Dermatology Exam I
1/473
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
474 Terms
This is the largest organ and functions as a barrier to the outside world
Skin
What does the skin provide?
1. temperature regulation
2. Sensation
3. Vit. D production
4. Prevents water loss
What are the three basic layers of the skin?
1. Epidermis
2. Dermis
3. Subcutaneous
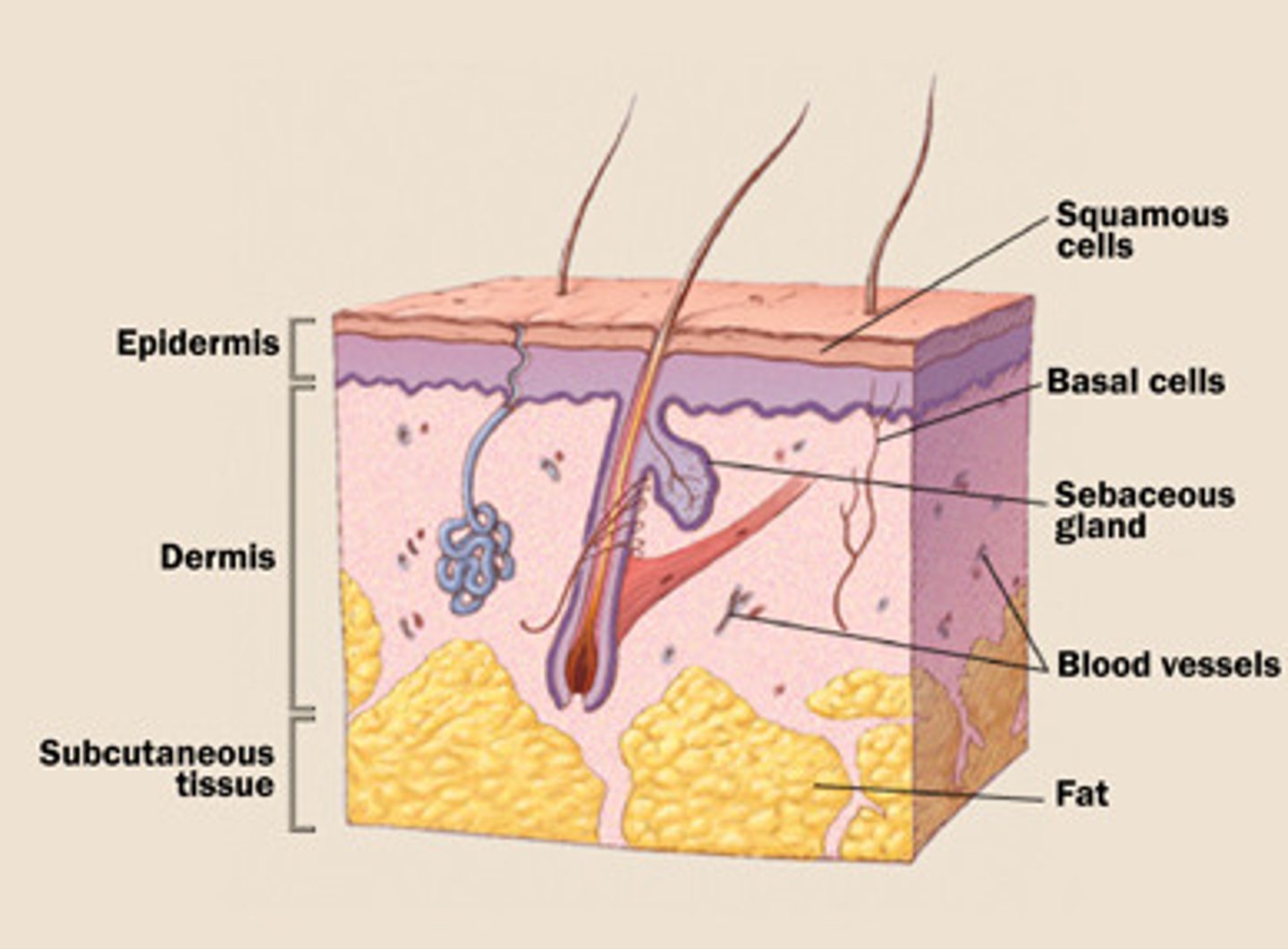
What are the 3 basic cell types in the epidermis?
1. Keratinocytes
2. Melanocytes
3. Langerhans' cells
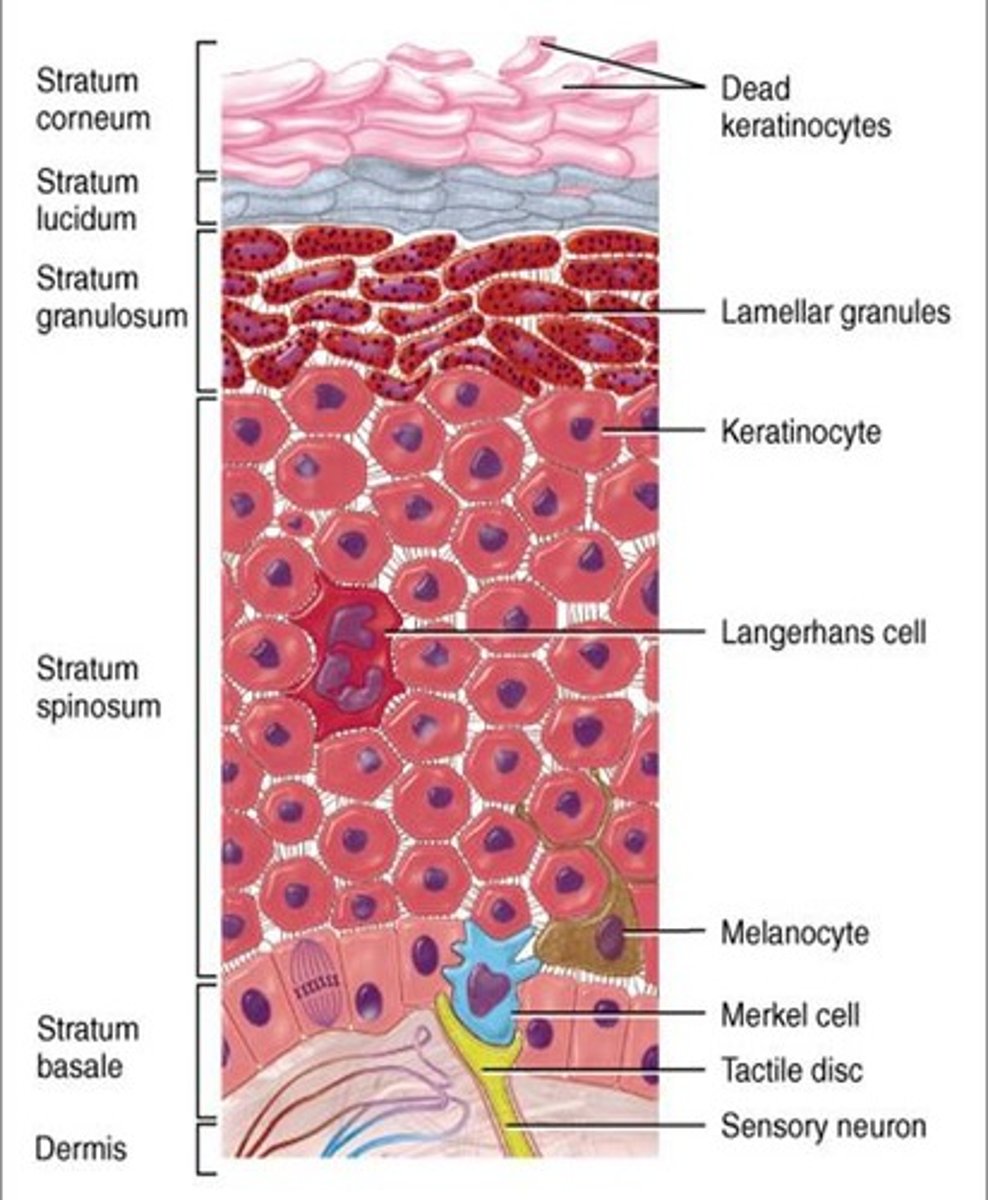
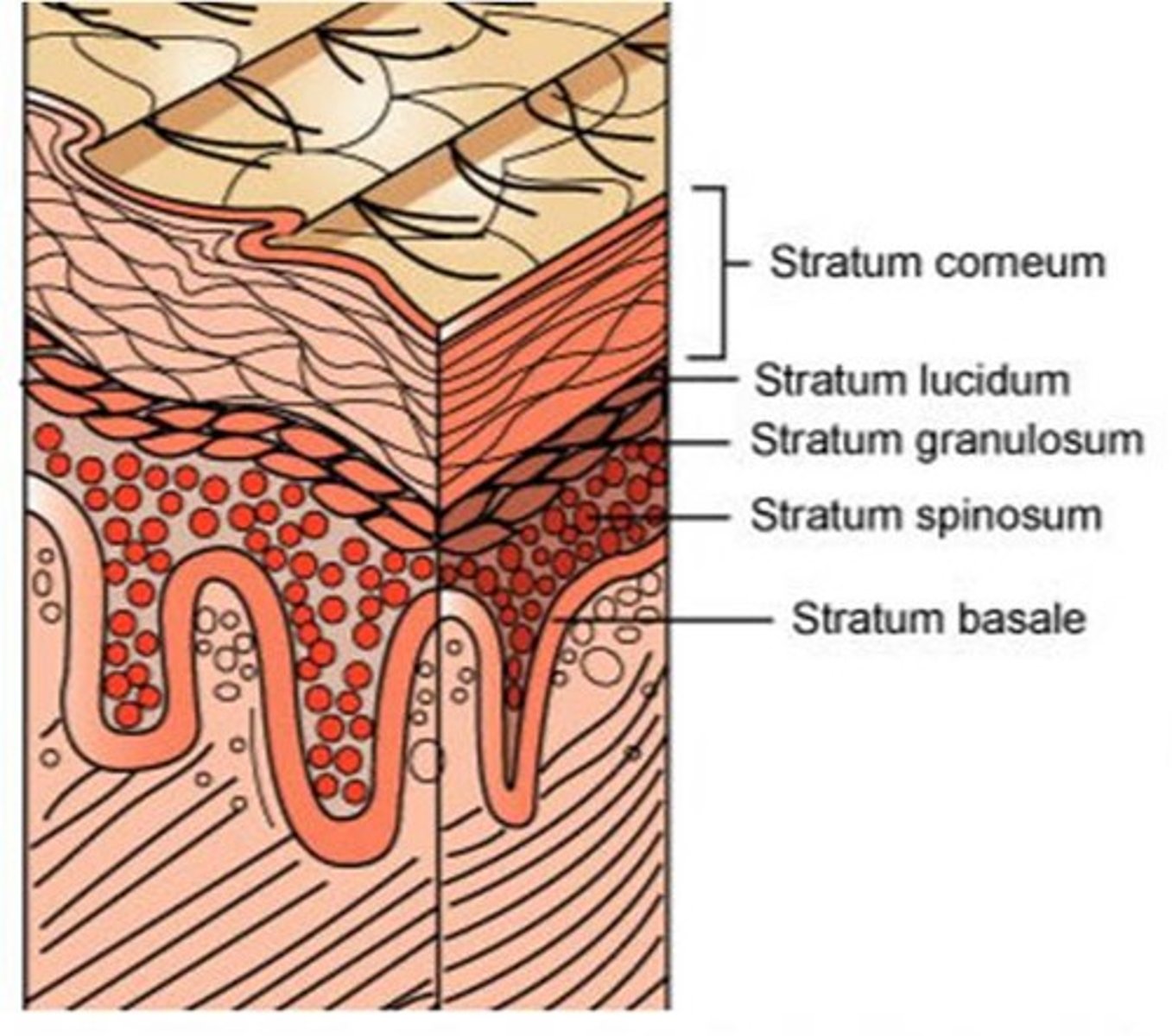
This layer of skin is the outer most layer responsible for protection. It is composed of keratinocytes, melanocytes and langerhans cells.
Epidermis
The epidermis has how many sublayers?
4 or 5, depending on the location (soles and palms have 5 layers)
The deepest layer of the epidermis consisting of stem cells capable of undergoing cell division to form new cells
stratum basale
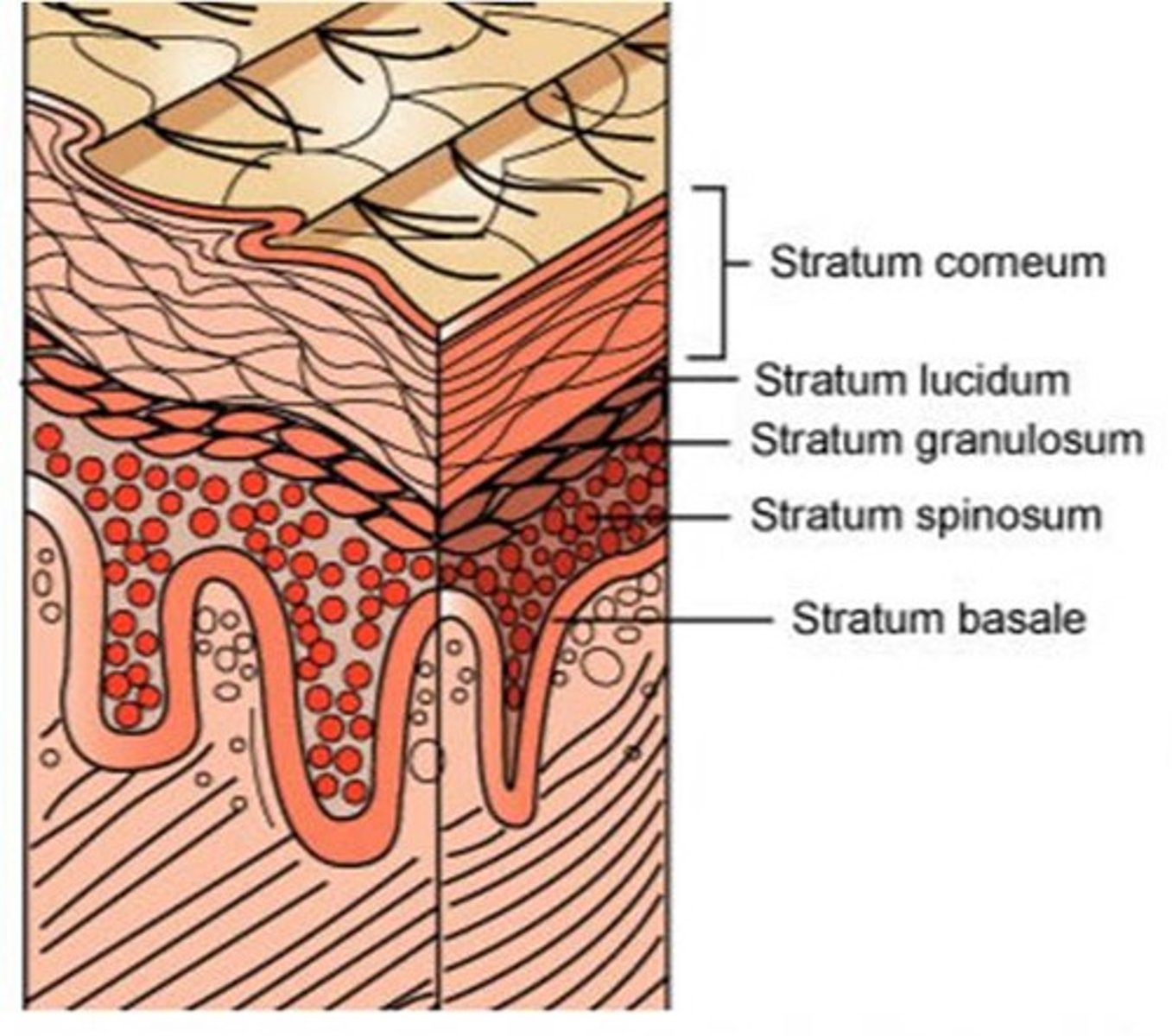
A layer of the epidermis that provides strength and flexibility to the skin. Langerhan cells are located here.
stratum spinosum
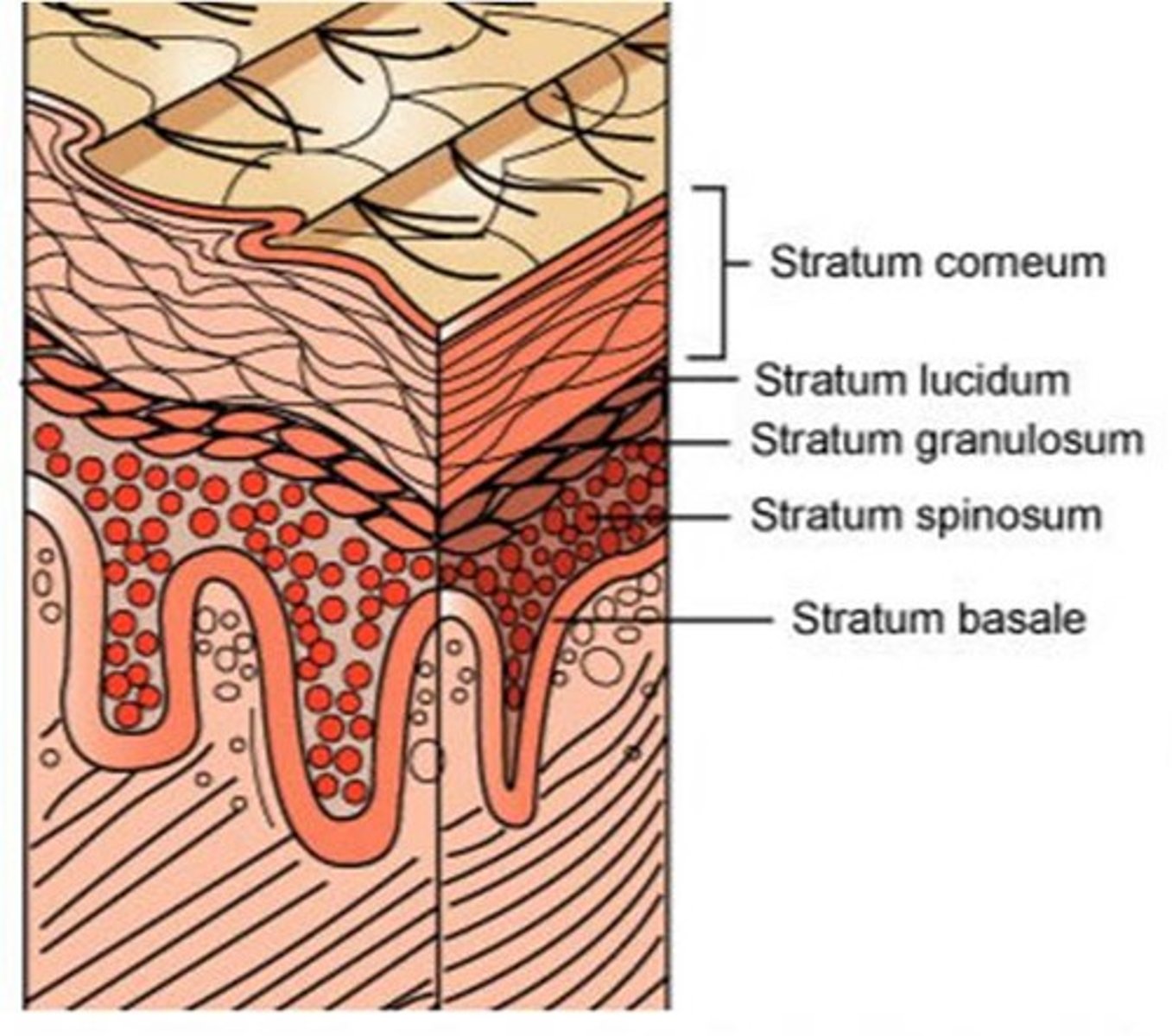
A layer of the epidermis that marks the transition between the deeper, metabolically active strata (living keratinocytes) and the dead cells of the more superficial strata
stratum granulosum
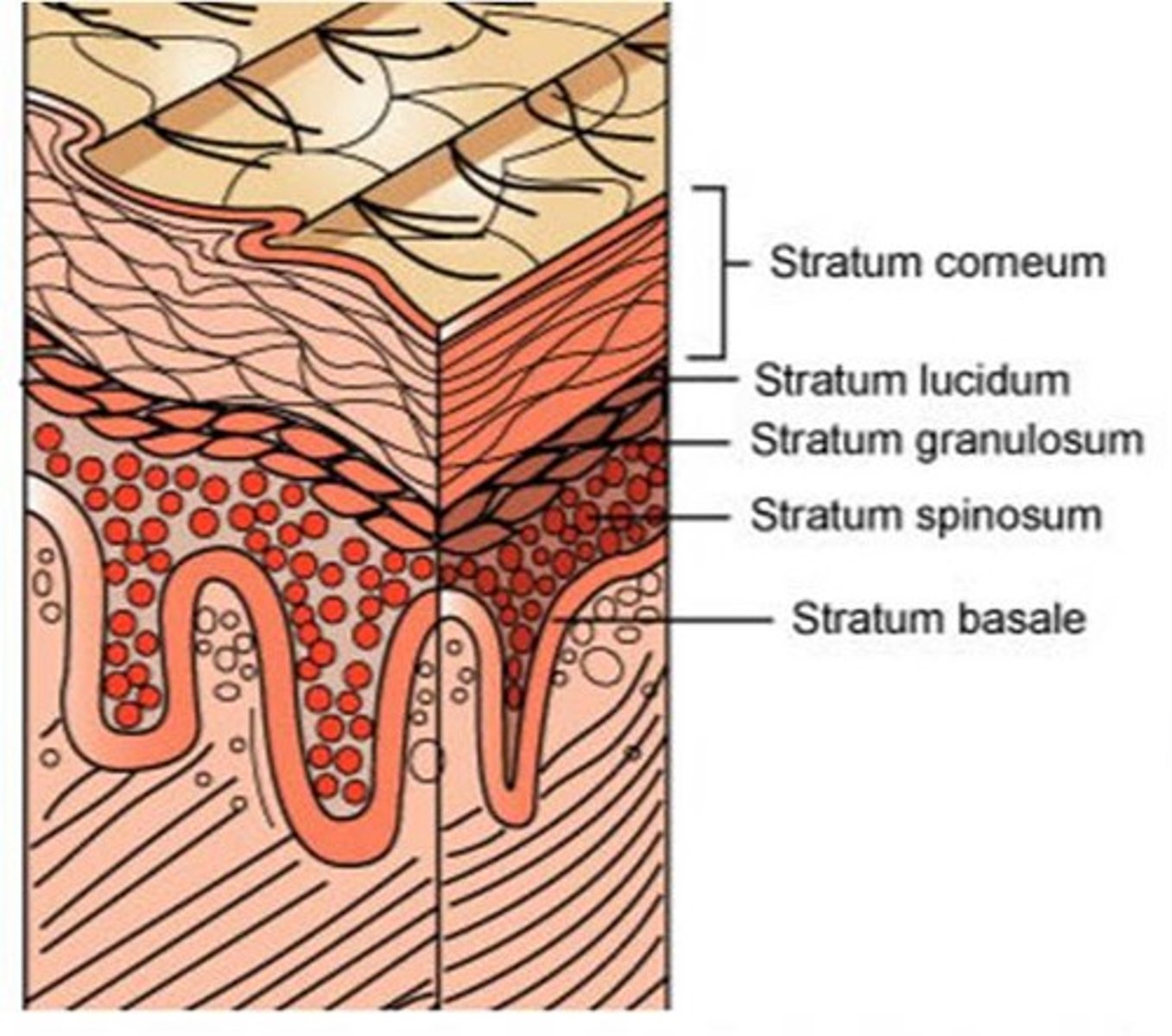
The most superficial layer of the epidermis consisting of dead cells
stratum corneum
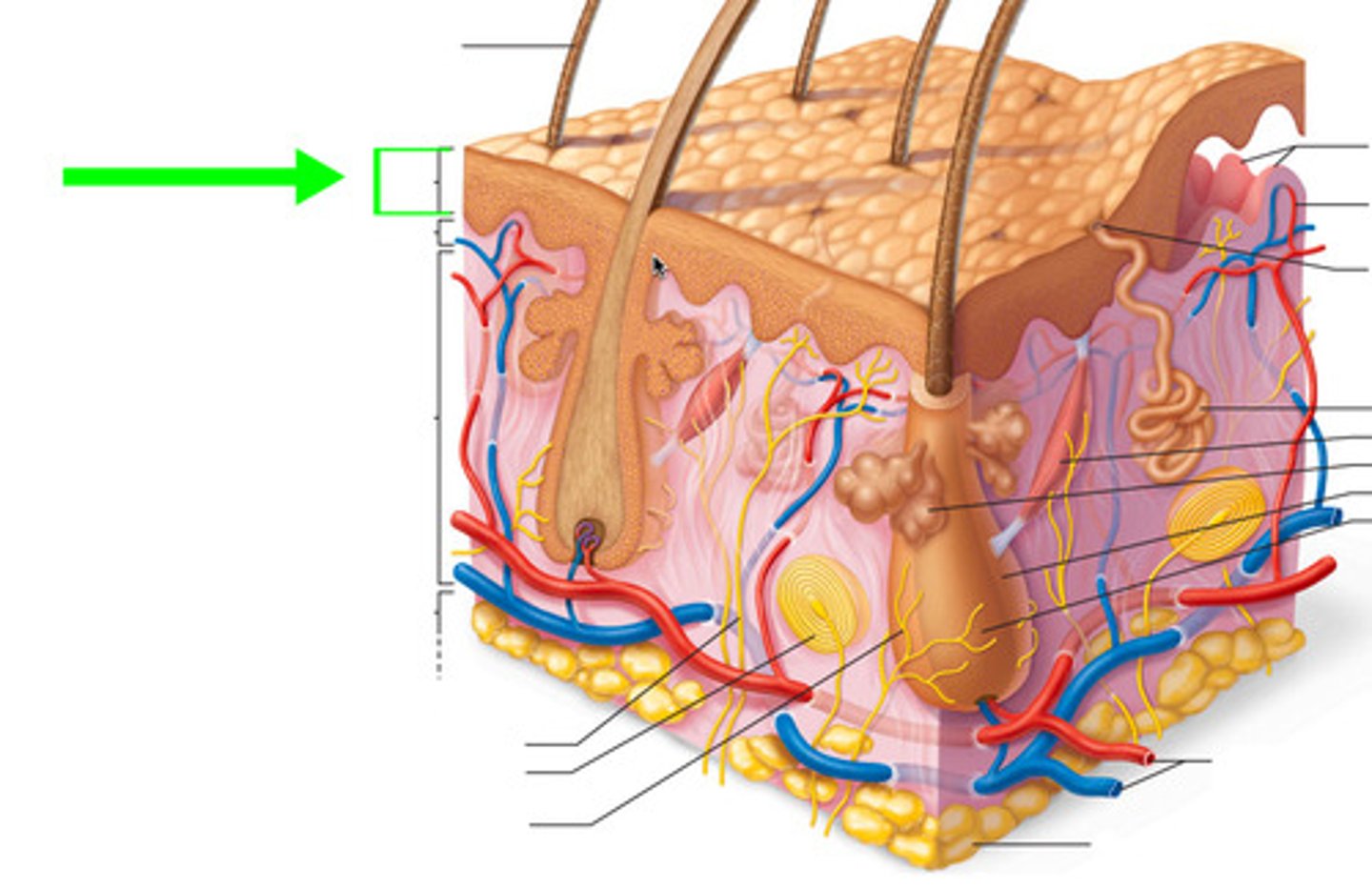
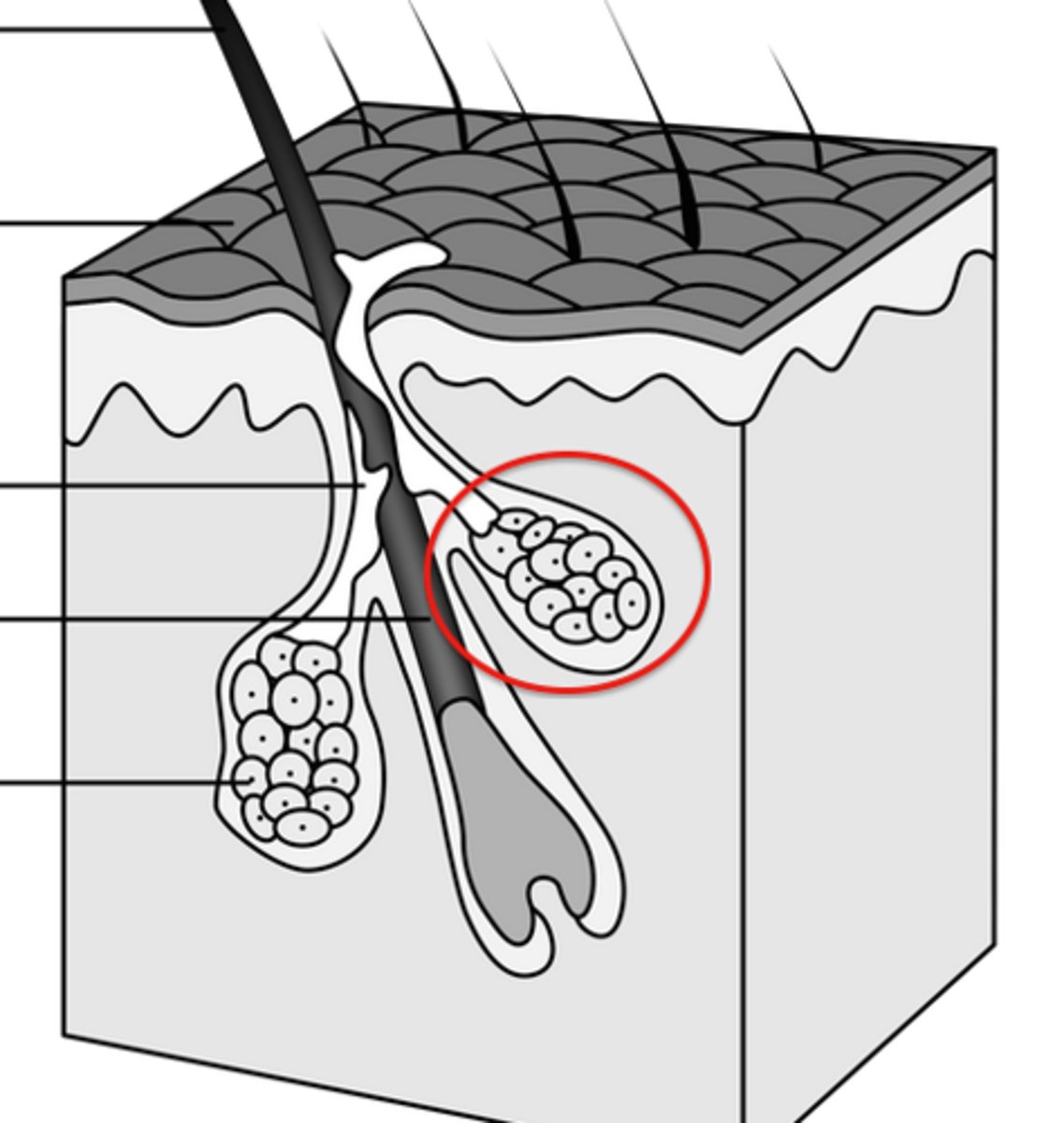
What 6 things does the dermis contain?
This layer of the skin contains sweat glands, hair follicles, and blood vessel. Additionally it has collagen, elastic tissue and reticular fibers.
