Microbio GI Infections-lecture 4
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
Herpes labialis pathogen
HSV1 (oral) or HSV2 (genital)
herpes labialis symptoms
Prodromal Tingling Pain
Vesicle Formation Ulceration with Crusting
anterior cervical adenopathy
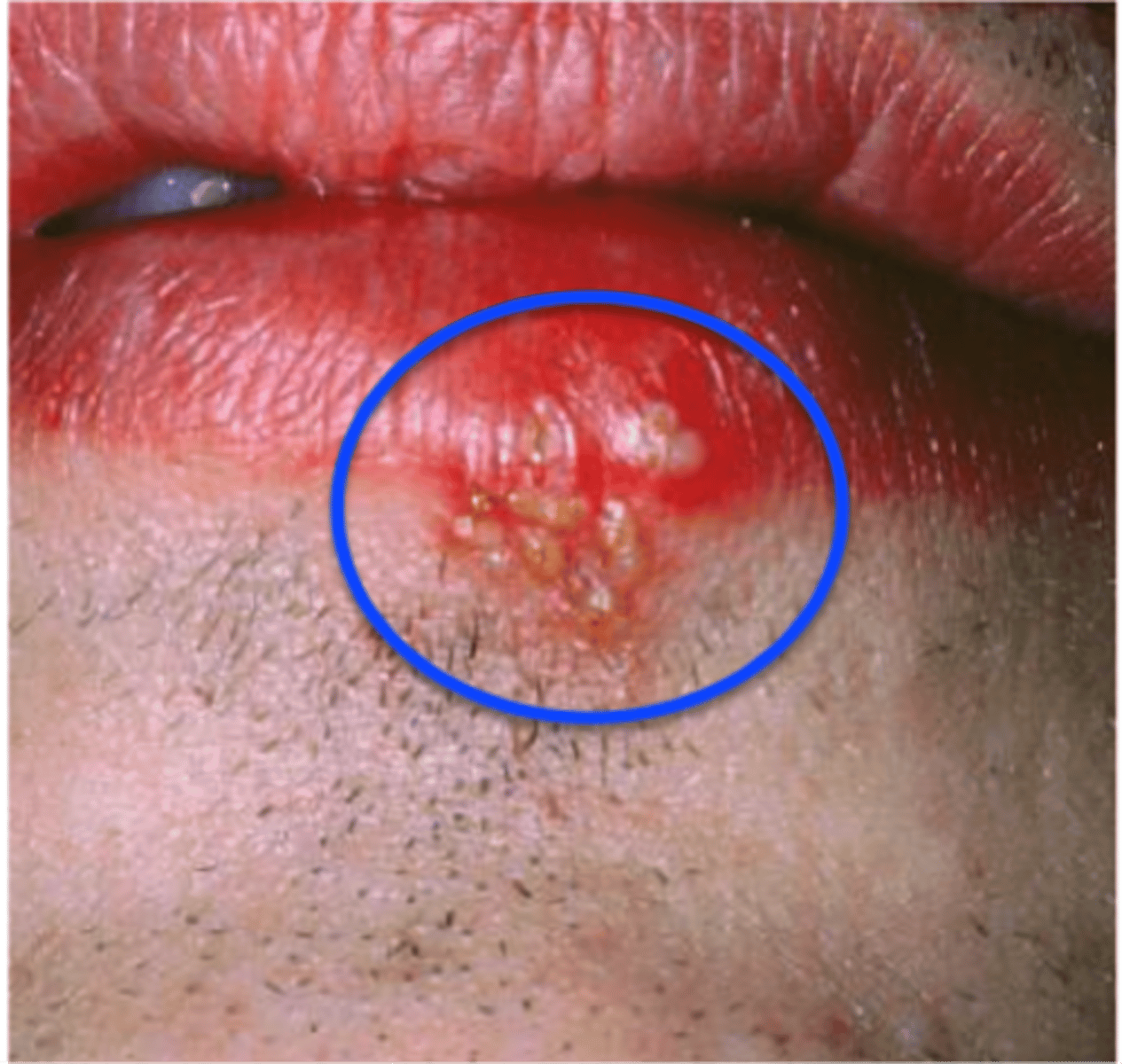
herpes labialis treatment
antivirals
Herpes gingivostomatitis pathogen
HSV1 or HSV2
Herpes gingivostomatitis symptoms
Prodromal Symptoms
Vesicle Formation/Ulceration
Edematous and Erythematous Gingivae
Resent on Gingiva and Hard Palate and buccal mucosa
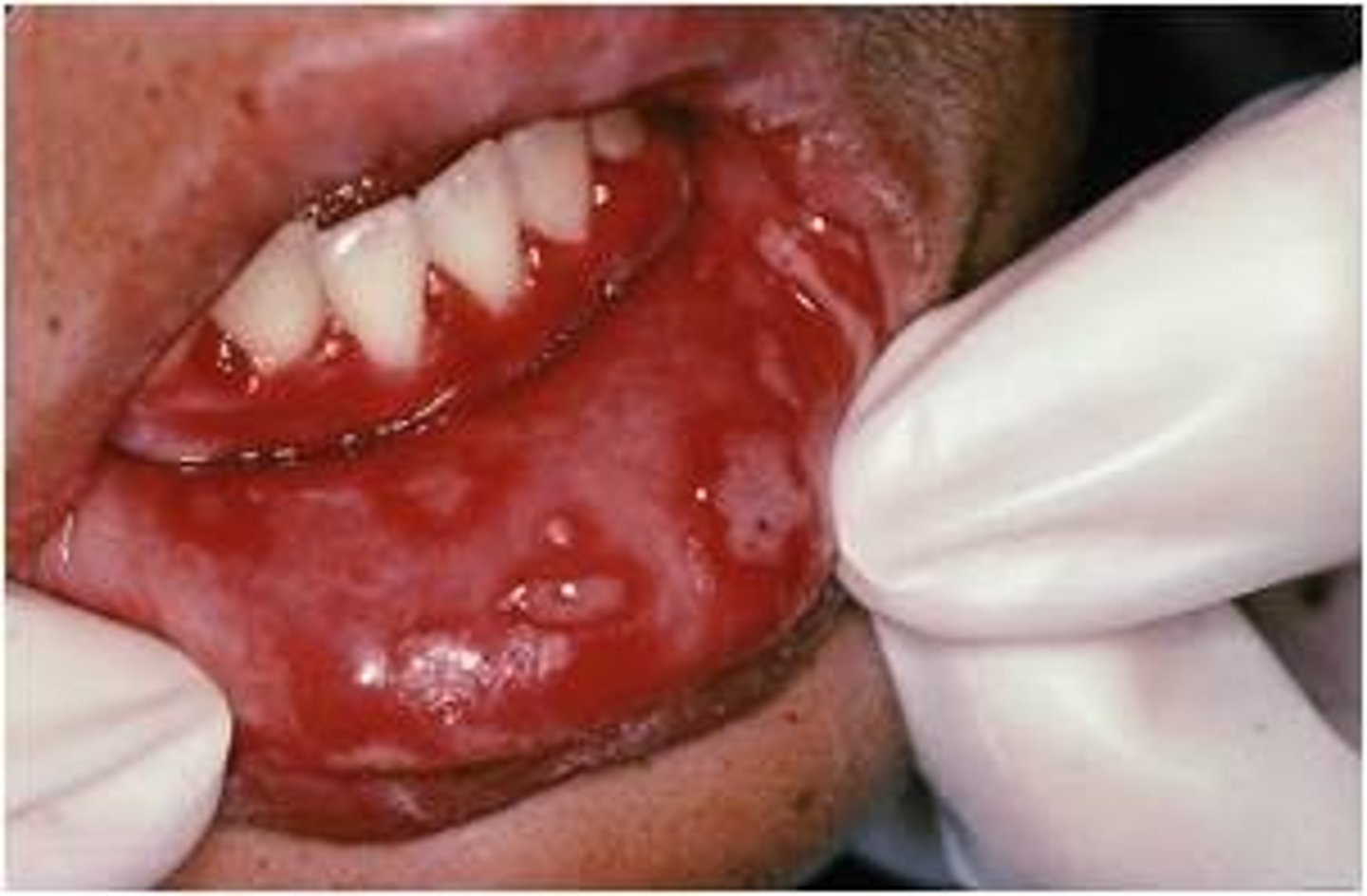
herpes gingivostomatitis treatment
antivirals
Trush / oral candidiasis pathogen
Candida albicans
Trush / oral candidiasis symptoms
white, flaky, curd-like plaques (non adherant)
burning sensation
-risk factor: antibiotics, immunocompromised, inhalers
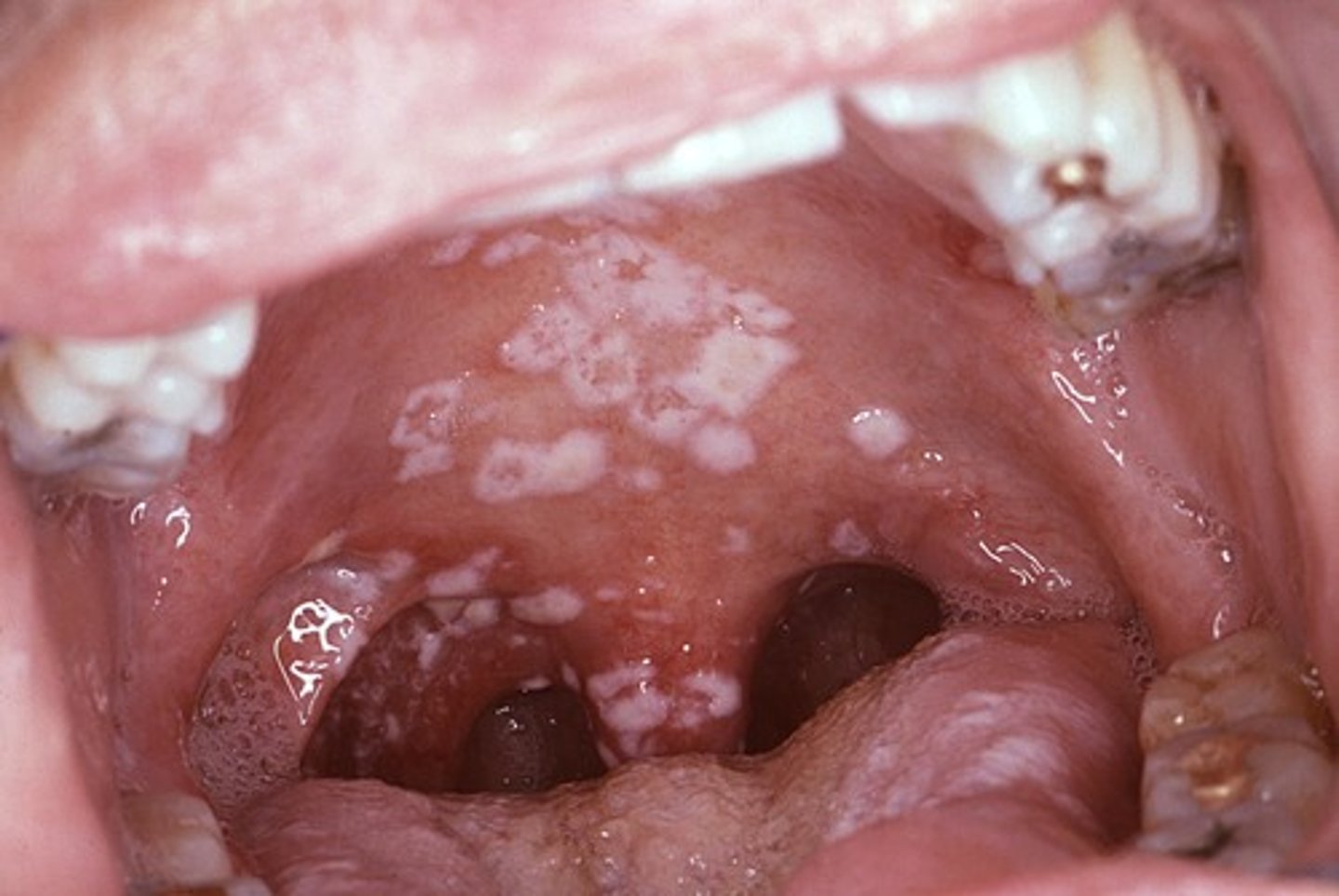
Trush diagnosis
-KOH prep
Trush / oral candidiasis treatment
Oral Nystatin Rinse or Lozenge
Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis "trench mouth" pathogen
Polymicrobial Infection: Oral Anaerobes
trench mouth risk factors
