Rocks and Weathering
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Crust/Lithosphere
Outermost layer of earth
Continental is thick and less dense as well as being old
Oceanic is thin and more dense as well as being young
Mantle/Asthenosphere
A layer of hot melted rock under the lithosphere
Core
The central part of the earth below the mantle
Has an inner and an outer
Inner is denser than outer
Divergent/Constructive Margins/Boundaries
Plates spreading apart
As plates move apart new material is erupted to fill in the gap
2 oceanic plates results in sea floor spreading and forms mid-ocean ridges
2 continental plates results in volcanoes
Convergent/Destructive Margins/Boundaries
Plates colliding together
May form mountains, trenches, and volcanoes
There are three styles
Continent-continent
Continent-oceanic
Oceanic-oceanic
Slab Pull
Mechanism that contributes to plate motion in which cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along in a downward force
Sea Floor Spreading/Mid-ocean Ridge
As the plates move further and further apart, new ocean floor is continuously added
Where two ocean plates are diverging, molten magma erupts, forming underwater mountains under the ocean
Island Arcs
A series of volcanic islands formed in an arc-shape when oceanic lithosphere is subducted beneath oceanic lithosphere
Ring of fire
Subduction Zones
Oceanic lithosphere subducts underneath the continental/oceanic lithosphere
Oceanic lithosphere heats up and melts forming magma
The magma rises forming volcanoes
The lithosphere subducting is the Benioff zone
Ocean Trenches
The subducting plate is bent downward to form a very deep depression in the ocean floor
Mariana
Transform Faults/Boundaries
Where plates slide past each other
Earthquakes frequently occur
Volcanic Activity
Form through subduction of convergent plates and rifting of divergent plates
Magma in the mantle’s cells slowly rise into the chamber releasing plumes that breach the surface
Creates more land
Part of the mid-ocean ridge
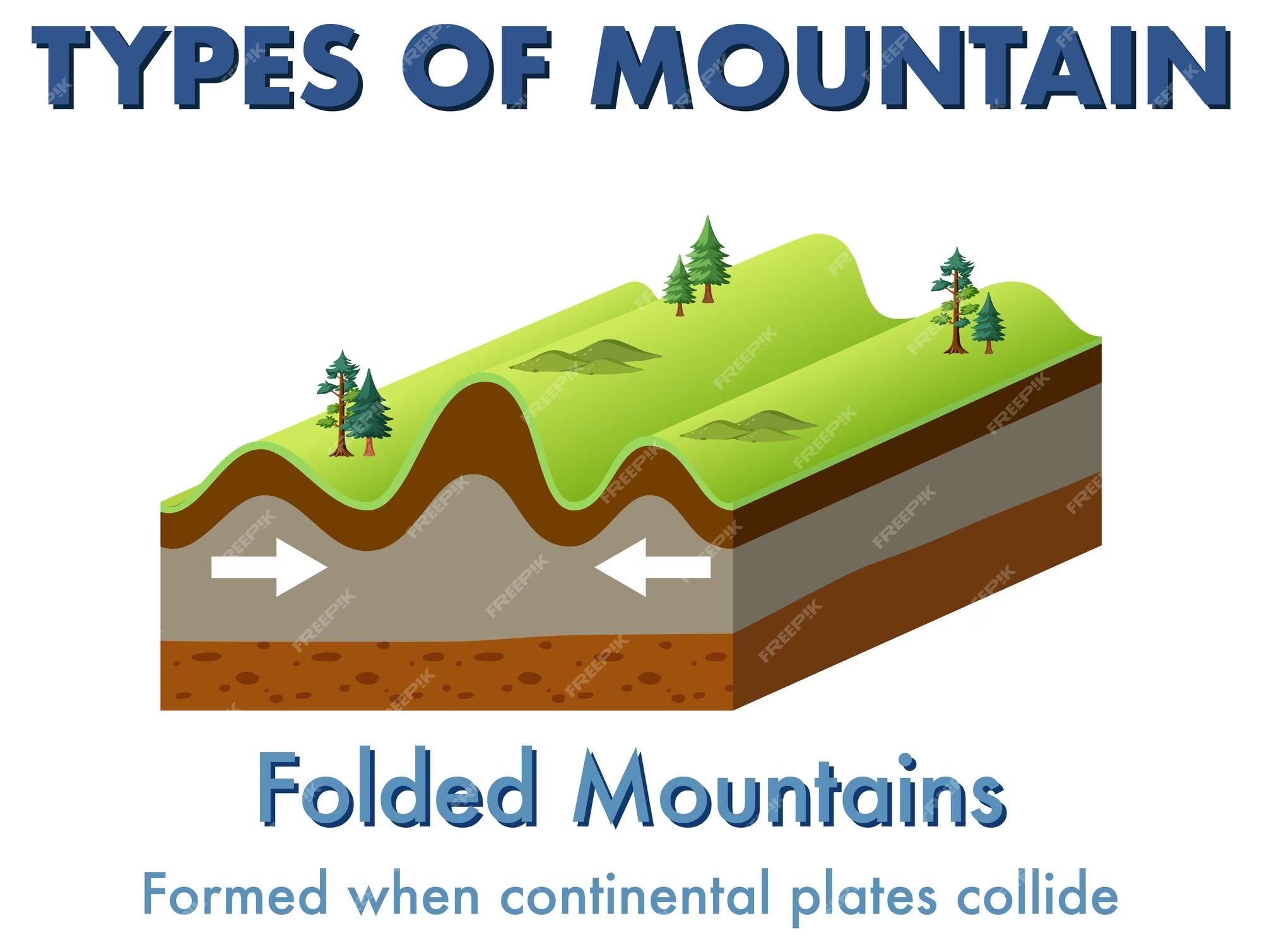
Fold Mountains
Plate tectonics associated with mountain building
At ocean-continent convergence: The less dense continental plate folds and buckles only on the continental side
At 2 continental plate convergences: Both buckle and fold with crust thickening on both sides over time
Freeze-thaw Action/Frost Shattering
Water in joints freezes and expands causing cracks
Occurs when pressure exceeds rock’s resistance to weathering
Where: Moisture is plentiful - fluctuating above and below freezing temperatures
Scree is produced which are smaller, angular fragments of the rock
Mechanical/physical weathering
Dilatation
Erosion removes the overlying rocks and the underlying rocks becoming exposed to then expand and fracture
Where: Very high pressure areas such as confined spaces in the Earth’s interior; removal of weight
