Cell Bio Chapter 9 The Cytoskeleton and Cell Motility
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Cytoskeleton
Network of filamentous structures in cells.
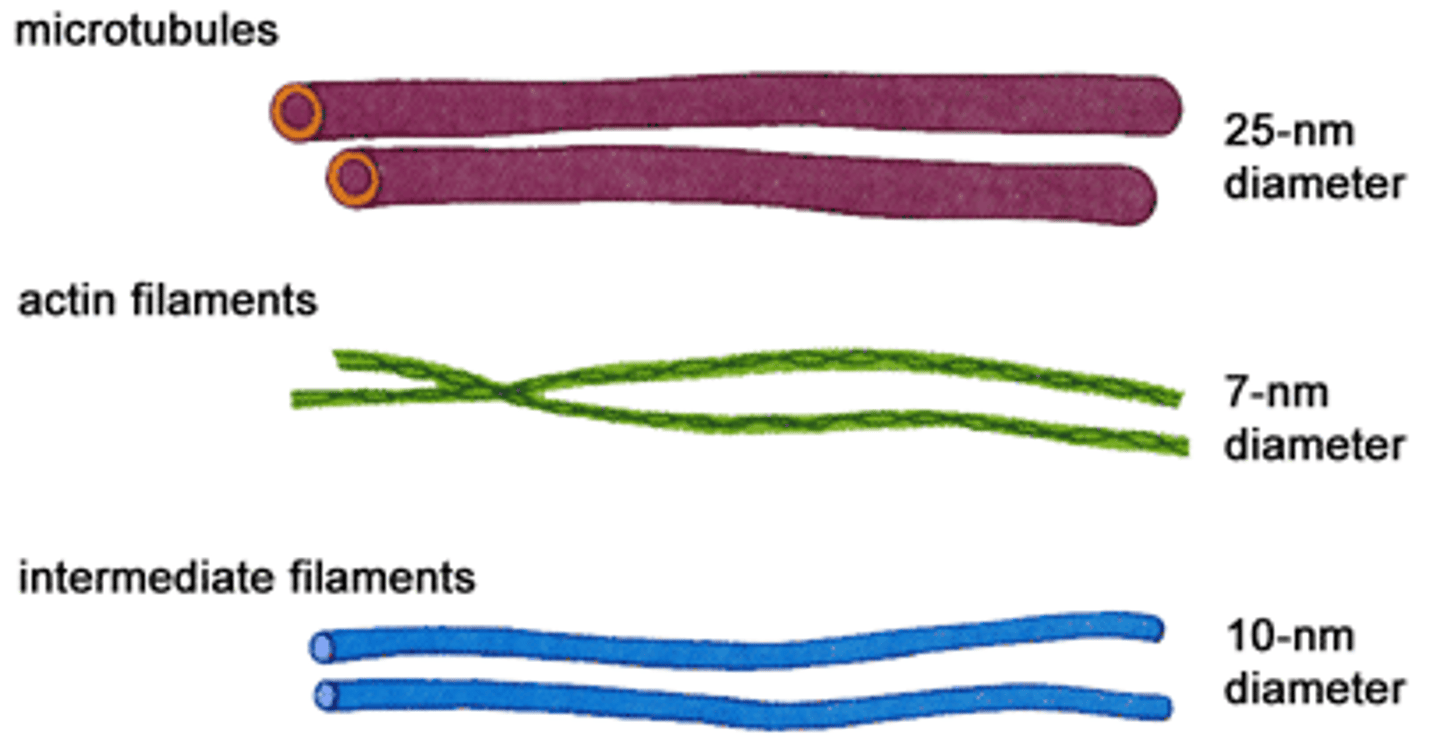
Cytoskeleton is composed of
microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments
Cytoskeleton Function
It serves as a scaffold providing structural support, organizes organelles within the cell, directs the movement of materials and organelles, Generates force to move cells, and is an essential component of the cell's division machinery.
Microtubules
Long, hollow, relatively rigid, unbranched tubes that universally exist in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells
Microtubules function
Provide mechanical support, organize organelles, and serve as tract for transport
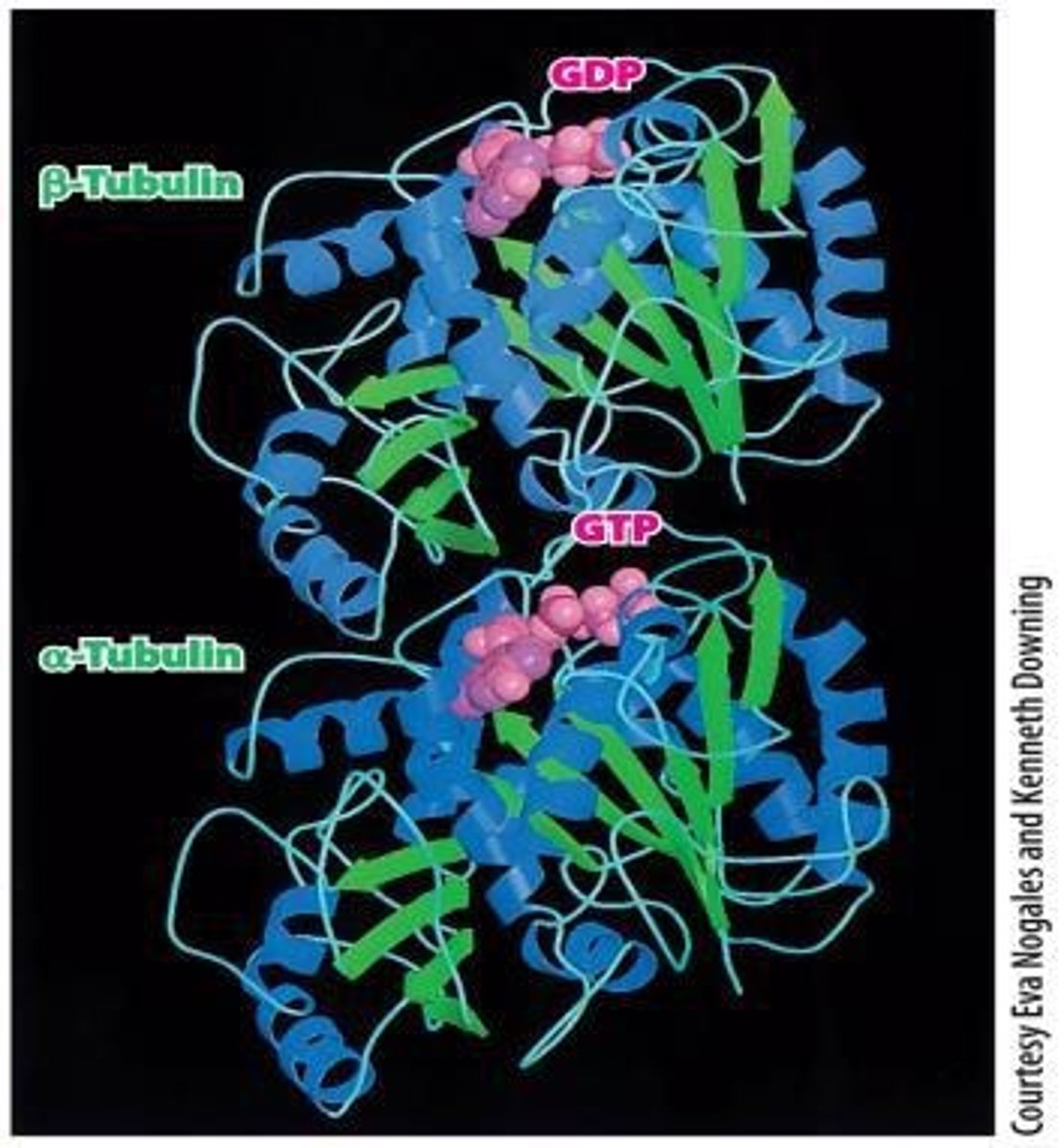
Protofilament
Linear array of tubulin subunits in microtubules.
