L35 Antibiotics and Resistance
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts related to antibiotics, their mechanisms of action, and antibiotic resistance.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Selective Toxicity
The ability of an antibiotic to harm bacterial cells without harming the host cells.
Paul Ehrlich's concept
By observing that some dyes stain microbes better than others, he comes up with idea of a chemical 'magic bullet' to kill microbial cells but not the host's cells (selective antibiotic).
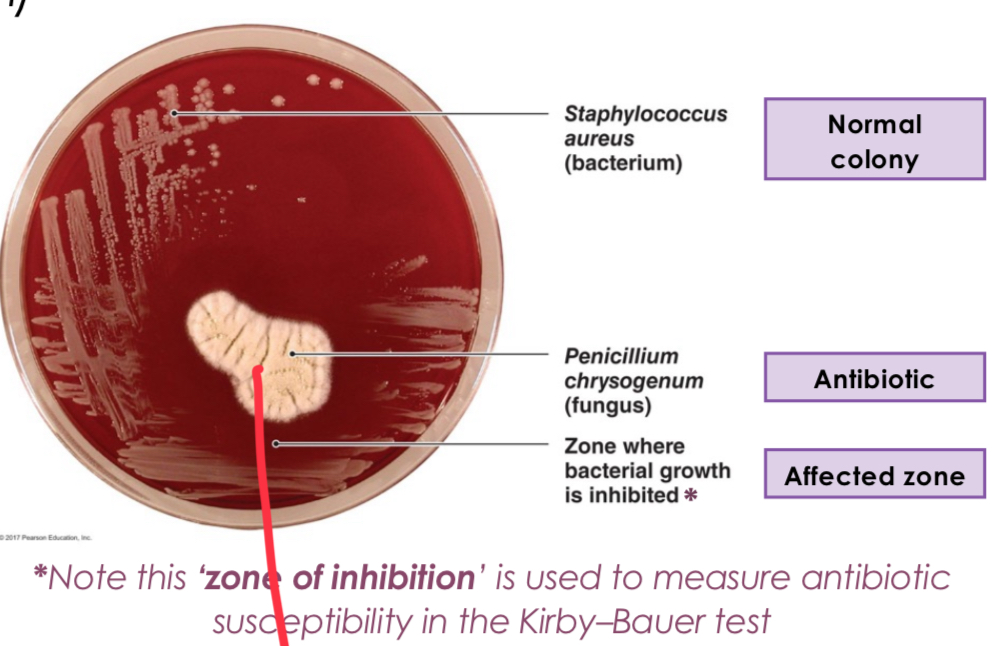
Alexander Fleming (1928) Penicillin
Observed that colonies of Staphylococcus bacteria could be destroyed by the mould Penicillium notatum.
How Penicillin works
Interfering with the normal formation of the bacterial cell wall by inhibiting the formation of peptidoglycan cross-links (peptide cross-bridge).
How selective toxicity of antibiotics target bacteria and not host
Eukaryotic DNA Pol, RNA Pol, ribosomes, plasma membrane, are different from those of bacteria, this difference helps in targeting .
