Laryngopharynx & Larynx
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
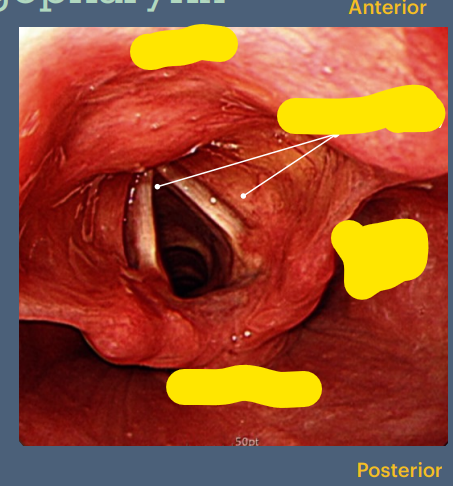
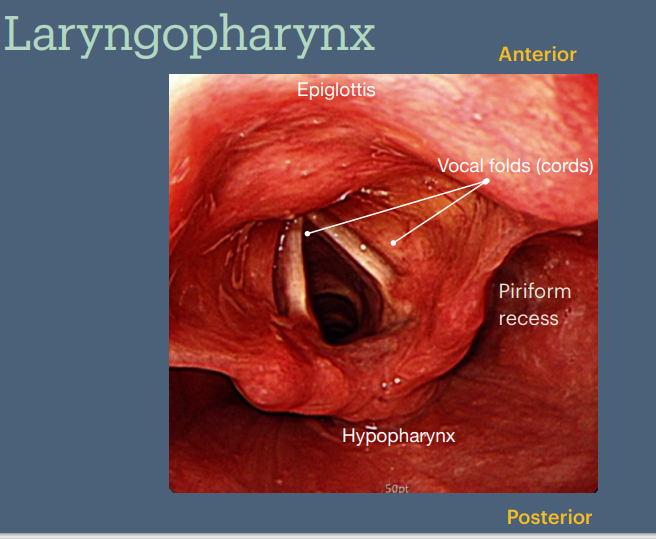
What part of the pharynx are we in & label
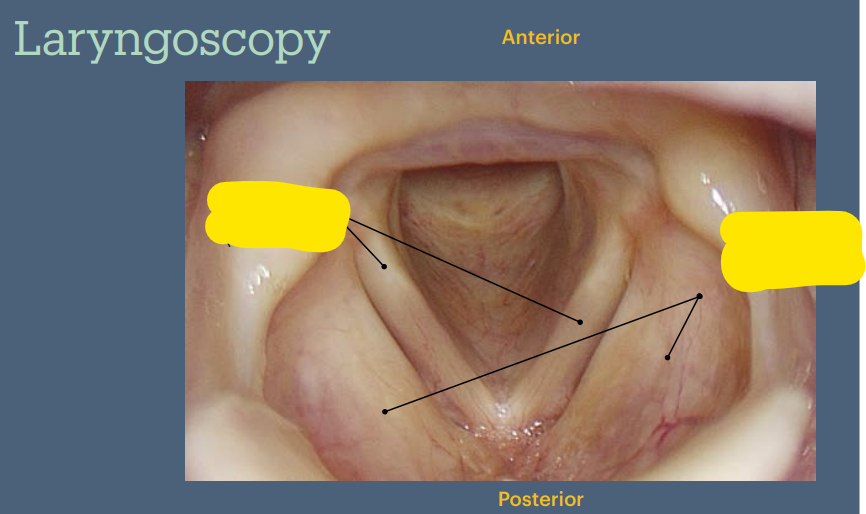
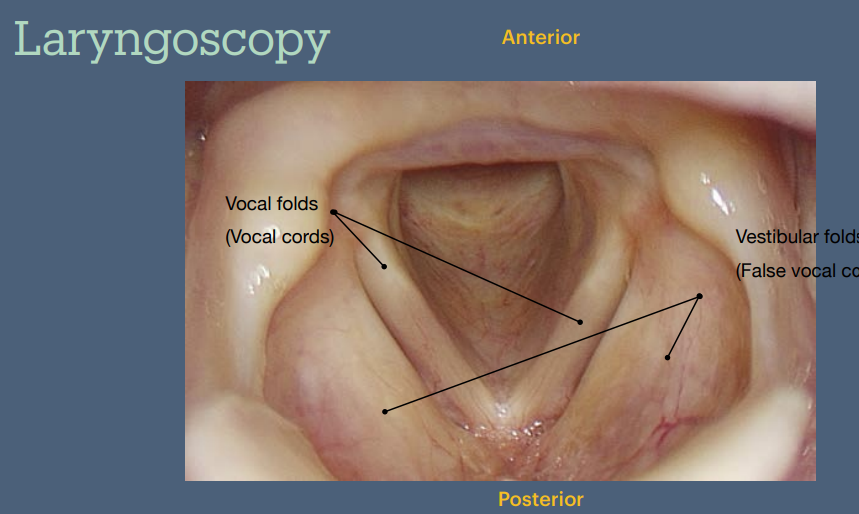
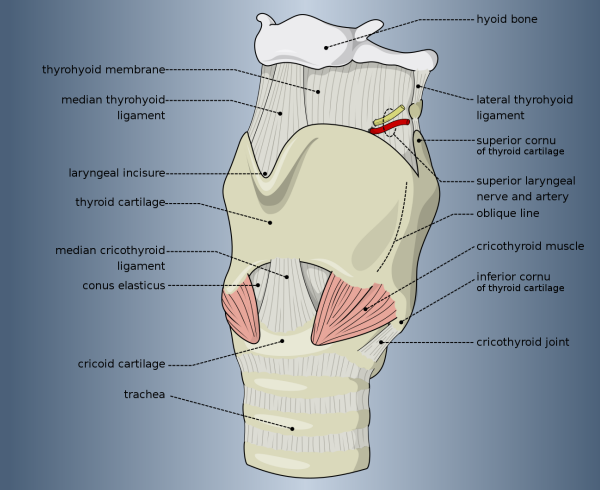
The laryngeal skeleton is made up of the hyoid bone & how many unpaired & paired cartilages
3 each
Unpaired:
Epiglottis
Thyroid
Cricoid
Paired
Arytenoids
Corniculate
Triticeal
Upper free margin of the quadrangular membrane is thickened to form what
the aryepiglottic folds
Lower free margin of the quadrangular membrane forms what
the vestibular ligaments
What forms core of the vestibular folds
quadrangular membrane
What forms the vocal ligament which forms the vocal folds
Superior free margin of cricothyroid membrane
Anterior midline of Cricothyroid membrane is thick to form what
median cricothyroid ligament
What is produced in laryngeal spaces
Mucus
Possible problem that arises in laryngeal spaces
Cysts
What muscles tense, relax, abduct & adduct the vocal folds
Cricothyroid (tense)
Thyroarytenoid (relax)
Posterior cricoarytenoid (abduct)
Lateral cricoarytenoid (adduct)
Motor and sensory innervation is to the larynx is all done by branches from 1 main nerve and 2 of its branches. What is it & what are the branches
Vagus nerve CNX
Branches:
Superior laryngeal nerve
