Art History (Roman Art- Gothic Art)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
1
New cards
Villanovan and Etruscan Period (900-270 BCE)
These people were from the village of Villanova and Etruria. They were the predecessor of the Romans with many of their artistic style influencing them. This period of artwork is defined by the Temple of Mnerva and Sarcophagus of the Spouses.
2
New cards
Sarcophagus
The Etruscans would practice both cremation and full body burials, both of these remains would be put in elaborate containers usually made of terracotta. These items are made usually depicting the people such as woman attending banquets.
3
New cards
The Roman Republic (509-27 BCE)
It was a republic formed when brothers Romulus and Remus founded the city of Rome. These people overthrew the Etruscans and adopted many aspects of Greek, Persian, and Egyptian cultures. This period of artwork is defined by the Pompeii’s amphitheater and the temple of Portunus.
4
New cards
Forum
The roman center of civic life that could have places or shopping, worshipping, and political events.
5
New cards
Amphitheater
The roman version of a theater that was created with barrel vaults
6
New cards
Julio-Claudians Roman Empire (27 BCE - 68 CE)
The empire that existed after the assassination of Julius Caesar in 44 BCE. The founder emperor was Julius Caesar adopted son known as Octavian or Augustus. The artwork of this period is defined by the Ara Pacis (Altar of Augustan Peace) and the Pont-du-Gard.
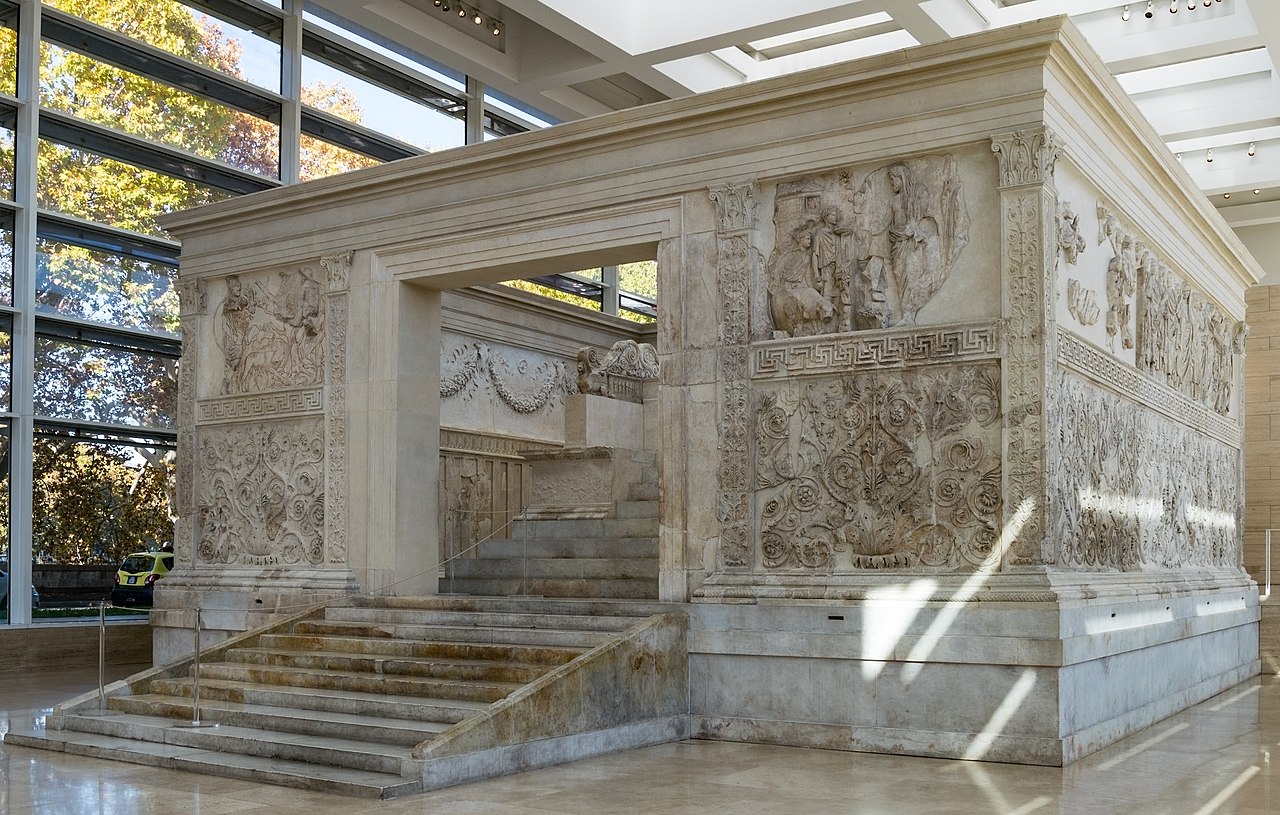

7
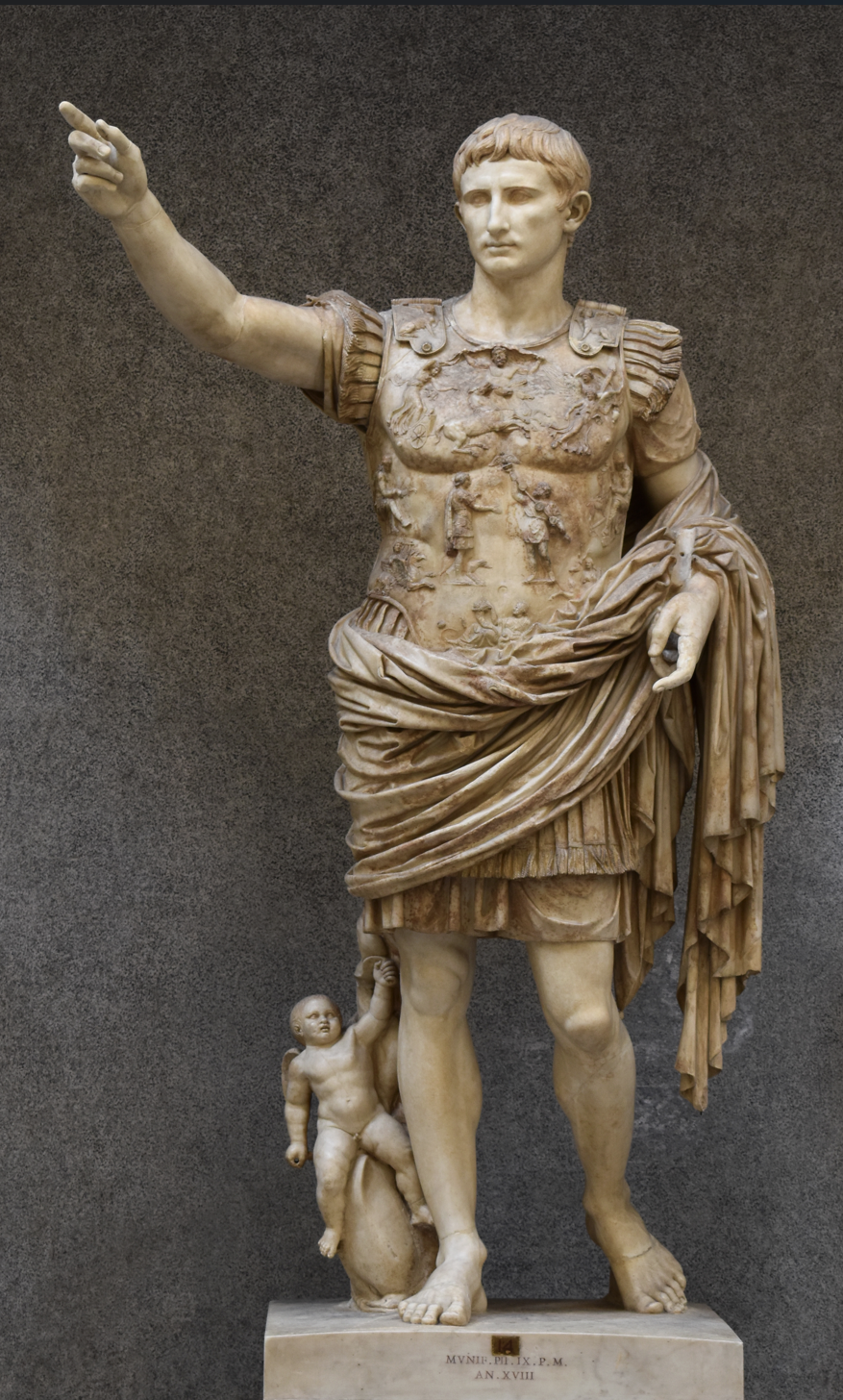
New cards
Augustus of Primaporta, Rome, 1st century CE
Portrays Augustus as a general with a cupid and a dolphin. The dolphin representing a victory of the Battle of Actium and was meant to show case his power as a ruler. The statue has a mixture of Polykleitos style of idealization and the verism that was common in Roman statues.

8
New cards
Pax Romana
The period of peace in the Roman Empire that lasted around 45 years.
9
New cards
High Empire of Rome (Flavians to Good Emperor ) (69-192 CE)
The period after Nero and began with the rulers of Vespasian. This period of artwork is define by the Colosseum or Flavian Amphitheater and the Arch of Titus.
10
New cards
Pantheon, Rome, 110-28 CE
Showcase the full potential of Roman concrete as this building was built over a drum with an oculus on top. The building was dedicated to all the gods of Rome and homed sculptures of the gods in the building.
