pharm 2: non and opioids, NSAIDS, APAP rx
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
NSAID: 1st gen names (8)
aspirin
Ibuprofen
Naproxen
Meloxicam
Etodolad
Indomethacin
Ketorolac
NSAIDS: 2nd gen name
Celecoxib
NSAIDS 1st gen are ____ of COX ___ and COX ___ inhibition → increase ____
mixed
cox 1
cox 2
prostagladin
NSAIDS 2nd gen: COX 2 ____
inhibitors
THERAPEUTIC effects of NSAIDS?
Analgesic (reduce pain)
Anti-inflam (reduce inflammation)
Antipyretic (reduce F)
ADE of NSAIDS?
GI (COX 1) → GI distress, PUD, bleeding
Kidney (COX 1 and 2) → nephrotoxicity, sodium and water retention
Cardiac (COX 1 and 2) → ⬆ risk of CVD events → more often with COX 2 only and not mixed with ASA (aspirin)
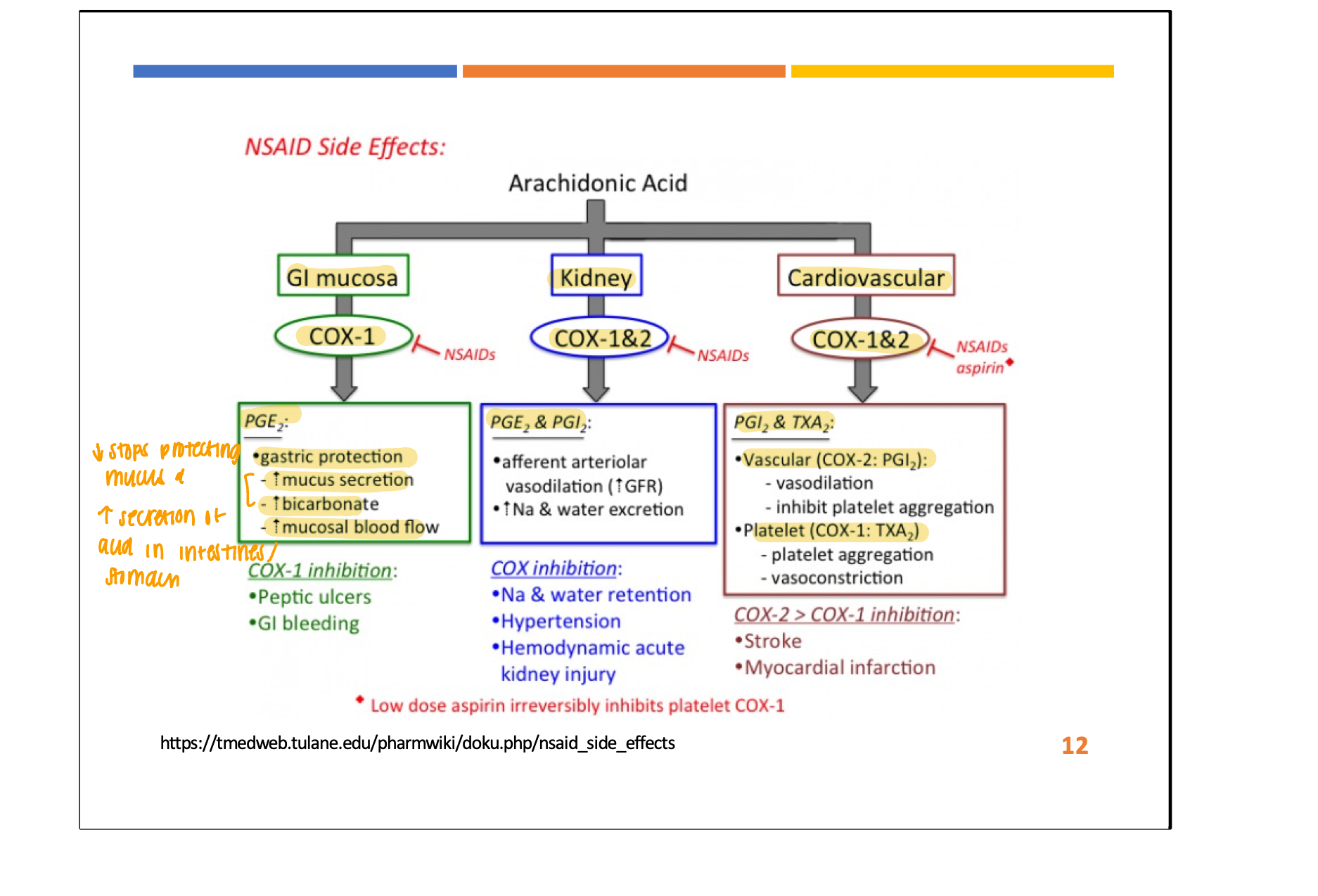
contradiction of NSAIDS (2)
caution in which pt population?
