topic 1 cell biology
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
sep-dec
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
cells definition
the basic building blocks of life
unicelular definition
organisms only made up of one cell e.g bacteria
multi celular definition
organisms made up of many cells e.g dog
cell membrane definition
surrounds the cell and controlls what substances enter and leave the cell
cytoplasm definition
where all the chemical reactions take place
mitochondria definition
breaks down glucose and oxygen and releases oxygen and releases energy, called respiration
nucleus definition
contains DNA in the form of chromosomes (which have genes on them) and control the activities of the cell
ribosones definitions
synthesizes proteins from amino acids
animal cell
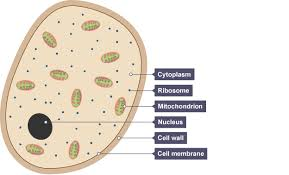
no cell wall
why are thwew many mitochondria in a muscle cell
so the mitochondria makes energy for the muscles to move
define permenwnt vacuole
contains cell sap (a solution of sugars and salt)
define chloroplasts
contains chlorophyll (green pigment) whuch absorbs light for photosynthesis
define cell wall
strengthens the cell. Contains cellulouse
plant cell
whats in a bacterial cell
cell wall
cytoplasm
ribosomes
loop of DNA
cell membrane
plasmid
capsule
flagellum-helps propell
Bacterial cells do not have their genetic material in a nucleus
define eukaryotic cell
a cel that has a nucleus e.g aniaml, plant, fungle cell
define a prokaryotic cell
a cell that does NOT have a nucleus e.g bacteria
difference between prokayotic cells and eukaritoc cells ()
Pro cells have a single loop of DNA
Pro cells may have a capsule
Pro cells have plasmaids
Pro cells are smaller in size
Pro cells dont have a nucleus
Pro cells dont have chromoaomwa
Euk cells may have mitochondria, chloroplasta and other orgenells present
what chromosomes do females have
what chromosomes do males have
XX - female
XY- male
gene definition
a short section of DNA that codes for a specific protein determing a characteristic (e.g eye colour)
what do we need cells for (2)
-growth and development of multicellular organisms
-replacing
what are the 3 stages in the cell cycle
stage 1
growth
replicates DNA to from 2 copies of each chromosone
makes new subcellular structures
stage 2
mitosis = nucleus divides
stage 3
cell divides
cytokinesis
mitosis
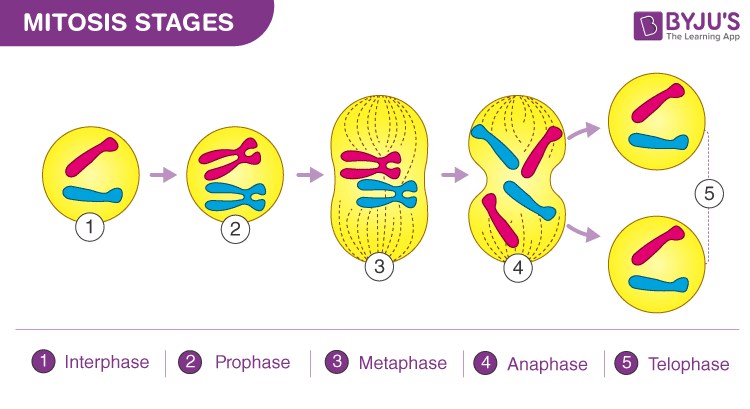
stem cells definition
undifferented cells
what can stem cells do (2)
-divide repeatedly to produce lots more undifferented cell
-differentiate into any type of human cell
where are stem cells from
and what can they do (3)
embryos and the embryos will be destroyed after being used
divide rapidly
can be cloned
differentiate into any type of human cell
what conditions can be treated with stem cells (3)
paralysis
type 1 diabities
replaces blood cell damage
what are stem cells from plant meristems used to produce
used to produce new plant clones
pros and cons of stem cells (2,1)
pros
can be grown quickly/economically
used for research and farming
cons
concern that using embryonic stem cells to treat people might cause cancer
treating conditions are relatively slow, difficult and expensive
ethical,social, economical issues
How many cells are in an early embryo?
