A&P Central Nervous System
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Will probably add slides about how differing parts of the brain do similar functions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
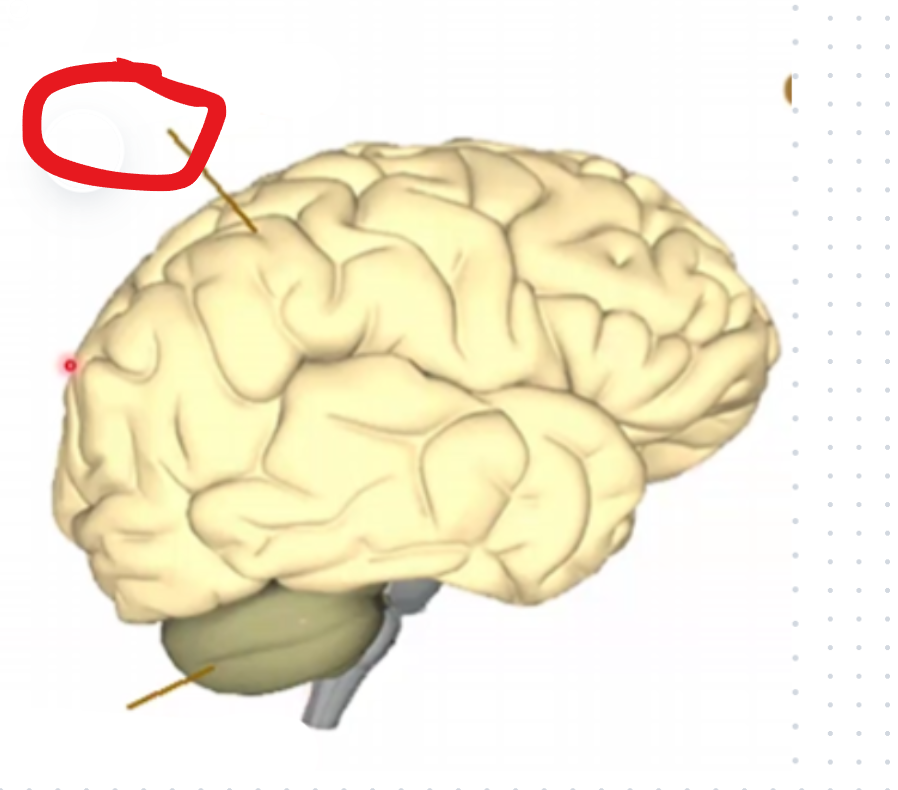
Cerebrum
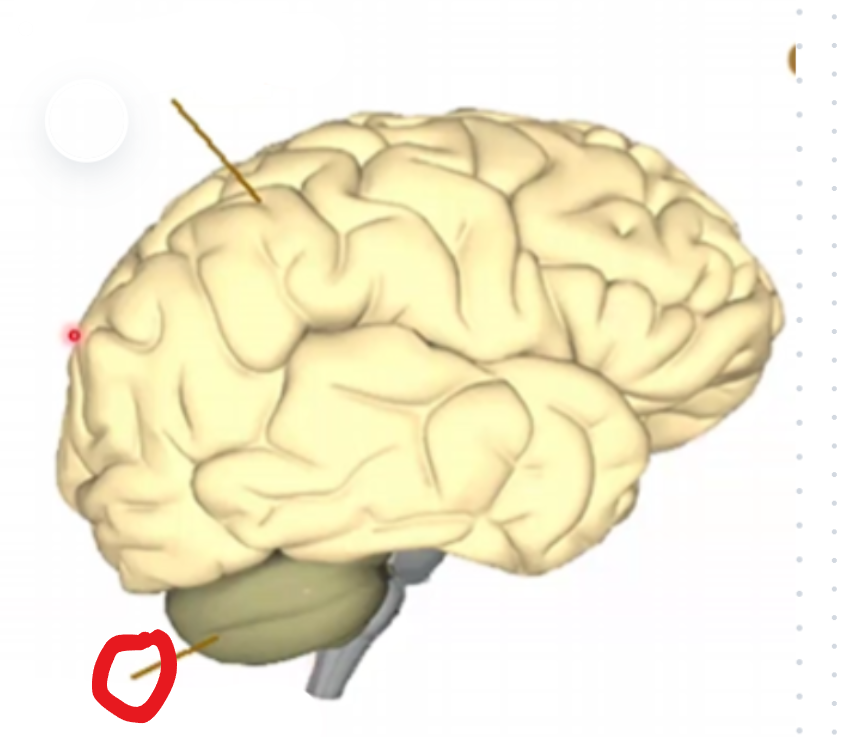
Cerebellum
Cerebral hemisphere
Think of the hemispheres like paired bones
Brainstem
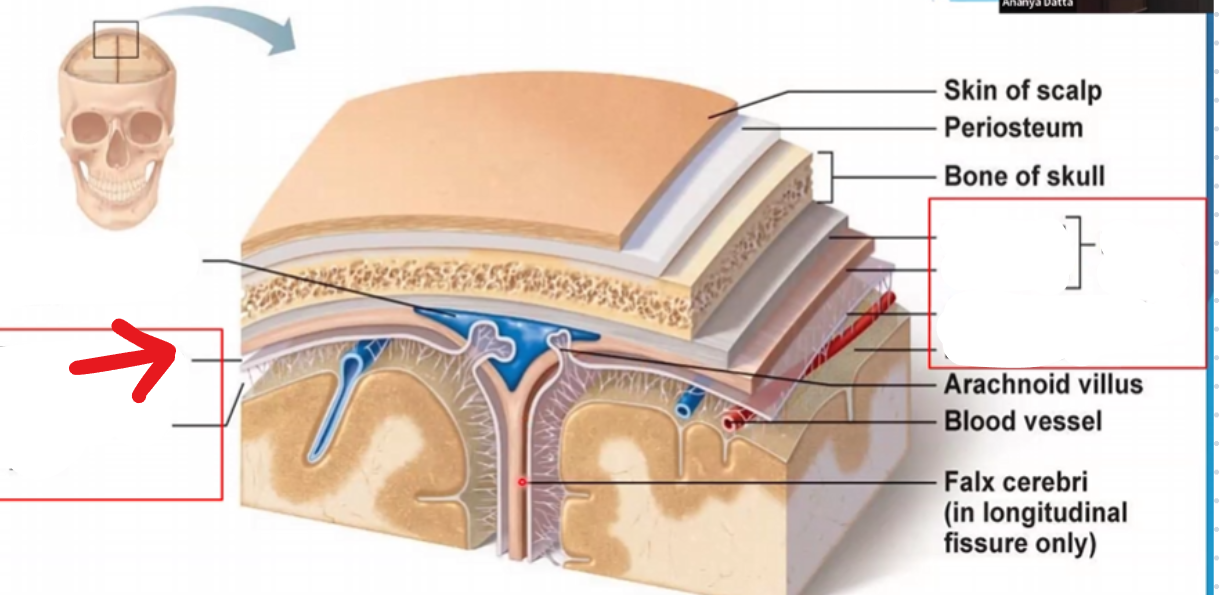
Subdural space
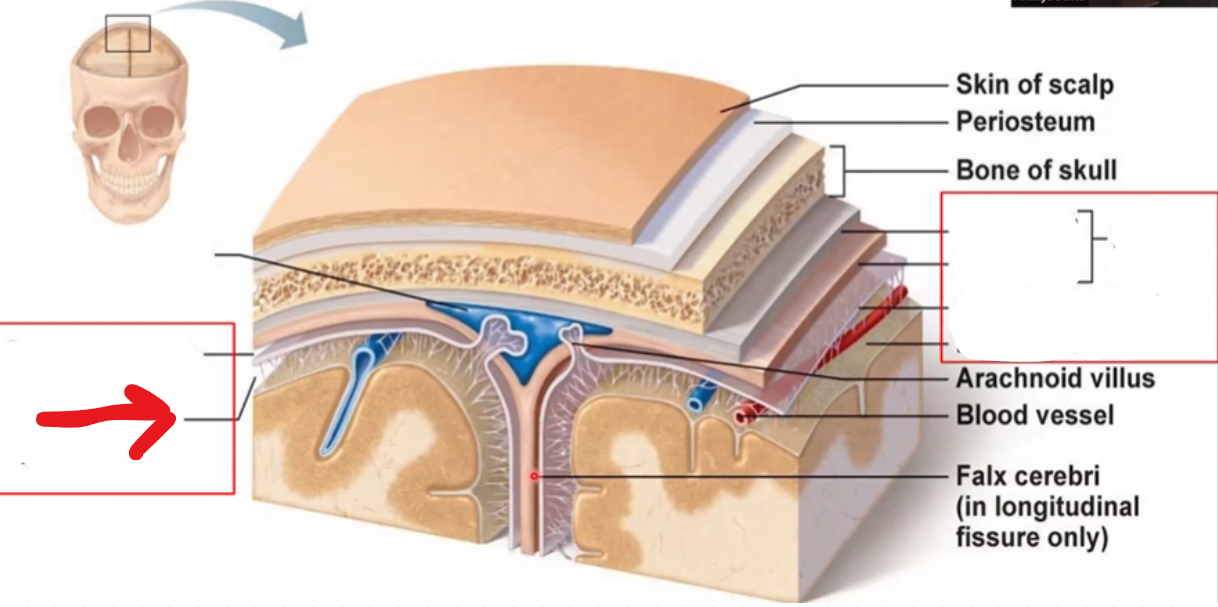
Subarachnoid space
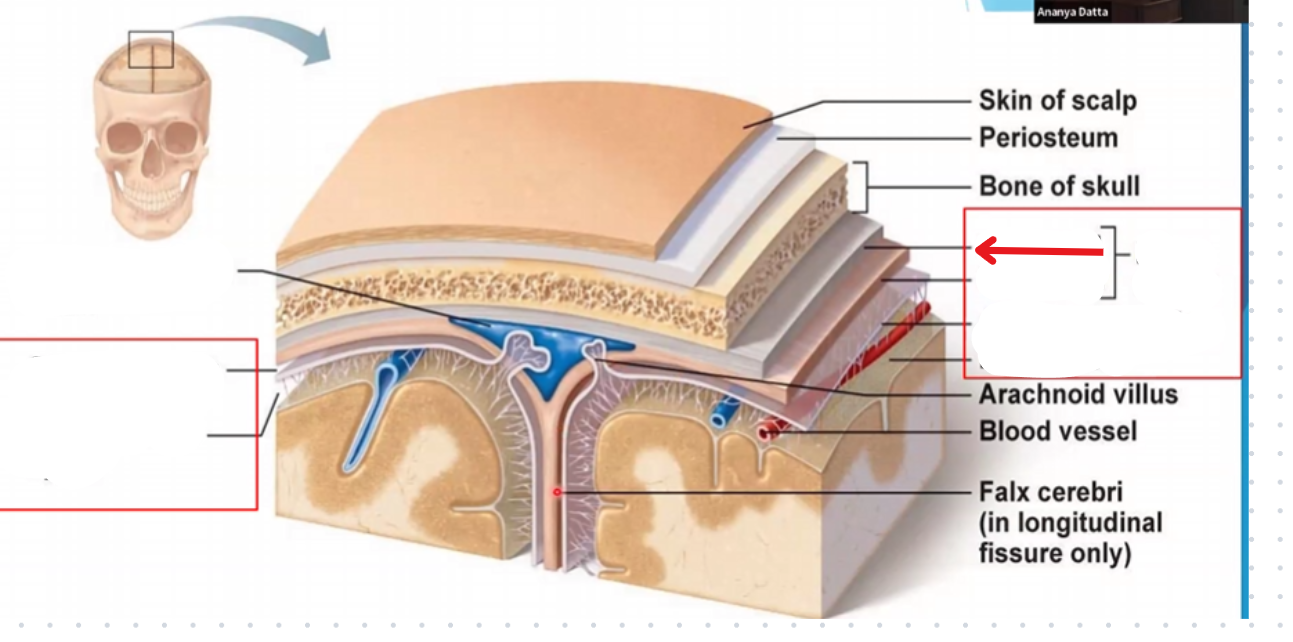
Periosteal layer of the dura mater
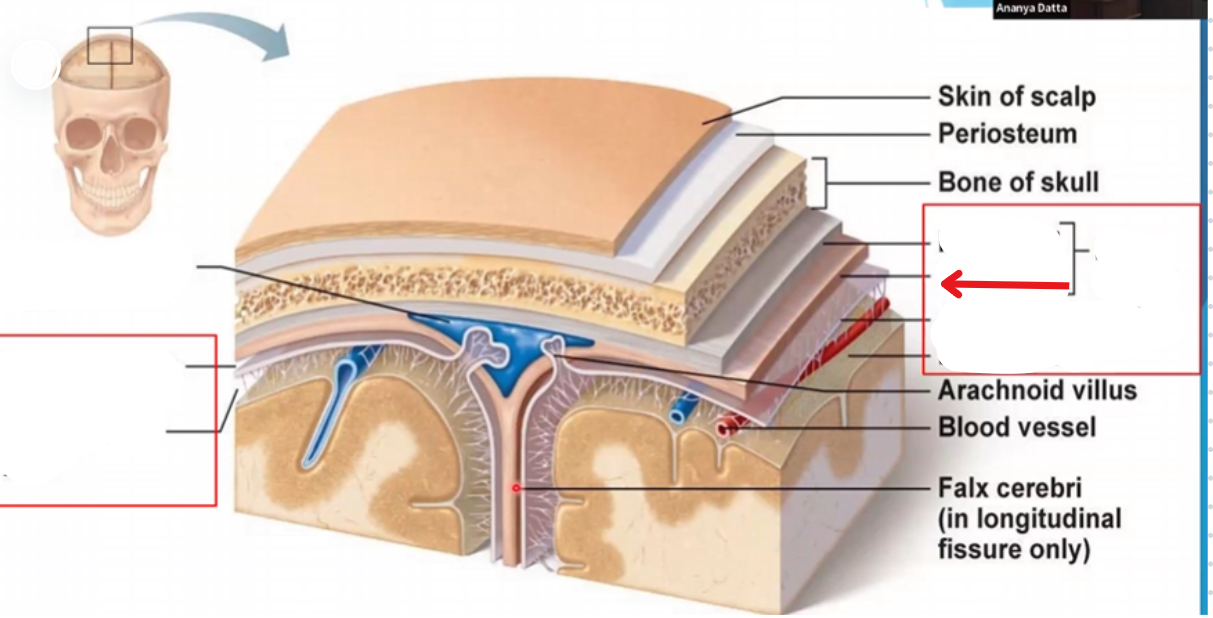
Miningeal layer of the dura mater
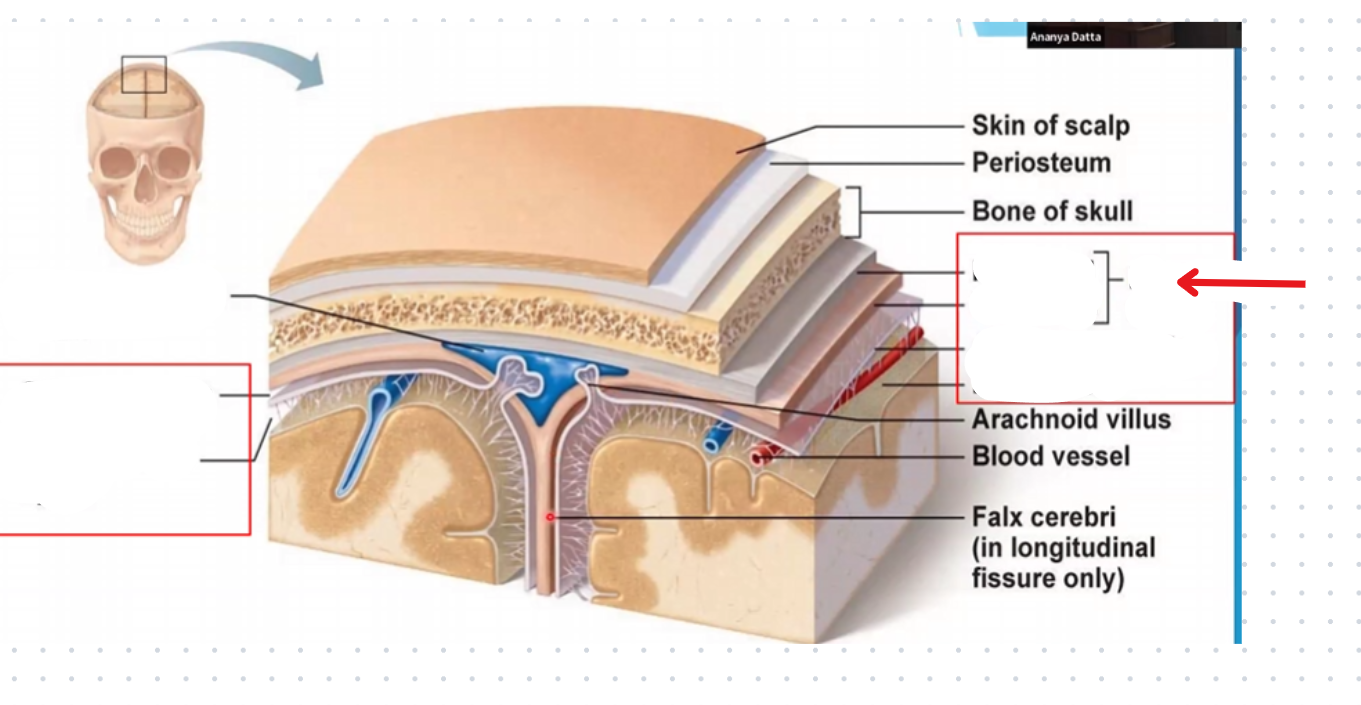
Dura mater
Makes up the fissure between the cerebral hemispheres
Merges at the corpus collosum
Thick enough to project inwards towards the brain and provide support
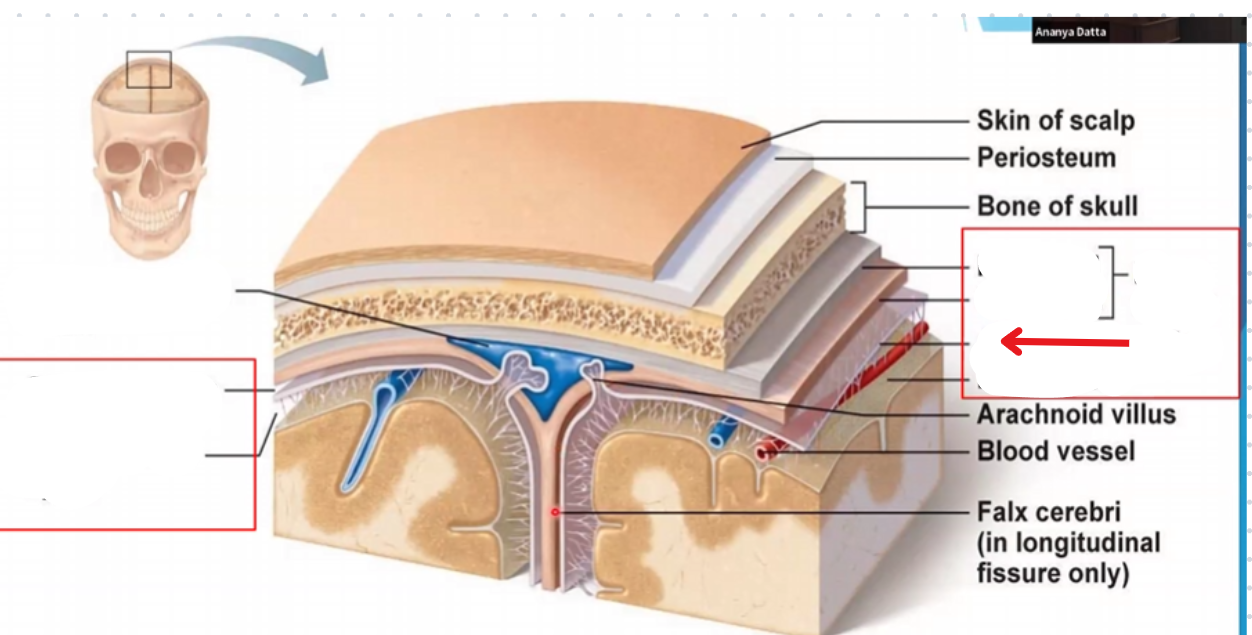
Arachnoid mater
Follows entire surface of the brain like cling wrap
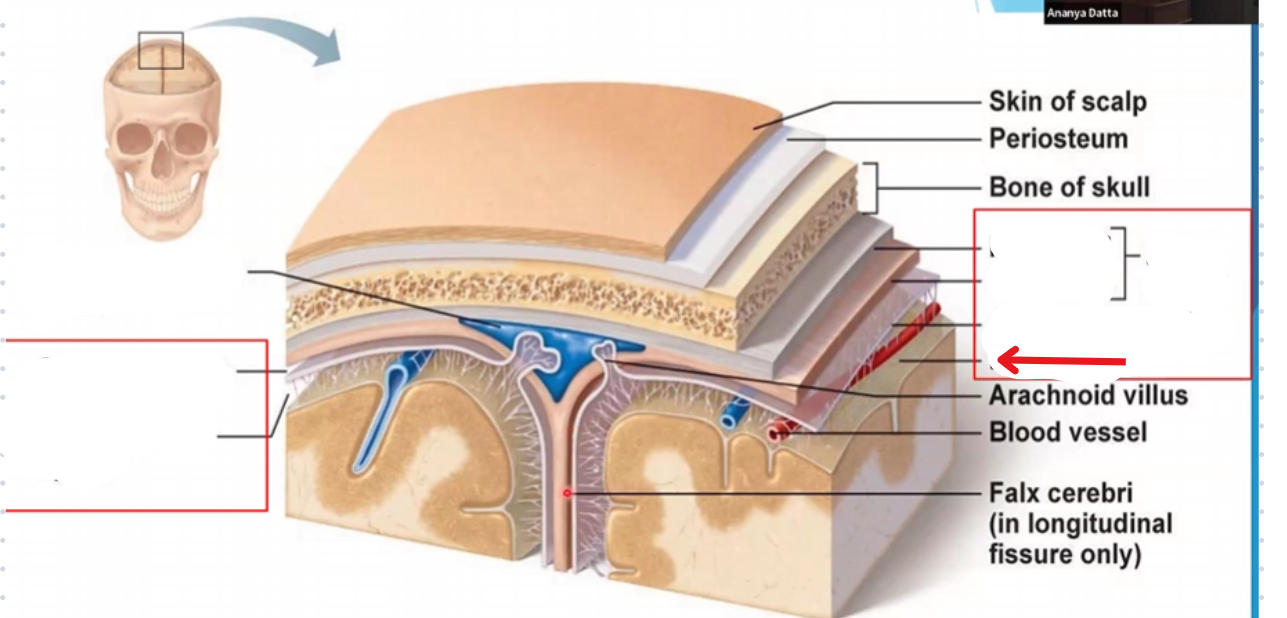
Pia mater
Follows entire surface of the brain like a coat of paint
Periosteum
Connective tissue layer between the skin of the scalp and the skull