PUD
bleeding disorders
CAUTION in renal disease, preg, CVD RF
Aspirin (ASA) MOA:
_____ inhibits _____ synthesis by ____ COX 1 and 2 activity
IRRVERSIBLY inhibits prostaglandin synthesis by ⬇ COX 1 and 2 activity
ASA have ____ duration and ______ bleeding risk
longer
increase
when should you d/c ASA before sx?
5-7 days before
indication of ASA:
low dose: reduce risk of ____ and ____ ____
moderate - high dose: mild to moderate ____ and ____
low: ⬇ risk of CVD and acute stroke
moderate - high: mild - moderate pain, F
ADE for ASA: (2)
tinnitus
reyes syndrome
COX 2 MOA:
_____ inhibits prostaglandin synthesis → _____ COX 2 activity
REVERSIBLY inhibits prostagladin synthesis → ⬇ COX 2 activity
COX 2 indication:
mild to moderate ____, ____, _____, ____, _____
mild - moderate pain, GOUT, OA, F, BURSITIS
what does COX 2 inhibitors NOT protect?
NO protection against MI and stroke → ⬆ risk
contraindications for COX 2 inhibitors?
SULFA ALLERGY (celecoxib)
Ketorolac
____ - ____ ____ NSAID
High-potency parenteral NSAID
indication for ketorolac?
long or short term use?
when do we typically use rx?
SHORT TERM (5 days) tx of moderate - severe pain
used post op / sx
ADE for ketorolac? (2)
GI risk, nephrotoxicity → longer duration of action
PK for ketorolac? (3)
IM, IV, PO
Diclofenac 1% Gel - TOPICAL NSAIDS
indication?
MILD OA pain → ONLY for 1-2 SMALLER joint (hands, knee)
≠ recommended for back, hip, shoulder
OTC diclofenac systemic absorption %?
< 10%
OTC diclofenac pt edu?
≠ use > 21 days CONSECUTIVELY
limit other topicals in AA
≠ combine PO and topical NSAIDS
what do you try first? PO or topical NSAIDS for pain?
TOPICAL
what NSAID do you give this pt?
LOW CV risk + HIGH GI risk
celecoxib
GI RF: 65+, hx of PUD / previous bleeding, multiple NSAIDS, high NSAIDS dosing, long duration, other meds that ⬆ risk of bleeding
what NSAID do you give this pt?
HIGH CV risk + LOW GI risk
naproxen
CV RF: HF, unstable angina, MI, HIGH NSAIDS dosing / long duration
what NSAID do you give this pt?
HIGH CV risk + HIGH GI risk
AVOID NSAIDS
CV RF: HF, unstable angina, MI, HIGH NSAIDS dosing / long duration
GI RF: 65+, hx of PUD / previous bleeding, multiple NSAIDS, high NSAIDS dosing, long duration, other meds that ⬆ risk of bleeding
Acetaminophen (APAP) MOA:
______ brain _____ synthesis → analgesic and antipyretic activity
inhibits brain prostaglandin synthesis → analgesic and antipyretic activity
highlighted in yellow on drug fact of med
indication for APAP?
MILD ___, ___, ____
MILD pain, F, arthritis
ADE for APAP? (3)
N, stomach pain, hepatotoxicity
DRUG INTERACTION of APAP?
alcohol (hepatotoxicity), WARFARIN
pt edu for APAP?
take with food → avoid stomach s/s
therapeutic effect for APAP?
Analgesic (reduce pain)
Antipyretic (reduce F)
when does APAP toxicity occur?
APAP → metabolized → N-acetyl-p-benzoquinon-imine (NAPQI)
Normal dose: NAPQI combine w/ glutathione → produce NON TOXIC metabolites
Overdose: glutathione = depleted and NAPQI = accumulates
APAP overdosing is ___ lethal and initial s/s = ____
s/s shows ___ hrs - ___ hrs after
highly
minimal
24 - 72 hrs after
antidote for APAP?
other antidote?
