Periodontal Risk Assessment: Local and Systemic Factors
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Primary etiology
Bacterial plaque
Secondary etiology
Local and systemic factors
initiate
There is no concrete evidence that any of the contributing (secondary) factors can ___ periodontal disease by themselves; simply, they enhance the ability/virulence of the bacterial plaque to cause periodontal disease.
Local factors that make plaque removal more difficult
• Calculus
• Caries
• Iatrogenic
• Anatomical features
• Trauma
Primary occlusal trauma
injury to a healthy periodontium resulting from excessive occlusal forces
Secondary occlusal trauma
injury to the periodontium from normal occlusal forces applied to a periodontium previously damaged by periodontitis
w/out
Occlusal trauma __ inflammation will not cause attachment lost
w/
Occlusal trauma __ inflammation will cause attachment loss
gingival margin trimmer (GMT)
Caries which approximates the __ can complicate plaque removal.
repaired
Lesions should be __ early in therapy to allow easier plaque removal.
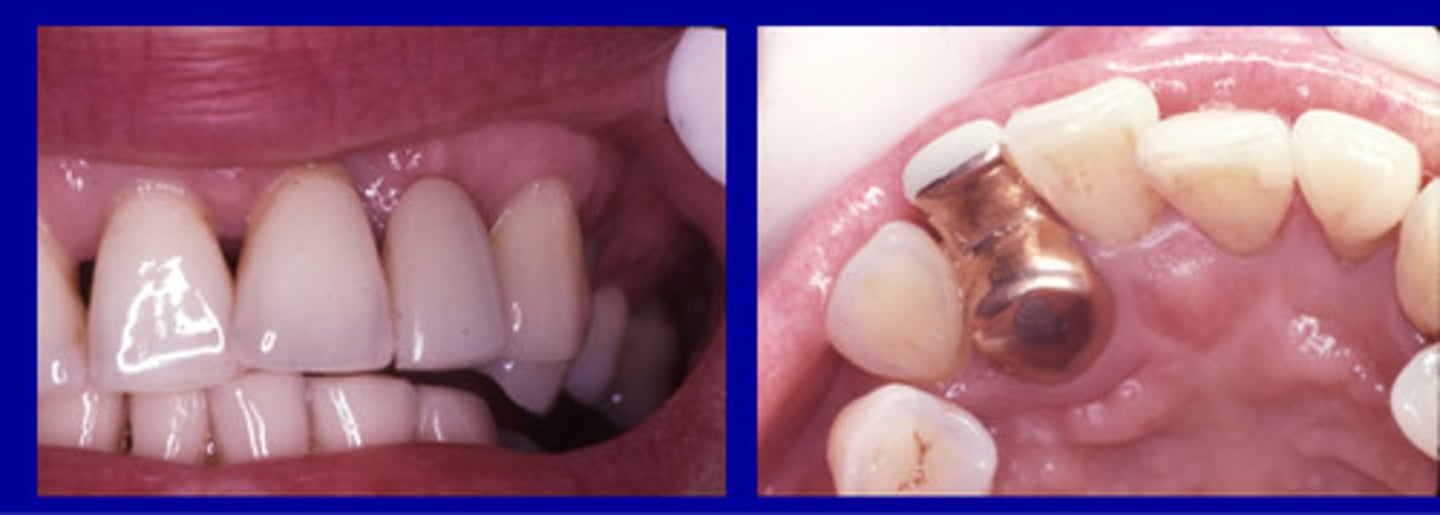
Iatrogenic factors
• Open margins
• Overhanging margins
• Open contacts/food Impaction
• Over contoured restorations
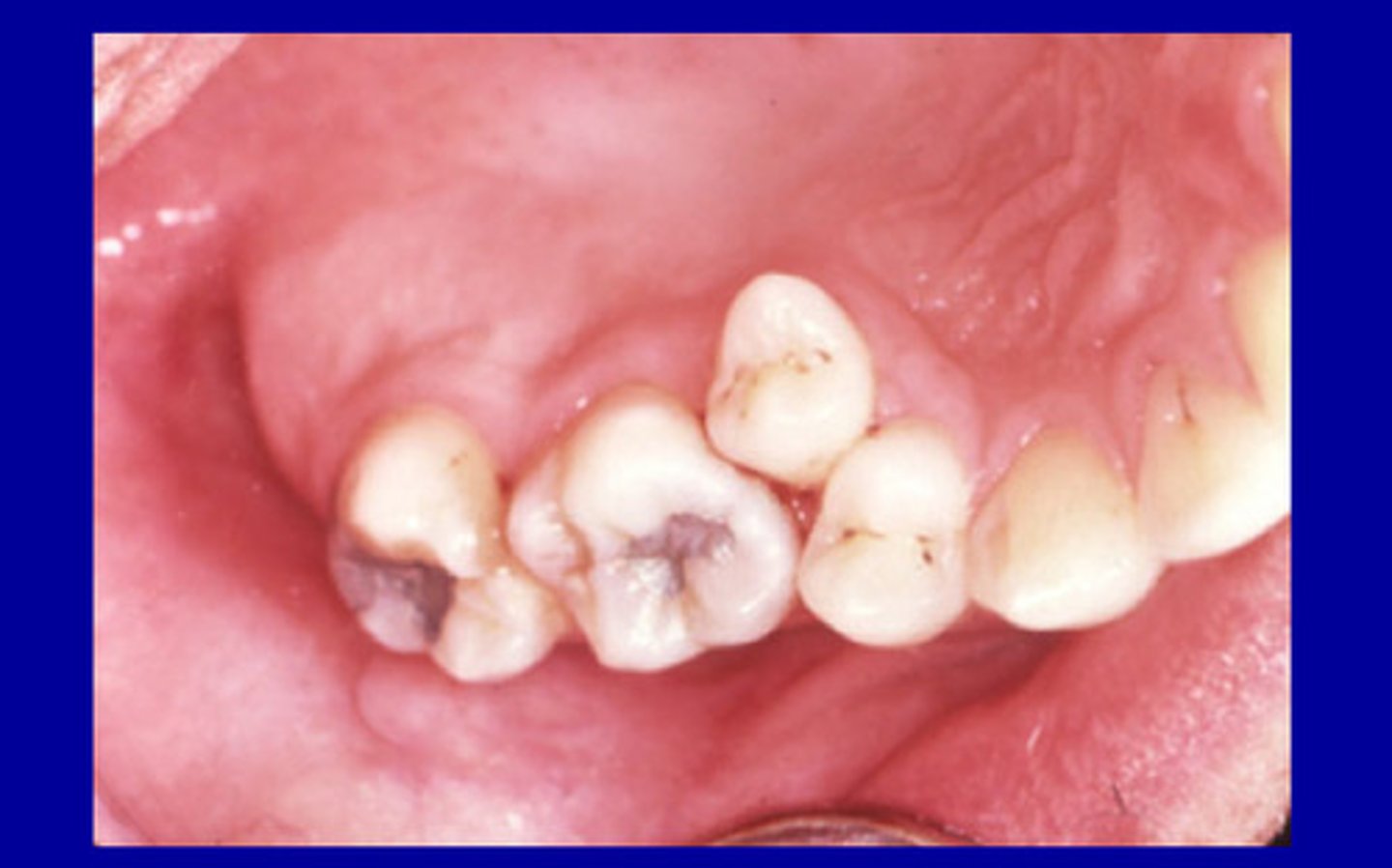
Tooth position
• Crowding
• Tipping
• Root proximity
Anatomical factors
__ such as furcation involvement, enamel pearls, enamel projections and developmental grooves and concavities can complicate oral hygiene.