Βeta-tubulin end of Protofilament
plus end
Αlpha-tubulin end of Protofilament
minus end
number of protofilaments in microtubule
13
MAPs
Proteins stabilizing and connecting microtubules.
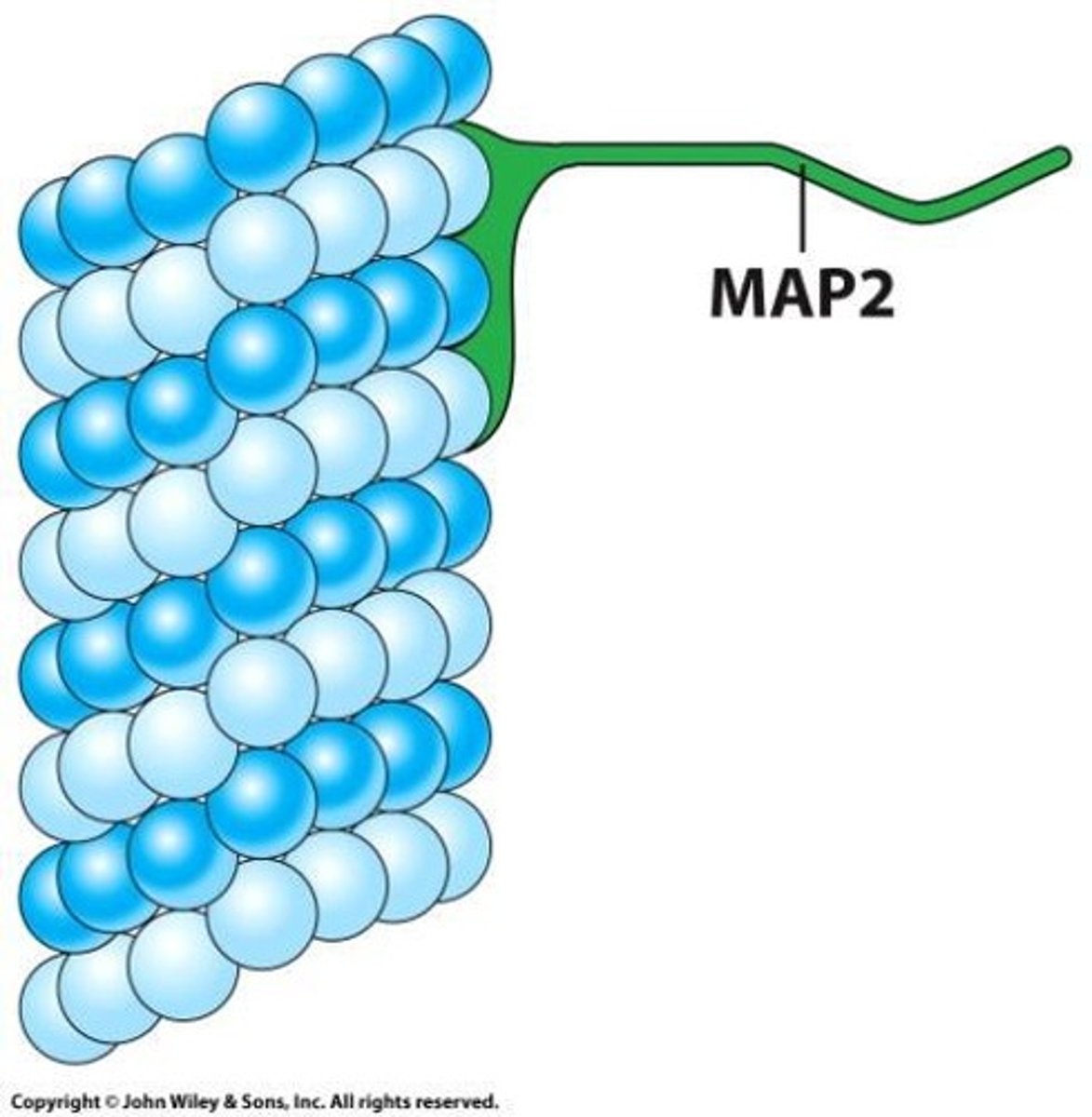
Vesicle transport
Microtubules facilitate movement of vesicles.
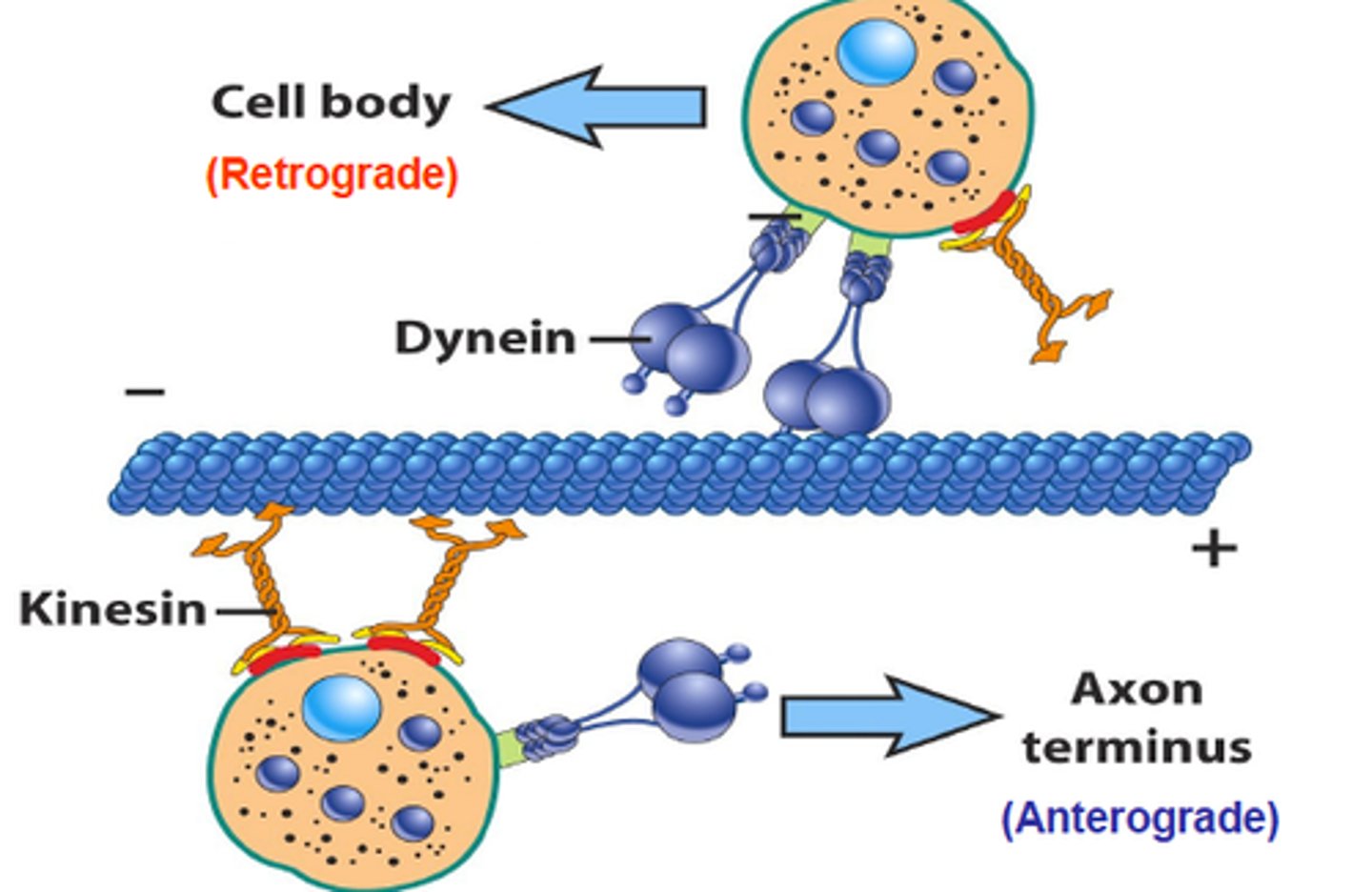
Motor proteins
the proteins required to interact with cytoskeleton to provide strength for the movement
Kinesin
Plus end-directed microtubular motor protein moving along microtubules.
