Livestock Breeding Genomics
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is the primary focus of genomic information in livestock breeding?
To describe the basis of genomic information used in livestock breeding.
What are Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)?
Single base pair positions in DNA where different sequence alternatives (alleles) exist in a population, considered SNPs if the least abundant allele has a frequency of 1% or more.
Why are SNPs considered useful in genomics?
They are distributed throughout the genome, provide a high density of markers, and allow for cost-effective automated genotyping.
What are the three categories of SNP arrays used in livestock?
Low density (5K-20K SNPs), Medium density (40-50K SNPs), and High density (700-800K SNPs).
What is the main disadvantage of SNPs compared to microsatellites?
SNPs only have two alleles at any given position, making them less variable than microsatellites.
What is the original method of whole genome sequencing?
Sanger Sequencing, which constructs a base-by-base copy of DNA fragments.
What is Genotyping by Sequencing (GBS)?
A method that uses restriction enzymes and PCR to efficiently sequence 100 bp fragments of DNA.
How is genomic information utilized in livestock breeding?
For parentage assignment and verification, maintaining accurate pedigree records, and avoiding handling at birth.
What are polygenic traits?
Traits that are quantitative, controlled by many loci with small additive effects, and measured on a continuous scale.
What distinguishes single gene traits from polygenic traits?
Single gene traits are qualitative, controlled by a single locus or a few loci, and have minimal environmental effects.
What is Complex Vertebral Malformation (CVM)?
A condition caused by a mutation in the SLC35A3 gene, leading to axial skeletal abnormalities.
What is a haplotype in the context of genetics?
A short section of DNA passed on to the next generation, often used in haplotype tests to identify combinations of SNPs associated with recessive genes.
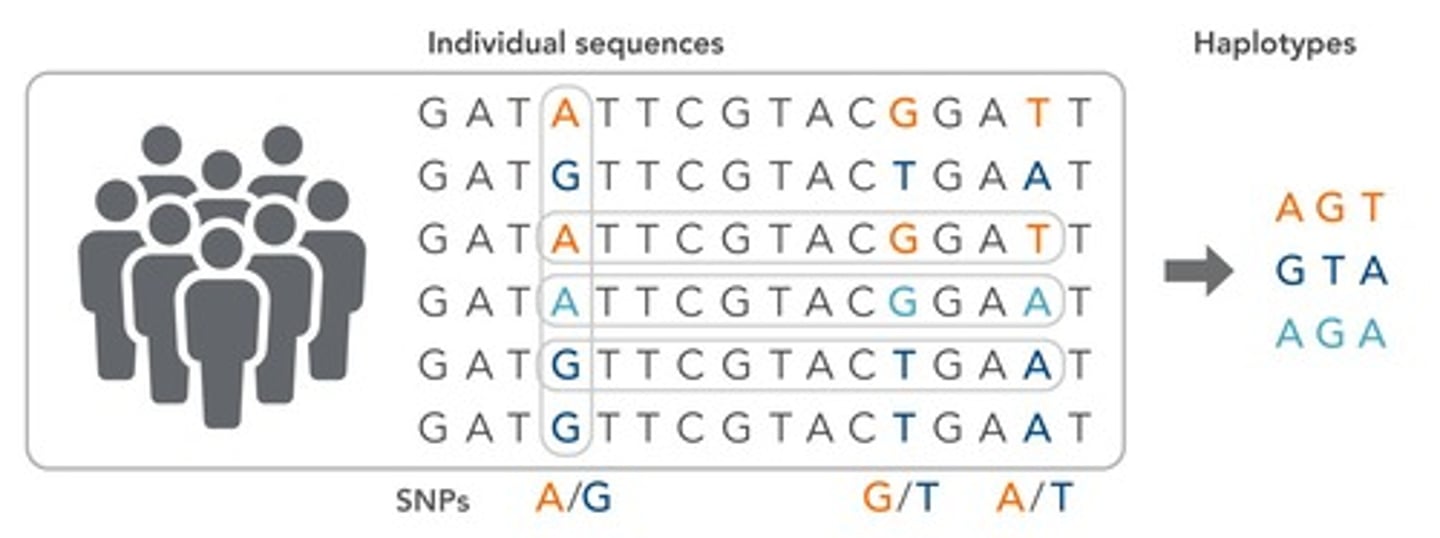
What is marker-assisted selection?