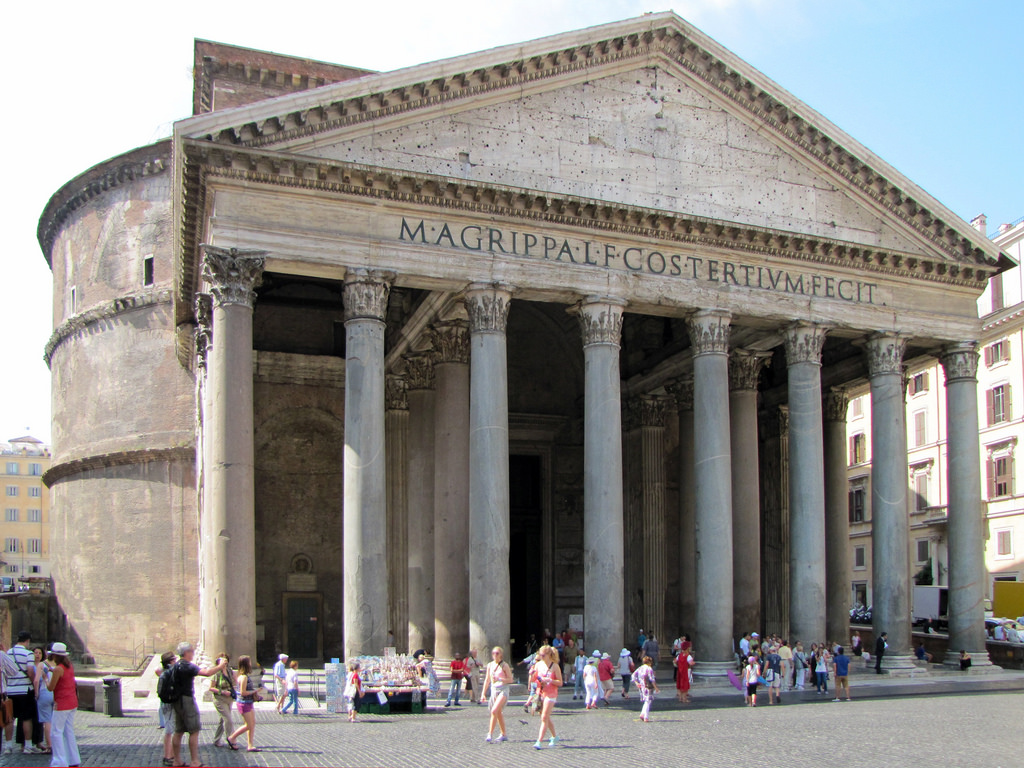

11
New cards
Verism
A technique used in Roman sculptures in which we see the use of realism in order for the people to recognize a person after death as well as emphasizing the age and wisdom of the person.
12
New cards
Barrel vault
Vaults are rounded and are used to create a tunnel or rounded roof. Barrel vaults in the Roman period were used to support the seating in Amphitheater or Arches. These vaults are also later used in early Romanesque Cathedrals.
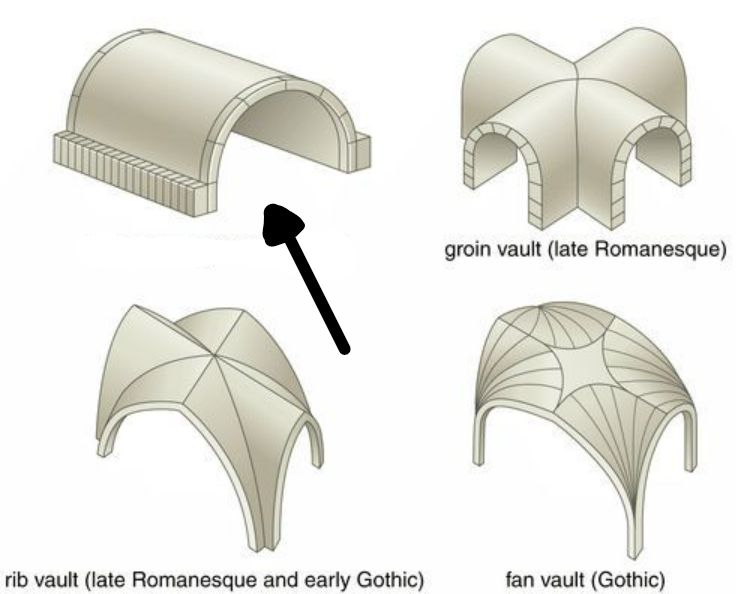
13
New cards
Triumphal arch
Part sculpture part barrel vault passageway that was built in the Roman time to celebrate victories. One of the most famous one is called the Arch of Titus which showcase the capture of Jerusalem.
14
New cards
Late Roman Empire (Severan to Tetrarchs) (193-337 CE)
This period is the declining of the Roman empire with the Severan Dynasty and the Tetrarchy. This period ended when Emperor Constantine converted to Christian. Due to fact the empire was declining artwork during this time was less grand with many of the pieces that define the artwork was the Portraits of the Tetrachs and the tondo portrait of Caracalla.
15
New cards
Tetrarchy
A period of time where four rulers share power amongst themselves. In these roman times they were called Augustus and Caesars.
16
New cards
Tondo
A rounded portraits, we see several made in the Severan Dynasty such as the Septimius Severus with his children.
17
New cards
Jewish and Early Christian Art in Late Antiquity (150-500 CE)
Some of the earliest Christian and Jewish art was found in Catacombs and burial areas. Many early Christian artwork held influence from Roman art including with the depiction of Christ himself.
18
New cards
Good Shepherd Mosaic, Galla, Placidia, 425 CE
One of the earliest examples of Christian artwork depicts Jesus as the Shepard for humanity or the flock of sheep. We also see Jesus depicted more serenly and youthful which is closer to the Roman style of the past.
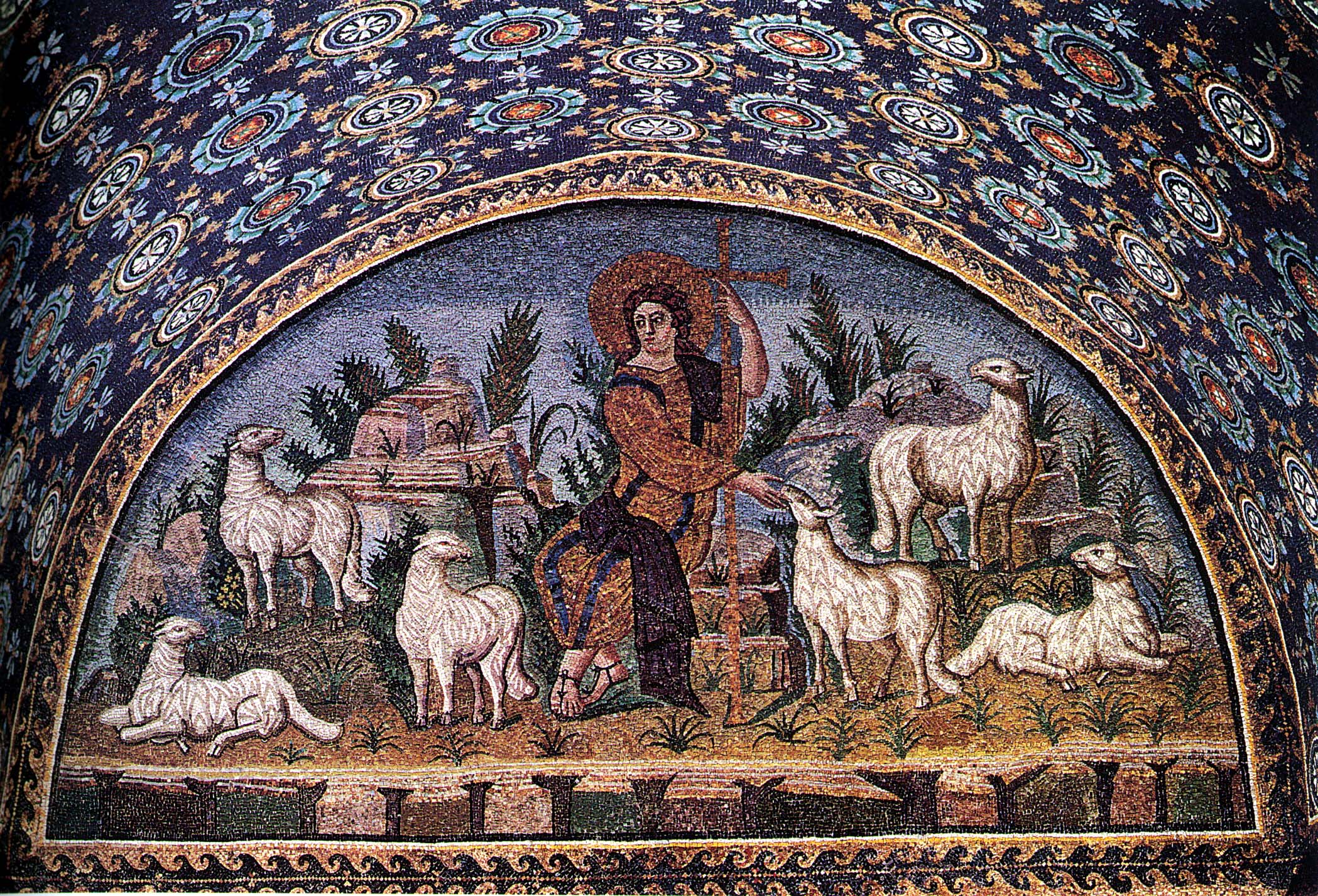

19
New cards
Lunette
A moon shape area above a door or window that depicts scenes from Christian canon.