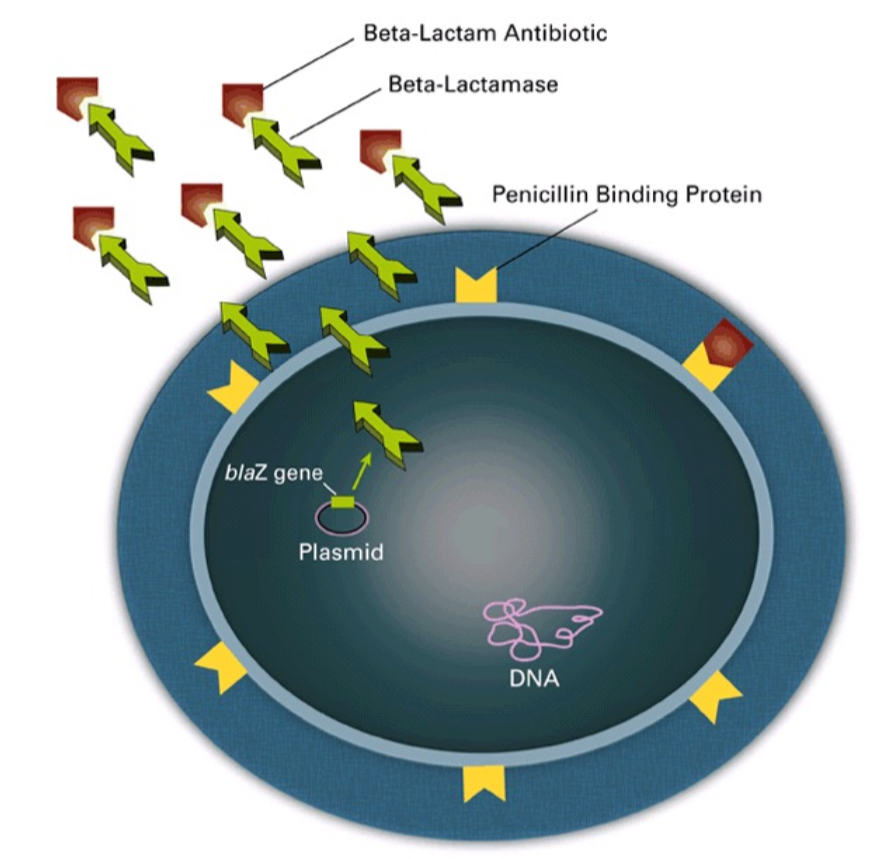
Beta Lactamase
Enzyme produced by bacteria and used to destroy (chew up) penicillin. Breaks bond in B-lactam ring of penicillin to disable molecule. Bacteria with this enzyme resists effects of penicillin and other B-lactam antibiotics.
Antibiotics on different cell components
Bacterial cell components targeted by different classes of antibiotics.
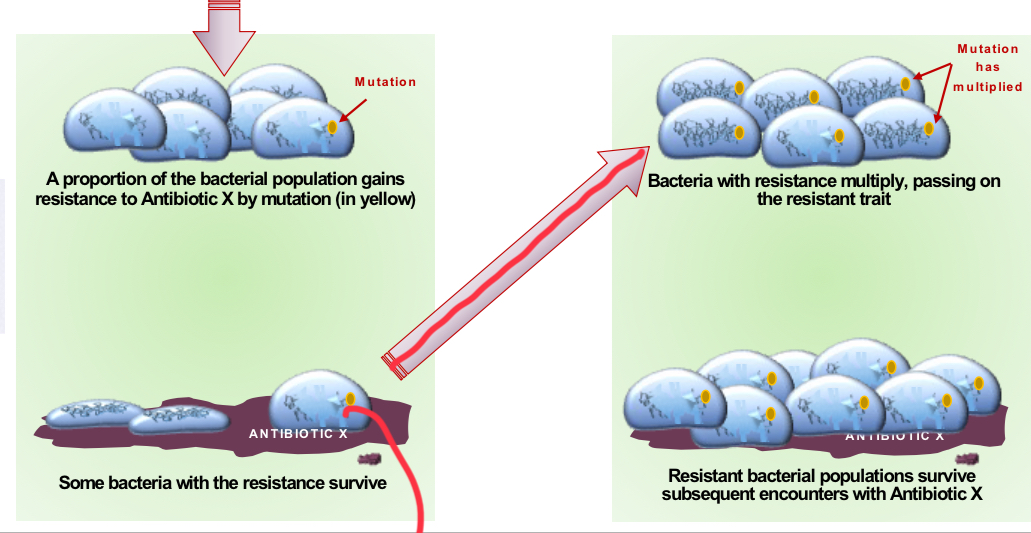
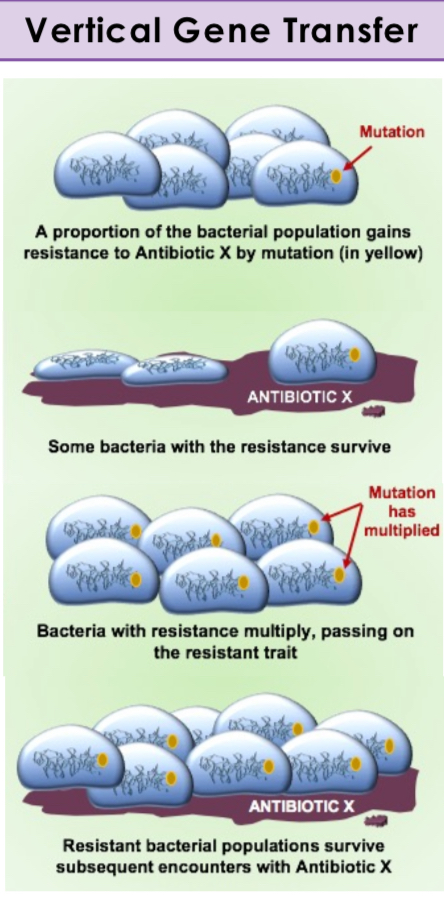
Antibiotic Resistance: Selection of Mutants
A proportion of bacterial population gains resistence to antibiotic X by mutation, some bacteria with resistance survive. Then they multiply passing on resistance, which survives subsequent encounters with antibiotic X.
