frst 386 terminology and concepts
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
what characteristics can we look at to tell species apart?
shape, presence and colour of fins, presence of sensory organs
are there non-morphological ways to distinguish between species?
life history traits
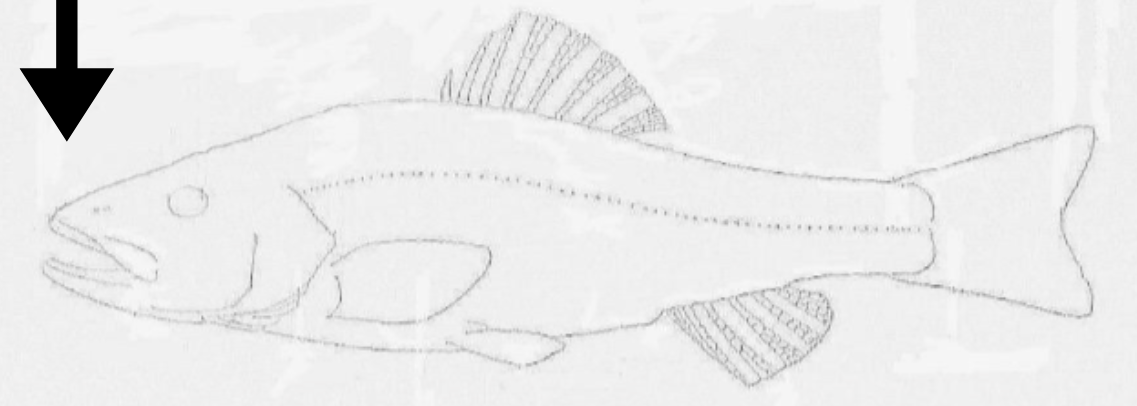
what is this orientation?
anterior
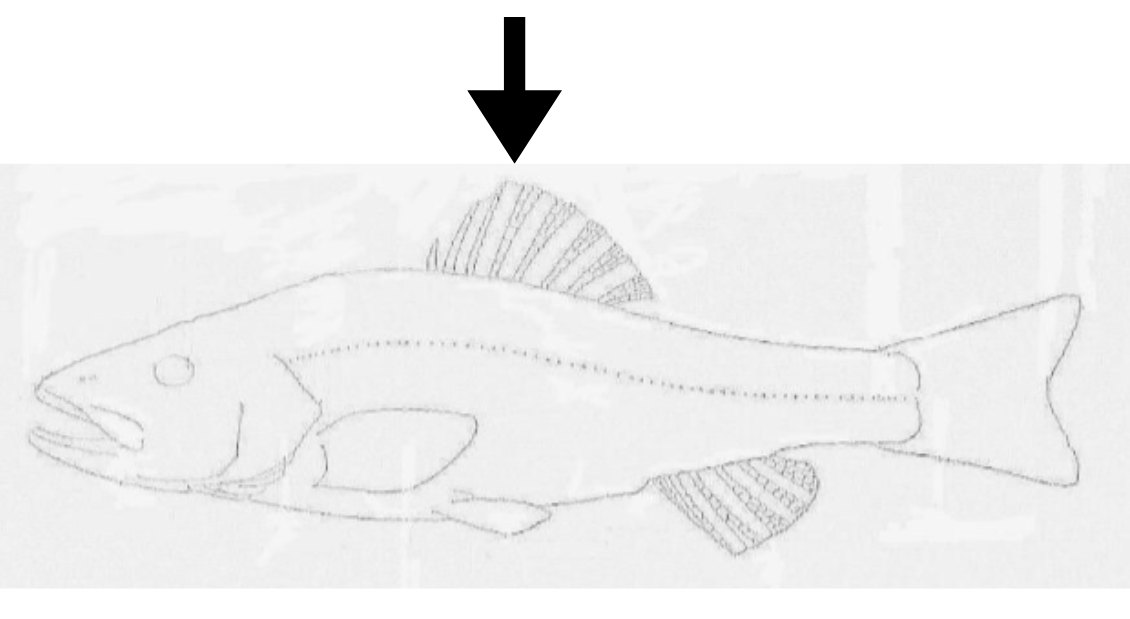
what is this orientation?