20
New cards
Nave
The central aisle of the Basilica church.
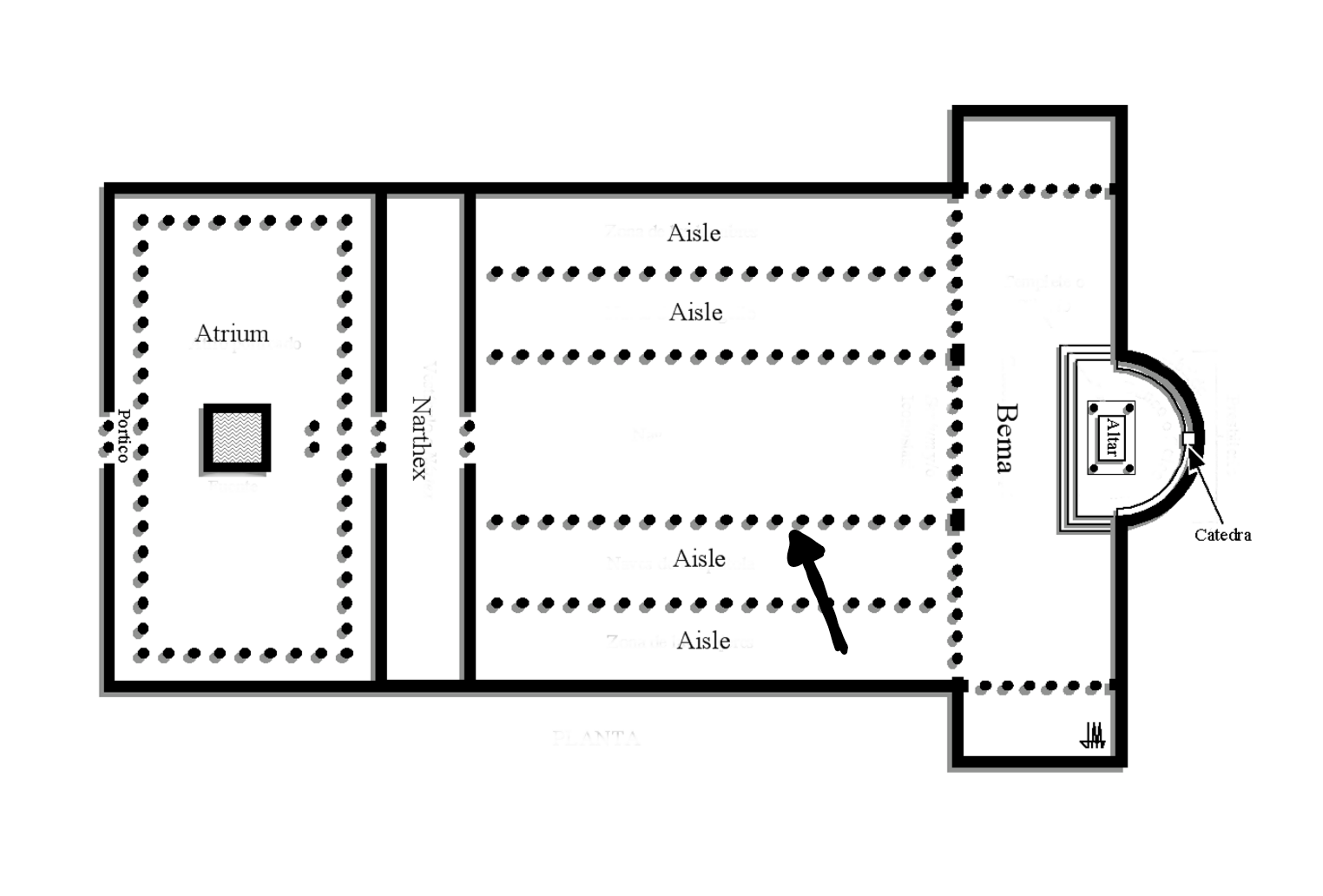
21
New cards
Aisle
The four aisles that are side by side of the nave.
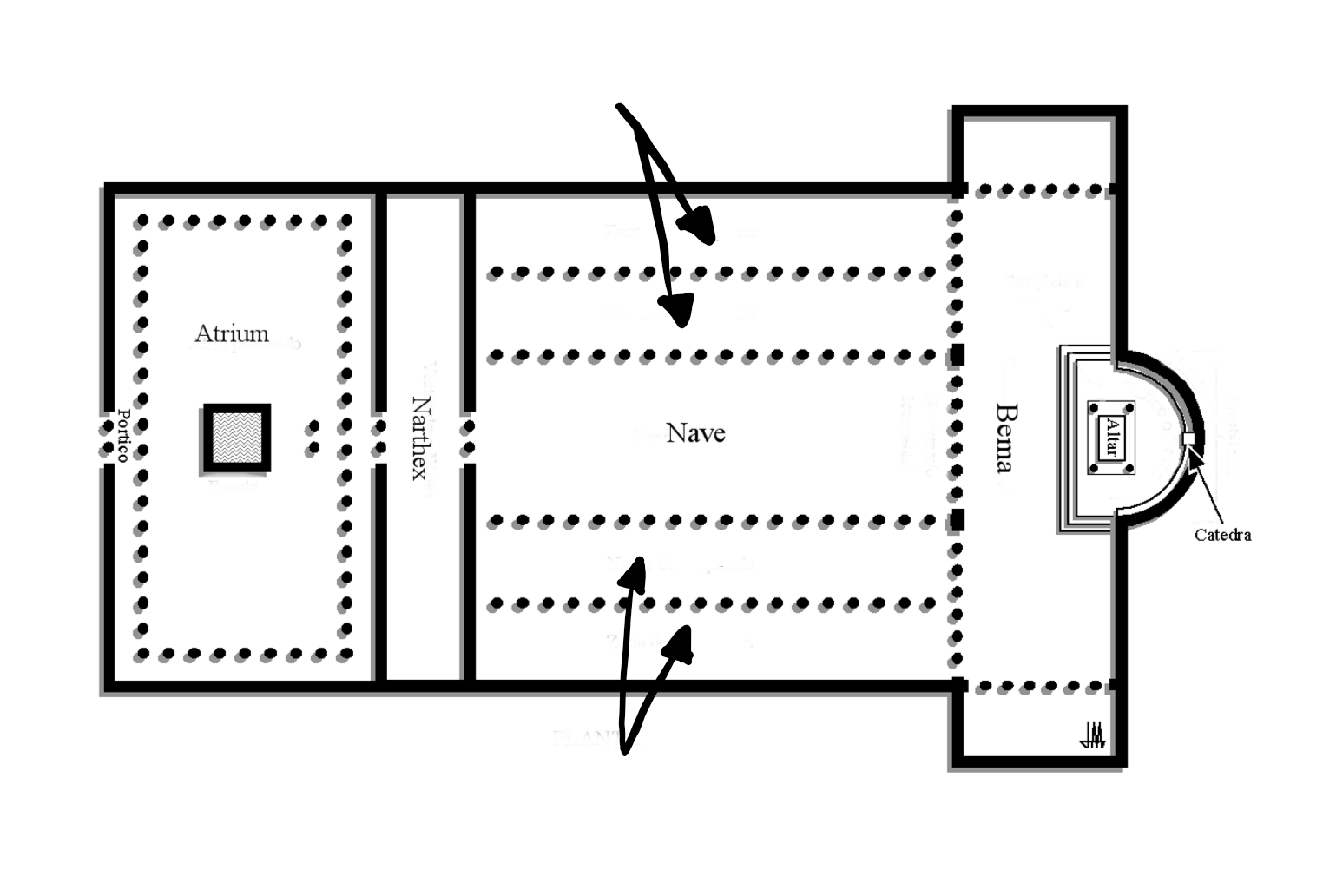
22
New cards
Transept
Section of the church before the alter that extend outwards.