N-acetylcystein (NAC) = main one
⬇ production of NAPQI due to increasing stores of thiols
other: activated charcoal
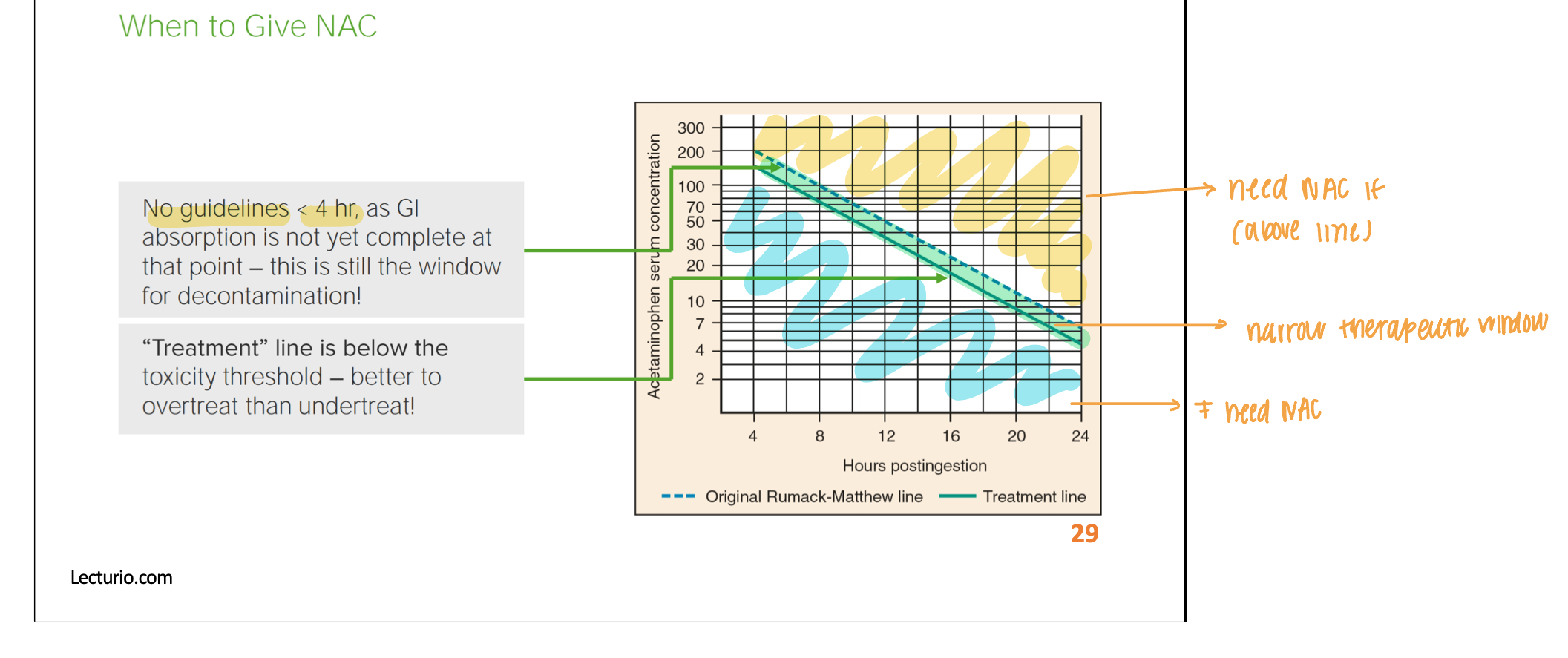
when should you give NAC?