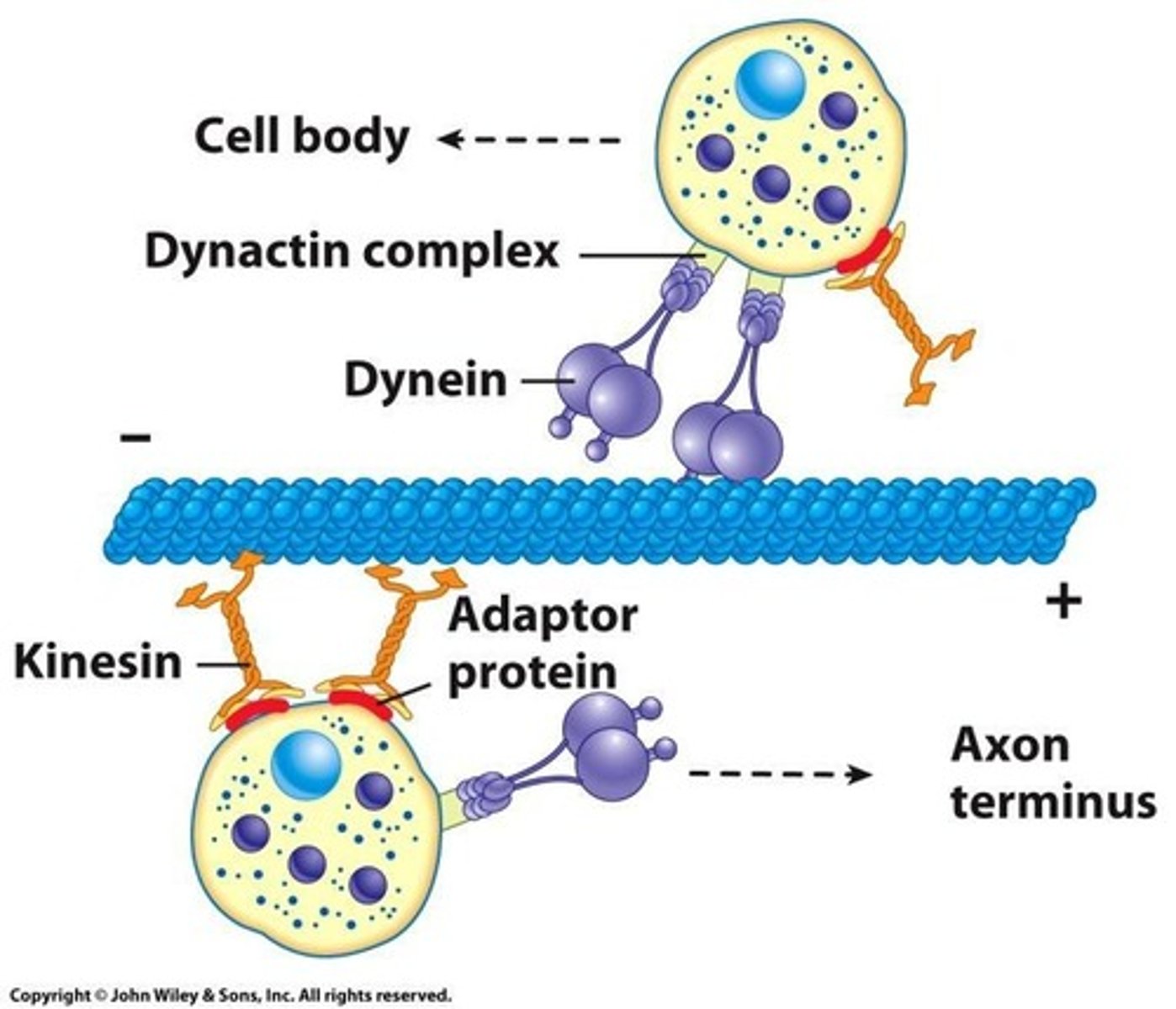
Dynein
Minus end-directed microtubular motor protein moving along microtubules.
Dimeric building blocks
α- and ß-tubulin forming protofilament.
Microtubule-Organizing Centers (MTOCs)
specialized structures for the nucleation (assembly) of microtubules
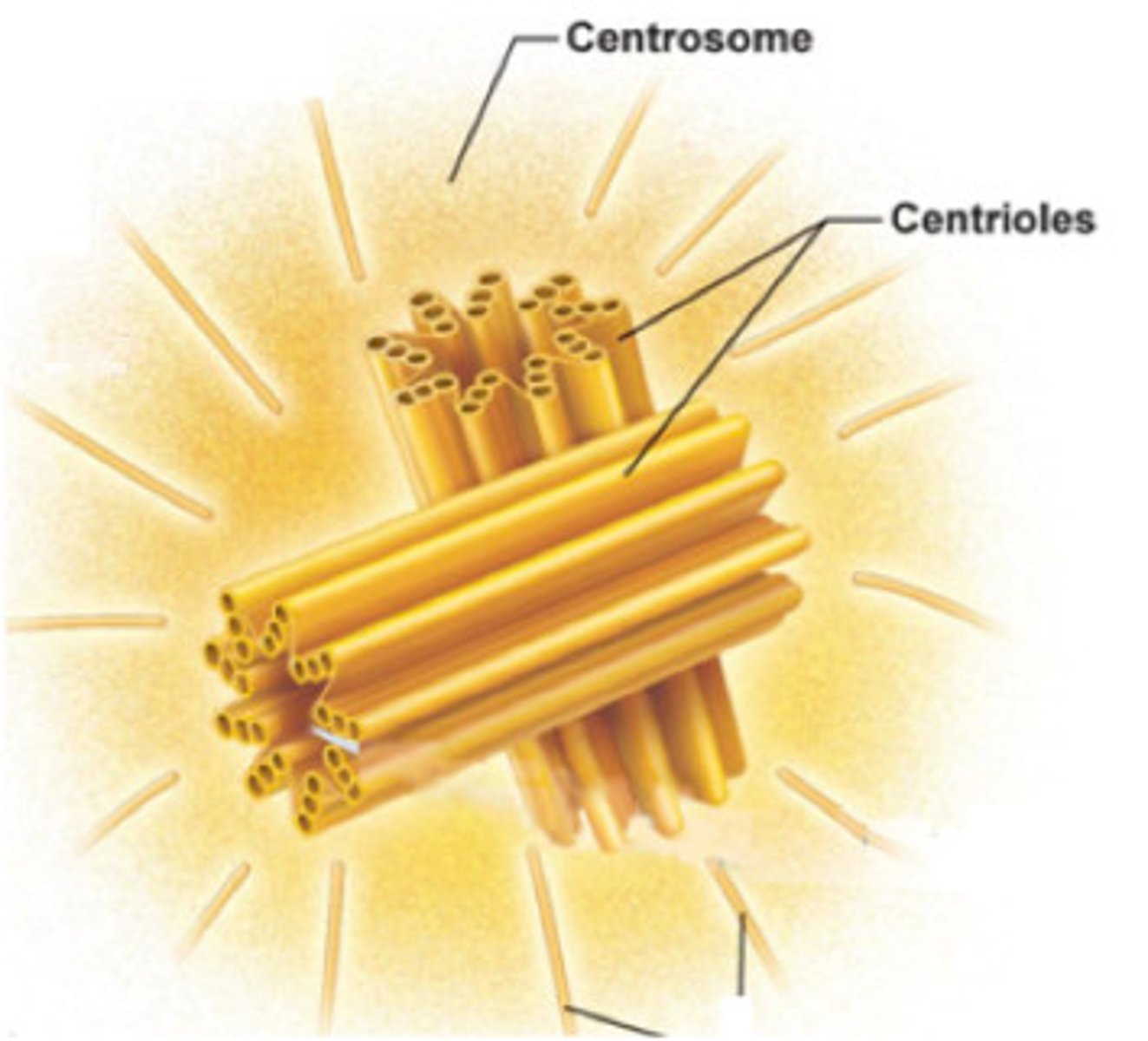
Centrosomes
Best studied microtubule-organizing centers in animals.