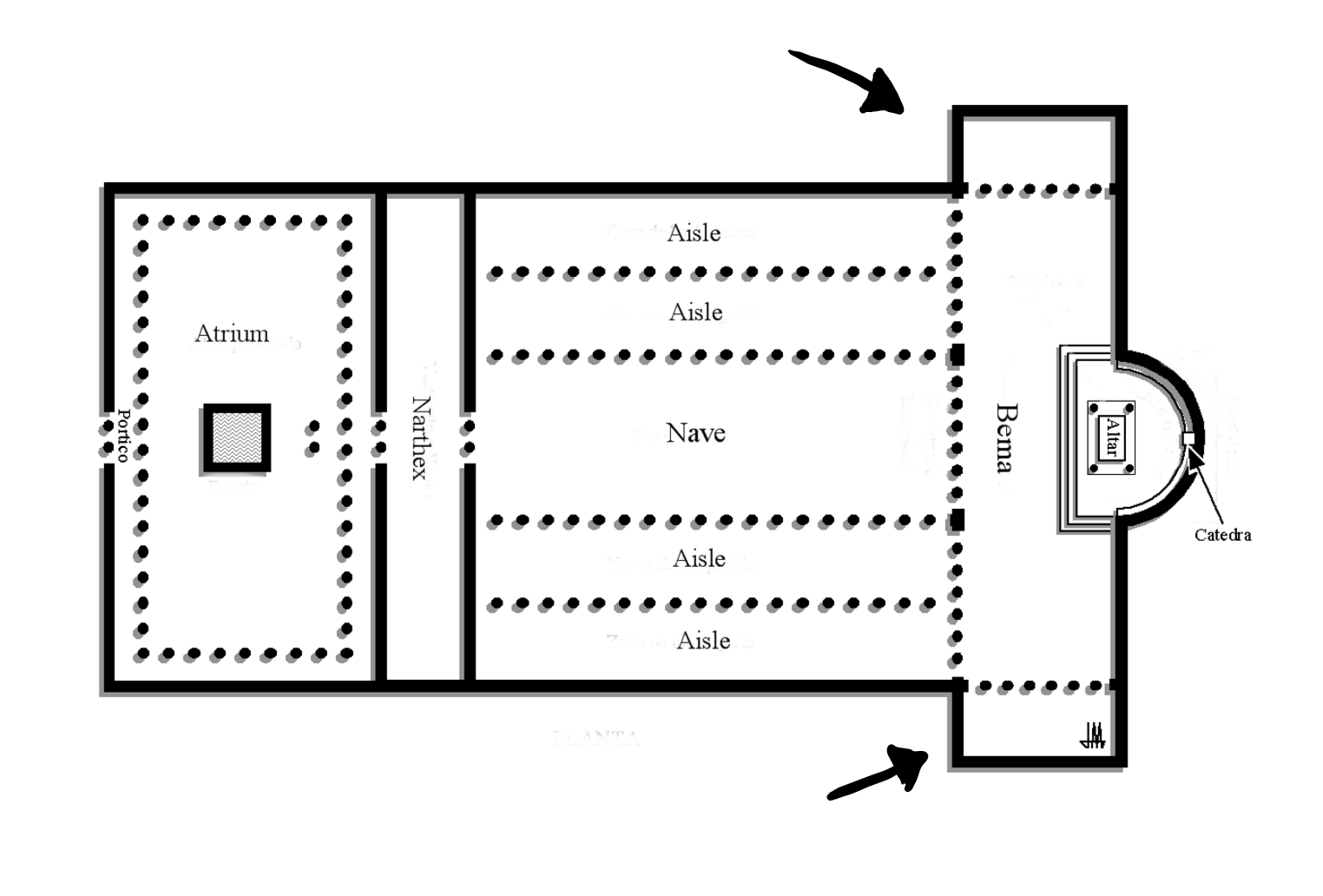
23
New cards
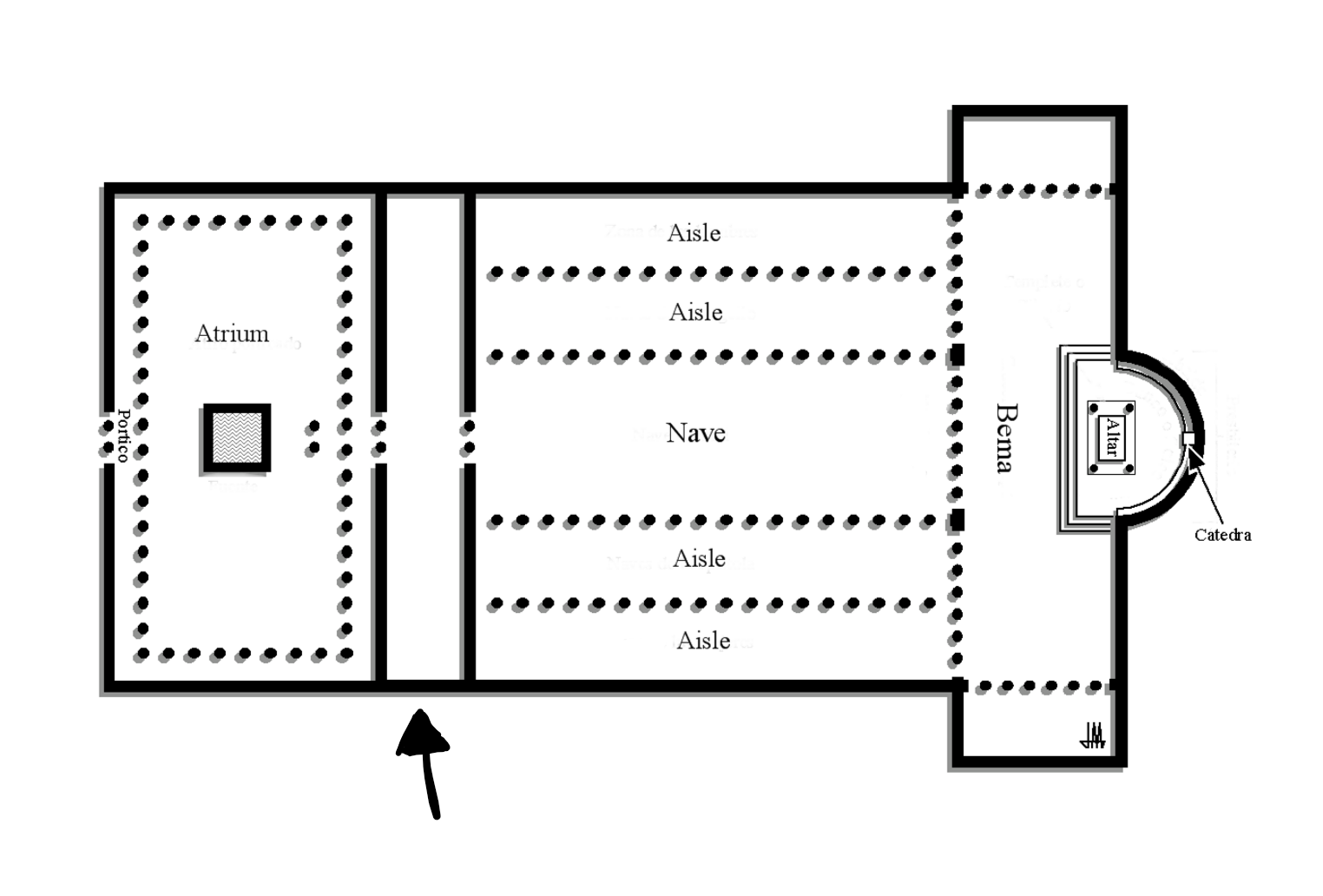
Narthex
Entrance hall
24
New cards
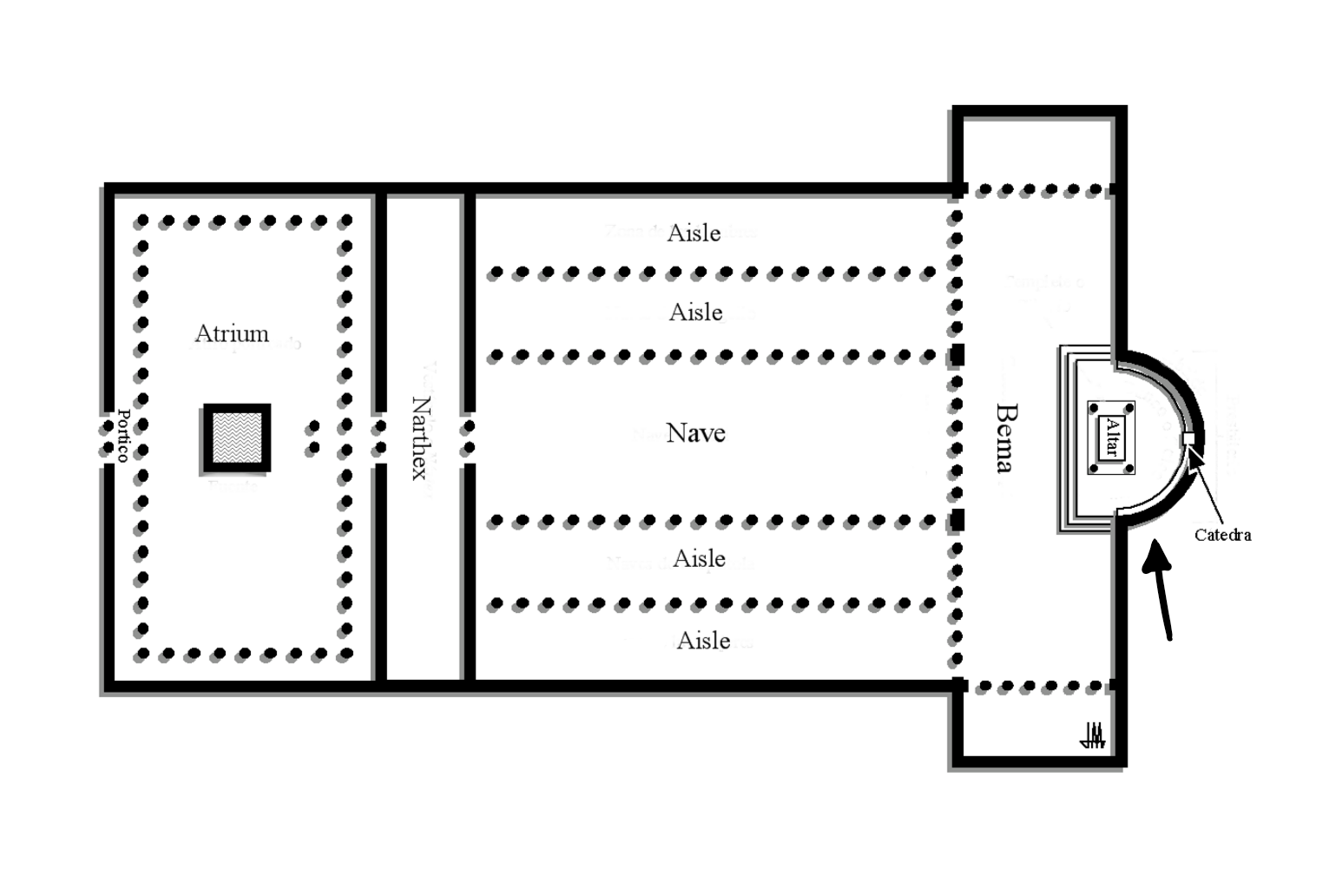
Apse
Where the altar is located in a Basilica church
25
New cards
Clerestory
The upper section of the wall that homes the windows.