young adults under stress
immunocompromised, malnourished
polysubstance abusers
Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis symptoms
Oral Pain, Halitosis, Ulceration
metallic taste, tooth mobility, lymphadenopathy
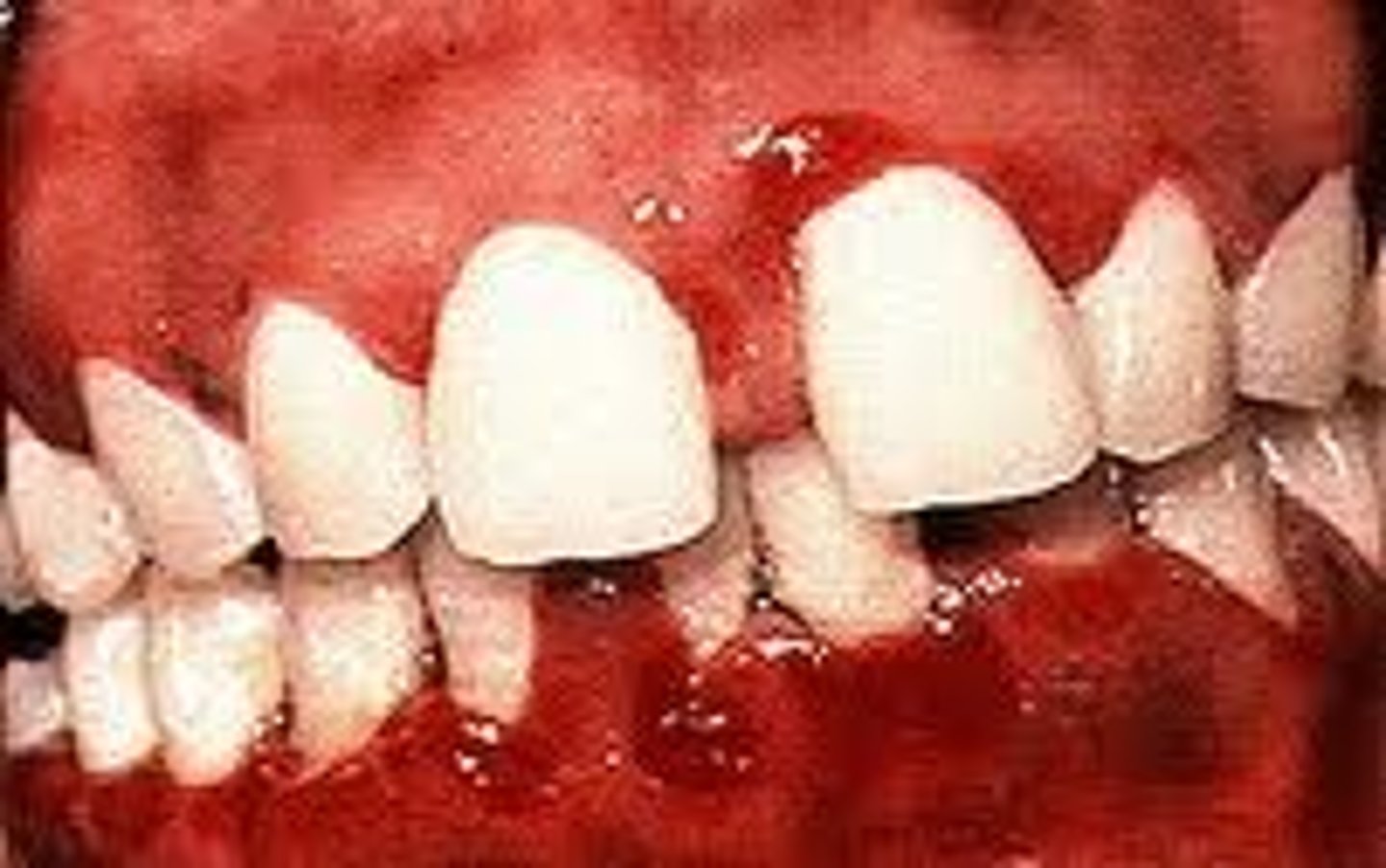
Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis treatment
eliminate contributing factors
chlorohexidine rinses
surgical debridement
antimicrobial therapy
sialadenitis pathogen
S. aureus
sialadenitis symptoms
Swelling and Pain of Gland (parotid and submandibular)
Pus can be expelled from duct
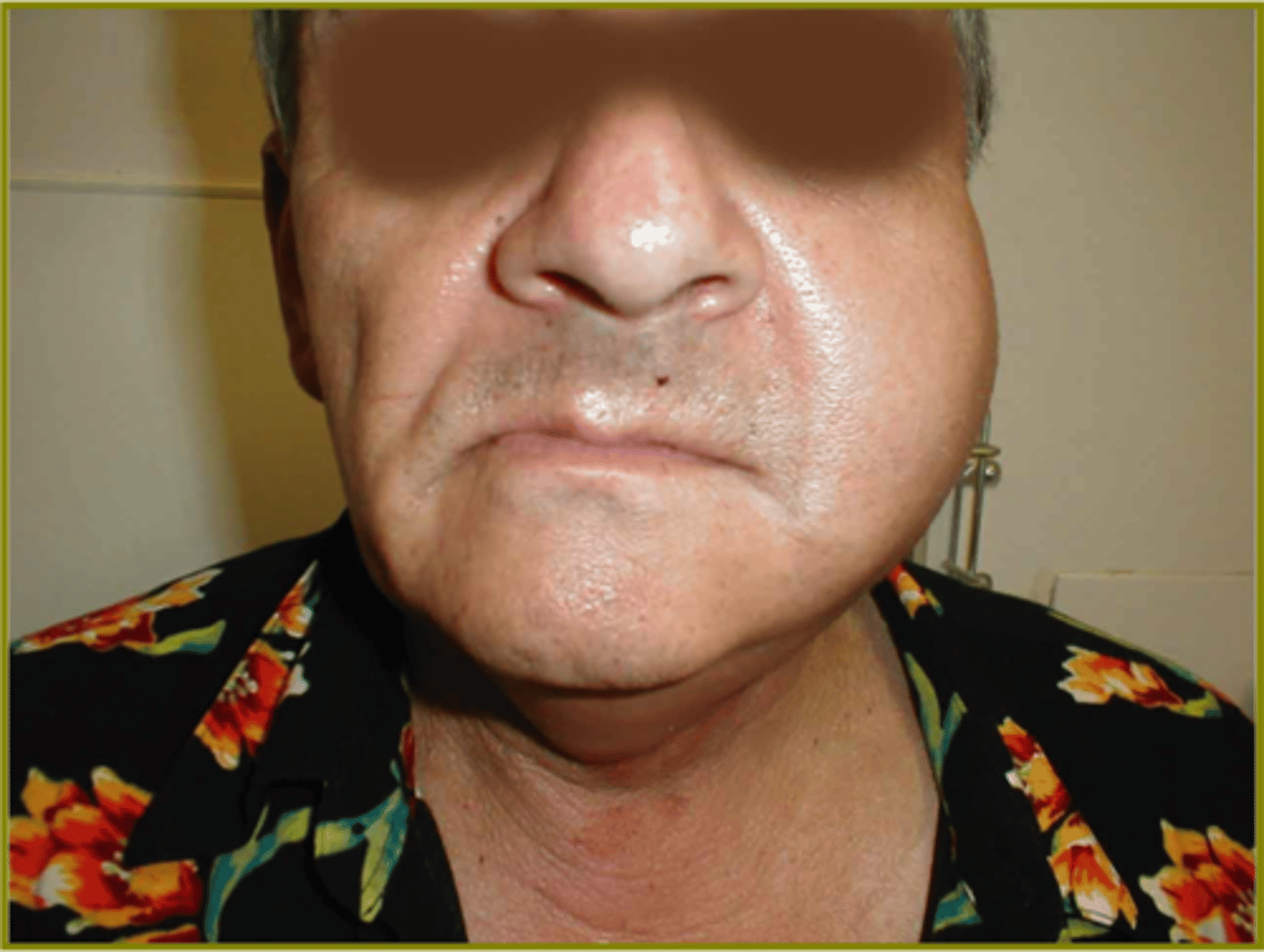
Sialadenitis treatment
PO or IV antibiotics
Gastritis
inflammation of the stomach
presents with nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain
Gastroenteritis
inflammation of the stomach and small intestine
presents with N/V, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea
Diarrhea
watery, loose, non-formed stool, large volume loss
can be quantified by # of episodes
-small intestine related pathologies
Dysentery
-Bloody, pus containing episodes of diarrhea
-fever, distrucable bleeding
-colon and large instestine with mucosal destruction