Furcation involvement
bone loss between the roots of multi-rooted teeth
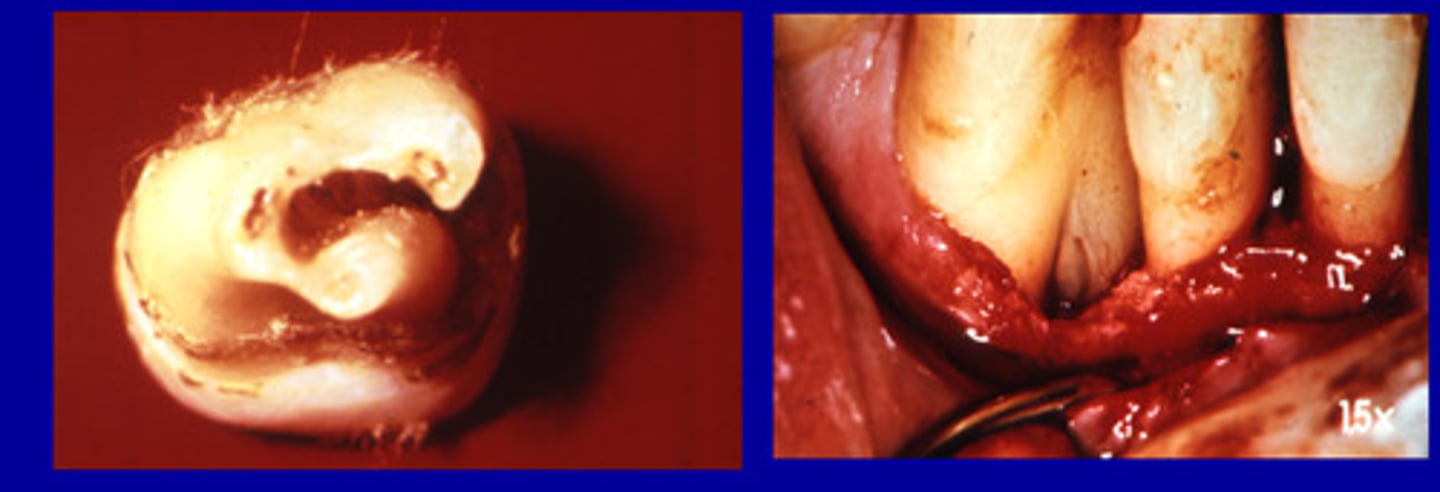
Enamel pearls
small masses of excess enamel on the surface of teeth located APICALLY to the CEJ
1.1-5.7%
___ of permanent molars have enamel pearls
75%
__ of maxillary third molars have enamel pearls
Enamel projections
Extension of enamel beyond the cervical margin
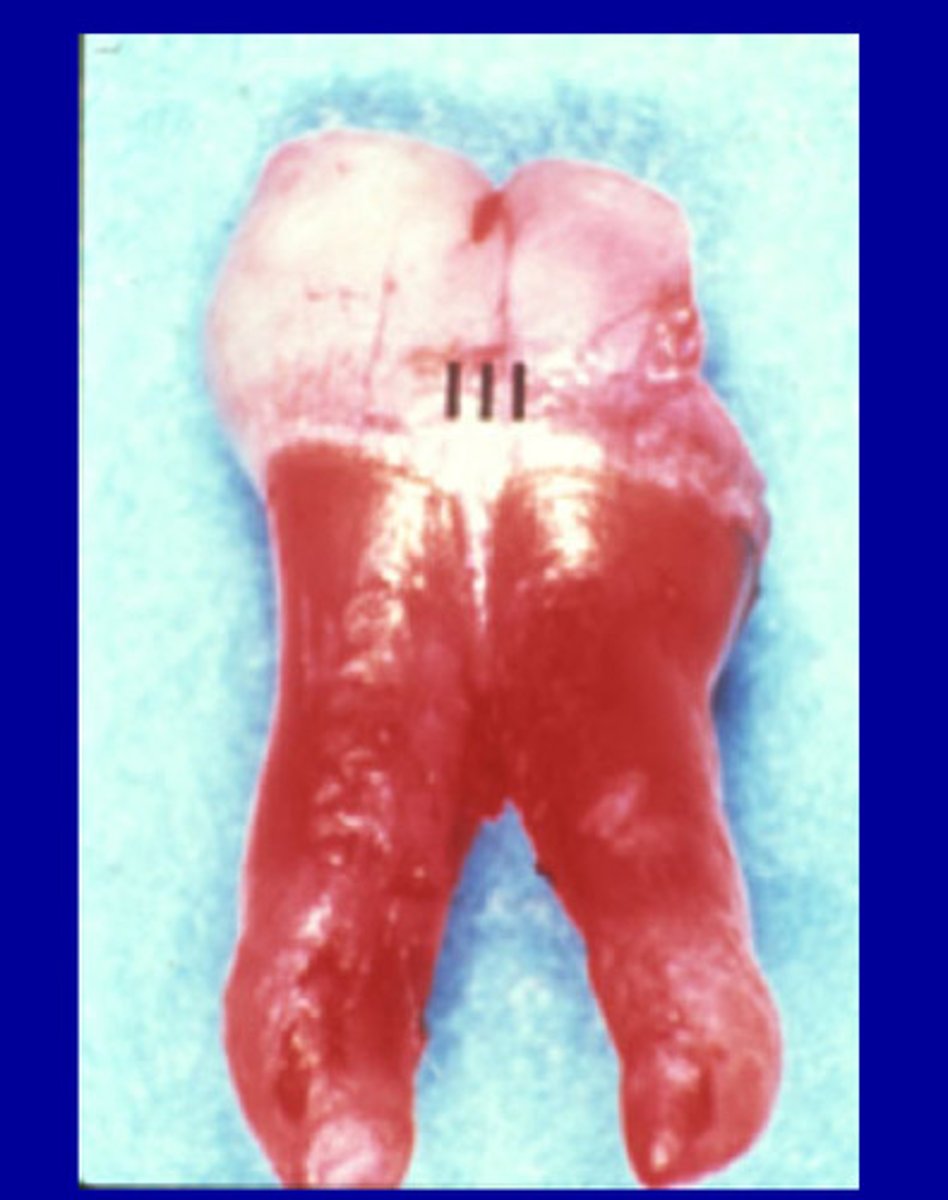
28.6%
___ of Mandibular molars have enamel projections
17%
____ Of maxillary molars have enamel projections
Concavities
Dental floss may be less effective than an interdental brush on long root surfaces with _____.