26
New cards
Early Muslim Art Period
Early artwork of the religion of Islam that started around the early 7th century in areas such as North Africa, West and Central Asia. Islam artwork is mostly found in their religious places of worship known as Mosques or the calligraphy in their religious text the Qur’an. This period artwork is defined by the Great Mosque in Cordoba and the Blue Qur’an from Tunisia.
27
New cards
The Dome of the Rock, Jerusalem, 691 CE
This mosque was built the mark the new religion once they took over Jerusalem from the Byzantines. It uses elements from Byzantine architecture along with the Mulism elements to create this building. The interior dome uses arabesque or flowing linear plant motifs along with calligraphy.
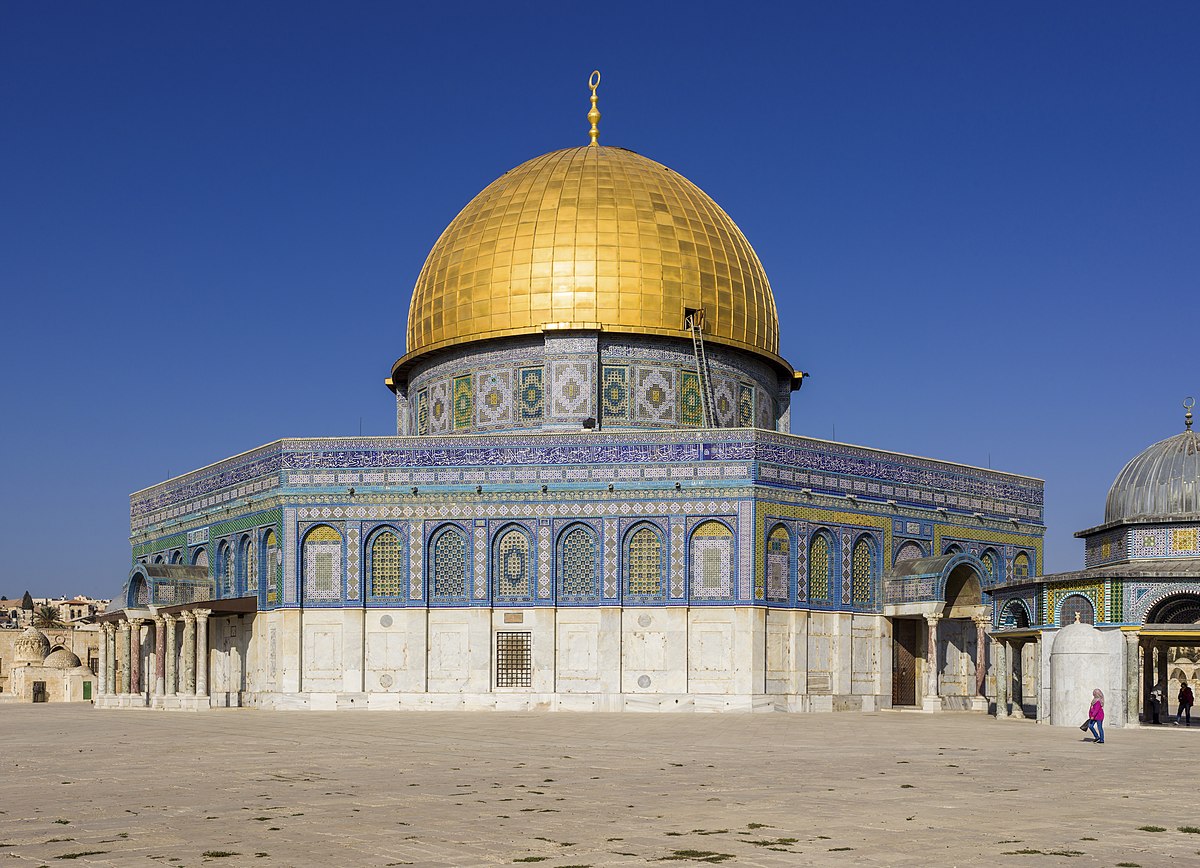

28
New cards
The Great Mosque of Djenne, Mali, founded 1300
Made in inland Niger delta in Mali from the 26th king of Djenne after he converted to Islam. Was made with adobe and was one of the largest buildings made with the material.
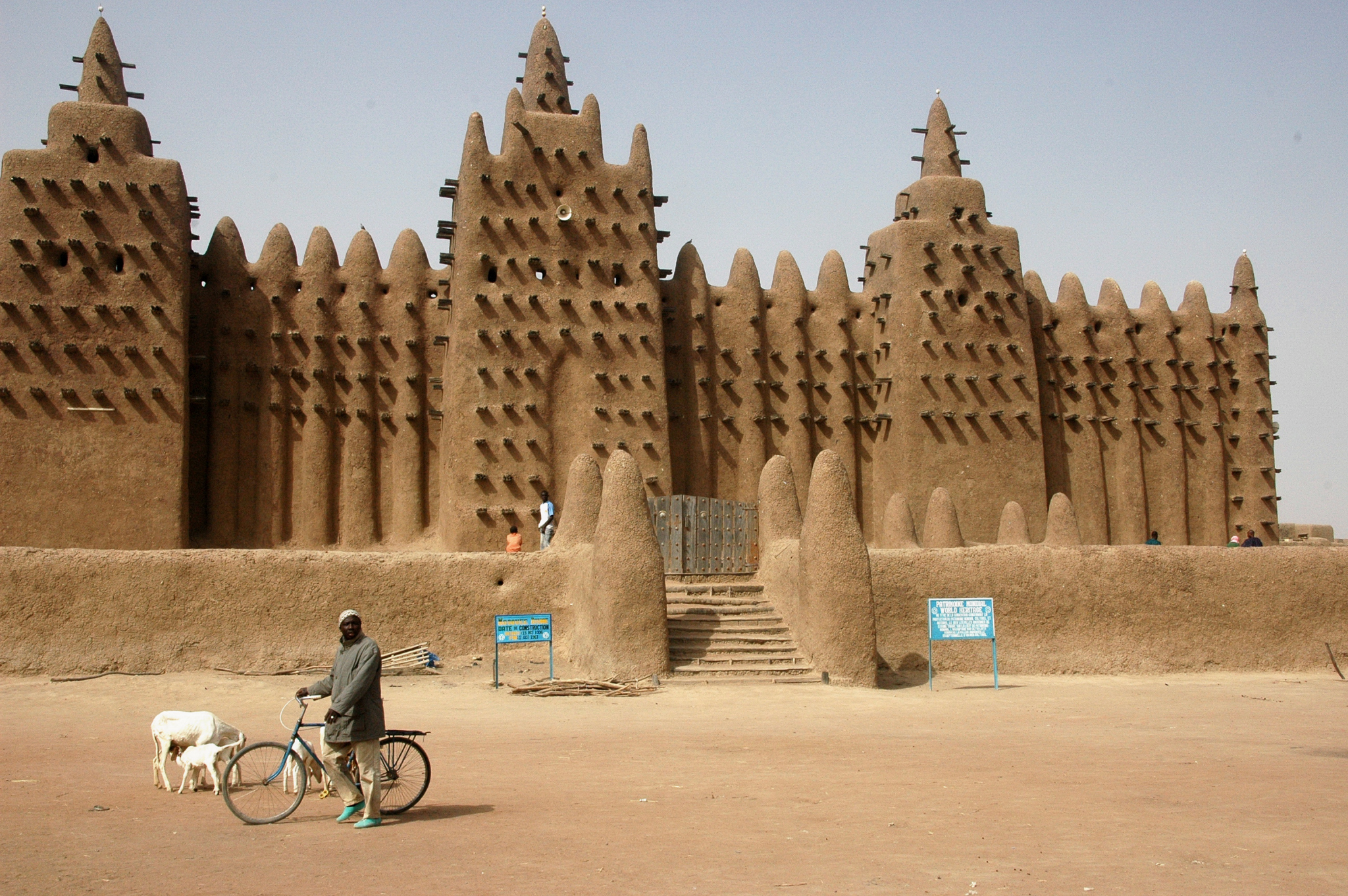

29
New cards
Mosque
Places of worship for the Muslim faith.
30
New cards
Hypostyle hall
The style many mosques were built in as it uses rows of columns for support.
31
New cards
Minaret
A tower at mosque that was a way to call people to pray.
32
New cards
Mihrab
A niche inside of the mosque that would allow people to pray pointing towards Mecca.
33
New cards
Minbar
A pulpit or seated area for a person to give a sermon at Friday’s prayer.
34
New cards
Byzantine Empire (540-1450 CE)
The empire that continued after the fall of the Roman empire with the capital being Constantinople (Istanbul). Throughout the empire time we see four periods of art with the Early Byzantine age with Emperor Justinian to the Iconoclasm or destroying of Icons to the Middle and Late Byzantine ages which ended with the defeat to the Ottoman Turks. Many of this empire artwork is define by pieces such as Hagia Sophia and the Virgin of Vladimir.