A breeding method that uses genotype information from specific genetic markers associated with traits.
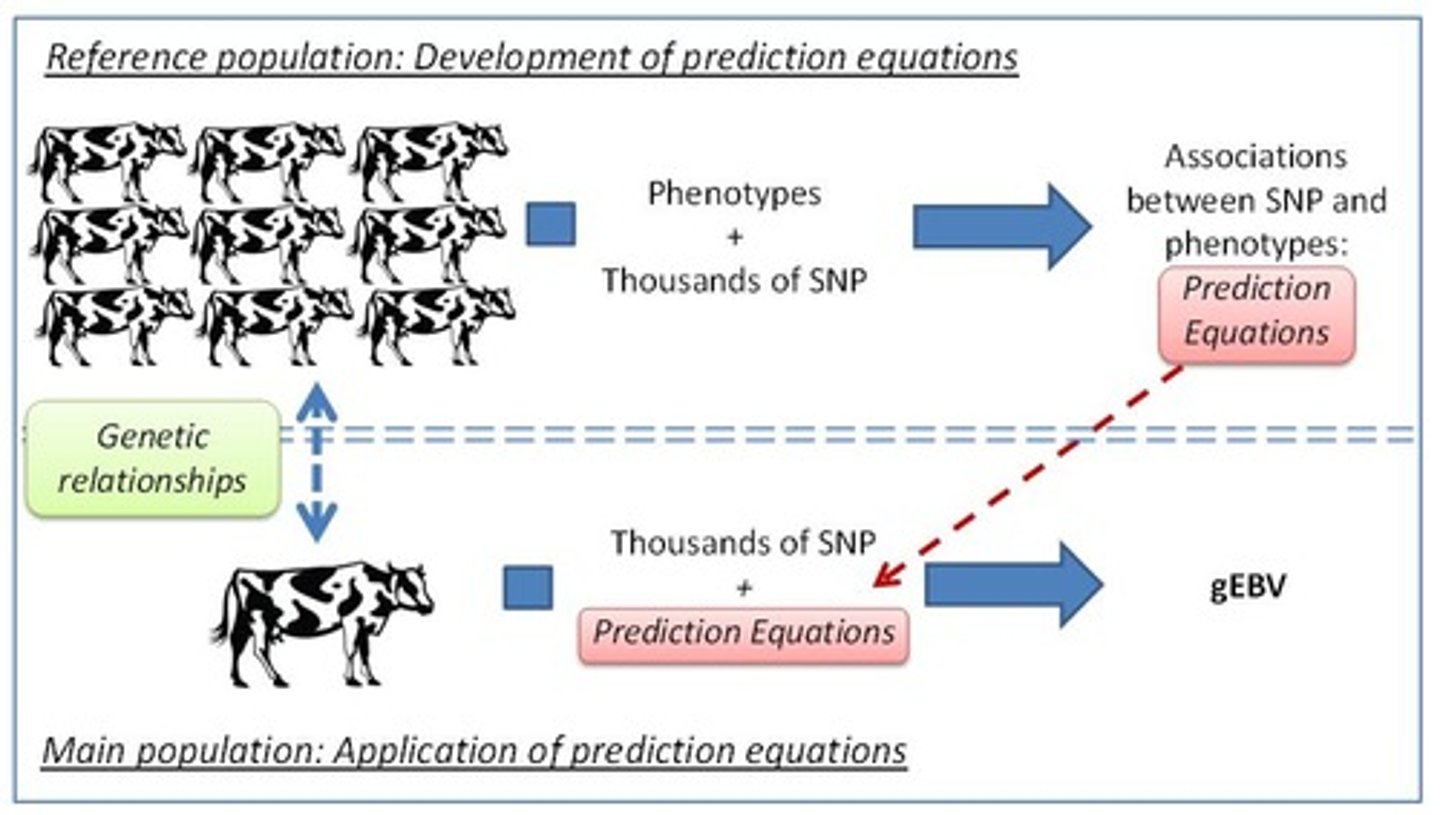
What are Genomic Breeding Values (gEBVs)?
Values derived from thousands of SNP genotypes across the genome, improving the accuracy of breeding values based on genetic relationships.