dorsal
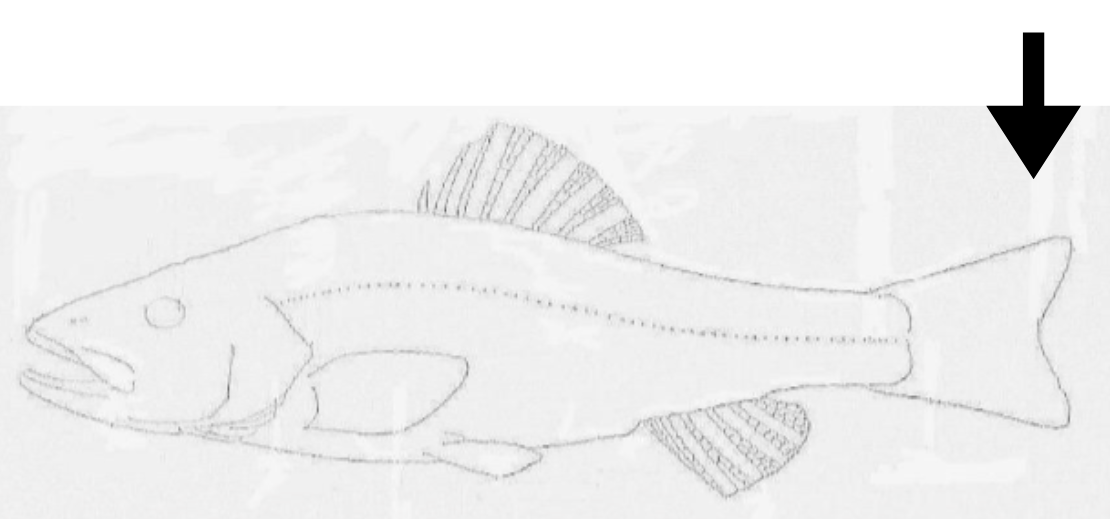
what is this orientation
posterior
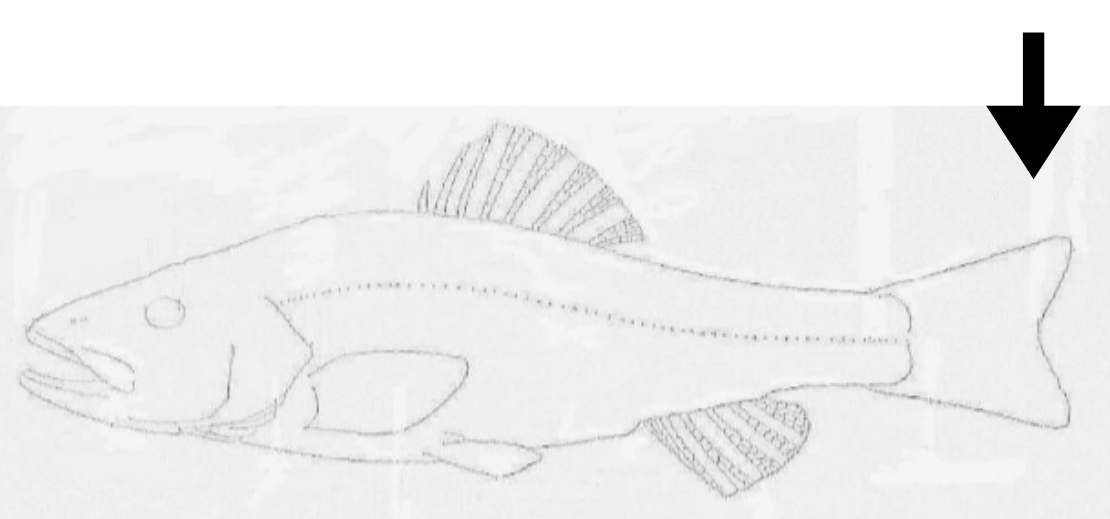
what is this orientation?
ventral
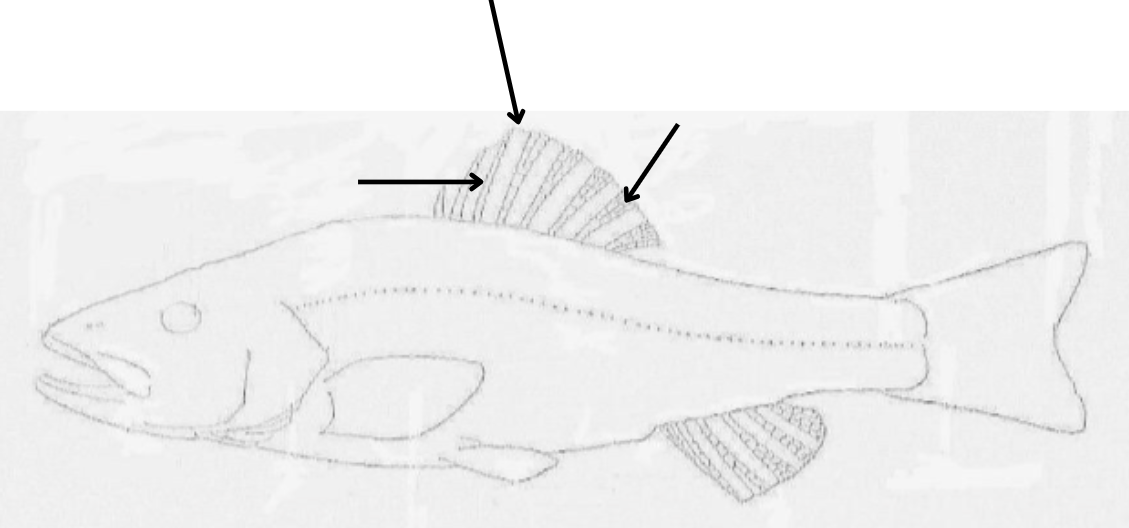
what is the top arrow pointing to, and what components make it up?
top: dorsal fin
left: spine
right: ray
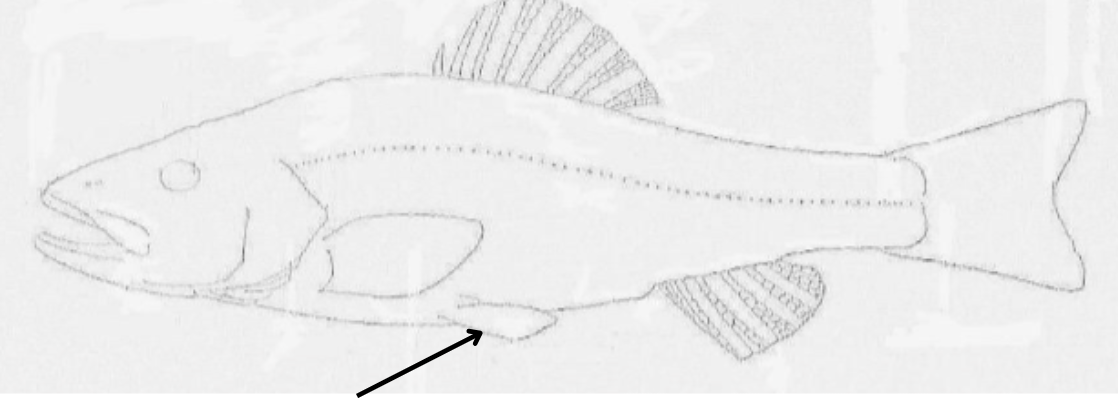
what is this pointing to?