35
New cards
Hagia Sophia, Constantinople (Istanbul), 532-537 CE
Was the most grand church built by Justinian during the Early Byzantine period. The Church has a large dome with buttresses and stone piers as well as large interior space. The building allowed light in to show not only God’s power but Justinian’s.
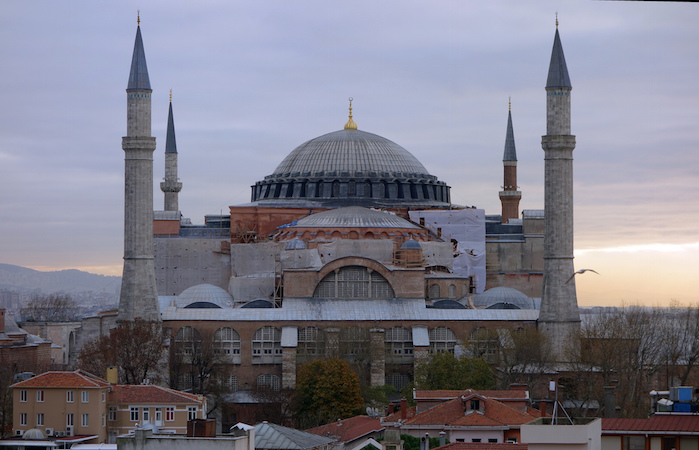

36
New cards
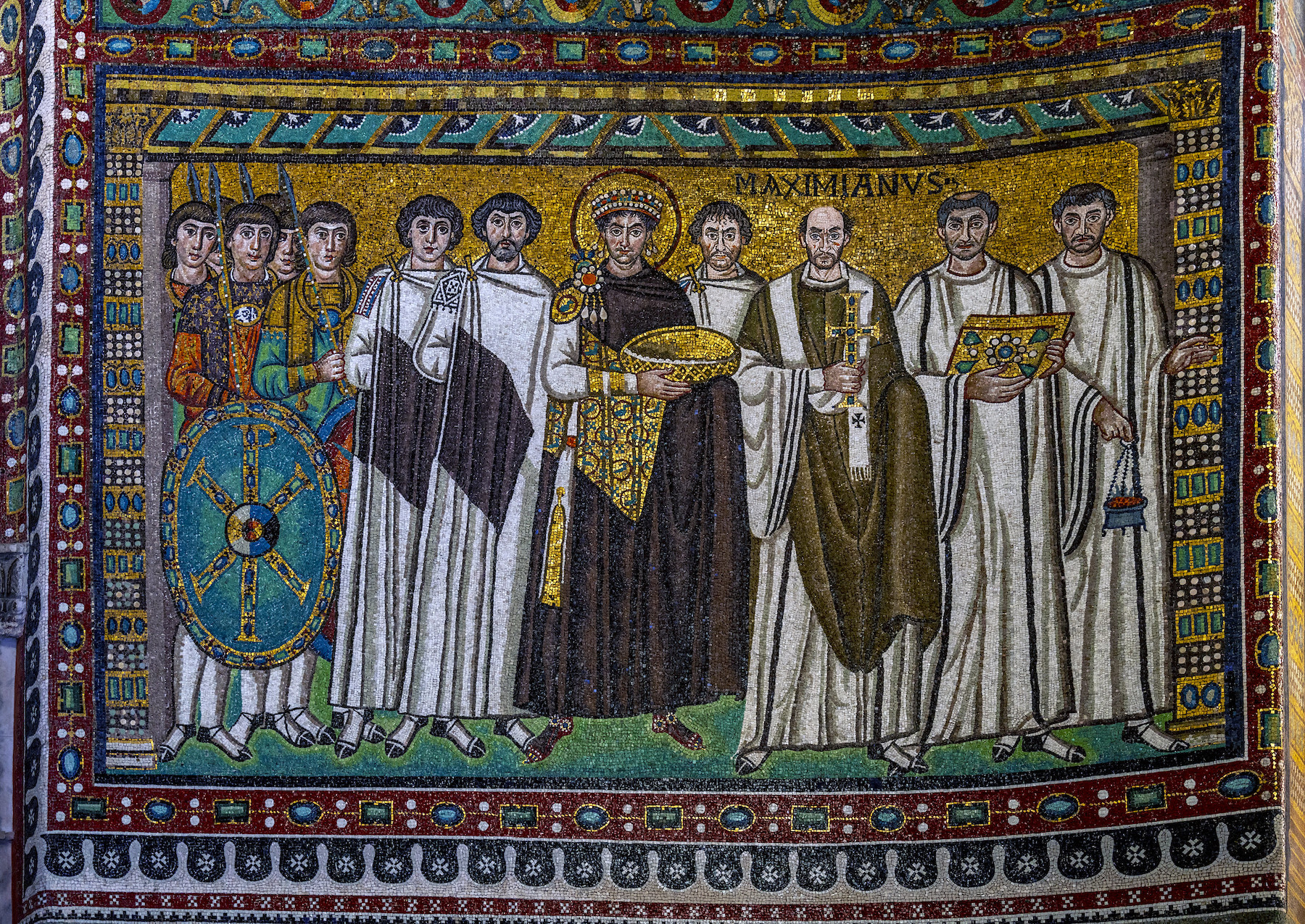
Justinian and his entourage, Church of San Vitale, 546 CE
A mosaic from the Church of San Vitale in Ravenna, Italy which showcase emperor Justinian along with the Bishop of Ravenna and his men. This mosaic was meant as a way of propaganda and showcase Justinian as in line with Christ as he was wearing purple imperial robes like Christ and holding the bread of the Eucharist.

37
New cards
Pendentive
The square based in which a dome is placed on top of in order to transfer the weight of the dome and give a more unified look.
38
New cards
Codex
Bound volume of leaves or parchment/vellum pages that allowed illuminations or painted illustrations to be home.
39
New cards
Illumination
Painted manuscripts that can depict biblical scenes.
40
New cards
Icon
A painted image on wood usually of a religious subject. It was used for contemplation and believe to be the direct link to said religious person and could invoke miracles.
41
New cards
Iconoclasm
The period from 726-843 in which Iconoclast under Pope Leo III destroyed icons which were believe to go against the second commandment as it would lead to the worship of false idols and idolatry.
42
New cards
Pantocrator
The depiction of Christ as the ruler of the world and the one who will judge all.
43
New cards
Early Medieval Europe (600-1250)
Period of when Christianity began to spread throughout Europe.
44
New cards
Purse cover, Sutton Hoo Ship Burial, Suffolk, England, Early 7th
Found in the ship wreck it is a purse that has inlaid garnets in the claps along with zoomorphic imagery made by cloisonne.

45
New cards
Cloisonne
Intricate metalwork that as inlaid gold, glass, and enamel put on a item in a interlacing pattern or design.
46
New cards
Carpet Page
Pages that are devoted to just decorations and allow the reader to lose themselves in the design for meditation
47
New cards
Parchment
Prepared animal skin that was used for codex or carpet pages.
48
New cards
Vellum
Parchment made from the skin of a calf, can be used in carpet pages
49
New cards
Romanesque period (1000-1200)
During this period pilgrimage became popular as Europeans would travel to sacred sites to see holy relics of holy people in places such as Rome and Jerusalem. Church were built as places for pilgrims traveling to visit with many of these churches taking influence from Roman architecture such as the use of the barrel vault.
50
New cards
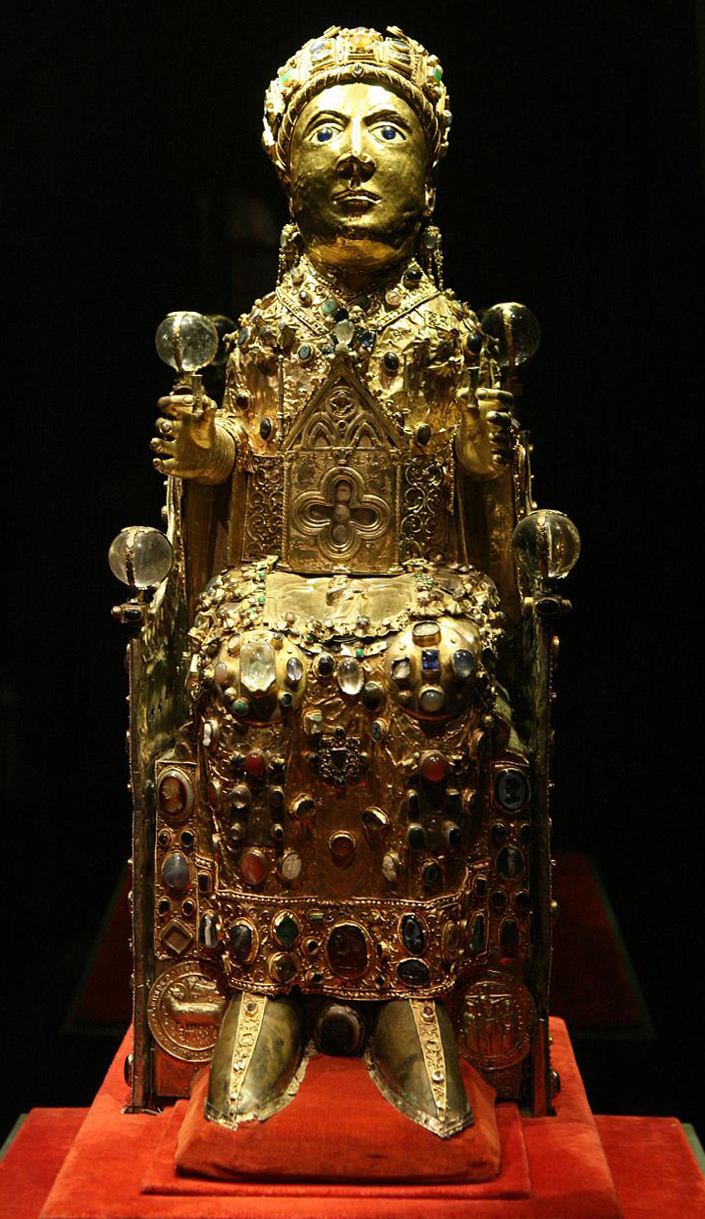
Reliquary of St. Foy (St. Faith), France, 10th century
One of the most famous relics in Europe which house the skull of a child martyr who was killed after she refused to worship the Roman pagan gods. It home in the Church of Saint Foy in Conques, France.

