CP II Cumulative (new content)
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
A patient with a HbA1c of 6.0% and a Fasting Plasma Glucose of 110 mg/dL is indicative of which of the following conditions?
Pre-diabetes
A patient with a history of Type II diabetes that is excessively sweating, confused, and reporting shakiness and weakness during exercise is most likely exhibiting symptoms of:
Hypoglycemia
A diagnosis of essential hypertension must be confirmed by:
A minimum of 2 measures taken on at least 2 separate days
The amount of exercise required for long term weight loss maintenance is:
250 minutes or more of moderate to vigorous exercise 5-7 days/week
In patients with cardiac ischemia, the _____ is the level of exertion that provokes symptoms.
anginal threshold
In patients with cardiac ischemia, the ______ (anginal threshold) is the level of exertion that provokes symptoms.
Steady state aerobic exercise below symptoms threshold
Important points related to Hypothesis Algortihms
be alert to the presence of other, more general signs of intolerance - note relative to workload
ensure patient safety by monitoring constantly
never use one or two isolated findings, use all available data to make clinical decisions
4 things PTs & PTAs must know
state physical therapy practice act, code of ethics for PT & standards of ethical conduct for PTA, PTA supervision & teamwork, and payer regulations related to PTAs
4 rules in all practice settings regarding PTs & PTAs
PTs maintain control of and responsibility for patient/client management
PTs are legally and ethically responsible for the PTAs under their direction and supervision
In patient/client management, PTAs assist with the intervention component only. Examination, evaluation, diagnosis, prognosis, and outcomes are the sole responsibility of the PT