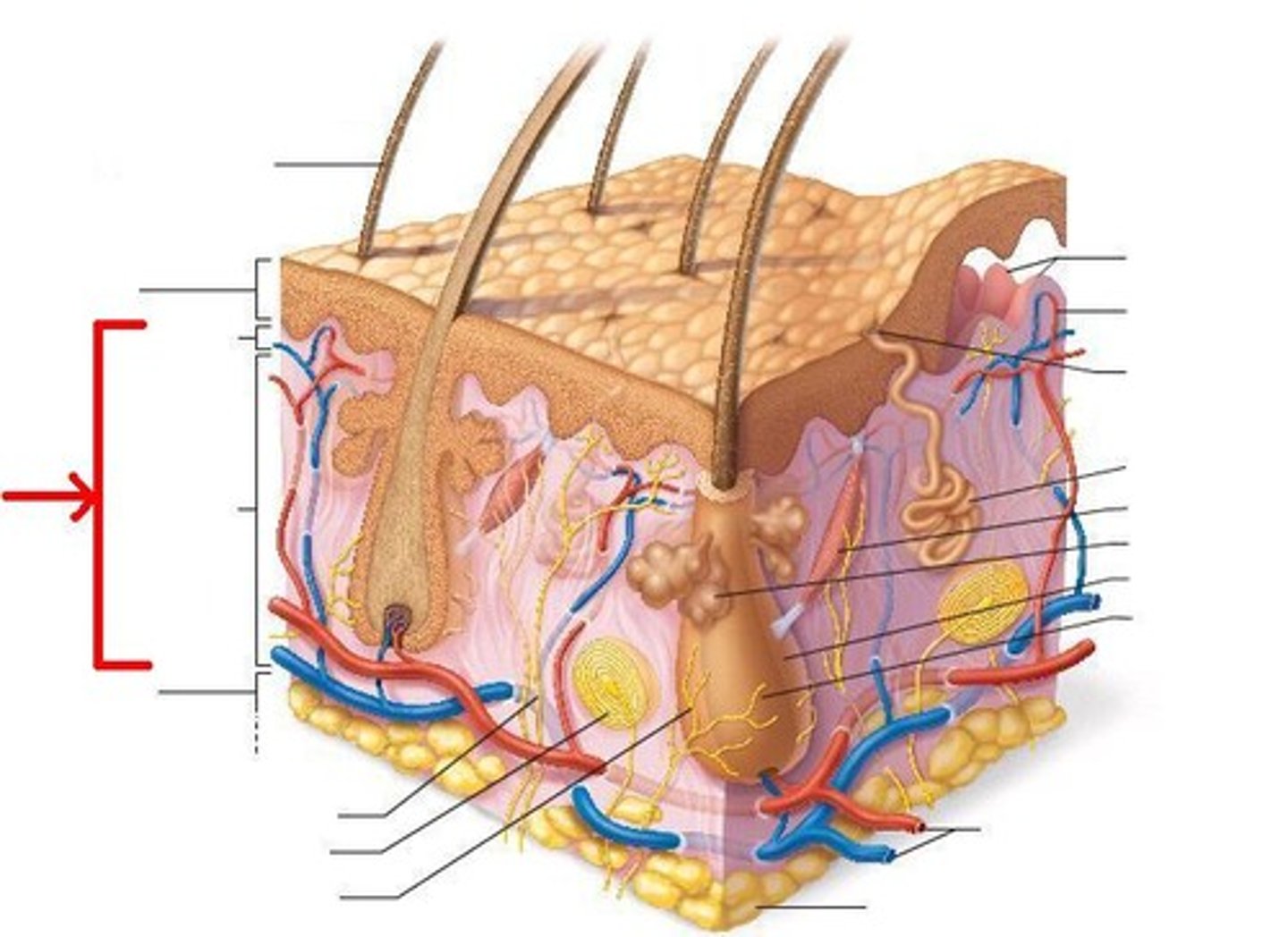
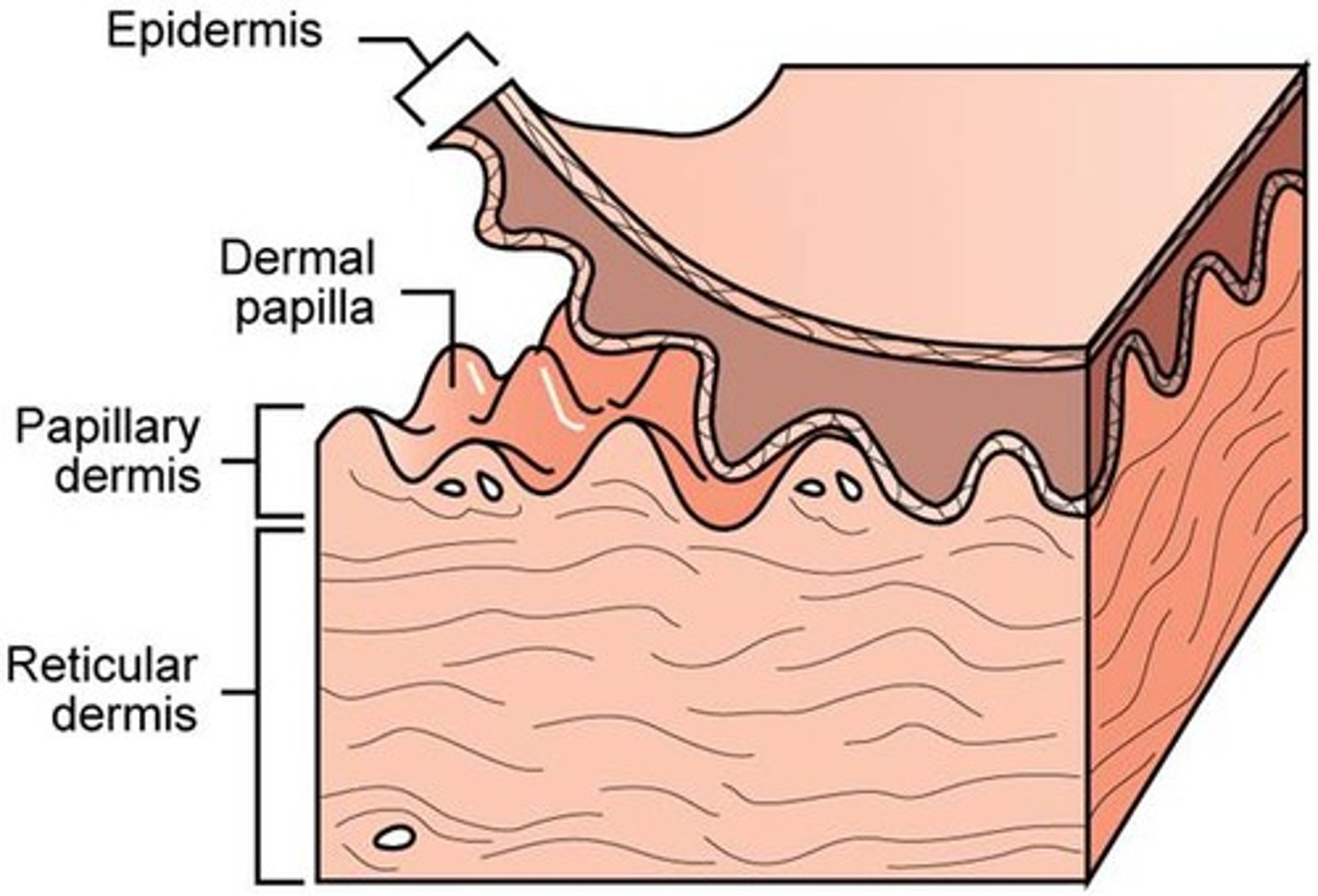
The dermis has a thin upper layer called the ?
papillary dermis
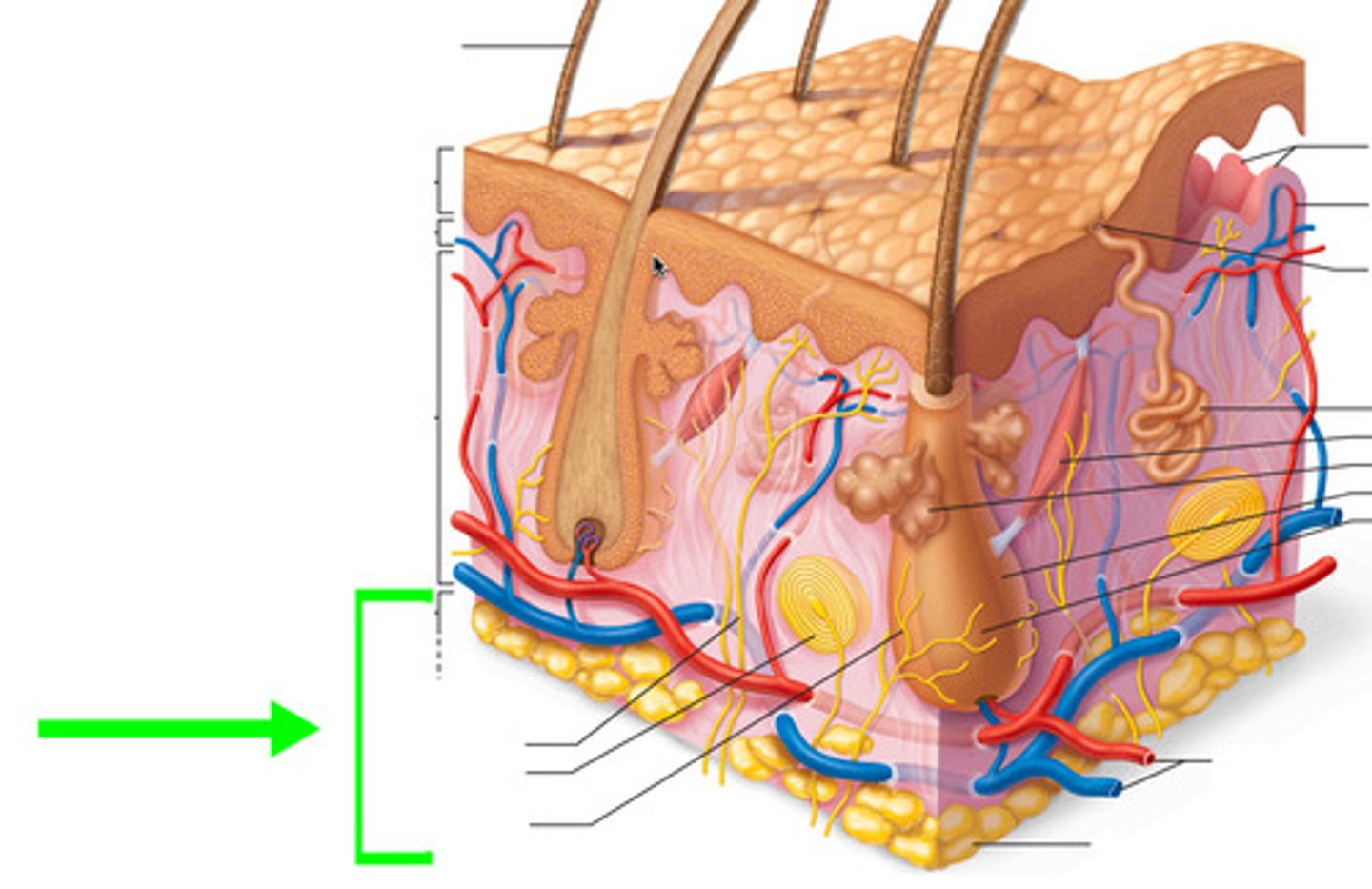
The thick lower layer of the epidermis extends toward?
Sub-Q
This layer of skin is composed of adipose tissue
Subcutaneous
This is a source of heat insulation and cooling where arrector pili muscle attach to, contract, causing them to stand erect and trap heat
hair follicle
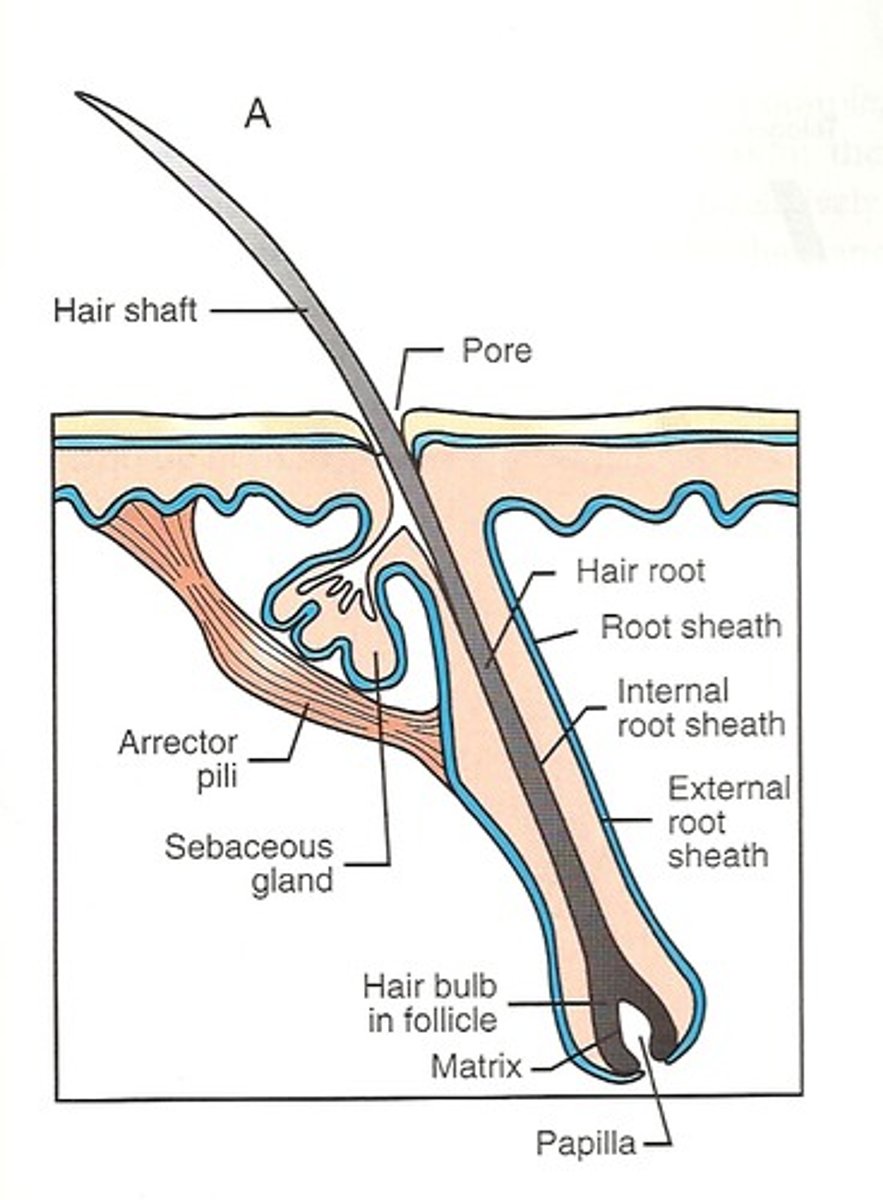
These lubricates hair follicles and provides water proofing and protection from friction to skin
sebacous glands
Fingernails grow _____ mm per week.
What is the visible portion of the nail?
0.5-2mm/week
Lunula
How long does it take a fingernail to grow from matrix to free edge?
5.5 months
How long does it take for a toenail to grow from matrix to free edge?
12-18 months
When describing lesions what does
1. discrete
2. confluent
1. lesions are separated
2. running together
how the lesions are defined
margination
What type of surface changes can we characterize lesions?
1. Keratotic
2. Necrotic
3. Ulcerated
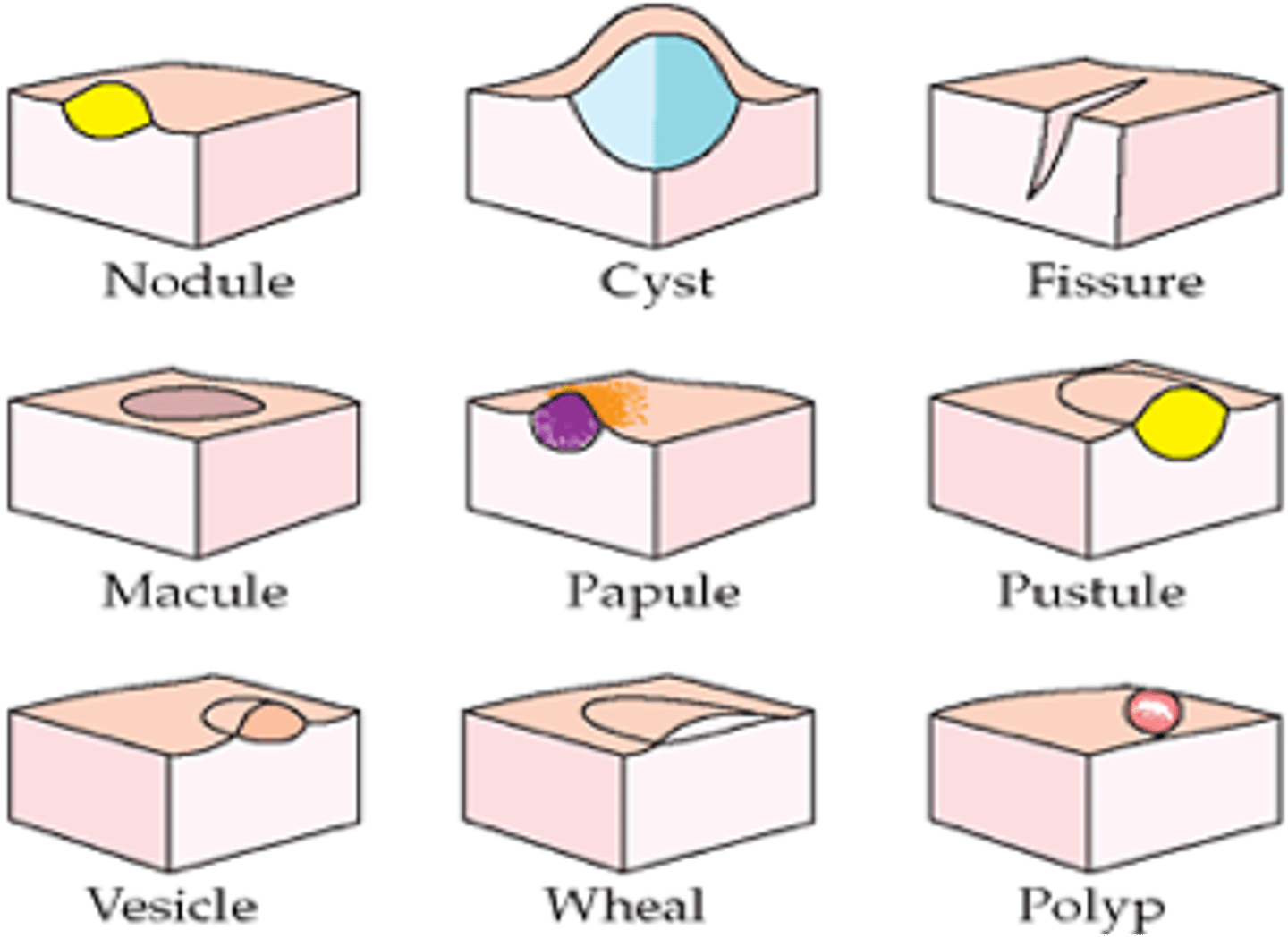
What are the primary lesions?
1. Macules
2. Patches
3. Papules
4. Plaques
5. Nodules
6. Wheals
7. Vesicles
8. Bullae
9. Pustules
Flat discoloration less than <1 cm
- Ex: Ephelid (freckle)
Macule (primary lesion)
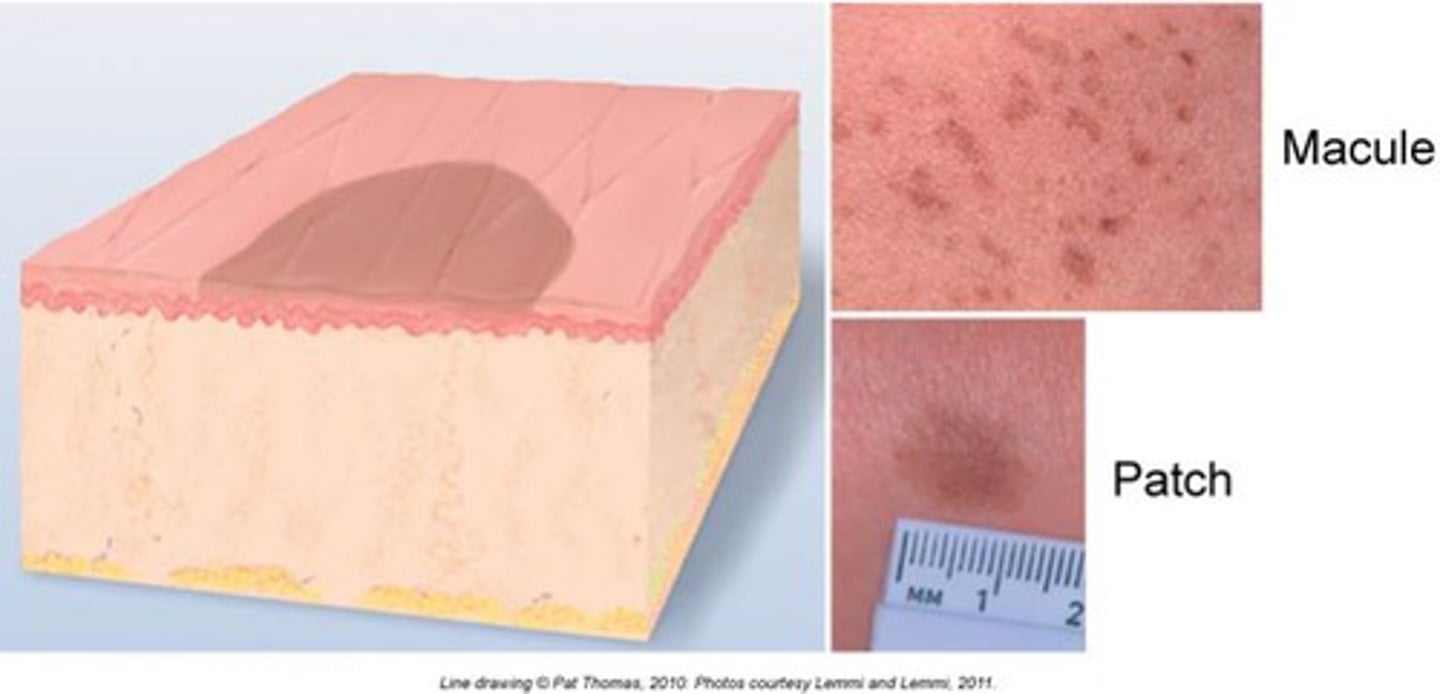
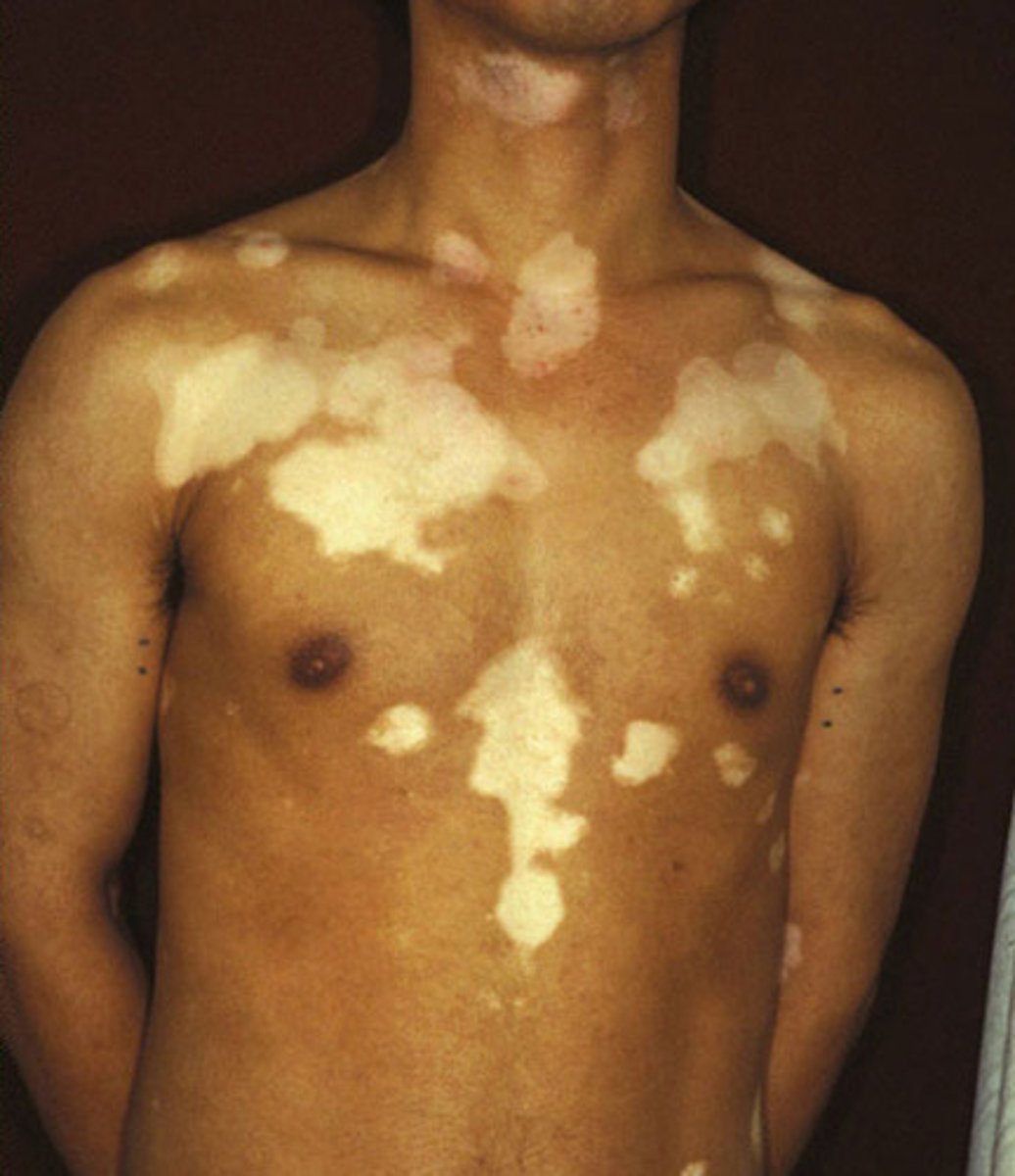
Flat discoloration greater than 1 cm
- Ex: Vitiligo, Cafè Au Lait
Patch (primary lesion)
Raised lesion < 5 mm
- Ex: verruca (wart), Molluscum contagiosum
Papule (primary lesion)
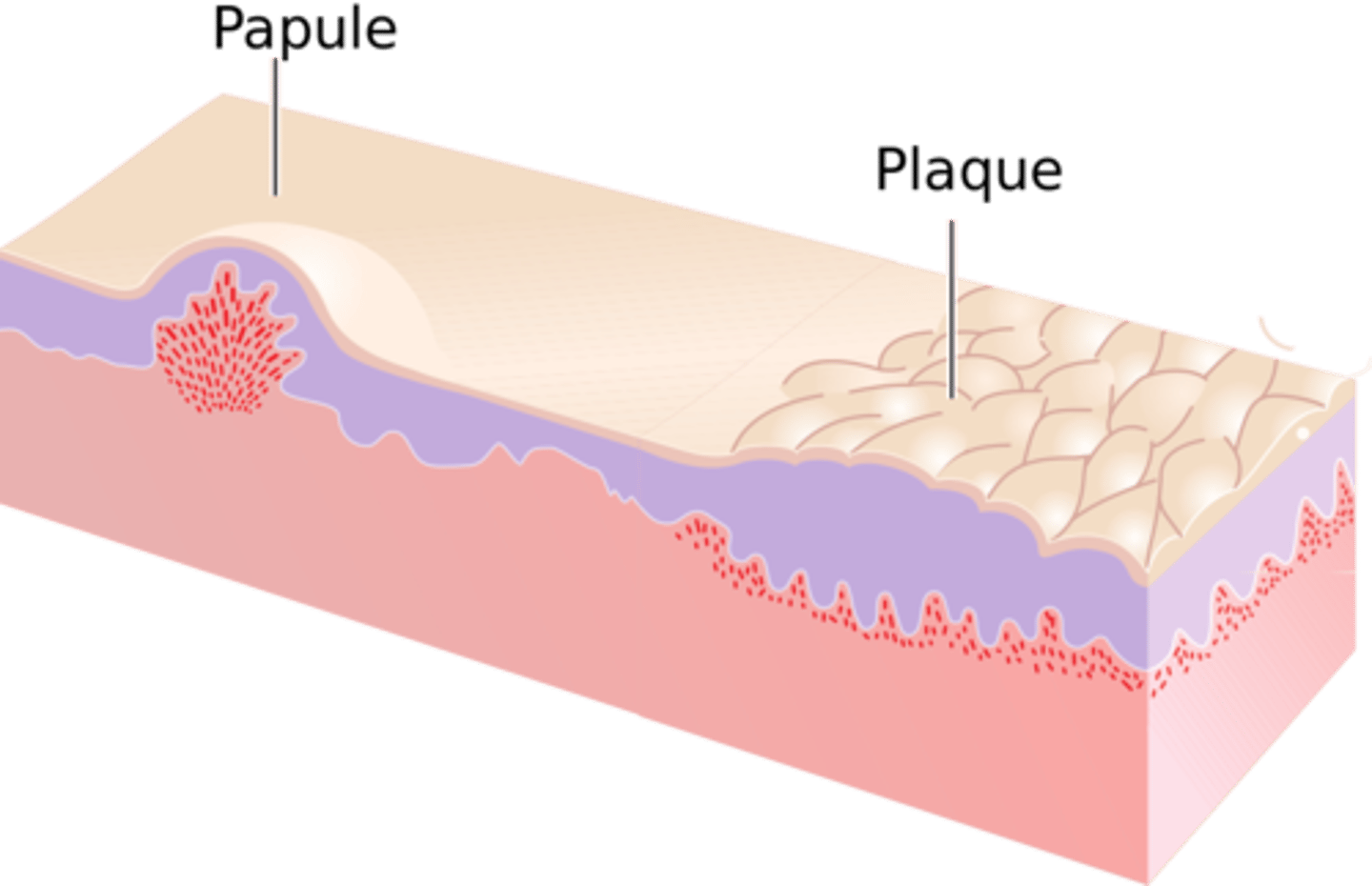
Raised lesion > 1 cm
- Can have secondary changes (scale, crust, erosion)
- Ex: Psoriasis
Plaque (primary lesion)
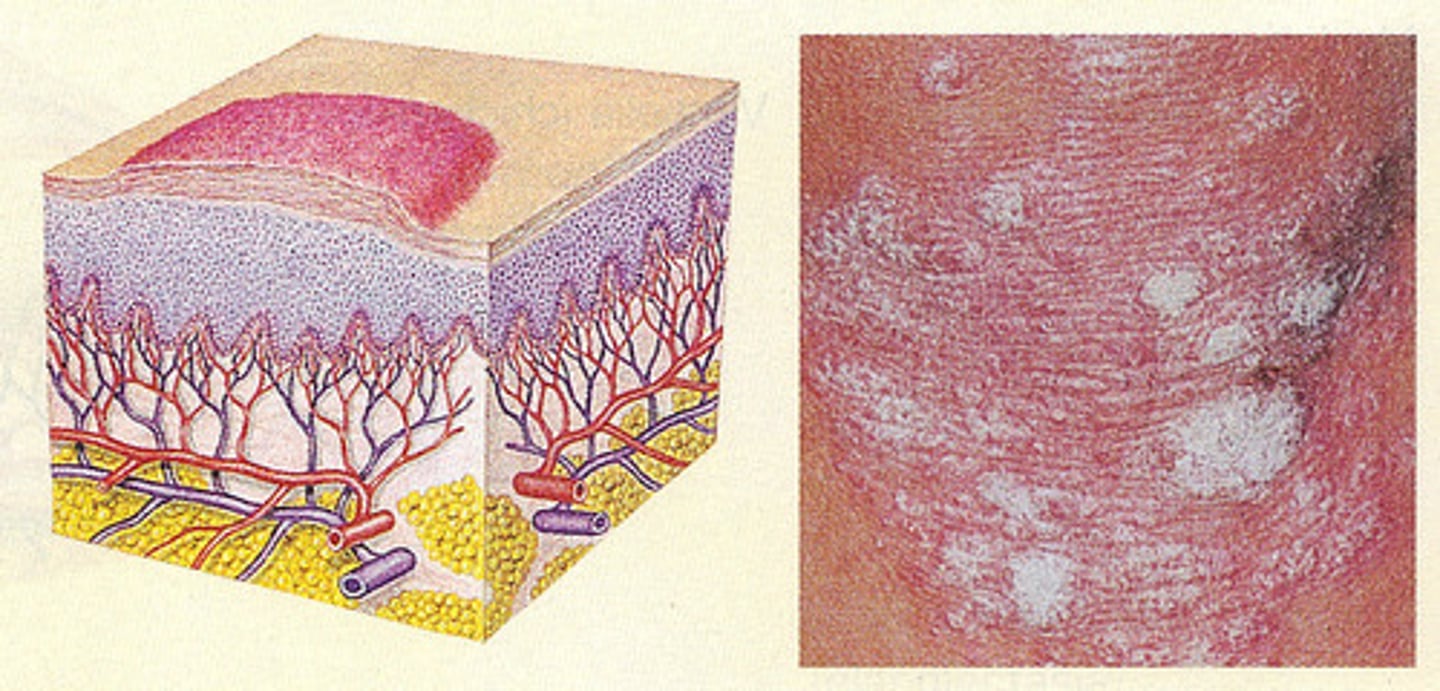
- Solid, circumscribed, raised, deeper and firmer than a papule.