Antibiotic resistence: Vertical Gene Transfer
Transfer of genes from parent to offspring.
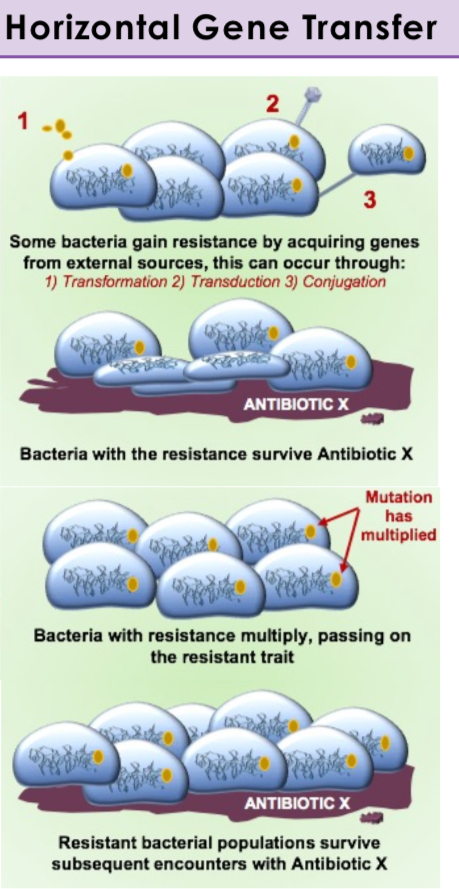
Antibiotic resistence: Horizontal Gene Transfer
Transfer of genes between bacteria that are not parent and offspring (e.g., through plasmids).
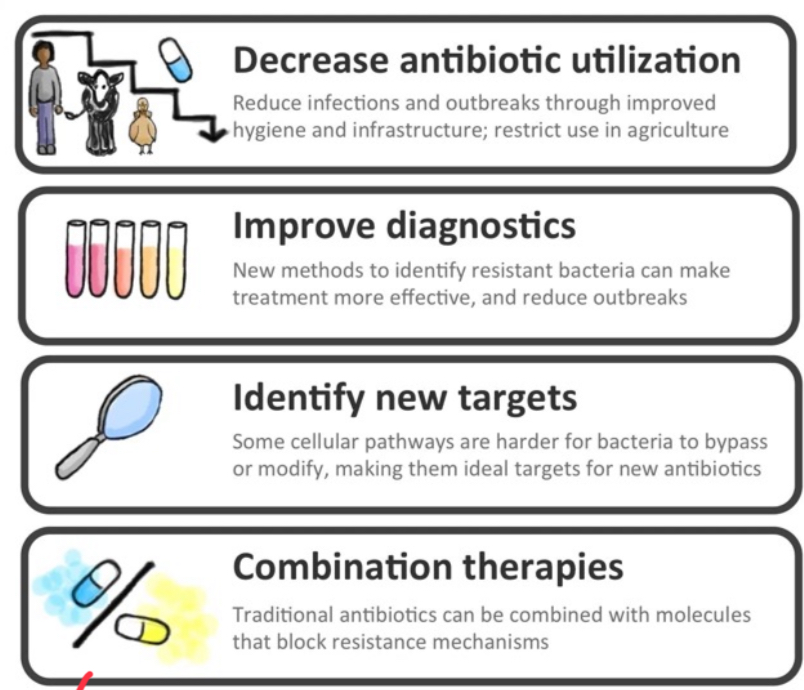
Reducing antibiotic resistance spread requires
Completing prescribed courses, avoiding inappropriate use for viral infections, implementing combination therapies to prevent resistance emergence, and developing new targets and resistance-blocking molecules.