51
New cards
Bayeux Embroidery, France, 1070-1080
One of the few secular pieces of art that was made during the Romanesque period. It is a 230 feet long embroidery that shows the linear narrative of Duke William of Normandy becoming the King of England.

52
New cards
Relic
Either the body part or object of Martyrdom that was of an holy person such as Christ, Mary, or one of the saints. These items believed to have either healing powers or were the closest way for you to get close to the holy person.
53
New cards
Reliquary
The container of a holy relic.
54
New cards
Pilgrimage
When hundreds of Christian Europeans traveling to visit Pilgrimage churches in order to see holy relics.
55
New cards
Mandorla
A body halo that can be seen around the figure of Christ in some of these art pieces.
56
New cards
Bay
The space between columns.
57
New cards
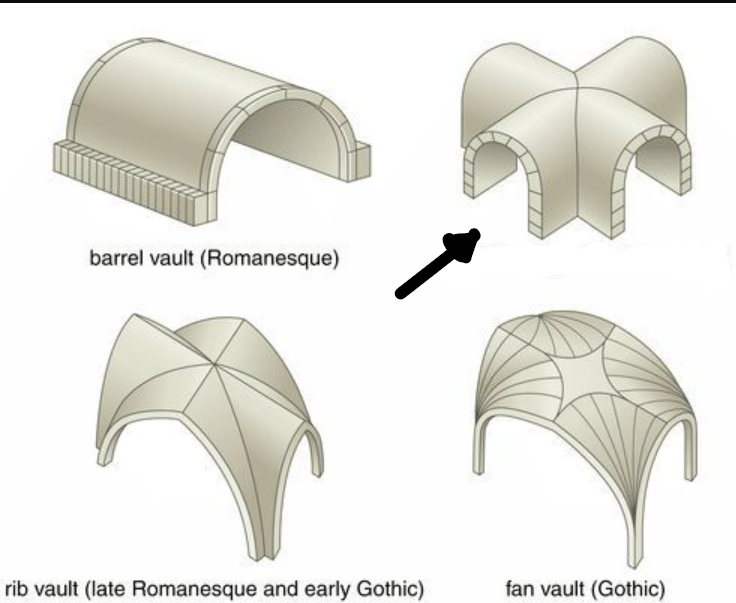
Groin vault
Two intersecting barrel vaults that help distribute weight amongst four points which allow the height of the nave and allow the clear story on the upper wall of a Romanesque church.
58
New cards
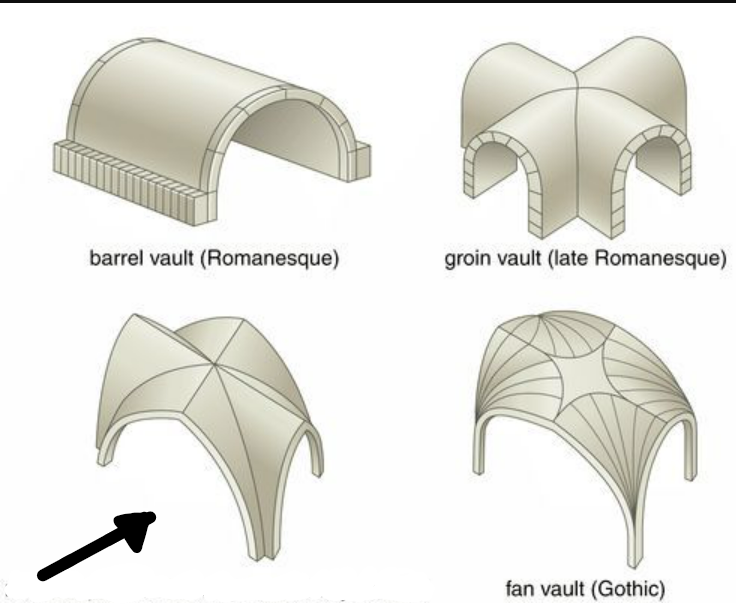
Rib vault
A vault made with two to three intersecting vaults that can be of varying widths and made with arched vaults.
59
New cards
Ambulatory
A rounded apse that goes behind the alter that allows people to walk around.
60
New cards
Transverse arch
Arches from the vault that define each side of a bay
61
New cards
Portal
The entrance of an Romanesque church, it usually has stone craving that meant to be looked at before entering into the church.
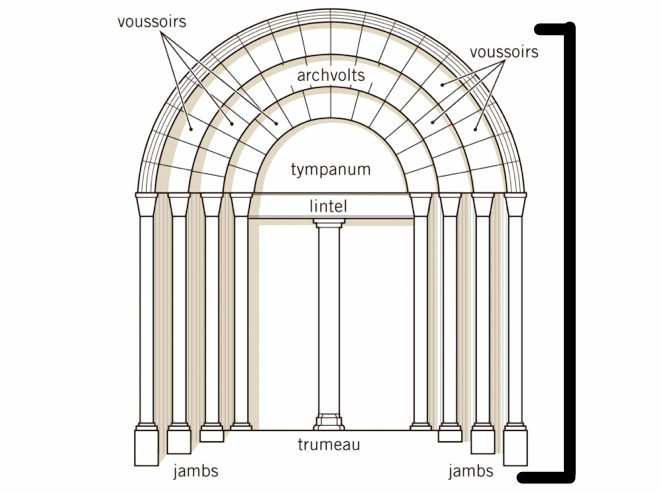
62
New cards
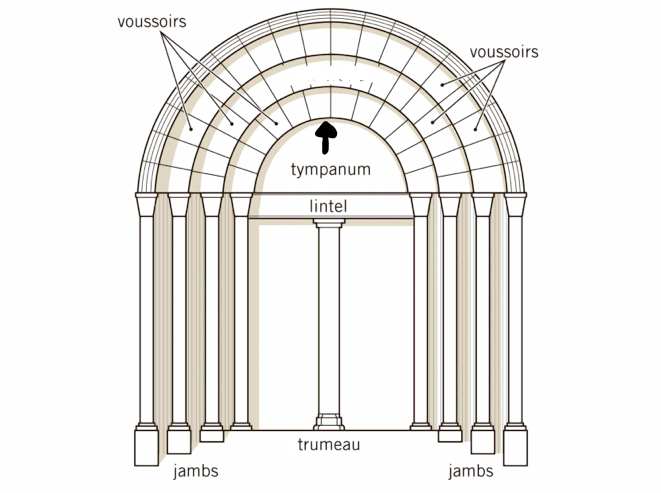
Tympanum
A lunette shape in the portal that would have decorative imagery from Christian canon.
63
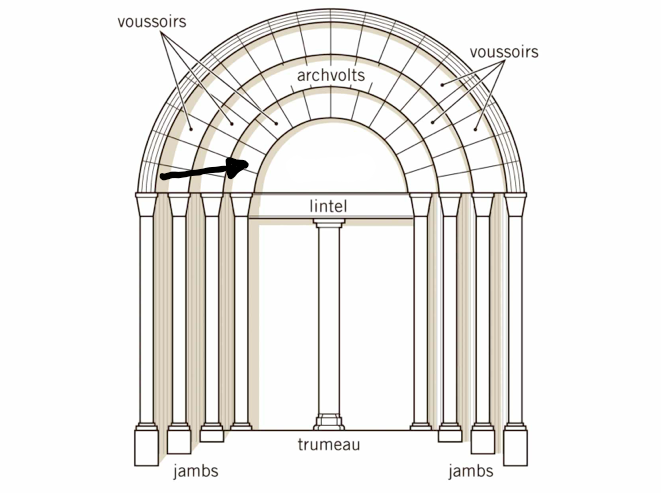
New cards
Archivolt
The upper part of the portal that could also hold stone relief
64
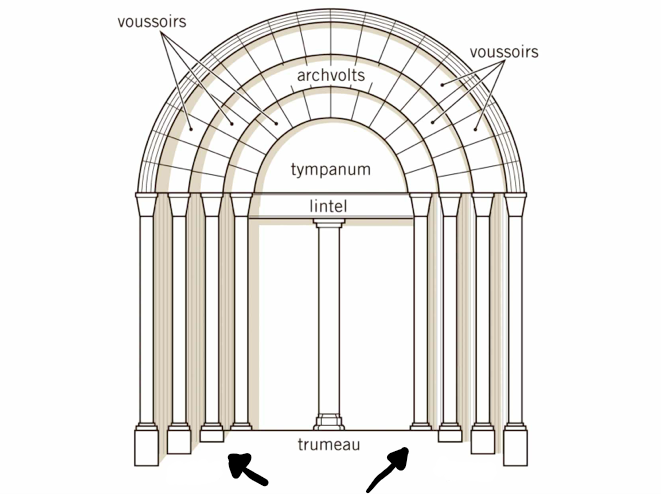
New cards
Jamb
Vertical parts of the portal frame that can be decorated with sculptures of saintly figures
65
New cards
Trumeau
A post that supports the lintel or portal that can also be decorated.