Pseudo-bedding planes: Parallel fractures
Mechanical/physical weathering
Salt Crystalization
Caused by decomposition due to salt being left on rock after evaporation
Sodium expands when left in joints, causing rock to crack
Where: Hot desert regions with low rainfall and hot temperatures cause salt accumulation as well as polar regions with salt deposition from snowflakes
Mechanical/physical weathering
Hydration
Minerals in rock absorb water, expand and change
Chemical weathering
Does include some mechanical stress
Hydrolysis
Rocks react with water and becomes more acidic
Chemical weathering
Occurs on rocks with orthoclase feldspar, like granite, and produces clay or salts
Carbonation
Rainfall combined with dissolved carbon dioxide or organic acid to form a weak carbonic acid
Chemical weathering
Occurs on rocks with calcium such as chalk and limestone
Oxidation
Occurs when iron compounds react with oxygen
Chemical weathering
Changes coloration in mineral like rust
Granular Disintegration
Finer materials being exfoliated gradually
Certain grains being more prone to expansion and contraction than other - this exerts great pressure on the grains surrounding them and forces them to break off
Block Disintegration
Successive heating and cooling which causes the expansion and contraction of rocks
Joints
A brittle-fracture surface in rocks along which little or no displacement has occured
Shear Stress
Function of gravity pulling the object down
Increases adds weight to the slope
Steeper slope = increase in stress
Bad
Shear Strength
Resistance of an object to move downhill
Higher when there is friction or higher cohesiveness (particles being held together)
Good
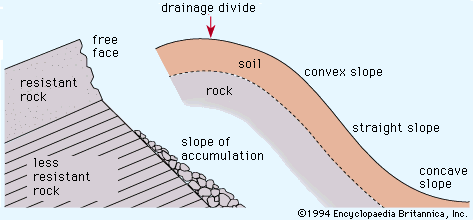
Concave Slope
Slumps happen with this slope
Declines in steepness with movement downslope
Flow (Mudflow)
Soil or weaker rocks become saturated with water and flow downhill
Causes failed landmass/slope to slide, slows down due to firction
Watery surface, structureless failed landmass with high water content
Occurs at slow to fast speeds depending on the water content
Fall (Rockfall)
Rock fragments are detached
Causes: frost shattering or earthquakes
steep cliff face is formed
No/low water content and occurs at high speeds
Soil Creep
Extremely slow
Downward progression of rock and soil down a low-grade slope
Occurs during alternate heating and cooling or wetting and drying
Low to moderate water
Solifluction
Frozen slope (occurs during winter) that melts during summer months, causing soil to be saturated with water
Bottom layer acts as an impermeable layer - a sliding plane
High water content
Occurs at slow speeds
Landslide
Coherent materials (debris/large rocks) moving across a clearly defined sliding plane
Common along slopes made of rock which allows for more infiltration to occur due to the permeable surface
High water content
Occurs at high speeds