pelvic fin
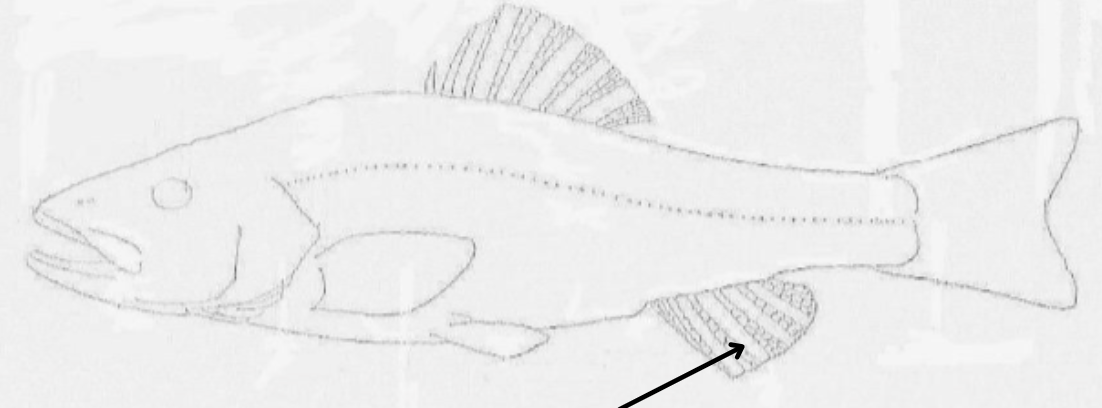
what is this pointing to?
anal fin
5 major rays
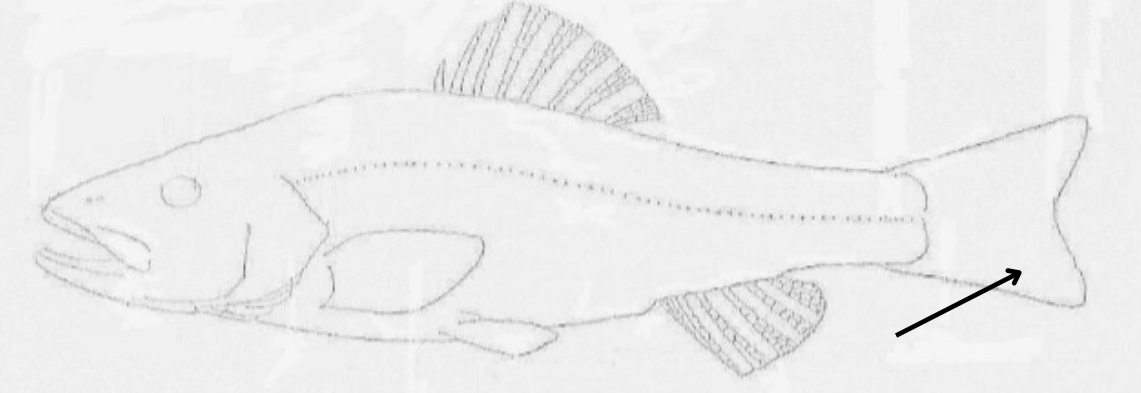
what is this pointing to?
caudal fin
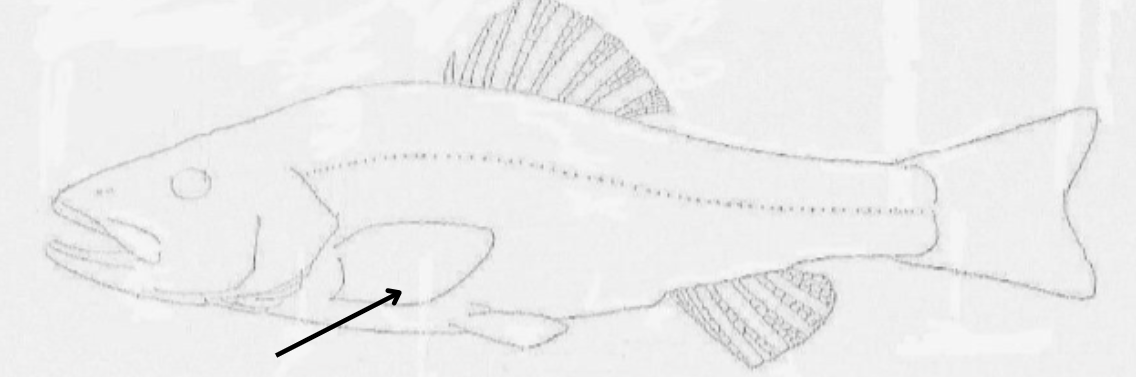
what is this pointing to?
pectoral fin
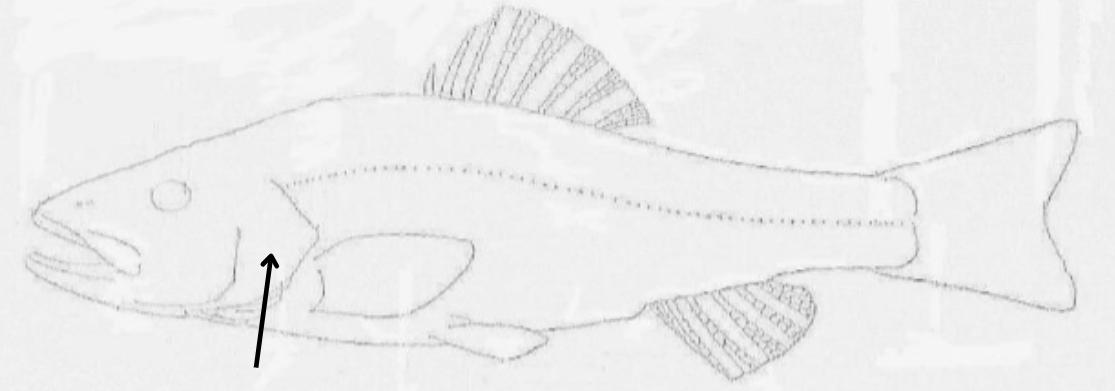
what is this pointing to?