tx should be administered if level is ABOVE solid line
better to OVERTREAT than UNDER
above doted line = HIGH RISK
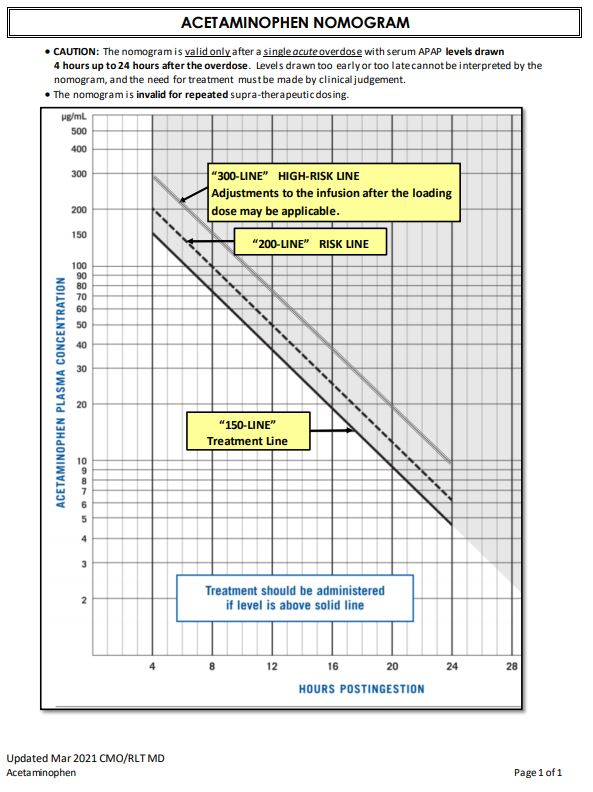
Maximum Adult APAP Dose
3000 mg / day → self suggestion
4000 mg/day → doctor suggested / advised
CENTRAL Muscle Relaxants MOA:
acts w/n _______→ ______ hyperactive reflexes
Structural analog of GABA
acts w/n spinal cord → suppress hyperactive reflexes
Structural analog of GABA
DIRECT acting muscle relaxant MOA:
_____ spasms → suppresses release of ______ from SR → skeletal muscle ≠ _____
RELIEVES spasms → suppresses release of CALCIUM from SR → skeletal muscle ≠ contract
indication for DIRECT acting muscle relaxant? (2)
cerebral palsy or multiple sclerosis
general muscle relaxant indication?
Chronic: treat _____ (stiffness) due to _____ sclerosis, _____ ______injury
≠ benefit _____ back pain
Acute: _____ pain
Chronic: treat spasticity (stiffness) due to MULTIPLE sclerosis, spinal cord injury
≠ benefit CHRONIC back pain
Acute: back pain
DRUG INTERACTION of muscle relaxants? (3)
opioids
benzodiazepines
alcohol (resp depression and death)
MAX time you can take muscle relaxants?
≠ LONGER than 2-3 weeks or 7+ days
high sedation muscle relaxers?
carisiprodol
cyclobenzaprine
tizanidine
key safety concern for cyclobenzaprine?
anticholinergic (≠ shit, see, spit)
fall risk
key safety concern for baclofen?
seizures if ABRUPTLY d/c
seizures cause you cant come BAC
key concern for tizanidine?
hypotension
key safety concern for methocarbamol?
urine discoloration
carisoprodol is ONLY recommended for? ____ term use
short
cariSOprodol only works SO SO (short term use only)
population you should avoid with cyclobenzaprine?
older or CVD risk pts
similar to TCA
what should you monitor when taking tizanidine?
BP (alpha 2 agonist)
what drugs are considered anticonvulsants?
gabapentin
pregabalin
MOA for anticonvulsant?
analog of _____ and enhance ____ release
analog of GABA and enhance GABA release
indication for anticonvulsants? (6)
neuropathy (DM)
seizures
migraine prophylaxis
fibromyalgia
restless less syndrome
alcohol withdrawal
DRUG INTERACTION with anticonvulsants?
opioids, alcohol, benzodiazepines
same as muscle relaxers
ADE for anticonvulsant?
peripheral edema
weight GAIN
cognitive difficulties
pt edu with anticonvulsants?
AVOID driving / hazardous activities until aware of ADE
caution: preg
ANTI-driving/activities
what drugs are Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) (5)?
Amitriptyline (MC)
Nortriptyline (MC)
Desipramine
Imipramine
Doxepin
MOA for TCA?
____ neuronal ___ of ___ and ___
BLOCK neuronal reuptake of norepi and serotonin
Block receptors for histamine, acetylcholine, norepi
indication for TCA? (4)
insomnia, depression, fibromyalgia, neuropathic pain
ADE for TCA? (4)
anticholinergic s/s
weight gain
cardiac toxicity
lower seizure threshold
ADE for TCA overdose? (3 Cs)
Overdose → cardio toxicity, convulsion, coma
DRUG INTERACTION for TCA? (2)
MAOIs
Sympathomimetics (CNS stimulants and pseudoephedrine)
CAUTION for TCA? (2)
Anticholinergic agents
CNS depressants
Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) drugs?
-ine
duloxetine, venlafaxine
MOA for SNRI?
