CSD 303 Unit 3
5.0(1)Studied by 32 people
Card Sorting
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:28 PM on 12/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
1
New cards
Air-bone gap
significant difference between air conduction and bone conduction thresholds in the same ear at any particular frequency
2
New cards
Air conduction (AC)
method of testing with earphones, insert earphones or loudspeakers such that the signal is delivered through the entire hearing mechanism, including the periphery and central auditory nervous system
3
New cards
Audiogram
graph displaying hearing sensitivity, showing frequency in Hz across the x-axis and intensity in dB along the y-axis
4
New cards
Audiometer
piece of equipment used by audiologists to help estimate hearing threshold and to aid in differential diagnosis
5
New cards
Bone conduction (BC)
method of testing with a bone conduction oscillator such that the signal bypasses the outer and middle ears and delivers to the inner ear and central auditory nervous system
6
New cards
Conditioned play audiometry
audiometric technique utilized with small children, most often of preschool developmental age, where the child responds by game-playing upon hearing a stimulus
7
New cards
Conductive hearing loss
type of hearing impairment where the disorder lies in the outer and/or middle ear
8
New cards
Sensorineural hearing loss
type of hearing impairment where the disorder lies in the inner ear and/or the VIII nerve (vestibulocochlear)
9
New cards
Mixed hearing loss
type of hearing impairment where the disorder lies within the conductive and sensorineural mechanisms
10
New cards
Configuration of hearing loss
parameter used in audiogram interpretation to determine shape of the audiogram and severity as a function of test frequency
11
New cards
Hughson-Westlake procedure
common procedure for obtaining threshold; the audiologist decreases stimulus intensity by 10 dB with a (+) response and increase by 5 dB with a (-) response
12
New cards
Interaural attenuation
refers to level at which stimulus intended for the test ear crosses over and is perceived by the non-test ear - always going to be 40 dB less on the other side
13
New cards
Magnitude of hearing loss
parameter used in audiogram interpretation to help determine severity of hearing impairment, if any
14
New cards
Masking
procedure whereby the audiologist delivers a noise stimulus to the non-test ear to prevent it from participating in the testing session, so that accurate results may be obtained in the test ear
15
New cards
Otoacoustic emissions (OAEs)
physiological measure correlating with outer hair cell function of the cochlea, utilized by the audiologist to help estimate hearing threshold and to assist in different diagnosis