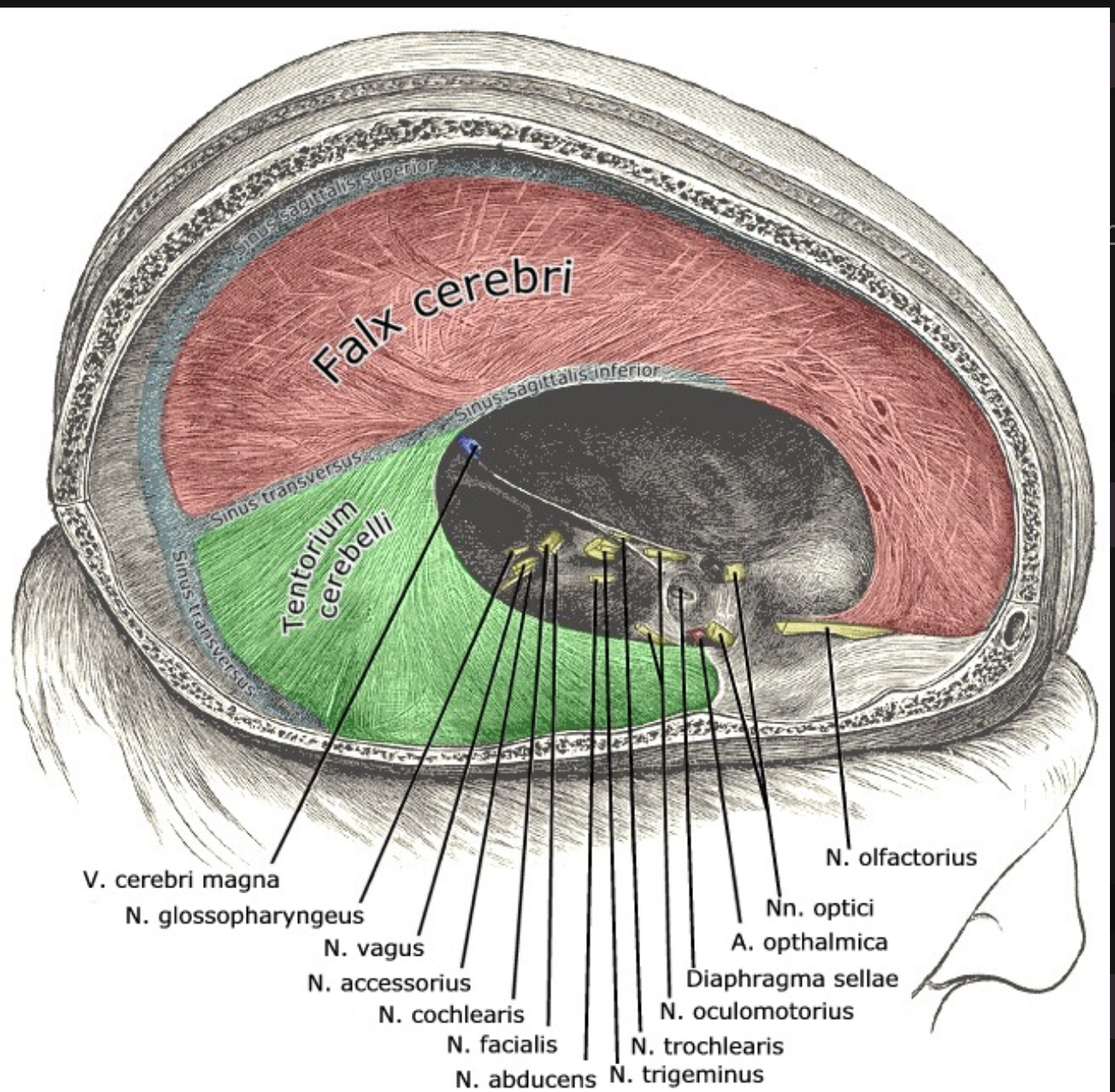
Falx cerebri
Portion of meningeal dura mater that supports the great longitudinal fissure between the two brain hemispheres
Extends from the cranial roof to the corpus collosum
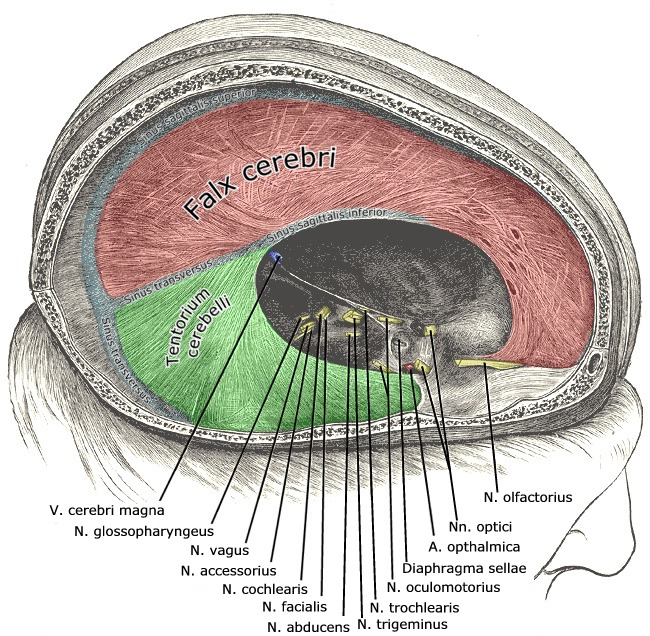
Tentorium cerebri
Portion of the meningeal dura mater that separates the occipital lobe and cerebellum
Supportive structure located at the posterior cerebrum (Where the cerebellum is located)
The cerebrum
largest portion of the brain
Contains five lobes
Consists of L and R hemispheres
Corpus callosum
Connects the two cerebral hemispheres
Transmits messages from one side to the other
Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body
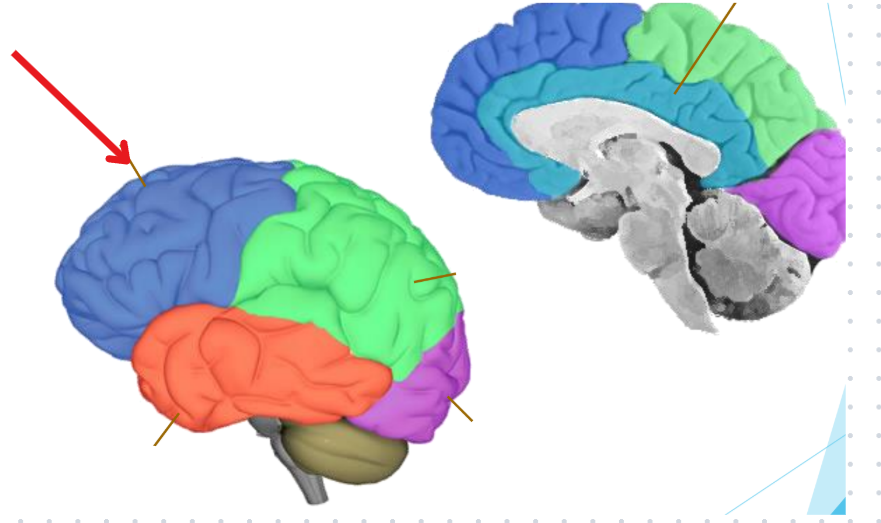
Frontal lobe
Motor and executive functions
Front motor of a car
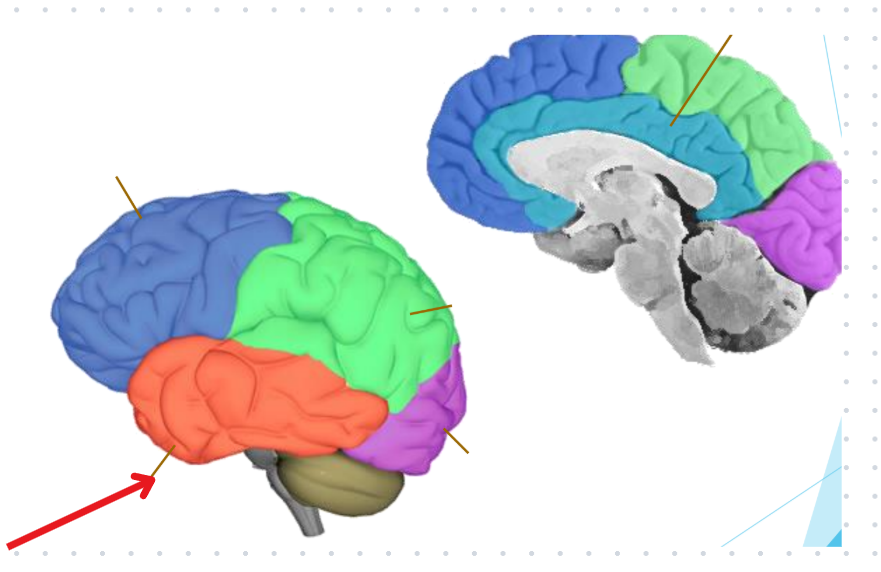
Temporal lobe
Hearing
Tempo (Like in music)
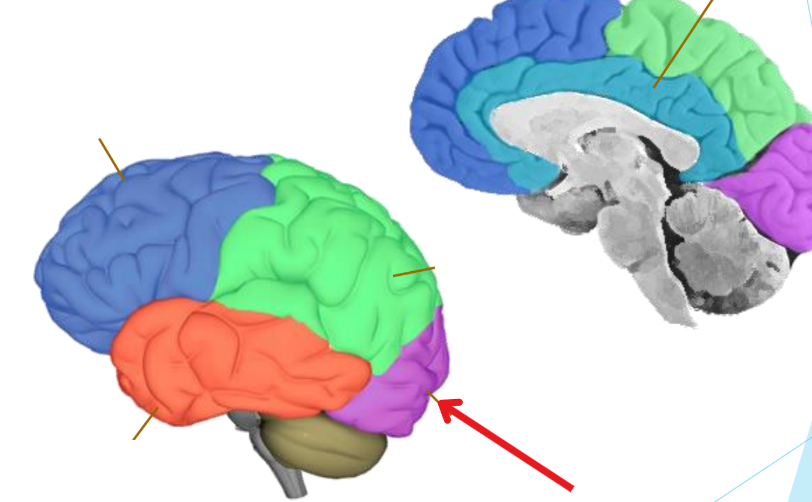
Occipital lobe
Vision
Binoculars
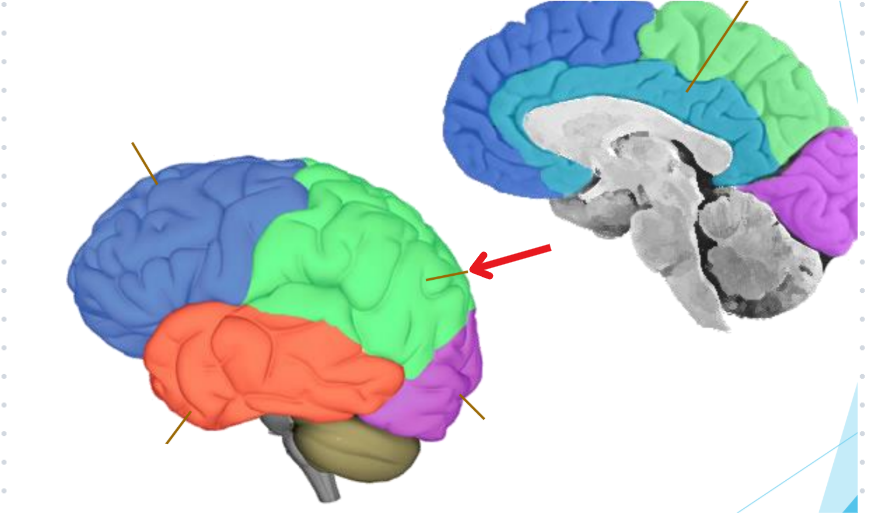
Parietal lobe
Somatosensory information
Pressure, Pain, Position, Proprioception
