CEN5087 Midterm Study Guide
5.0(1)Studied by 36 people
Card Sorting
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:16 PM on 2/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
1
New cards
What is Software?
* Models, Design, Tests
* A set of instructions (Programs)
* A set of instructions (Programs)
2
New cards
What are characteristics of software?
Invisible
Complexity - size
Changeability - bugs, adding functionality, adapting
Complexity - size
Changeability - bugs, adding functionality, adapting
3
New cards
What is software crisis?
Low productivity
Poor quality
High Cost
High Demand
Poor quality
High Cost
High Demand
4
New cards
What is software engineering?
Process Products
Management Methods
Management Methods
5
New cards
What is software modeling?
Complexity - Abstraction (vertical)
Divide & Conquer (Horizontal)
Behavior
Functionality
Structure
Divide & Conquer (Horizontal)
Behavior
Functionality
Structure
6
New cards
Water Fall
System Engineering
Software Requirements Analysis
Software Design
Coding & Unit Testing
Integration & Integration testing
Acceptance Testing
Maintenance
(Can't go back up past Maintenance)
Software Requirements Analysis
Software Design
Coding & Unit Testing
Integration & Integration testing
Acceptance Testing
Maintenance
(Can't go back up past Maintenance)
7
New cards
Water Fall Pros and Cons
\+Simple, Straight sequence of phases
\+It supports function-oriented project organization
\-Inflexible to requirement change
\-The system is outdated when delivered from long development duration
\-No early feedback from the users
\-May lose entire investment from customer if the project fails.
\+It supports function-oriented project organization
\-Inflexible to requirement change
\-The system is outdated when delivered from long development duration
\-No early feedback from the users
\-May lose entire investment from customer if the project fails.
8
New cards
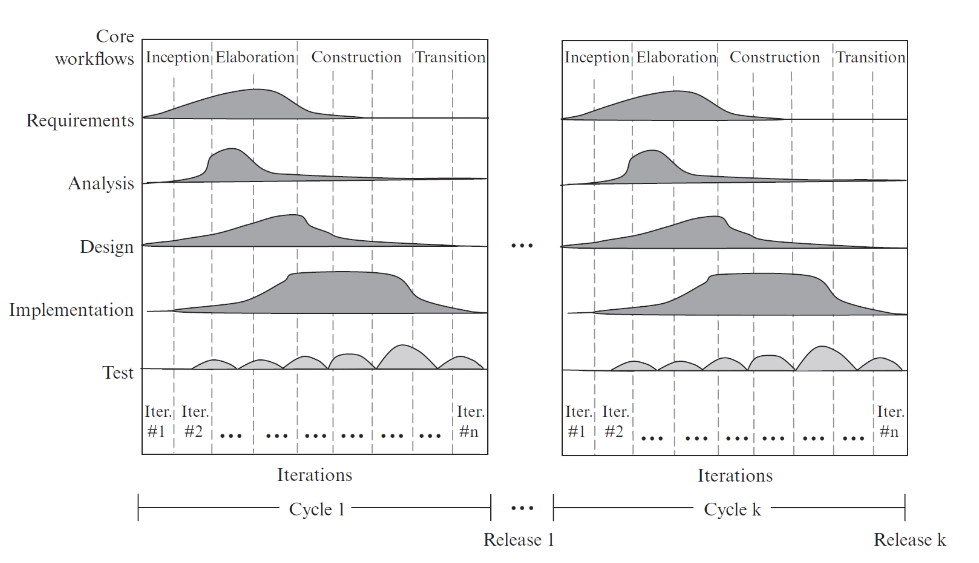
Rational Unified Process (RUP)
Inception: 1-2 iterations, produces a simplified use case model, a tentative architecture, and a project plan.
Elaboration: Produces the most critical use cases and architectural design
Construction: remaining use cases are implemented into the system
Transition: System is deployed, users are trained, and bugs are fixed
Elaboration: Produces the most critical use cases and architectural design
Construction: remaining use cases are implemented into the system
Transition: System is deployed, users are trained, and bugs are fixed
9
New cards
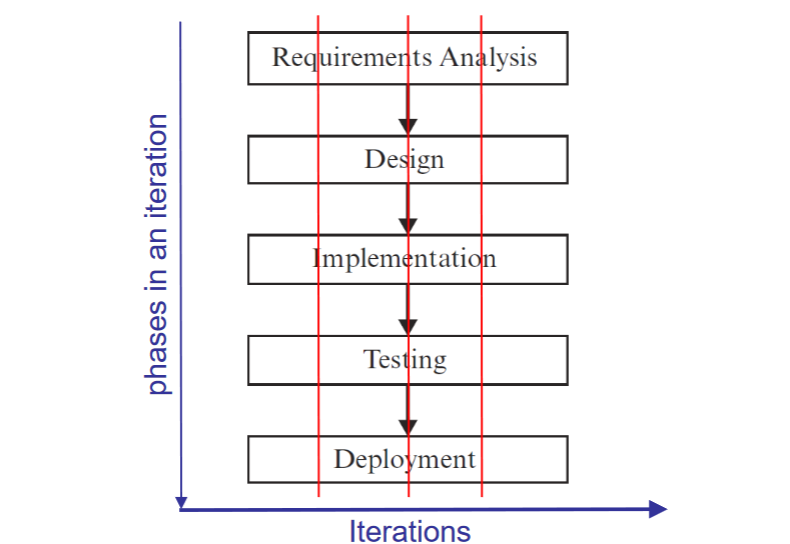
Agile Process Models
\+Flexibility
\+Immediate feedback
\-Scope creep
\-Time
\-Lack of predicitability
\+Immediate feedback
\-Scope creep
\-Time
\-Lack of predicitability
10
New cards
Functional Requirements
Statements of services the system should provide, how the system should react to particular inputs and how the system should behave in particular situations.