PTAs are responsible for following the plan of care established by the PT, including ensuring patient/client comfort and safety during the intervention and related data collection
Physical exertion that results symptoms of ischemia is known as the:
anginal threshold
How much physical activity must one engage in on a weekly basis to result in clinically significant weight loss?
4 hours
To reduce mortality in patients with obesity, it is important to prioritize:
increasing both cardiorespiratory fitness and lean muscle mass
BMI is the most accurate reflection of risk for CVD (T/F)
false
Patients with diabetes may not present with typical symptoms of angina during a cardiac event (T/F)
true
A patient with an HbA1c of 6% has:
pre-diabetes
According to ACSM, patients with diabetes should perform resistance exercise:
At least twice per week on non-consecutive days
What blood glucose level is a relative contraindication to initiate exercise?
200 mg/dL
Patients with pulmonary hypertension should engage in physical activity that is:
steady-state at an intensity below their symptom threshold
Laws related to PT and PTA collaboration can be found in:
each state's practice act
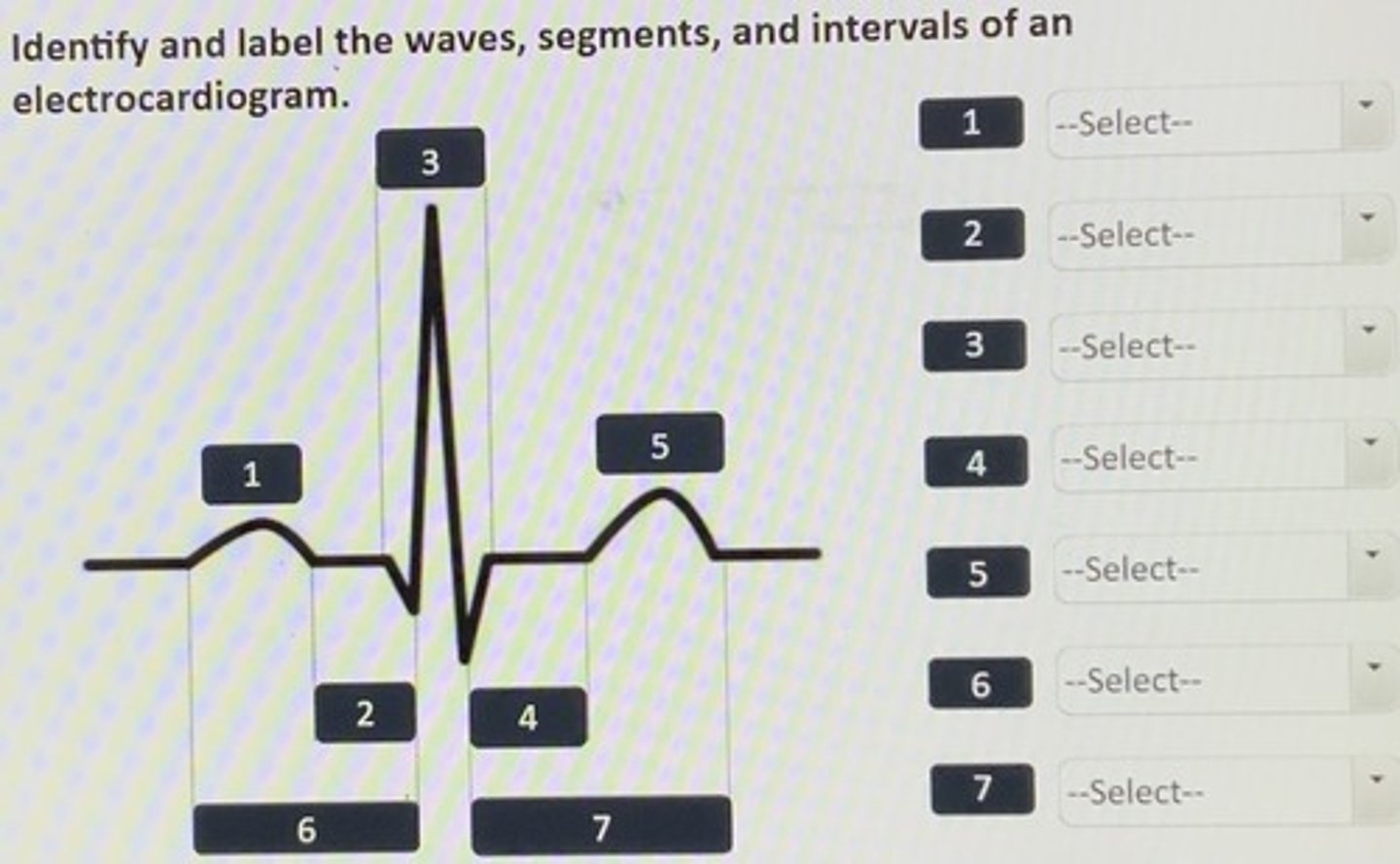
Identify and label the waves, segments, and intervals of an electrocardiodiogram.
1. P wave
2. P-R segment
3. QRS complex
4. S-T segment
5. T wave
6. P-R interval
7. S-T interval
What does the P wave represent on an electrocardiogram?
Atrial depolarization
What does the QRS complex represent on an ECG?
ventricular depolarization
What does the T wave represent on an ECG?
ventricular repolarization
What rhythm is displayed?
Sinus bradycardia
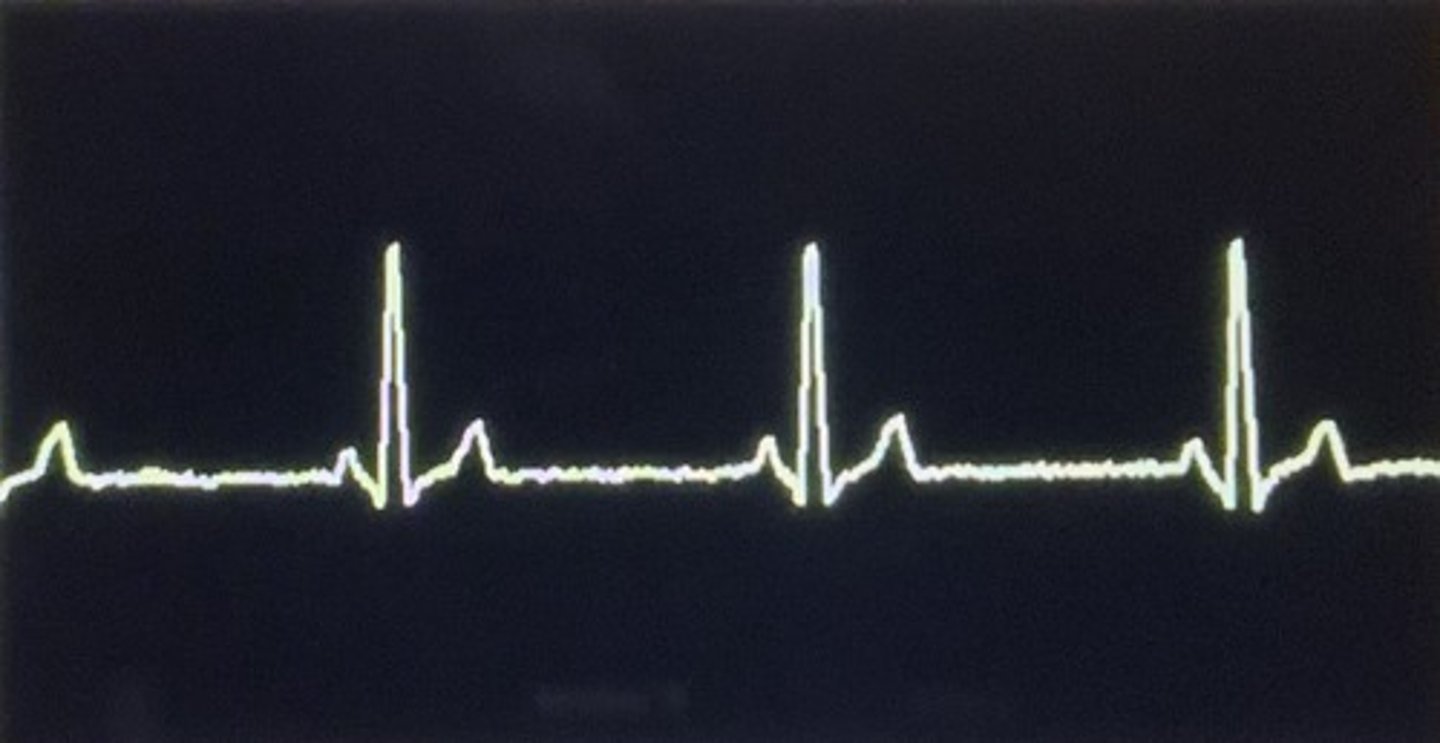
What heart rate is considered sinus bradycardia?
< 60 bpm
Each ECG strip is 6 seconds long. How many beats per minute does the ECG of sinus tachycardia display?
140 bpm