Peptic Ulcer Disease-H pylori gastritis pathogen
Helicobacter pylori
-adheres to gastric/duodenal cells
peptic ulcer disease symptions
Dyspepsia (pain in epigastrium)
Nausea/Vomiting
+/- GI Bleeding
Melena
Exacerbation with Food (pepetic ulcer-during eating)
Alleviation with food (duodenal ulcer-aftering eating)
perforation
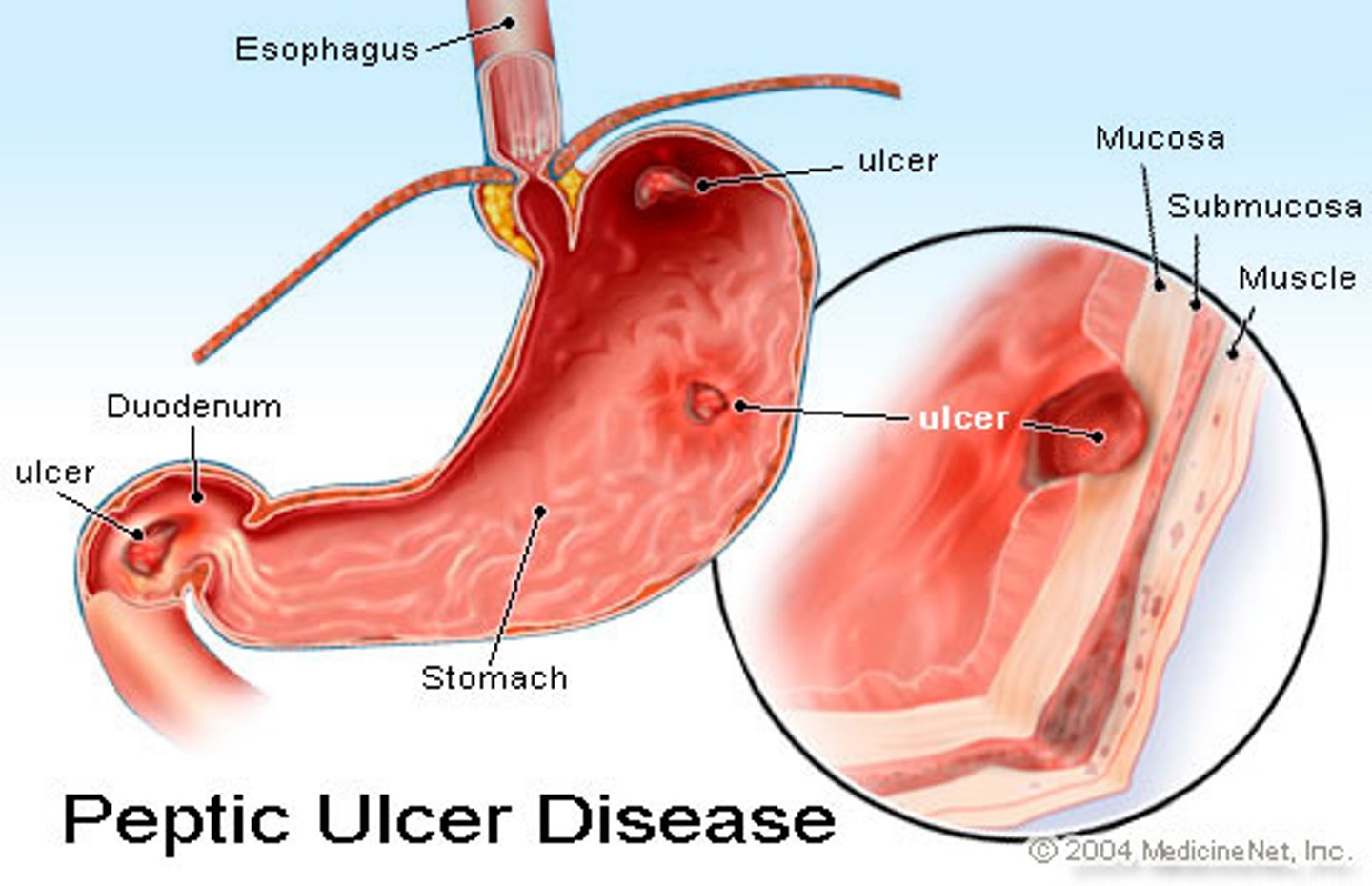
H pylori diagnosis
Urea breath test
Stool antigen test
Serum
H pylori treatment
quadruple therapy (anti acid and antibiotics)
Viral Gastoenteritis pathogens
Rotavirus and Notovirus
rotavirus
fecal contaiminated food (1-3 days)
notorious
shellfish, fecal contaminated food (12-48 hrs)
Viral Gastroenteritis symptoms
N/V
Diarrhea
General Abdominal Pain/Cramping
Dehydration
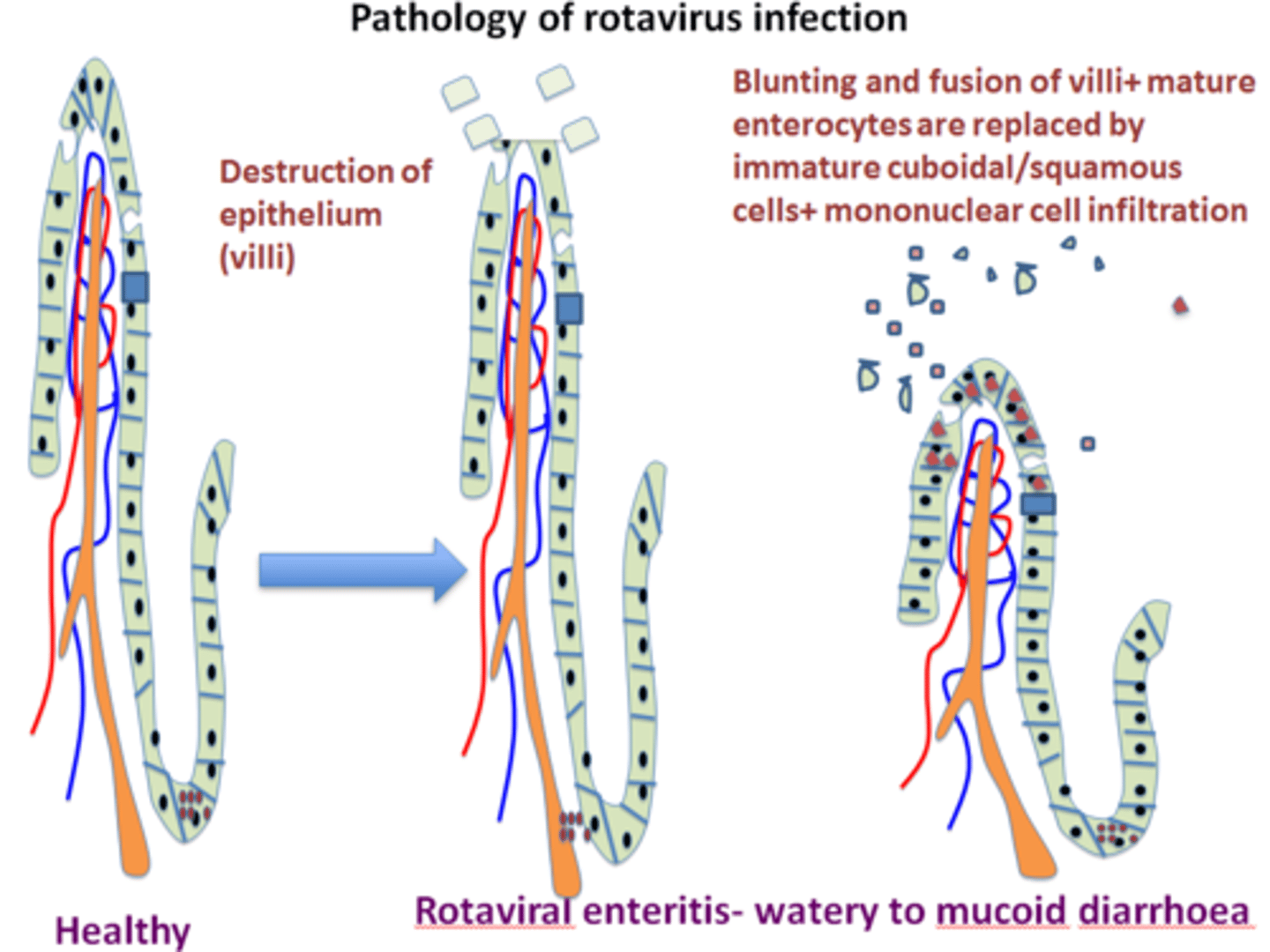
Viral Gastroenteritis treatment
fluid and electrolyte replacement
supportive care
Bacillus cereus gastroenteritis dietary association
reheated fried rice (short incu.: 2-3hrs)-PREFORMED
Meat, stews, gravy (incu. 10-16hrs)-ENTEROTOXIN
B. cereus gastroenteritis treatment
supportive care, self limiting
B. cereus gastroenteritis symptoms
