaltered - proton-oncogenes
altered - oncogenes (cancer)