Interdental brush
If there are concavities you may want to recommend a
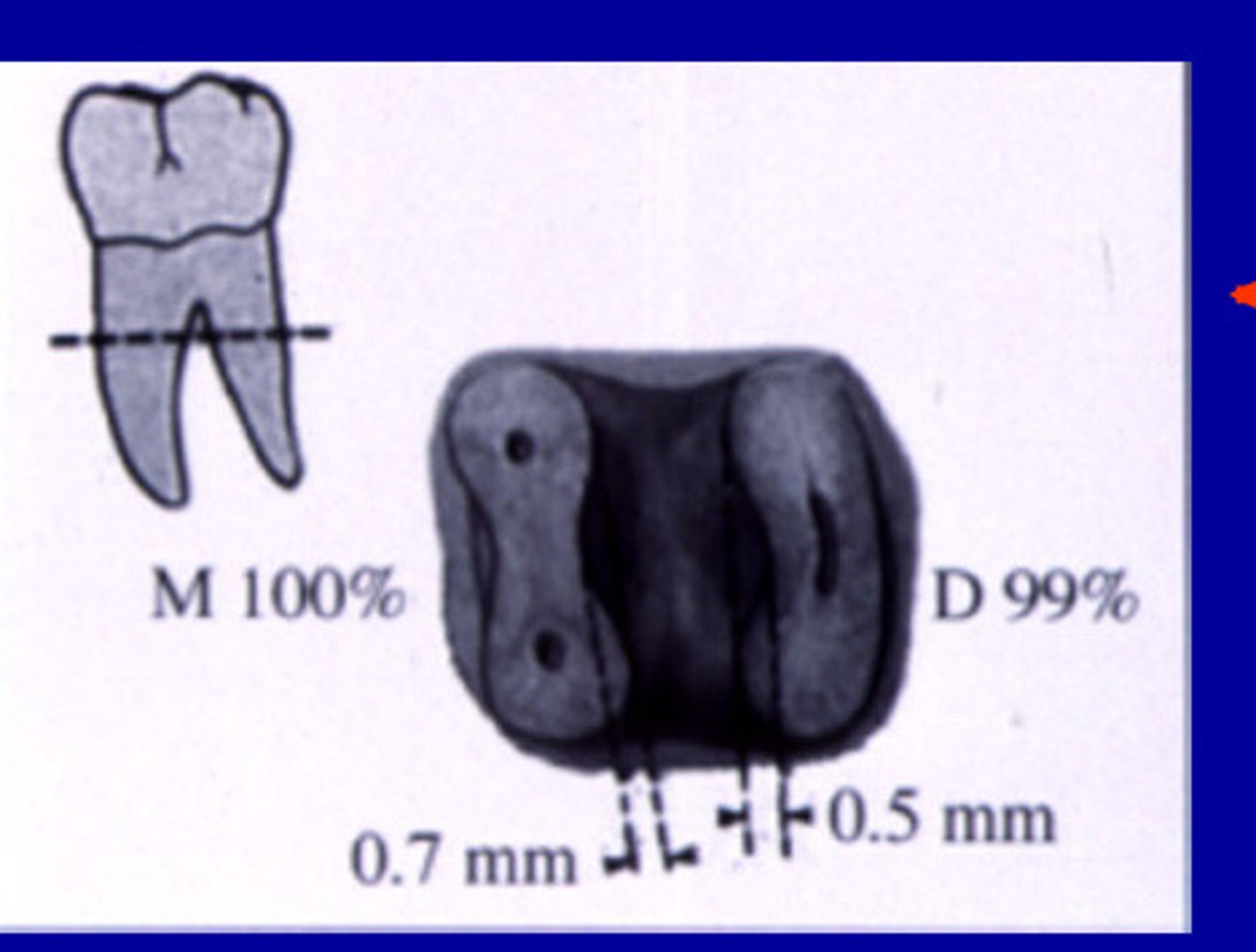
Mandibular molar furcation concavity
Maxillary molar furcation concavity
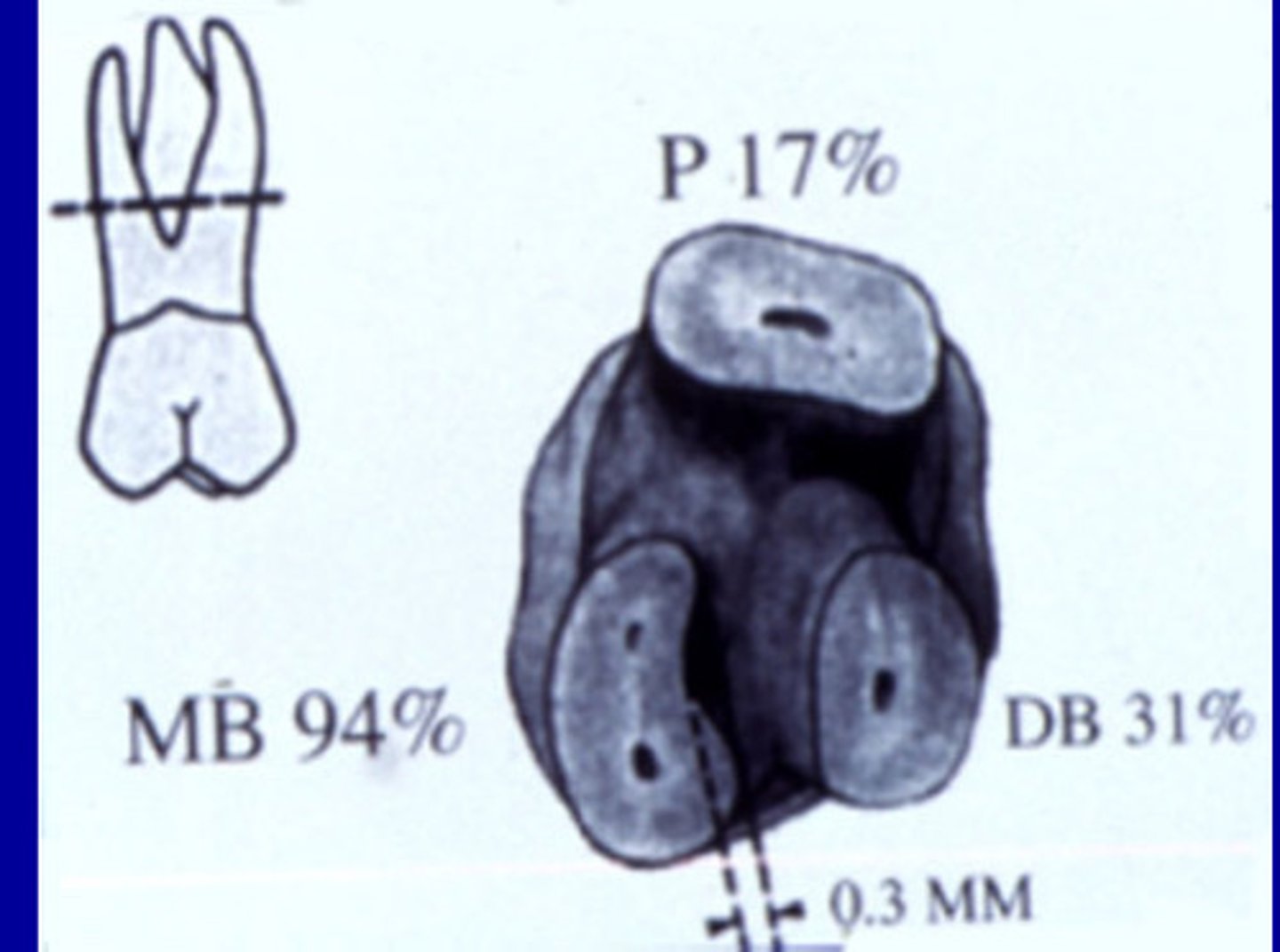
Root amputation
A surgical procedure that is used to remove one or more roots of a multirooted tooth without removing the crown (maxillary)
Hemisection
Surgical separation of a multirooted tooth through the furcation area (mandibular)
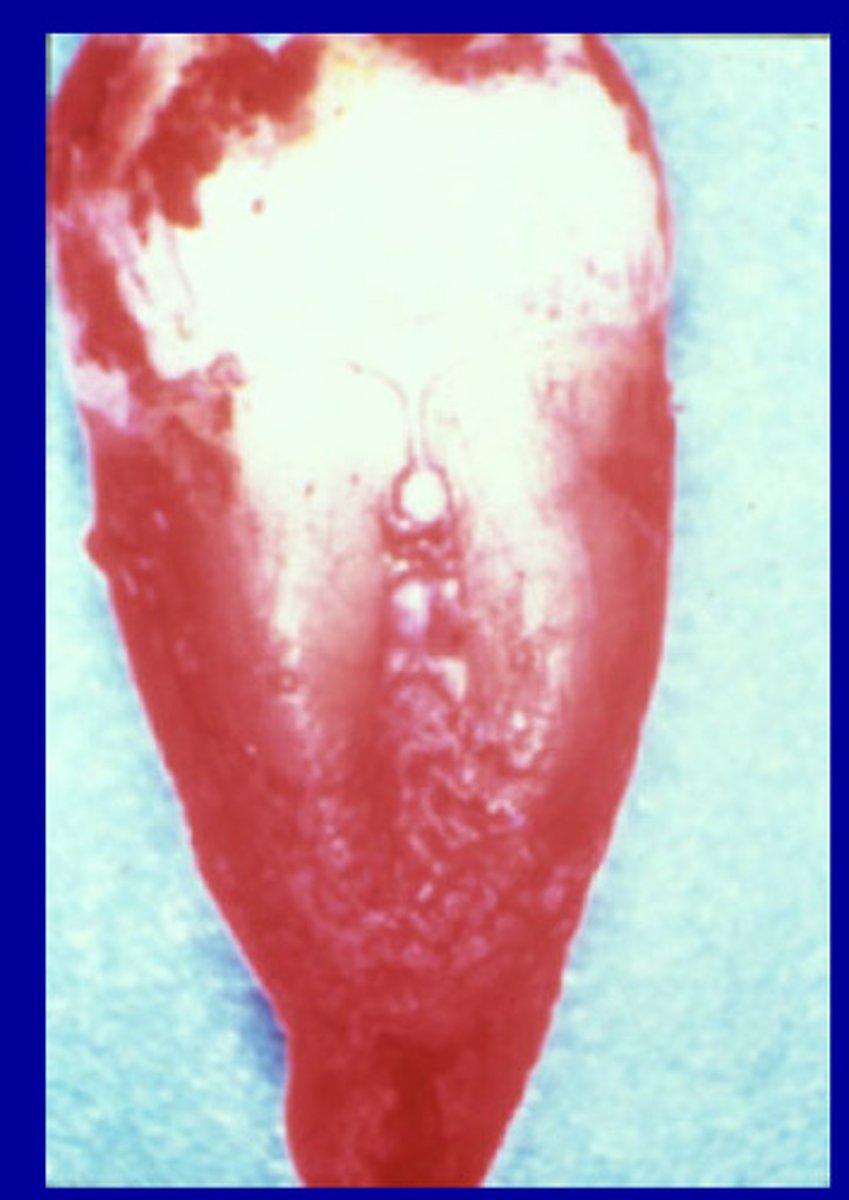
Developmental grooves
Fine depressed lines in the enamel of a tooth that mark the union of the loves of the crown.