- Extends to the dermis and possible subcutis
- >5mm, Often >1.5cm
- Can be compressible, soft,rubbery, or firm
- Ex. Lipoma, nodular melanoma, erythema nodosum
Nodule (primary lesion)
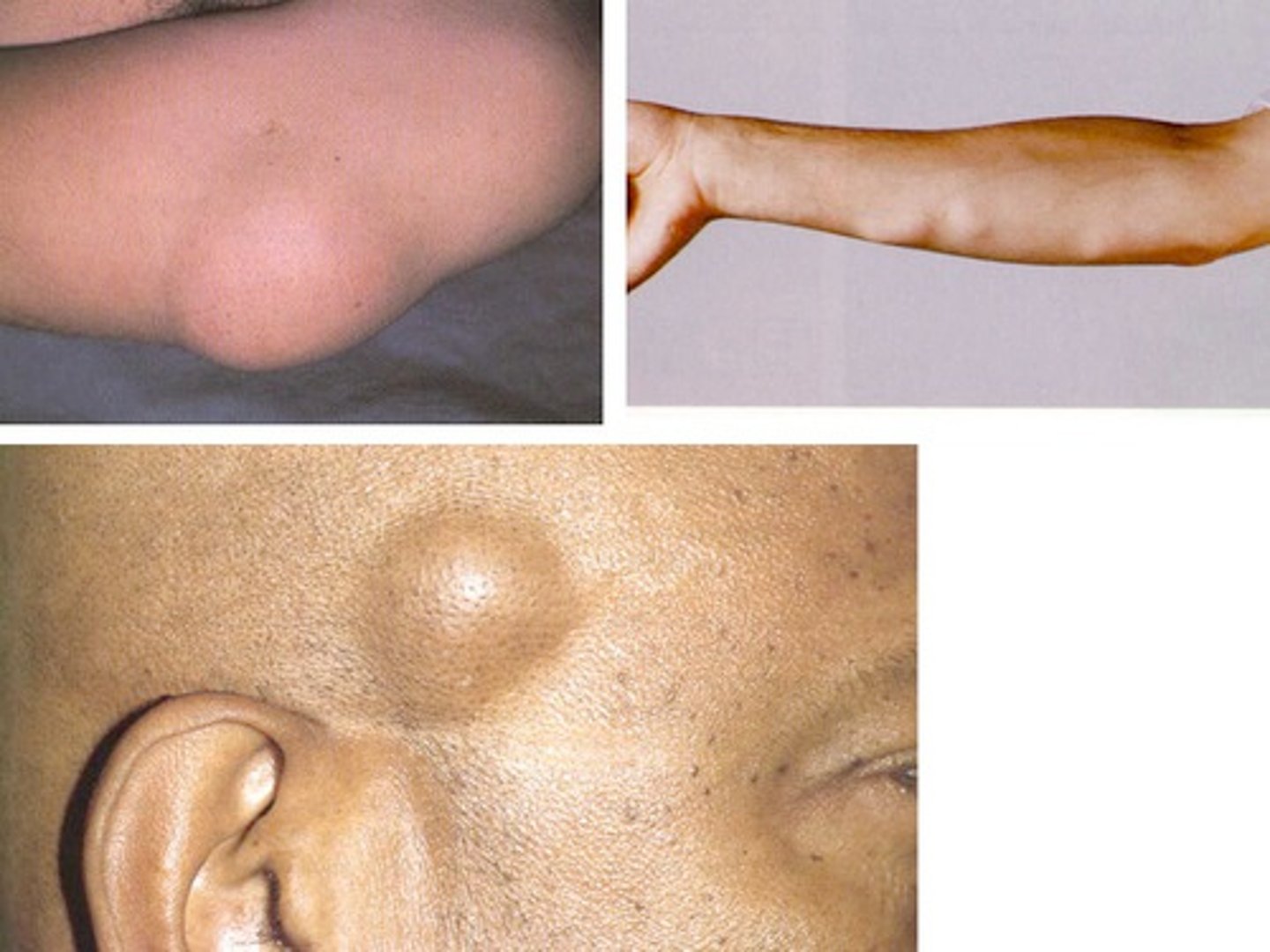
- Transient elevated lesion that lasts only a few hours
- Local edema
- >0.5/10 cm
- Ex. Urticaria/hives
Wheal (primary lesion)
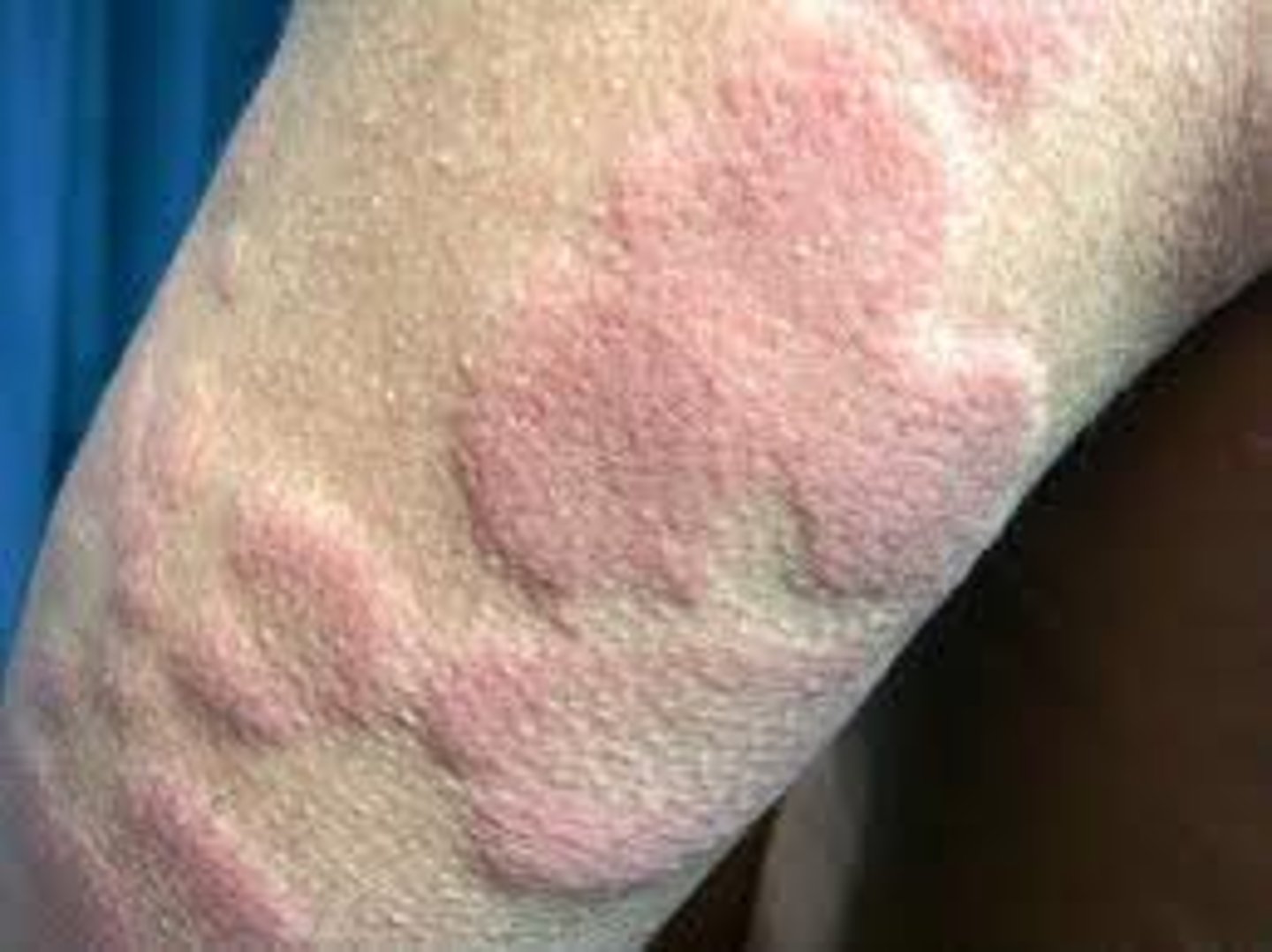
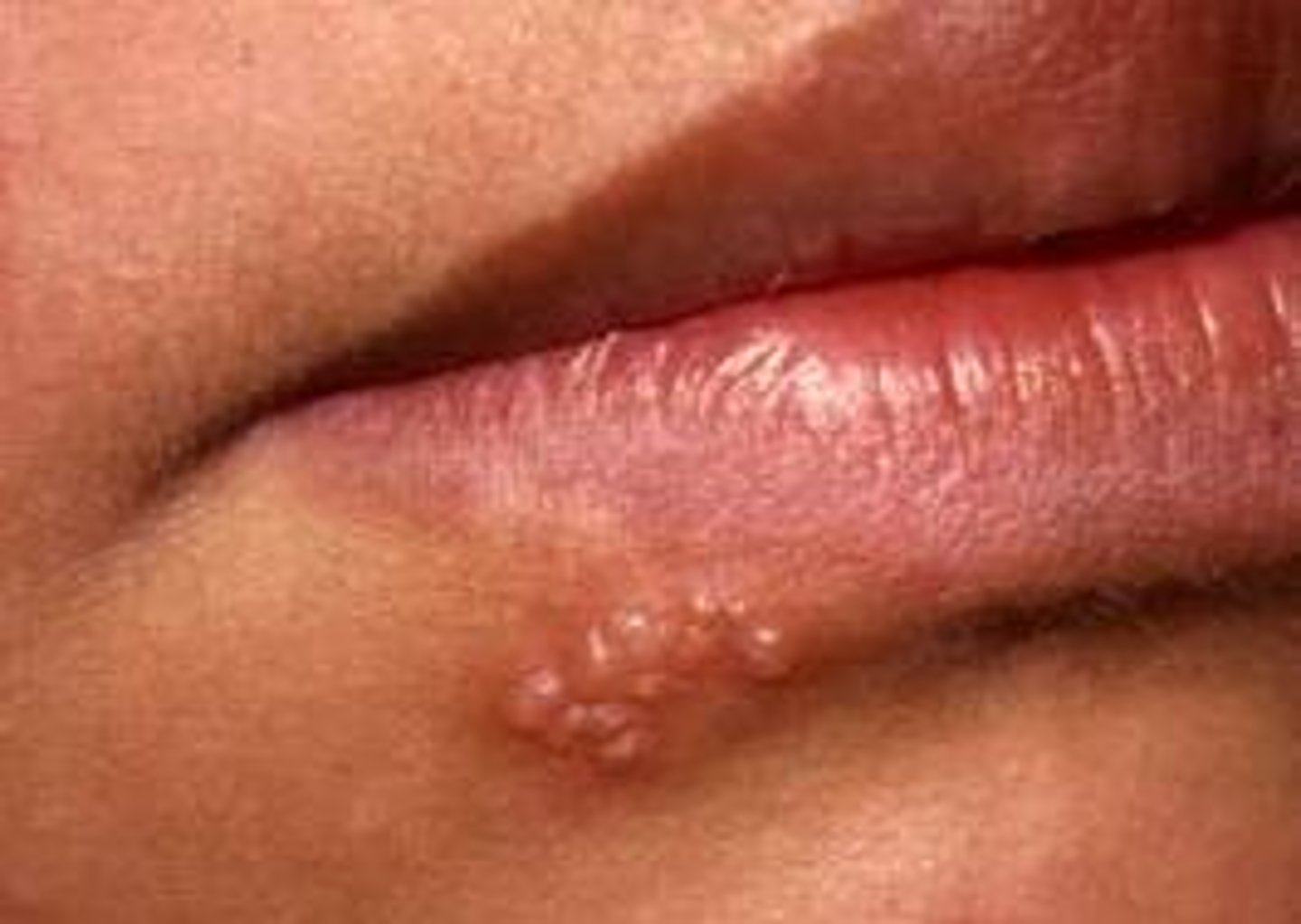
- Circumscribed fluid filled, elevated lesion
- <5mm
Ex. Herpes Simplex, dyshidrotic eczema, allergic contact dermatitis
Vesicle (primary lesion)
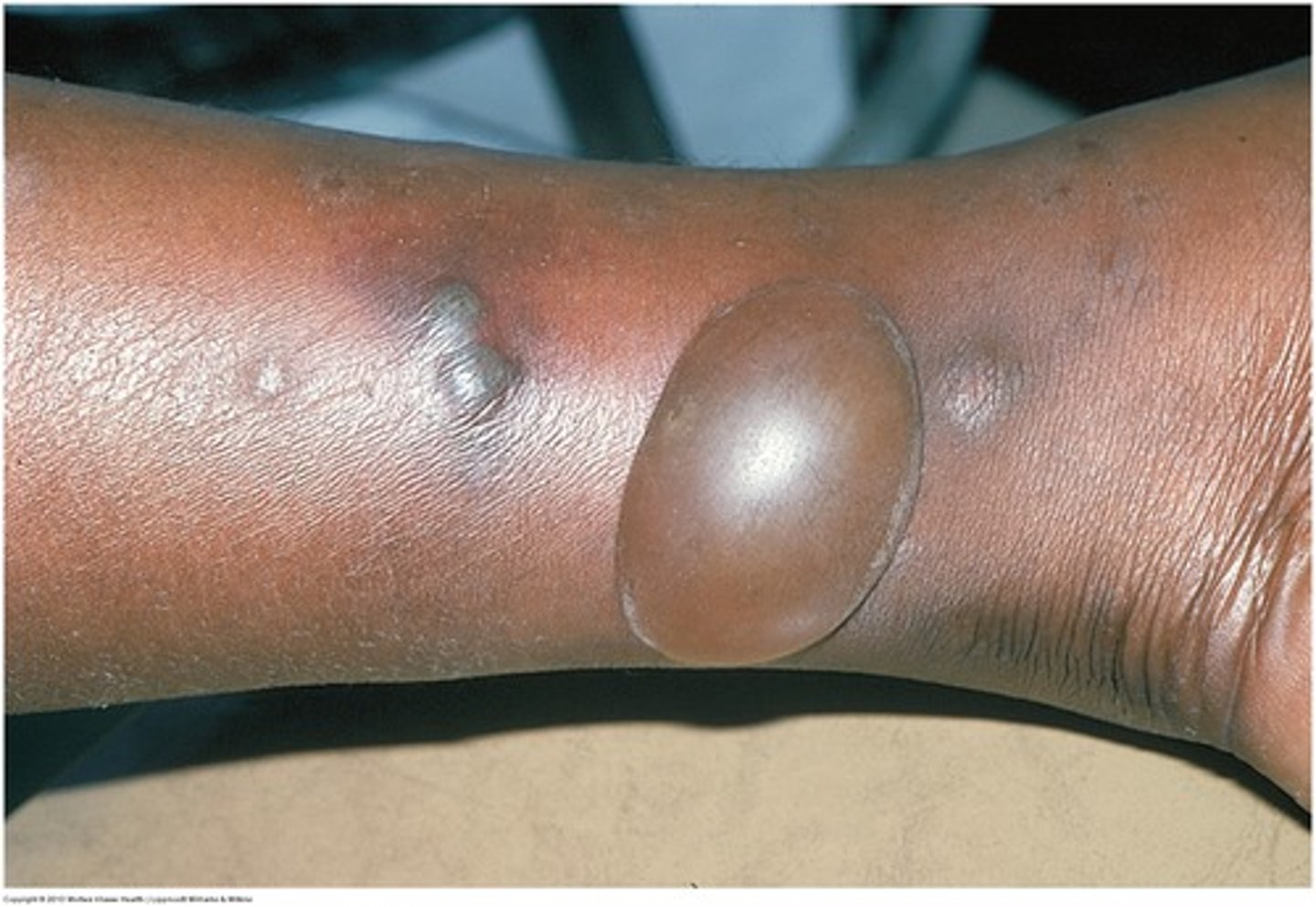
- Circumscribed, fluid filled lesion
- >5mm
Bullae (primary lesion)
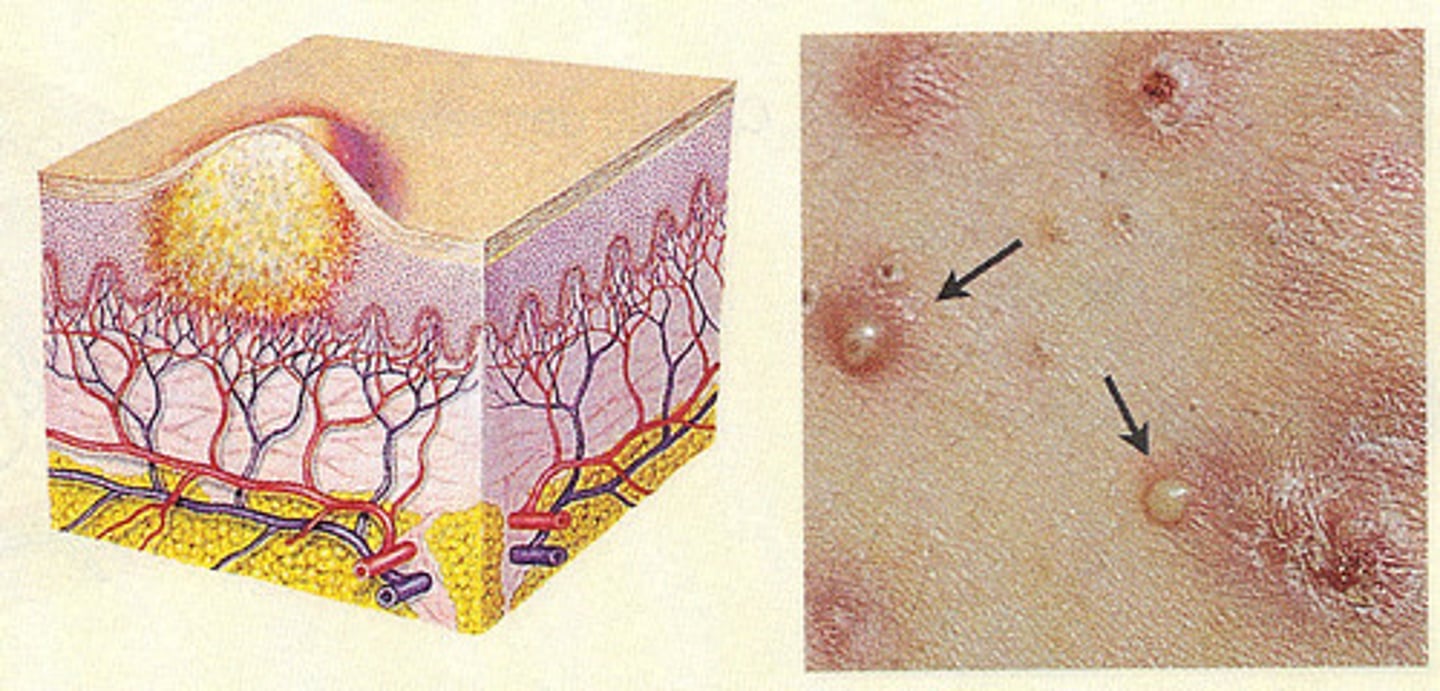
- Elevated, circumscribed, filled with purulent material
- May be infectious or sterile
- Ex. Pustular psoriasis, Folliculitis, Acne vulgaris, Rosacea
Pustule (primary lesion)
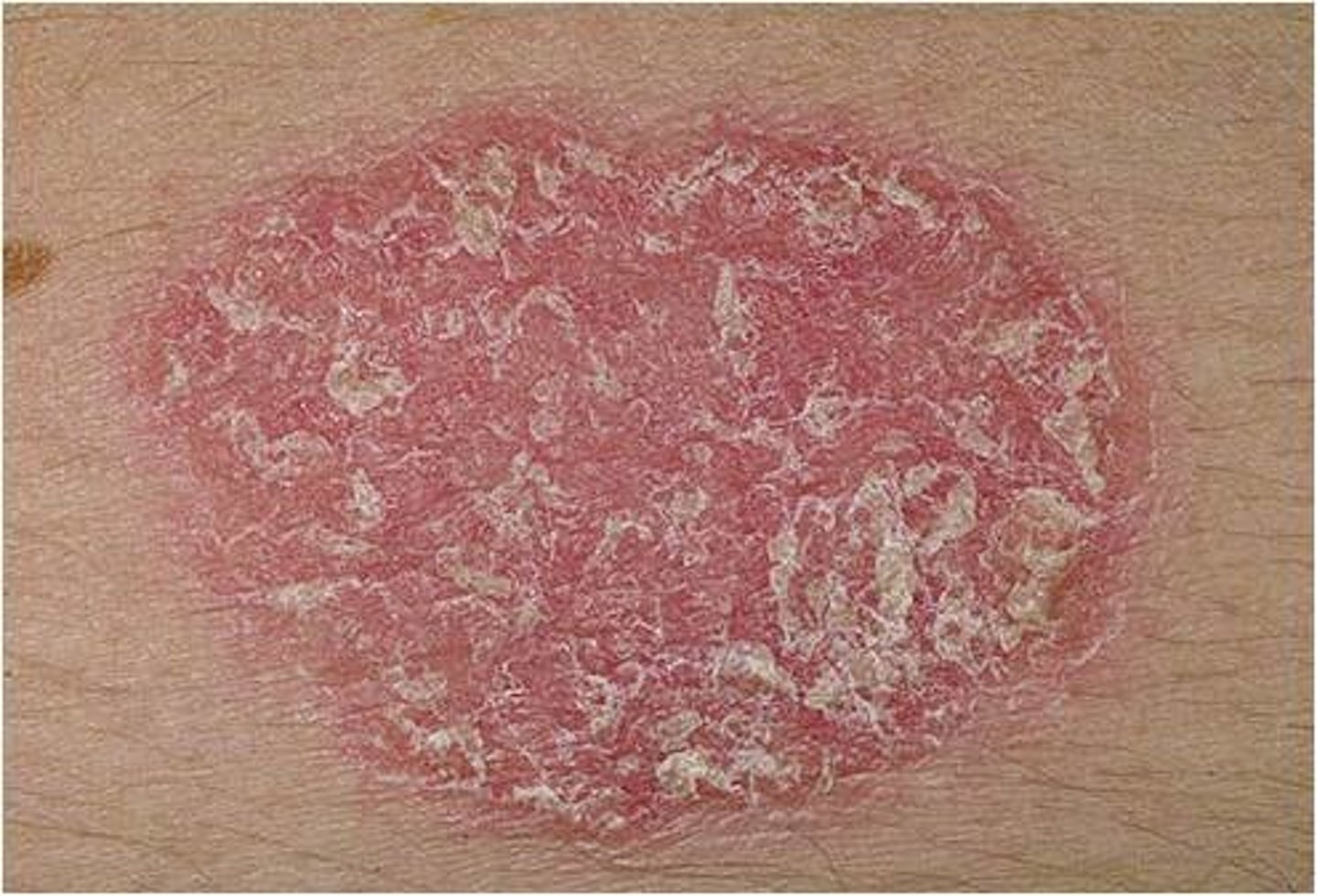
Secondary lesion characterized by excess dead skin
- Hyperkeratosis
- Increased stratum corneum due to increased proliferation or delayed desquamation
Ex. Psoriasis, Tinea corporis, actinic keratosis
Scales (secondary lesion)
Secondary lesion characterized by dried sebum (serous), blood (hemorrhagic), or pus
-Ex. Impetigo
Crusts (secondary lesion)
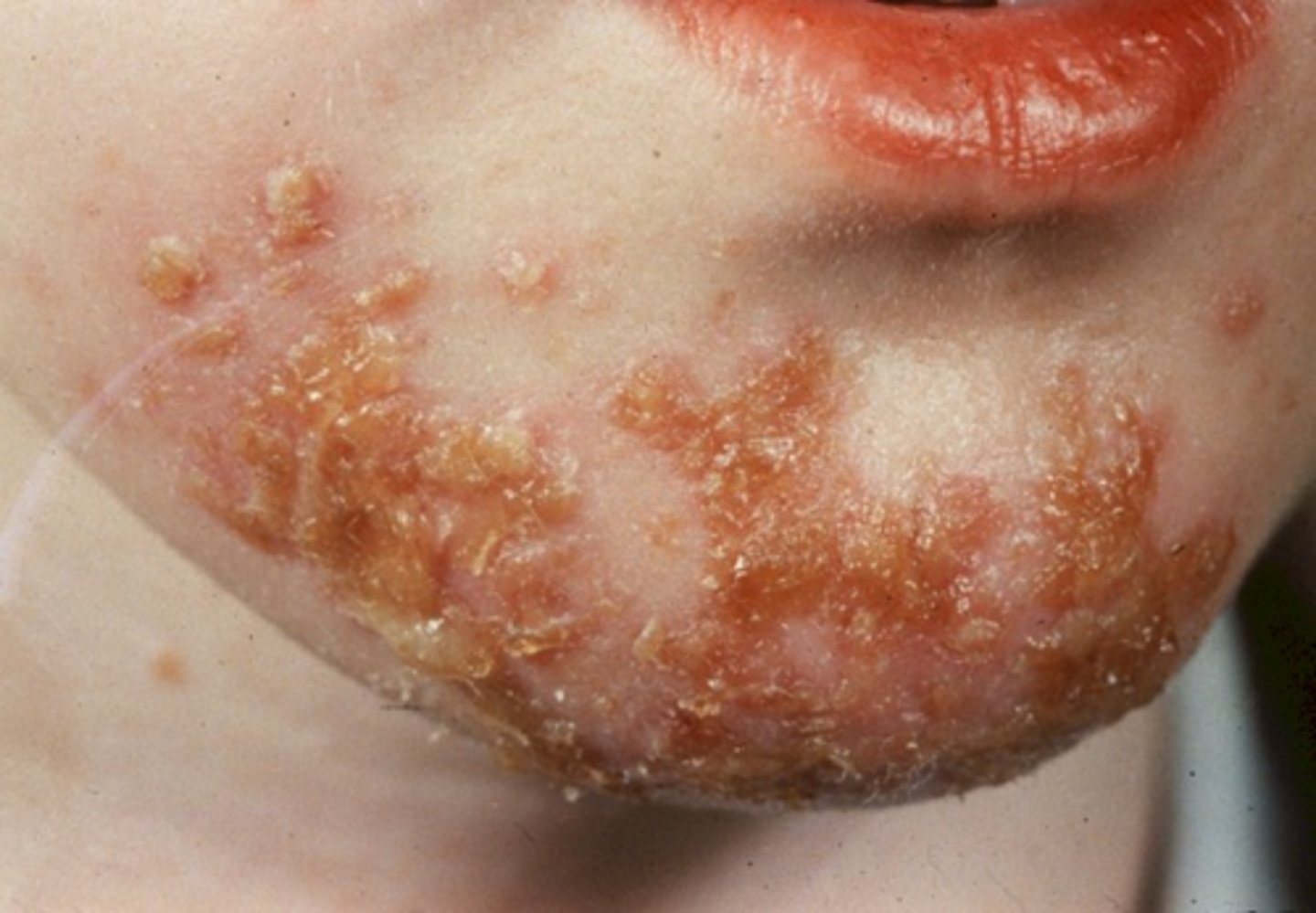
- Exogenous injury to all or part of the epidermis often due to scratching
- Ex. Acne excoriee, neurotic excoriations, any pruritic condition
Excoriation (secondary lesion)
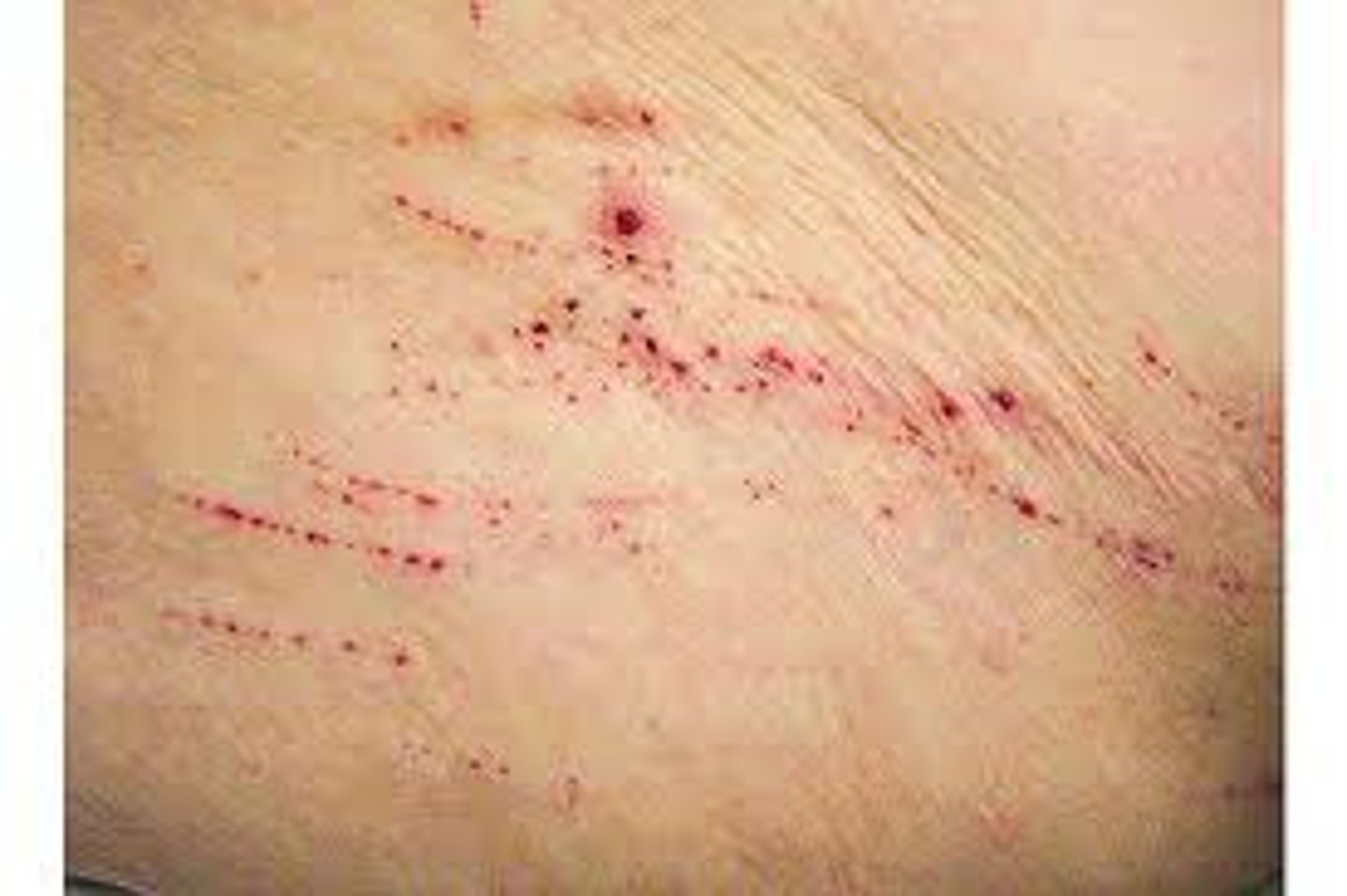
-Linear loss of epidermis. Crack/slit in skin that is painful
- Can be caused by dry skin, skin thickening, and loss of elasticity
- Ex. Hand dermatitis
Fissures (secondary lesion)
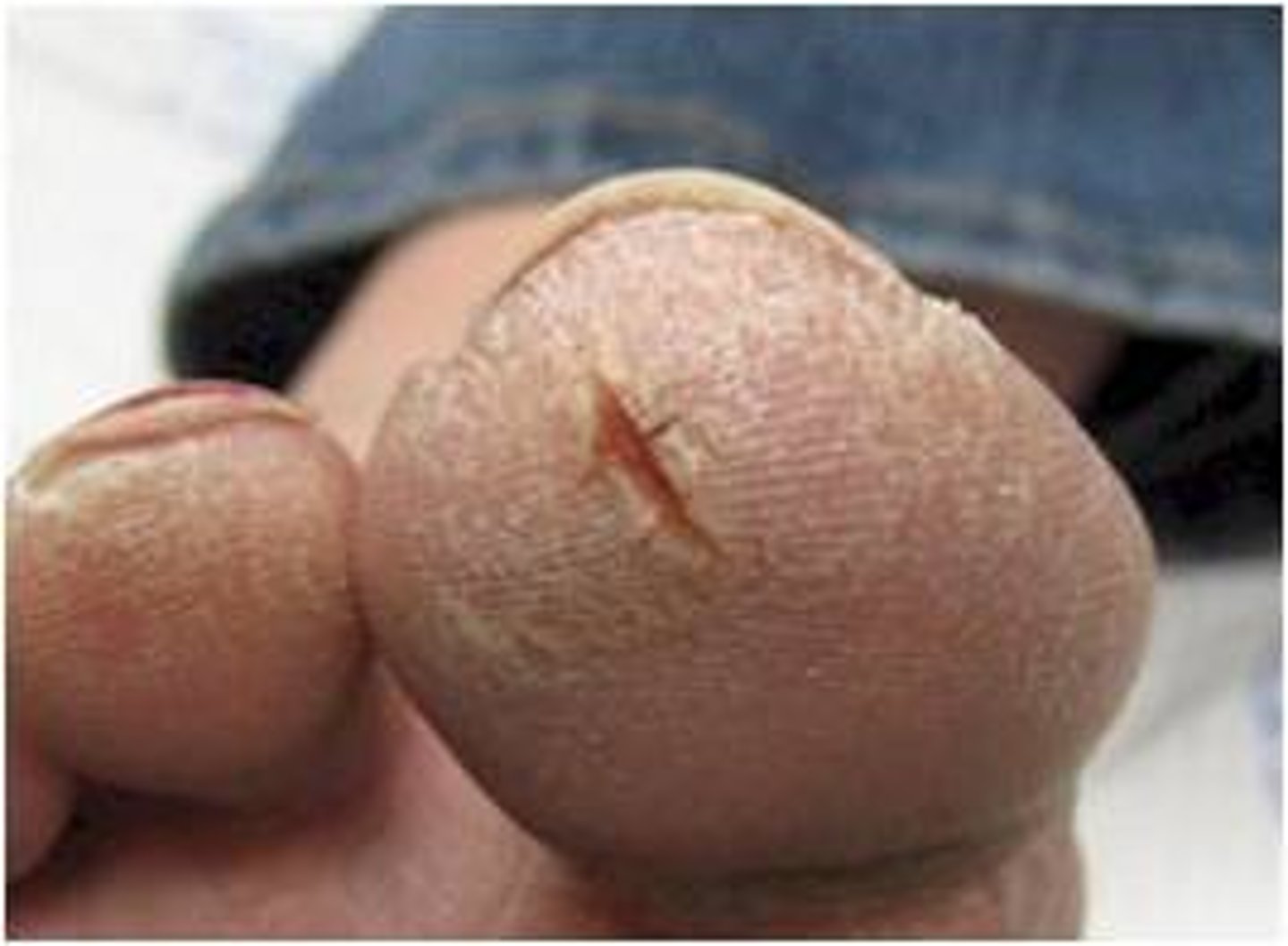
- Partial or complete loss of epidermis.