_____ normal reuptake of serotonin and norepi in _____ ______
BLOCKS normal reuptake of serotonin AND norepi in nerve block
similar to TCA
SNRI: therapeutic effects takes ____ _____ to see an effect
several weeks
indication for SNRI? (3)
anxiety, depression, chronic pain disorders
ADE for SNRI?
same as SSRI + ⬆ sweating, HTN, ⬆ risk of mania
CAUTION with SNRI?
⬆ risk for ____
⬆ risk for SUICIDE
BBW of SNRI?
antidepressants ⬆ risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior (PEDS and adults)
MOA for lidocaine?
______ _____ ion channel required for initiation and conduction of neuronal impulses
BLOCK Na ion channel required for initiation and conduction of neuronal impulses
indication for lido? (3)
skin relief, itching, soreness
ADE for lido? (4)
bradycardia
heart block
seizures
resp depression
RISK with lido?
_____ INCREASES
TOXICITY INCREASES
pt edu with lido?
caution against activities → unintentional harm
____ patch topically in AA up to ____ hrs
MAX ____ patch on body at 1 time
LIMIT: ___ week
caution against activities → unintentional harm
1 patch in AA up to 12 hrs
MAX 1 patch on body at 1 time
LIMIT: 1 week
topical capsaicin MOA:
____ and _____ reaccumulation of ______ ______ in peripheral sensory neurons
depleting and preventing the reaccumulation of substance P in peripheral sensory neurons
indication for topical capsaicin? (3)
arthritis, MSK pain, neuropathic pain
ADE with topical capsaicin?
erythema and pain (burning) on site
pt edu with topical capsaicin?
avoid thick application
≠ apply on wounds
≠ touch mucous membrane after
what are pure strong agonist of opioids? (3)
hyromorphone (IV,PO)
morphine (IV, PO)
fentanyl (IV, transdermal)
HATE MY FEELS
what are pure moderate - strong agonist of opioids? (3)
codeine (PO)
oxycodone (PO)
hydrocodone (PO)
meperidine (IM)
mixed effect opioids?
pentazocine
butorphanol
puprenophrine
opioids MOA?
binds to ____ and ____ receptors in brain, spinal cord, GI tract
binds to mu and kappa receptors in brain, spinal cord, GI tract
what does MU receptor activation do when activated?
analgesia
resp depression
euphoria
sedation
⬇GI motility
what do KAPPA receptors do when activated?
analgesia
sedation
ADE for opioids?
Euphoria
Drowsiness
Resp depression (90 mins after PO ingestion)
Constipation
Urinary retention
N
Tolerance
V
Orthostatic hypotension
mnemonic: E-DR. CUNT VO
pt edu with opioids?
monitor opioid overdose and administer narcan
morphine is used in ____ and cause ____?
NOT recommended in ___ ____ pts
used in MONA, cause itching (histamine mediated)
NOT RECOMMENDED IN RENAL FAILURE PTS
fentanyl increased by _____ inhibitors
increased by CYP3A4 inhibitors
fentanyl patch: applied _____ hours
fentanyl IV: last _____hrs → used for ____
Patch: applied Q72 hours
IV: last 1-2 hrs → used for post op
fentanyl indication?
_____ SEVERE pain in opioid tolerant pts
PERSISTENT SEVERE pain in opioid tolerant pts
codeine is ______ and can combo with _____
monotherapy and can combo with APAP
codeine indication?
Effective COUGH SUPPRESSANT (10 mg)
Converted to MORPHINE in liver → careful with FAST metabolizers
Hydrocodeine/oxycode is _____ and can combo with _____
Hydrocodeine/oxycode: monotherapy and combo with APAP
tramadol is a ____ agonist and have ____ attributes
weak agonist and have SRNI attributes
what drugs help with OUD? (2)
Binds tightly to _____ -______ receptors → prevent others from binding effectively
Methadone and buprenorphine
Binds tightly to mu - opioid receptors → prevent others from binding effectively
OUD: chronic brain disease with compulsive drug seeking
MOA for methadone and buprenorphine?
stabilize opioid receptors in brain → ⬇ _____ and _____ _____ producing a strong euphoric high
stabilize opioid receptors in brain → ⬇craving and withdrawals WITHOUT producing a strong euphoric high
ADE for methadone?
____ ½ life
T/F: need specific training to dispense and prescribe opioid (OTPs)
QT prolongation
long ½ life
T