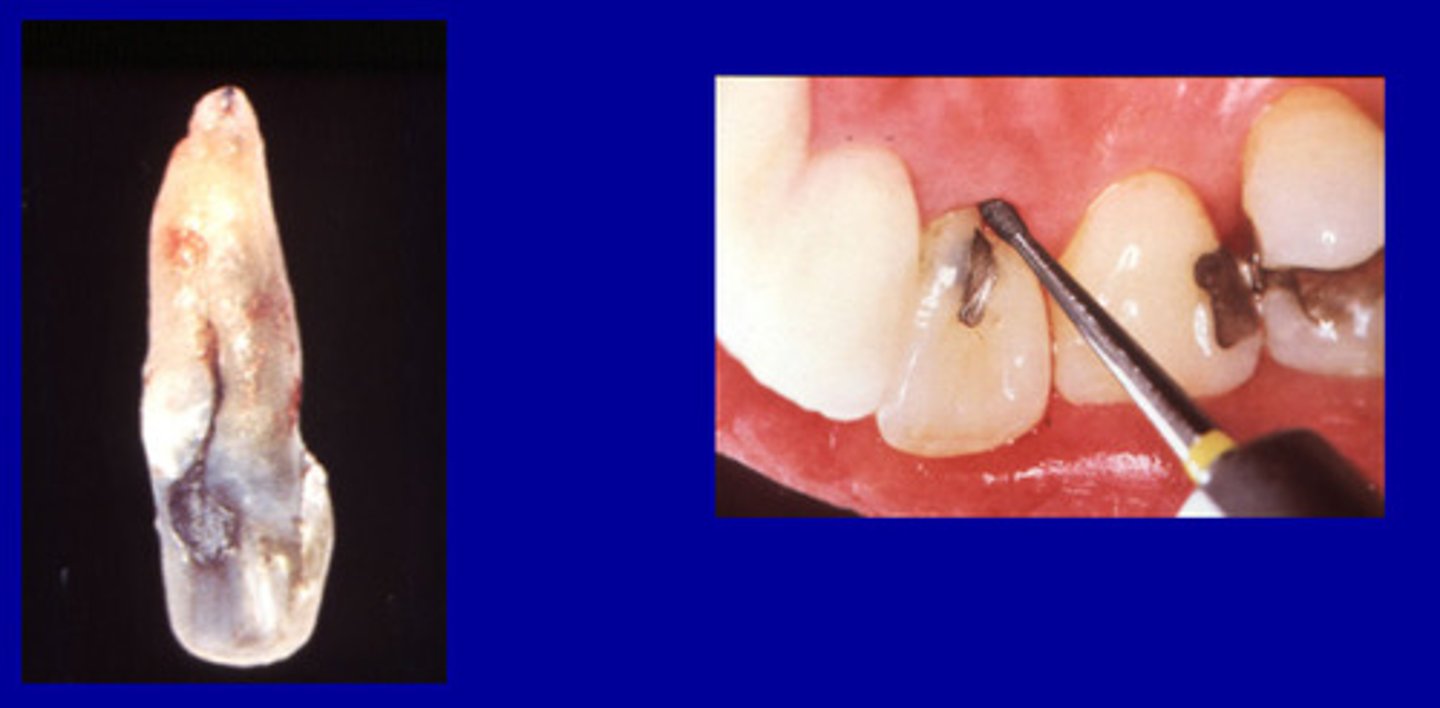
5.6%
_ of maxillary lateral incisors have developmental grooves
3.4%
__ of maxillary central incisors have developmental grooves
Soft tissue
__ defects such as inadequate attached gingiva, clefts, enlargements and craters can complicate oral hygiene.
mucogingival involvement (MGI)
areas with no attached gingiva present, the PPD will present below the mucogingival junction (worse than defect)
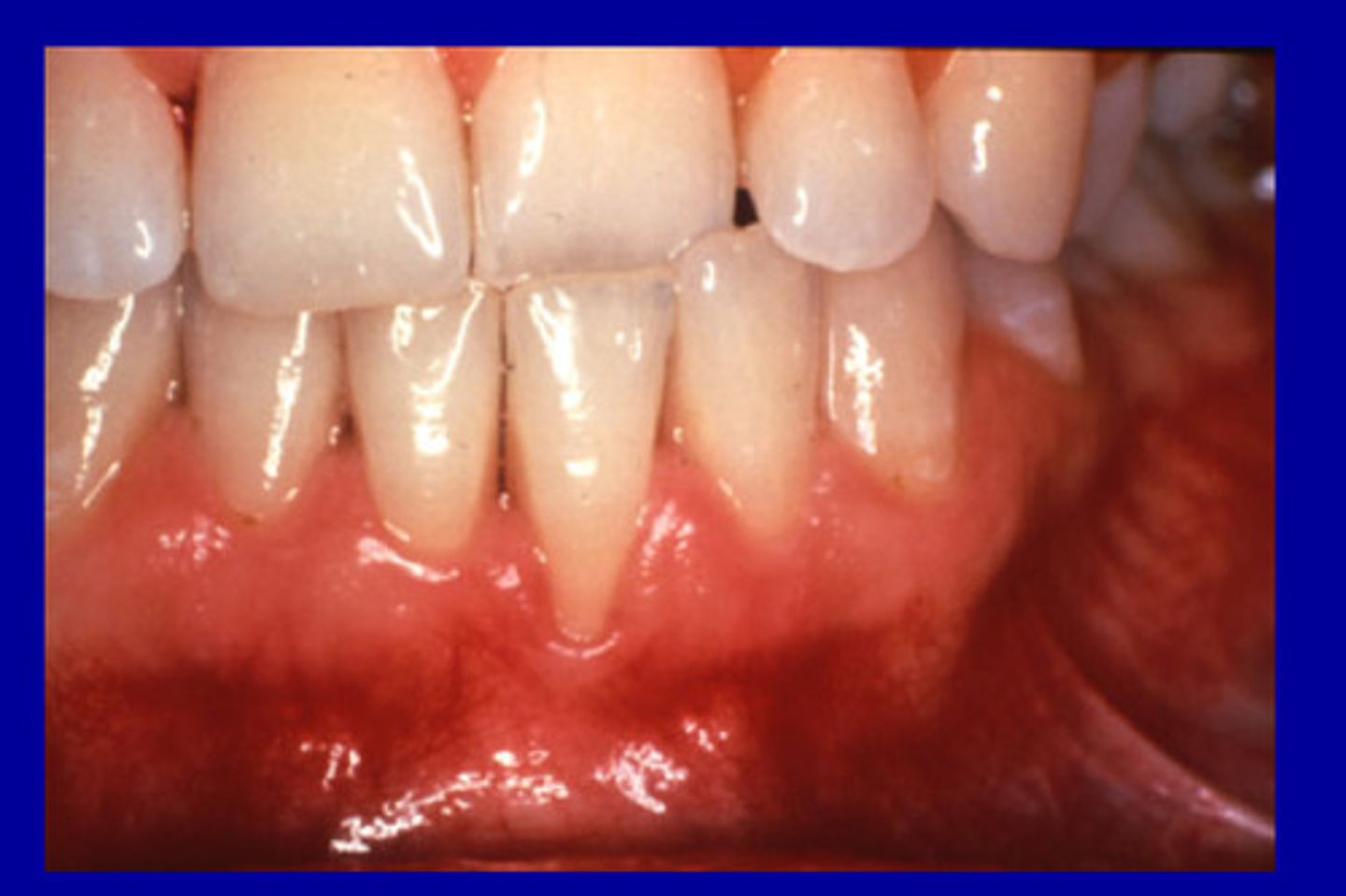
Mucogingival involvement (MGI)
Total gingival - Free gingival
<1 mm yes to MGI
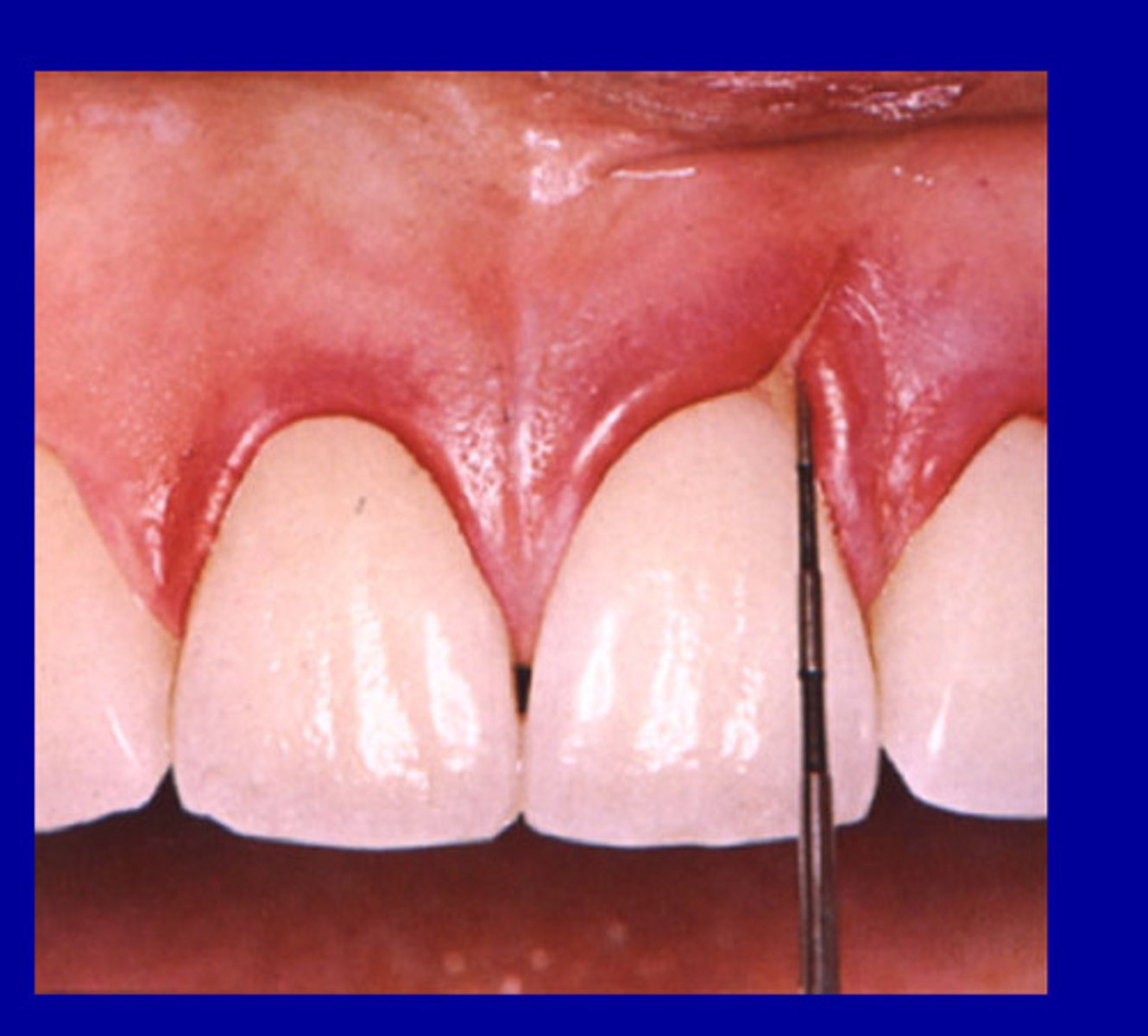
Clefts
Lack of oxygen can lead to receding, openings, cracks due to inflammation, etc
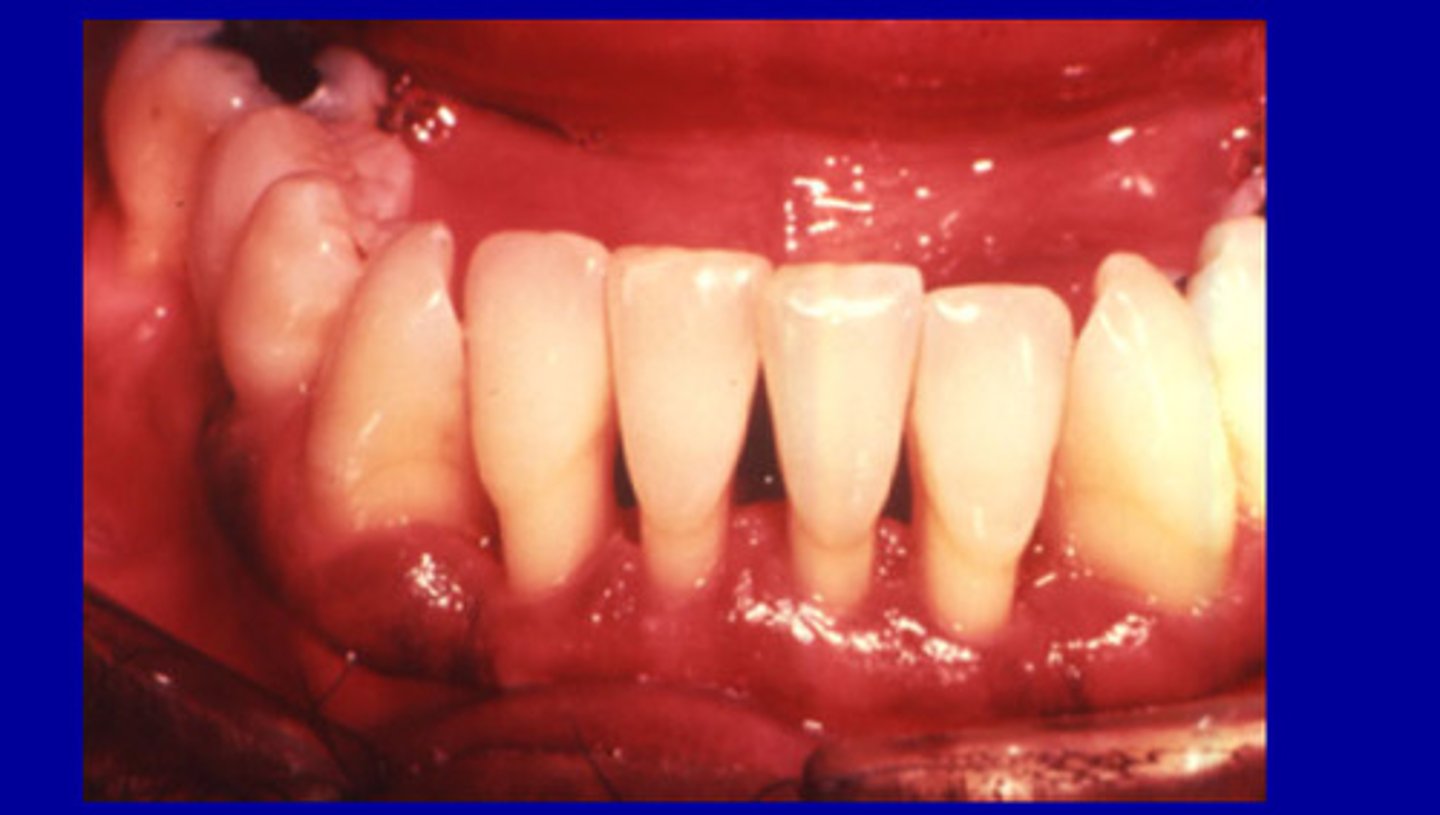
Gingival enlargements
Gingival overgrowths that are generalized or localized

Soft tissue craters
Occur after periodontal surgery, dips down cervically and usually self corrects