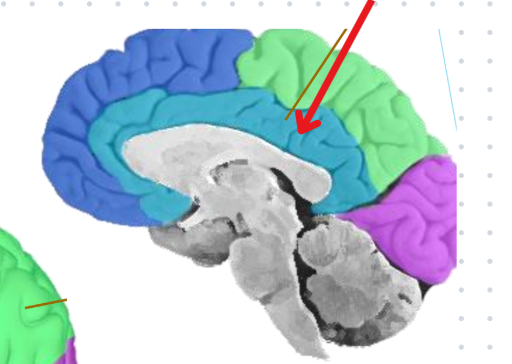
Limbic lobe of the cerebrum
Name given due to its close proximity to the limbic system, but not a part of it
Emotions & Memory
Love and Learning
How to assess function of the frontal lobe
Spelling backwards and digit span
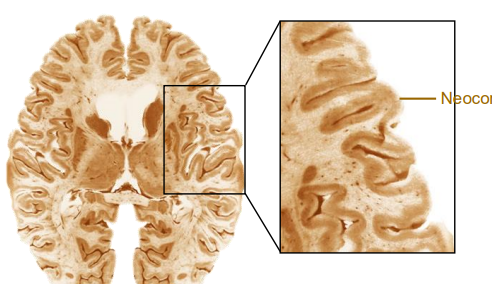
Cerebral cortex (Neocortex)
The cerebrums surface
Convoluted into hundreds of folds
Where all the higher brain functions take place
Contains ~20% of all neurons
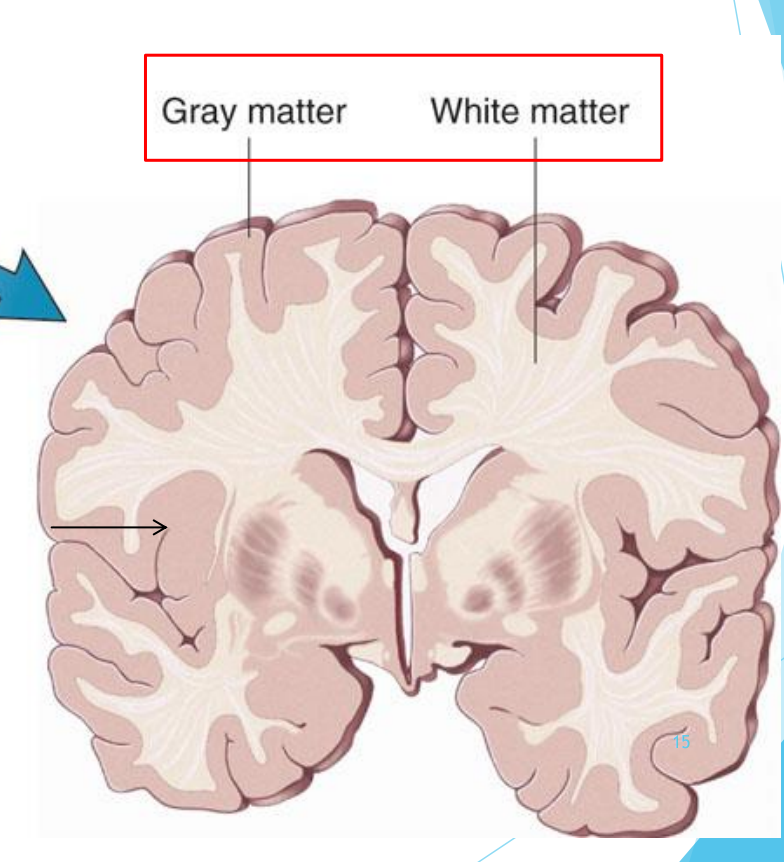
Gray vs. white matter
The outer portion (Gray matter) contains the neuron’s body
The inner portion (White matter) contains axons which are sheathed in myelin, which is white
The cerebellum
10% of total brain weight, but 80% of all neurons in the brain
-Maintains balance
-Coordinating movement
-Vision
-Motor learning
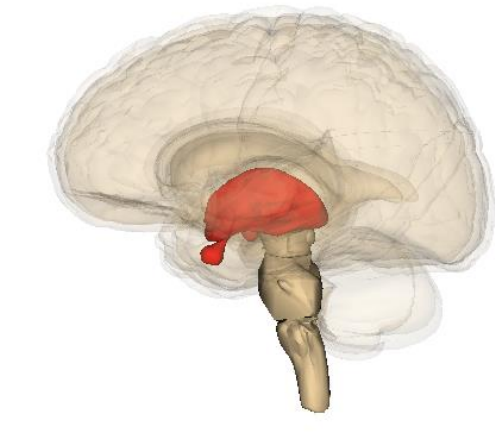
Diencephalon
Contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, subthamalus
Thalamus
Brains “relay station”
Sends sensory signals (Vision, touch, hearing, taste) to the cerebral cortex
Epithalamus
AKA pineal gland
Helps regulate biological rhythms (Like sleep) and produces melatonin