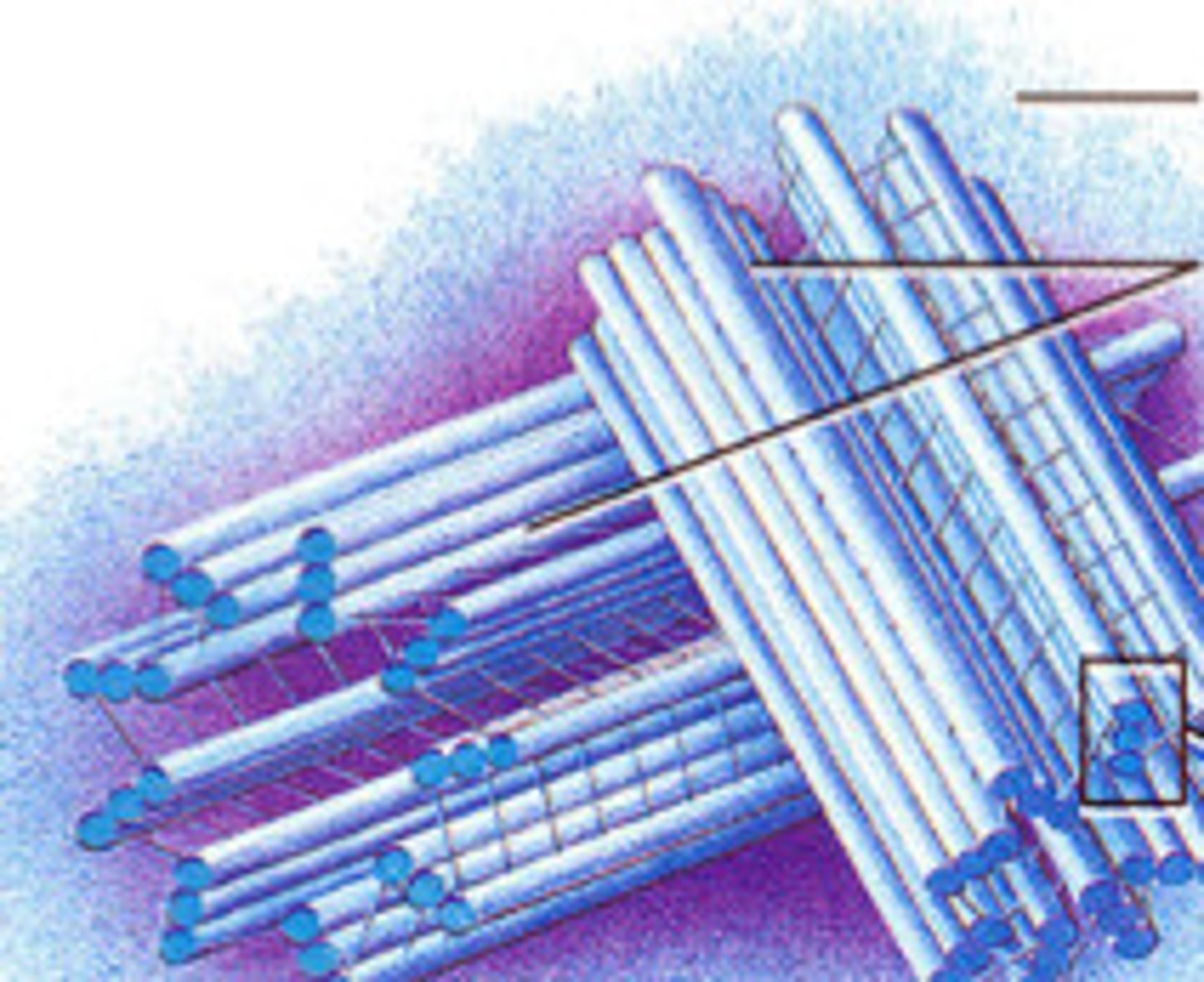
Centrosomes function
Responsible for initiation and organization of microtubules in animal cells
Pericentriolar Material (PCM).
Initiates assemble of microtubules
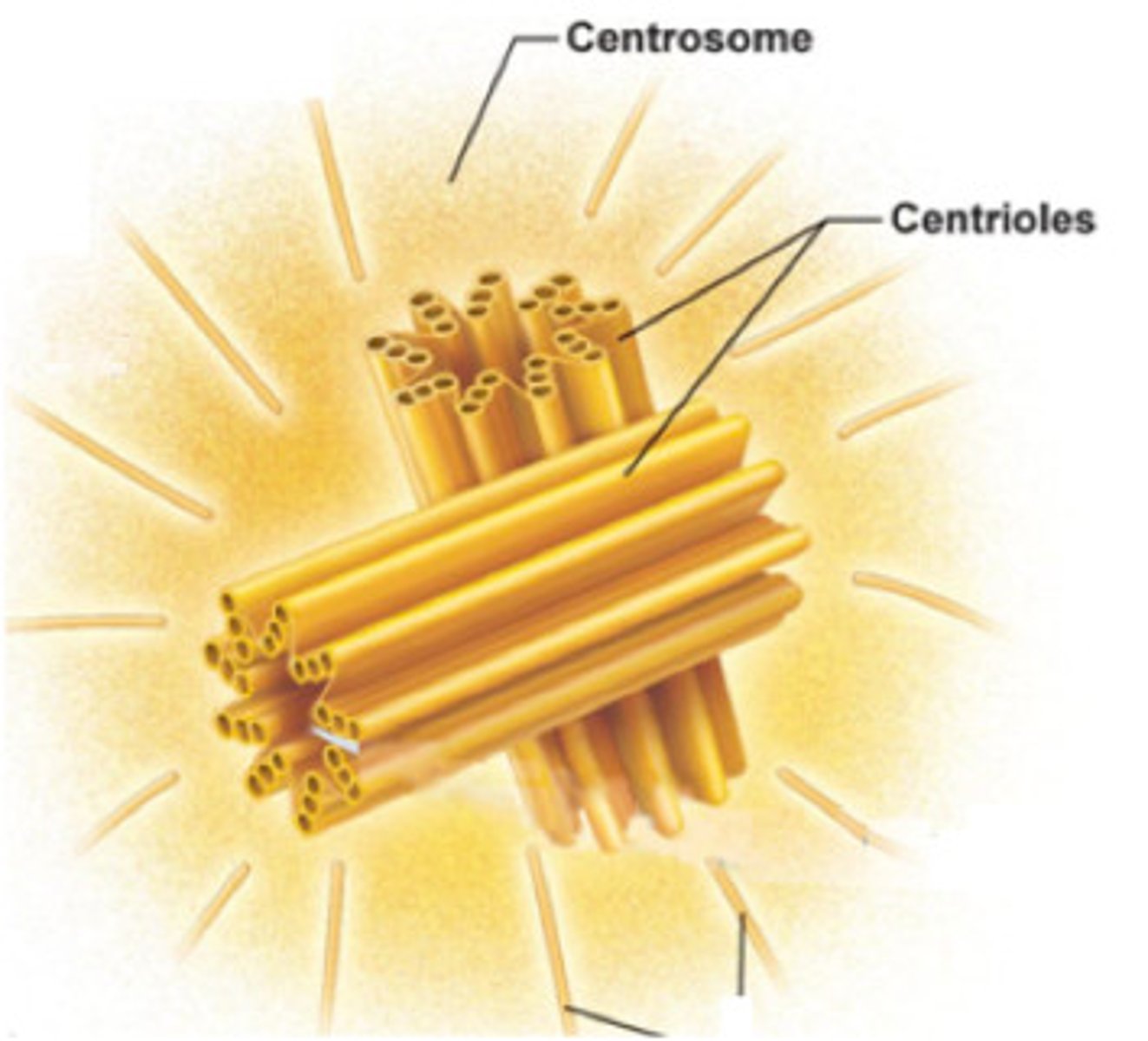
Centrioles
Barrel-shaped structures within centrosomes.
