A2.1 - origin of cells
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Conditions of early earth
3.5 - 3.9 billion years ago
75 - 95 degrees
single global ocean
How was water and compounds brought to the planet
Comets and asteroids
Collisions released ammonia gases and methane, also by volcanic eruptions
What gases formed early atmosphere
ammonia gases
methane
also contained water vapour and CO2
What did early atmosphere lack
lacked O2, no ozone layer
The inner core was a lot hotter and there was more UV radiation (Due to liquid core resulting in smaller protective magnetic field)
What is reducing gases in the atmosphere
able to donate electrons to other molecules, enabling chemical reactions
reactions resulted in formation of carbon compounds (simple amino acids and hydrocarbons)
eventually formed proteins, lipids and nucleic acids
What happened with more complex carbon compounds
came from simpler carbon compounds
developed ability to self-replicate & become packaged into membranes
enable different environments, leading to cells
provide structural and functional components for cells to survive
Why could there no longer be spontaneous biological molecules
changed environmental conditions
What components are necessary to carry out life processes (8 of them)
metabolism
response to stimuli
homeostasis
movement
growth
reproduction
excretion
nutrition
Why are viruses non-living
they are unable to reproduce outside of host
What are necessary steps for spontaneous origin of cells
simple organic molecules formed (A.A and hydrocarbons)
Chemical reaction accelerates - catalyst
larger organic molecules formed , polymers,- including RNA & phospholipids assembled after smaller molecules
some molecules, including RNA, able to self replicate
Formation of membrane bound compartment allowed internal chemistry of cell to become dif than outside
Difficulties of spontaneous origin of cells
happened a long time ago
first protocells didnt fossilise
thought to have origianted deep in the ocean, harder to get samples to analyse
uncertainty of exact prebiotic condition, hence can’t replicate them
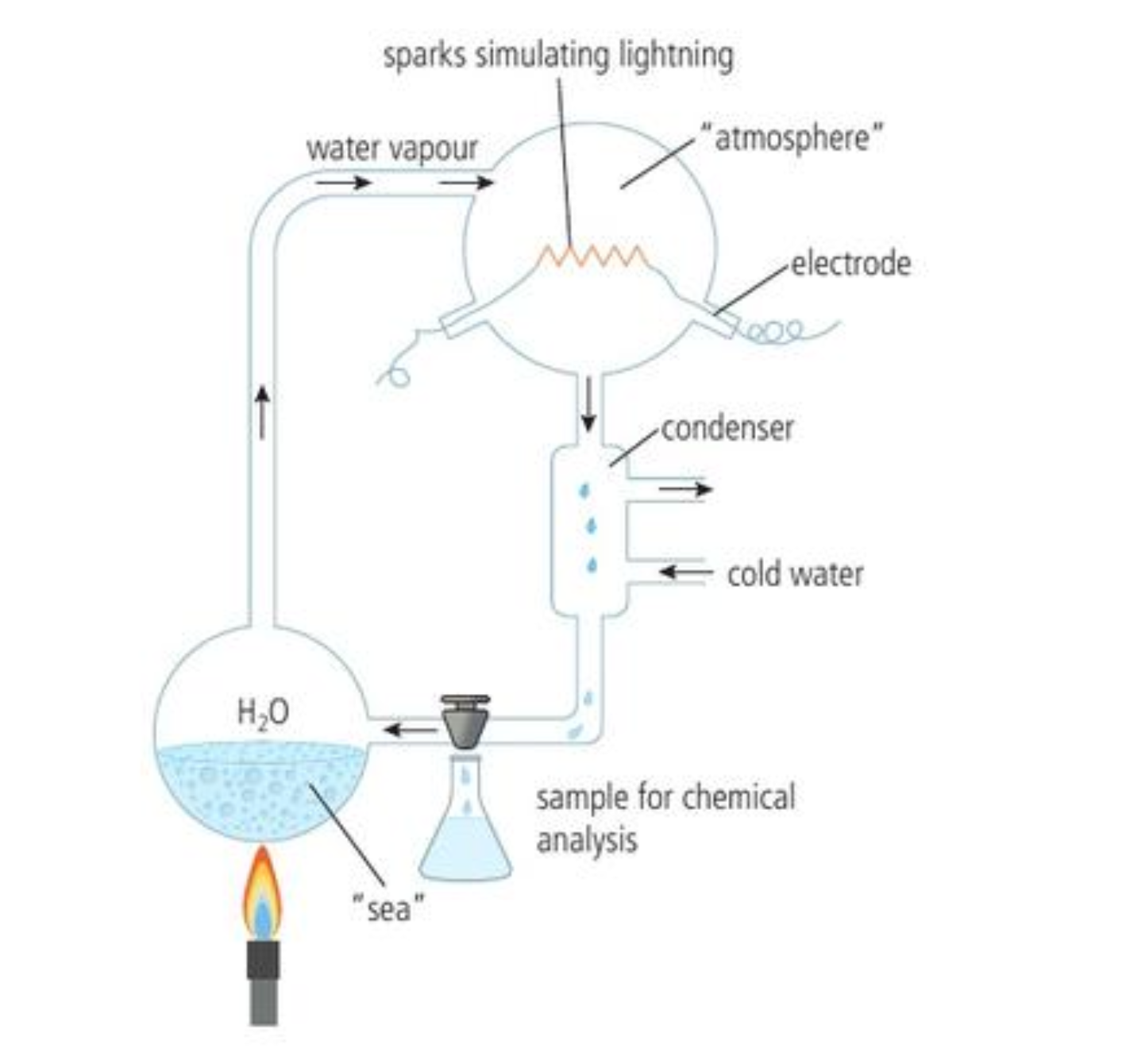
What was the miller-urey set up
water, stimulated the ocean
gas inlet adding reducing gases, methane, ammonia and hydrogen
electrical sparks stimulating electrical storms
How did miller urey experiment work
water was vaporised and run through gases and electrical sparks, cooling jacket used to condense water
condensed water dropped to bottom, representing primordial soup (water based sea of organic molecules)
after a week, soup contained organic molecules
Miller urey experiment diagram
important step in first formation of cell
formation of membrane bound compartment, from fatty acid into spherical bilayer
allow for interior to be different to exterior, cell can control and maintain conditions needed
What did RNA serve as
basis for cell like structure
genetic material
catalyst
Step of RNA becoming first genetic material
RNA formed from inorganic sources
Able to replicate using Ribozymes
Able to catalyse protein synthesis
Membrane compartmentalisation occurred
Inside cell, RNA produced protein and DNA
DNA took over, more stable
Protein took over as enzymes because more capable of variability
Evidence to support RNA hypothesis
Short RNA sequences able to duplicate, replication
RNA has catalytic activity
Ribozymes in ribosome still used to catalase peptide bond formation
Evidence for LUCA
genetic code is universal
Bacteria and archea arose from LUCA, eukaryotes from endosymbiosis
Horizontal gene transfer - LUCA
scientists focused on conserved genes, in bacteria and archea which don’t seem to have undergone horizontal gene transfer
found to have 355 genes presumed to have been in LUCA
Stromatolites
fossils found within rocks that thought to have been formed by layered communities of microorganisms
Features and characteristics of LUCA
Existed between 2.5 - 3.5 mil years ago
deep in ocean, in hydrothermal vents, rich in hydrogen and minerals, energy source
anaerobic, fits with lack of O2
autrophic, combining C and H