Hypothalamus
The “control center” for homeostasis
Regulates: Temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep, and hormones
Subthalamus
Involved in movement control
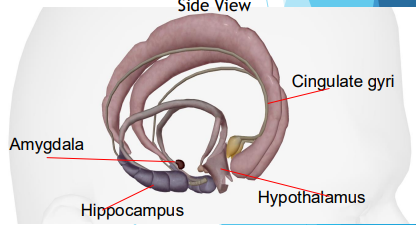
Limbic Lobe
Located deep in the brain
Center of our emotions, learning, and memory
Contains cingulate gyri, amygdala, hypothalamus, hippocampus
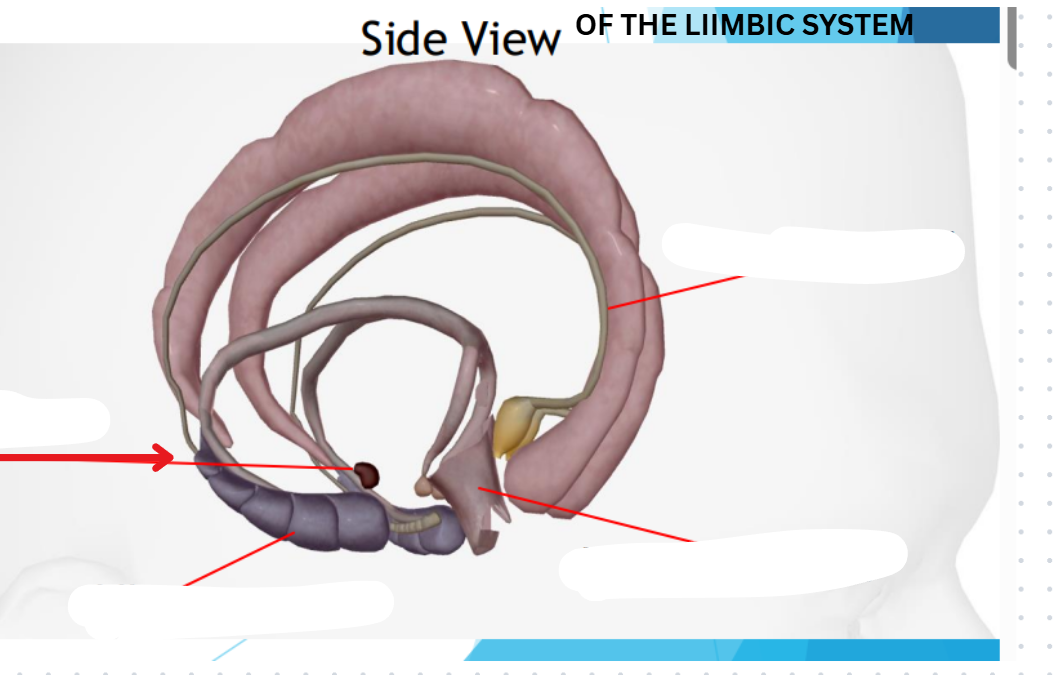
Amygdyla
Emotional reactions
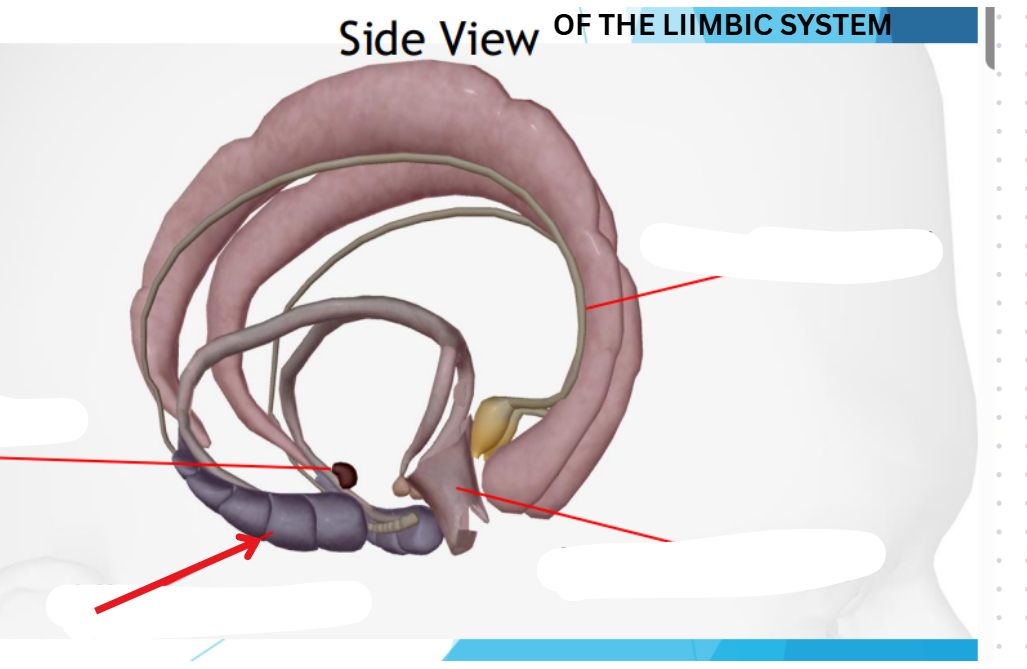
Hippocampus
Memory
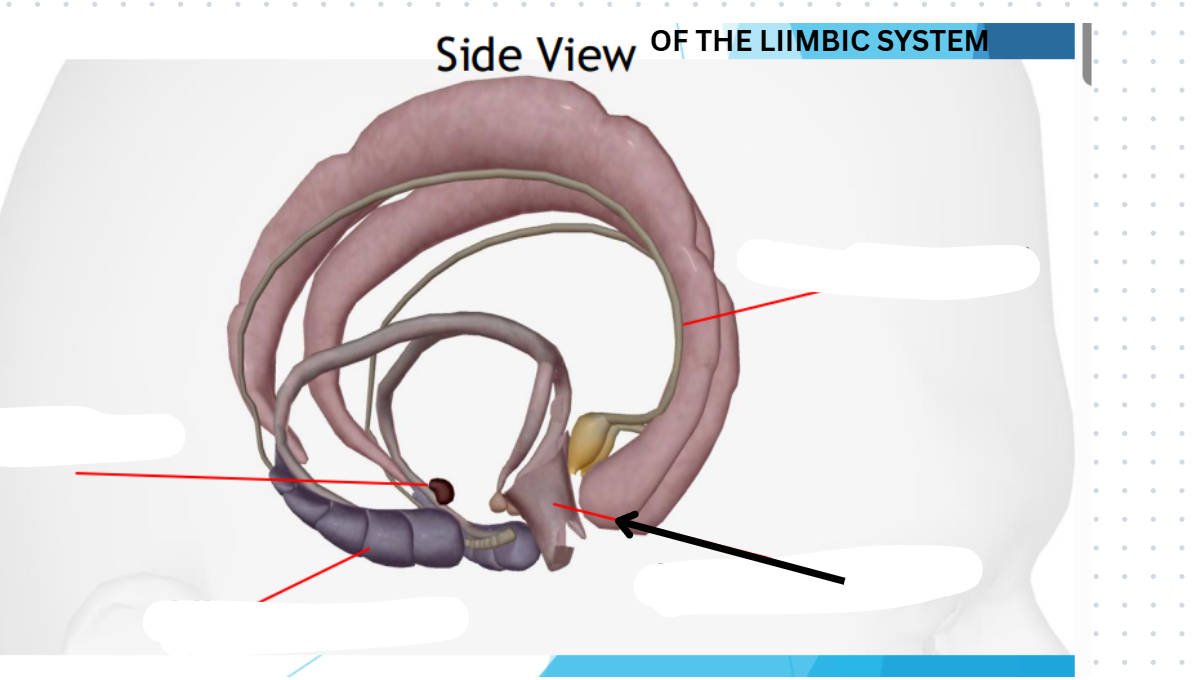
Hypothalamus
Homeostasis
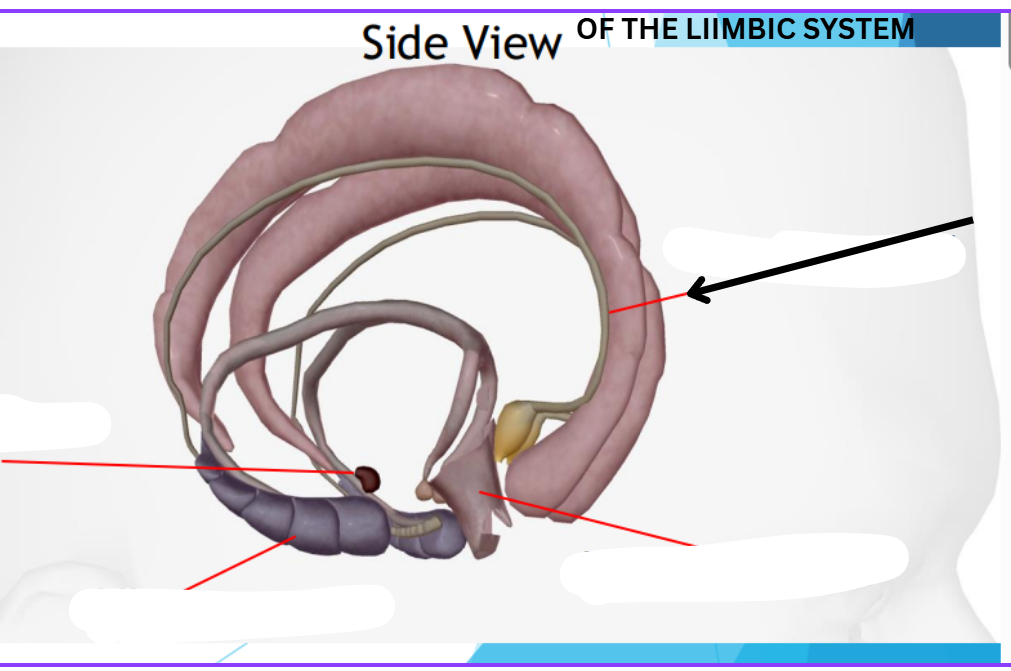
Cingulate gyri
Emotional and behavior
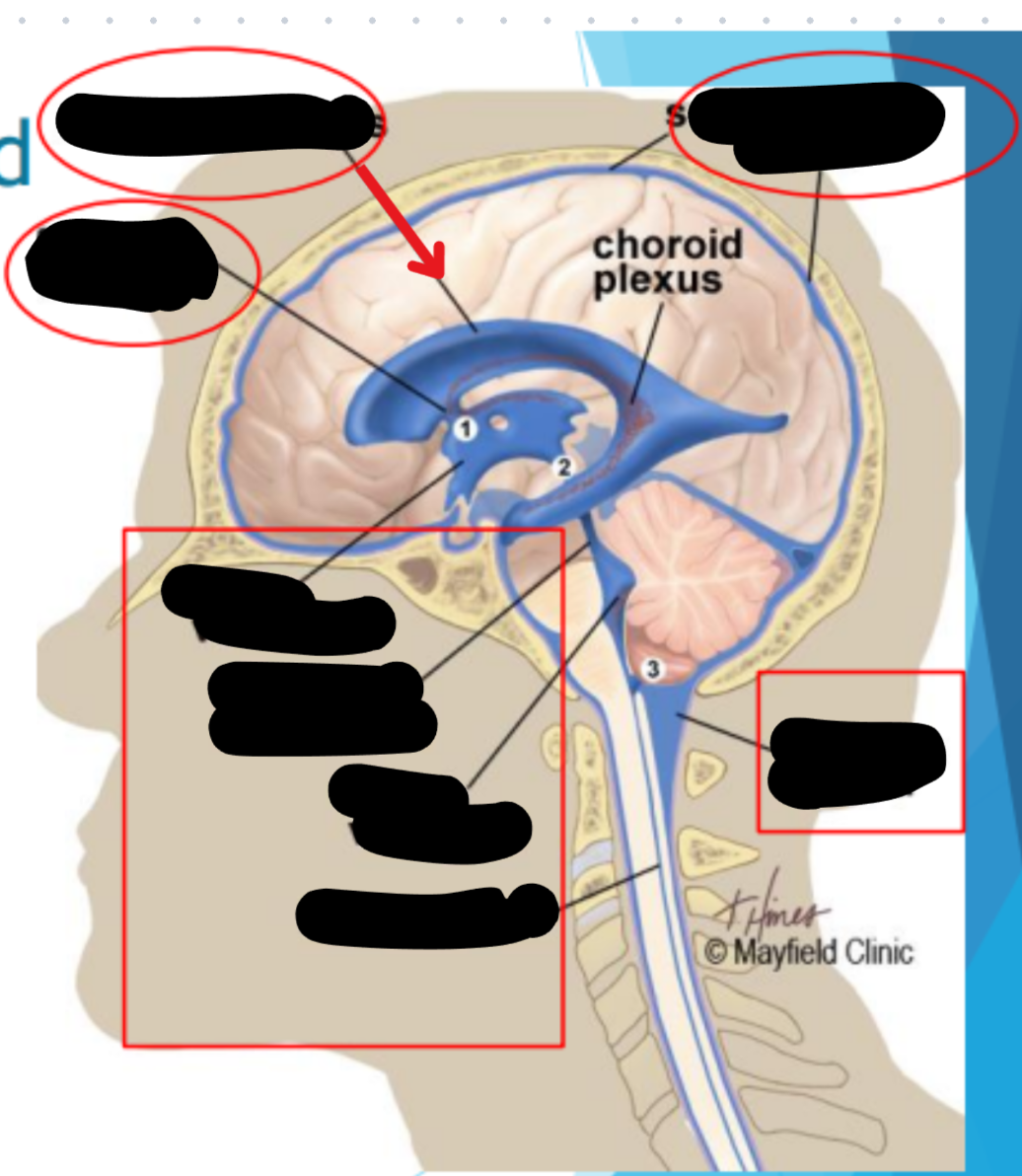
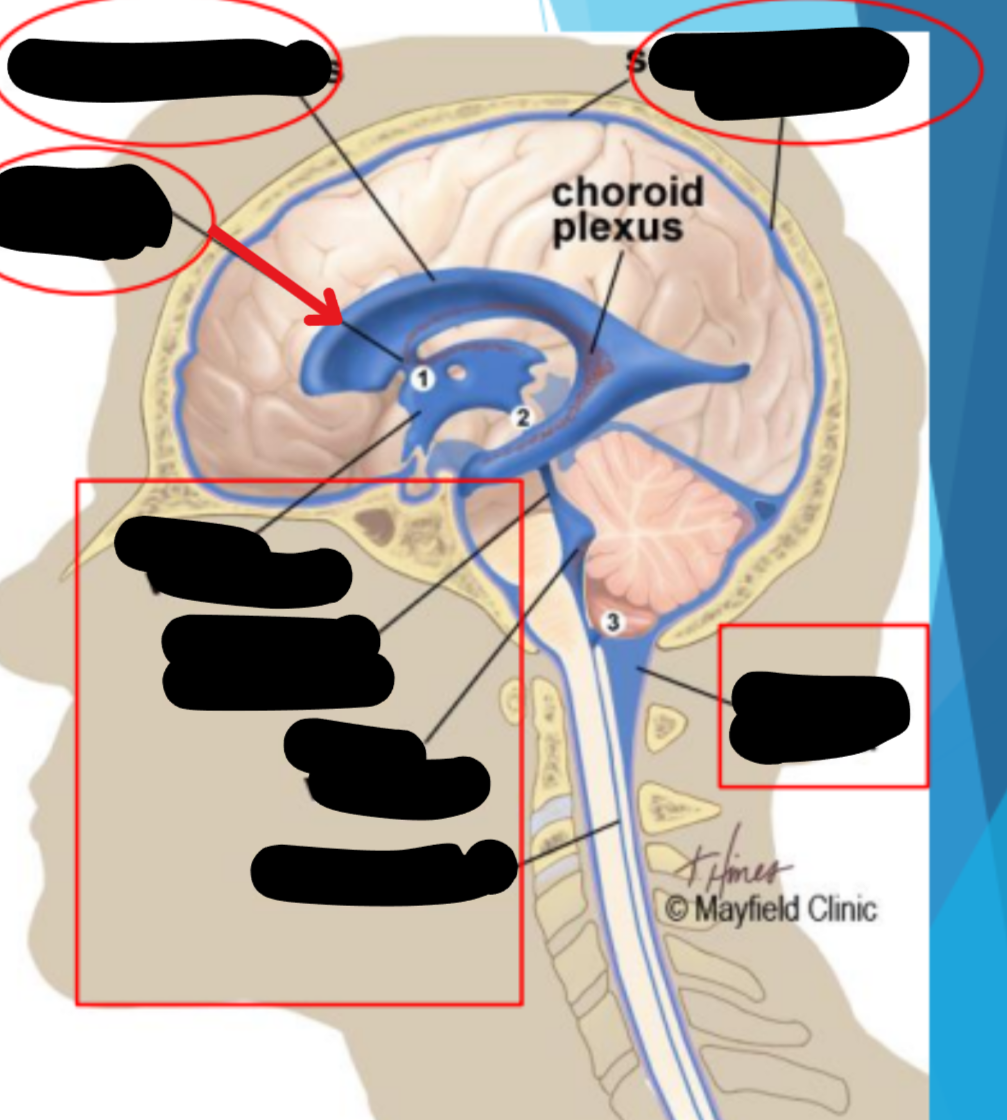
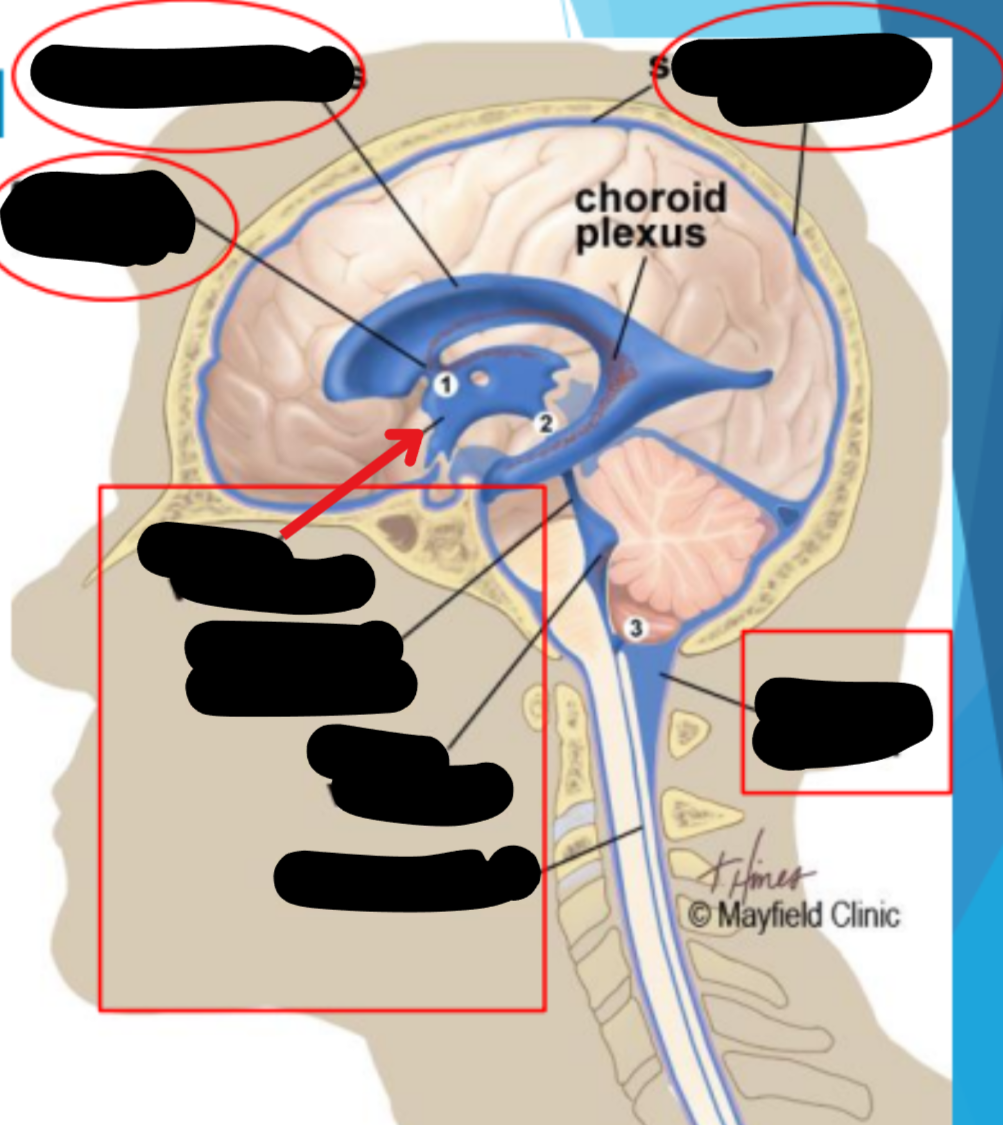
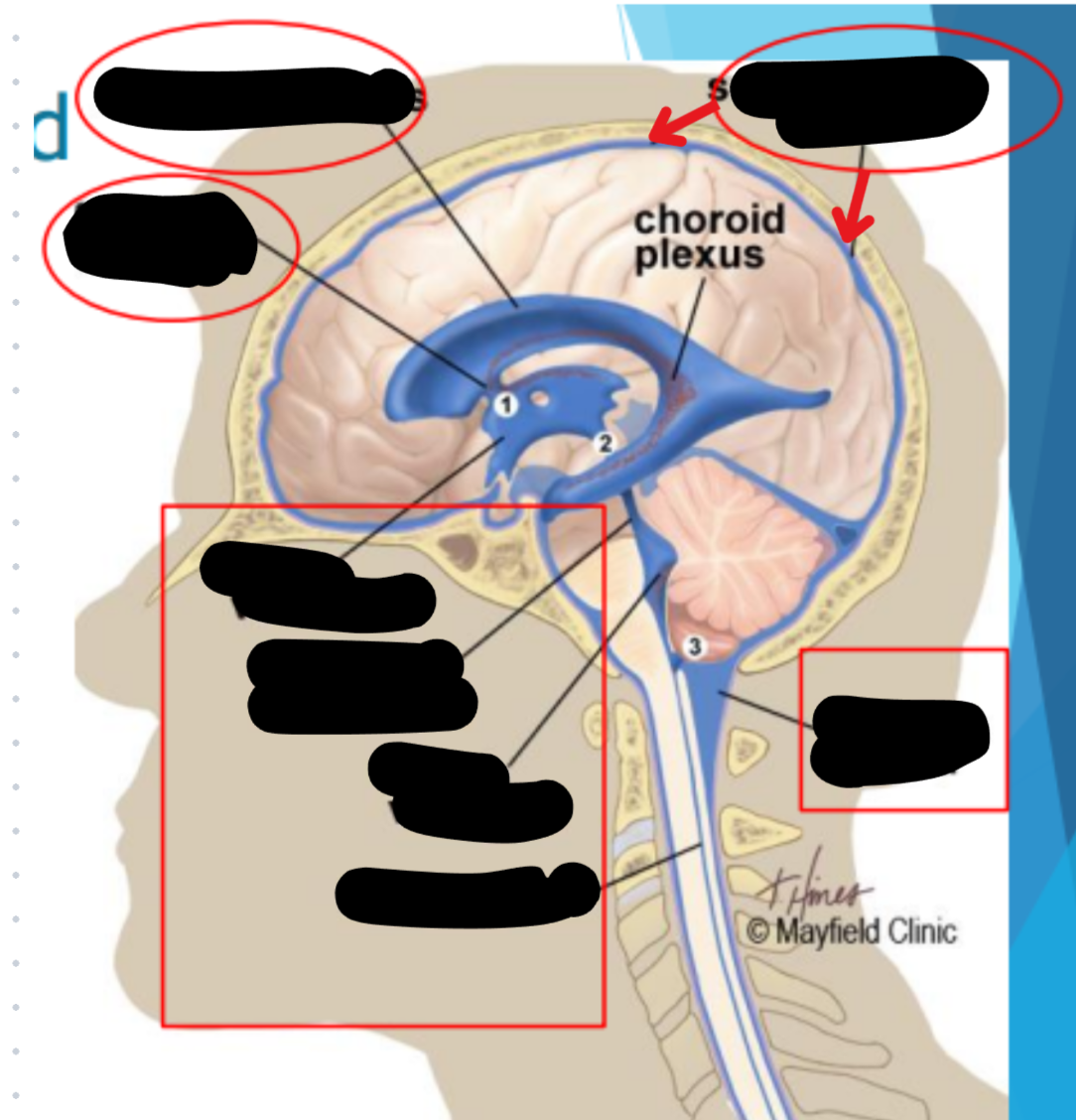
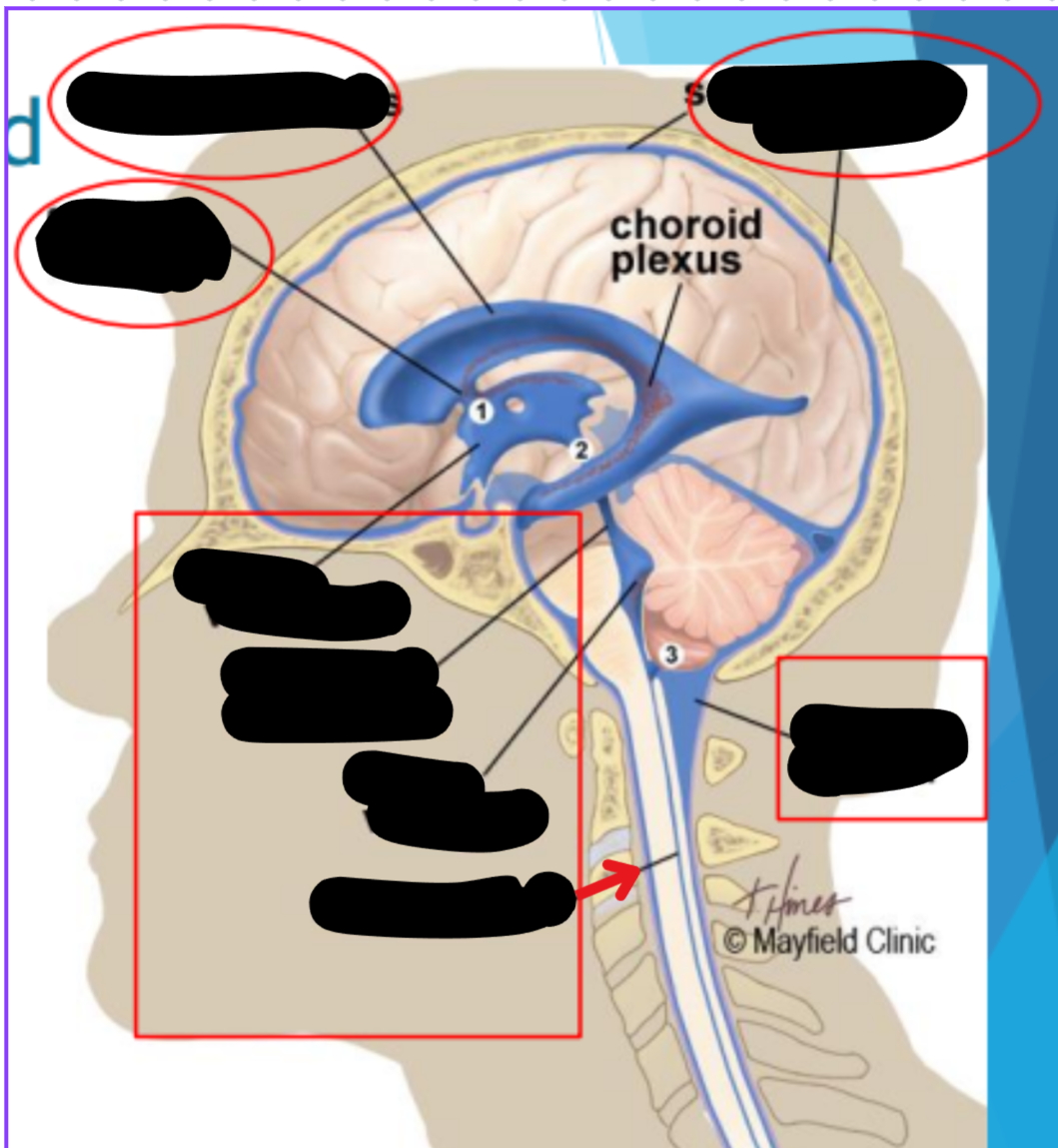
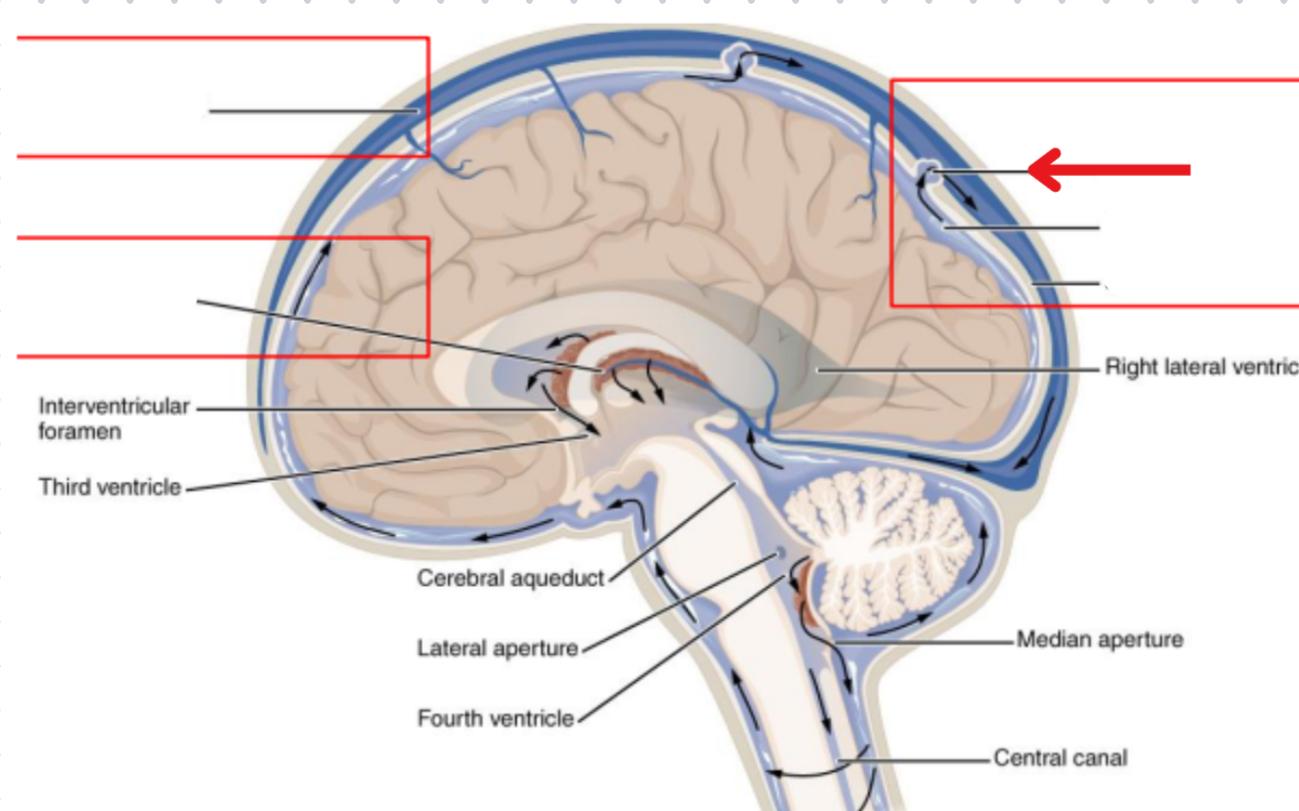
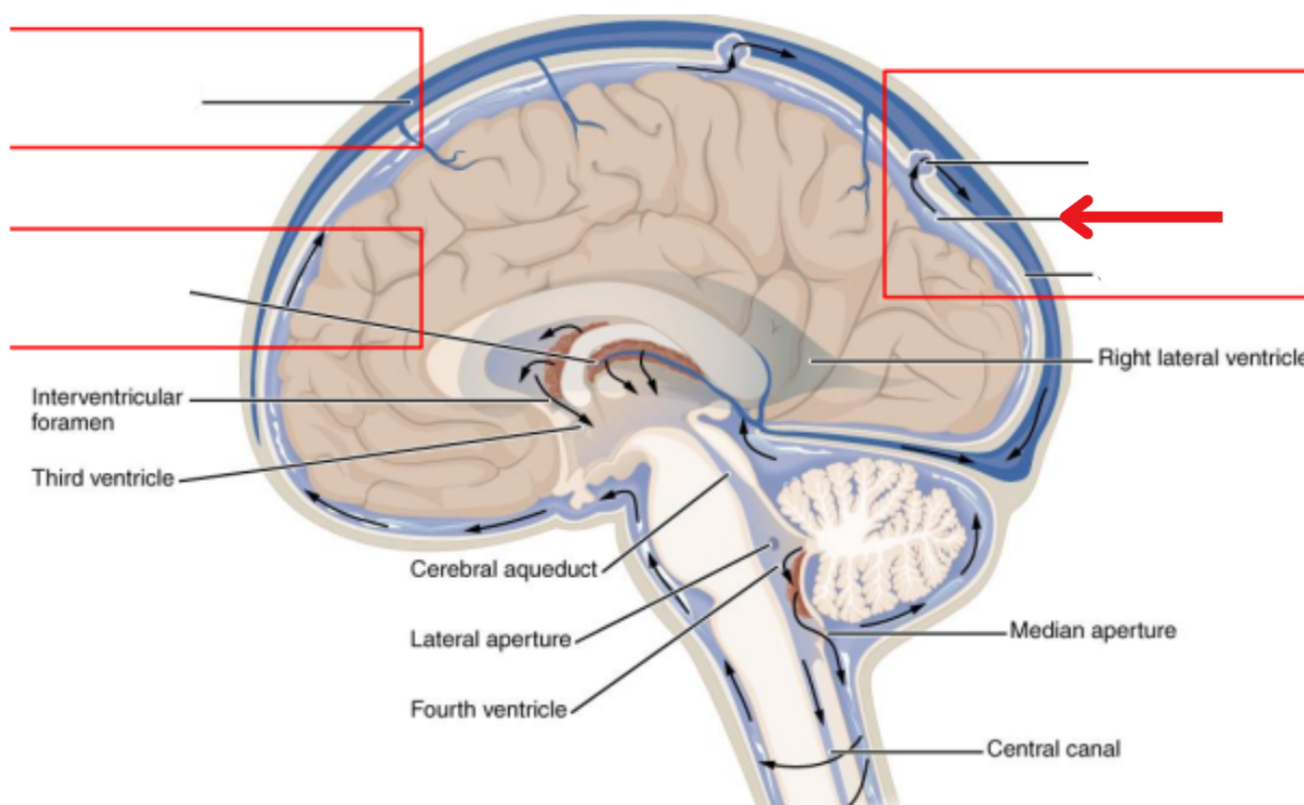
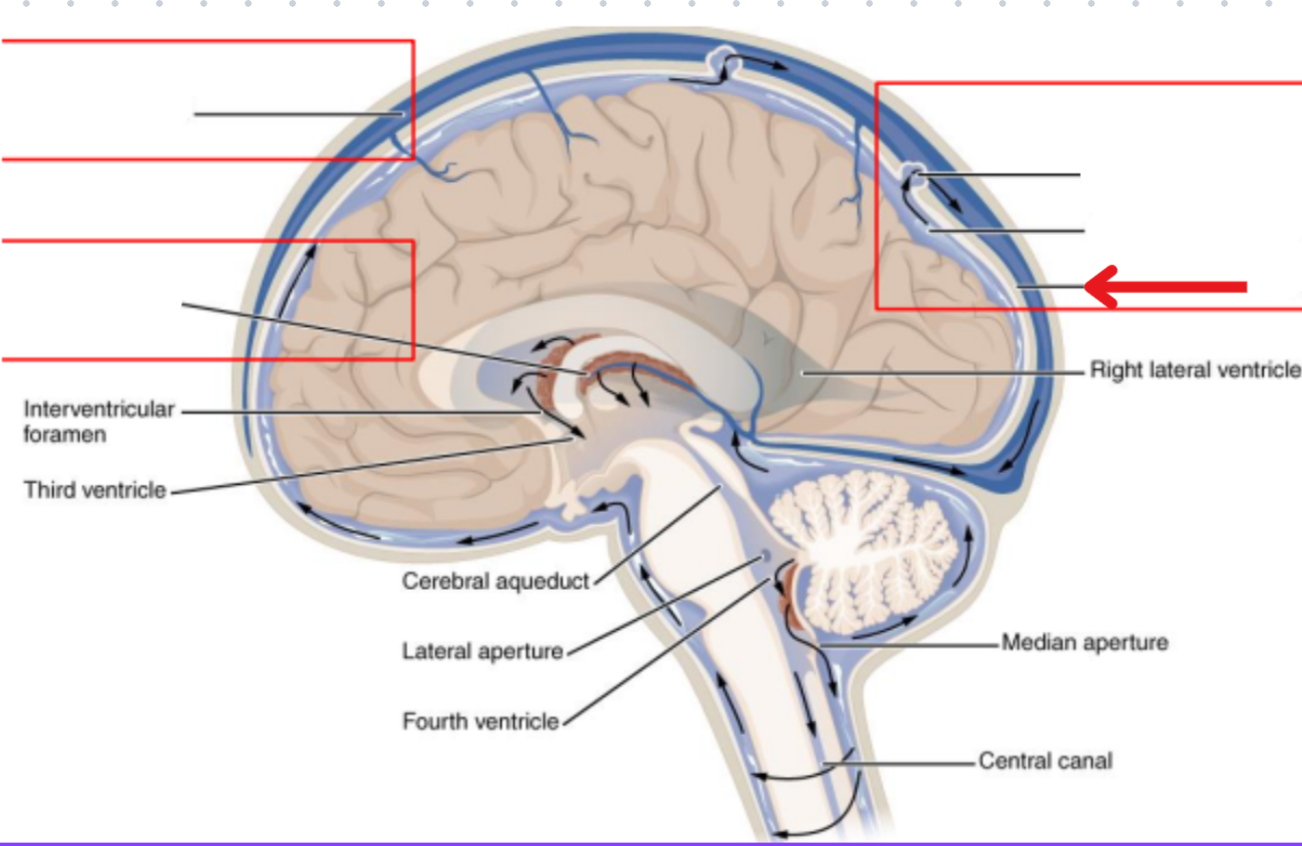
Ventricles
Hollow fluid-filled cavities
The ventricles contain the choroid plexus which creates CSF
Choroid plexus
Produces cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Maintains pressure in the brain