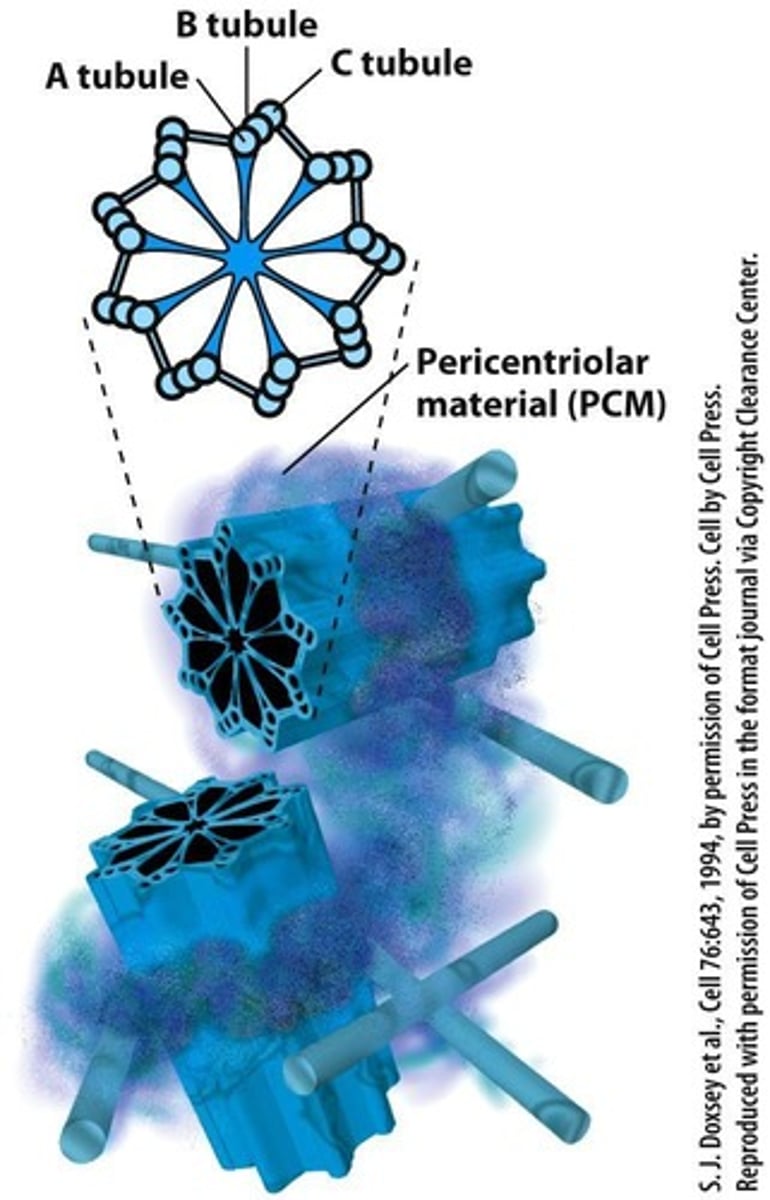
Microtubule Polarity
Minus end is associated with the centrosome, Plus (or growing) end is at the opposite tip.
γ-tubulin
required for microtubule nucleation and located in the centrosomes.
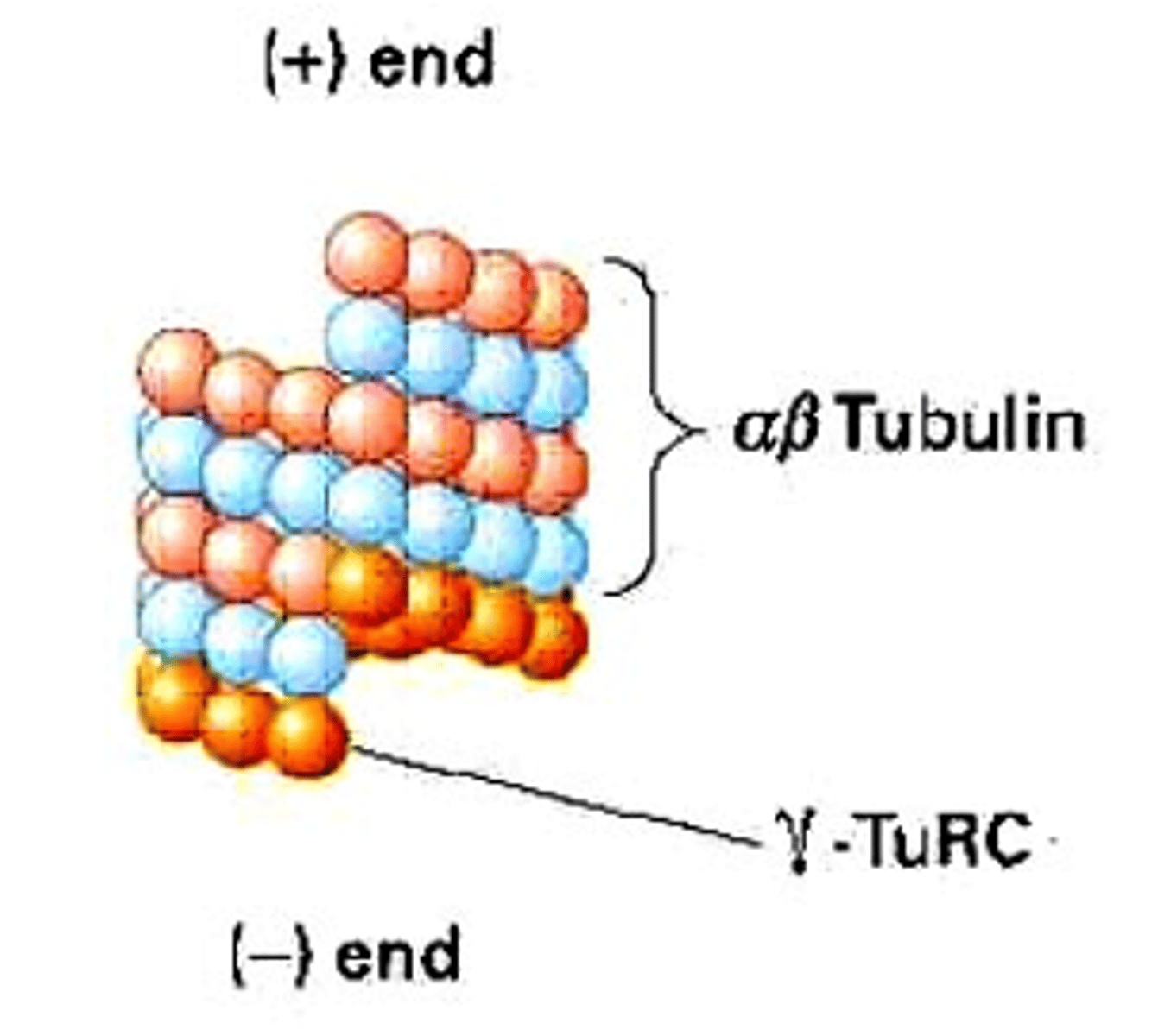
γ-tubulin Ring Complex
Structure that aids microtubule nucleation.
αβ-tubulin Dimers
Building blocks that bind to γ-tubulin.
Basal Body
MTOC responsible for the initiation and organization of microtubules for outer microtubules in cilia and flagella.
Plant Cell Microtubules
Organized around the nucleus, lacking MTOCs.
Microtubule Growth
occurs by the addition of subunits at the plus end of the polymer away from the centrosome
Functions of MTOCs
Initiates microtubule nucleation, Control the number of microtubules, polarity of microtubules, number of protofilaments that make up the wall of microtubules, and time and location of microtubule assembly.