11
New cards
Non-functional requirements
Performance, reliability, usability, security, maintainability, quality.
12
New cards
Requirements Elicitation Approaches
Identifying problems and needs
Constructing analysis models to help understanding
Formulating system/software requirements
Conducting feasibility study
Checking the requirements and models for desired properties such as correctness, and consistency
Specifying acceptance tests
Formulating an iterative development plan
Constructing analysis models to help understanding
Formulating system/software requirements
Conducting feasibility study
Checking the requirements and models for desired properties such as correctness, and consistency
Specifying acceptance tests
Formulating an iterative development plan
13
New cards
Use Cases
A business process that begins with an actor, ends with the actor, and accomplishes a business task useful for the actor.
Usually a circle.
Usually a circle.
14
New cards
Actors
Played by and on behalf of a set of business entities or stakeholders that are external to the system and interact with the system.
Usually a stick figure
Usually a stick figure
15
New cards
System Boundary
It encloses the use cases and show the capabilities of the system.
Usually a box.
Usually a box.
16
New cards
Inheritance
Indicates that one use case is more general/specialized than the other.
Notation: -
⇨
Notation: -
⇨
17
New cards
Extension
Indicates that one use case can optionally continue the process of another use case.
Notation
\----\>
<
Notation
\----\>
<
18
New cards
Inclusion
Indicates that one use case includes another use case as part of its business process
\----\>
<
\----\>
<
19
New cards
What is actor-system interaction modeling?
The modeling and design of how the system interacts with the actors to carry out the use cases. A two-column table that describes each interaction (actor input and system response)
20
New cards
Abstract Use Case
using a verb or noun phrase
21
New cards
High Level Use Case
stating exactly when and where the use case begins and when it ends. (This use case begins with, This use case ends with)
22
New cards
Expanded Use Case
describing step by step how the actor and system interact to accomplish the business task using a two-column table
23
New cards
Precondition
use case assumes that the actor has already taken action that does not directly interact with this use case
24
New cards
Postcondition
system changes based on the completion of use case
25
New cards
What are activity diagrams?
Diagrams that are a more understandable visual representation than textual description. Show use cases with multiple scenarios and use cases with concurrent activities.
26
New cards
What is a class?
An abstraction of objects with similar properties and behavior. A collection of objects.
27
New cards
Association Class
defines properties and operations for an association between two classes
28
New cards
What are the different type of class relationships?
Inheritance, Aggregation, Association
29
New cards
Inheritance Class Relationship
expresses the generalization/specialization relations between concepts. One concept is more general/specialized than the other. IS-A relationship
Example: Vehicle is a generalization of car, car is specialization of vehicle
Example: Vehicle is a generalization of car, car is specialization of vehicle
30
New cards
Aggregation Class Relationship
expresses the fact that one object is part of another object. Also called PART-OF relationship
Example: engine is part of a car
Example: engine is part of a car
31
New cards
Association Class Relationship
expresses general relationship other than inheritance and aggregation. Can be application specific relationships between two concepts
Example: instructor teach course, user has account
Example: instructor teach course, user has account
32
New cards
What is software architecture?
High-level system structural organization that consists of a collection of components, their interactions (connectors), and constraints.
33
New cards
Benefits of software architecture
Important because it helps with better understanding of the system and enables as early system level analysis. The "blueprint."
Facilitates maintenances and future system evolutions
Facilitates maintenances and future system evolutions
34
New cards
What are the major types of software systems?
Interactive, event-driven, transformational, object-persistence
35
New cards
Interactive System
interaction between system and actor consists of a relatively fixed sequence of actor requests and system responses.
Actor and system have a "client-server" relationship.
System has to process and respond to each request.
Actor and system have a "client-server" relationship.
System has to process and respond to each request.
36
New cards
Event-Driven System
interacts with more than one external entity at the same time.
Receives events from, and controls external entities
Does not need to respond to every incoming event. Its response is state dependent - the same event may result in different responses depending on system state
Receives events from, and controls external entities
Does not need to respond to every incoming event. Its response is state dependent - the same event may result in different responses depending on system state
37
New cards
Transformational System
consist of a network of information-processing activities, transforming activity input to activity output
Activities may involve control flows that exhibit sequencing, conditional branching, parallel threads, synchronous and asynchronous behavior
systems may perform number crunching or computation intensive algorithms
Activities may involve control flows that exhibit sequencing, conditional branching, parallel threads, synchronous and asynchronous behavior
systems may perform number crunching or computation intensive algorithms
38
New cards
Object-Persistence
Provides object storage and retrieval capabilities to other subsystems
Responsible only for storing and retrieving objects, and does little or no business processing except performance considerations
Hides implementation from the rest of system
Responsible only for storing and retrieving objects, and does little or no business processing except performance considerations
Hides implementation from the rest of system
39
New cards
Components
o define the computation logic and data organization: objects, databases, filters, clients, and servers
40
New cards
Connectors
define the interactions among components: procedure call, access protocol, and pipers
41
New cards
Constraints
define system level properties: pre-post conditions, safety properties, liveness properties