Systemic conditions that affect periodontal disease
• Endocrine Conditions
• Obesity
• Hematologic Disorders
• Neutrophil Disorders
• HIV positive
• Medications
• Stress
• Smoking
• Nutrition
• Heredity
Diabetes and hormones
Endocrine conditions such as ___ can affect periodontitis
Hormonal conditions
• Puberty
• Pregnancy
• Estrogen deficiency
Puberty gingivitis
• peaks at 11 to 13 years of age, self limiting w/ age
• related to hormonal changes creating a more favorable environment for pathogens
• both male and female

Pregnancy gingivitis
Increased hormone levels in gingival crevicular fluid associated with dramatic increases in P. intermedia, which use hormones as growth factors.
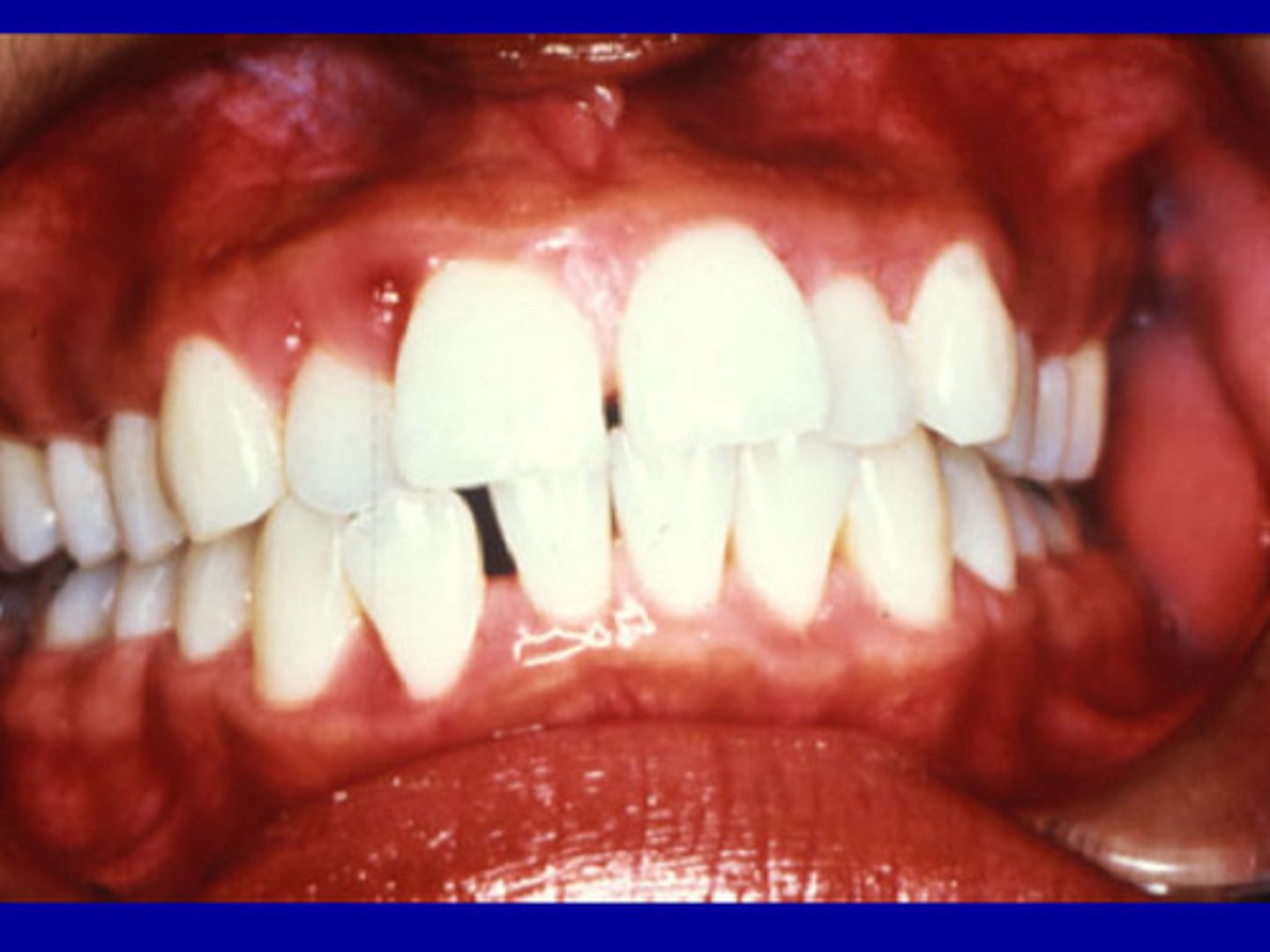
P. intermedia
In pregnancy gingivitis, increased hormone levels in gingival crevicular fluid associated with dramatic increases in ___, which use hormones as growth factors.