- Appears moist, oozing, and/or crusted
- Ex. Friction, trauma, impetigo, staphyloccal scaled skin syndrome
Erosions (secondary lesion)
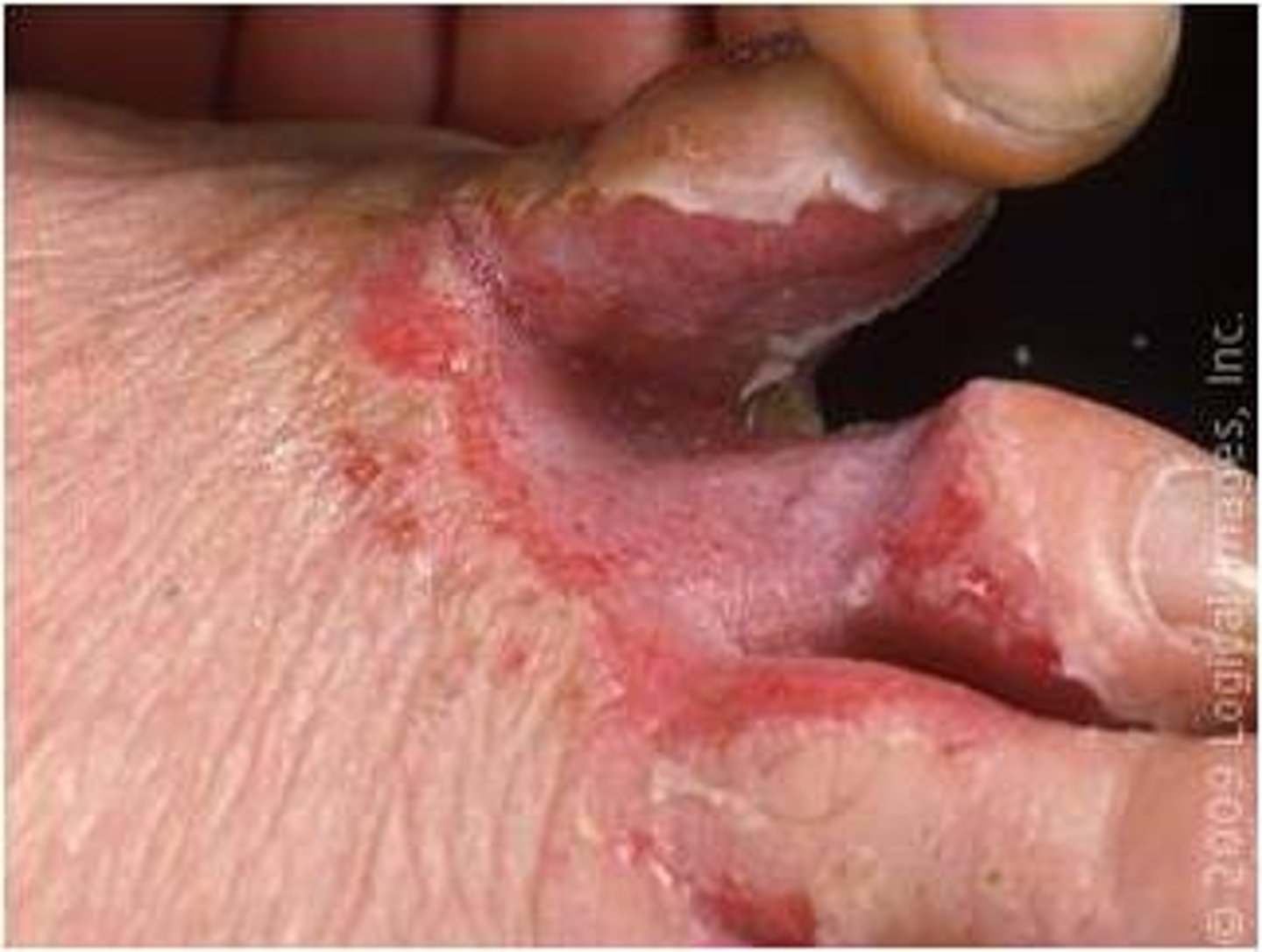
- Deeper than erosion with loss of epidermis and at least superficial dermis
- Can extend deeper
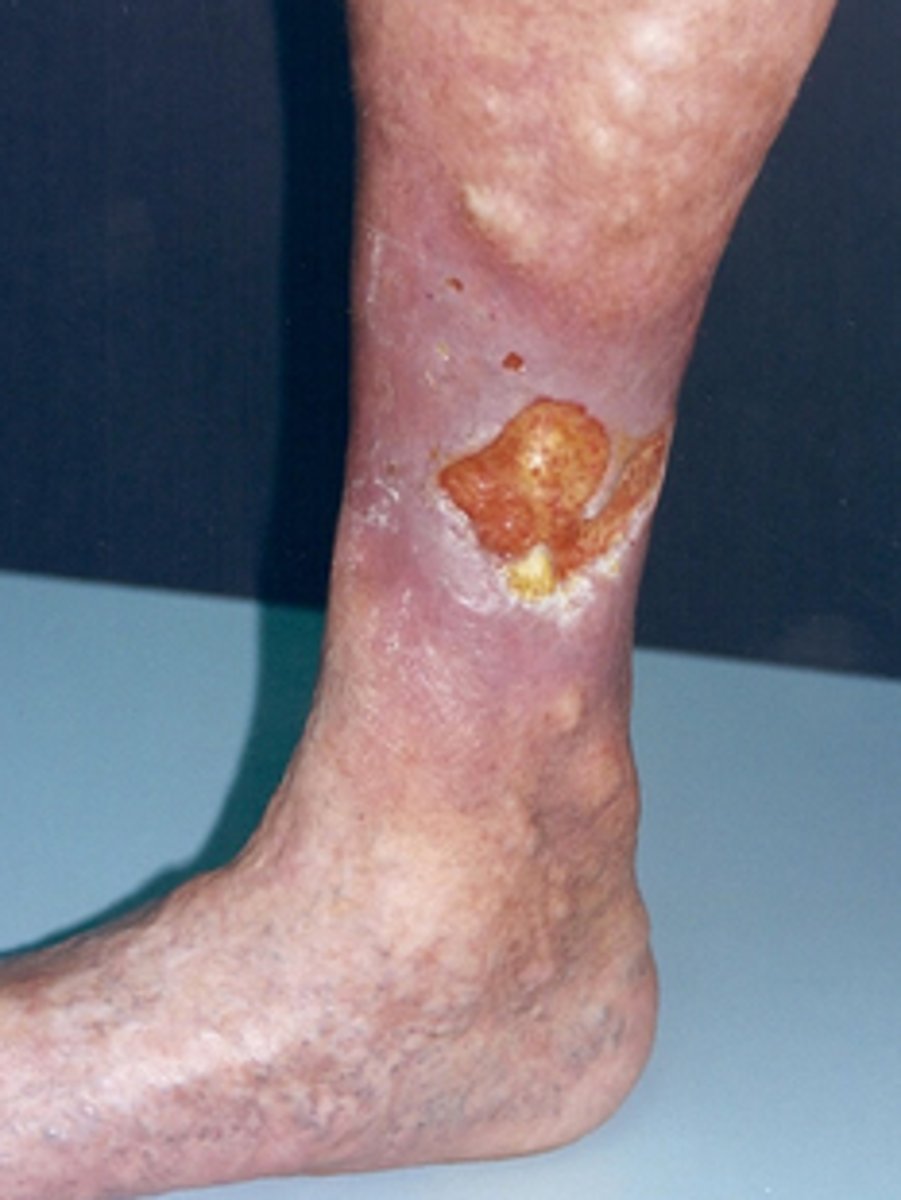
- Ex. Stasis dermatitis, aphthous ulcer, decubitus ulcer, arterial ulcer
Ulcer (secondary lesion)
Fibrous tissue replacement after a tissue defect
(Wound or ulcer)
Scars (secondary lesion)
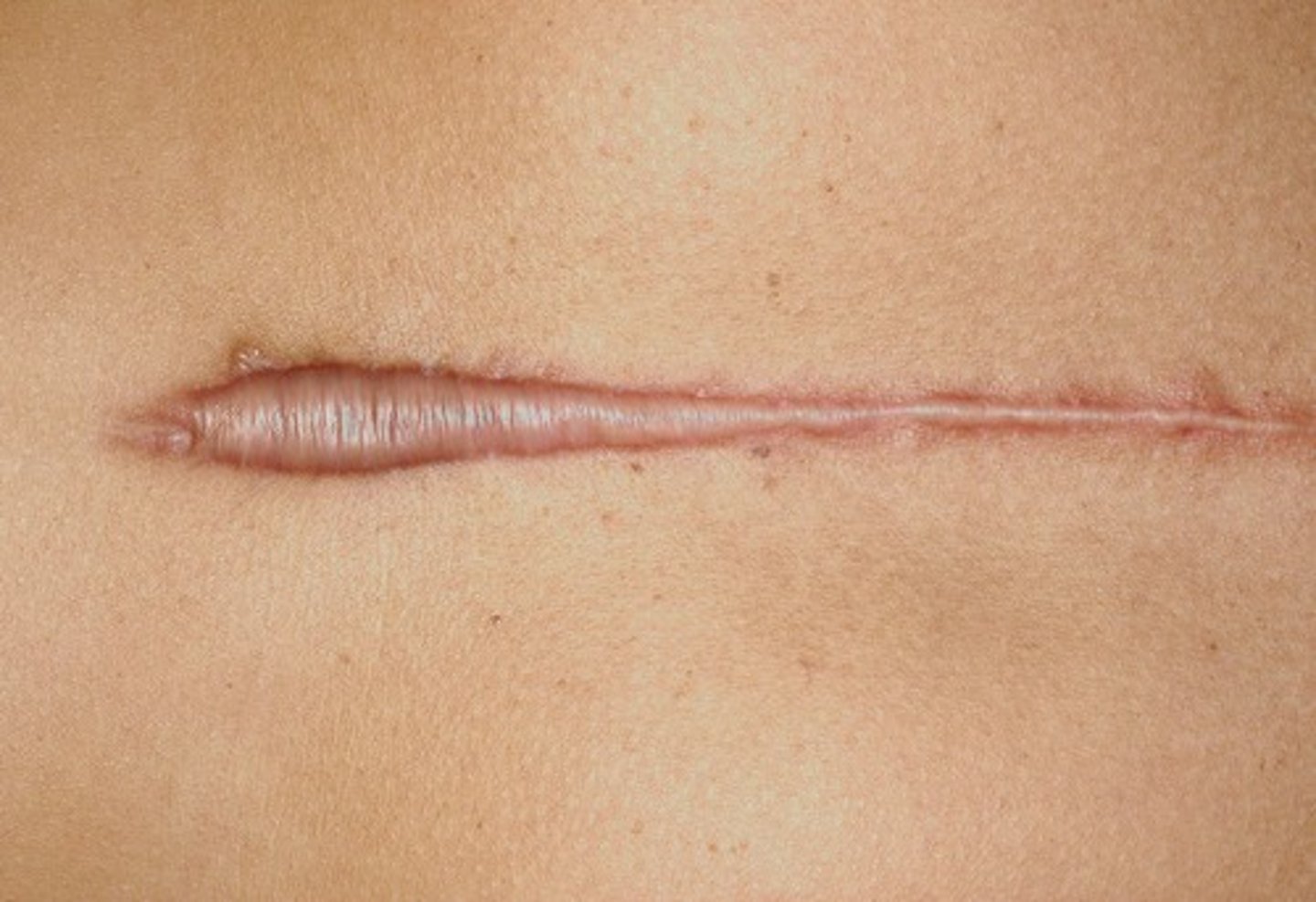
These types of scars grow being the site of injury
Keloids (secondary lesion)
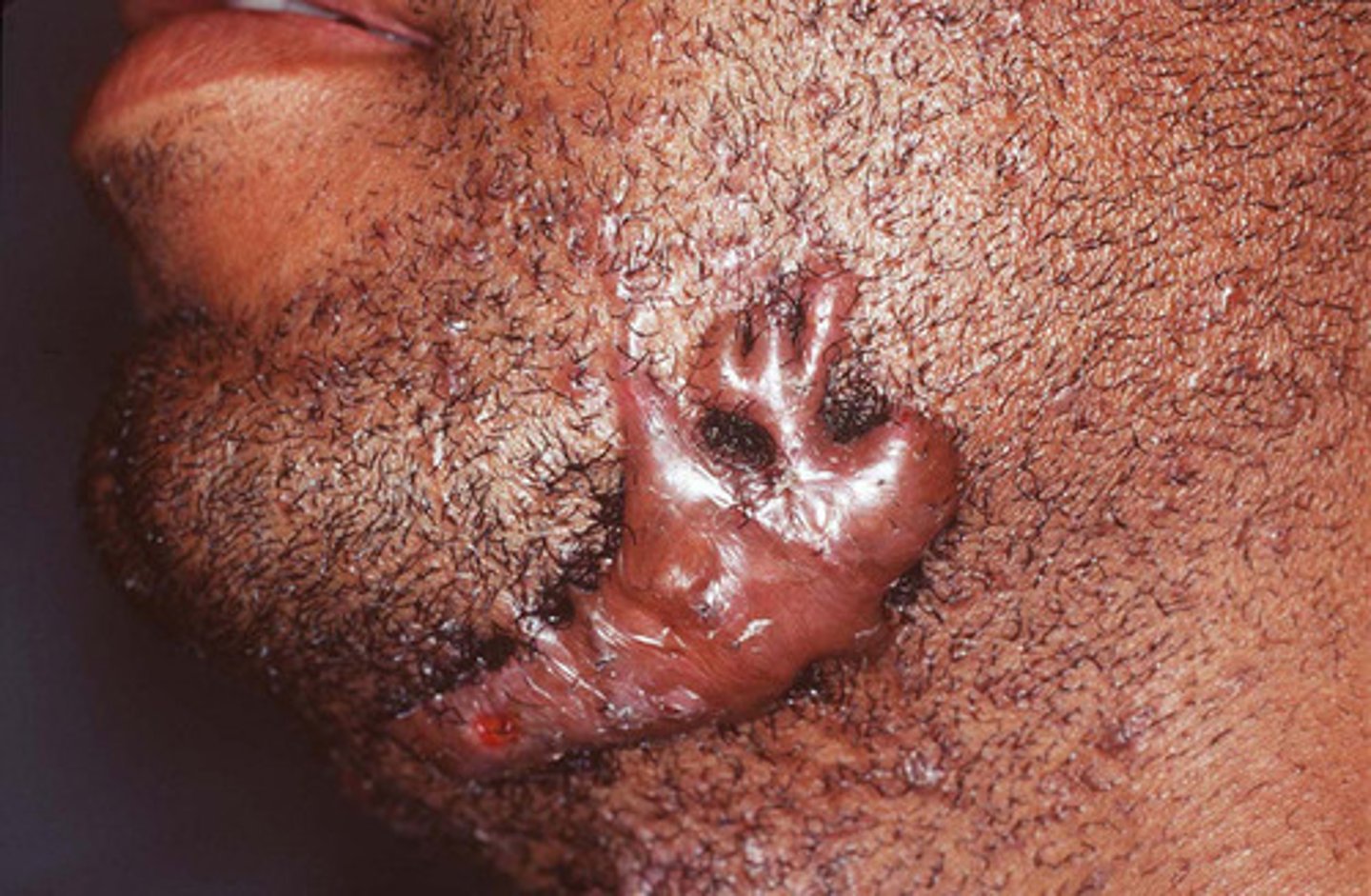
Thickening of epidermis and accentuation of natural skin lines
- Ex. Lichen simplex chronicus, atopic dermatitis
Lichenification (secondary lesion)
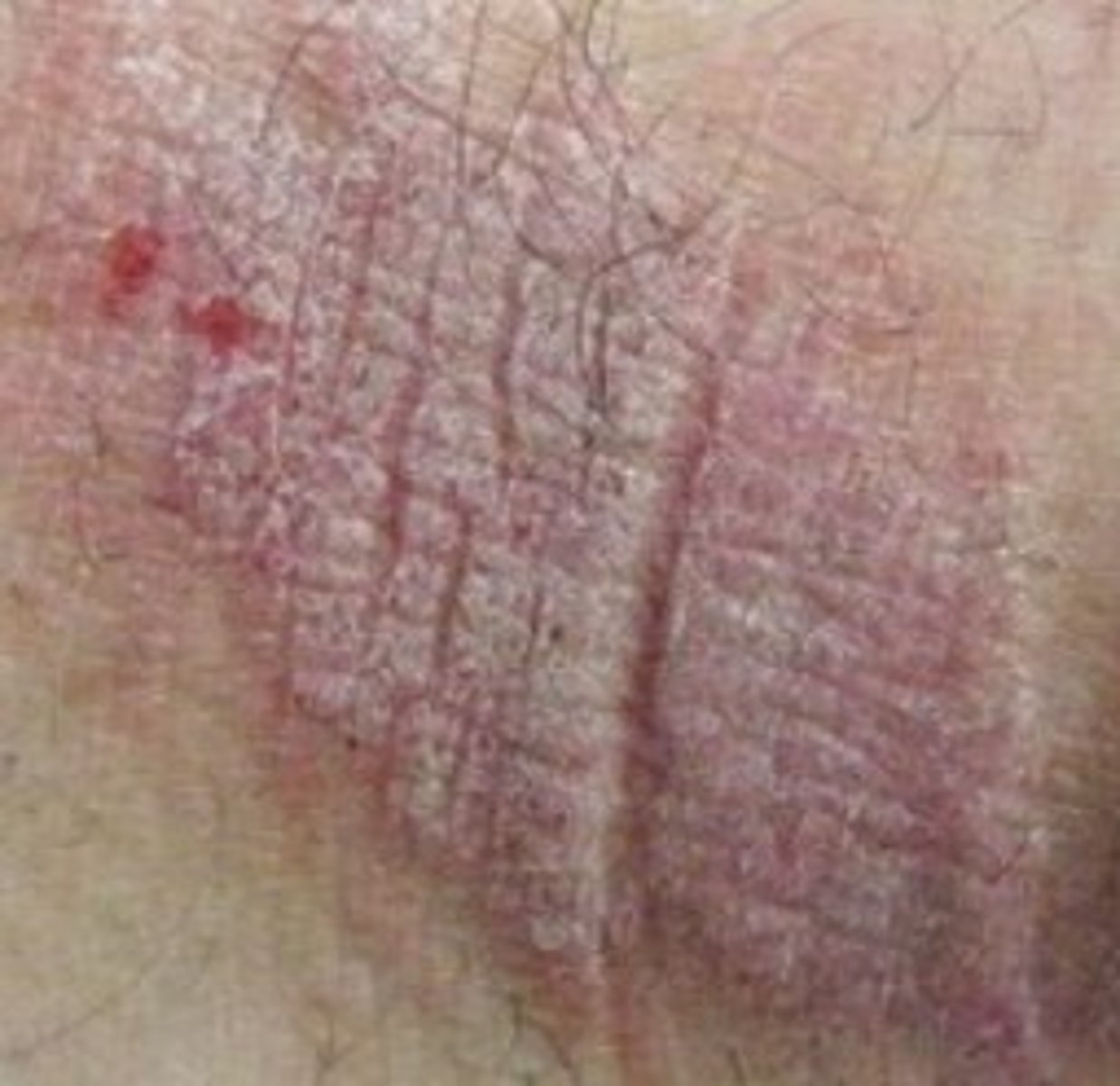
What does lichinification indicate?
Chronic eczema/chronic scratching
- Thinning of epidermis
- Appears wrinkly and shiny
- If loss of dermal collagen or elastin can appear depressed
Atrophy (secondary lesion)
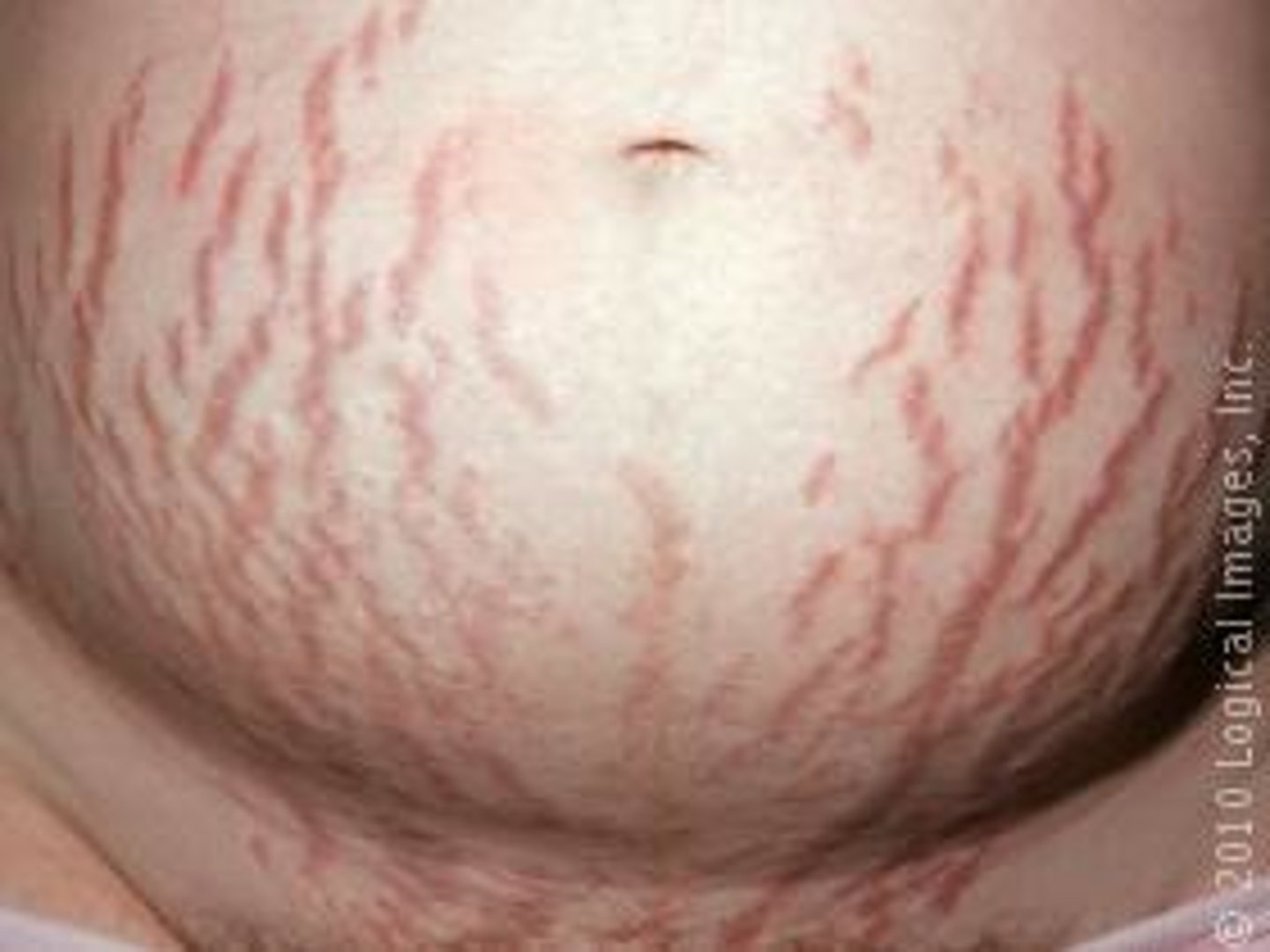
Cavity containing liquid, solid, or semisolid material
Cysts
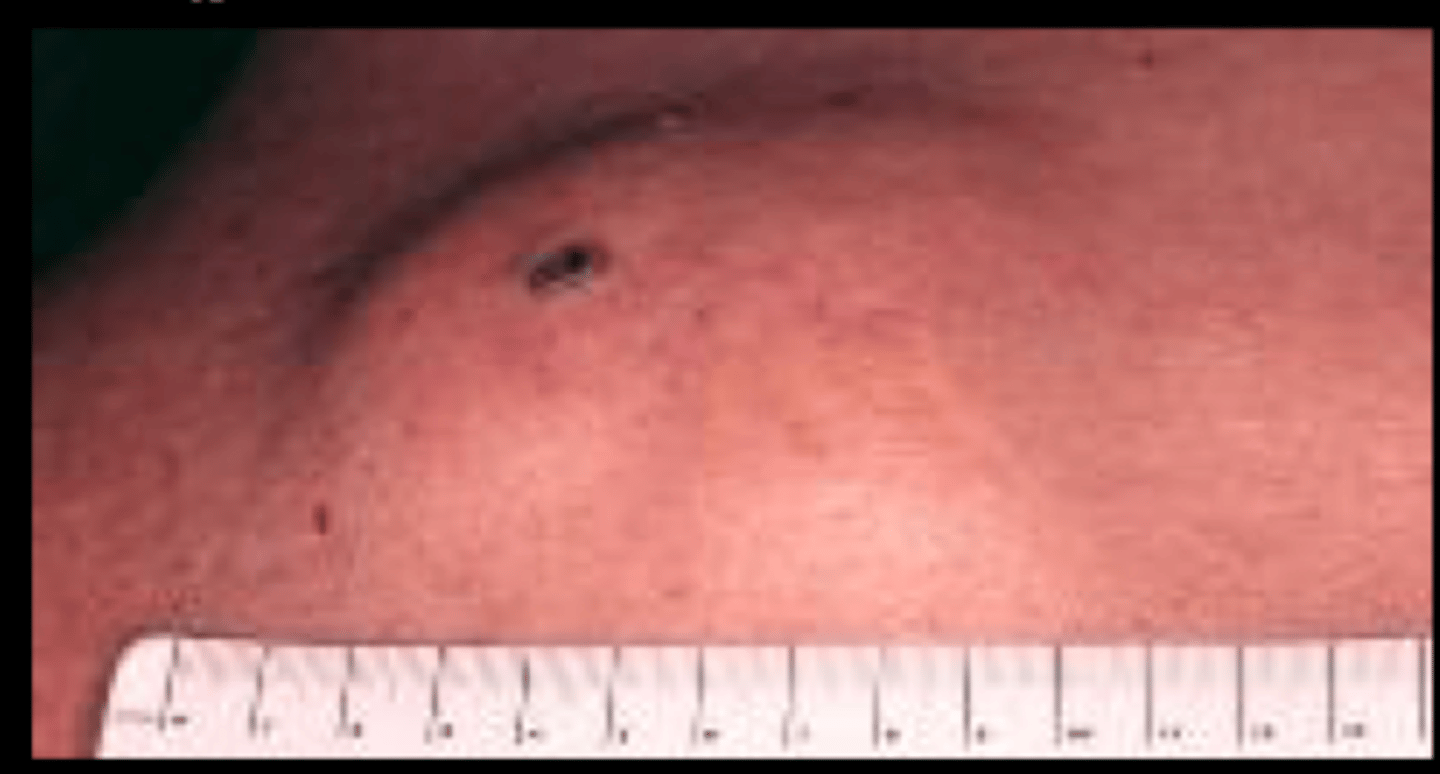
- Small superficial round, pinhead sized hemorrhages under the skin