Vomiting +/- diarrhea (Pre-formed)
OR
diarrhea, abd cramping +/- Nausea (enterotoxin)
S. aureus gastroenteritis dietary association
Mayonnaise-containing Salads at Room Temperature, Cream/Custard/Dairy-Based Foods
S. aureus gastroenteritis symptoms
vomiting > diarrhea
S. aureus gastroenteritis treatment
supportive care
incu. 1-8 hrs
C. perfringens gastroenteritis dietary association
rewarmed meat and poultry
C. perfringens gastroenteritis symptoms
Diarrhea
+/- vomiting
C. perfringens gastroenteritis treatment
supportive care
incu. 8-16 hrs
C. botulinum gastroenteritis dietary association
Improperly Canned Foods
Infantile: Honey
C. botulinum gastroenteritis symptoms
N/V, Diarrhea Diplopia
Neurological progression
CN Palsies
Bilateral Descending Flaccid Paralysis
C. botulinum gastroenteritis treatment
Antitoxin
Emergent clinical diagnosis
Campylobacter jejuni gastroenteritis transmission
fecal-oral
-poultry, unpasteurized milk, food contaminated with animal feces
-Travel
3 day incubation
Campylobacter jejuni gastroenteritis symptoms
Watery Foul Smelling Diarrhea
Bloody Stools
Fever
Abdominal Pain
Guillain-burre syndrome