opercle
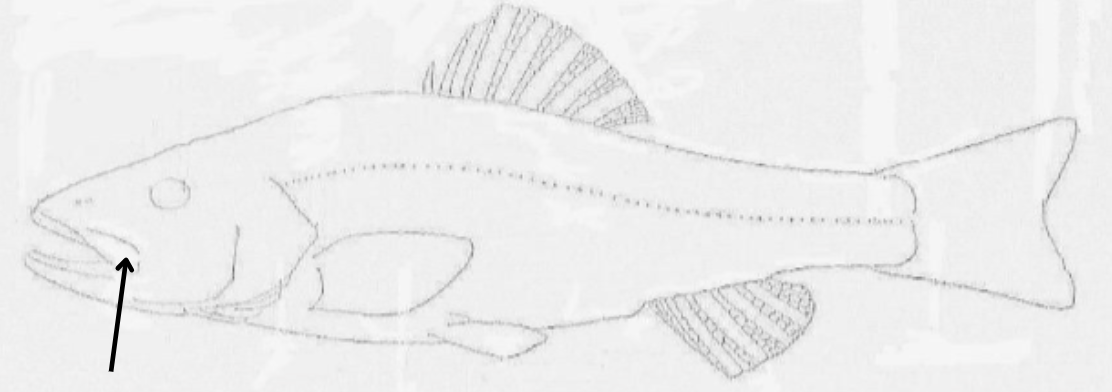
what is this pointing to?
maxilla
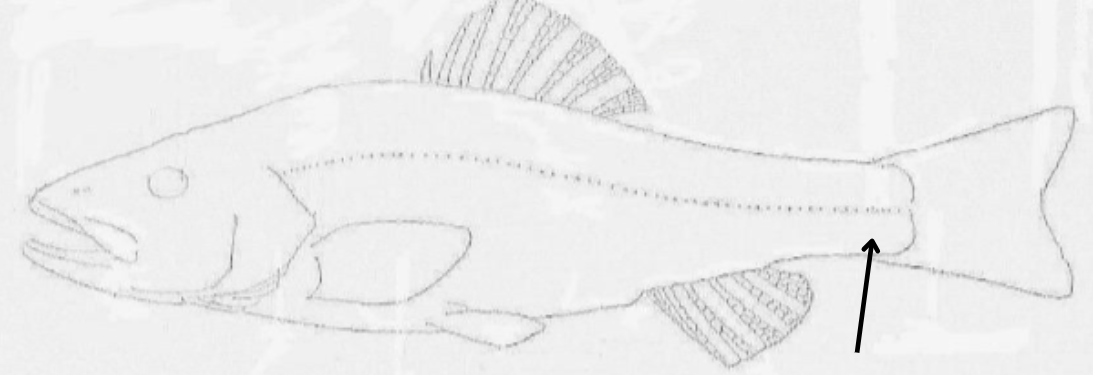
what is this pointing to?
caudal peduncle
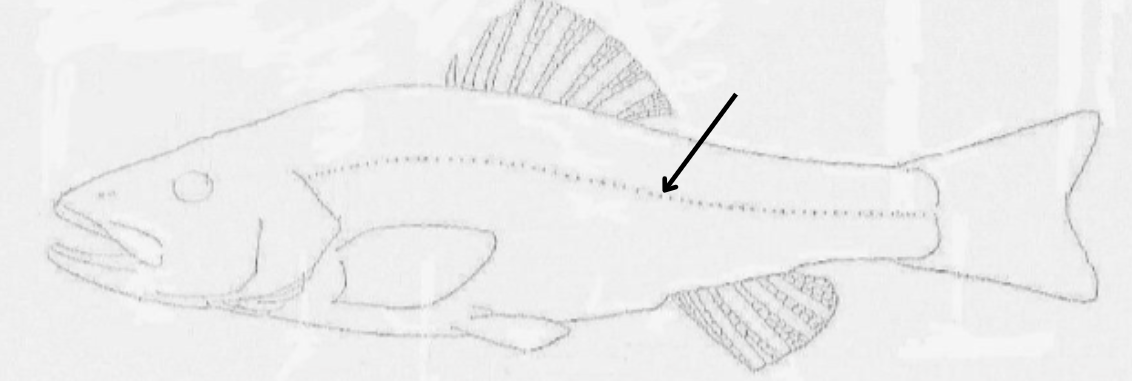
what is this pointing to?
lateral line
what is this pointing to?