Two to three hundred
How are embryonic and adult stem cells different? (2)
Embryonic stem cells are only found in embryos. They can differentiate into all the cell types that make a human.
Adult stem cells are found in children and adults. They can only differentiate into a limited number of cell types.
where are stem cells found
meristems
function of red blood cell
to transport oxygen cells around the body
red blood cell
adaptions and how its good (3)
it has a biconcave disc shape- to maximize its surface area so more oxygen can diffuse in and out of the cell
has many mitochondria - to release energy so it can absorb mineral ions by active transport
doesnt have a nucleus - so the cell can carry more haemoglobin to transport more oxygen to body cells
sperm cell
function
to reach the egg and fertilise it so the male DNA can combine with the female DNA
sperm cell
adaptations and how its good (4)
has many mitochondria - to release energy so it can swim to the egg
has a streamlined head - to help it swim to the egg
carries enzymes in its head - to digest through the egg cell membrane to fertilise it
it has a tail - to help it swim to the egg
palisade mesophyll cell
function
to absorb light energy to carry out photosynthesis
palisade mesophyll cell
adaptations and how there good (1)
it contains many chloroplasts - to absorb light for photosynthesis
neuron (nerve cell)
function
to carry electrical signals from one part of the body to another
neuron (nerve cell)
adaptaions and why its good (1)
it has many branched connections at its ends - to connect to other nerve cells and form a network throughout the body
root hair cell
function
to absorb water and mineral ions from the soil
root hair cell
adaptions and how its good (2)
has a root hair extension - to increase its surface area so it can absorb more water and mineral ions
has many mitochondria - to release energy so it can absorb mineral ions by active transport
mussel cell
function
to contract
muscle cell
adaptation and why its good (1)
has many mitochondria - to release energy for muscle contraction
total magnification equation
total magnification = magnification x magnification of eye pieces
how to use a microscope to use a microscope to view onion cells (8)
put a thin epidermal sample of onion cells onto microscope slide
add iodine solution to the specimin to stain the starch granu/es
place slide on stage
once the slide is on stage, adjust mirror OR switch light on so light passes through slide
use lowest power (x4 objective lens) initially
use coarse focus knob initially to focus the image
adjust fine focussing knob to focus the image further until you get a clear image
change objective lens to x40 the 10x eyepiece and 40x objective lenses will give you a total magnification of x400

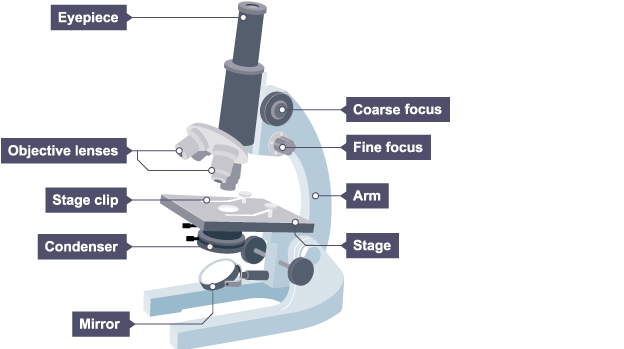
dont need condenser
metres (m)→ centimeters (cm) →milimeters (mm) → micro metres (µm) →nanometers (nm)
m—-x100—>cm—x10—>mm—x1000—>µm—x1000—>nm
image size formular
Image size= Actual size x Magnification
(I AM)
magnification define
how many times bigger the image is compared to the origional origonal object
resolution define
the ability to distinguish between two points. A higher resolution gives a sharper (less blurred image)
difference between light microscope and electron microscope (3,9)
light microscope
can be used on live specimens
uses light as its source of illuminating radiation
uses lenses to focus the source of illuminating radiation
electron microscope
has a higher resolving power
can only produce black and white images
more expensive to purchace and operate
uses electrons as its source of illuminating radiation
uses electromagnets to focus the source of illuminating radiation
can achieve higher magnification
specimen must be prepared so needs to be dead
can be used on small organelles within the cell e.g mitochondria
can be used to view thin sections of a specimen or 3D structure of cells/tissues
define diffuse
the particles spread out from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
what happens when moving down a concentration gradient
no extra supply of energy is needed to move the particles down their concnetration gradient
particles move as they have energy
what moves into the cells (2)
oxygen
nutrients (e.g glucose, AA, fatty acids)
what moves out of cells(4)
waste products
carbon dioxide
urea