Campylobacter jejuni gastroenteritis treatment
antibiotics
Vibrio cholerae food
fecal oral
-water, shellfish, raw fruit.veggies
Vibrio cholerae symptoms
"rice water stools"-
~15L fluid loss per day
dehydration-will die if not given water
2 day incubation
Vibrio cholerae treatment
Fluid and Electrolyte Replacement
Antimicrobial Therapy (Shorten Duration of Illness)
salmonella enterica dietary association
Eggs, Poultry, Unpasteurized Milk
Seen with improper food handling
salmonella enterica symptoms
diarrhea
low-grade fever
24-48 hrs
-stoool culture to diagnose
salmonella enterica treatment
fluid and electrolyte replacement
antibiotic if immunocompromised
salmonella enterica pathophysiology
limited to submucose (lamina propria)
salmonella typhi transmission
fecal-oral, normally from asymptomatic carriers
salmonella typhi symptoms
Enteric fever
matastatic infx: UTI, biliary tree carreir asymptomatic
6-30 days
ASYMPTOMATIC Carrier State: Still Can Spread Disease
Diagnosis: stool or blood cultures
salmonella typhi treatment
IV or PO antibiotics
salmonella typhi pathophysiology
disseminated disease/bacteremia
enteric fever
stepwise fevers and headahce
intermittent diarrhea
bacteremia
intestinal perforation and hemorrhage (>2 weeks after infection)
shigella spp. transmission
fecal-oral
contaminated food/water
shigella spp. enterocolitis symptoms
Dysentery/ severe diarrhea
Vomiting
Fever
Abdominal Pain
tenesmus
1-7 days
diagnosis: stool culture
shigella spp. enterocolitis treatment
Supportive Care
Antibiotic Therapy
Shigella Spp pathophysiology
only 10 bacterial cells needed to cause disease, very resistant
C. diff transmission
fecal-oral
C diff pathogenesis
colonization of large intestine
antibiotic use
over-proliferation of C diff
development of pseudomembranous colitis
C. diff symptoms
Fever
Abdominal Pain
Foul-Smelling Non-Bloody Diarrhea
C. diff diagnosis
stool sample
-Elisa: exotoxin
-PCR: toxin-encoding gene
C. diff treatment
Oral antibiotic
E. coli prevention
catheter care
thoroughly cooking good/boiling water
E. coli enterotoxigenic acquisition
contaminated food/water, traveling
E. coli enterotoxigenic toxin
Heat Labile/Heat Stable Toxin
E. coli enterotoxigenic disease location
Small Intestine
E. coli enterotoxigenic symptoms
watery diarrhea