Cushions brain to prevent injury
Ventricular system
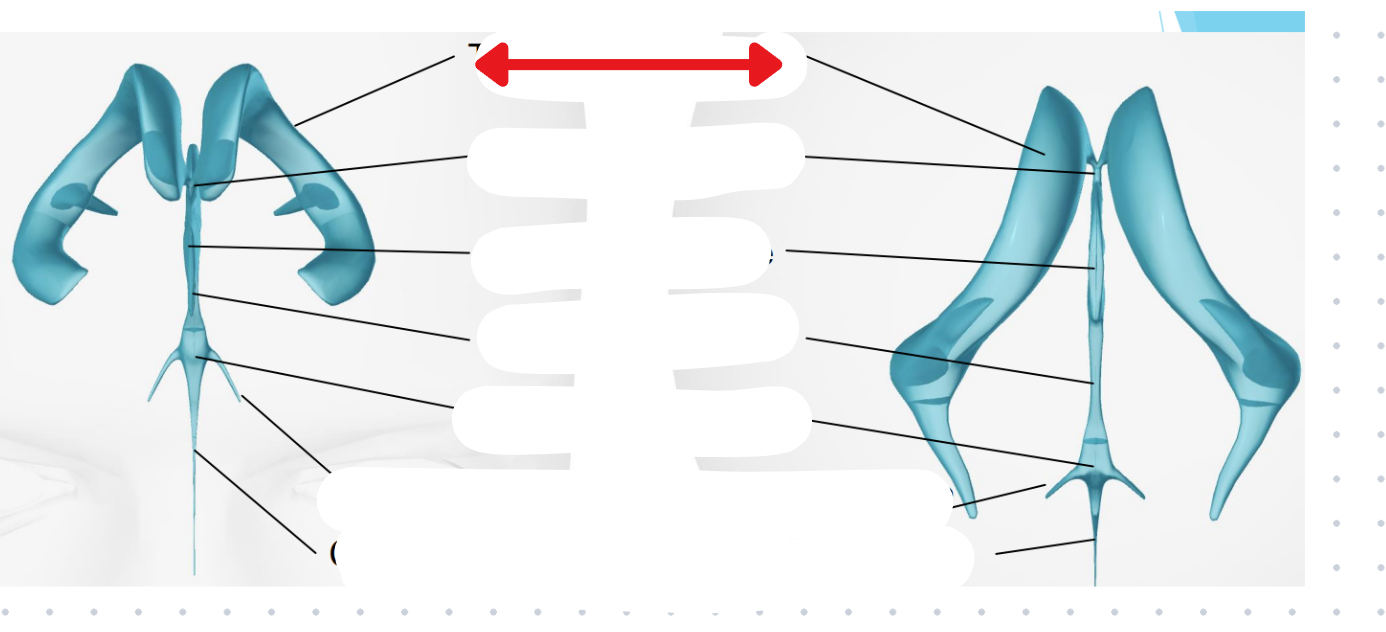
Two lateral ventricles
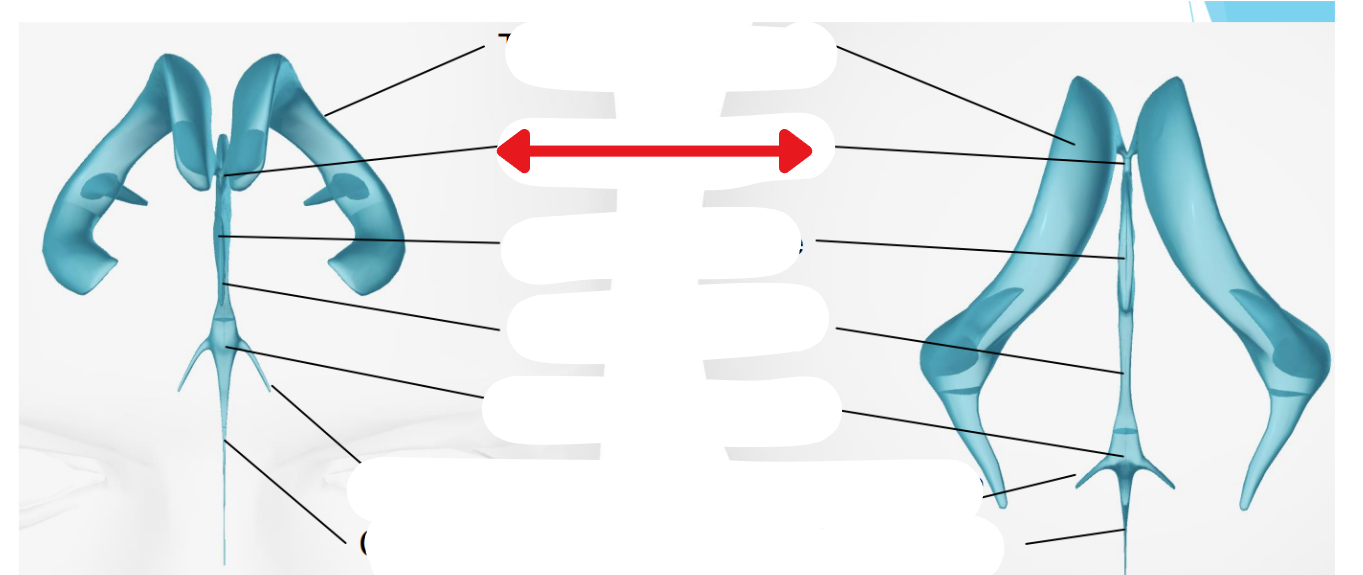
Foramen of Monro
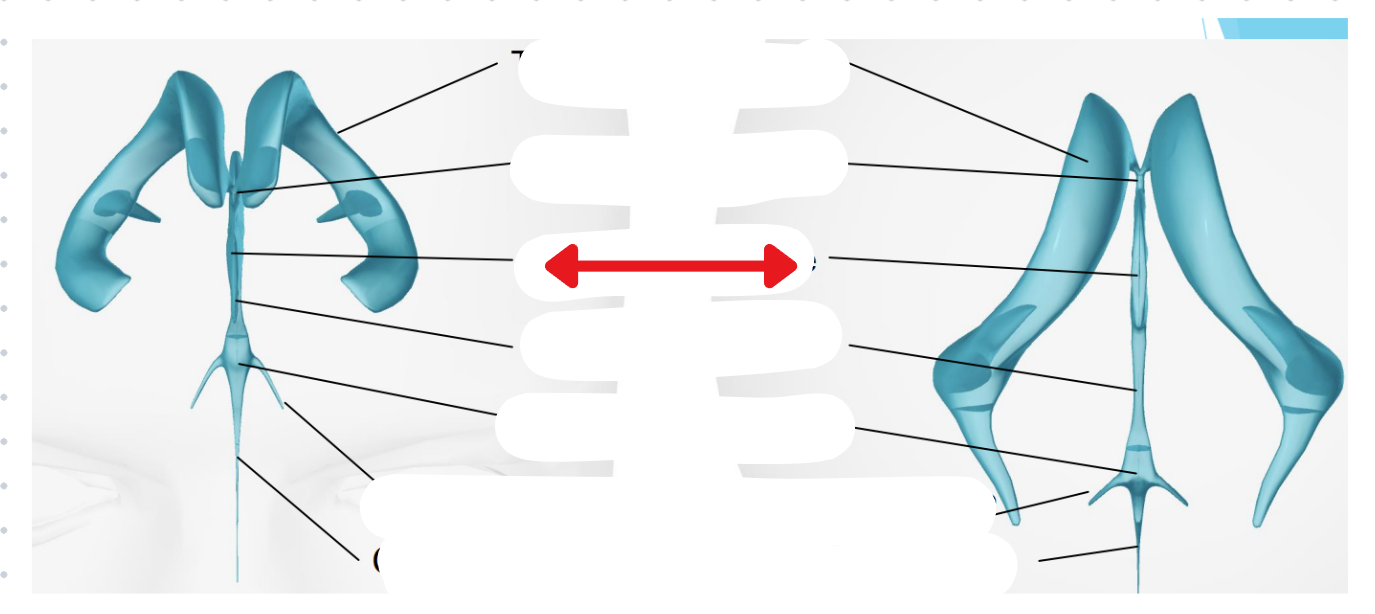
Third ventricle
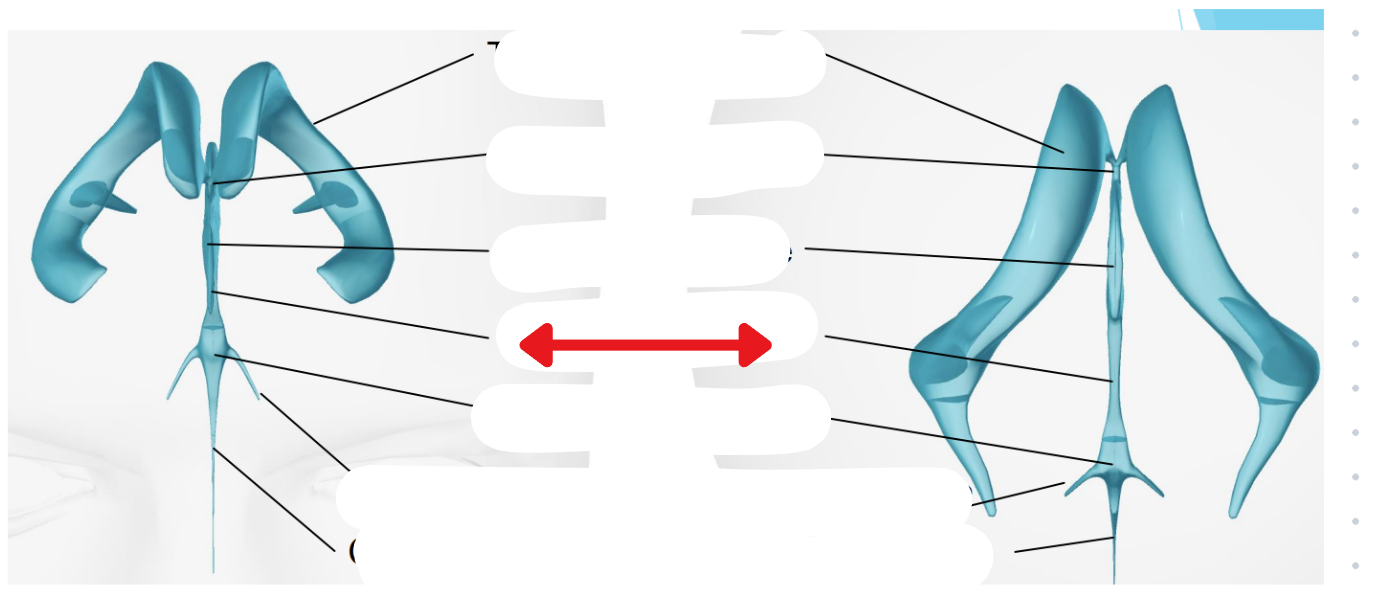
Aqueduct of Sylvius
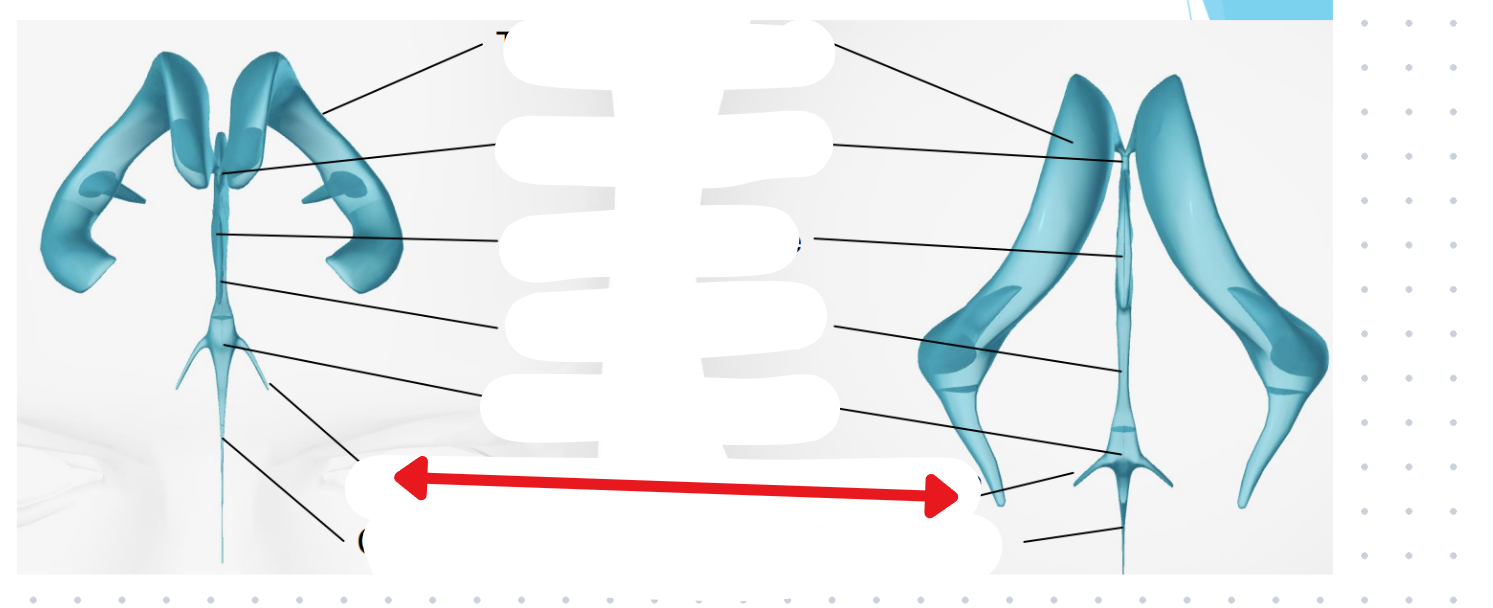
Lateral Horns
End in subarachnoid space
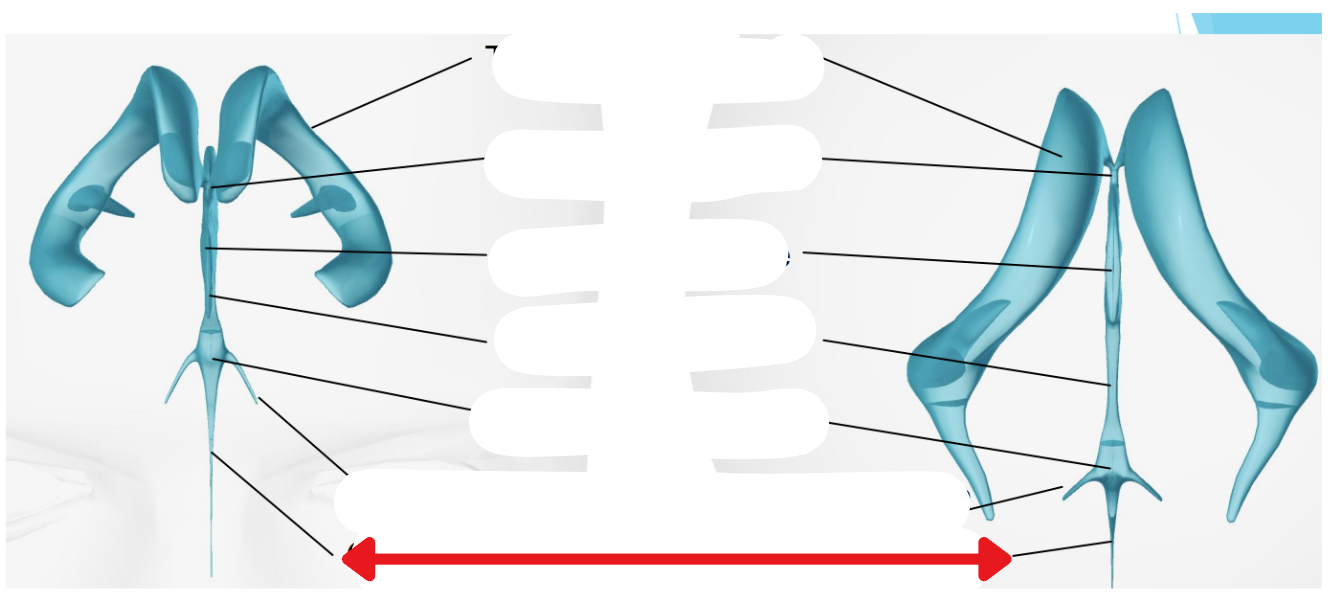
Central horn (connects inside spinal cord)
Fourth ventricle
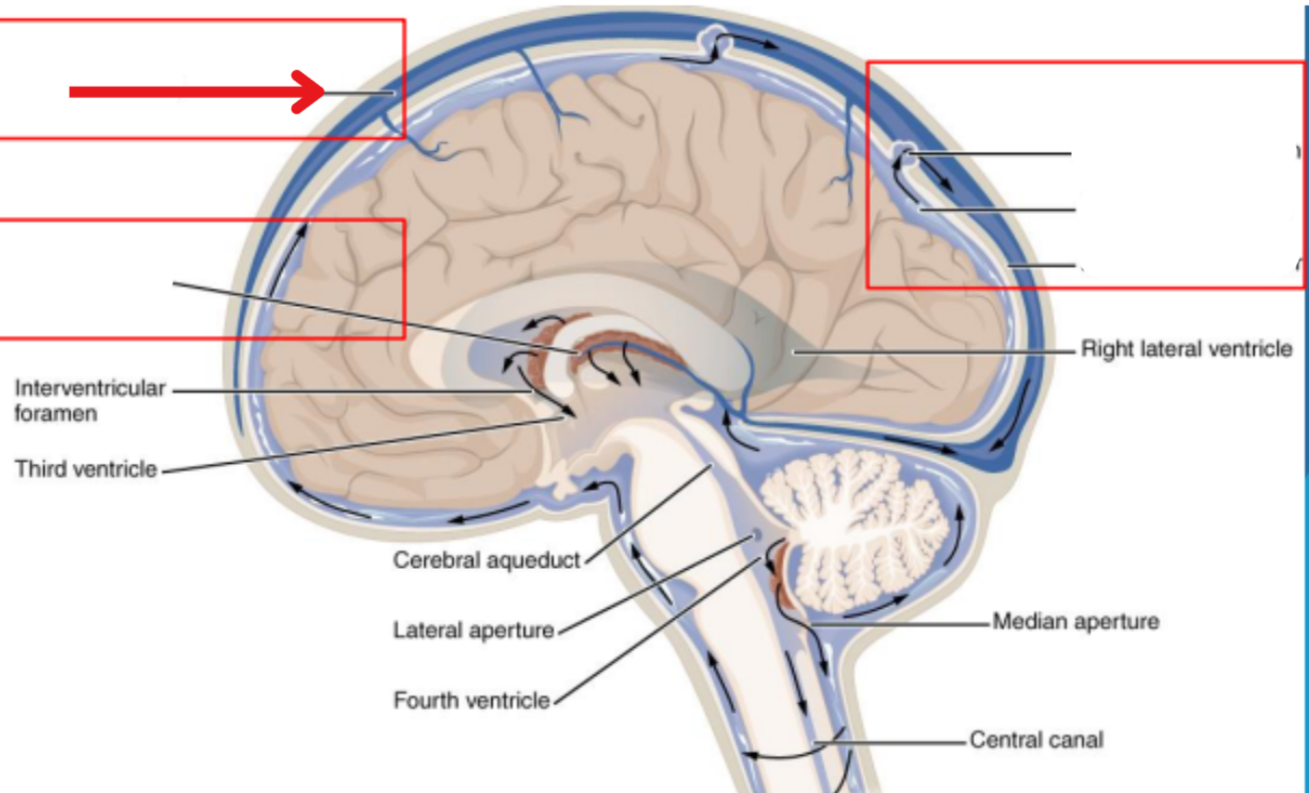
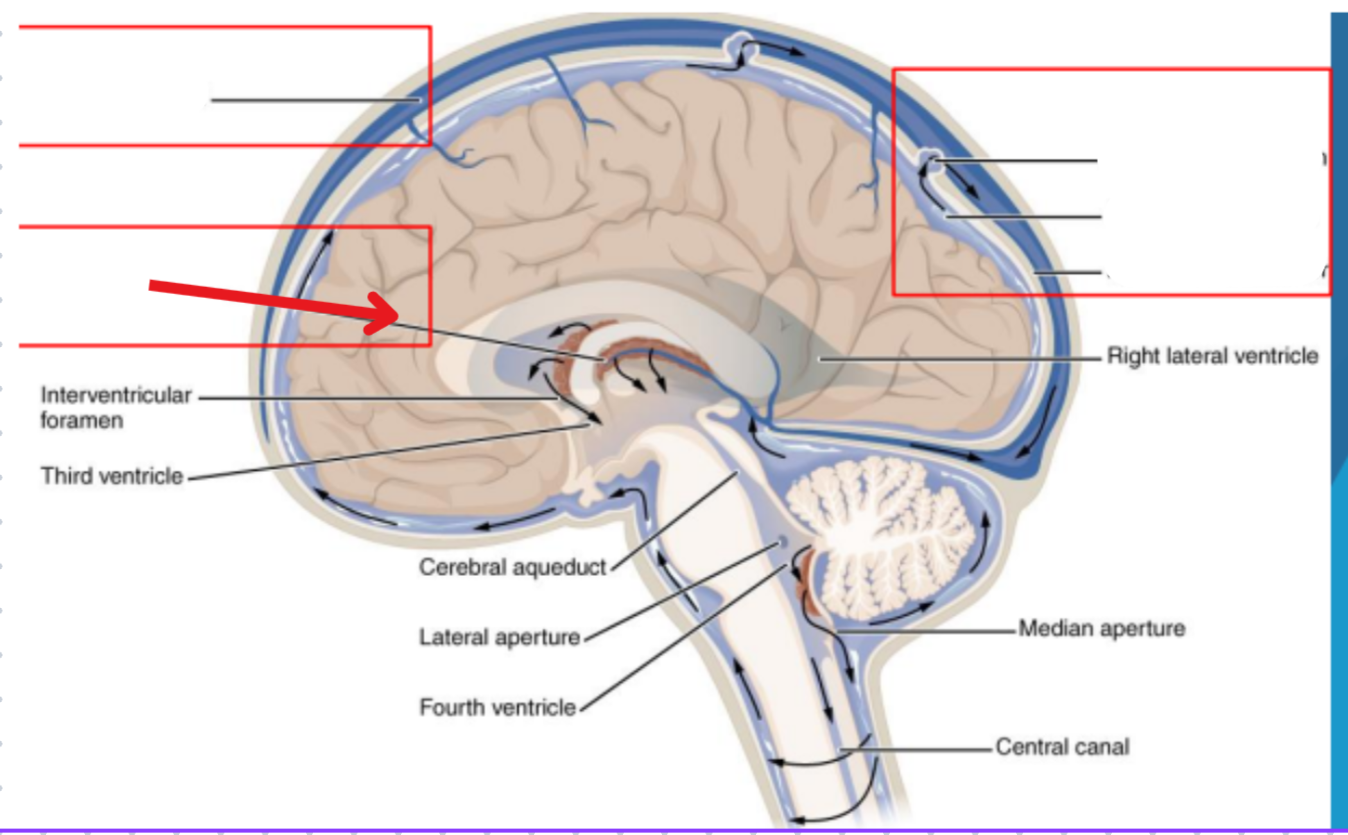
Cycle of CSF
Lateral ventricles → Foramen of monro →Third ventricle → Aqueduct of sylvius → Fourth ventricle → Lateral horns + Central horn → Subarachnoid space (Brain and spine) → Arachnoid granulations (Absorb and recycle CSF) → Superior sagitall sinus → Jugular veins
Places where CSF flow can become obstructed
Foramen of monro
Aqueduct of sylvius
Obex
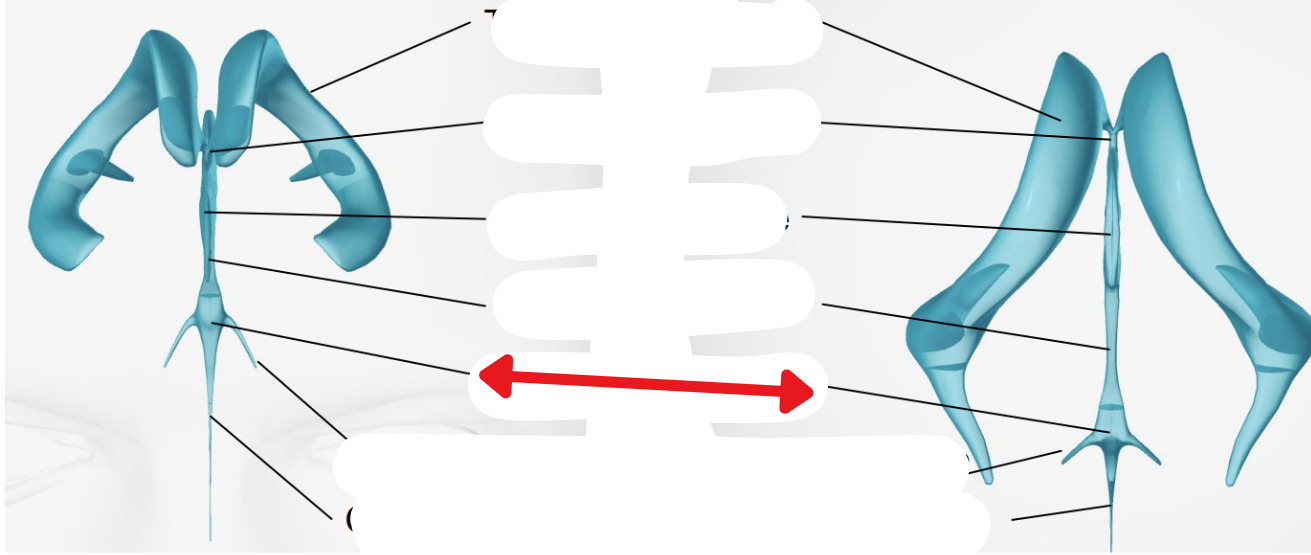
Lateral ventricles
Foramen of monro
Third ventricle
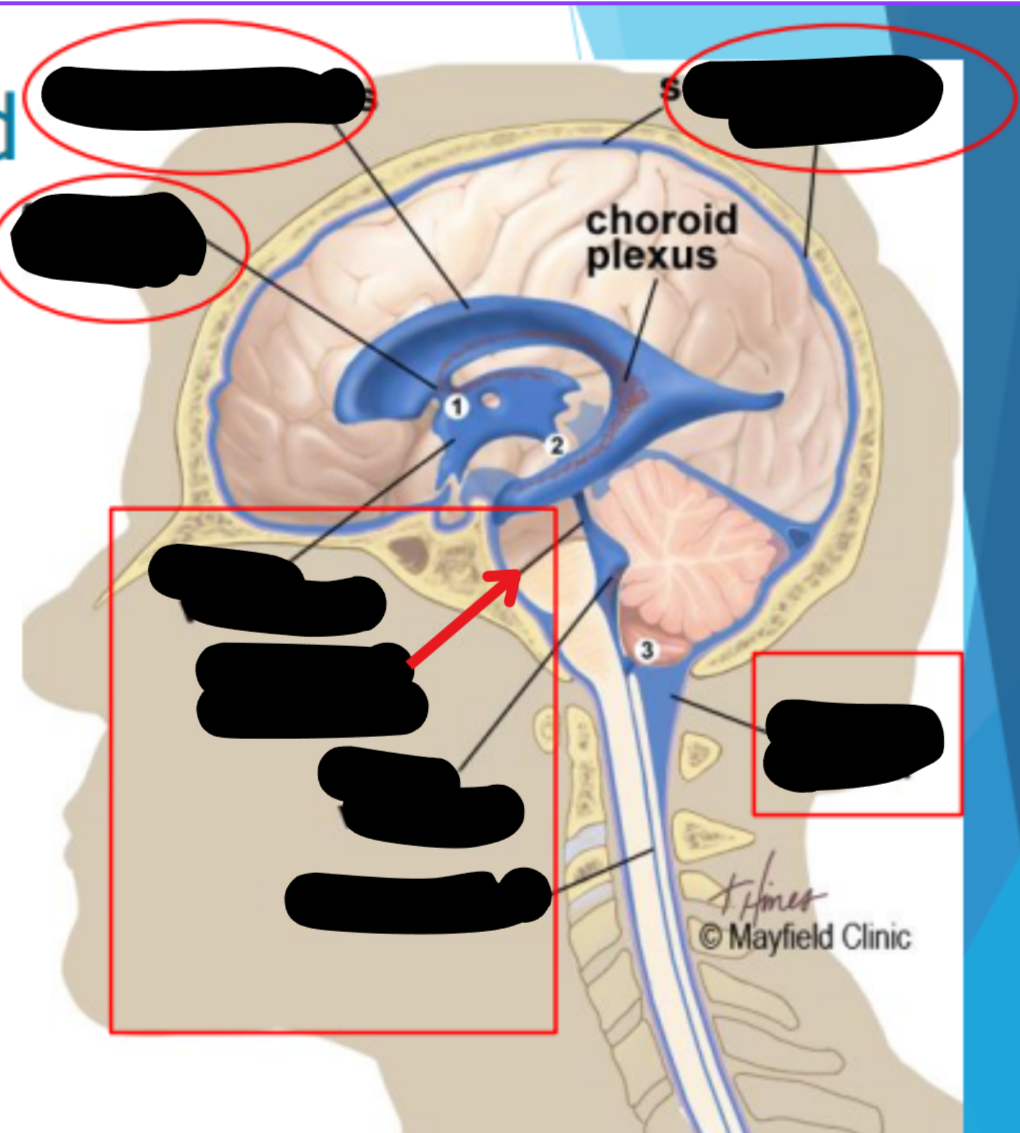
Aqueduct of sylvius
Fourth ventricle
Cisterna magna