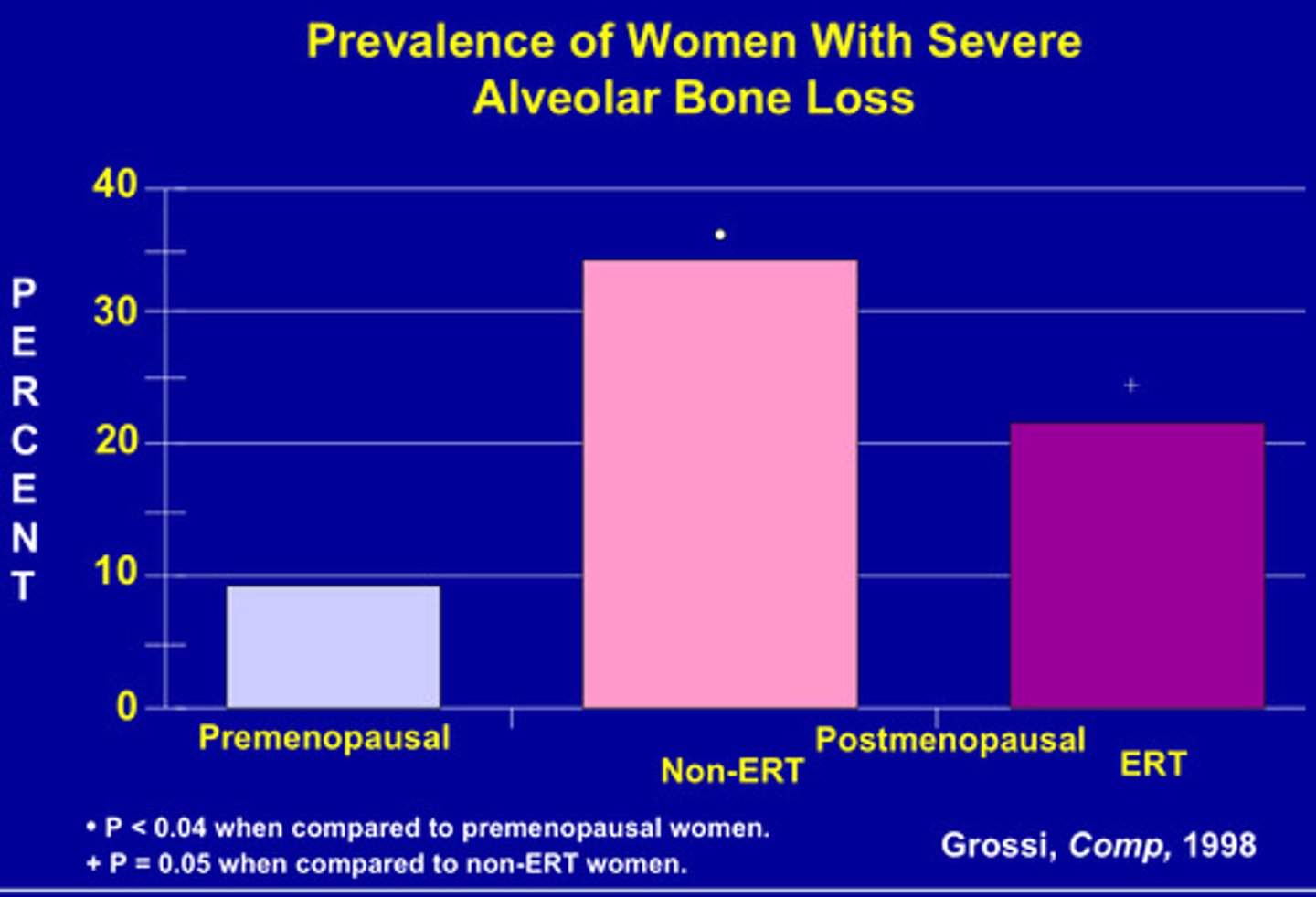
Estrogen deficiency/osteoporosis
• Bone mass peaks age 20 - 30
• Reduction accelerates at menopause
• Estrogen is protective
• Estrogen deficiency is a possible modifying factor in alveolar bone loss
estrogen replacement therapy (ERT)
Reduces alveolar bone loss post menopause
Diabetes
• Increased incidence of gingivitis /periodontitis
• Defective PMN chemotaxis
• Enlarged gingiva
• Periodontal abscesses
Attachment loss
Diabetics have a way higher chance of
3mm
Periodontitis is defined as __ LOA
4mm
Periodontitis is defined as ___ probing depth
NHANES III database
Showed how obesity will increases probability of periodontal disease

Hematologist disorders
Conditions of blood
*Anemia
*Sickle cell anemia
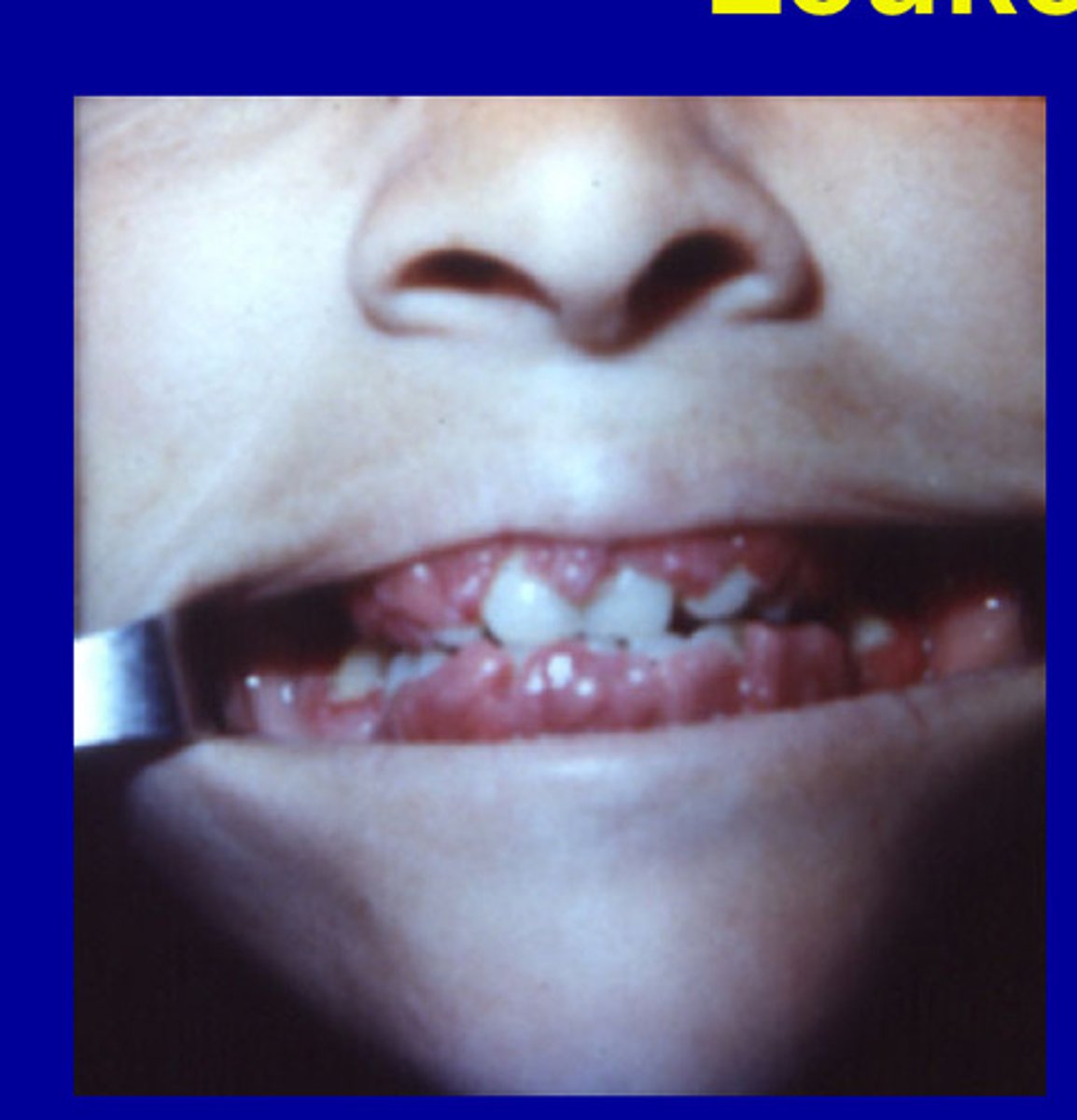
Acute leukemia
67% change for gingival enlargement and 18% for bleeding
Leukemia
Gingival enlargement and bleeding
Chronic leukemia
Rare chance for gingival enlargement and 4% for gingival bleeding
Neutrophil disorders
The neutrophil is the first line of defense to combat acute bacterial infection.