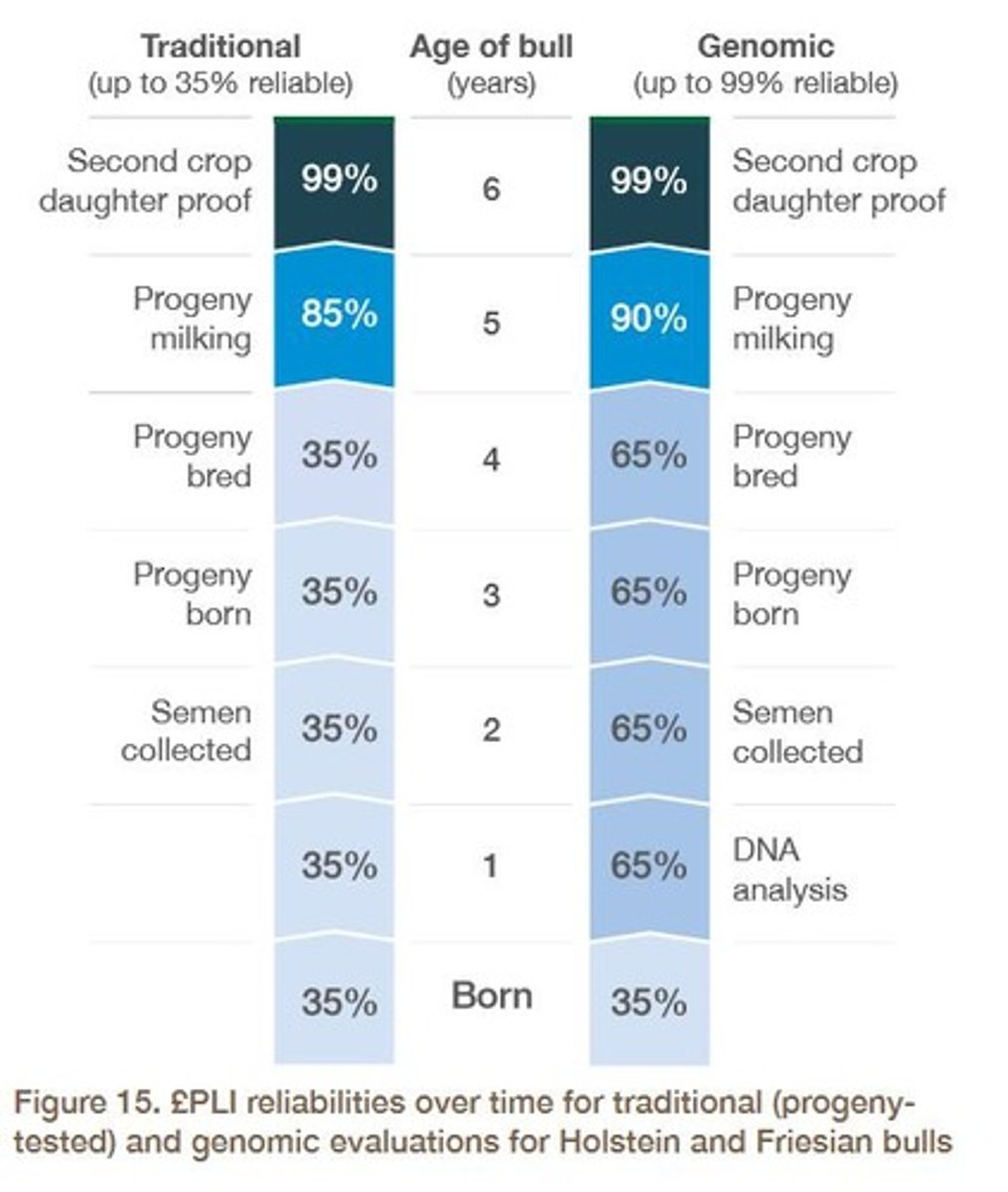
How does the accuracy of genomic breeding values compare to traditional breeding values?
Genomic breeding values have a reliability of 60-70%, compared to parent averages which have a reliability of around 25%.