Subarachnoid space
Central canal
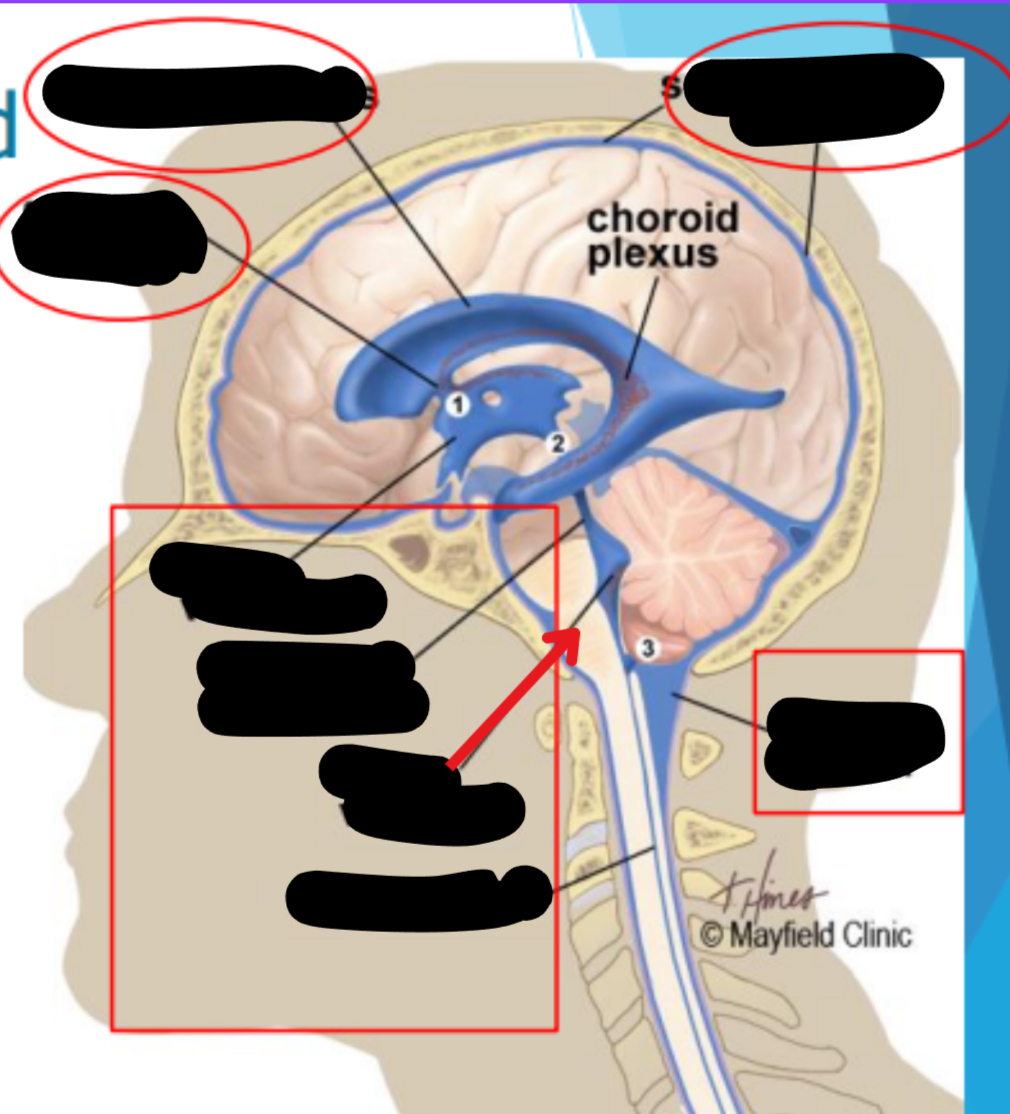
CSF recycling
Absorbed by arachnoid villi (granulations) into the superior sagittal sinus
Works it way through the transverse sinus → sigmoid sinus → Jugular veins
Balance is maintained by the CSF absorbed and the amount produced
Superior sagital sinus
Choroid plexus
Arachnoid granulation
Subarachnoid space
Meningeal dura mater
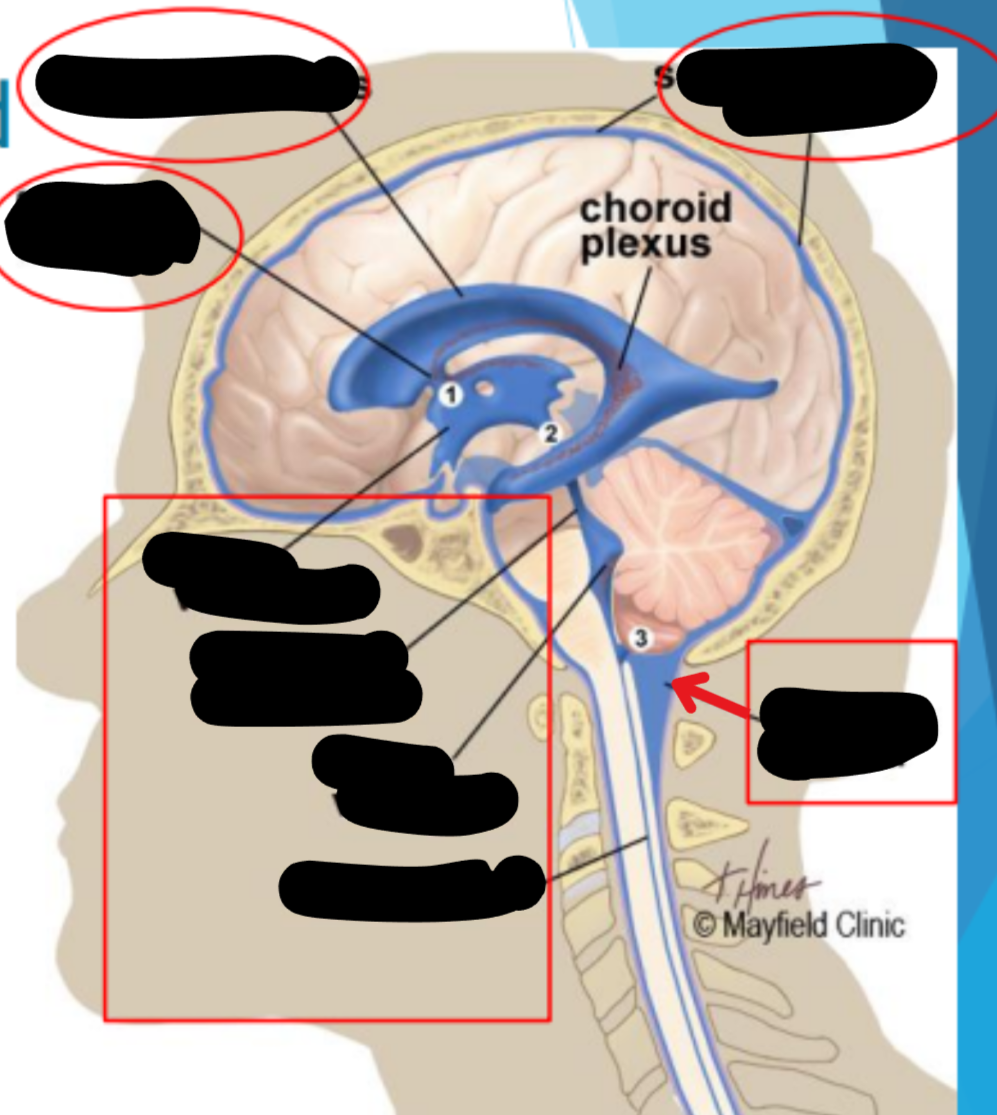
Hydrocephelus
Enlargement of the ventricles due to blockage of CSF cycling
Syringomyelia
Collection of CSF in the spinal cord
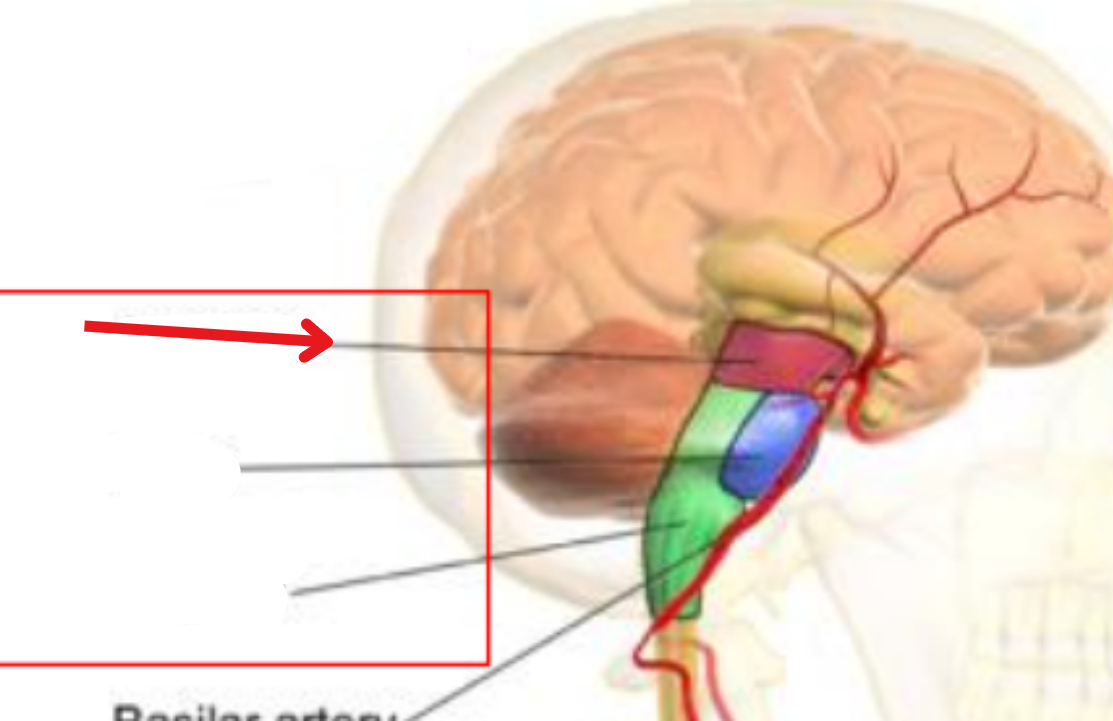
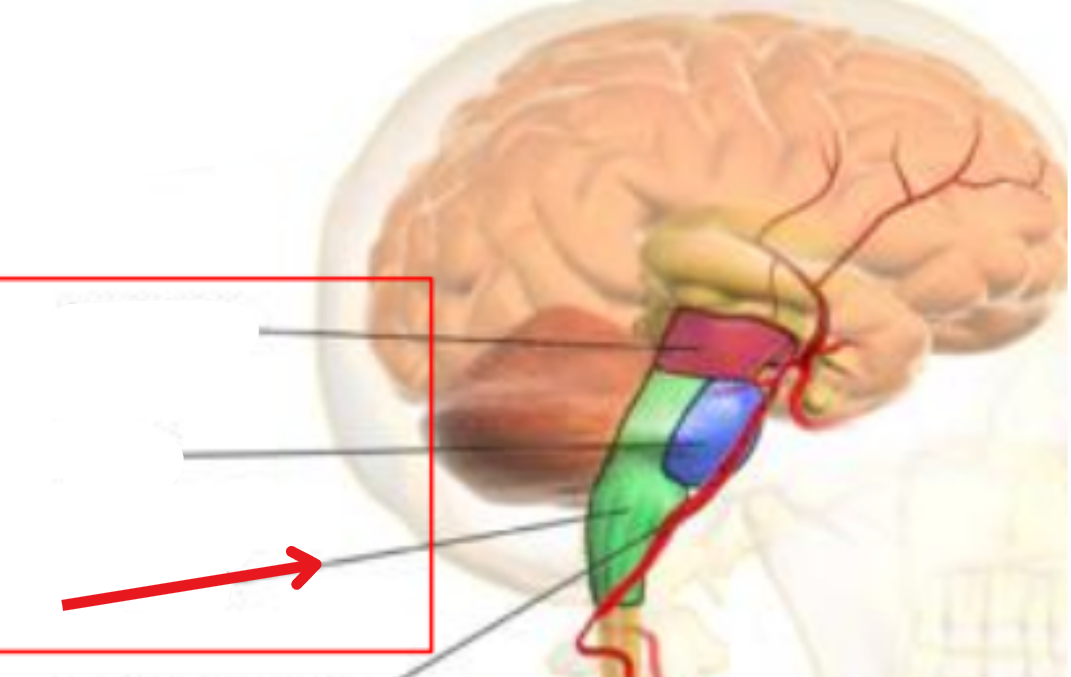
Midbrain
Produces dopamine
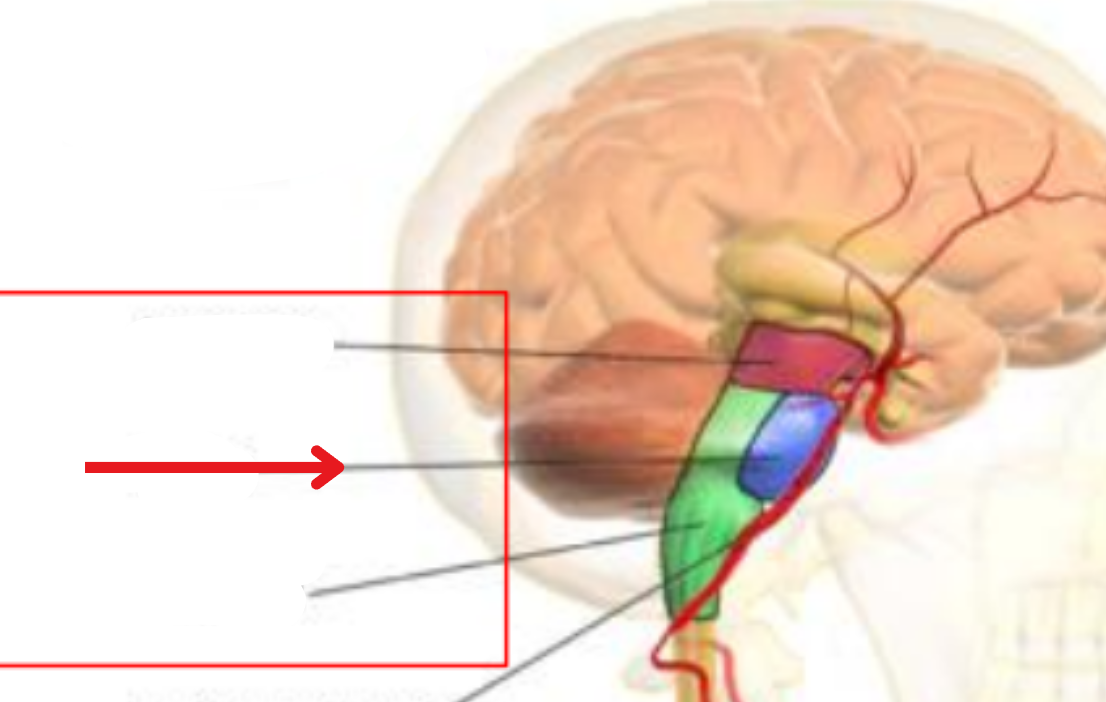
Pons
Stimulation of breathing and controlling sleep cycles
Medulla oblongata
Controls respiration, the cardiovascular system, consciousness
Really, all of the unimportant things
The brain stem
Connects narrow spinal cord with the forebrain
Spinal cord
Connects brain and peripheral nervous system
Suspended in vertebral canal, protected by vertebrae
Surrounded by meninges and CSF
45cm long in adults