NON- BLOODY
E. coli enteropathogenic acquisition
Fomites, Nursery-Related Outbreaks (KIDS)
E. coli enteropathogenic disease location
small intestine
E. coli enteropathogenic symptoms
watery diarrhea
NON-BLOODY
E. coli Enterohemorrhagic acquisition
undercooked hamburger meat
E. coli Enterohemorrhagic toxin
shiga-like toxins
E. coli Enterohemorrhagic disease location
large intestine
E. coli Enterohemorrhagic symptoms
hemorrhagic colitis
Hemolytis Uremic Syndrome
BLOODY DYSENTERY
E. coli enteroinvasive acquistion
Contaminated Food/Water
E. coli enteroinvasive toxin
Shigella-Like toxin
E. coli enteroinvasive disease location
large and small intestine
E. coli enteroinvasive symptoms
DYSENTERY Fever
E. coli enteroaggregative acquisition
Contaminated Food/Water
Traveling
E. coli enteroaggregative toxin
Enteroaggregative Heat Stable Enterotoxin
E. coli enteroaggregative disease location
small intestine
E. coli enteroaggregative symptoms
Recurrent Watery Diarrhea (>14 days)
hwmolytic uremic syndrome
hemolytic anemia
thyrobocytopenia
acute fenal failure
E coli intestinal infection treatments
Supportive Care
Hepatitis A pathogen