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
Vagus nerve = king of the larynx,
through its superior laryngeal and recurrent laryngeal branches.
What supplies sensory innervation to the larynx
internal laryngeal nerve (Internal branch of superior laryngeal nerve) → sensory to:
Mucosa above the vocal folds
Epiglottis
Aryepiglottic folds
Piriform recess, etc.
(sensory to supraglottis & glottis)
What supplies motor innervation to the larynx & sensory innervation to the infraglottic space
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
Motor to all intrinsic laryngeal muscles (except cricothyroid)
Sensory to mucosa below the vocal folds (i.e., infraglottic space)
What supplies motor innervation to the cricothyroid
External laryngeal nerve (External branch of superior laryngeal nerve)
Paralysis of recurrent laryngeal results in
inability to abduct the focal folds on same side
- Cord on that side falls into ‘neutral’ position
- Hoarseness
- N.B. Aortic arch aneurysm
Blood supply to supraglottic internal larynx
Superior Laryngeal artery
Branches:
External carotid artery
↓
Superior thyroid artery
↓
Superior laryngeal artery
Blood supply to infraglottic internal larynx
Inferior laryngeal artery
Branches:
Subclavian artery
↓Thyrocervical trunk
↓Inferior thyroid artery
↓Inferior laryngeal artery
What is venous drainage for the the larynx like
Venous drainage parallels arterial supply
Explain lymph drainage from the larynx