Transmission of neural signals between the brain and body
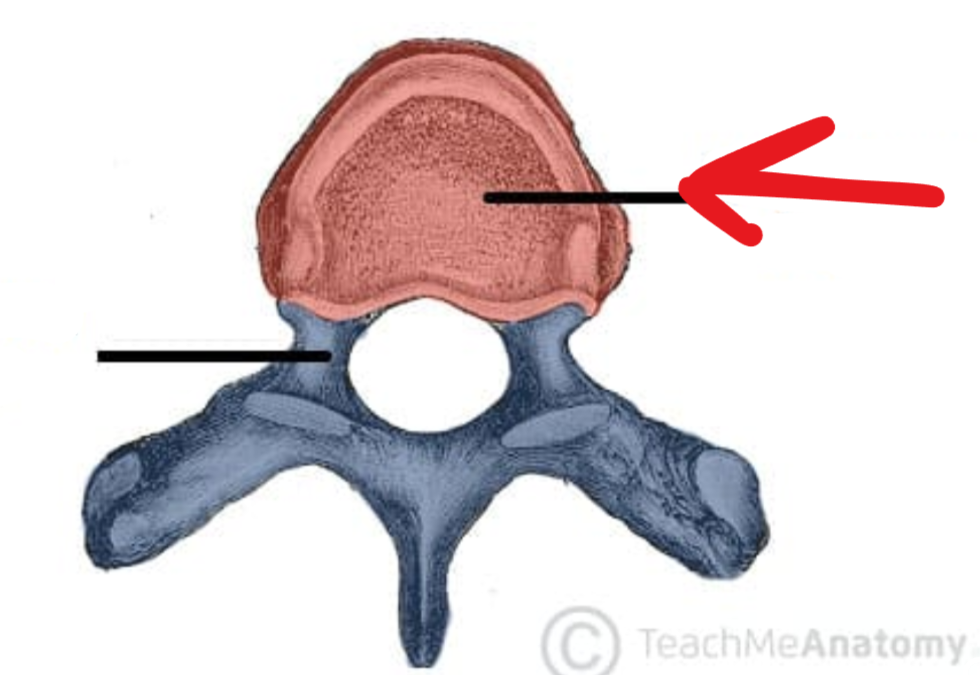
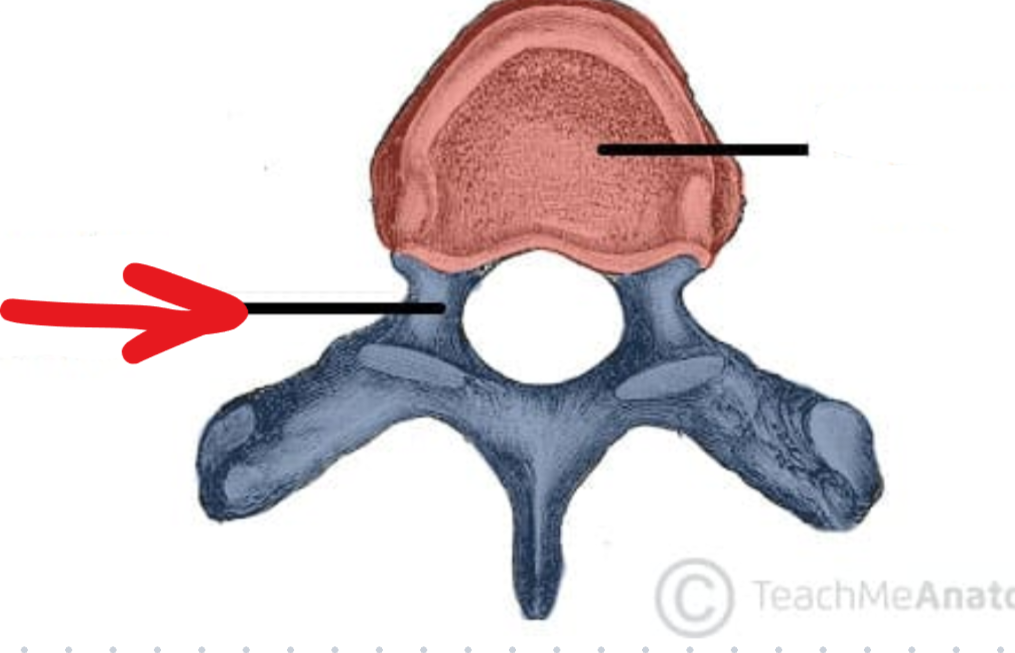
Vertebral body
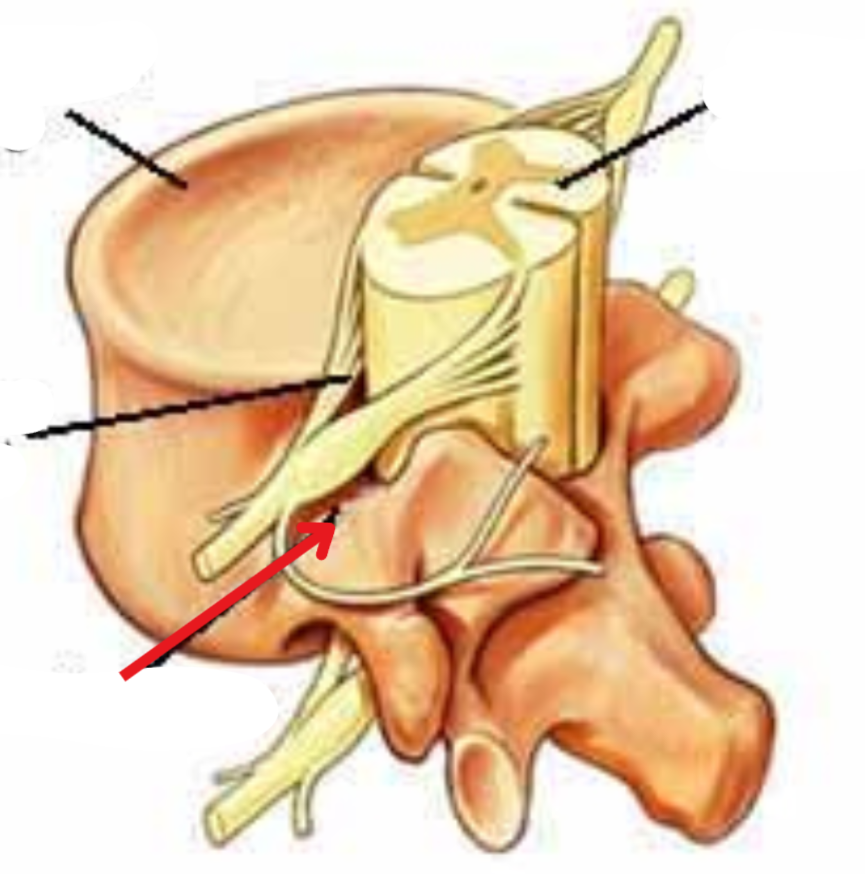
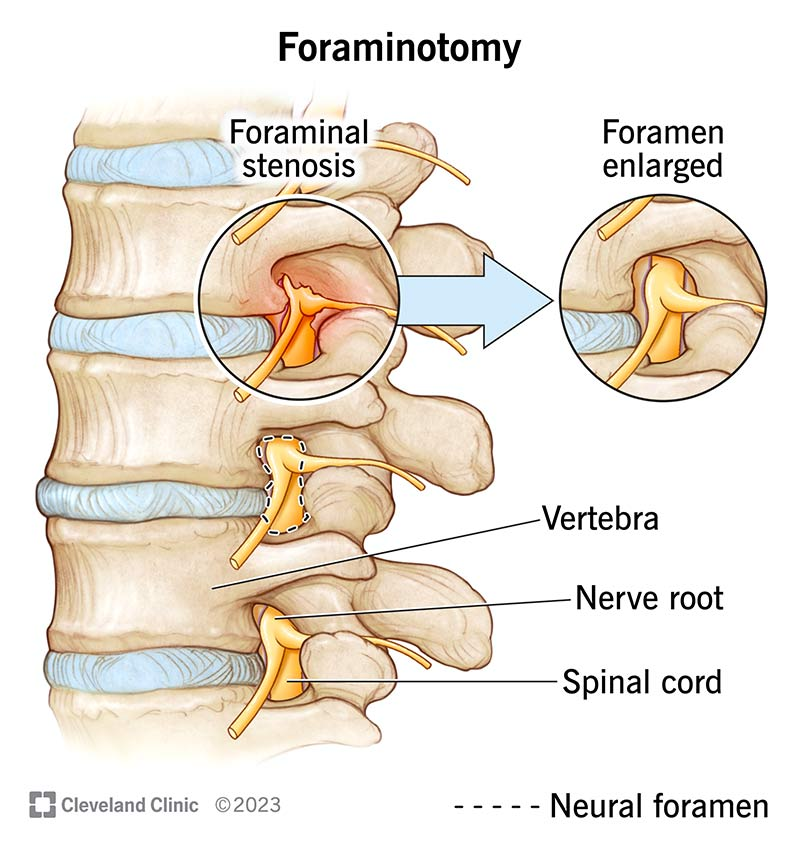
Neuroforamen
Hard to tell from other picture, but its a foramen where the neurons come out of
The vertebrae (arch)
Bones of complex anatomy
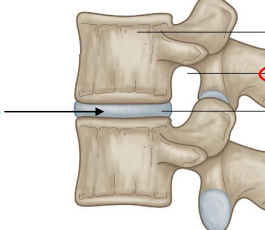
Intervertebral disks
Provide shock absorption
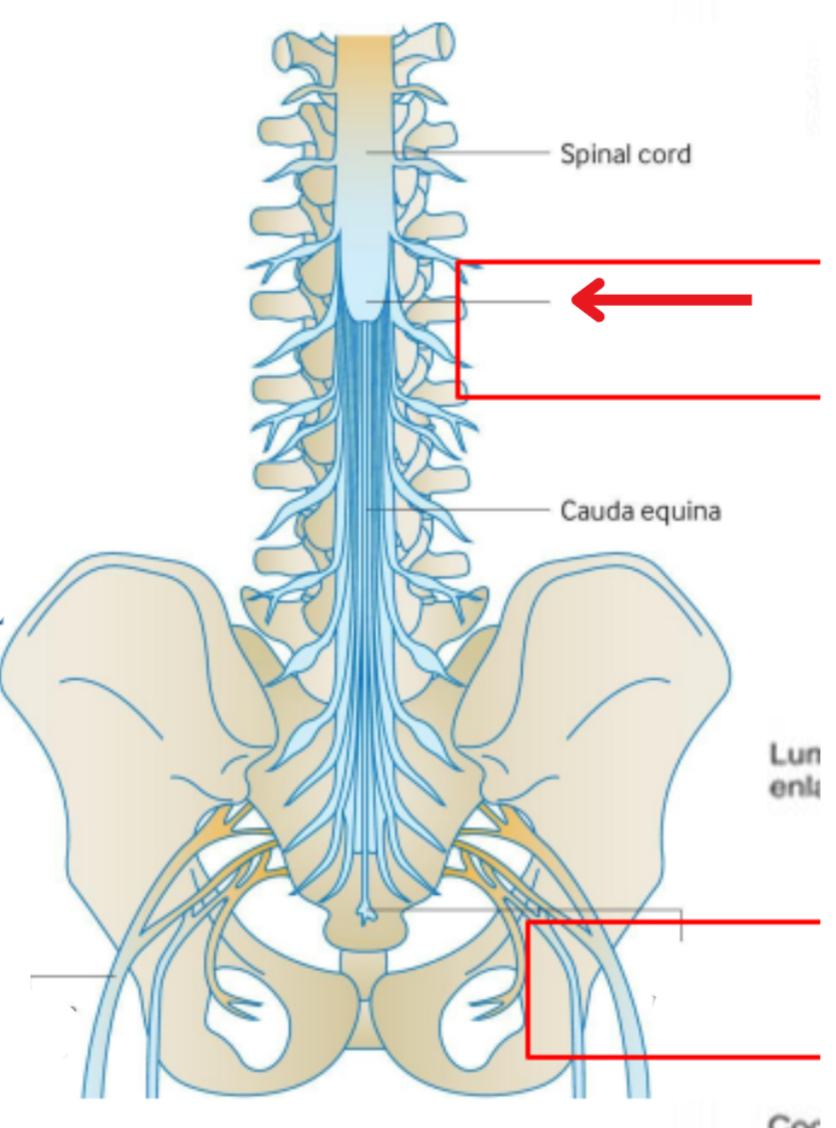
Conus medullaris
The tapered, inferior end of the the spinal cord
From here the spinal cord turns into strings called caude equina
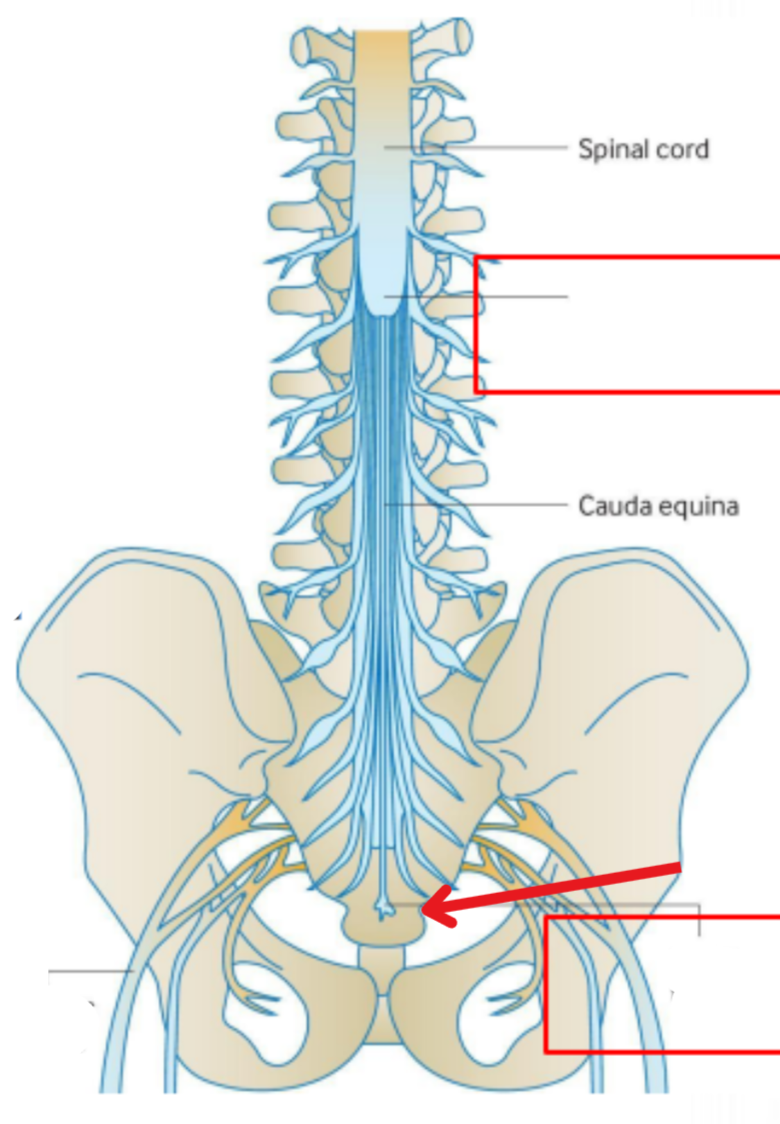
Filum terminale
Non-neural cord
Connects the spinal cord to the coccyx
“End” of the spinal cord
Order of spinal nerves superior to inferior
Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
Number of cervical spinal nerves
8
Number of thoracic spinal nerves
12
Number of lumbar spinal nerves
5
Number of sacral spinal nerves
5
Number of coccygeal spinal nerves
1
Cervical enlargement
Where spinal cord enlarges to supply the upper limbs
Between the C4 to T2 vertebrae