16
New cards
Overmasking
during clinical masking, this term refers to an inaccurately high intensity level of noise presented to the non-test ear, such that the noise crosses over to the test ear and interferes with obtaining true thresholds
17
New cards
Undermasking
during clinical masking, this term refers to an inaccurately low intensity level of noise presented to the non-test ear, such that the tone still crosses over (to the non-test ear) and interferes with obtaining of true thresholds in the test ear
18
New cards
Maximum effective masking
highest intensity level of masking noise theoretically presented to non-test ear that will allow the clinician to obtain accurate thresholds in the test ear without over-masking
19
New cards
Minimum effective masking
lowest intensity level of masking noise theoretically presented to non-test ear that will allow the clinician to obtain accurate thresholds in the test ear without under-masking
20
New cards
Plateau
a clinical masking term referring to a range of noise at which effective masking occurs and true thresholds may be obtained
21
New cards
Symmetry of hearing loss
parameter used in audiogram interpretation to compare sensitivity in one ear to that of the other ear
22
New cards
Three-frequency pure tone average (PTA)
average of thresholds at 500, 1000, and 2000 Hz in the same ear. This measure should correlate with the speech threshold and configuration warrants whether a two or a three-frequency PTA is calculated
23
New cards
Threshold
the softest intensity level at which a stimulus is heard, at least 50% of the time
24
New cards
Visual reinforcement audiometry (VRA)
technique utilized for ascertaining threshold with pediatric patients, whereby the child lateralizes to a lighted toy whenever the stimulus is heard
25
New cards
Artificial ear
a type of cochlear implant use to help provide a sense of sound; used for electroacoustic calibration process - a chamber with a 6-cc volume
26
New cards
Speech audiometry
a test that is used to determine the lowest level that speech can be heard
27
New cards
Phonetically balanced word list
the phonetic composition of all lists are equivalent and representative of everyday english speech
28
New cards
PB max
the maximum score on the PI-PB; word recognition score improves as intensity increases
29
New cards
PB rollover
a reduction of speech recognition scores that occur at intensities above the level where PB max is obtained
30
New cards
Spondee words
two syllable word that is pronounced with equal stress on both syllables
31
New cards
Speech recognition threshold