____ results in severe periodontitis.
Neutrophil disorders (depressed chemotaxis)
- Chediak - Higashi Syndrome
- Diabetes mellitus
- Prediabetic
- Down's syndrome
- Lazy leukocyte syndrome
- Papillon - Lefèvre syndrome
- Malnutrition
HIV associated periodontal diseases
• Linear gingival erythema
• Necrotizing gingivitis
• Necrotizing periodontitis
No deep pockets
The difference between periodontitis and necrotizing periodontitis is that in necro there are ___ because gingival is at bone level
Linear gingival erythema
• persistent, linear, easily bleeding, erythematous gingivitis
• possible etiologic role for candidial species
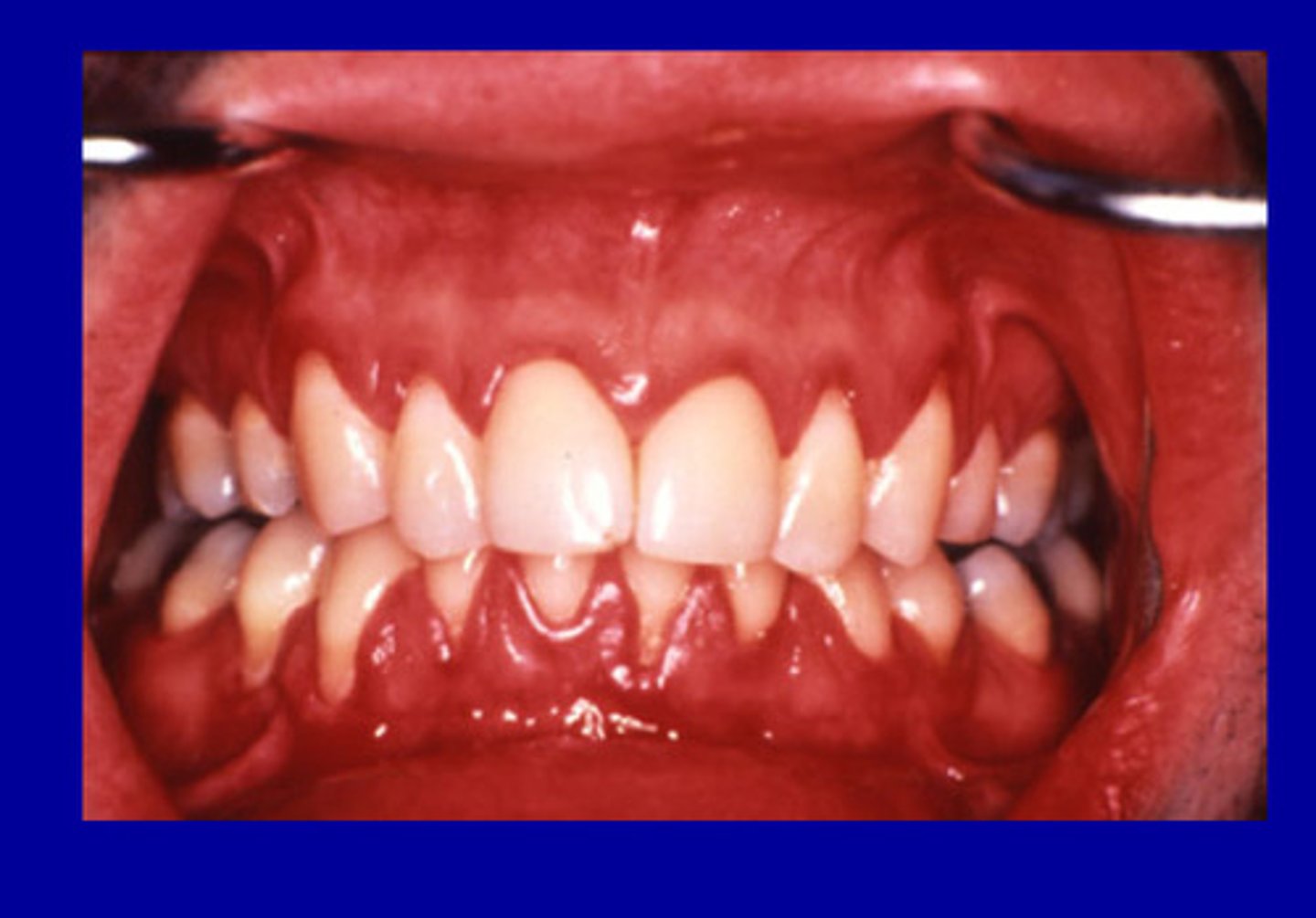
Necrotizing gingivitis and periodontitis
painful infections characterized by tissue ulceration, swelling and sloughing of dead epithelial tissue from the gingiva, and fetid oral odor
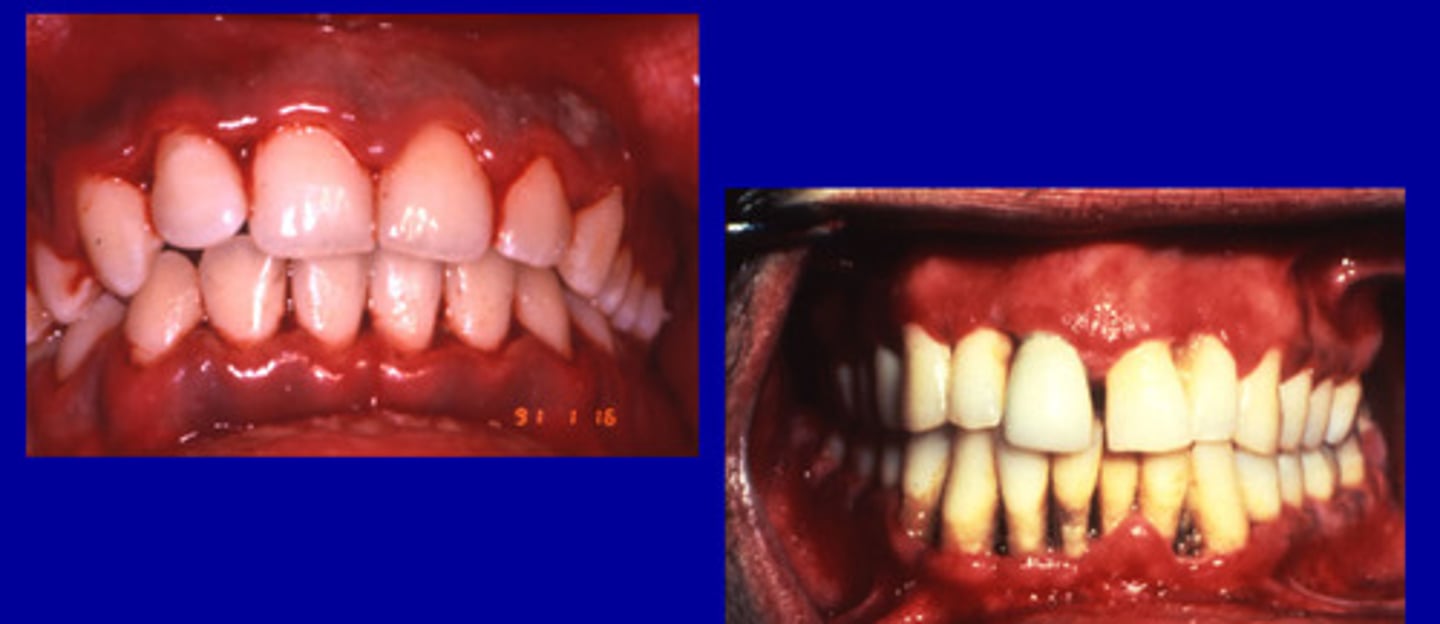
Drug manifestations w/ periodontitis
• Phenytoin (Dilantin)
• Cyclosporine
• Nifedipine (Calcium Channel Blockers)
• Cannabis
• Oral contraceptives
-pine
calcium channel blockers
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
• enlargement occurs in about 50% of patients
• genetic predisposition suspected
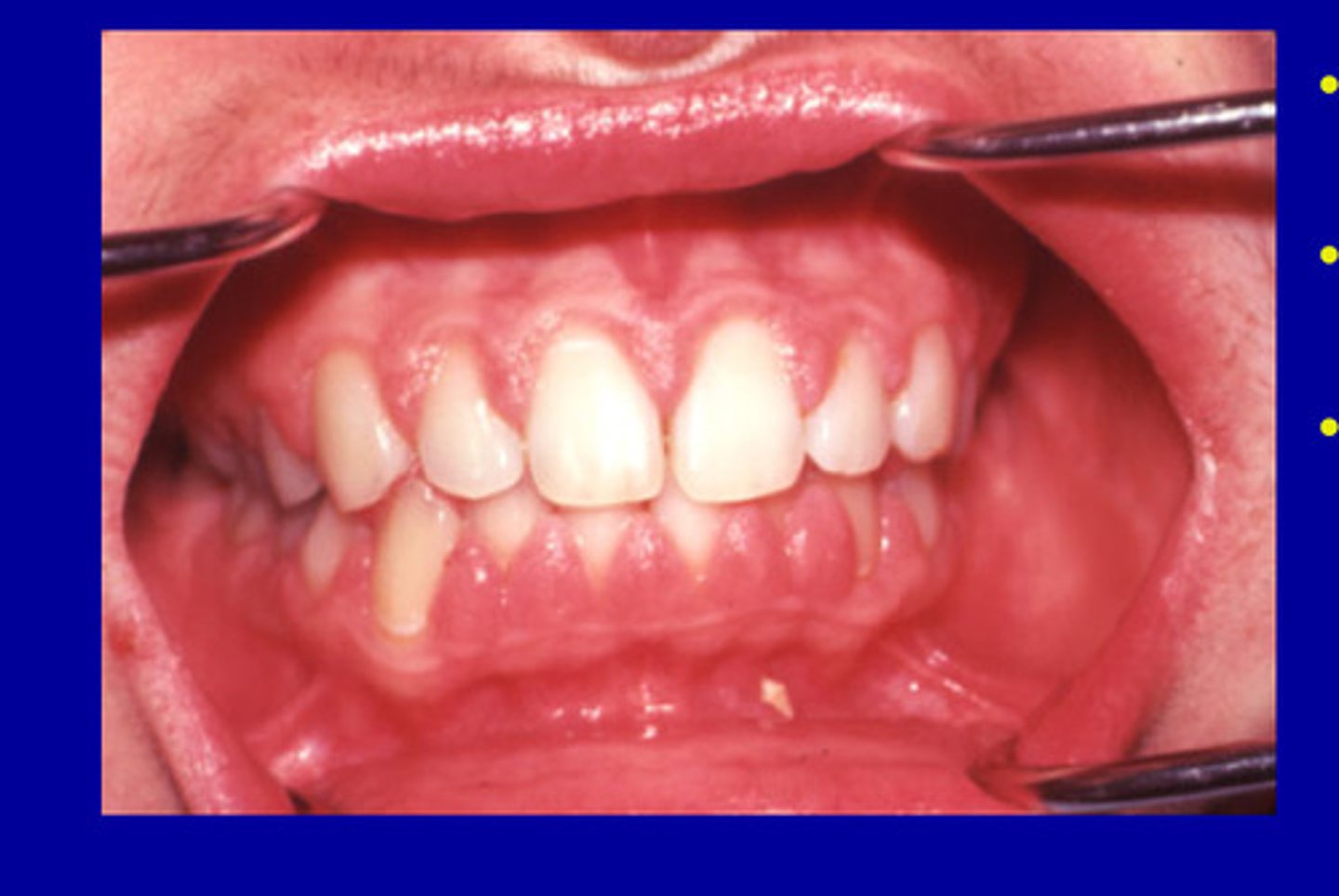
Interdental, facial
Phenytoin enlargement usually occurs first at
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
__ evidence links pathogenesis to direct effect on fibroblasts, inactivation of collagenase, and plaque-induced inflammation
Cyclosporine
Immunosuppressant
• more vascularized than phenytoin induced enlargements
• 20-70% occurrence
• plasma cell infiltrate suggests hypersensitivity response