anus
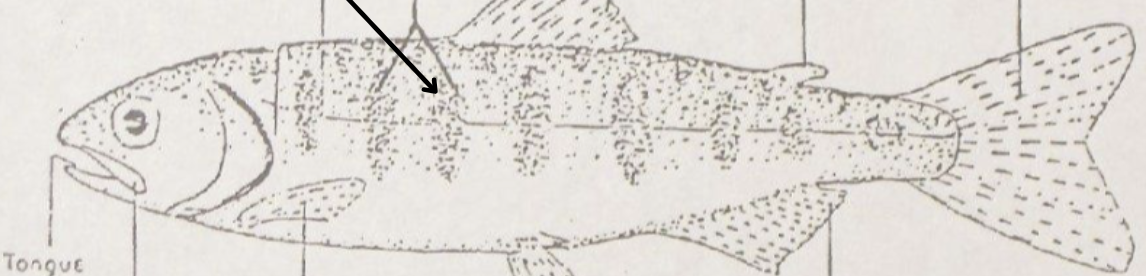
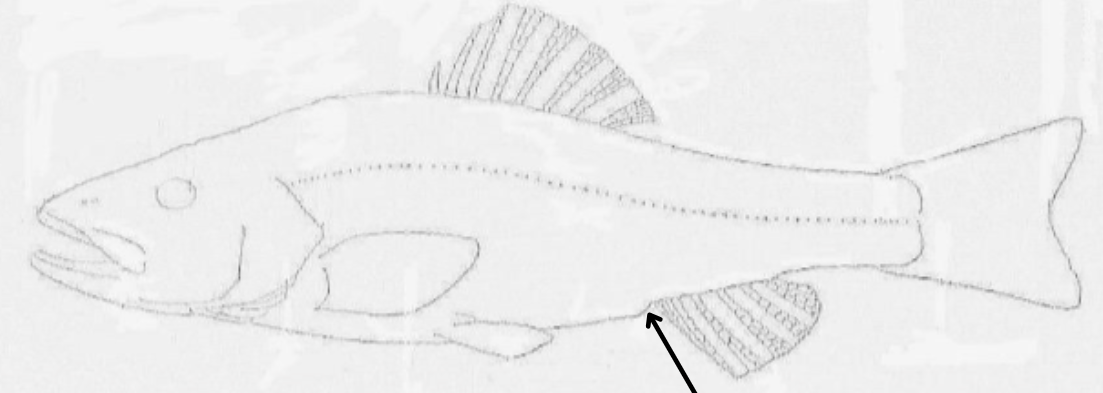
what is this pointing to?
parr marks
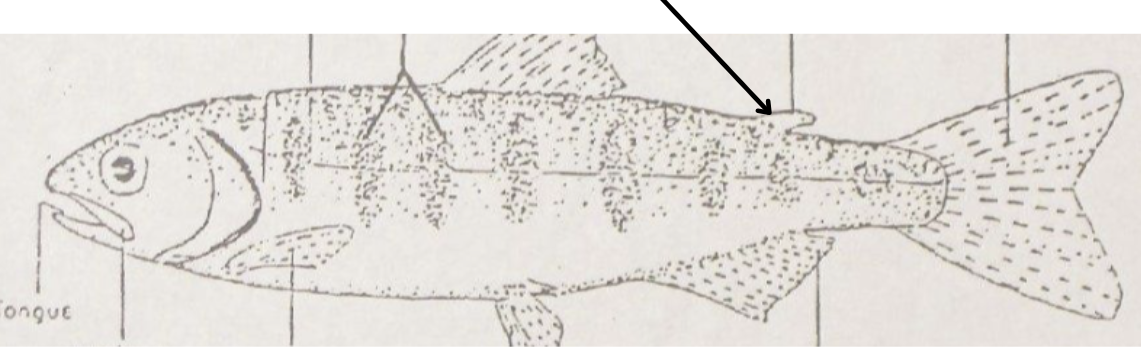
what is this pointing to?
adipose fin
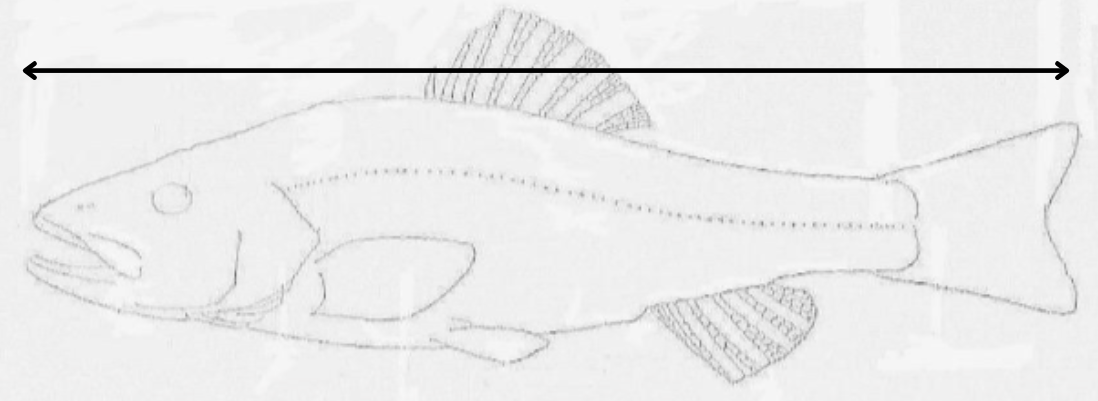
what length is this?
total length
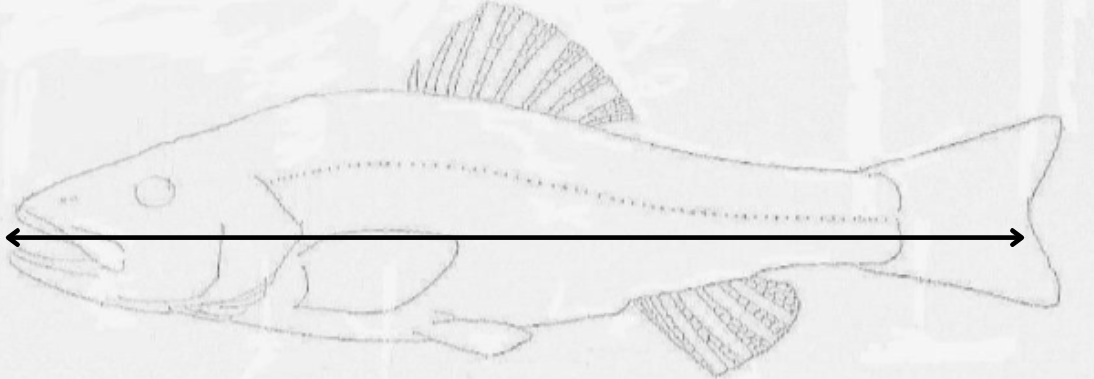
what length is this?