the minimum hearing level for speech at which an individual can just discern the presence of speech material 50% of the time
32
New cards
Word recognition score
percentage of words recognized when speech is presented at a particular level above the SRT
33
New cards
Transducer
piece of audiometric equipment that transforms one form of energy to another and is utilized to deliver stimuli to the patient
34
New cards
Supra aural earphones
goes straight into the ear, outer, middle, and inner ear, also shakes the bone a little ; use when AC threshold exceeds BC threshold by 40 dB or more
35
New cards
Insert earphones
goes straight into the ear canal and just shakes the bone a little ; use when AC thresholds exceeds BC threshold by 50 dB or more
36
New cards
Bone conduction vibrator
skips outer and middle ear, goes straight to inner ear, vibrates skull
37
New cards
Sound level meter
piece of laboratory equipment used to measure sound intensity in dB sound pressure level
38
New cards
6-cc coupler
used for calibrating insert earphones
39
New cards
2-cc coupler
intended for measurements on all types of hearing aids and is optimized for repetitive use in the laboratory and on the production line
40
New cards
Reference equivalent threshold sound pressure level
used when calibrating audiometric equipment to a hearing threshold level oof zero at various frequencies
41
New cards
Listening check
when you make sure your baby is hearing and noticing the specific speech sounds you say to them known as the ling six sounds (without the baby seeing you) right after you put on their hearing technology
42
New cards
Normal hearing loss
0 - 25 dB HL
43
New cards
Mild hearing loss
26 - 40 dB HL
44
New cards
Moderate hearing loss
41 - 55 dB HL
45
New cards
Moderately severe hearing loss
56 - 70 dB HL
46
New cards
Severe hearing loss
71 - 90 dB HL
47
New cards
Profound hearing loss
91+ dB HL
48
New cards
Otitis media
- conductive hearing loss
- middle ear infection
- most commonly occurring childhood diseases especially in first few years of life
- mild hearing loss
- middle ear infection
- most commonly occurring childhood diseases especially in first few years of life
- mild hearing loss
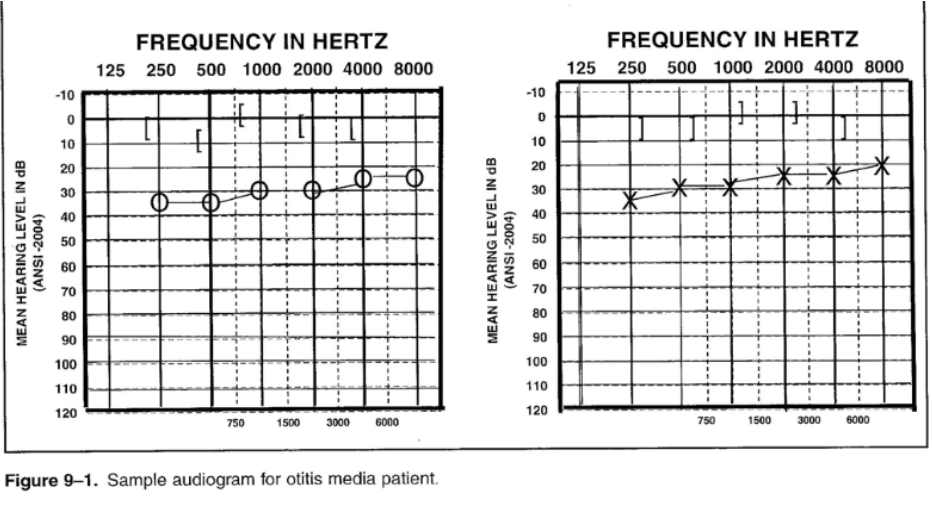
49
New cards
Otosclerosis
- conductive hearing loss
- growth of abnormal bone tissue
- more common among women then men
- often bilateral
- mild hearing loss
- growth of abnormal bone tissue
- more common among women then men
- often bilateral
- mild hearing loss
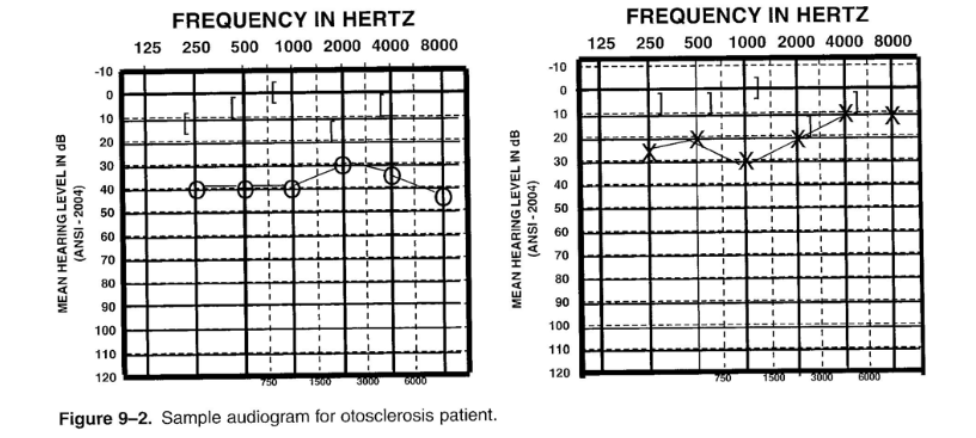
50
New cards
Ossicular chain disarticulation
- conductive hearing loss
- disarticulation of the ossicular bones due to head trauma or other injury