- Do not blanch with pressure
- <3mm
Petechia
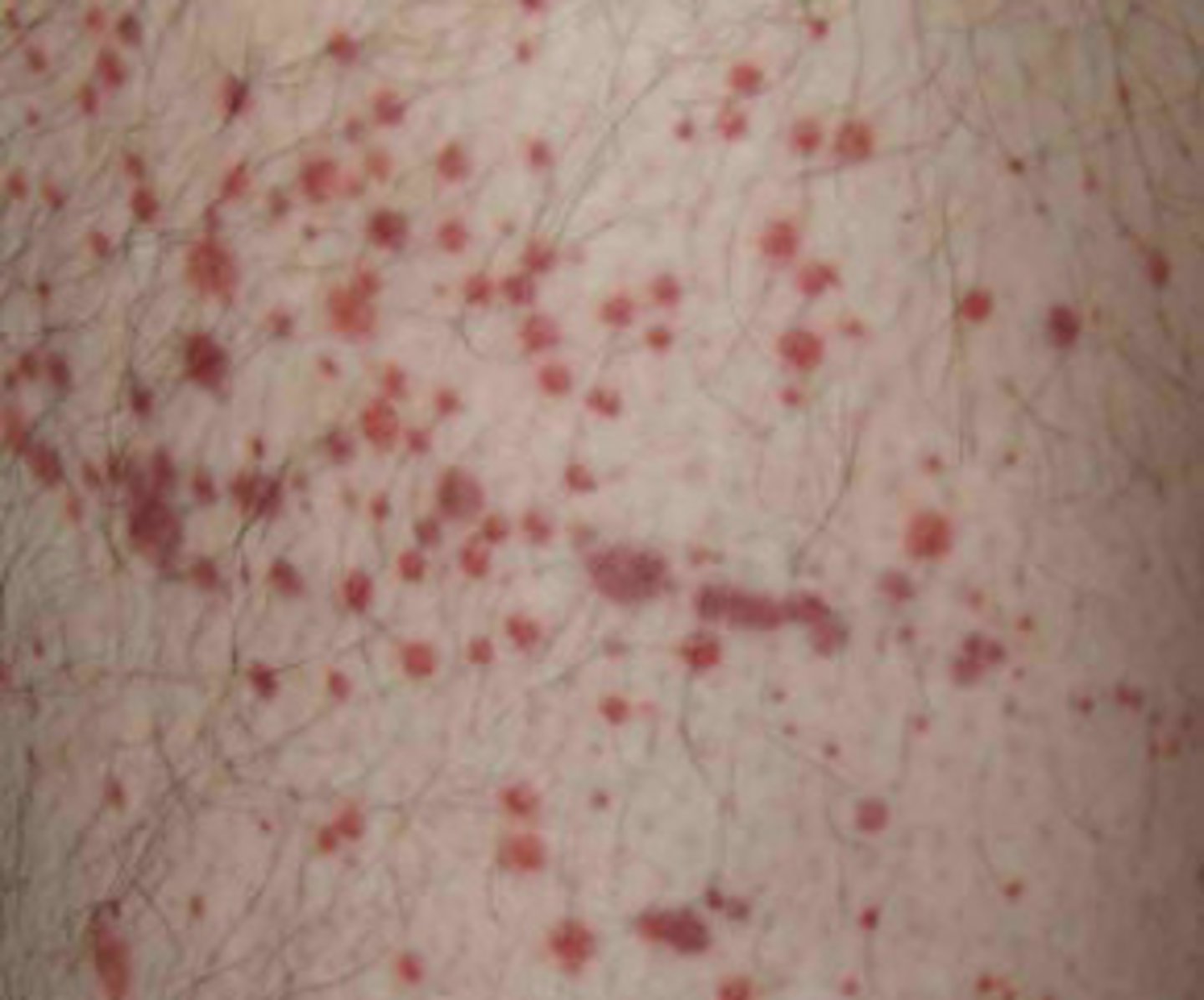
- Larger petechiae > 3mm
- Visible hemorrhage into skin
- Do not blanch with pressure
Purpura
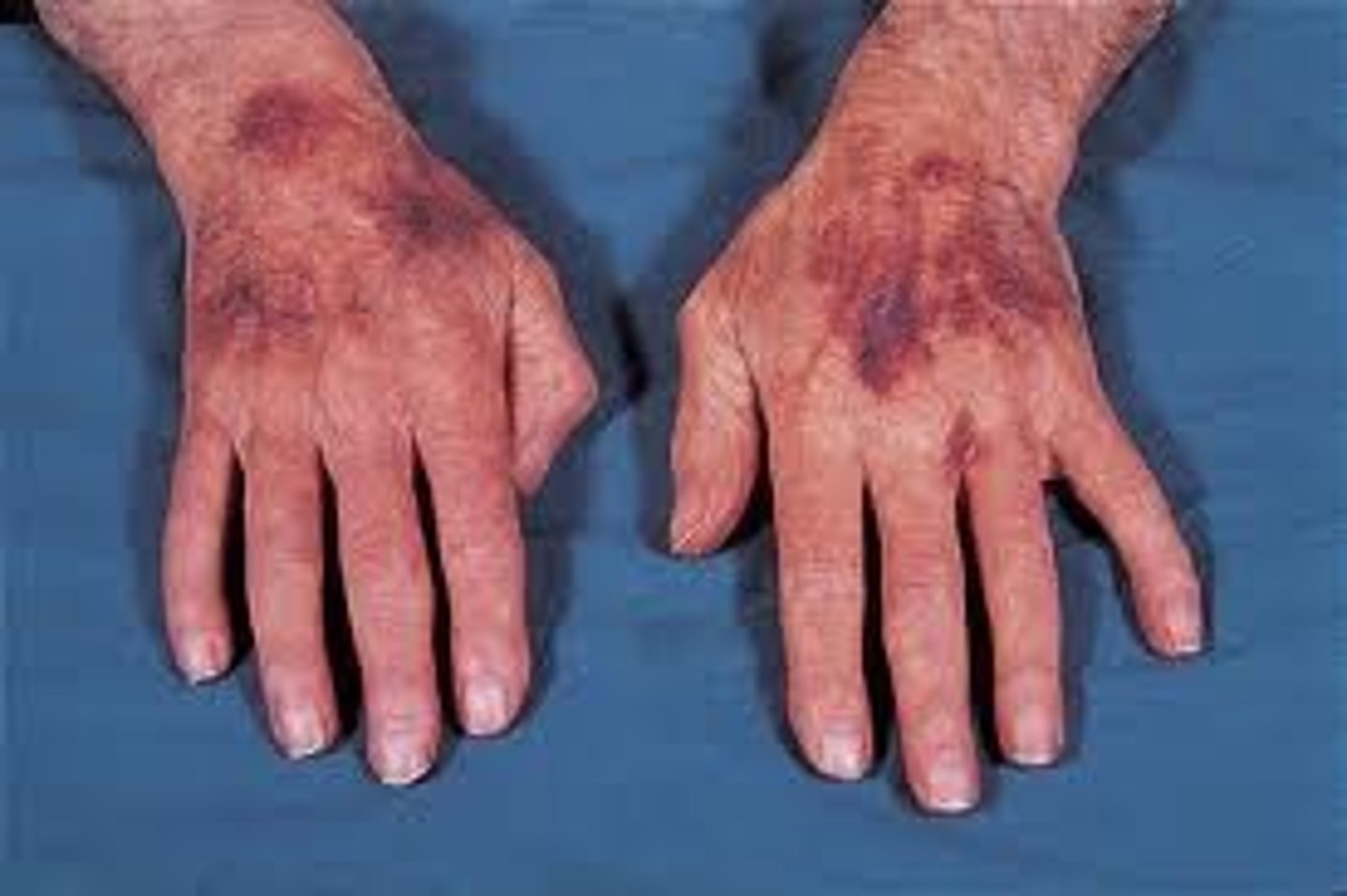
- Fine, linear vessels on surface of skin
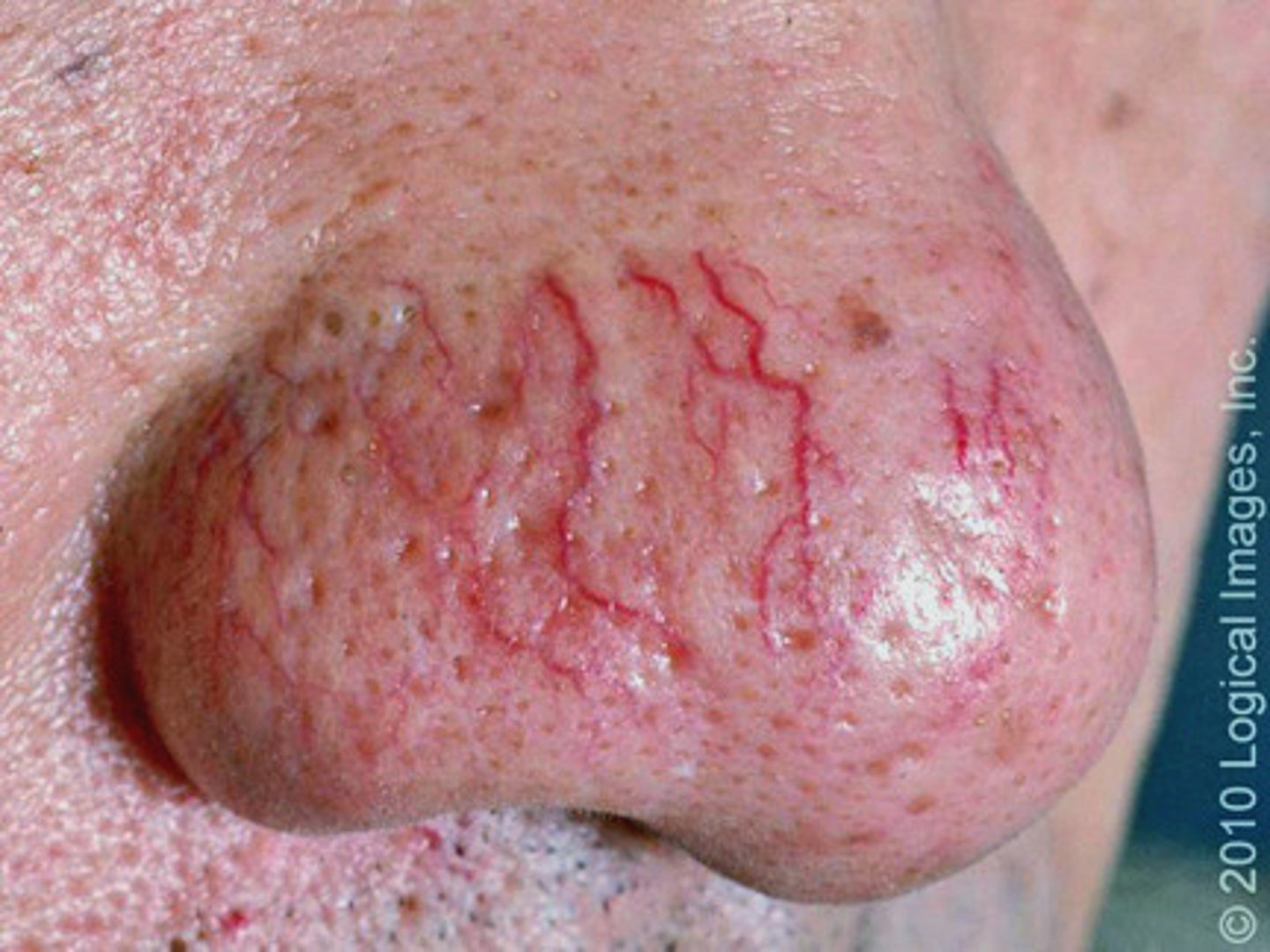
- Dilated superficial cutaneous blood vessels
- Fade or blanch with pressure
- Ex. Rosacea, pregnancy, chronic sun exposure, many conditions
Telangiectasias
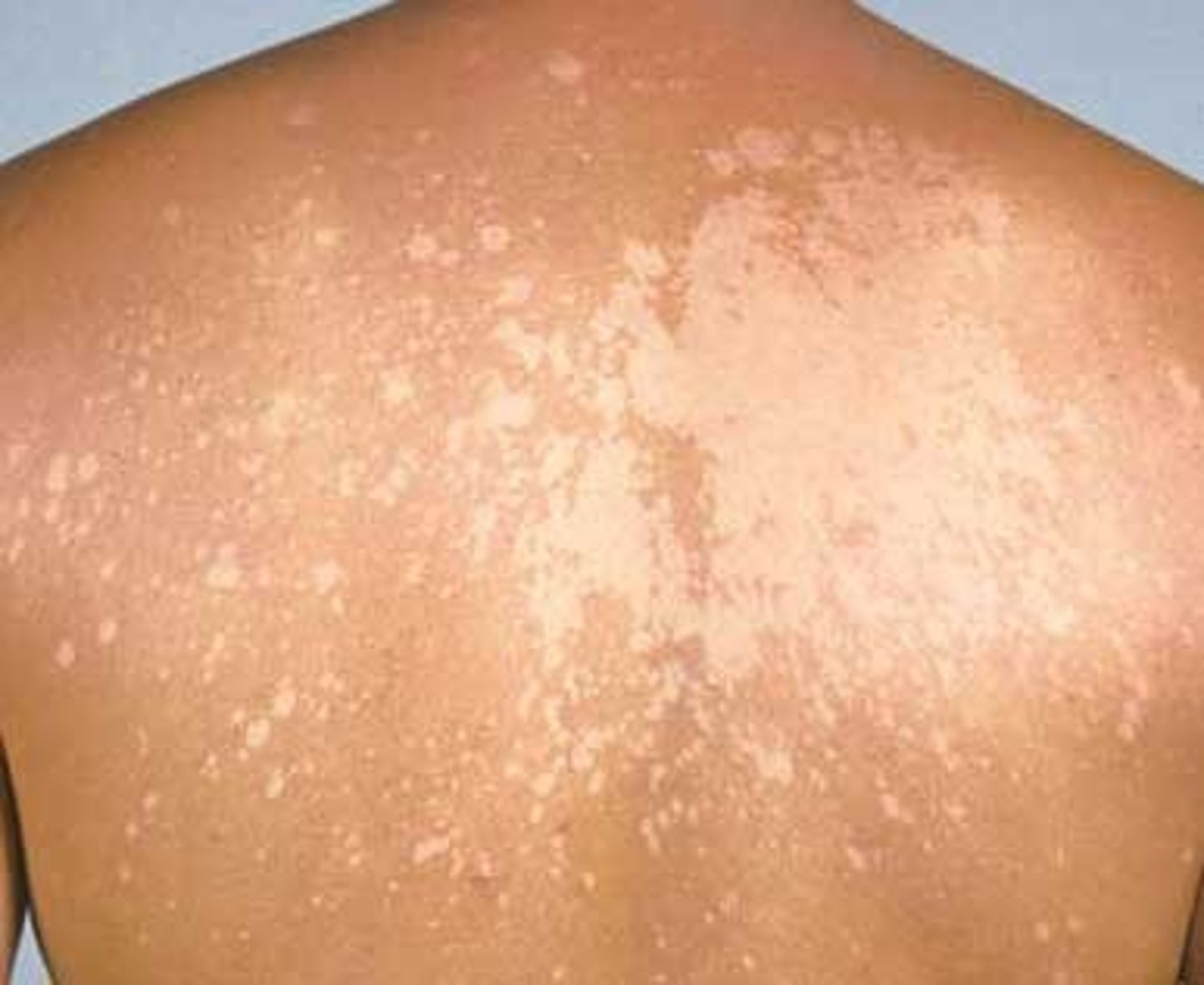
Light than normal skin
Hypopigmentation
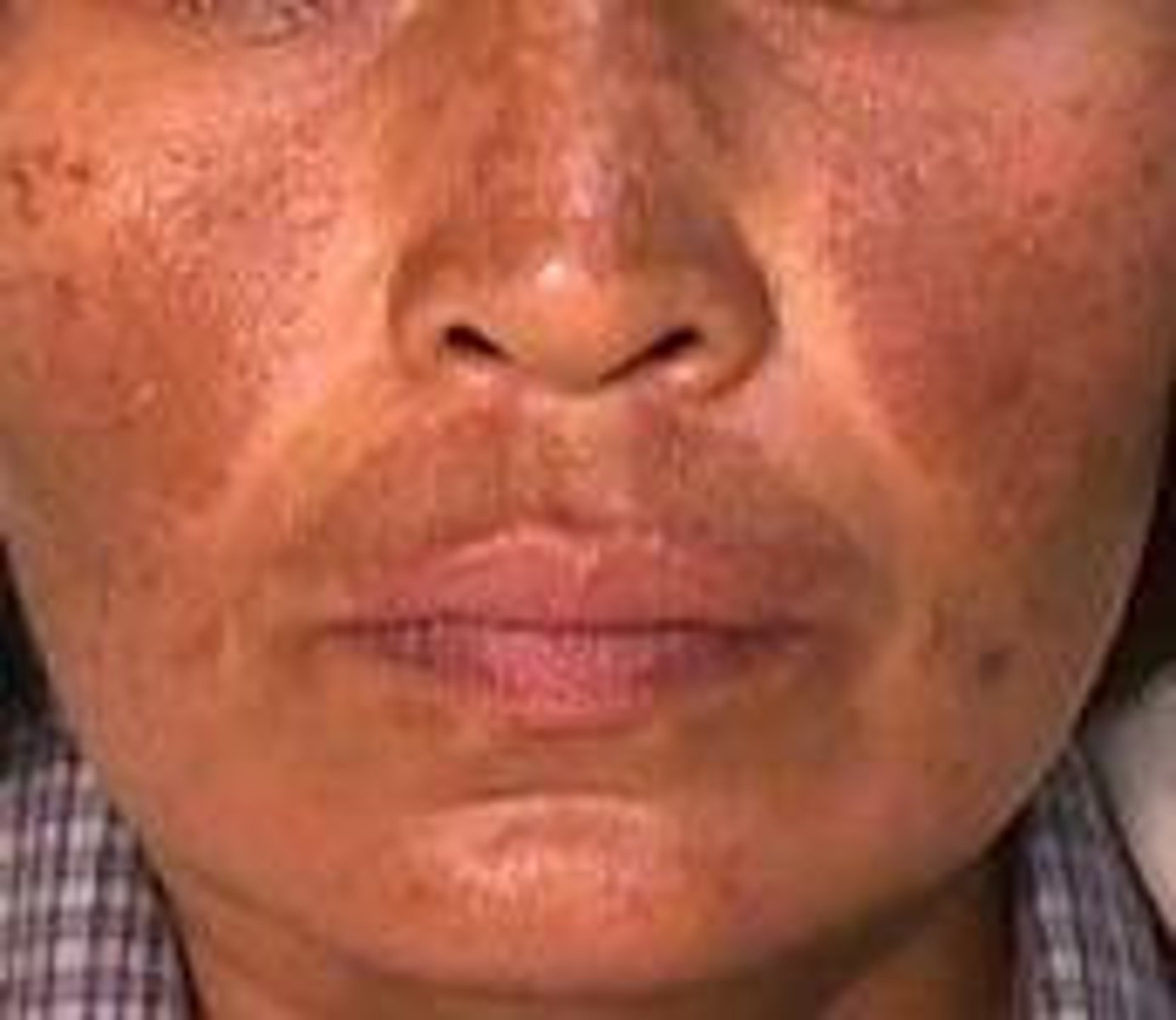
Darker than normal skin
hyperpigmentation
How lesions change (or dont over time). Can be fully evolved or develop from smaller lesions.
Evolution of lesions
Regression of a lesion that may disappear completely, leave residual pigmentation or scarring.
Involution of lesions
Refers to how lesions are spread out on the body
Distribution
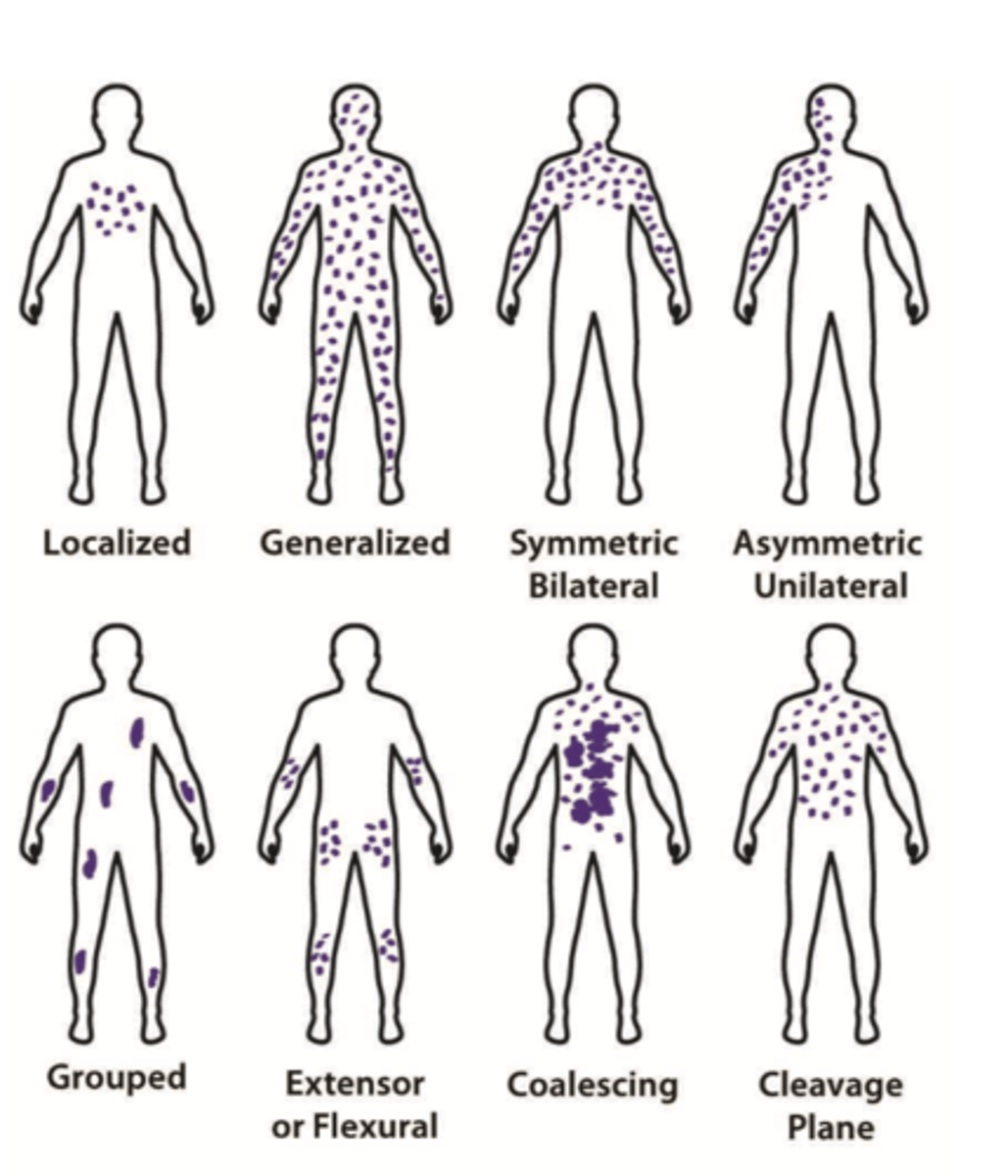
This type of distribution occurs on distal areas of body (hands, feet, nails)
Ex: Subungal melanoma
Acral
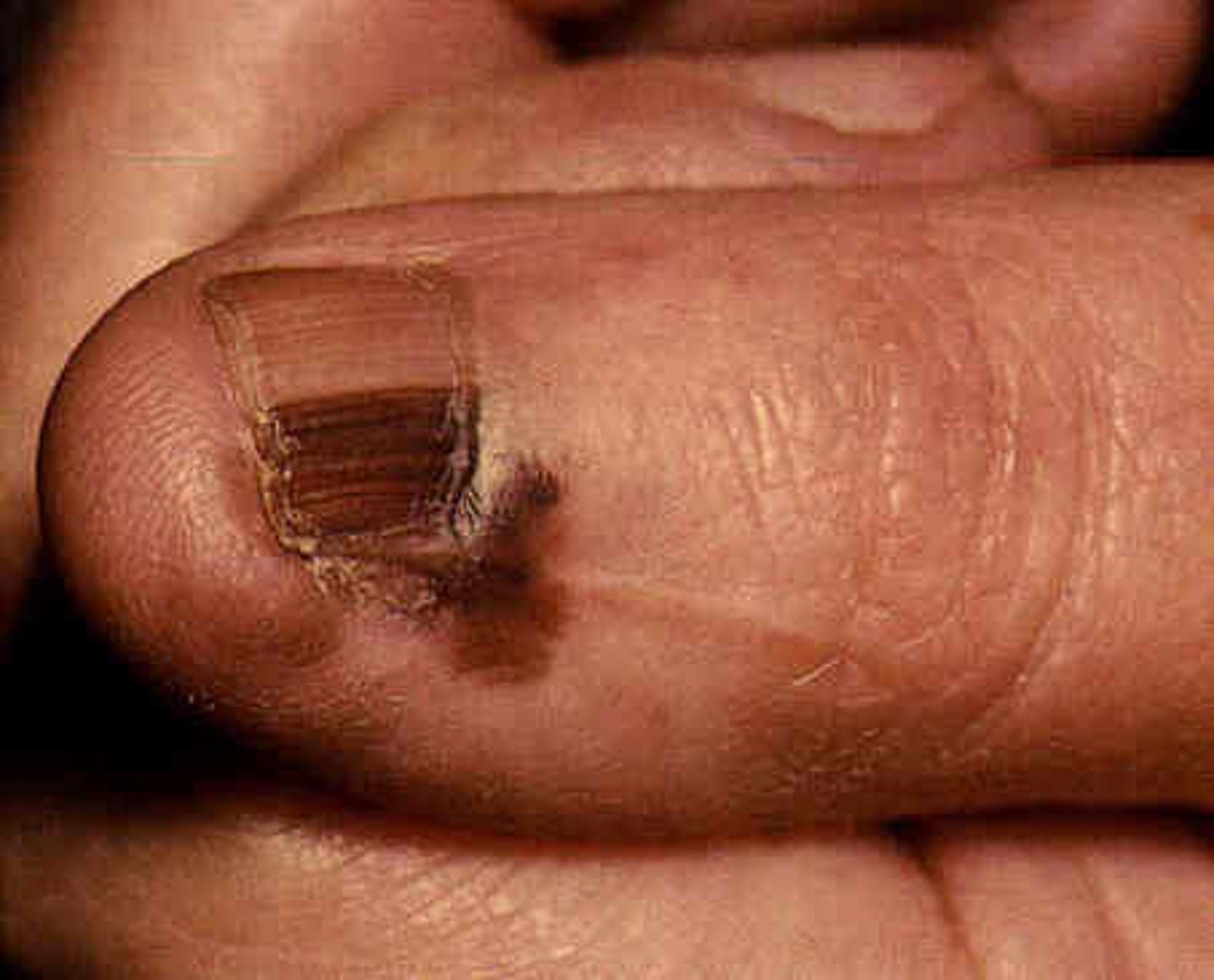
This type of distribution is where lesions are confined to a path along single spinal nerve.
Ex: Herpes Zoster
Dermatomal/Zosteriform
What is the different between configuration and arrangement?