Dynamic Properties of Microtubules
Microtubules can assemble or disassemble as needed.
Intermediate Filaments (IF)
Strong, flexible rope-like filaments only in animal cells with no polarity.
Composition of IF
Made of heterogeneous proteins, ~70 identified.
Classes of IF
Five major classes including lamins.
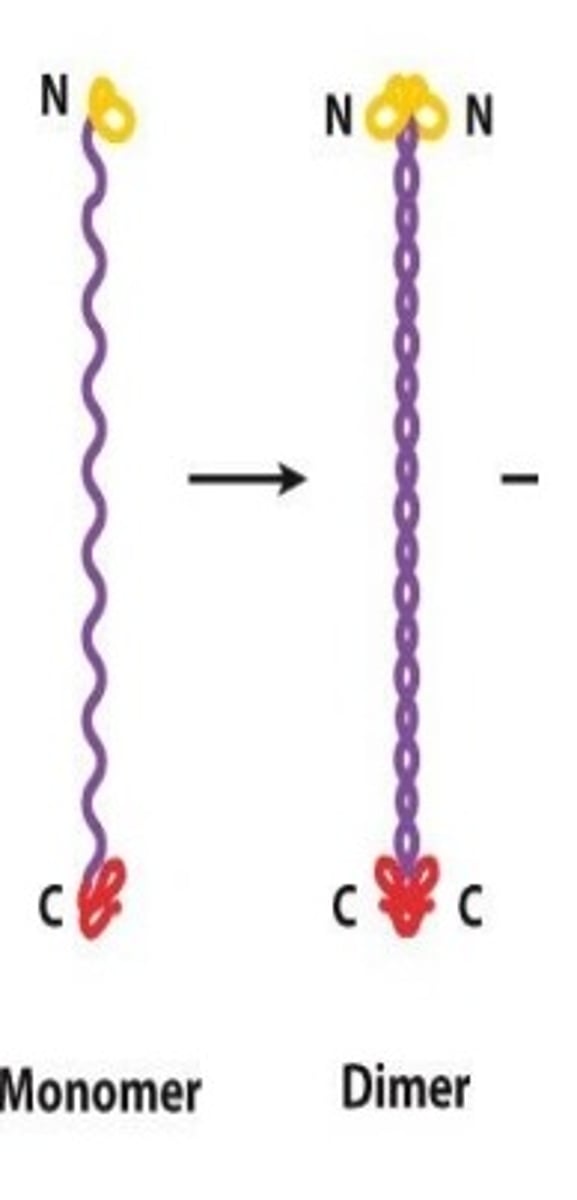
IF Assembly
Monomers form dimers, then tetramers.
Tetramer
Building block for IF made of two dimers aligned antiparallel, no polarity.
IF Filament Formation
Made from eight tetramers
Keratin Filaments
Primary structural protein for epithelial cells by anchoring to the nuclear envelope and connecting to the cell's outer edge through hemidesmosomes and desmosomes.
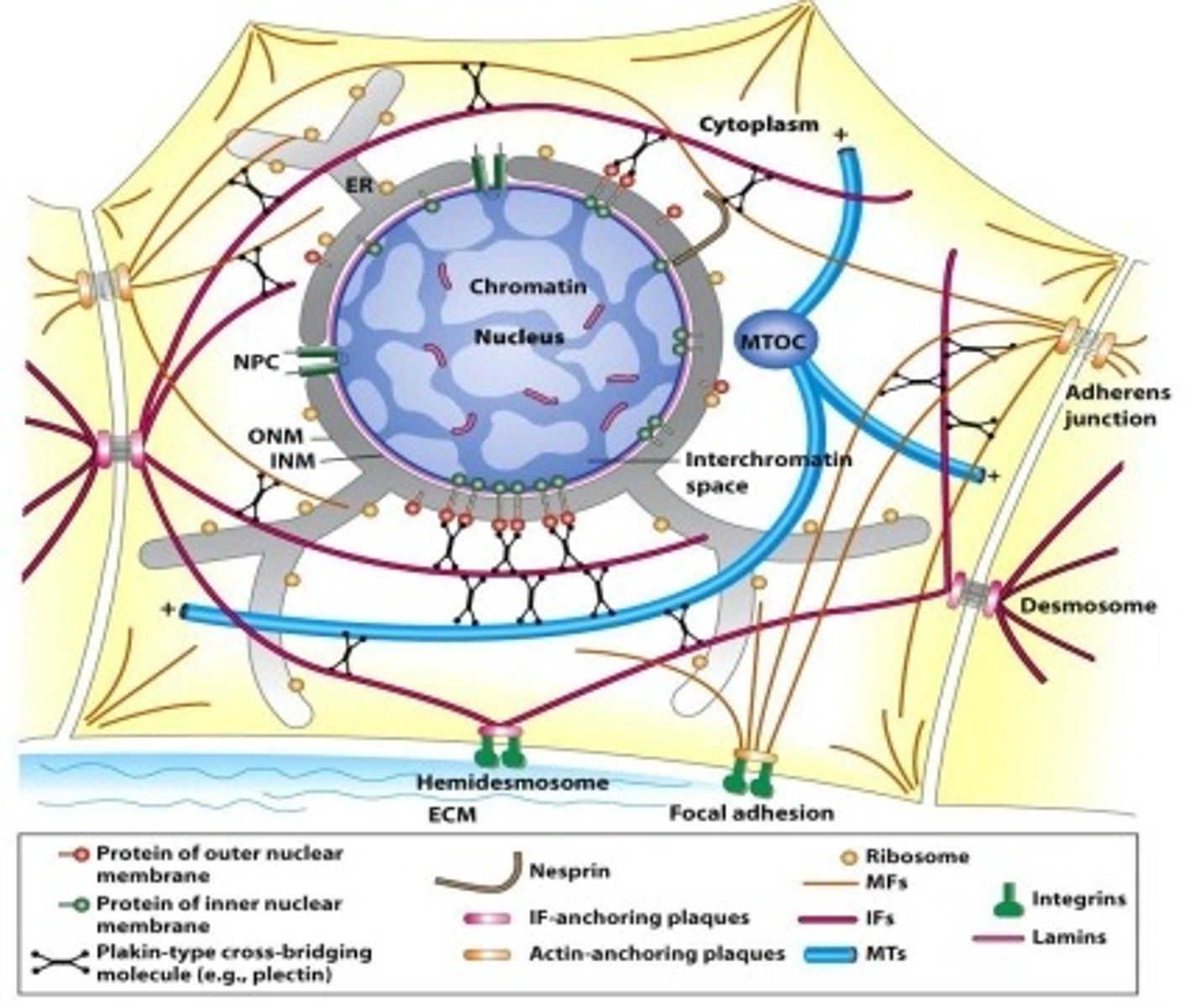
IF Function
serves as a scaffold for organizing and Support structure for cell and for absorbing the mechanical stress applied by the extracellular environment
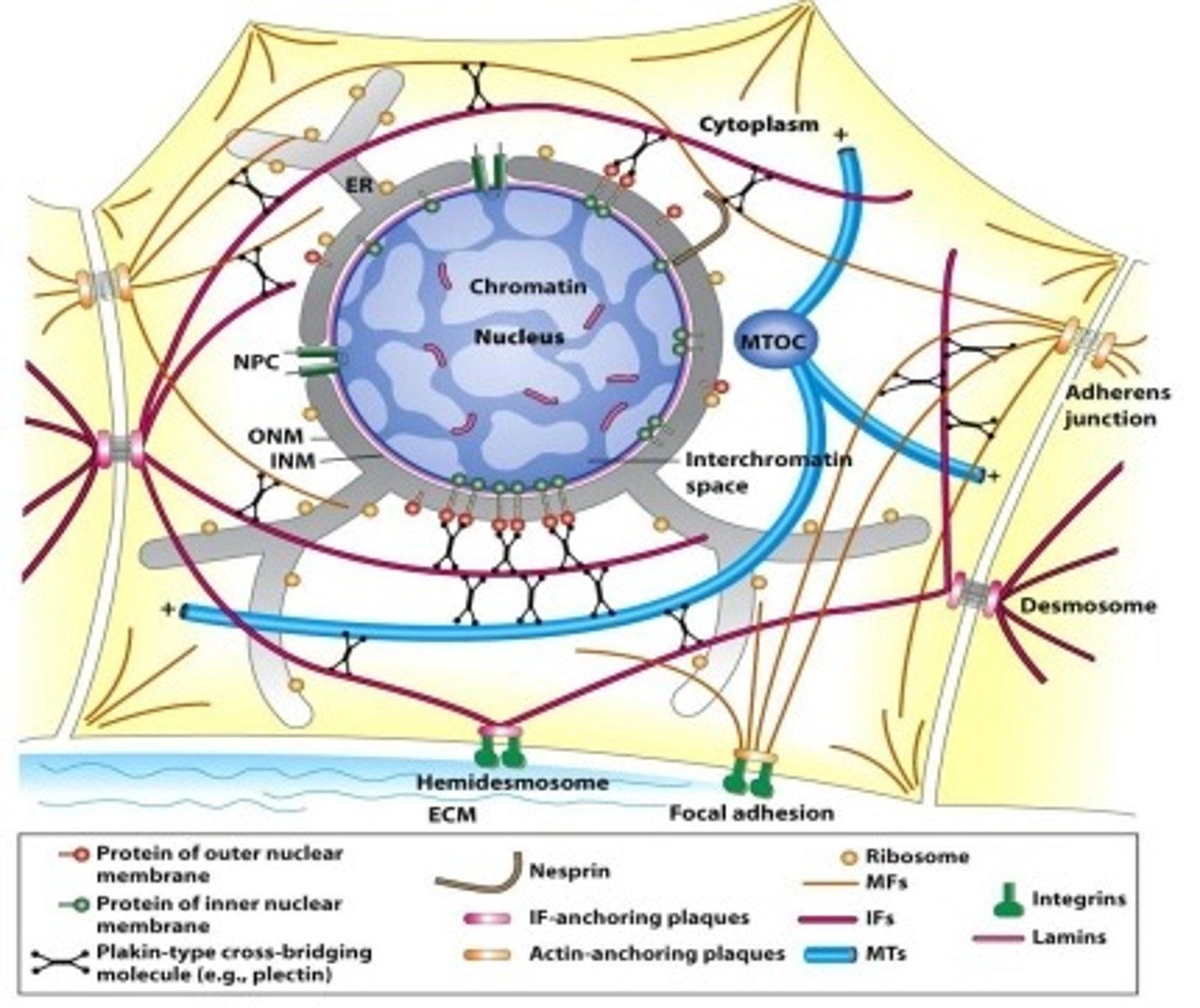
Polarity of IF
Dimers have C-termini and N-termini ends.
Cross-bridges in IF
Interconnect IFs with other cytoskeletal filaments.