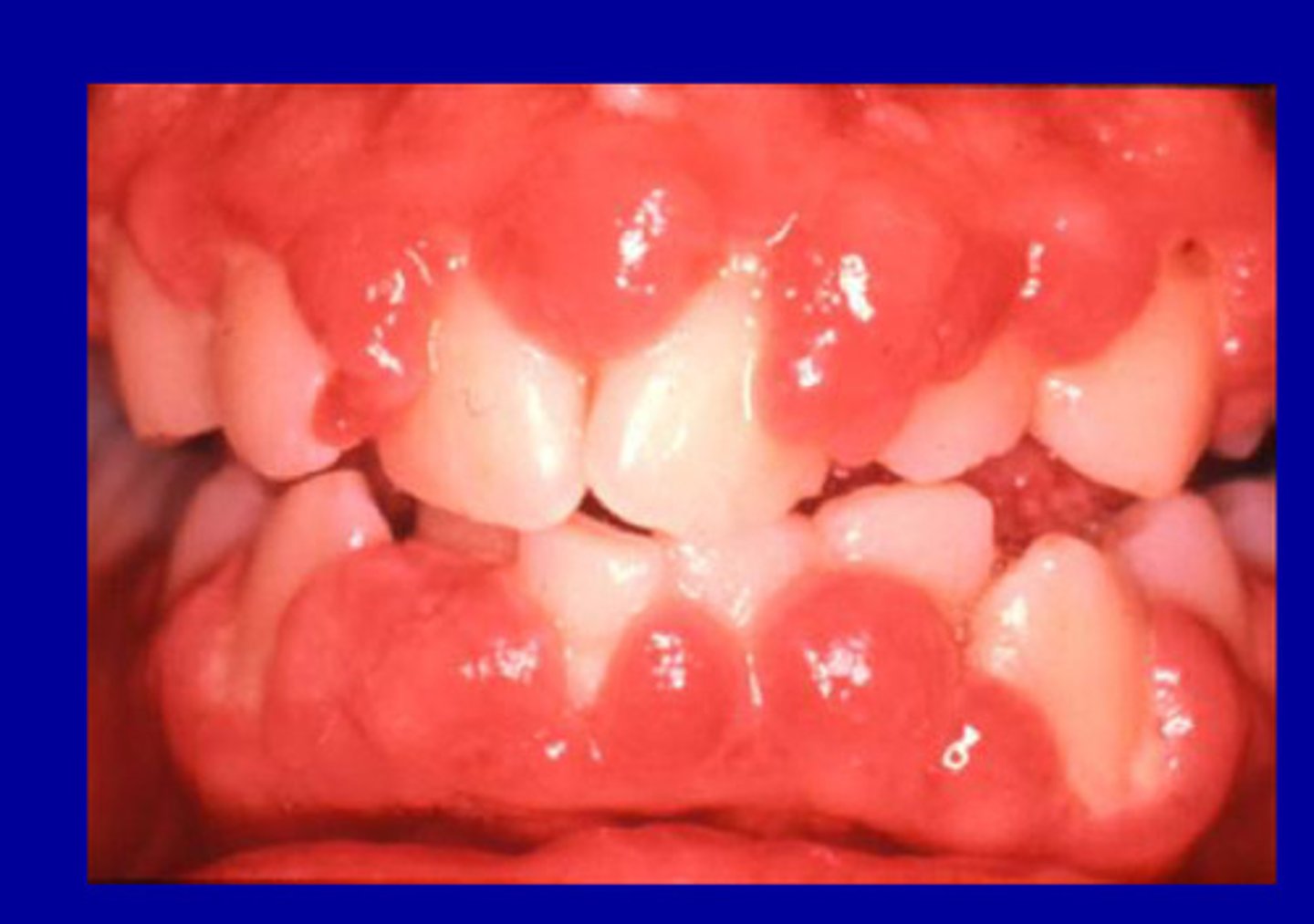
Cyclosporine
____ is more vascularized than phenytoin induced enlargements
plasma cell
Cyclosporine causes ___ infiltrate suggests hypersensitivity response
57%
___ had a positive relation between stress and periodontitis
29%
___ found mixed results between stress and periodontitis
14%
___ found negative relation between stress and periodontitis
How stress affects periodontitis
1) poor oral hygiene
2) alter immune response
• Neutrophil impairment
• Monocyte upregulation
Smoking
Important periodontal risk factor
• Increased incidence and severity of periodontitis
• Poorer response to therapy
• Associated with NUG
• Nicotine can impair neutrophil phagocytosis
• Decreased bleeding on probing
Bleed
Smokers do not ___ as much a non smokers (an important response)
nutritional deficiencies
Efforts to associate periodontal disease with ___ have yielded conflicting results.
lowers
In theory, poor nutrition __ resistance to periodontal disease.
Poor nutrition may slow the healing process.
Low serum calcium and periodontal disease
Results suggest that low dietary intake of calcium results in more severe periodontal disease
40%
Identical twins studies suggest that more than __ of the clinical signs of disease severity are the result of genetic factors.
Hereditary gingival fibromatosis
rare benign oral condition characterized by slow and progressive enlargement of both maxillary and mandibular attached gingiva
IL-1 Genotype
What is the genetic marker for perio?
30%
Those positive w/ IL-1 genotype had > ___ mean bone loss compared to those w/out IL-1 genotype