1. Configuration= single lesion
2. Arrangement= multiple lesions
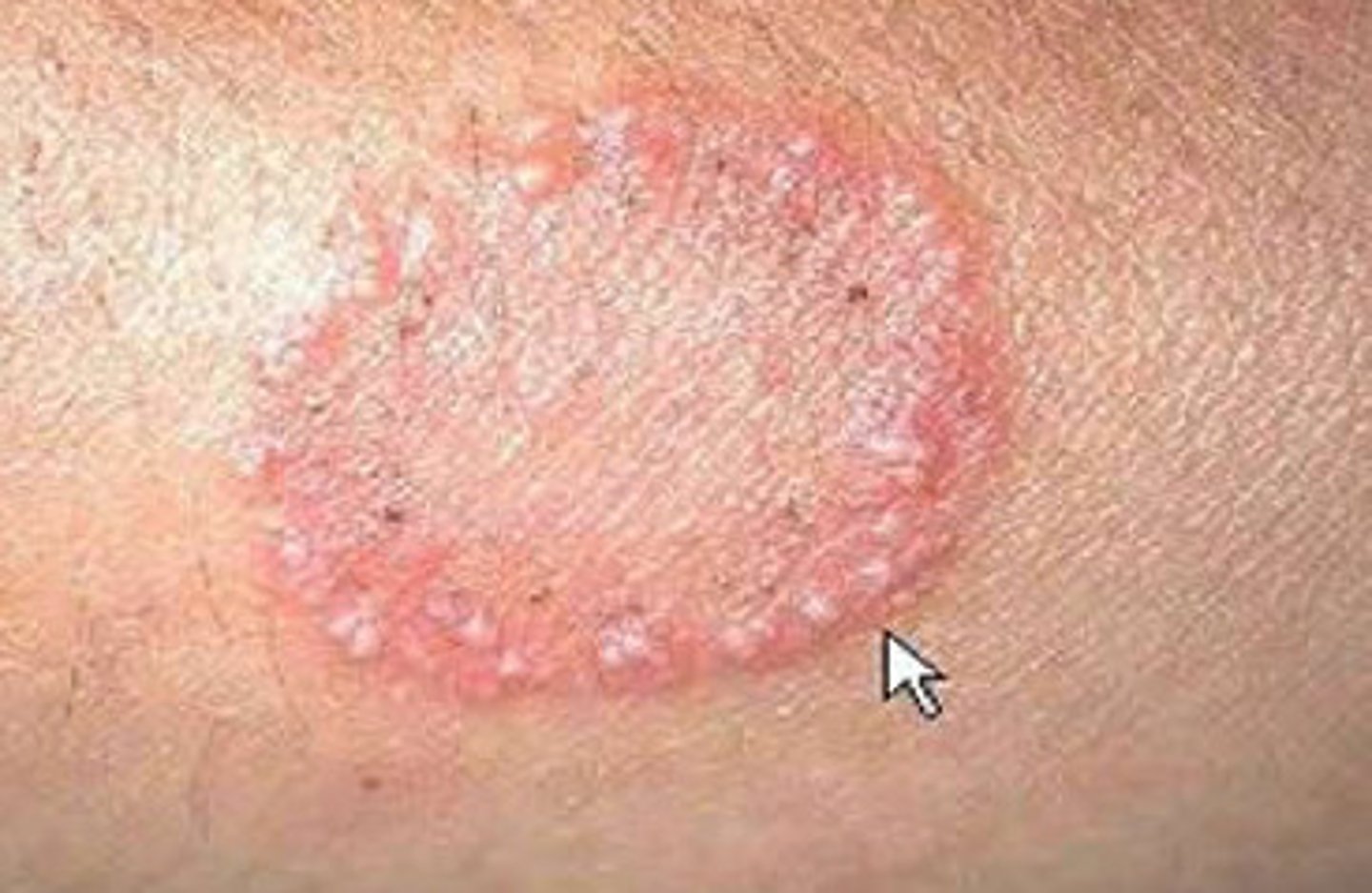
-Ring-shaped lesion
-complete circle with normal skin centrally
Annular
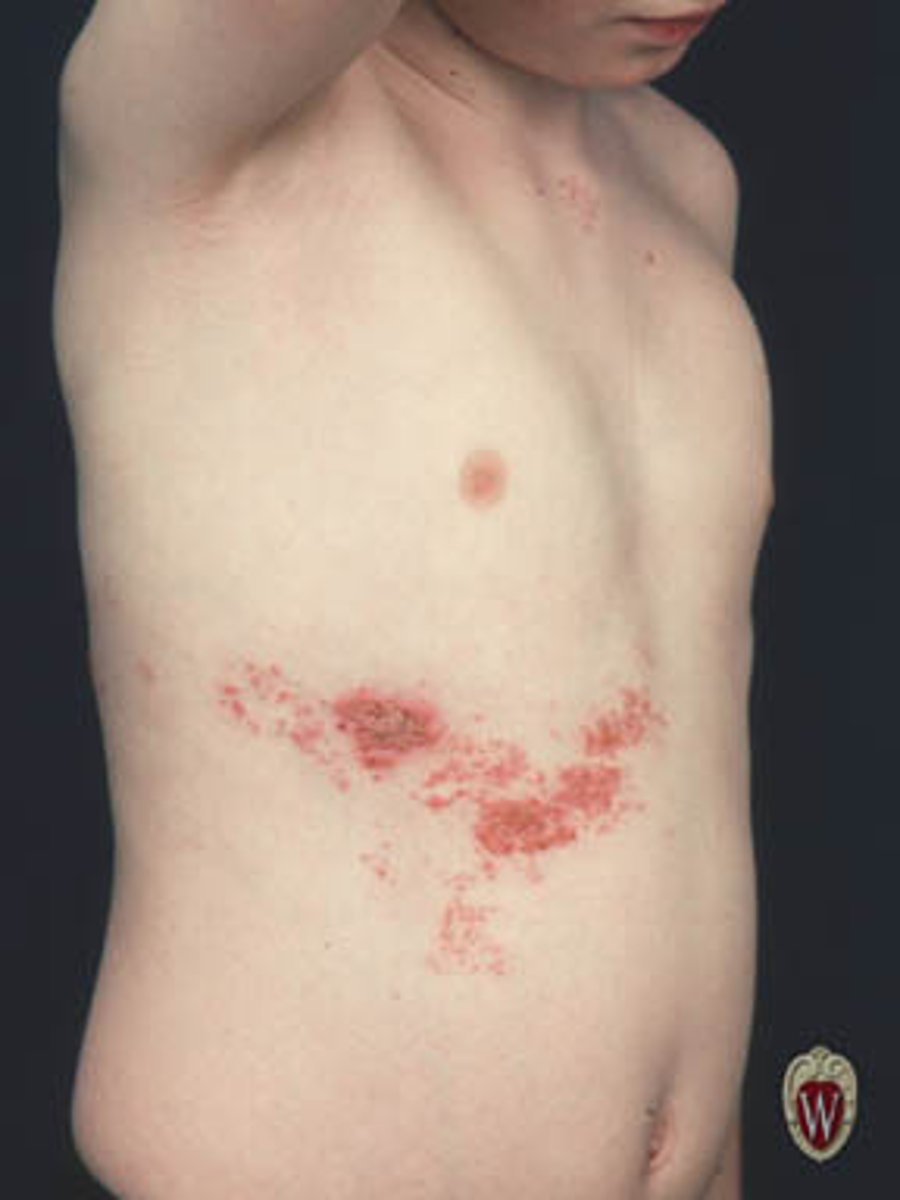
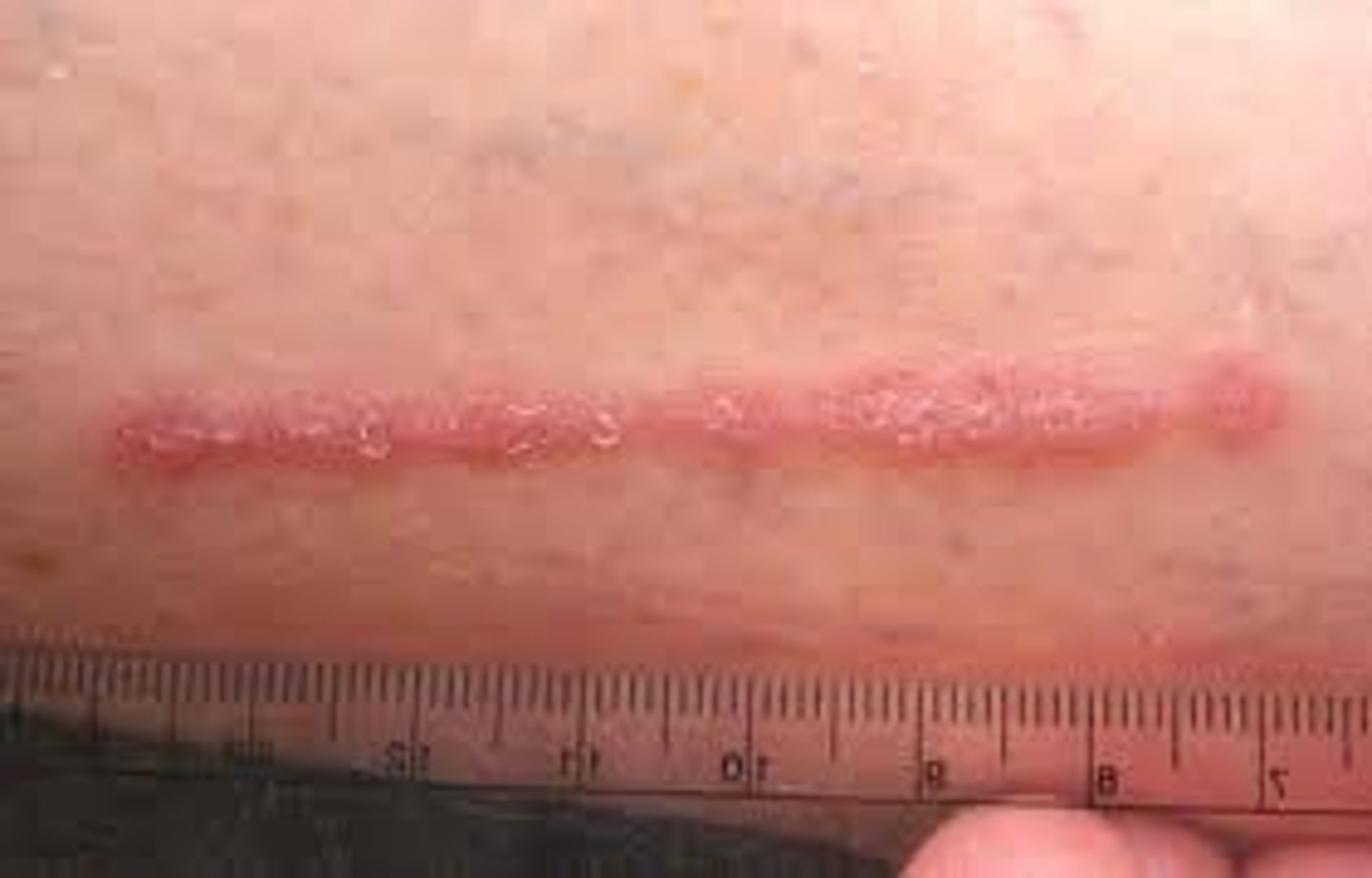
Lesions are in a line
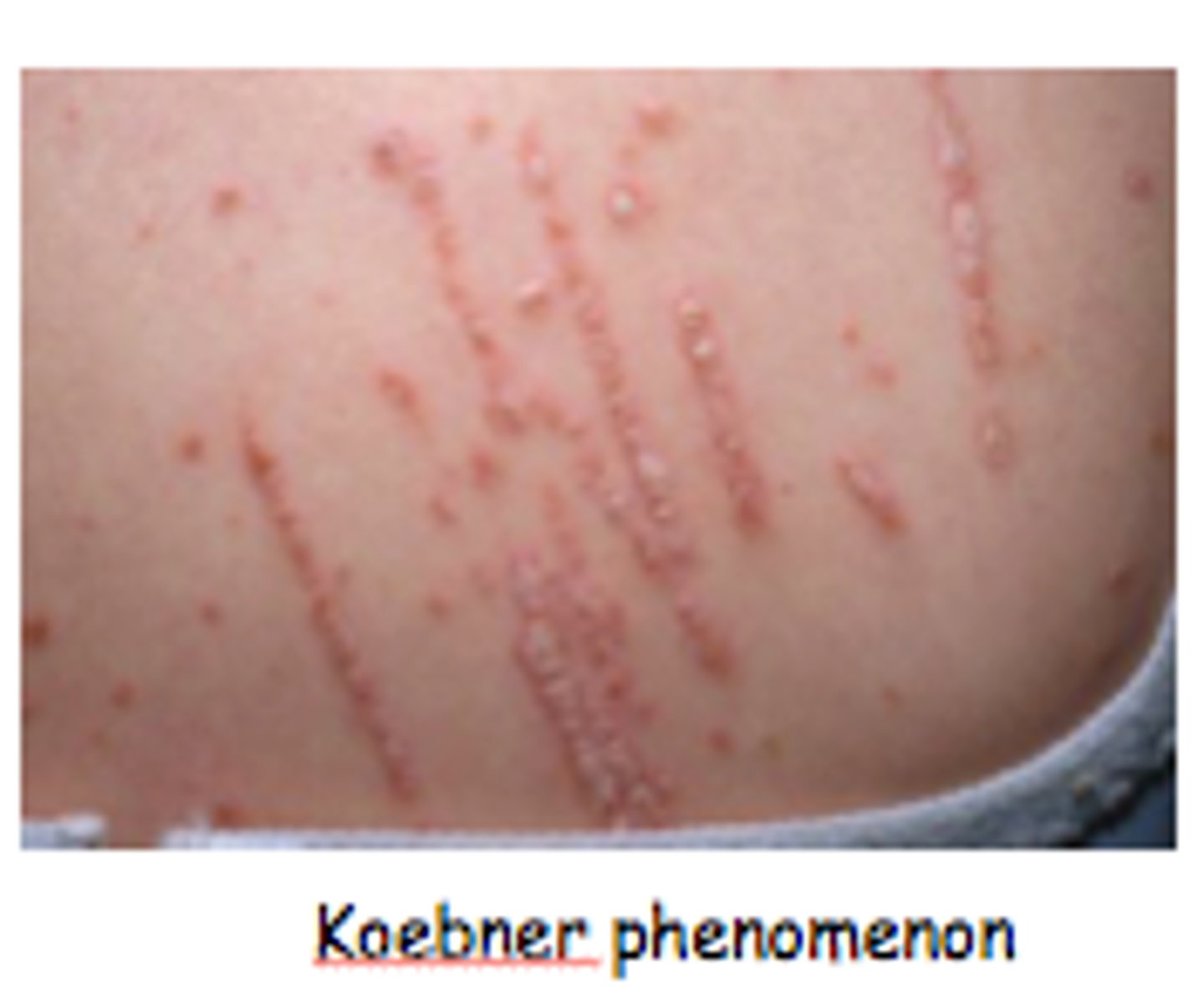
Linear
lesions induced by trauma that can be an example of linear lesions
Koebner phenomenon
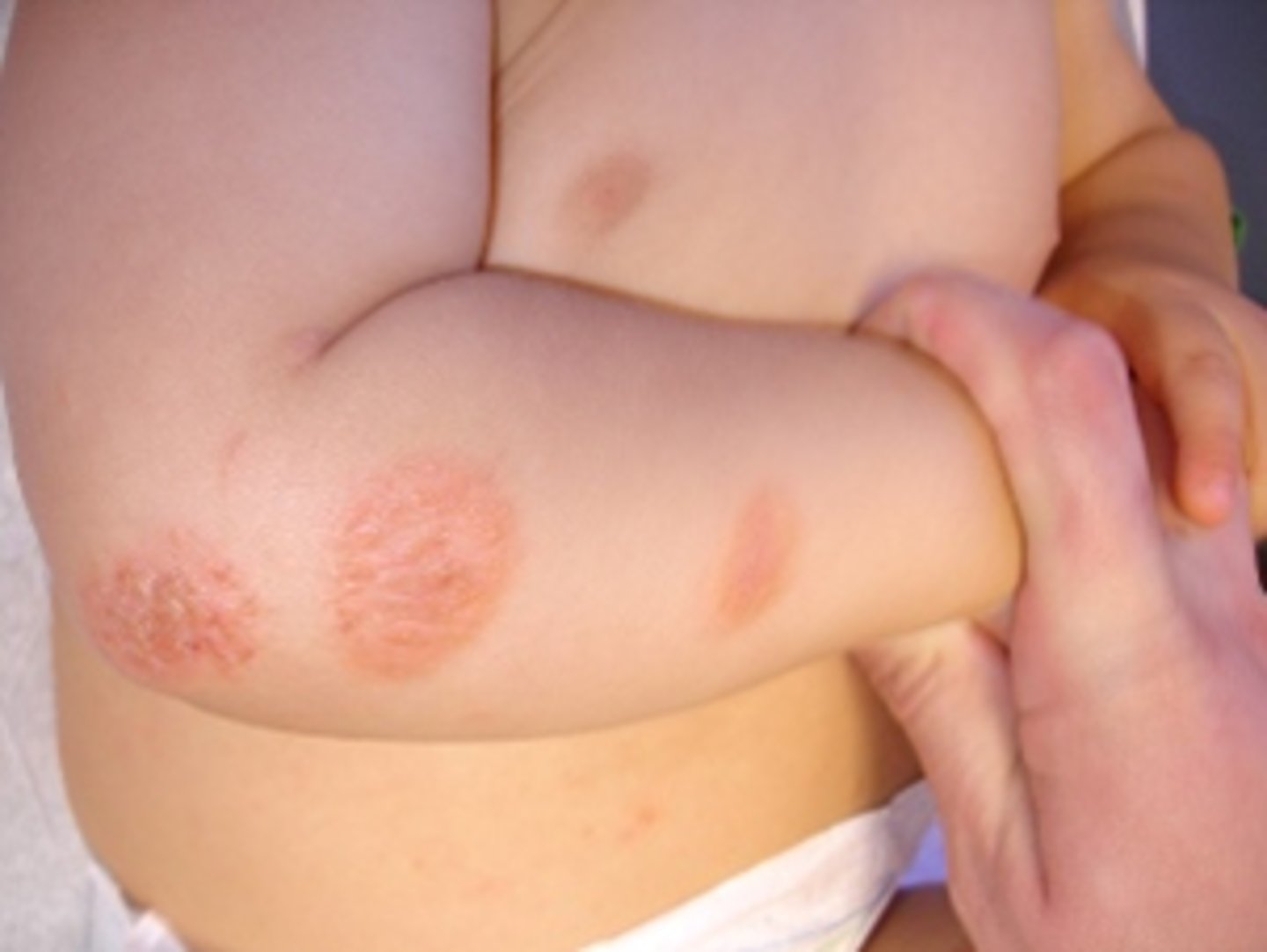
Coin-shaped lesion
Example: Eczema
Nummular
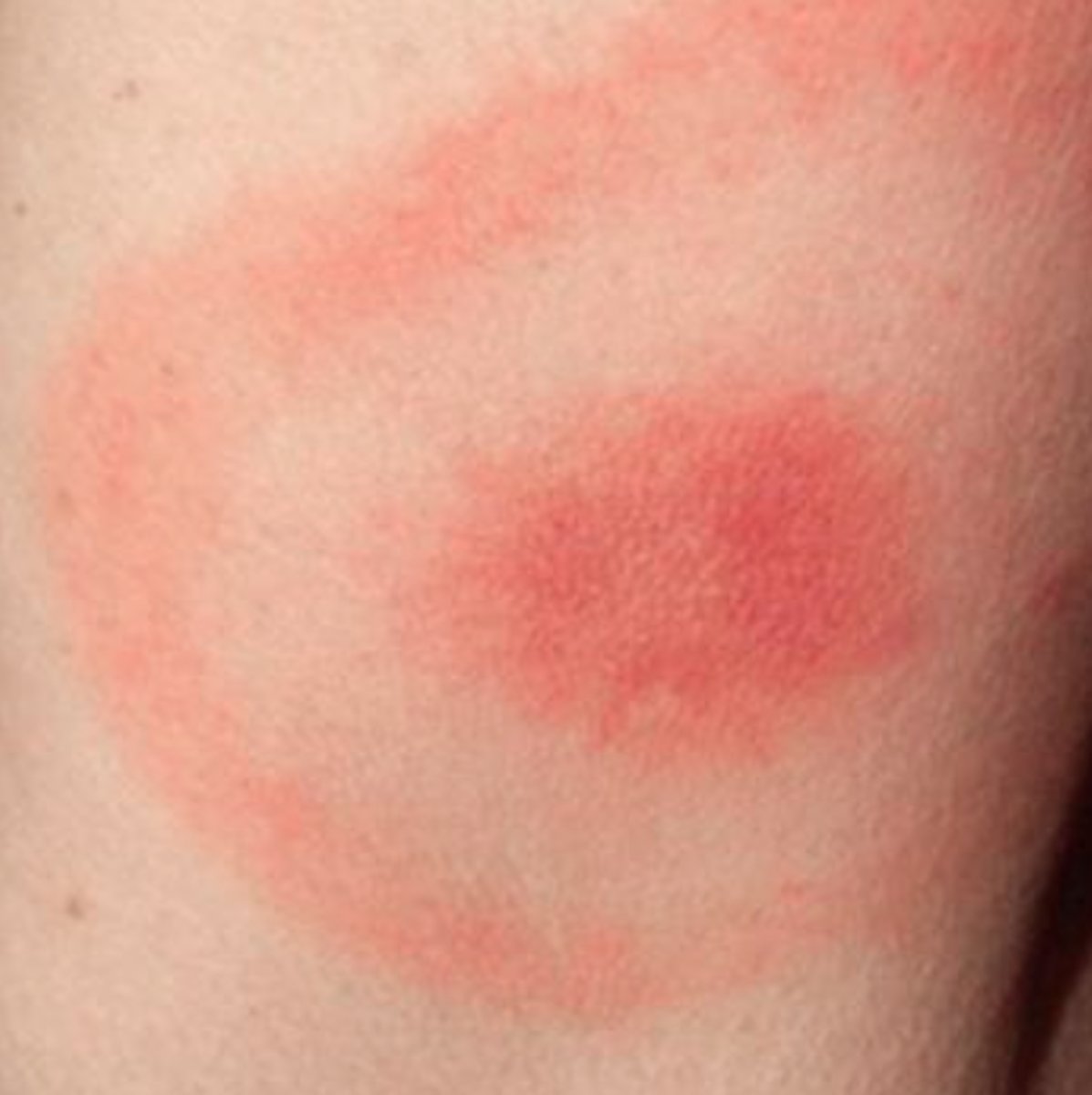
Concentric rings (think bullseye)
Targetoid
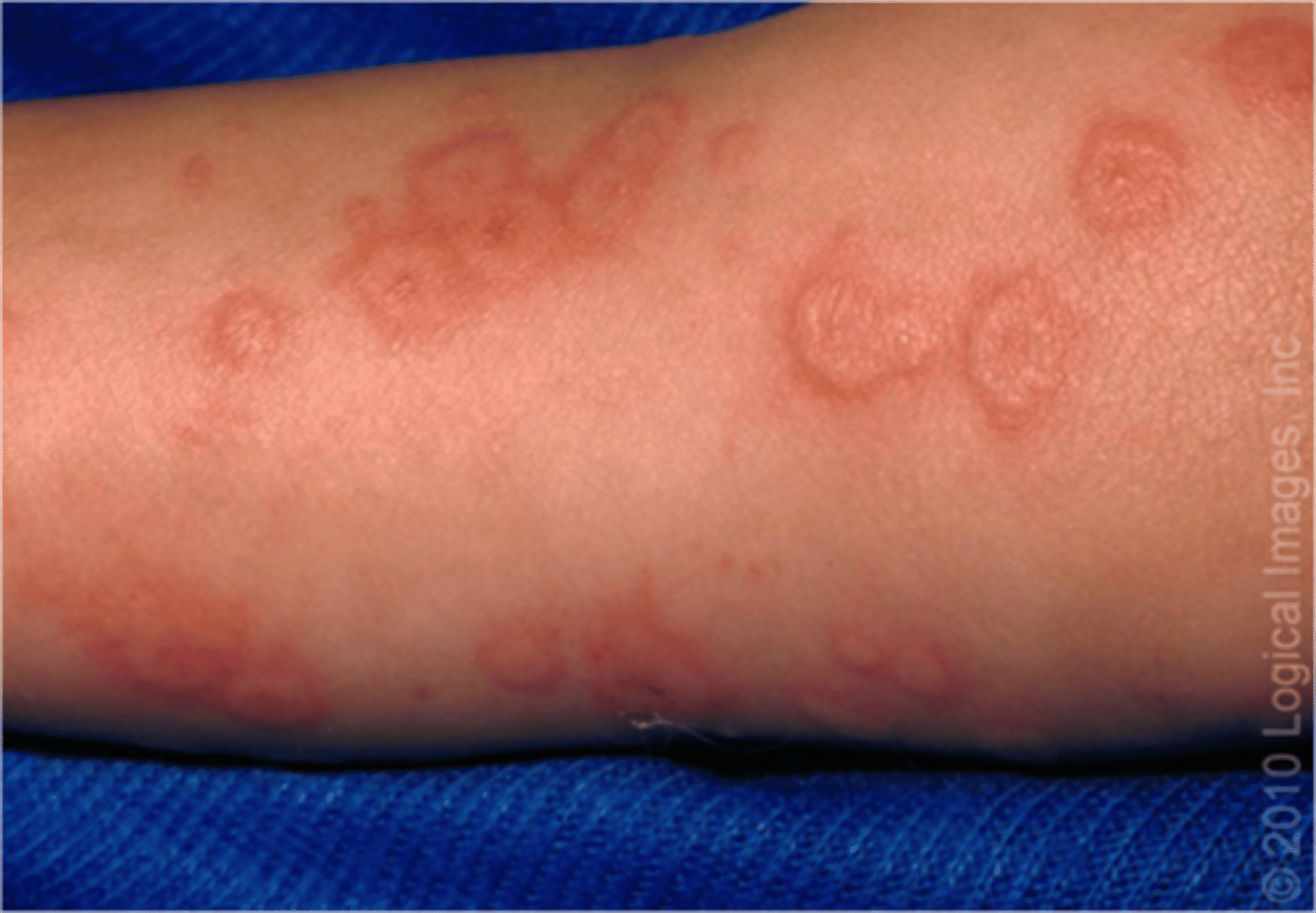
What is an example of a targetoid lesion?
lymes disease, Erythema multiforme
-Snake like
-Wandering, wavy borders
-Not straight and does not form part of a circle
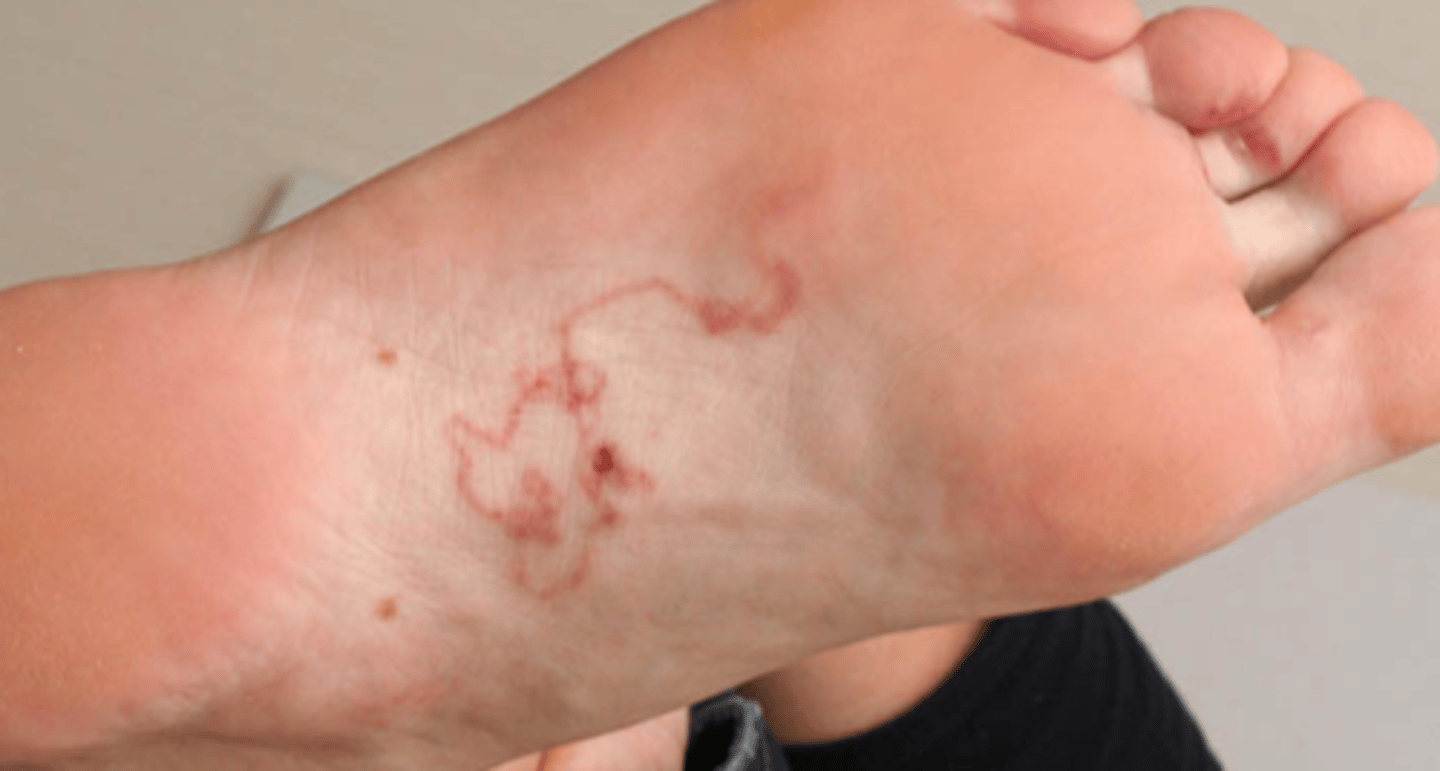
Serpiginous
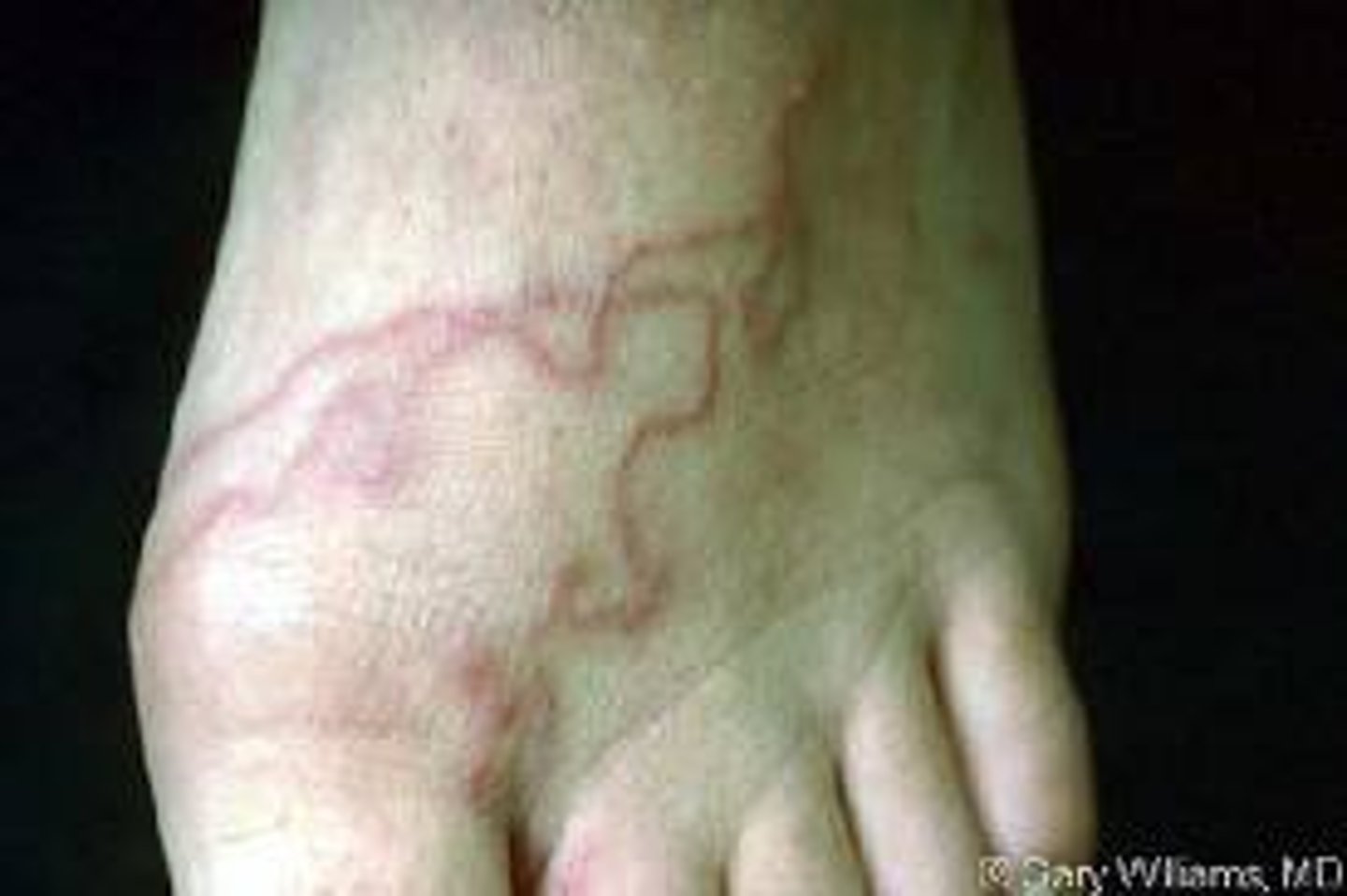
What is an example serpiginous lesion?