fork length
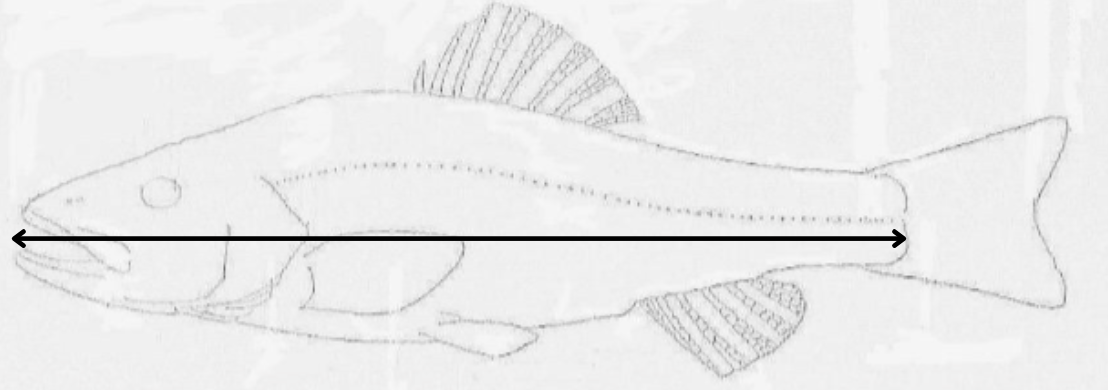
what length is this?
standard length
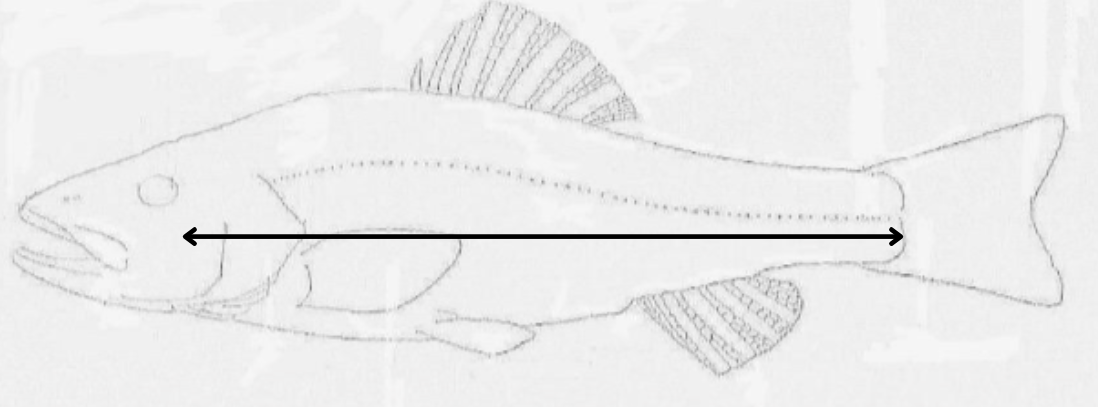
what length is this?
post-orbital hypural
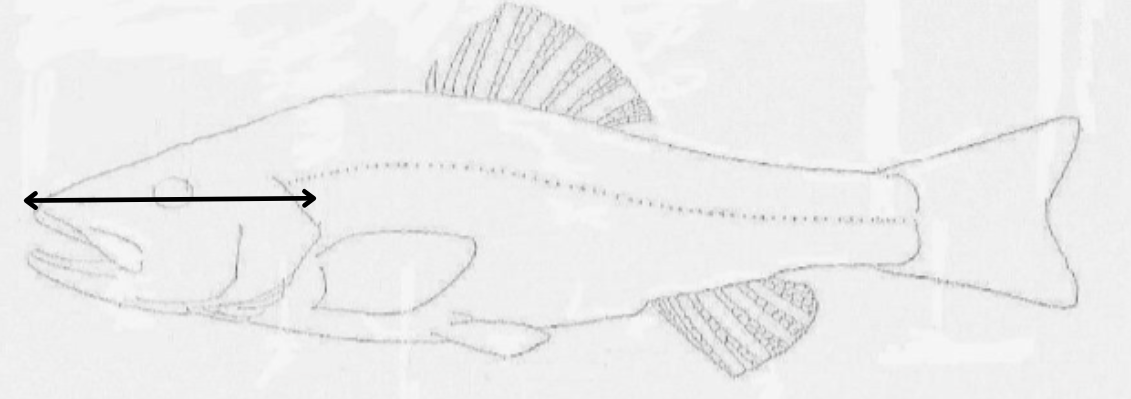
what length is this?