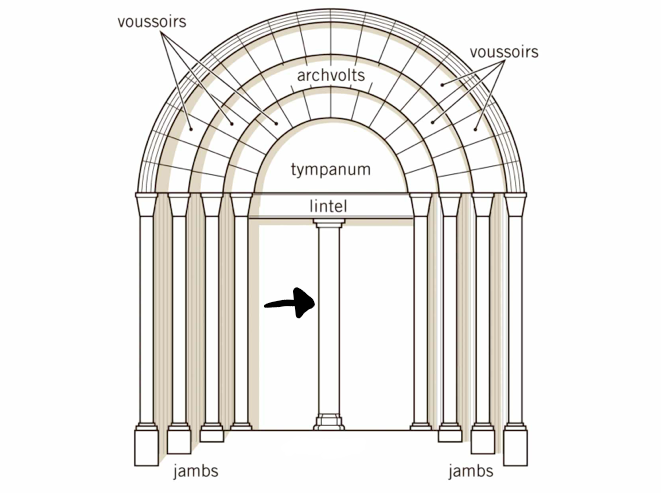
66
New cards
Lintel
A horizontal piece in the portal under the tympanum that is supported by the trumeau that also can have stone cravings.
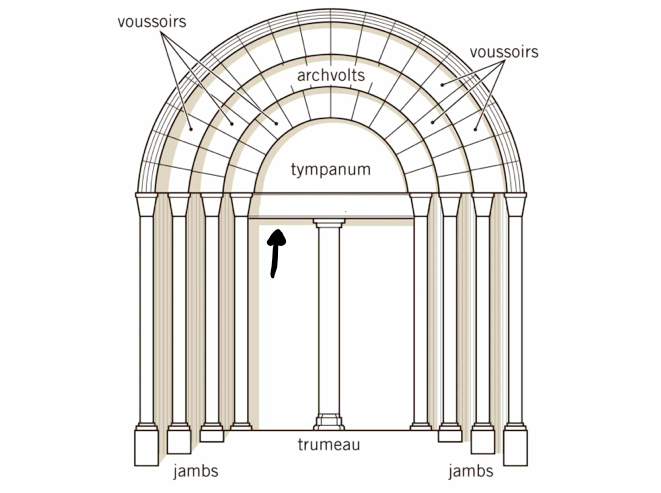
67
New cards
Gothic Art (1200-1400)
Started by Abbot Suger in France in the 12th century in which he built the Basilica of Saint Denis to be the bodies of the monarchs. Abbot Suger created a new style of cathedrals in which it allowed more light to flood into the church as he believed it would bring humans closer to heaven. Churches that define this period is the Church of Saint Denis and the St. Chapelle in Paris.
68
New cards
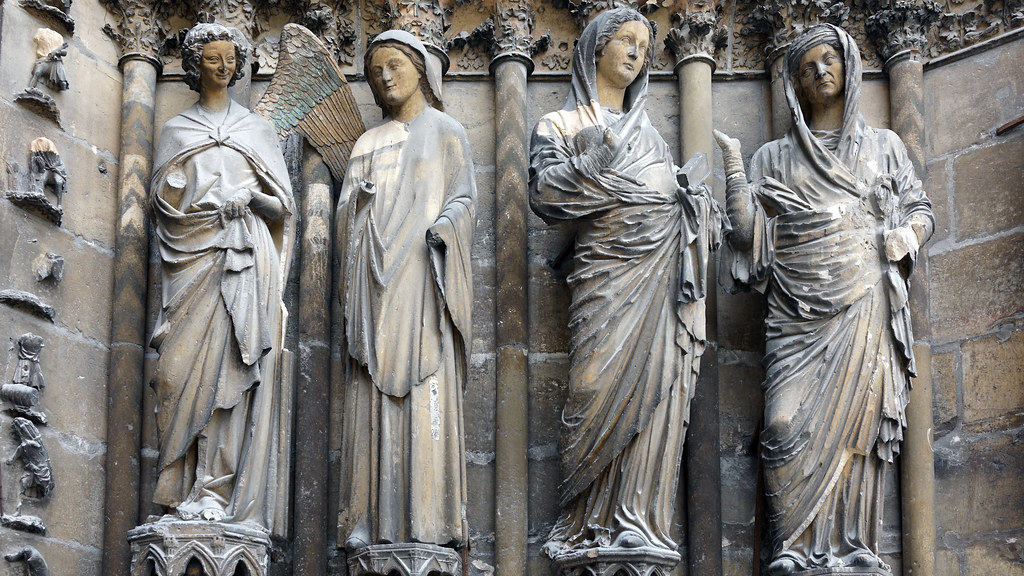
Annunciation and Visitation Jamb Sculptures, Reims Cathedral, 1230-1255
In these jamb sculptures we see figures of an angel giving the news to the Virgin Mary and Mary talking to her cousin Elizabeth who was the mother of John the Baptist. What interesting about the right jamb figures we see more roman elements of drapery and realism that gave the statues a more life-like appearance compared to the statues to the left.

69
New cards
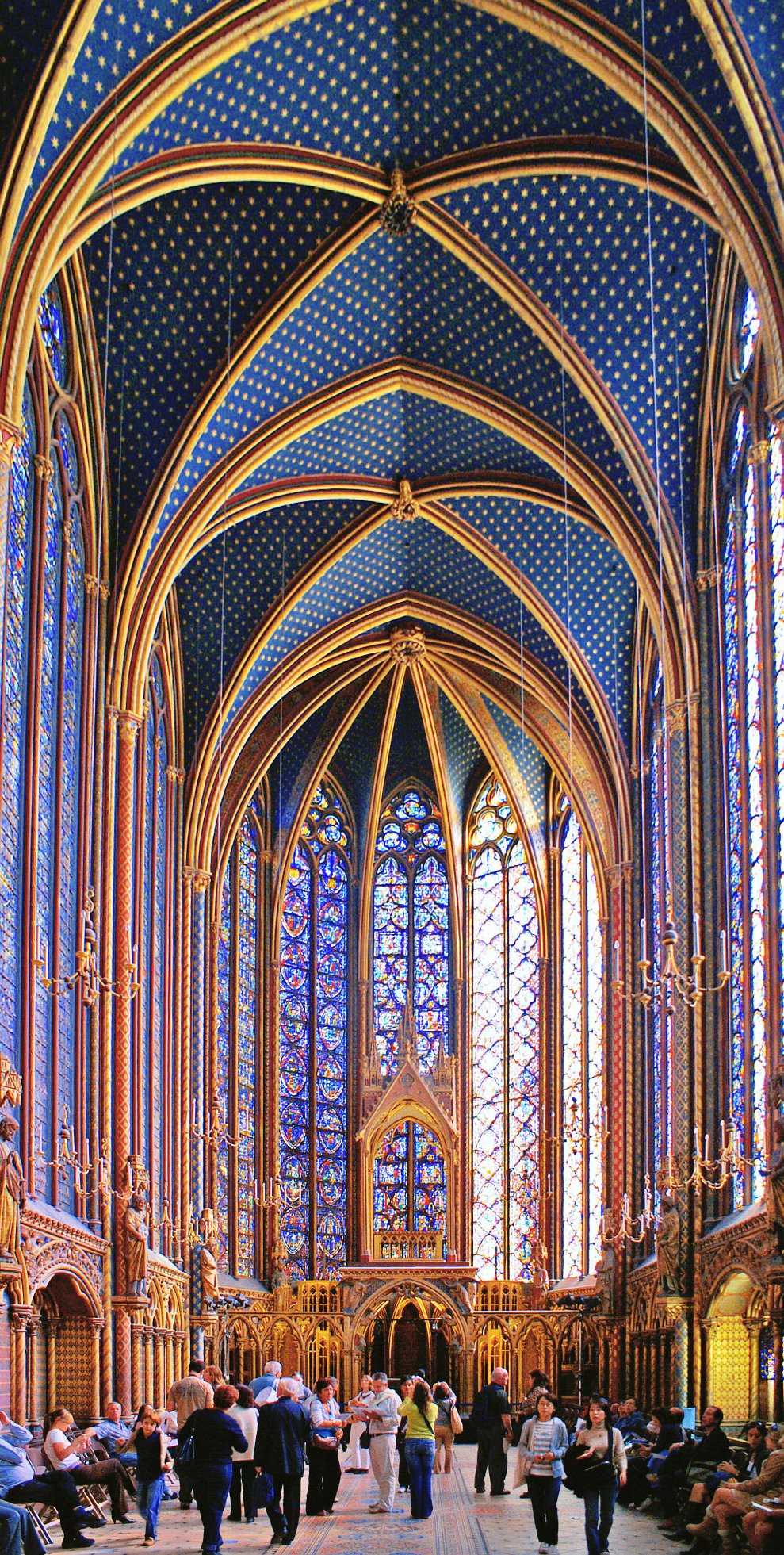
St. Chapelle, Paris, 1243-1248
Was the private chapel of Louis IX that was one of the most lavish chapels made in this Gothic period. It had one of the largest piece of stain glass that allowed light to flood into the church.

70
New cards
Rose Window
Large round stained-glass windows that are set in stone tracery which define Gothic churches.
71
New cards
Flying Buttress
Buttresses that are placed outside the church and in between the windows that helped support Gothic churches and allow more light to flood into the building.