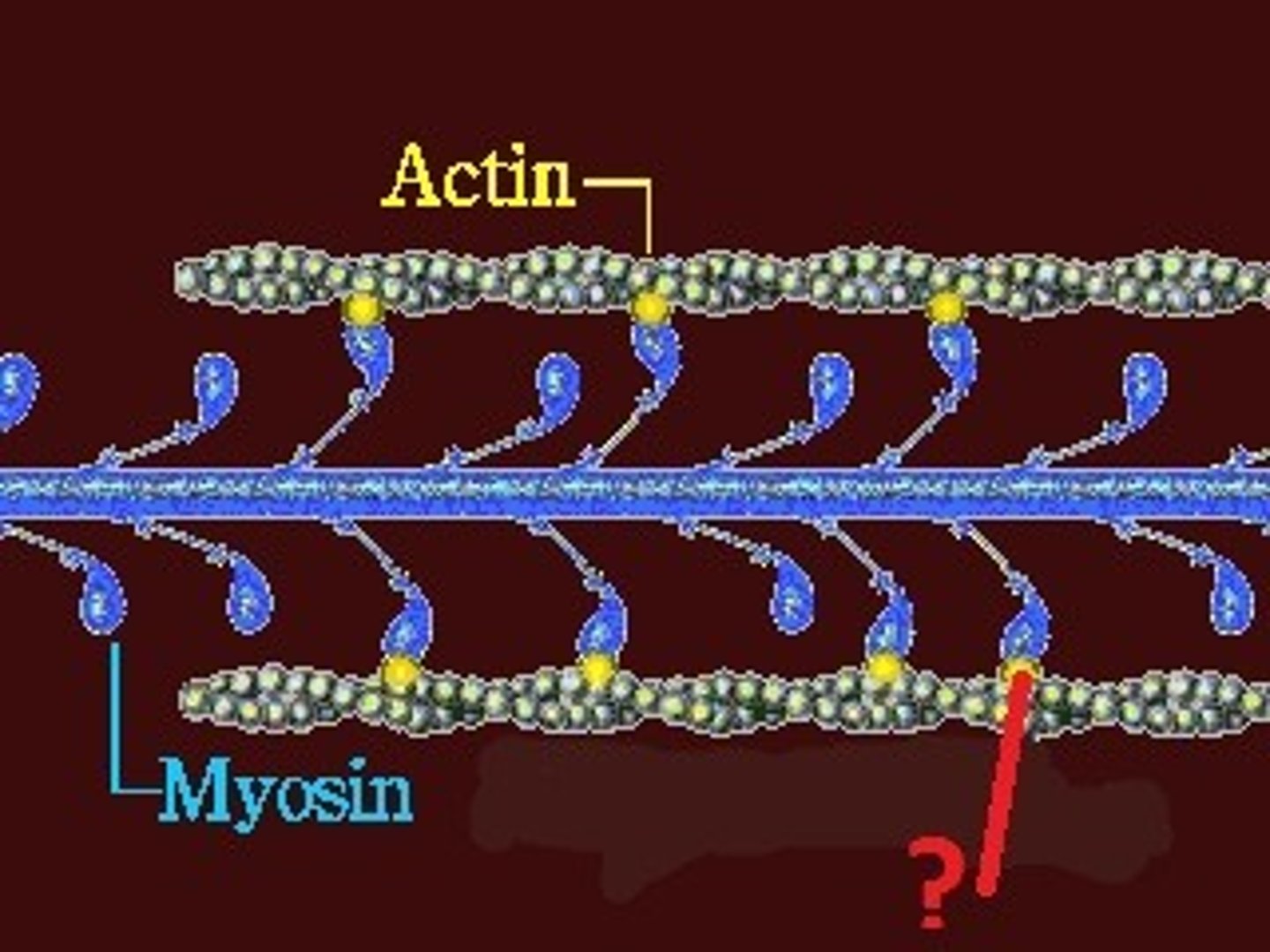
Actin filament
Also known as microfilament or F-actin, thinnest cytoskeleton structure with polarity.
Actin protein
Single component forming actin filaments.
Actin filament functions
Responsible for motility of cell and intracellular parts (White blood cell patrol and Movement of cilia lining the respiratory tract)
ATP-bound actin
Building block for microfilament assembly.
Nucleation of microfilament
Process requiring preformed filament as seed.
Barbed End/Plus End
Fast-growing end of microfilament, high ATP affinity.
Pointed End/Minus End
Slow-growing end of microfilament, low ATP affinity.
Critical concentration
Minimum ATP-actin concentration for filament elongation.
Steady state
where length of microfilament and free ATP-actin remain constant.
Myosin
The molecular motor of actin, moving along microfilaments tracks
Conventional (Type II) myosin
The primary motor for muscle contraction moves toward the barbed end (+). Moves unidirectionally and has Actin filament moved to the minus end.