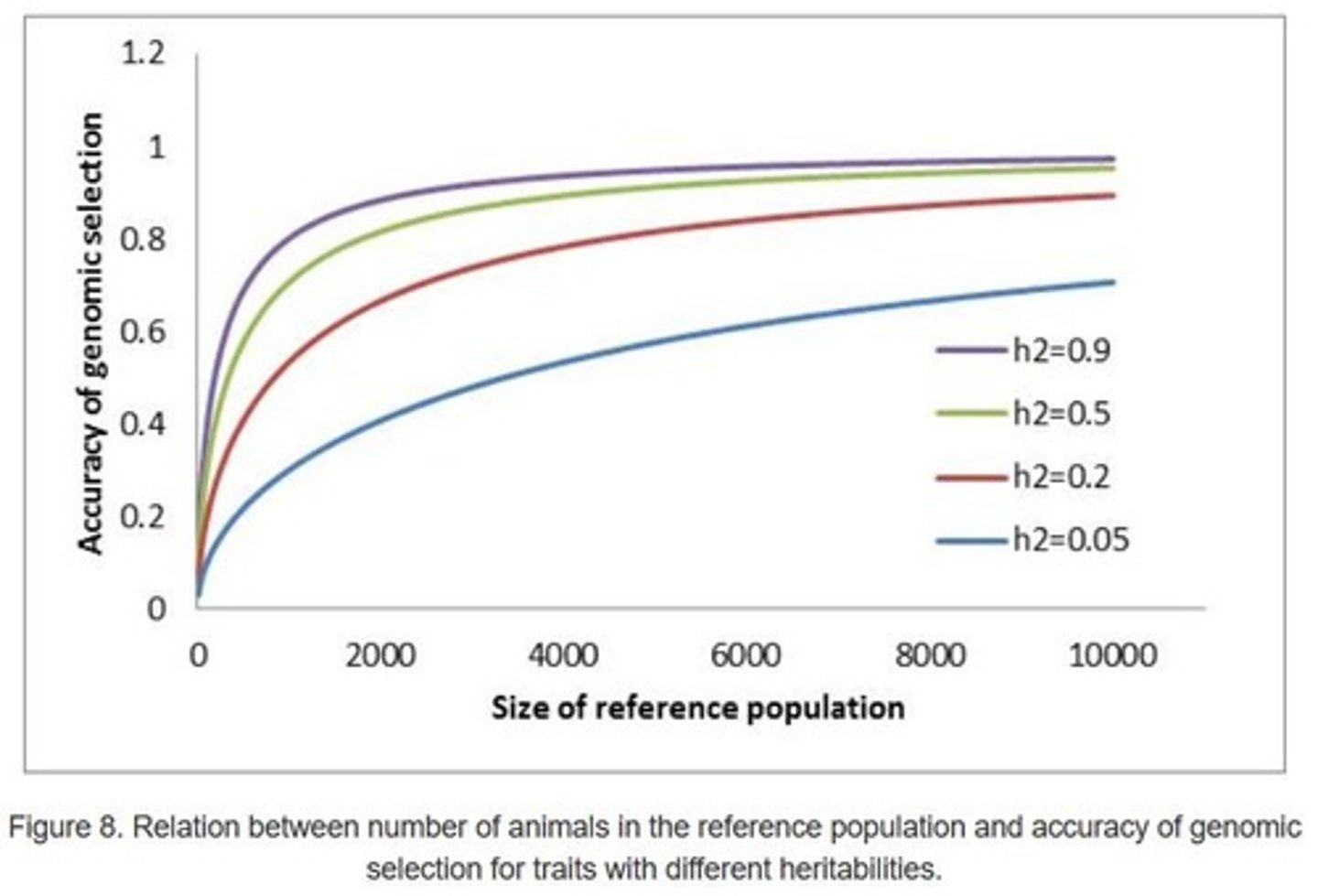
What factors influence the accuracy of genomic predictions?
Heritability, size of the reference population, and genetic correlations with other traits.
What is the inbreeding coefficient?
The probability of two alleles at a locus being inherited from the same ancestor, ranging from 0-100%.
How are genomic inbreeding coefficients calculated?
By measuring the proportion of an individual's DNA inherited from recent common ancestors.
What is the significance of SNP arrays in livestock breeding?
They provide a means to increase the accuracy of Estimated Breeding Values (EBVs) through detailed genetic information.