A patient with sinus tachycardia is a 40-year-old female with no history of CP pathologies and is ambulating on a treadmill with a moderate 6/10 RPE. What would be the appropriate response of the clinician in this scenario?
Instruct the patient to continue exercising at the same intensity
What is considered sinus tachycardia?
> 100 bpm
What cardiac rhythm can be described as a rapid and highly irregular rhythm caused by chaotic electrical impulses that arise from multiple ectopic sites in the atria?
atrial fibrillation
What cardiac rhythm is caused by the early discharge of an electrical impulse in the atrium?
premature atrial contraction
What cardiac rhythm is caused by an ectopic pacemaker site in the atria, where the atrial muscles respond to the rapid stimulation by producing wave forms that resemble a sawtooth pattern?
atrial flutter
What is the atrial rate during atrial fibrillation?
>400 bpm
What is the atrial rate during atrial flutter?
250-400 bpm
When is atrial fibrillation considered controlled vs uncontrolled?
controlled: <100bpm
uncontrolled: >100 bpm
A clinician examines ECG before starting cardiac rehabilitation with the patient that involves a walking regimen. After exam, the clinician determines the patient is experiencing A Fib with a HR of <100bpm and is asymptomatic. What is the correct response of the clinician?
Resume exercising while monitoring signs and symptoms of decreased cardiac output
When would atrial flutter require medical attention?
if >100bpm at rest
What is the atrial rate at rest for premature atrial contraction?
60-100bpm
A clinician examines the ECG before starting exercise with patient. After exam, the clinician determines the patient is experiencing atrial flutter at a HR of 120 bpm. What is the correct response of the clinician?
This patient will require immediate medical attention, refer to physician right away.