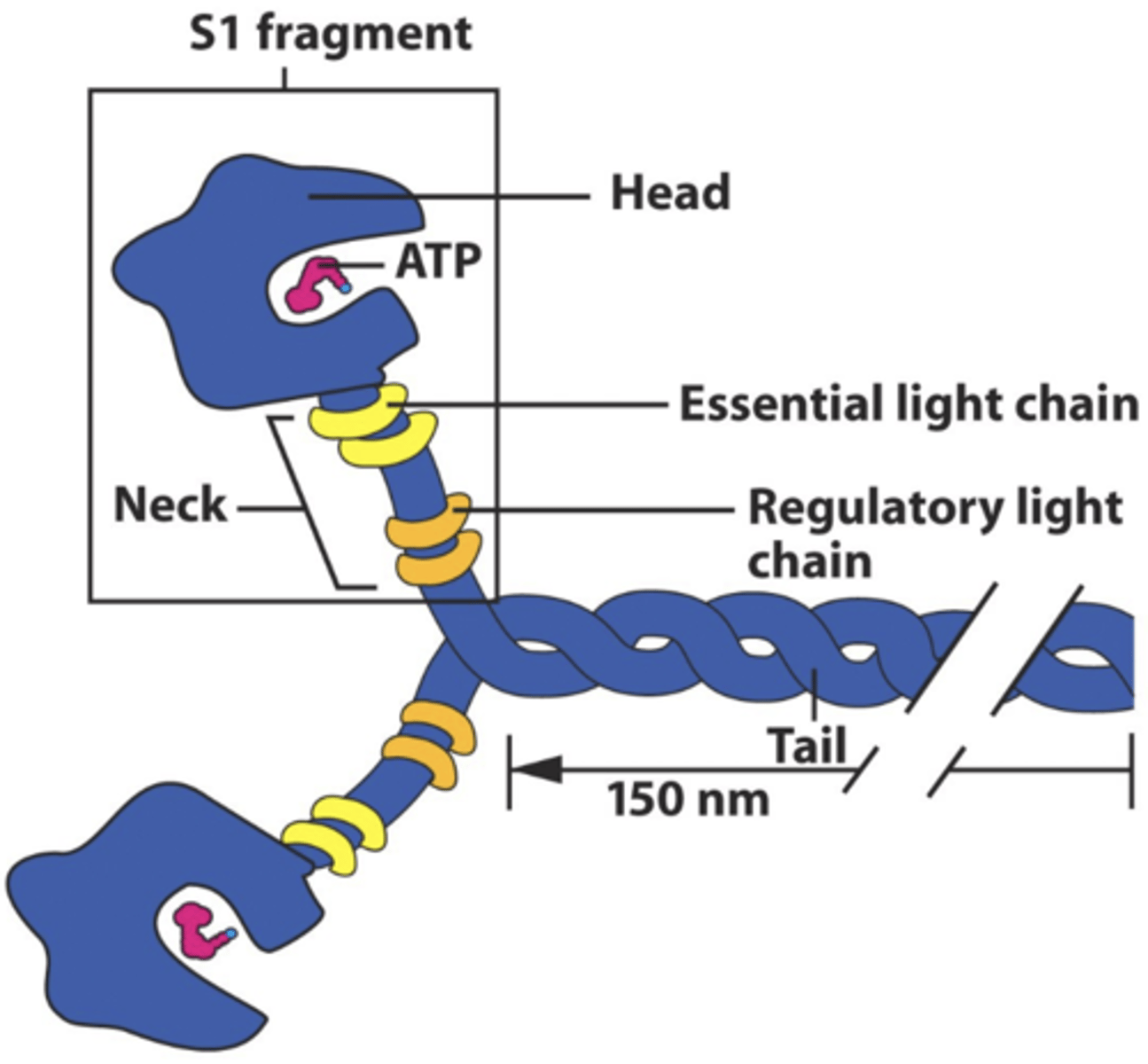
Unconventional (Type I) myosin
Transport vesicles, moves differently than conventional myosin.
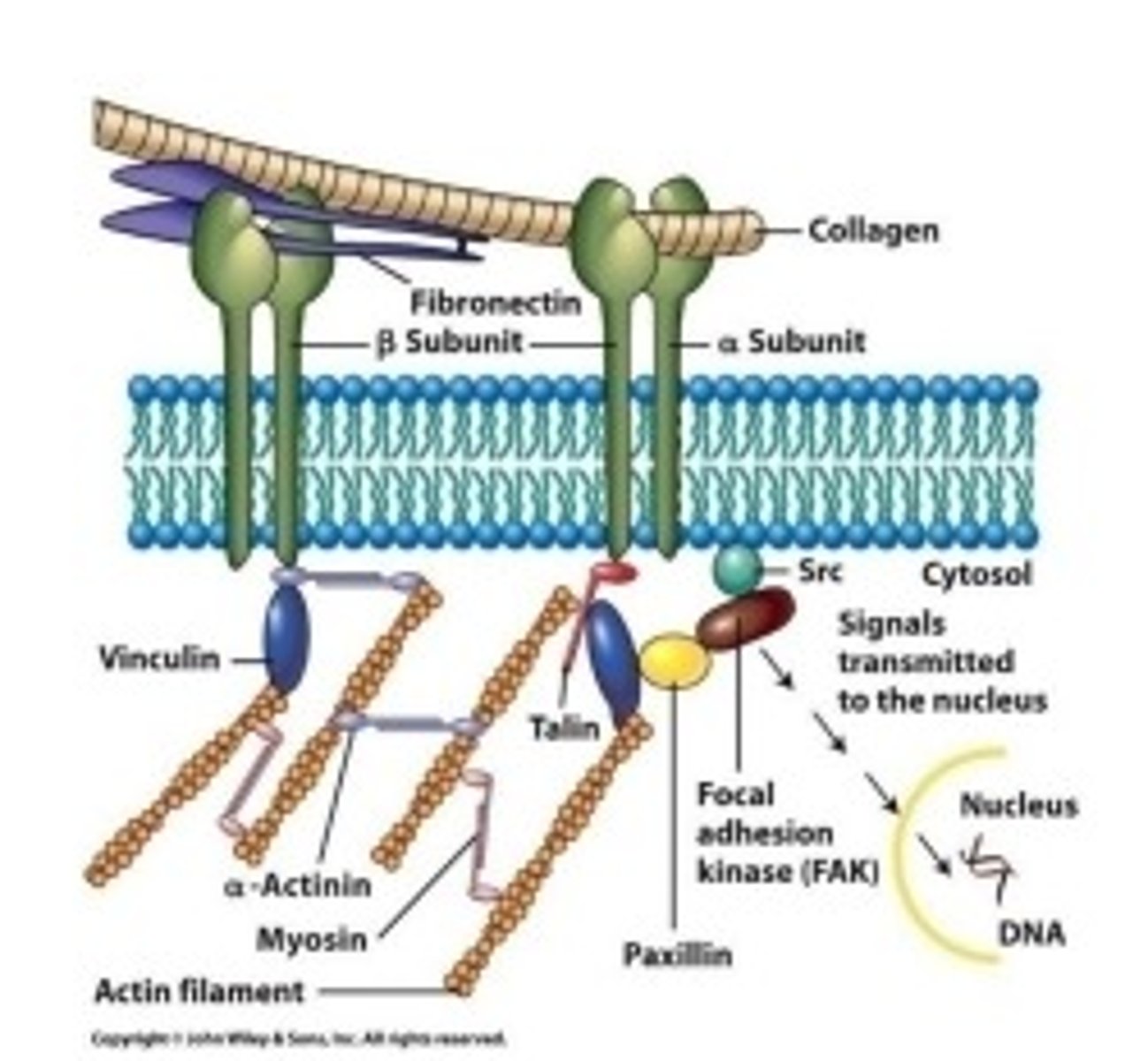
Function of Myosin
Muscle contraction, Required for splitting a cell(cytokinesis), Generation tension at focal adhesion and Adherens junctions, Cell migration, Intracellular Transportation