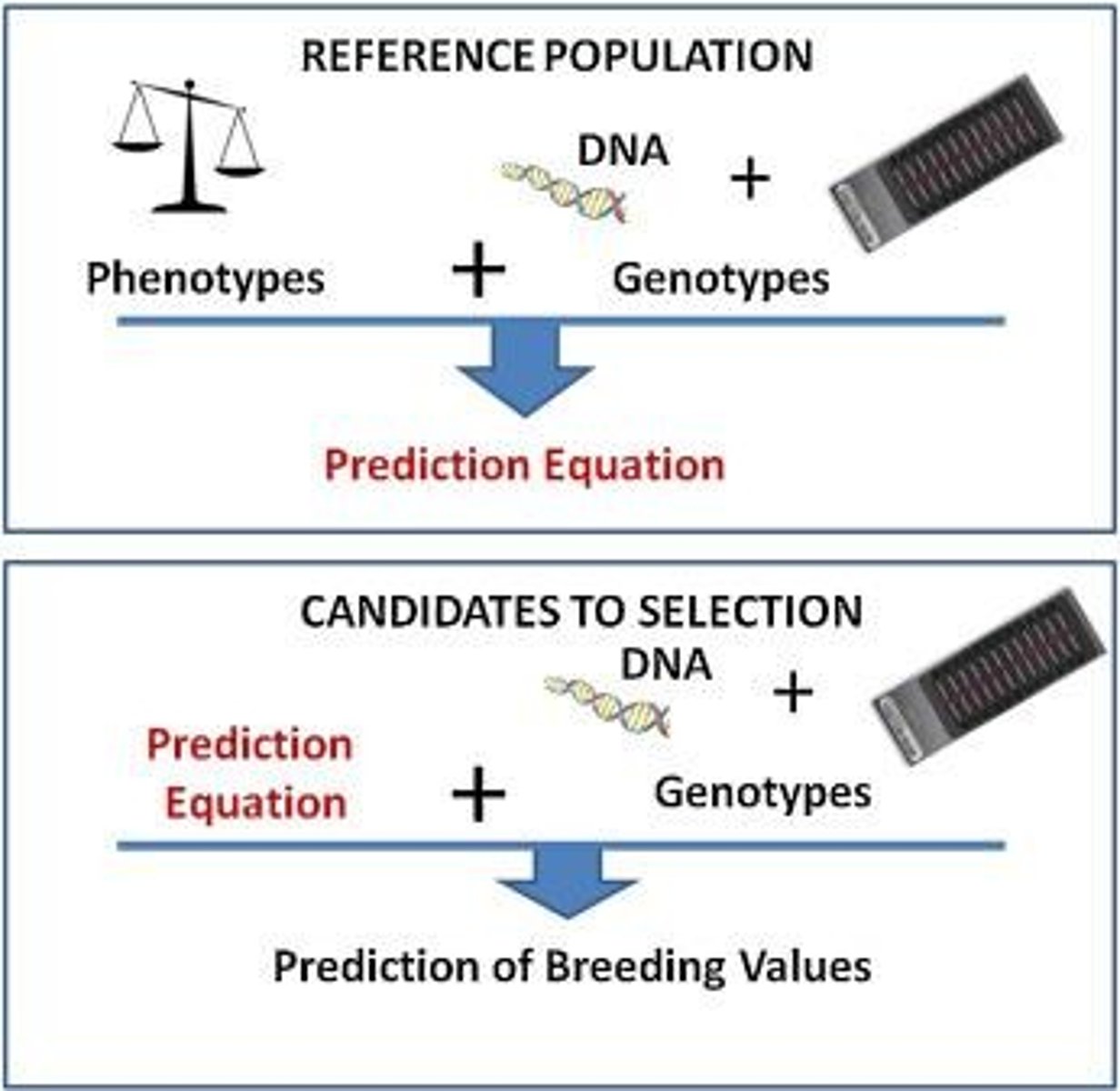
What is the role of prediction equations in genomic selection?
They relate genotypic variation to performance, enhancing the accuracy of breeding value predictions.
What is the impact of genomic information on generation intervals in breeding programs?
It can reduce generation intervals by providing more accurate breeding decisions.
What is the purpose of parentage panels in livestock breeding?
To verify parentage using SNPs that are variable across many breeds and populations.
What are the advantages of using genomic information in breeding decisions?
Better management of inbreeding, improved mate selection, and enhanced genetic diversity.
What is the importance of reference populations in genomic selection?
They are necessary for establishing prediction equations that relate genotypic variation to performance.
What is the potential of gene editing in livestock breeding?
To achieve better heterosis and manage genetic traits more effectively.
What is the significance of the 2013 introduction of gEBVs?
It marked a significant advancement in the accuracy of breeding values for livestock, particularly for post-slaughter traits.