Cutaneous larva migrans
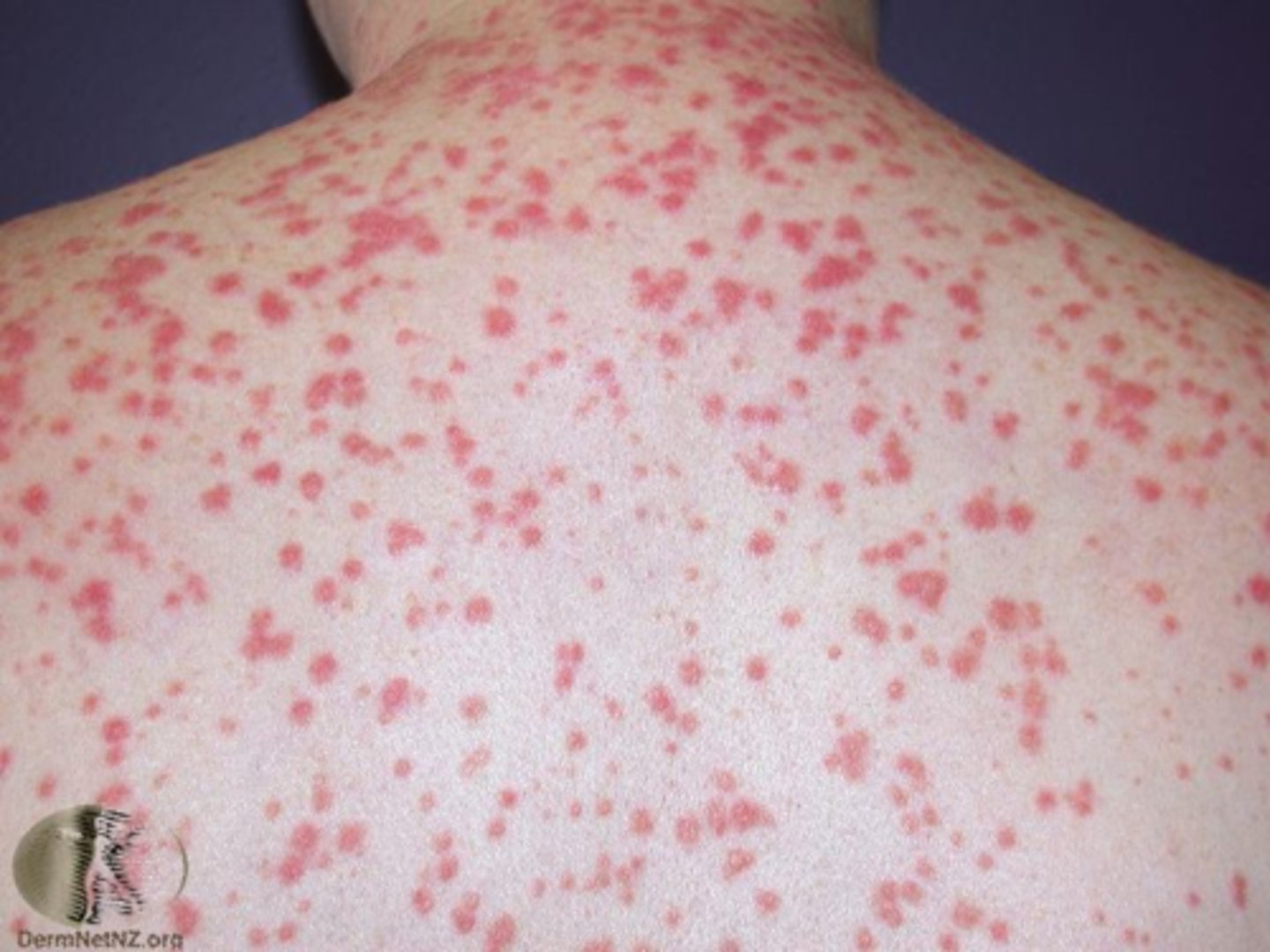
Discrete, Drop-like skin lesion
Guttate
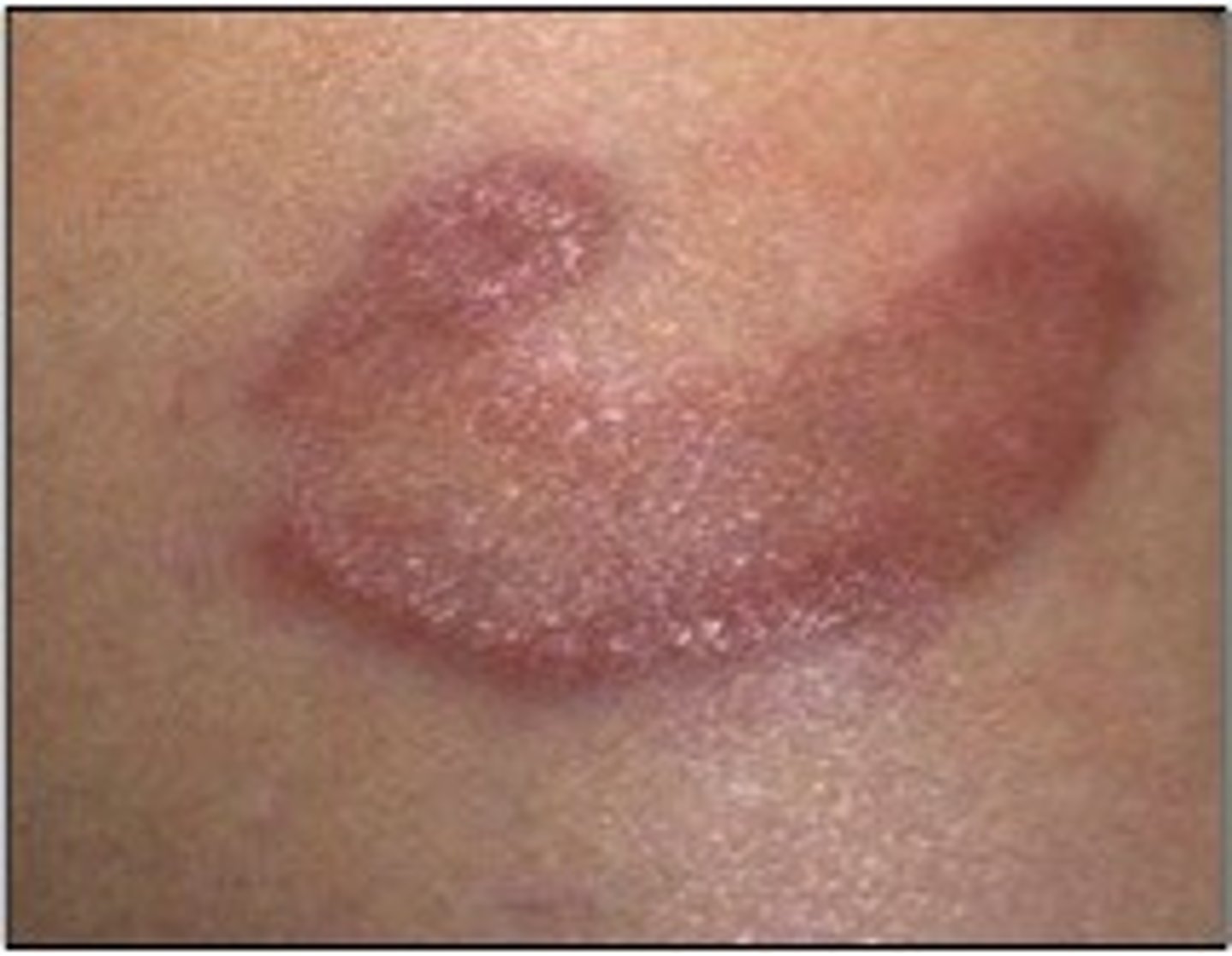
Arch shaped or portion of a circle skin lesion
Arcuate
Net-like, lace-like skin lesions
Reticular
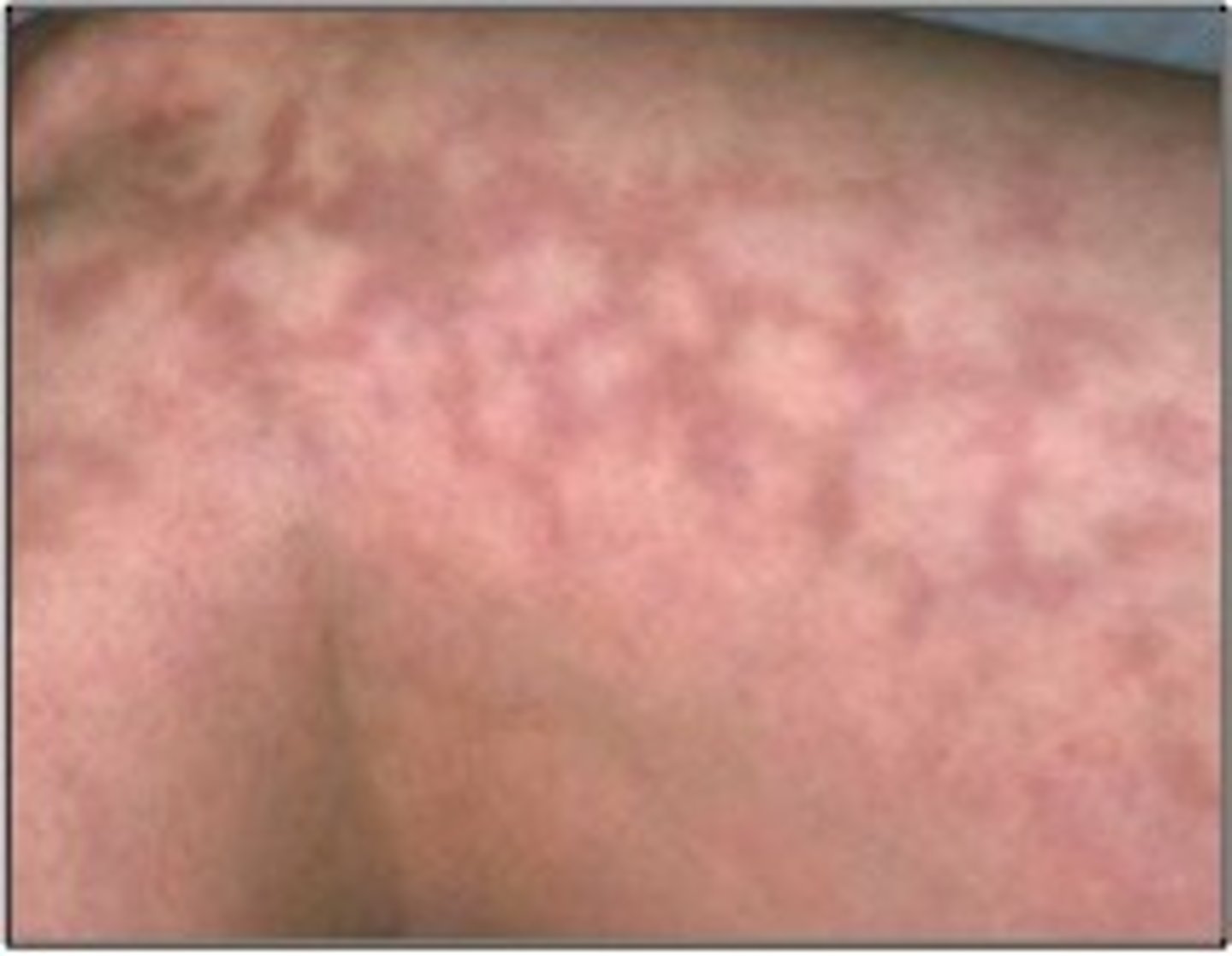
Twisted or spiraled skin lesions
Gyrate
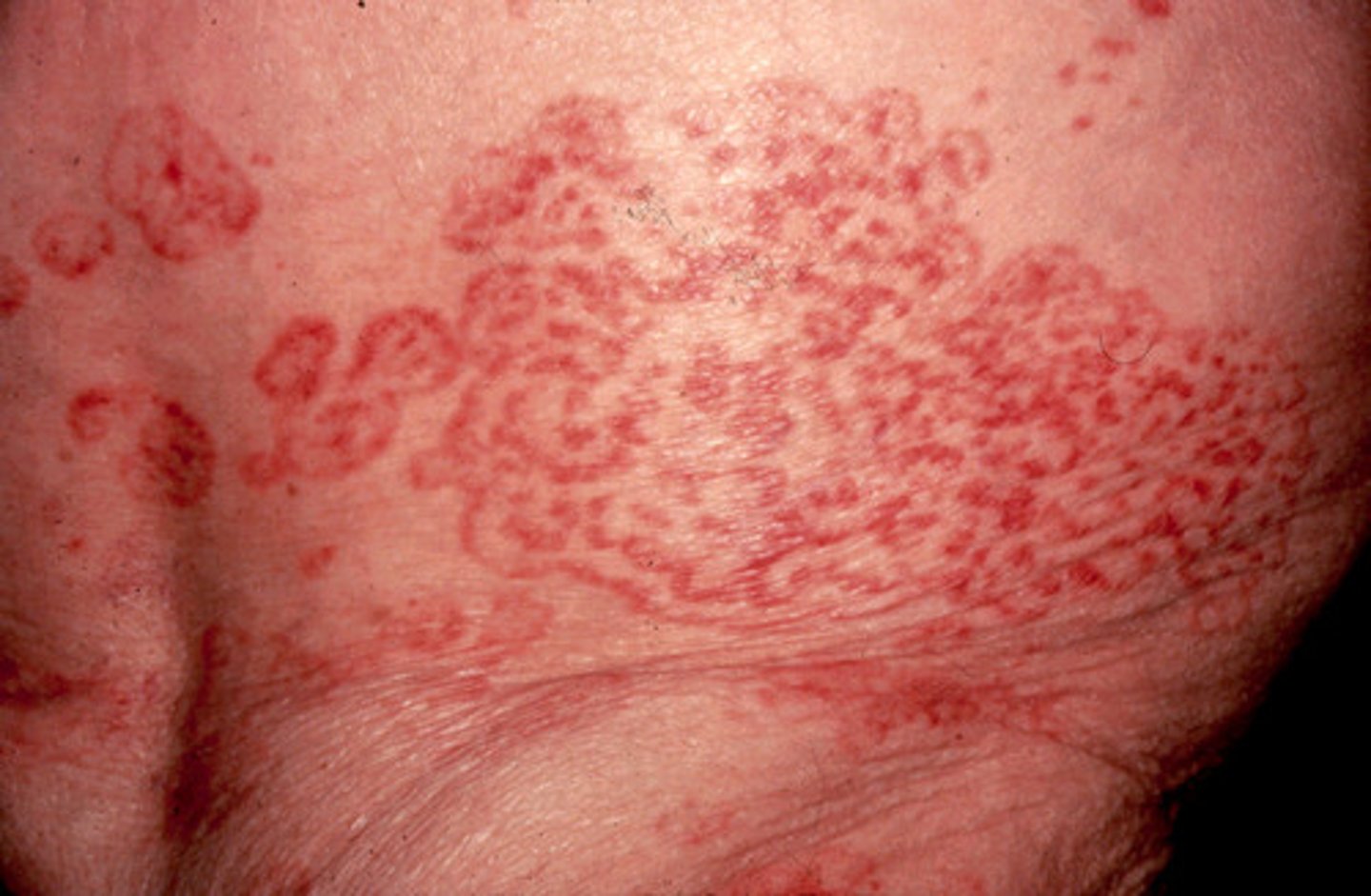
Linear shape of skin lesion along a nerve route
Zosteriform
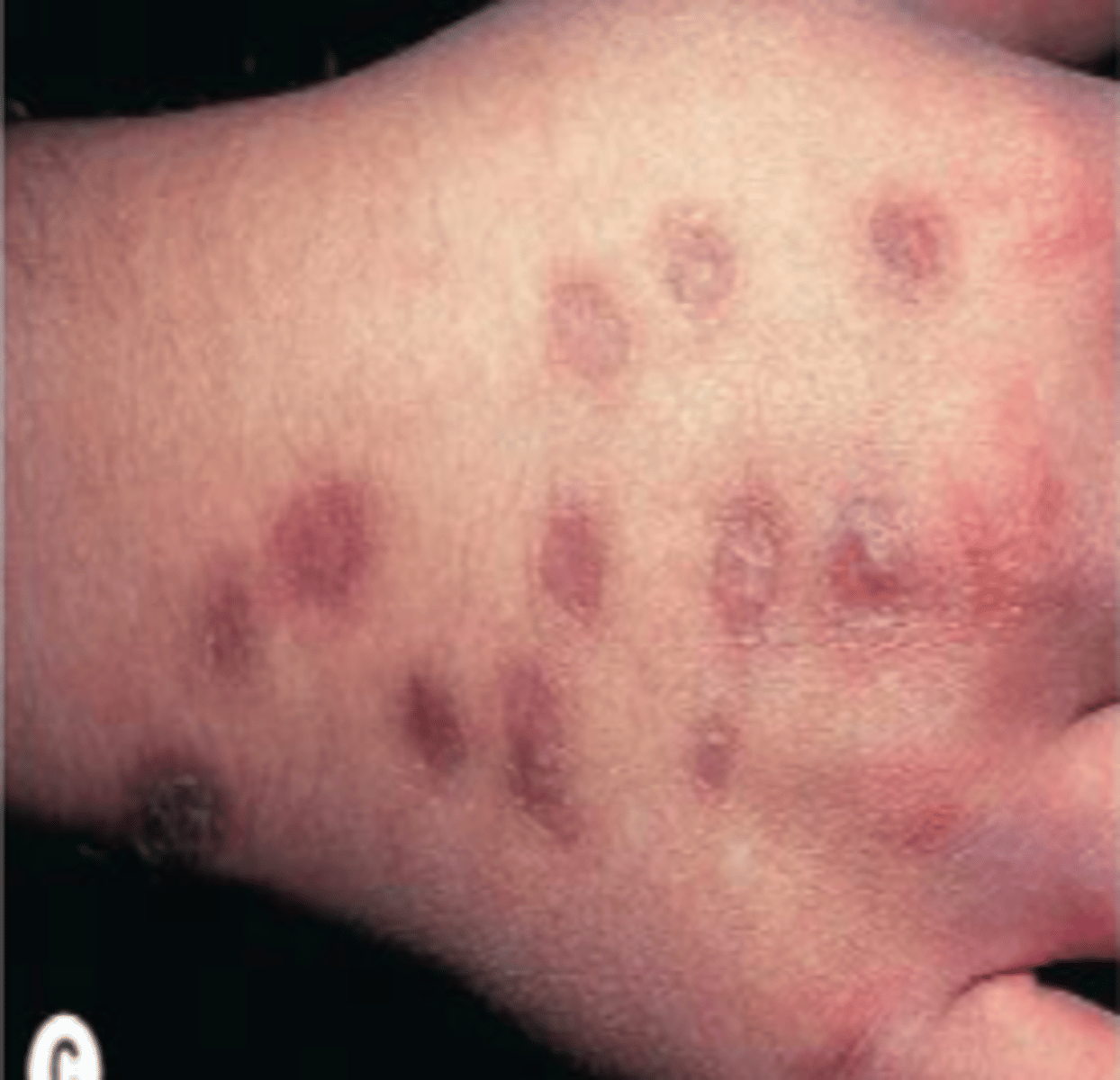
Geometric patterns, Same stage of development usually within reach of hands and has minimal hx because patient is doing it to themselves
Factitia
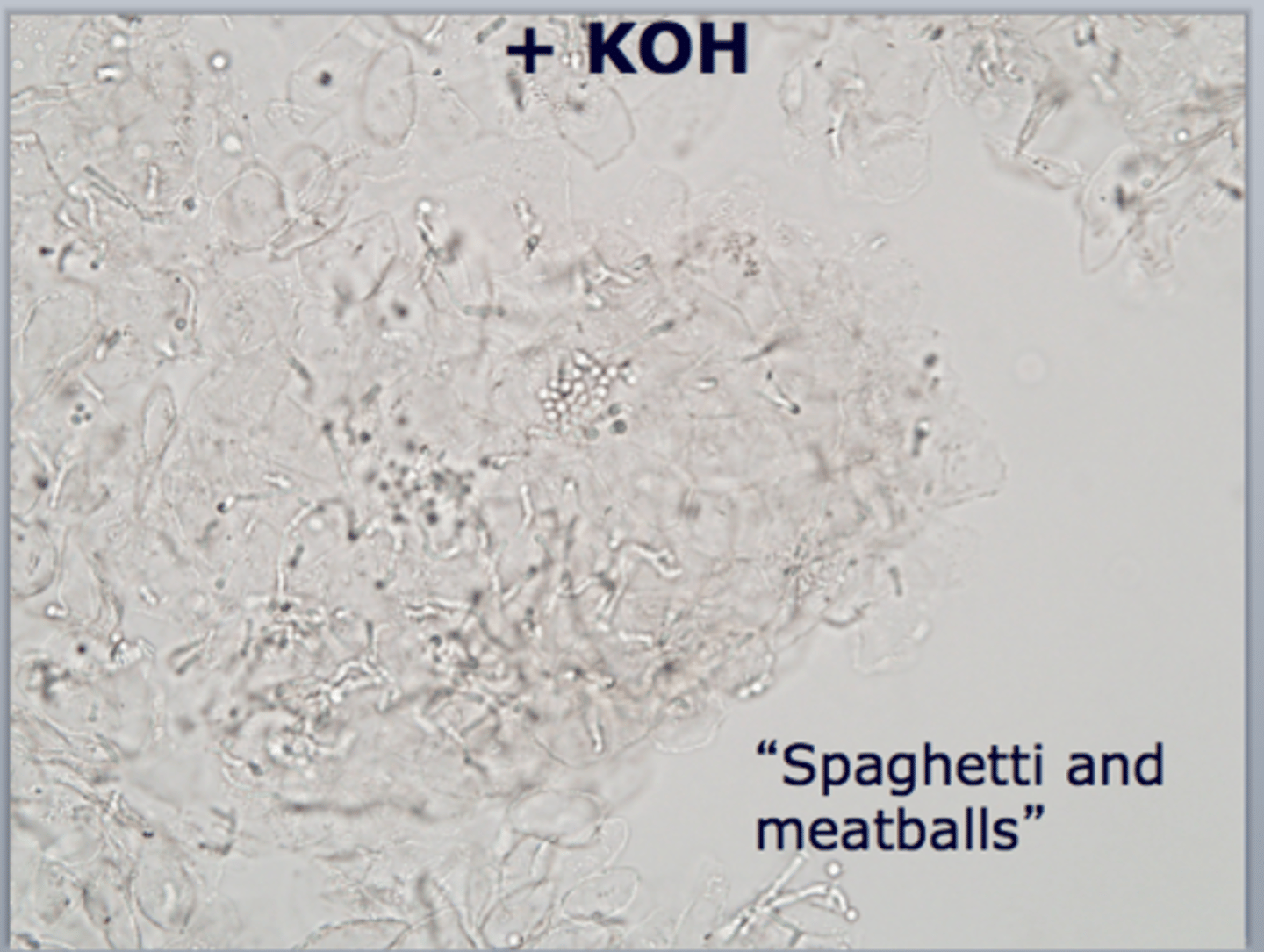
This is quick easy test to determine the presence of superficial cutaneous fungus. You will take scrapings of skin with a metal blade onto a glass microscope slide. Slide is mounted in this.
KOH

A positive KOH has an appearance of hyphae and spores. Classically called "Spaghetti and Meatballs". What's the diagnosis ?
Tinea versicolor
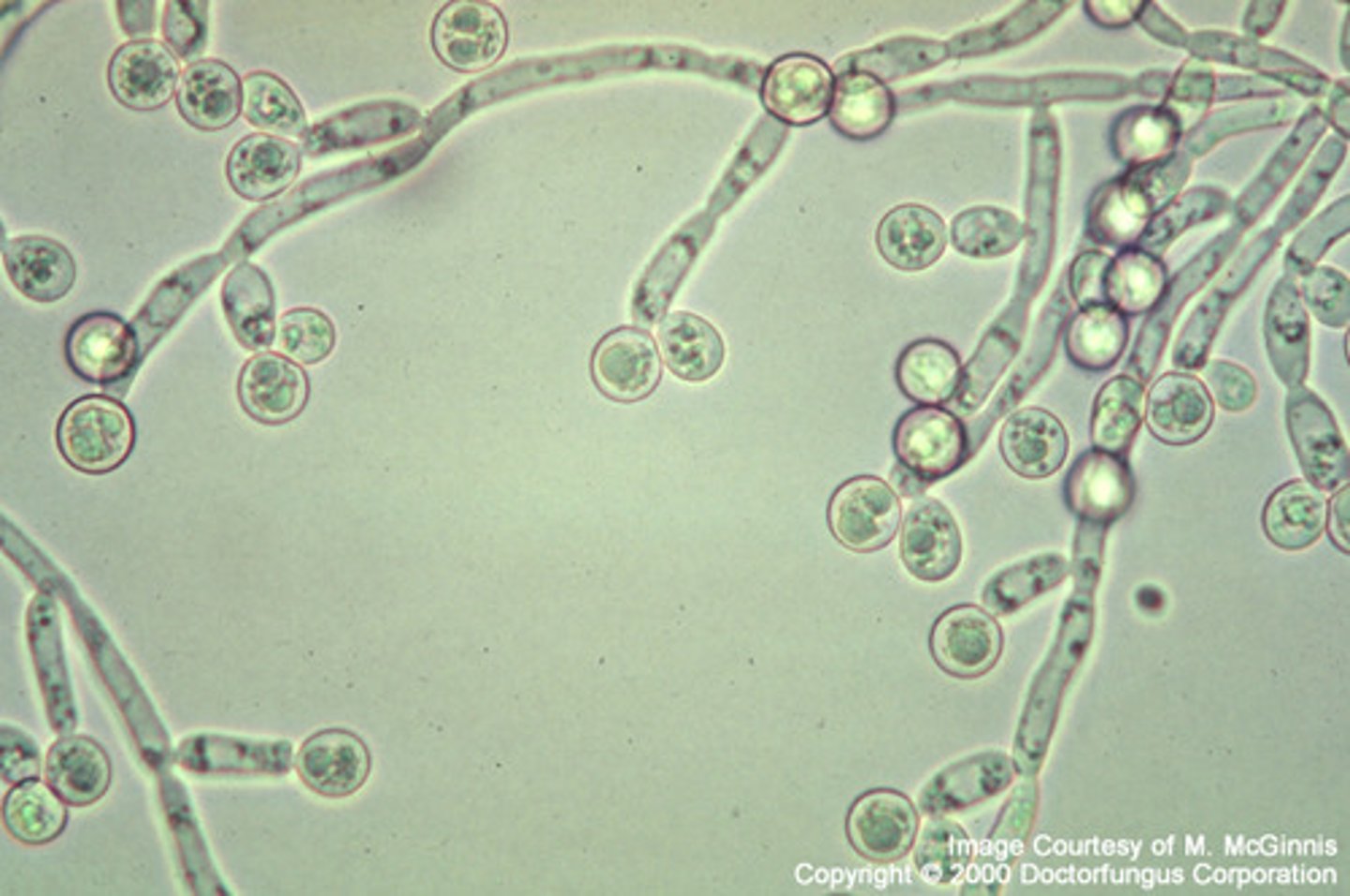
A positive KOH has an appearance of budding yeasts and pseudohyphae. What's the diagnosis ?
Candidasis
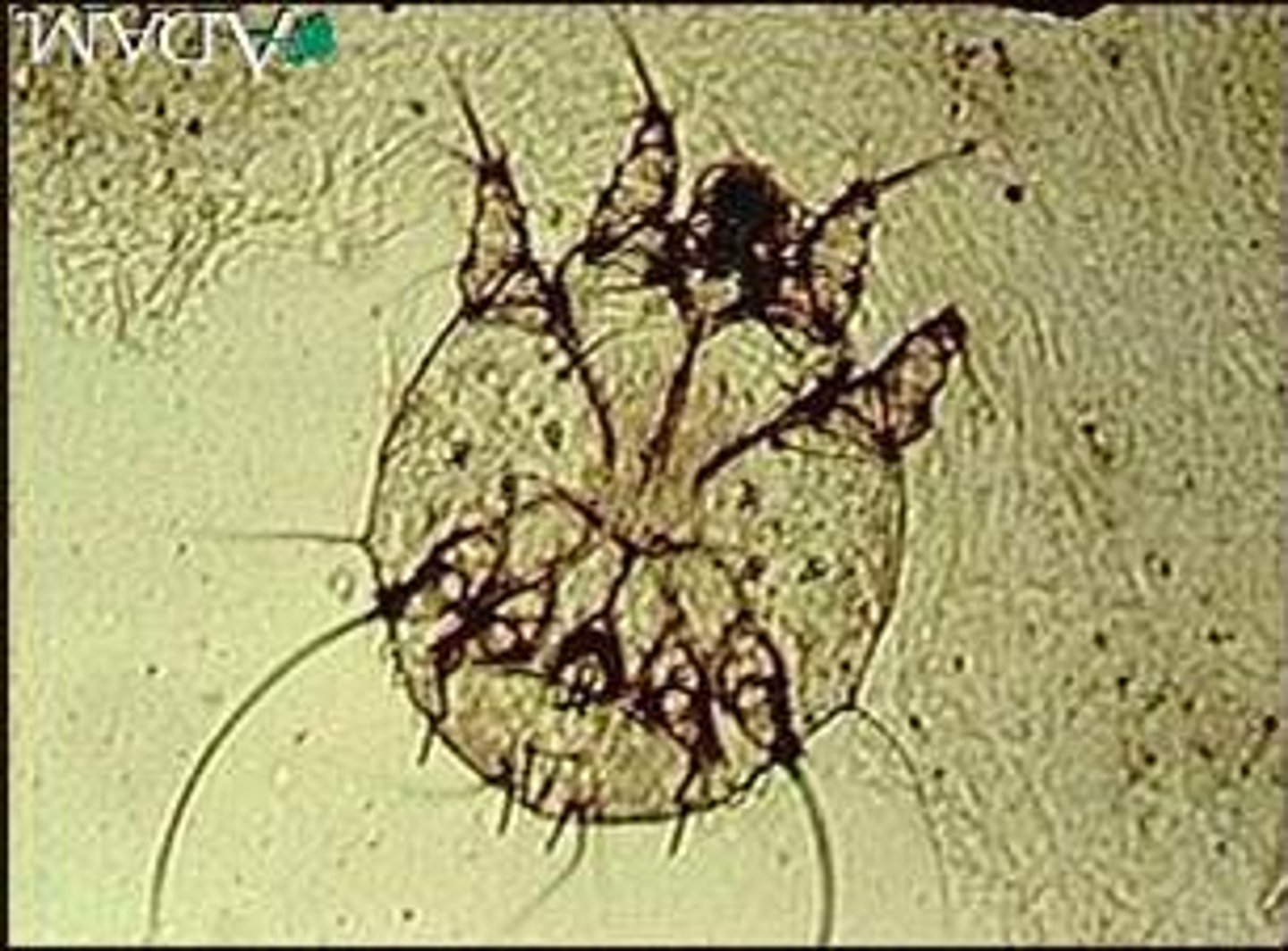
How do we test for scabies?
Mineral oil scraping
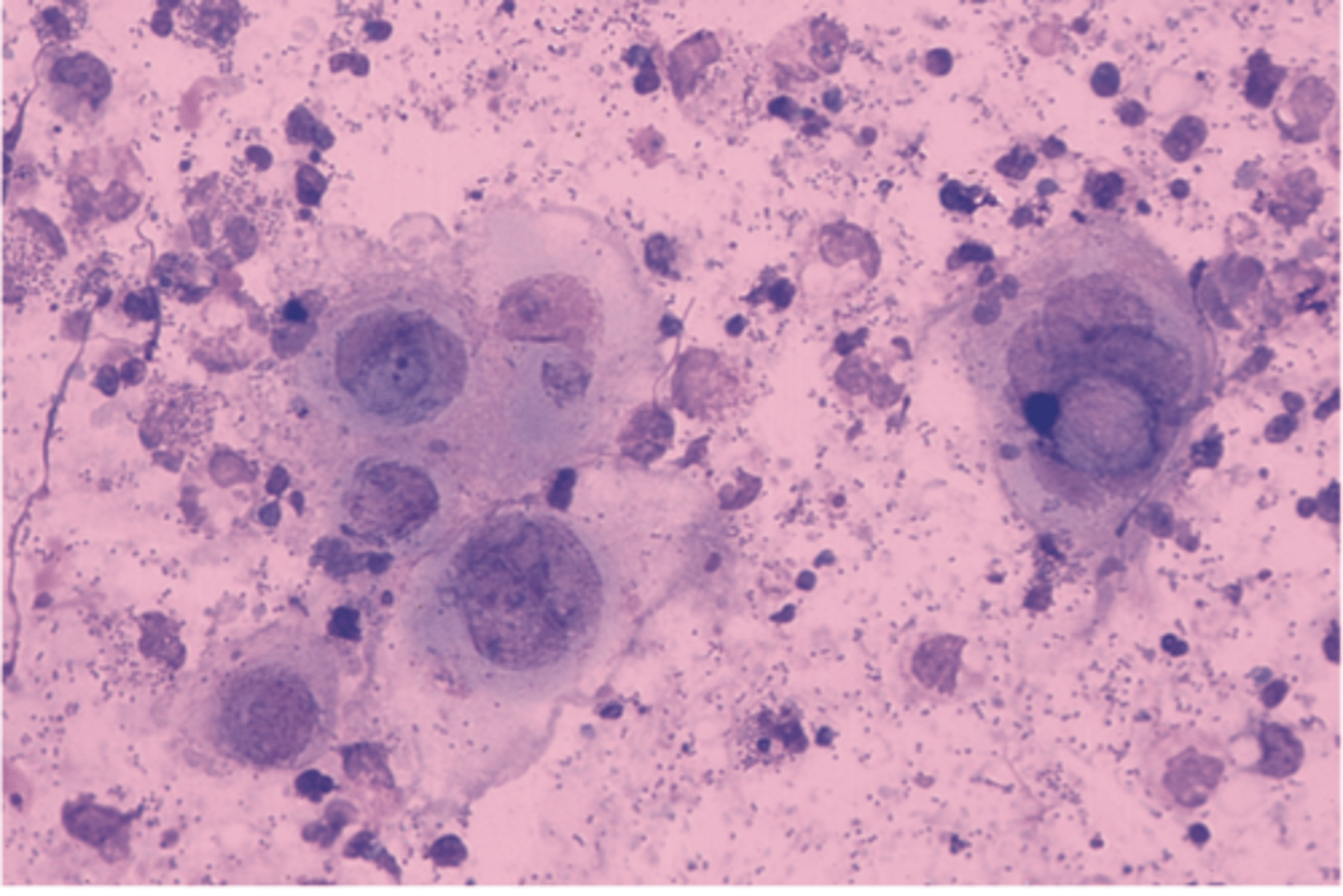
This type of smear is easy to perform and is a rapid test for HSV but it doesn't differentiate between HSV types.
Tzanck smear
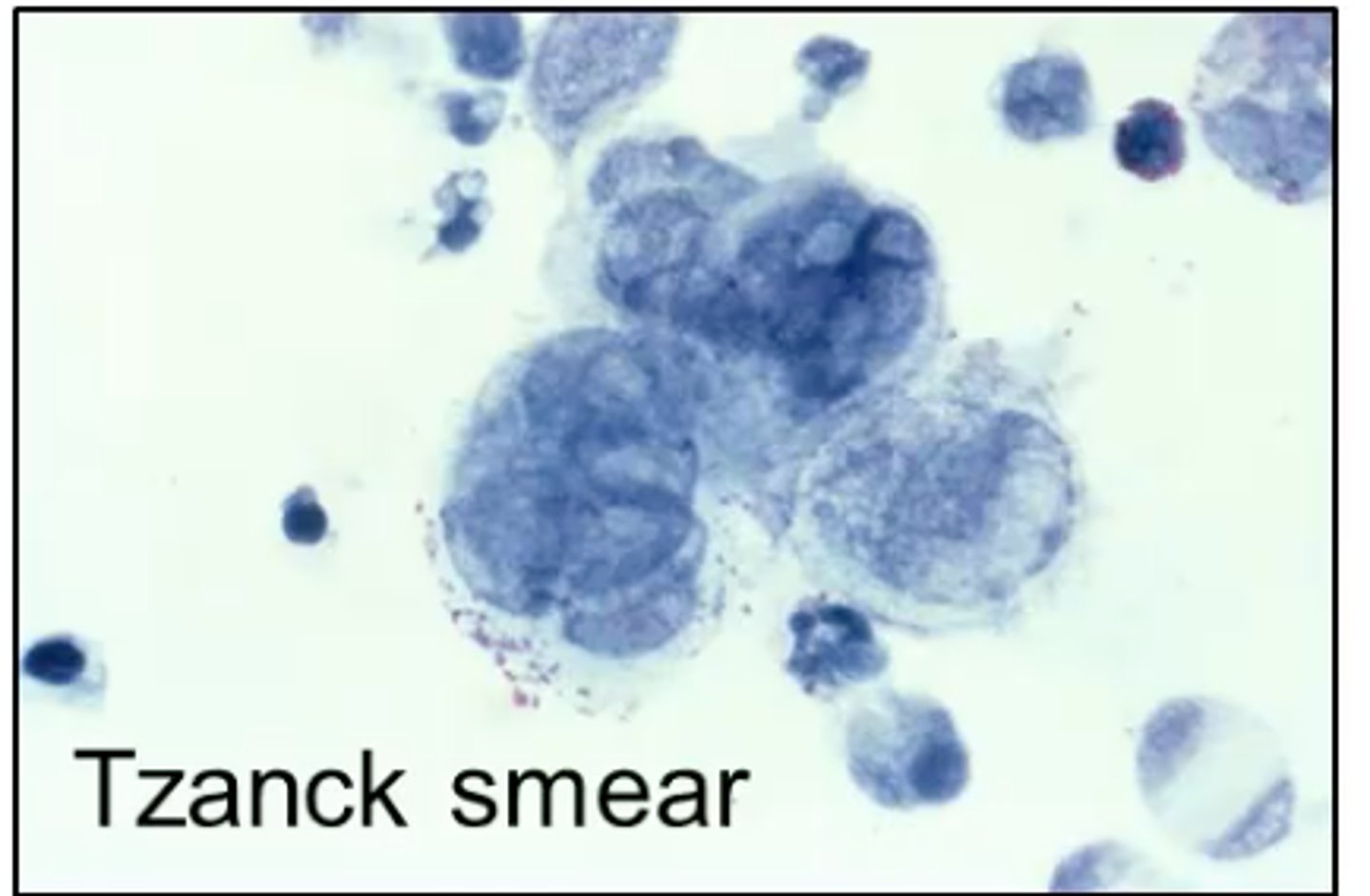
A Giemsa stain is used in a Tzanck smear, what will be seen under the microscope that is diagnostic for HSV?
Multinucleated giant cells
What do you use to clean/prep the site for a biopsy?
1. Betadine or
2. Alcohol or
3. Hibiclens
To numb the area we usually use 1% lidocaine with or without EPI. What areas would we want to avoid using Lidocaine WITH EPI on?
1. Fingertips
2. Nose
3. Ears
4. Genitalia
(NO EPI on these areas)
For wound care, what can we recommend our pt to apply to help heal faster?