- usually unilateral hearing loss with sudden onset
- normal to mild hearing loss
- disarticulation of the ossicular bones due to head trauma or other injury
- usually unilateral hearing loss with sudden onset
- normal to mild hearing loss
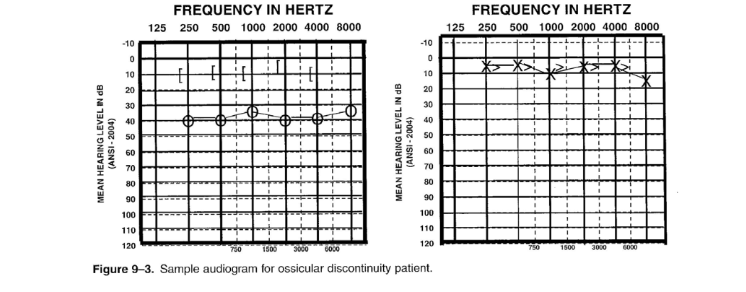
51
New cards
Presbycusis
- sensorineural hearing loss
- typically symmetrical
- hearing configuration is typically sloping
- will affect speech when hearing loss becomes mild - moderate
- typically symmetrical
- hearing configuration is typically sloping
- will affect speech when hearing loss becomes mild - moderate
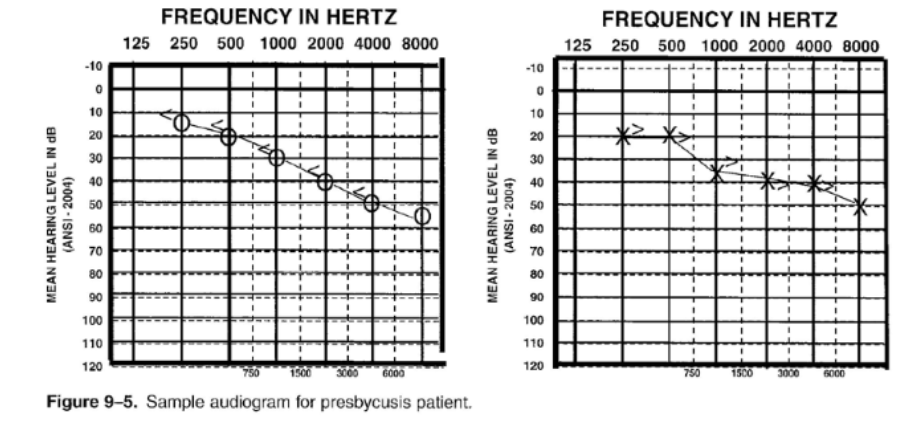
52
New cards
Meniere's disease
- sensorineural hearing loss
- affects the endolymph of the ear
- hearing loss is often unilateral
- affects the endolymph of the ear
- hearing loss is often unilateral
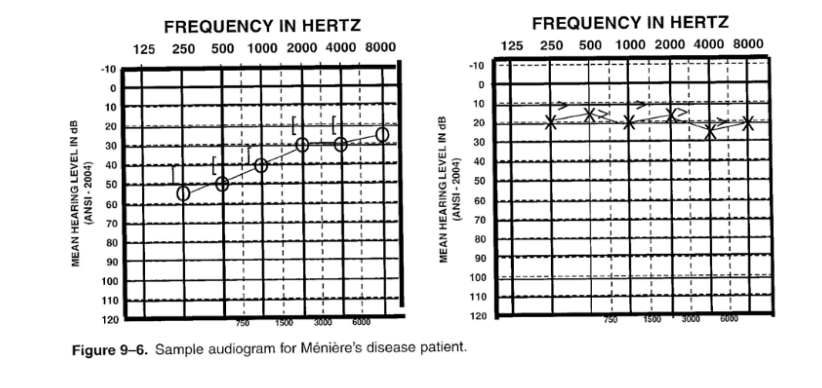
53
New cards
Ototoxicity
- sensorineural hearing loss
- from medications that have ototoxic side effects
- severe to profound hearing loss
- from medications that have ototoxic side effects
- severe to profound hearing loss
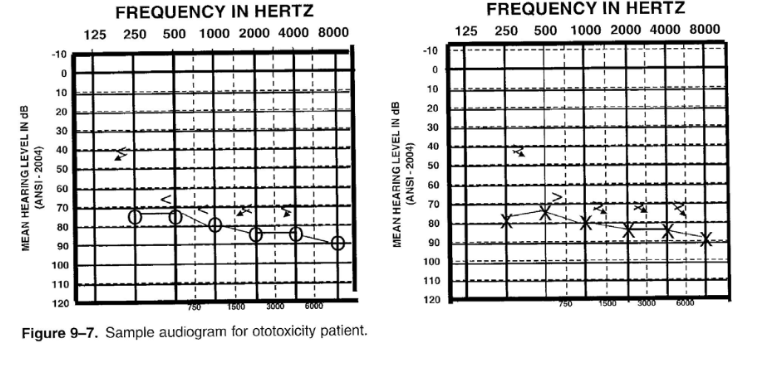
54
New cards
Noise-induced hearing loss
- sensorineural hearing loss
- threshold shifts due to noise exposure that may be temporary or permanent
- a "notch" is seen in the audiogram at 4-6 kHz
- threshold shifts due to noise exposure that may be temporary or permanent
- a "notch" is seen in the audiogram at 4-6 kHz
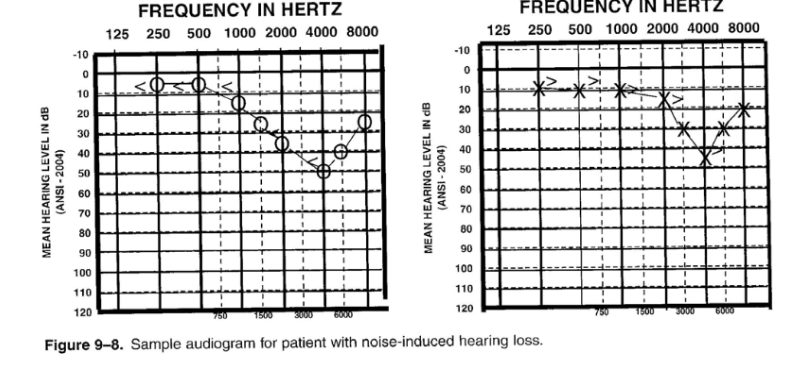
55
New cards
Auditory processing disorder
- significant difficulty processing speech and other complex sound patterns
- hearing threshold may be in normal range
- hearing threshold may be in normal range
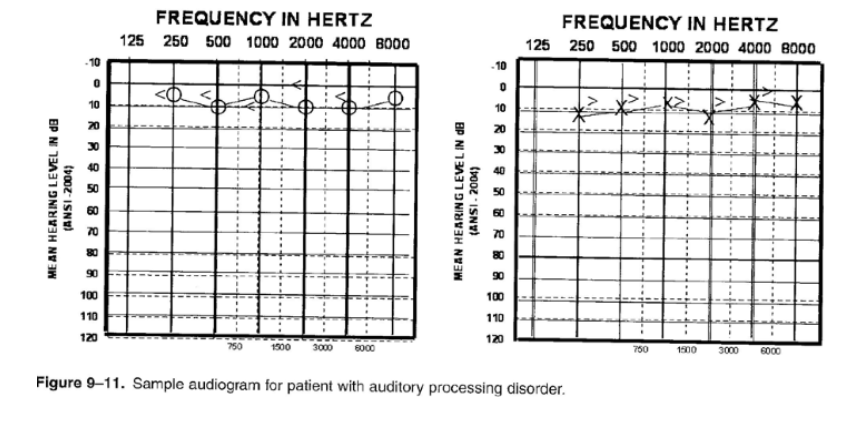
56
New cards
Threshold test
used during pure-tone test; determine a suitable presentation level for supra-threshold test
57
New cards
Supra-threshold test
determine the the percentage of speech recognition a patient can obtain
58
New cards
What are the two types of speech audiometry tests?
monitored live voice and prerecorded test materials
59
New cards
Flat configuration
thresholds are all within 20 dB of each other
60
New cards
Rising configuration
thresholds at low frequencies are at least 20 dB poorer than thresholds at high frequencies
61
New cards
Sloping configuration
thresholds at high frequencies are at least 20 dB poorer than thresholds at low frequencies
62
New cards
Precipitous configuration
thresholds are steeply sloping (at least 20 dB) in the higher frequencies
63
New cards
Auditory brainstem response (ABRs)
meant to determine the functional status of the neural pathways used for hearing