What is the ECG presentation of premature atrial contraction?
extra beats spread throughout
What abnormal rhythm is displayed?
premature atrial contraction
A clinician examines the ECG before starting exercise with patient. After exam, the clinician determines the patient is experiencing premature atrial contractions at a HR of 60 bpm. What is the correct response of the clinician?
Resume exercising while monitoring signs and symptoms of decreased cardiac output
An abnormal conduction pathway of a premature ectopic impulse that originates in the ventricles. It is then spread through the ventricular muscles to depolarize the ventricles one at a time.
premature ventricular contraction
What describes an arrhythmia originating at an ectopic site in the ventricles, discharging impulses at a ventricular rate of 140-250 bpm?
ventricular tachycardia
What describes a disorganized, chaotic, electrical sites in the ventricles that take over control of the heart?
ventricular fibrillation
What describes a ventricular standstill, or the absence of all electrical activity in the ventricles?
ventricular asystole
Which is NOT considered a medical emergency?
Premature ventricular contractions in combo w/ V Tach
R on T phenomena
Triplet premature ventricular contractions
4 premature ventricular contractions per minute
4 premature ventricular contractions per minute
What is a contraindication for a patient who has ventricular asystole?
exercise
How must the clinician respond if their patient is experiencing V Fib
Perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation with defibrillation, activate emergency response
How much time is required for ventricular tachycardia to be considered sustained?
> 30 seconds
What is the correct response of a clinician if their patient is experiencing V Tach?
Refer to physician immediately, this is a life threatening situation
What is a 1st degree heart block?
Electrical impulses conducted from the atria to the ventricles through the AV node are delayed
What is the ECG presentation for 2nd degree heart block, type 1 (Wenckebach)?
The P-R interval gets progressively longer each beach until finally a QRS is "dropped"
What is a clinicians' best response to 2nd degree heart block, type 2 (Mobitz II) ECG if patient is exercising?
Instruct the patient to discontinue exercise for the day and monitor signs and symptoms
What is a clinicians' best response to 2nd degree heart block, type 2 (Wenckebach) ECG if patient is exercising?
continue exercising with a lower intensity, and monitor signs and symptoms
What is true regarding a 2nd degree heart block type 1 (Wenckebach)?
The P-R interval that gets progressively longer each beat until finally a QRS is "dropped"
What is a clinician's best response to 1st degree heart block ECG if their patient is exercising?
Instruct the patient to continue exercising at the same intensity
What is a clinician's best response to 3rd degree heart block ECG if the patient is exercising?
Instruct the patient to stop exercising and refer to physician immediately
Which drug classes is most likely to cause bleeding?
anticoagulant
A medication that prevents clotting in the venous system is
an anticoagulant
A medication that prevents clotting in the arterial system is
antithrombotic
A medication that exerts a positive inotropic effect on beta-1 receptors on the myocardium is
dobutamine
Which drug class is likely to cause orthostatic hypotension in patients?
diuretics
Which drug class is most likely to cause bronchospasm?
non-selective beta blockers
A medication used to suppress a cough is known as
antitussive
A medication used to decrease the viscosity of respiratory secretions is a
mucolytic
A seconds generation antihistamine is preferred over first generation to decrease sedation because it
does NOT cross the blood-brain barrier
A sign of serious toxicity of a Xanthine derivative can include
cardiac arrhythmias and seizure
A well-known side-effect of metoprolol (Lopressor) is:
Blunted HR response during exercise
A type of medication that acts on the kidneys to excrete sodium and water is known as a:
Diuretic
A type of medication that breaks up both arterial and venous thromboses is called a:
thrombolytic
What medication would most likely cause skeletal muscle pain, cramps, weakness, and fatigue that may lead to rhabdomyolysis?
Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
What is a side effect of nitroglycerin?