Vaseline or bactroban
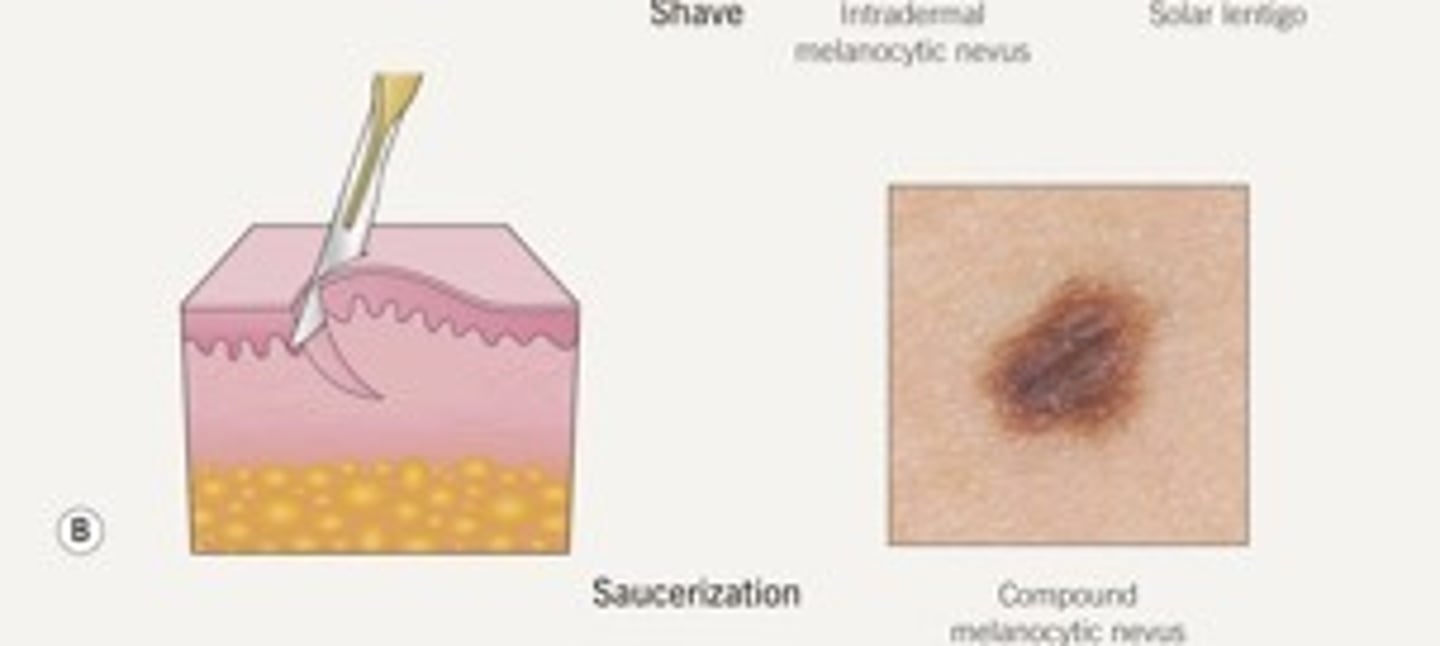
This type of biopsy is used for suspected superficial lesions in the epidermis
Shave Biopsy
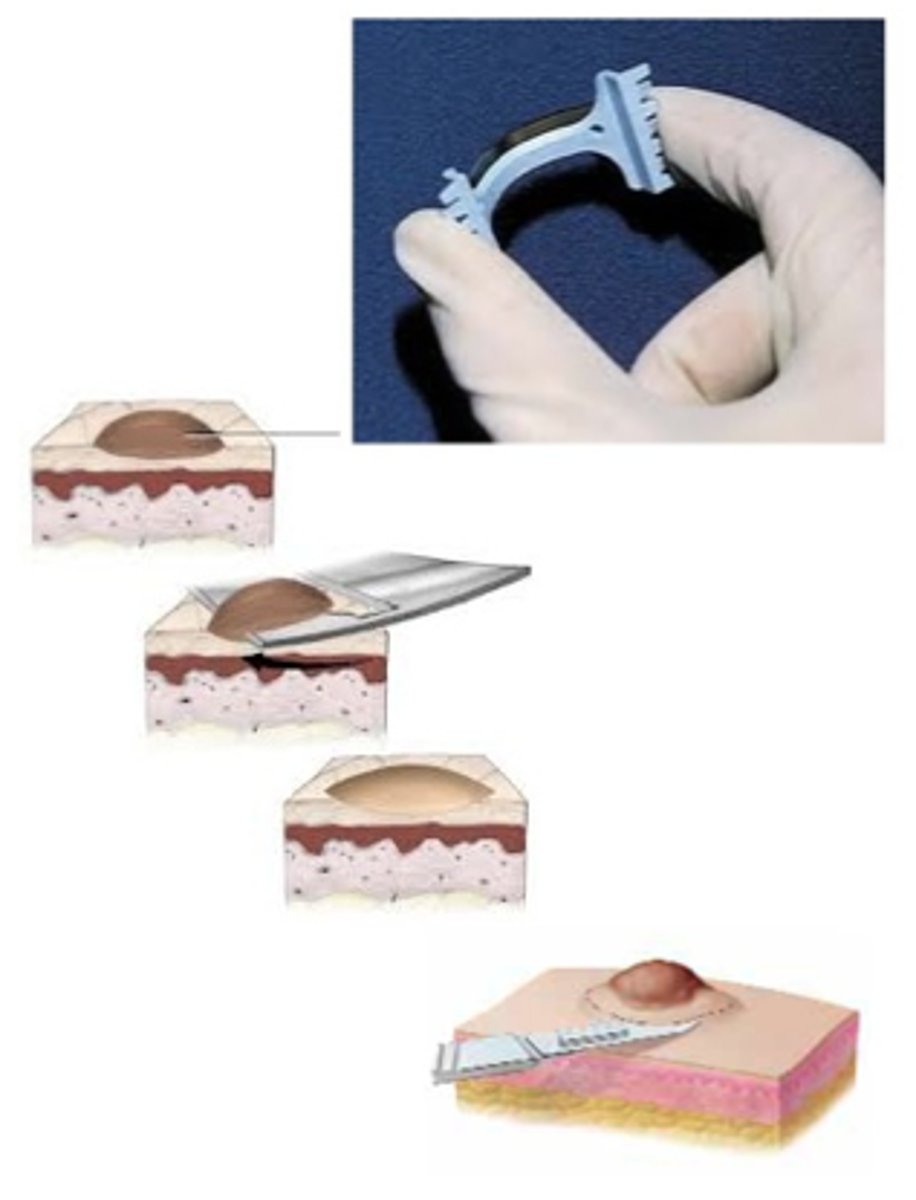
What type of biopsy would you use for a wart or skin neoplasm?
Shave biopsy
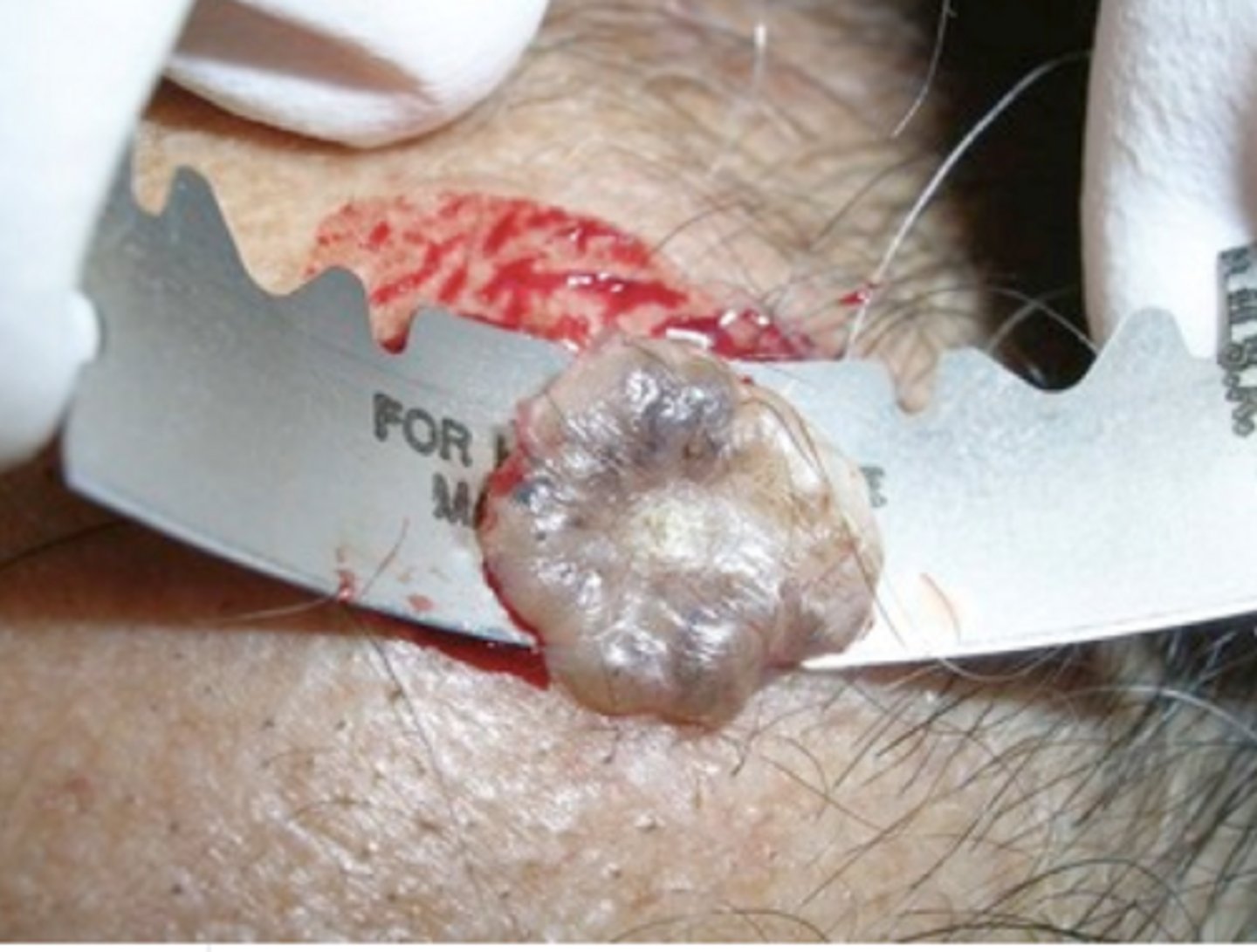
This type of biopsy is a deep shave biopsy and is good to use to remove a compound melanocytic nevus.
Saucerization biopsy
Biopsy which gives the pathologist full thickness of the skin. Leaves a small scar
Punch Biopsy
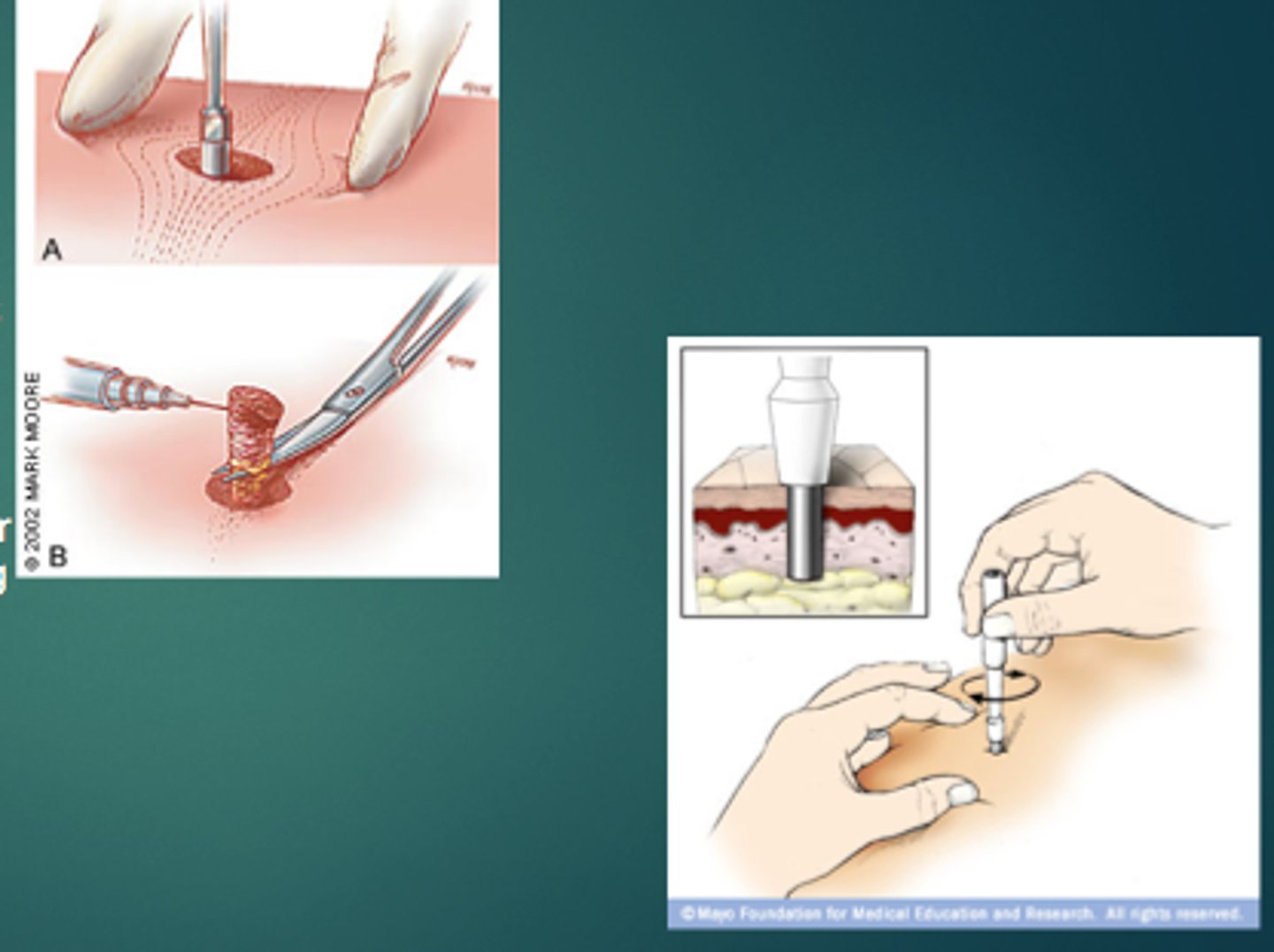
What kind of biopsy would be appropriate for suspected melanoma, erythema nodosum, drug rash or lupus?
Punch Biopsy
This type of biopsy is used to obtain clear margins or to remove a piece of a lesion and is appropriate for staging, diagnosis and tx.
incisional biopsy (taking a piece of the pie)
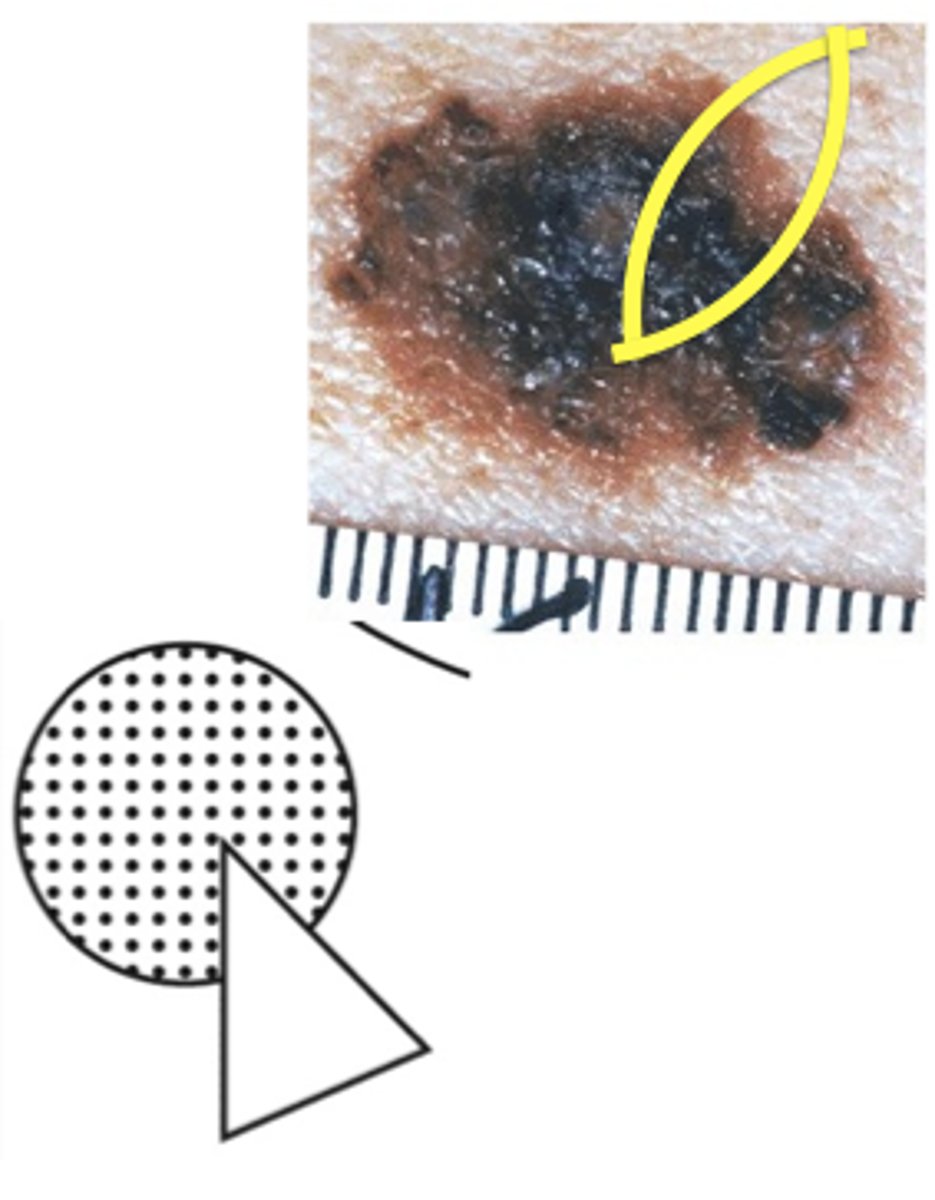
What type of biopsy would you use if a patient had an atypical melanocytic lesion?
incisional biopsy
What kind of lesions is gradle cautery good for?
Pedunculated lesions (skin tag)
This is referred to as inflammation of the skin
Dermatitis
This is an IgE-mediated hypersensitivity that requires two separate exposures to antigen. The first exposure causes sensitization. After the second exposure reaction can be minutes or hours.
Type I (Anaphylactic)
What type of hypersensitivity is anaphylaxis, urticaria and angioedema?
Type I
This type of hypersensitivity has IgG or IgM antibodies that react with cell antigens that results in complement activation. Requires 2 separate exposures to antigen. Considered cytotoxic reaction.
Type II Cytotoxic Hypersensitivity
This type of hypersensitivity has IgG or IgM immune complex that activate the complement system.
Type III immune complex hypersensitivity
This type of hypersensitivity activates T cells against cell surface bound to antigens.
Type IV cell mediated (delayed) hypersensitivity
Contact dermatitis and TB skin test are considered what type of hypersensitivity reactions
Type IV
Slight rubbing of the skin results in exfoliation of the outermost layer of skin resulting in erosions. This demonstrates a plane of cleavage at the dermo-epidermal junction.
Nikolsky sign
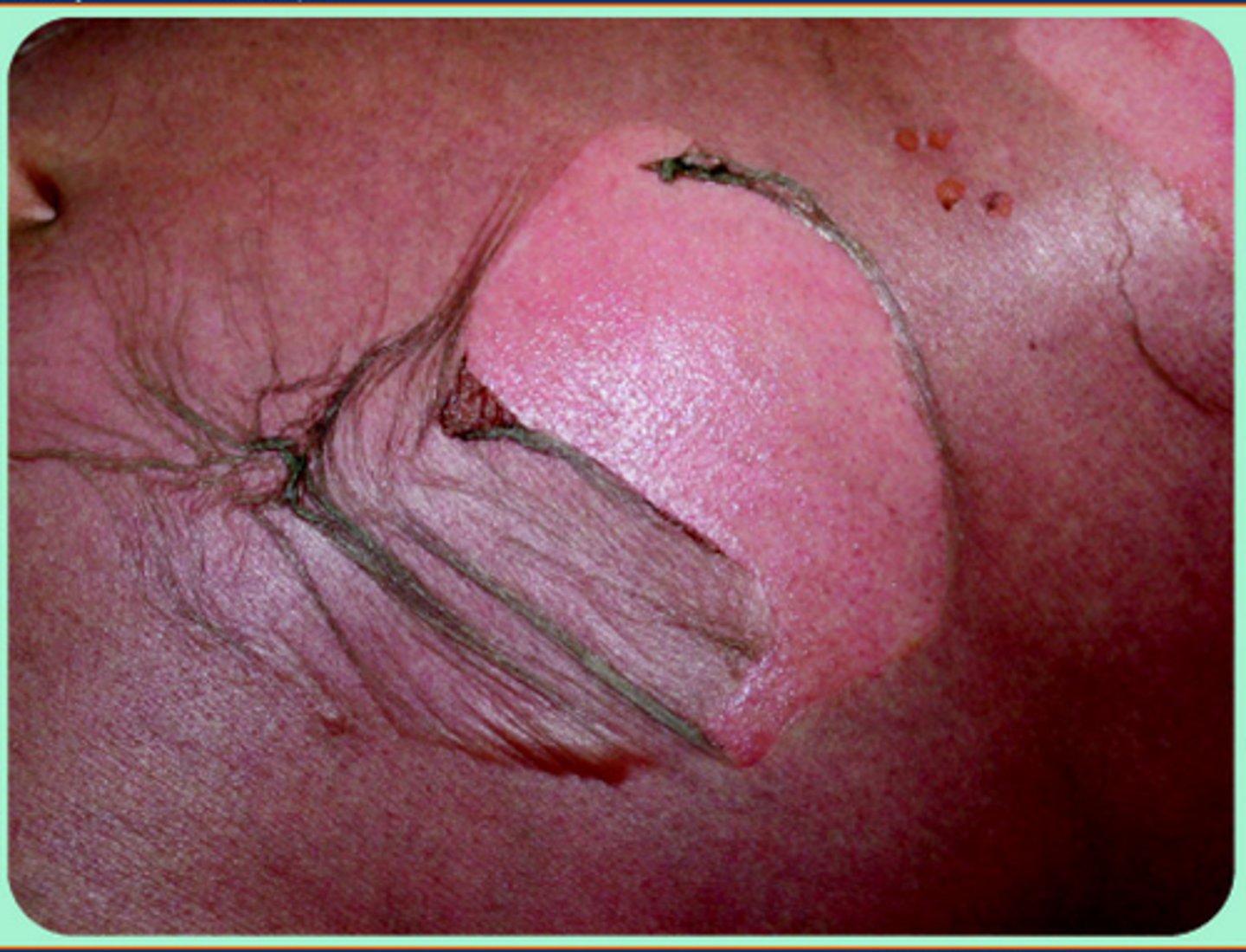
Pressure on a bulla leads to lateral extension in normal appearing skin
Asboe-Hansen sign (indirect Nikolsky sign)
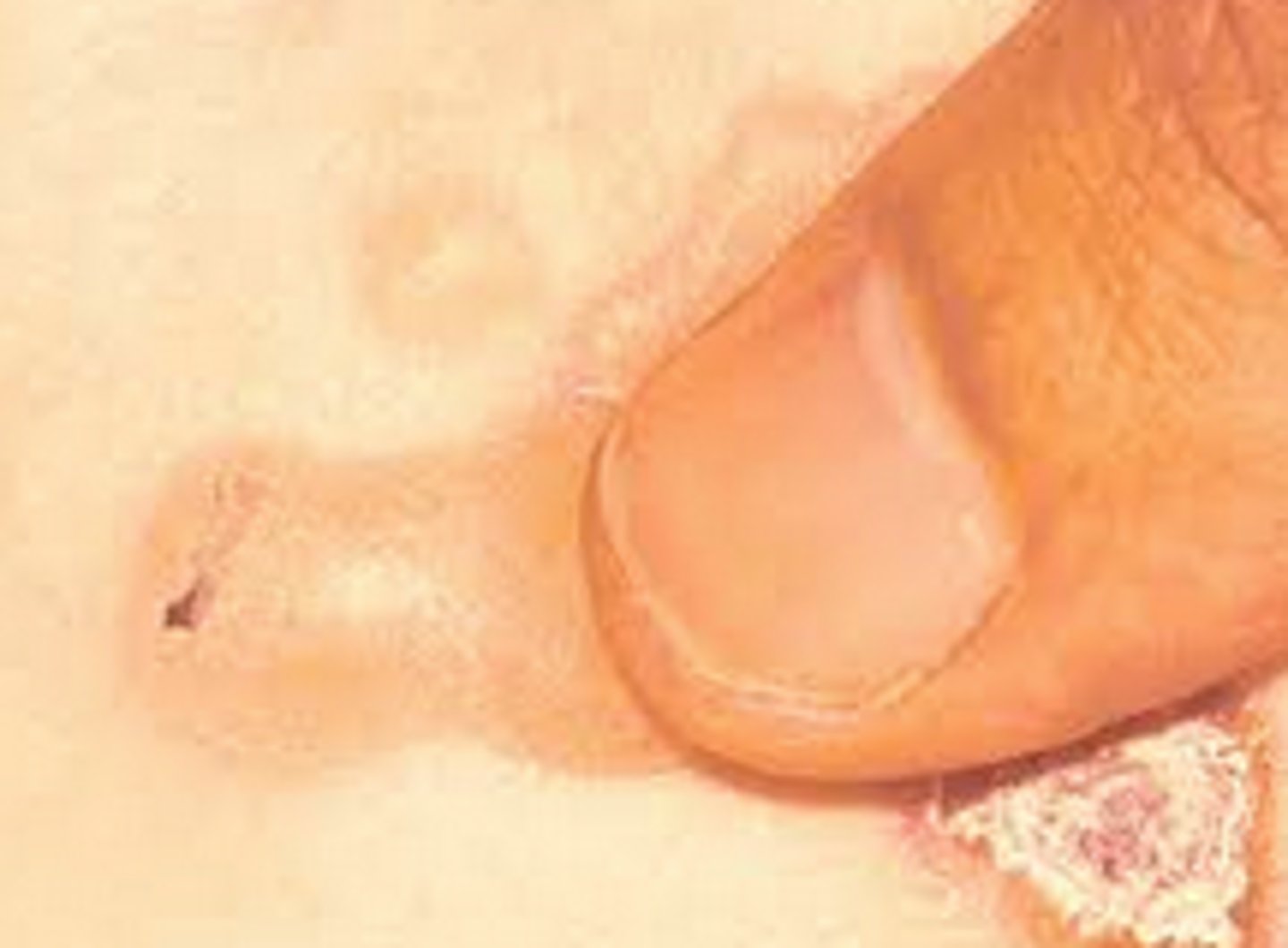
Measels-like rash, pink macules and thin papules that become confluent
Morbilliform
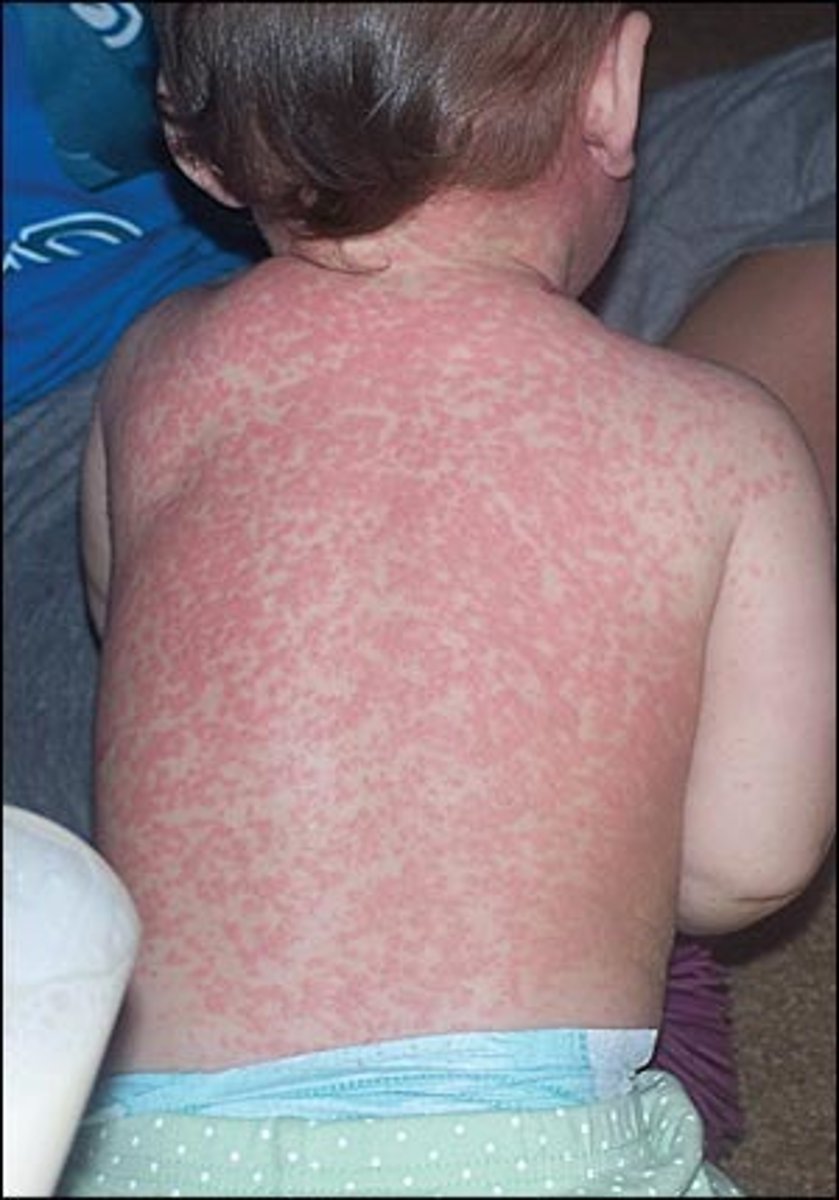
What is the hallmark skin symptom of an allergic reaction?
Pruritus
"Itch scratch cycle"
Erythematous, at times edematous papules, plaques, scaling, occasionally oozing secondary to scratching, excoriations. These are consider _____ lesions.
Acute lesions
What are examples of chronic lesions?
Lichenification, PIH
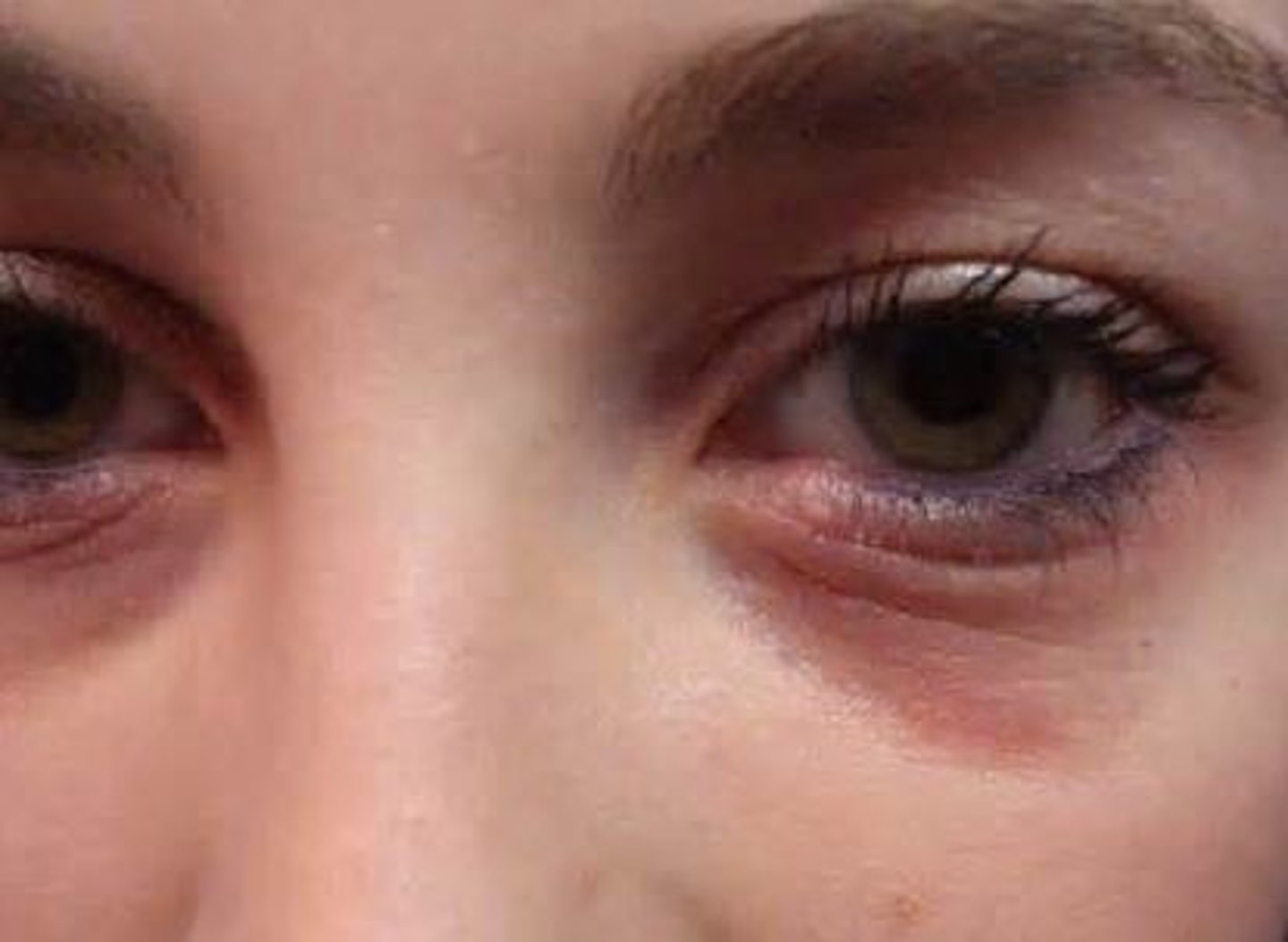
Accentuated lower eyelid fold associated with allergic shiners and pale nasal mucosa
Dennie-Morgan folds