head length
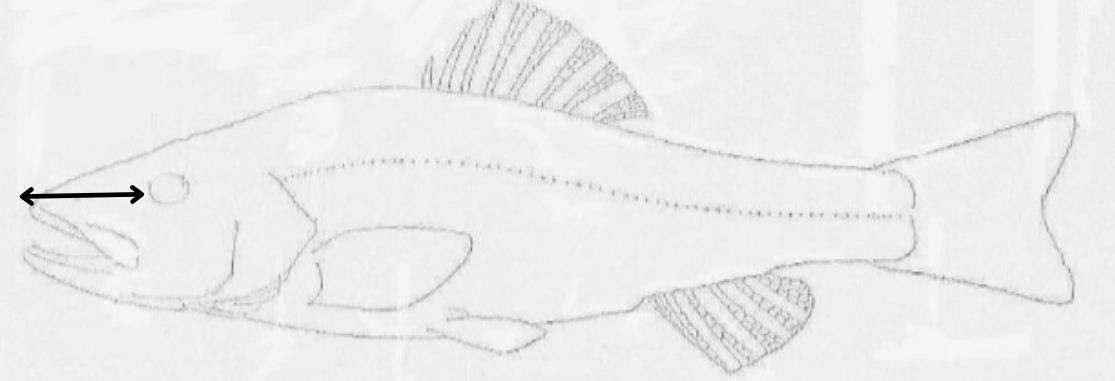
what length is this?
snout length
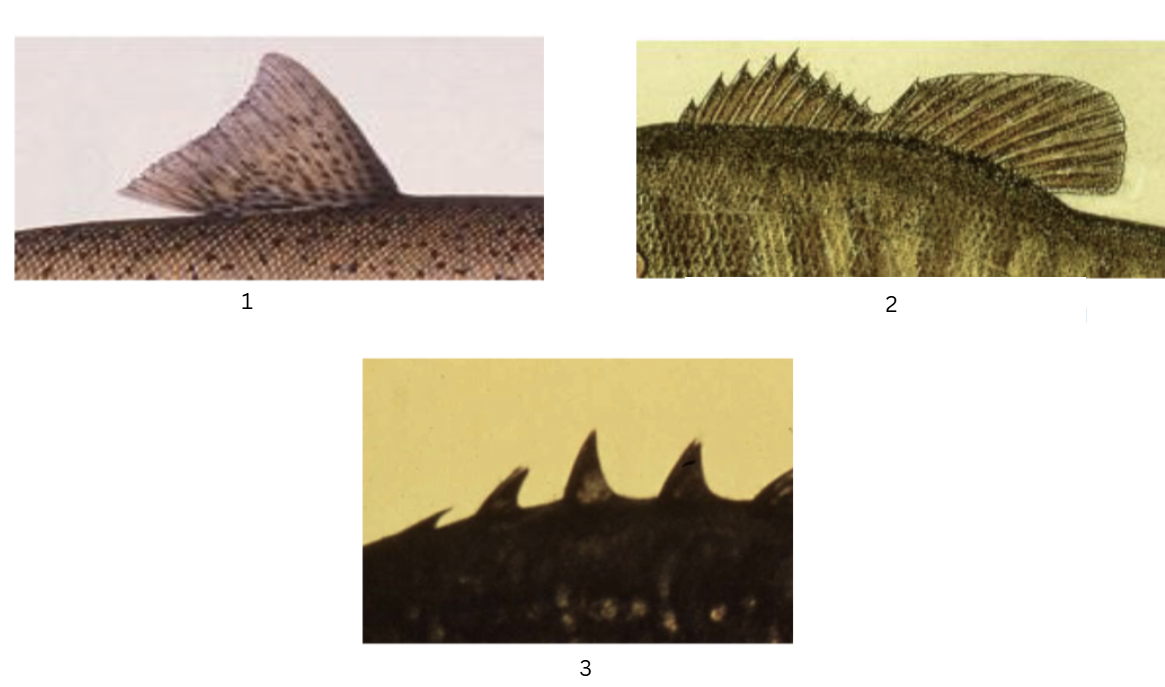
what types of fins are these?
fleshy dorsal fin
spiny-fleshy dorsal fin
spiny dorsal fin
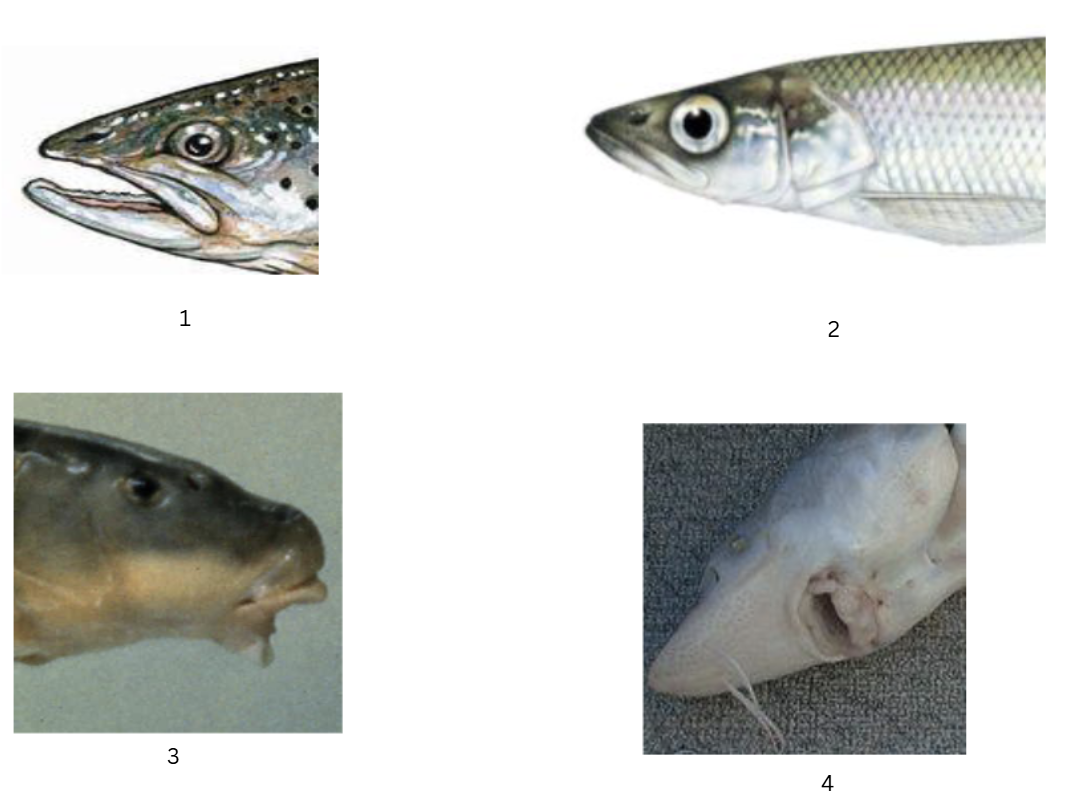
what types of mouths are these?