Lumbar enlargement
Where spinal cord enlarges to supply the lower limbs
Between the L2 to S3 vertebrae
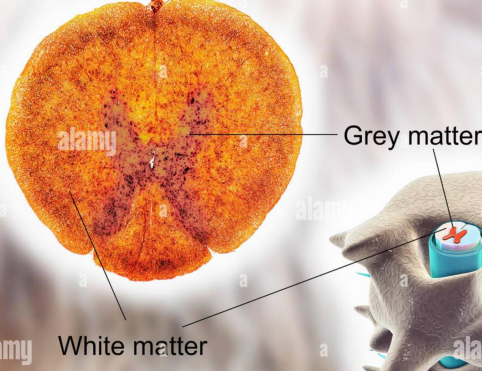
White and grey matter of the spine
Cell bodies are located in the middle of the spinal cord (Gray matter)
Myelinated axons protrude out of the spinal cord (White matter)
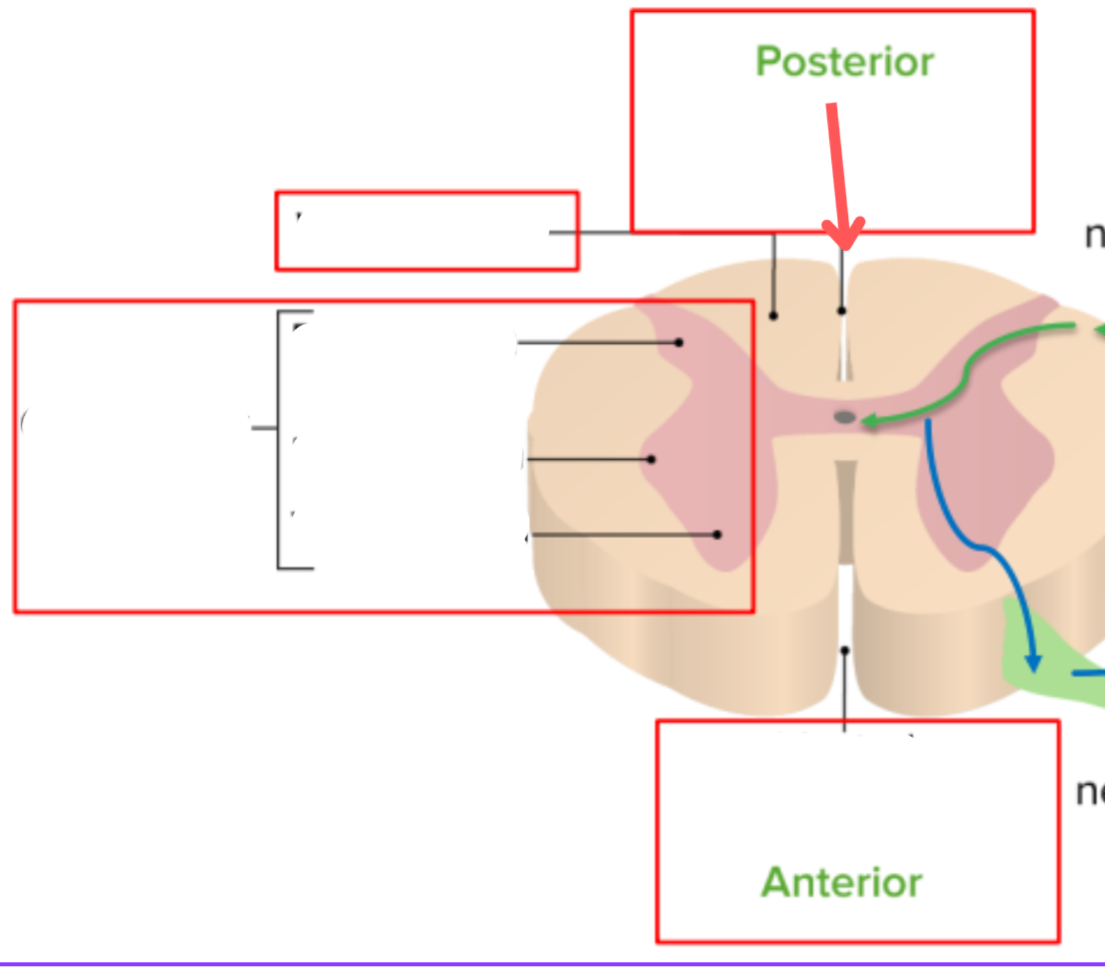
Dorsal median sulcus
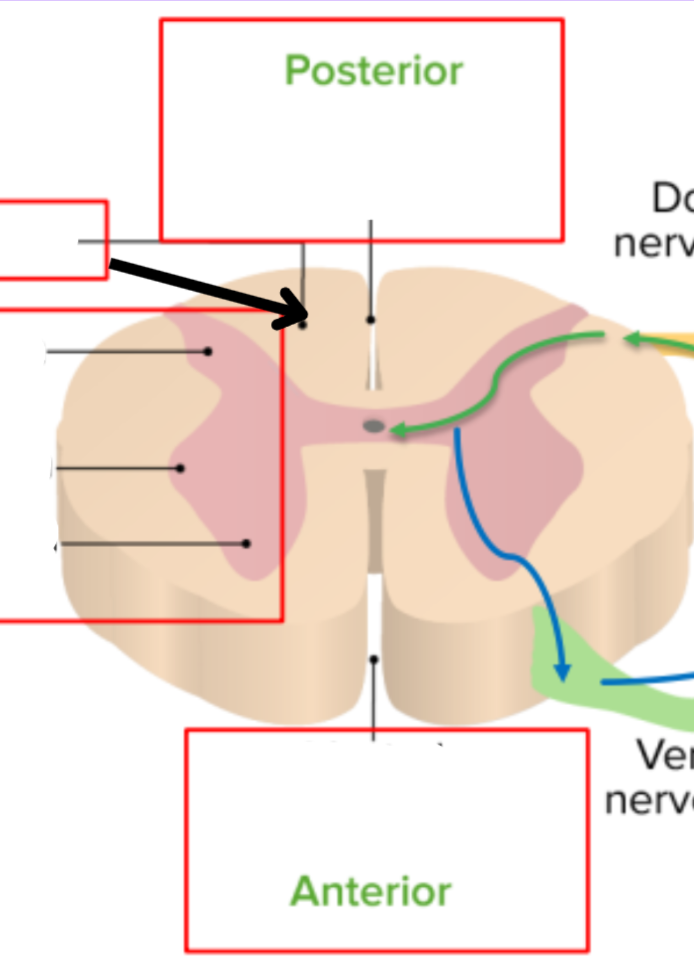
White matter
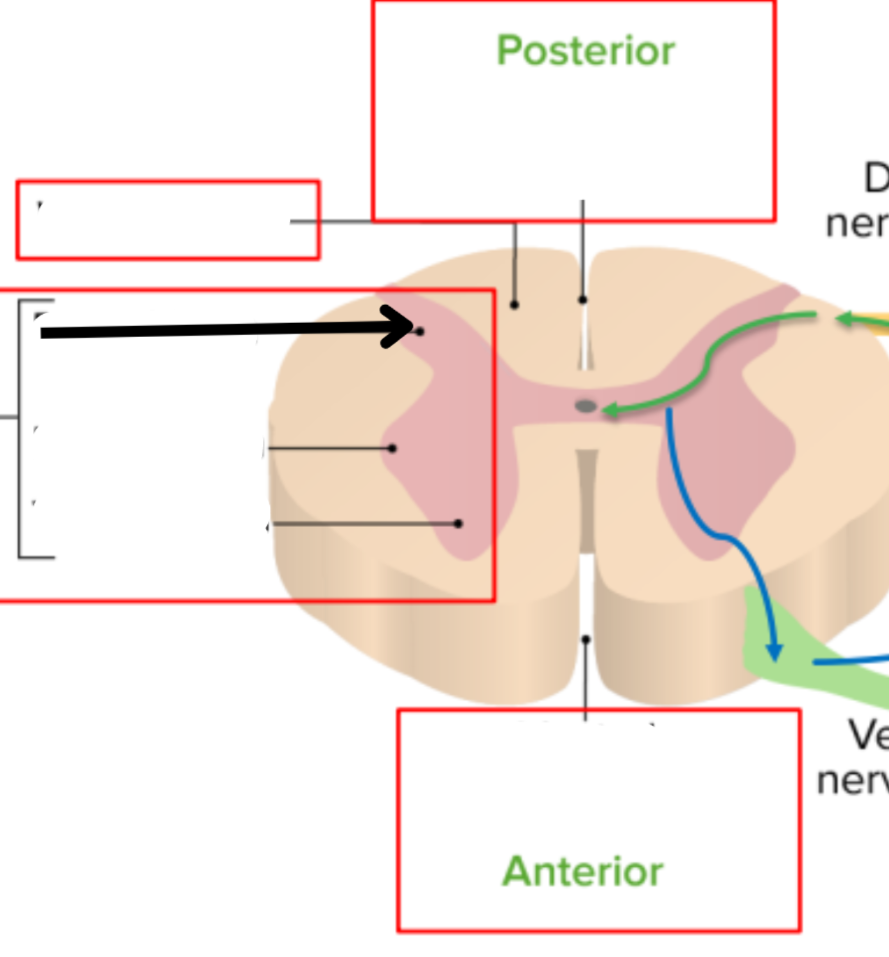
Dorsal horn of gray matter
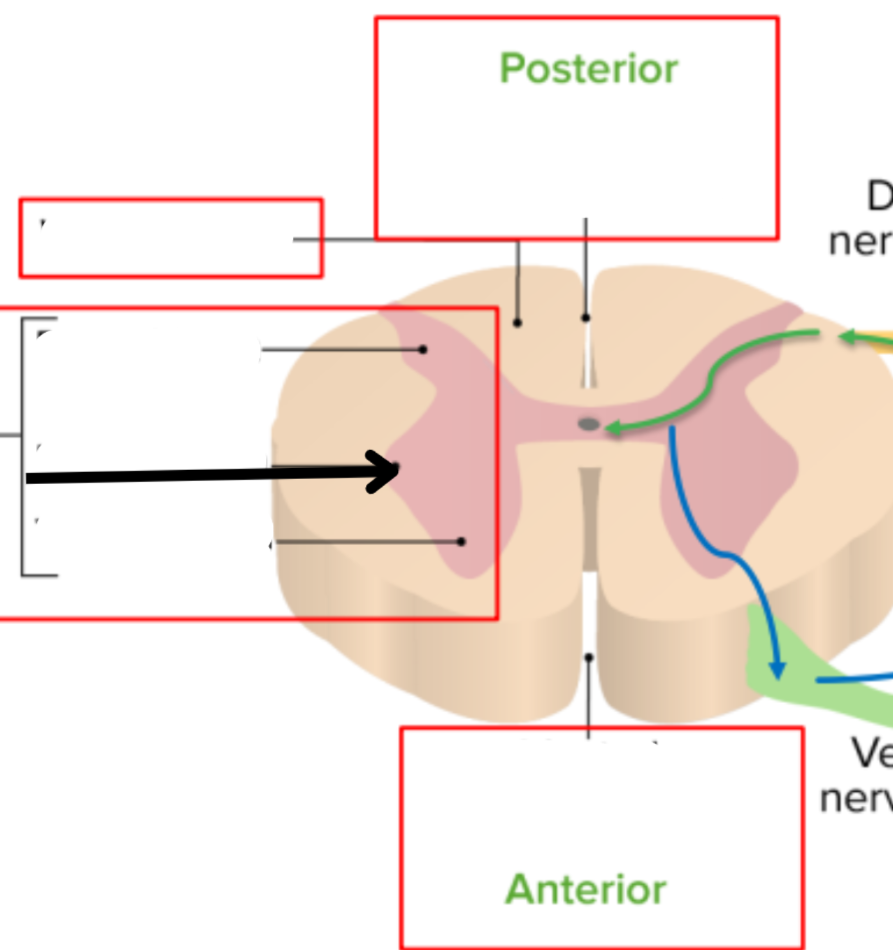
Lateral horn of gray matter
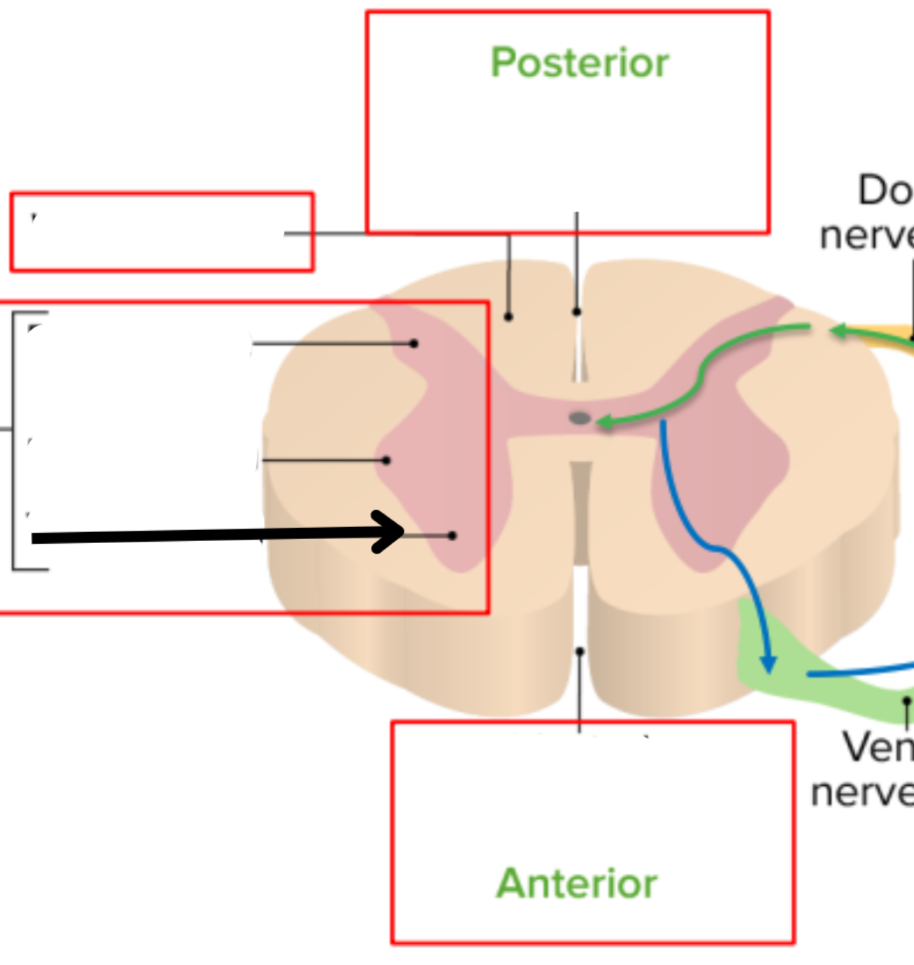
Ventral horn of gray matter
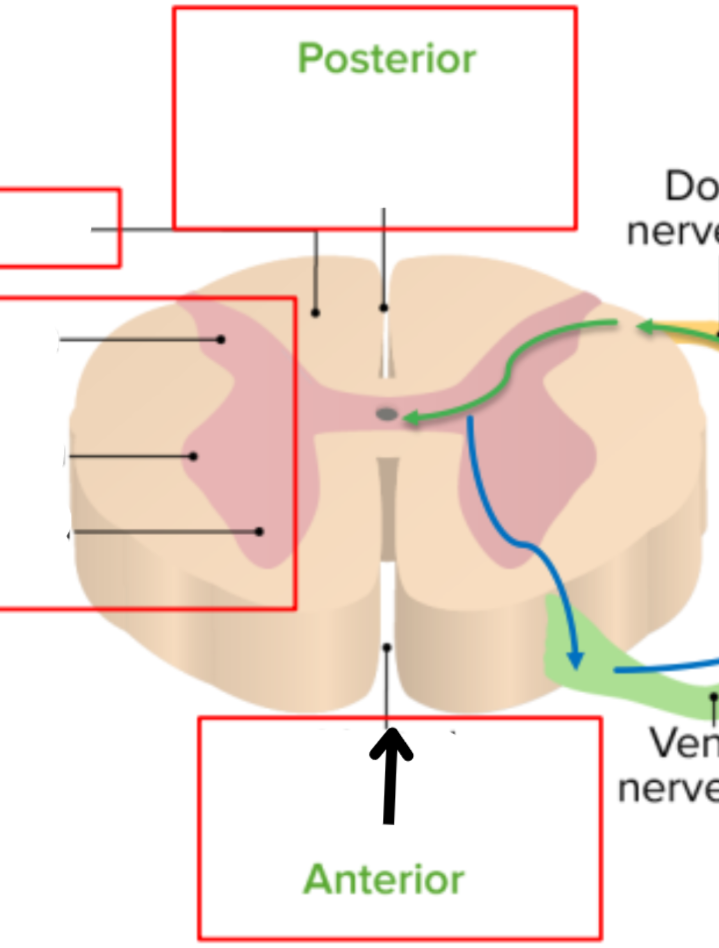
Ventral median fissure
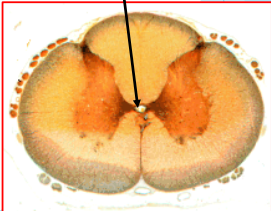
The central canal
Center of the spinal cord
Lined with ependymal cells
Contains CSF, protects the spine
Helps transport nutrients and waste
4th ventricle → Conus medullaris
Ganglion
A group of neurons (Cell bodies) outside the CNS
Nucleus
A group of neurons (Cell bodies) within the CNS
Nerve
A group of nerve fibers (axons) outside the CNS
Tract
A group of nerve fibers (axons) within the CNS