Orthostatic Hypotension
What is the mechanism of action of diuretics?
decrease fluid in the vascular system by increasing the formation and exertion of urine
What are the common side effects & rehab implications of diuretics?
fluid depletion and electrolyte imbalance (hyponatremia, hypokalemia), weakness, fatigue, and GI disturbances; can lead to orthostatic hypotension. Frequently end in "-ide" or "-one"
What is the mechanism of action of sympatholytic agents?
decrease sympathetic activity at various target tissues
What are the common side effects & rehab implications of sympatholytic agents?
excessive depression of HR and myocardial contractility, depression, fatigue, GI disturbances, and allergic reactions (beta blockers), bronchospasm (non-selective beta blockers), reflex tachycardia and orthostatic hypotension (alpha blockers). frequently end in "-olol"
What is the mechanism of action of vasodilators?
block calcium entry into vascular smooth muscle causing vasodilation and decreased vascular resistance or decrease heart rate and myocardial contraction force
What are the common side effects & rehab implications of vasodilators?
reflex tachycardia, dizziness, orthostatic hypotension, weakness, nausea, fluid retention, and headache
What is the mechanism of action of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors?
inhibit the effects of abnormal renin-angiotensin system activation by limiting the production of angiotensin II or block angiotensin II receptors on various tissues
What are the common side effects & rehab implications of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors?
dry cough, angioedema (serious) - specific to ACE inhibitors. frequently end in "-pril" or "-sartan"
What is the mechanism of action of calcium channel blockers?
block calcium entry into vascular smooth muscle causing vasodilation and decreased vascular resistance or decrease HR and myocardial contraction force
What are the common side effects & rehab implications of calcium channel blockers?
excessive vasodilation (swelling in LEs or orthostatic hypotension), abnormalities in HR, reflex tachycardia, dizziness, headache, and nausea. frequently end in "-pine"
What is the mechanism of action of Class IV: calcium channel blockers?
alter the excitability and conduction of cardiac tissues by inhibiting calcium influx into myocardial cells
What are the common side effects & rehab implications of calcium channel blockers?
excessive bradycardia, peripheral vasodilation that may lead to dizziness and headaches
What is the mechanism of action of Class II: Beta Blockers?
slow down conduction through the myocardium by decreasing the excitatory effects of the sympathetic nervous system and related catecholamines
What are the common side effects & rehab implications of beta blockers?
bronchoconstriction (in non-selective), may induce arrhythmias
What is the mechanism of action of Class I: Sodium Channel Blockers?
stabilize the cardiac cell membrane and normalize the rate of cardiac cell firing by inhibiting sodium channel function
What is the mechanism of action of Class III: Potassium Channel Blockers?
prolong repolarization and prevents the cell from firing another action potential too rapidly
What are the common side effects & rehab implications of potassium channel blockers?
arrhythmias (torsades de pointes), amiodarone specifically is associated with pulmonary toxicity, thyroid problems, and liver damage
What is the mechanism of action of anticoagulants?
control the function and synthesis of certain clotting factors (used primarily to prevent clot formation in the venous system)
What are the common side effects & rehab implications of anticoagulants?
hemorrhage, might include blood in the urine or stools; bleeding gums; unexplained nosebleeds; or an unusually heavy menstrual flow; back pain (abdominal hemorrhage) or joint pain (intrajoint hemorrhage)
What is the mechanism of action of antithrombotics?
inhibit abnormal platelet activity and preventing thrombus formation in arteries that lead to myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke
What are the common side effects & rehab implications of antithrombotics?
increased risk of bleeding, possible severe gastric disturbance and liver or renal toxicity
What is the mechanism of action of thrombolytics?
breakdown and dissolve blood clots to reestablish blood flow through vessels
What are the common side effects & rehab implications of thrombolytics?
intracranial hemorrhage and other bleeding problems (contraindications for some patients)
What is the mechanism of action of cardiac glycosides (digitalis)?
autonomic and electrical properties improve cardiac excitation and function
What are the common side effects & rehab implications of cardiac glycosides?
toxicity can result in GI distress and CNS disturbances, arrthymmias can occur (premature atrial and ventricular contractions, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, and high degrees of AV block)
What is the mechanism of action of sympathomimetic agents (dopamine & dobutamine)?
exert a positive inotropic effect on beta-1 receptors on the myocardium
What are the common side effects & rehab implications of sympathomimetic agents?
chest pain and cardiac arrhythmias, SOB and difficulty breathing
What is the mechanism of action of phosphodiesterase inhibitors?
increases the force of myocardial contraction through an AMP-mediated increase in intracellular calcium