lactic acid
when is diffusion faster (3)
when the diffusion is shorter
a higher temperatures because particles have more energy
a higher temp because particles have more energy
when there is a higher concentration gradient
difference between diffusion and active transport
`diffusion
particles moving down the concentration gradient
no energy needed
active transport
particles moving against the concentration gradient
energy if needed
what happens when plant root hair cells absorb the mineral ions in the soil
do they go with or against the concentration gradient
the plant root hair cells absorb the mineral ions in the soil. The plant root hair cells absorb the higher concentration of minerals which uses energy which is in the repiration so they go against concentration gradient
define diffusion
e.g of types of substances that move this way
diagram
when particles move from high concentration to low concentration down the concentration gradient
a prosses by which substances move down their concentration gradient from a region ofhigh concentration gradient to a region of lower concentration. Is a passive prosses (no energy required) (kind of like water moving down a hill)
all ways takes place
glucose
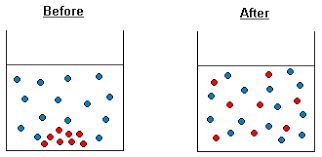
active transport definisition
diagram to represent this
e.g of types of substances that move this way
the movement of molecules across a cell membrane, from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentrationand requiring energyfrom cellular respiration

carbon dioxide
dilute solutions
concentrated solutions
contain a high concentration of water molecules
contain a lower concentration of water molecules
definne osmosis
osmosis is the diffusion of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a partially permable membrane
if we place a plant cell into a concentrated solution then would the cell shrink or expand
the water would move out of the plant cell by osmosis so it would shrink
if we place a plant cell in water then would the plant cell shrink or expand
the water will move into the cell by osmosis so the plant cell will expand
osmosis practicle (9)
peel the potato as the potato skin can affect osmosis
use a cork borer so each cylinder has the same diameter to produce 3 cylinders of potato
use a scalpel to trim each cyliner of potato so each cylinder is the same hight (3cm as a shorter cylinder then we mght not be able to measure the affect of osmosis)
measure length of each cyl with ruler and mass with a balance
place each cylinder into a test tube. Add 10cm3of a 0.5 molar sugar solution to the first test tube
add 10cm3of 0.25 sugar solution to the second test tube and 10cm3of distilled water to the third test tube (distilled not tap as distilled contains no dissolved substances which could affect the rate pf osmosis)
leave overnight to allow for osmosis to take place
remove potato cyl and gently roll on paper towl (dont press as we only want to remove surface water not force water out of cell)#
measure length and mass of cyli again and calcultae % change of length and mass (% change = change in value/ og value x 100) and plot a graph
what would a positive % change mean for the potato cylinder
negative
gained mass
lost mass
rp osmosis in plant tissues
independent variable(1)
dependent variable(1)
control variable (4)
I - concentration of sugar solution
D - percentage change in mass
C - size of potato cylinder
-type of plant tissue
-surface area of potato cylinder
-temperature
how could the osmosis investigation more reliable
repeat / use more potato chips in each solution
plasmolysed meaning
a plant cell losing water content and therefore contracting and shrinking its cytoplasm and plasma membrane away from the inside of its cell wall
turgid meaning
a plant cell that has been filled with water as a result of osmosis
flaccid meaning
cell that lacks turgidity, i.e. it is not swollen and plump, but loose or floppy and the cell has become drawn in and pulled away from the cell wall
alveoli
air sacks in lungs
gases exchange occurs here
millions of alveoli- large surface area- increased exchange
diffusion of O2 and CO2
small intestines →villi
one cell thick →(short diffusion distance)
micro villi on each cell = increased surface area
good blood supply - high concentration gradient and diffusion
mitochondria for active transport
diffusion also happens