RNA hepatovirus
Hepatitis A symptoms
RUQ Abdominal Pain
Acute onset of N/V, diarrhea, anorexia, fever/chills
Jaundice and Pruritus
Hepatitis A diagnosis
HepA IgM antibody blood test
(only way to tell which Hep it is)
Hepatitis A treatment
Supportive care
-does NOT cause chronic disease
-get lifelong immunity
hepatitis B pathogen
DNA hepadnavirus
hepatitis B transmission
perinatal, percutaneous, sexual contact, infected body fluids
-MAINLY IV DRUG USE
hepatitis B symptoms
Acute:
N/V
Diarrhea
RUQ Pain
Jaundice
Chronic:
Asymptomatic Progressive Necro-Inflammatory Disease of the Liver
Cirrhosis
SAME AS HEP A-----BLOOD TEST
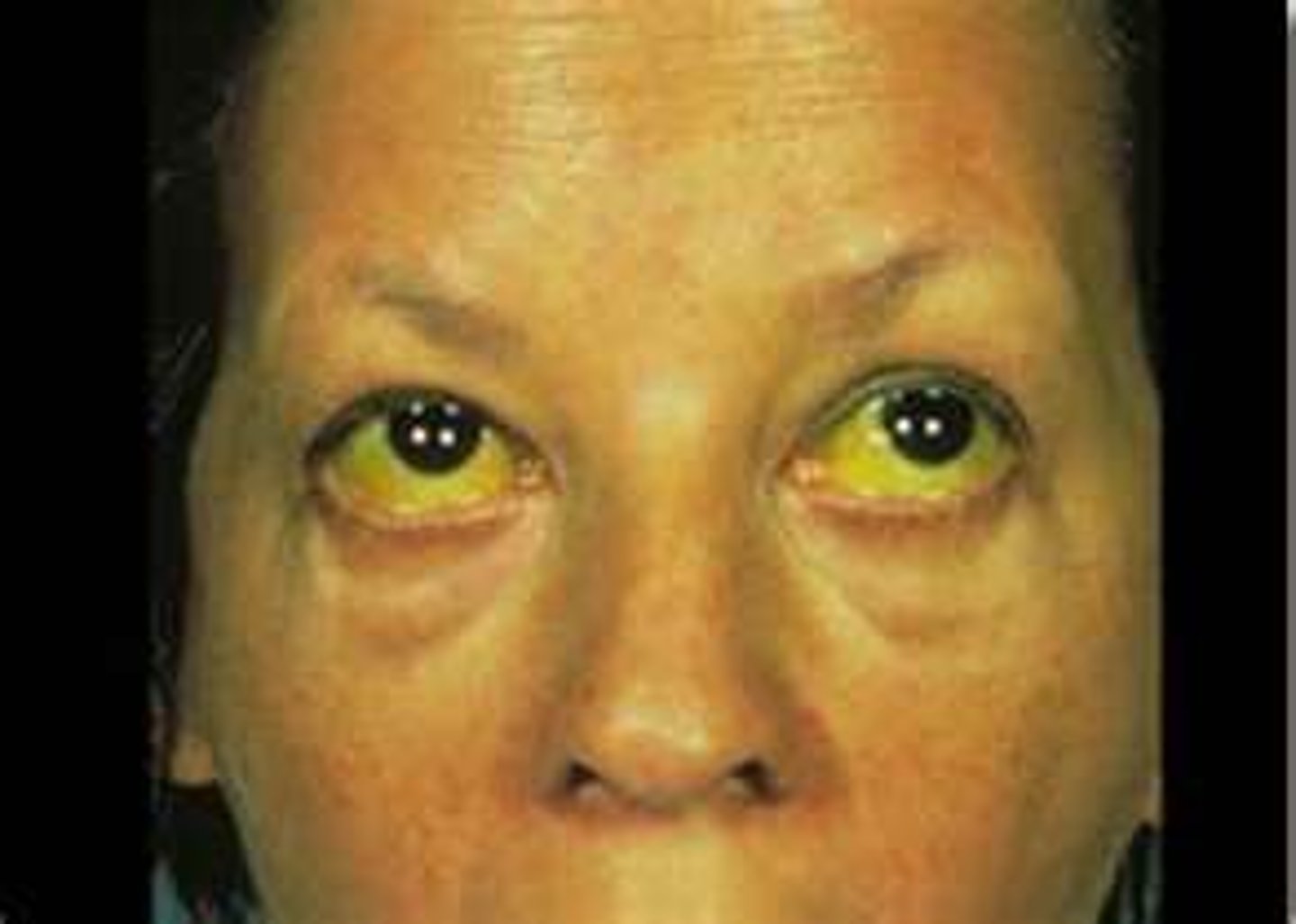
hepatitis B treatment
Antiviral Regimen and Prevention of Disease Spread
vaccination for prevention
hepatitis C pathogen
hepacivirus, single stranded RNA virus
Hepatitis C symptoms
Acute: N/V, RUQ Pain, Jaundice
Chronic: Progression to Cirrhotic Liver Disease
hepatitis C treatment
antivirals
-rare to self resolve-most become chronic if no treatment
-does not give lifelong immunity
Acute onset of Hepatitis
Surface antigen positive
antibody to core antigen positive