terminal
supra-terminal
sub-terminal
inferior
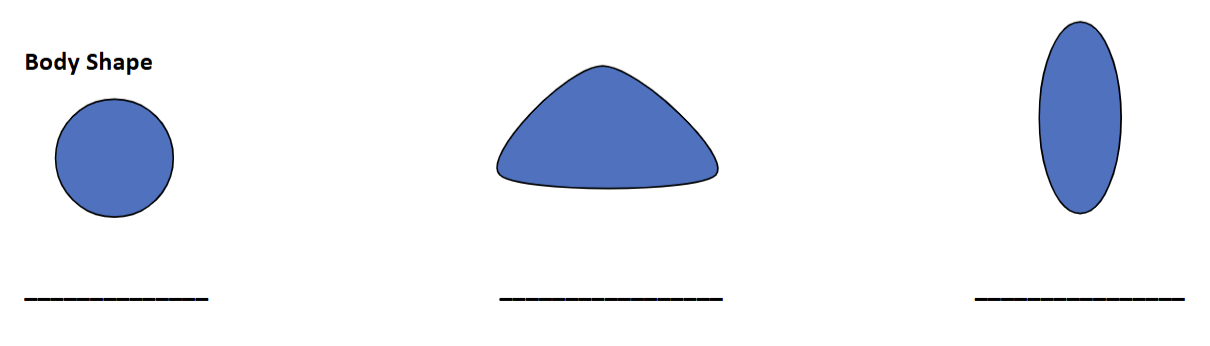
what body shapes are these?
left: torpedo
middle: dorsally compressed
right: laterally compressed
population
A group of organisms of the same species that interbreed and live in the same place at the same time
stock
semi-discrete groups of fish with some definable attributes of interest to managers; a harvested or managed group of fish
catadromous
A species of fish that does most of its growing in freshwater and returns to saltwater to spawn (e.g., The American eel - found in St. Lawrence River)
anadromous
A species of fish that does most of its growing at sea and returns to freshwater to spawn (e.g., Pacific salmon, Atlantic salmon, lampreys)
potadromous
A species that migrates entirely within freshwater
semelparous
A species that spawns only once (i.e., dies after spawning).
E.g., All “Pacific salmon”* (5 spp.), lamprey
iteroparous
A species that matures and spawns more than once.
E.g., Atlantic salmon, trout, char
what are three approaches to ageing fish
size frequency distributions
analysis of body parts/structures that retain growth information relatable to time
direct observation of individually identifiable animals whose histories can be followed through time
what are size frequency distributions?
ages are estimated by examining the relationship between fish abundance and length
assumes that fish of the same age are a similar size
what is analysis of otoliths/scales/fin rays?
structures such as otoliths, scales, and fin rays provide a record of growth
all three structures grow in rings, and growth rate is reflected by the space between the rings
what is the direct observation of individuals?
external tags, fin clips/markings, injecting dyes under skin, branding, inserting/attaching transmitters
what are pros, cons, and other uses for size frequency distributions?
pros:
quick
potentially cheap
non-lethal
no species equipment or training required
cons
there could be overlap between age groups
it is subject to sampling bias
requires a large sample size
other uses
monitoring fish populations over time
population dynamics
what are pros, cons, and other uses of analysis of otoliths, scales, or fin rays?
pros
accurate
non-lethal (scale and fin rays)
easy to collect
can get additional information (e.g. growth rates)
cons
can be expensive
lethal (otoliths)
requires training/knowledge
time consuming analyses
human error during collection
other uses
growth studies
habitat use
what are pros, cons, and other uses of following known individuals?
pros
non-lethal
a lot of additional data can be taken
100% accurate
cons
expensive
requires training/knowledge
requires tracking fish over long periods
tag loss is possible
other uses
all sorts of behavioral and physiological information
name the two types of paired fins
pelvic fins and pectoral fins
air bladder
can be open or closed if present
cavity connected to esophagus (regulates buoyancy)
open = connected to esophagus (need to go to surface)
closed = inflate/deflate with blood stream gas exchange (not connected to esophagus)
taxonomy
the practice and science of classification
order
-iformes
family
-idae
sub-family
-inae
genus and species
Genus species or Genus species
salmonidae sub-families
coregoninae, thymalline, and salmoninae
salmonidae main characteristics
adipose fin
lateral line present
no spines in fins, have a fleshy dorsal fin
juveniles (most, not all) have parr marks
salmoninae genus
oncorhynchus, salmo, and salvelinus
anadromous salmon life history
some rear for a year+ in the stream or lake
e.g. Chinook, coho (stream)
e.g. sockeye (lake)
some go directly to sea after the emergence
e.g. pink, chum
non-anadromous salmon life history
some salmonids spend entire life cycle in freshwater
e.g. rainbow trout and kokanee salmon (can do a migration from lake to stream but is more likely to spawn on the shores of a lake)