ANATOMY PRACTICAL 2 YOU GOT THIS BOO THANG
1/251
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
252 Terms
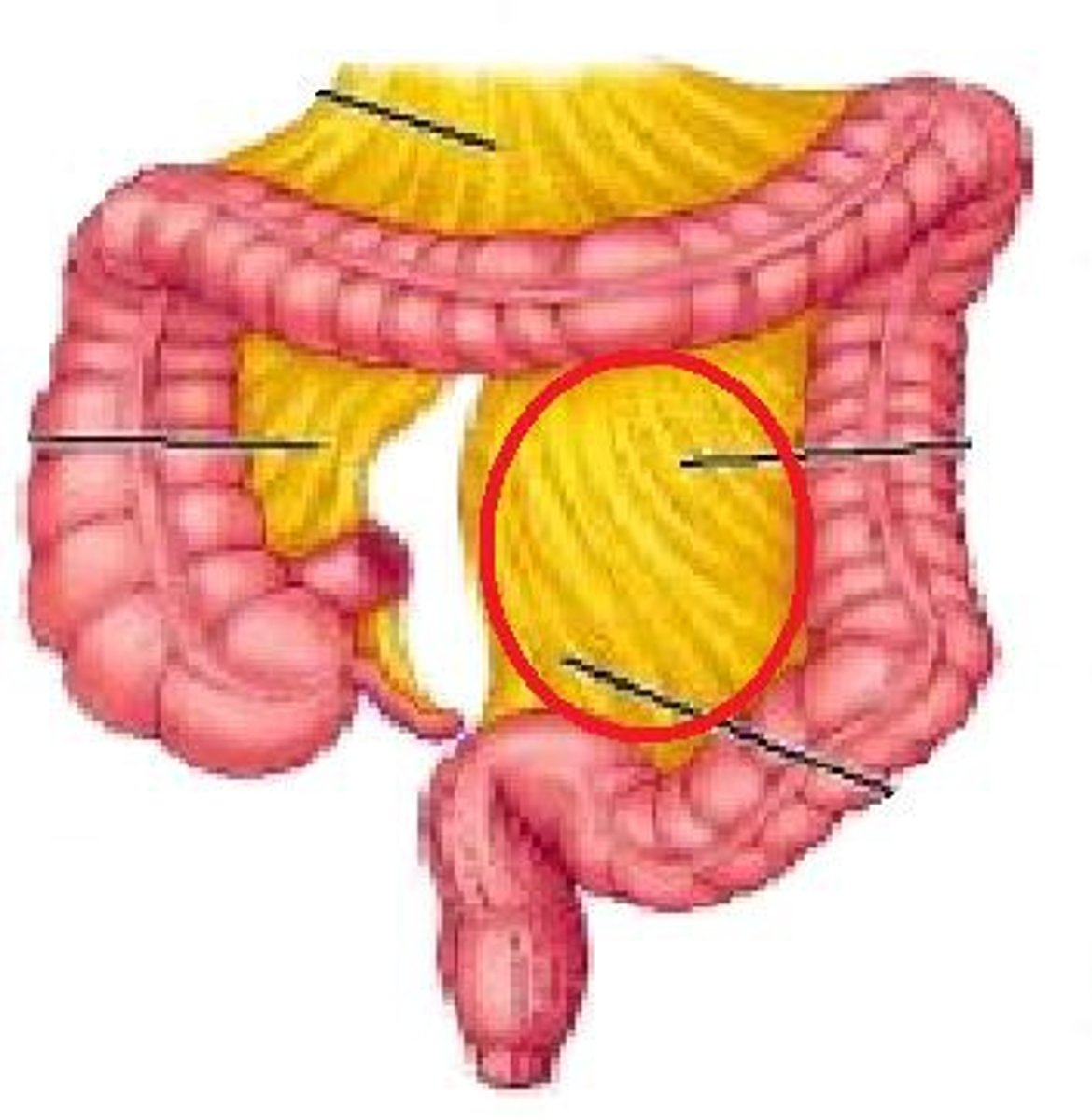
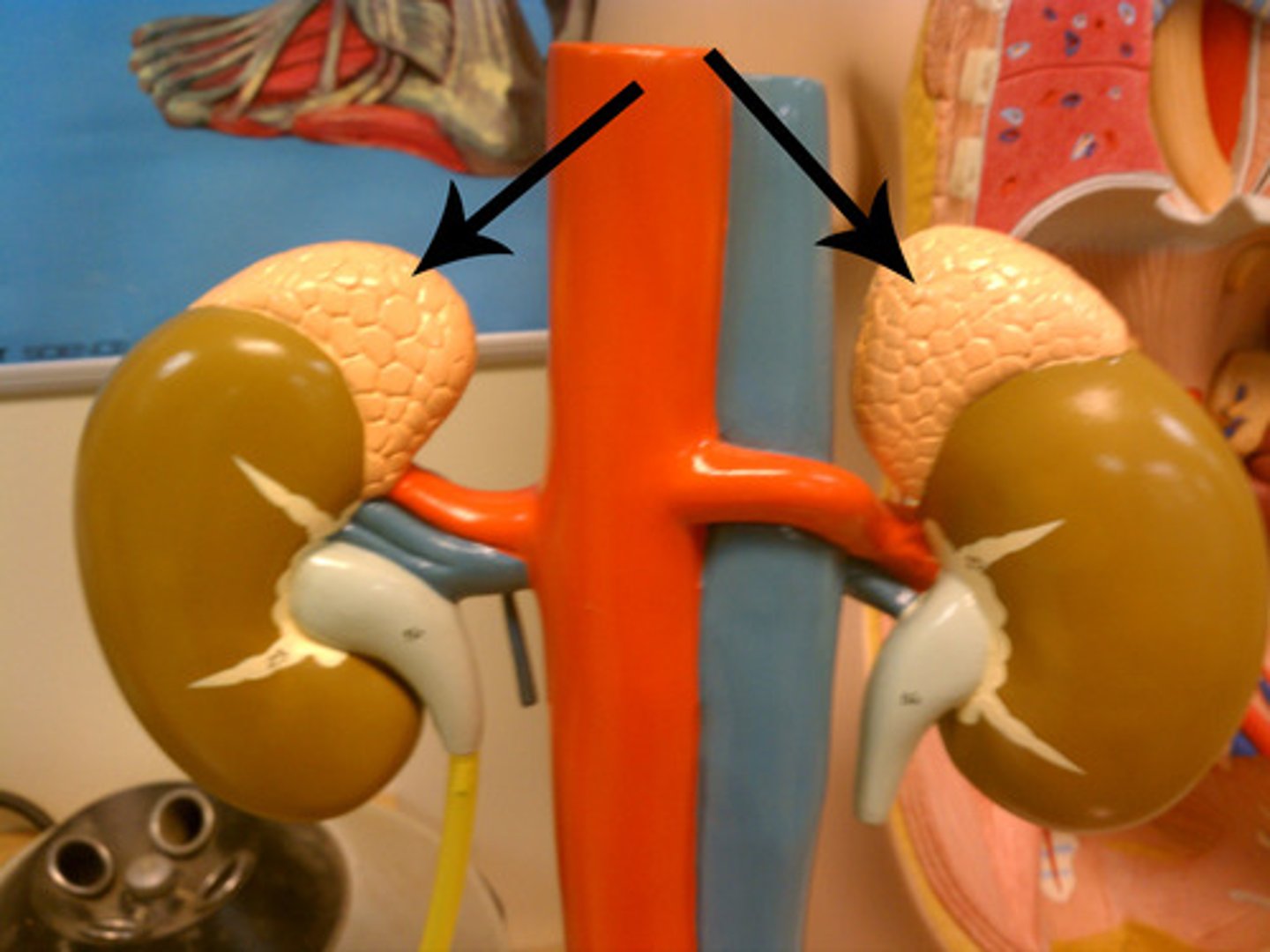
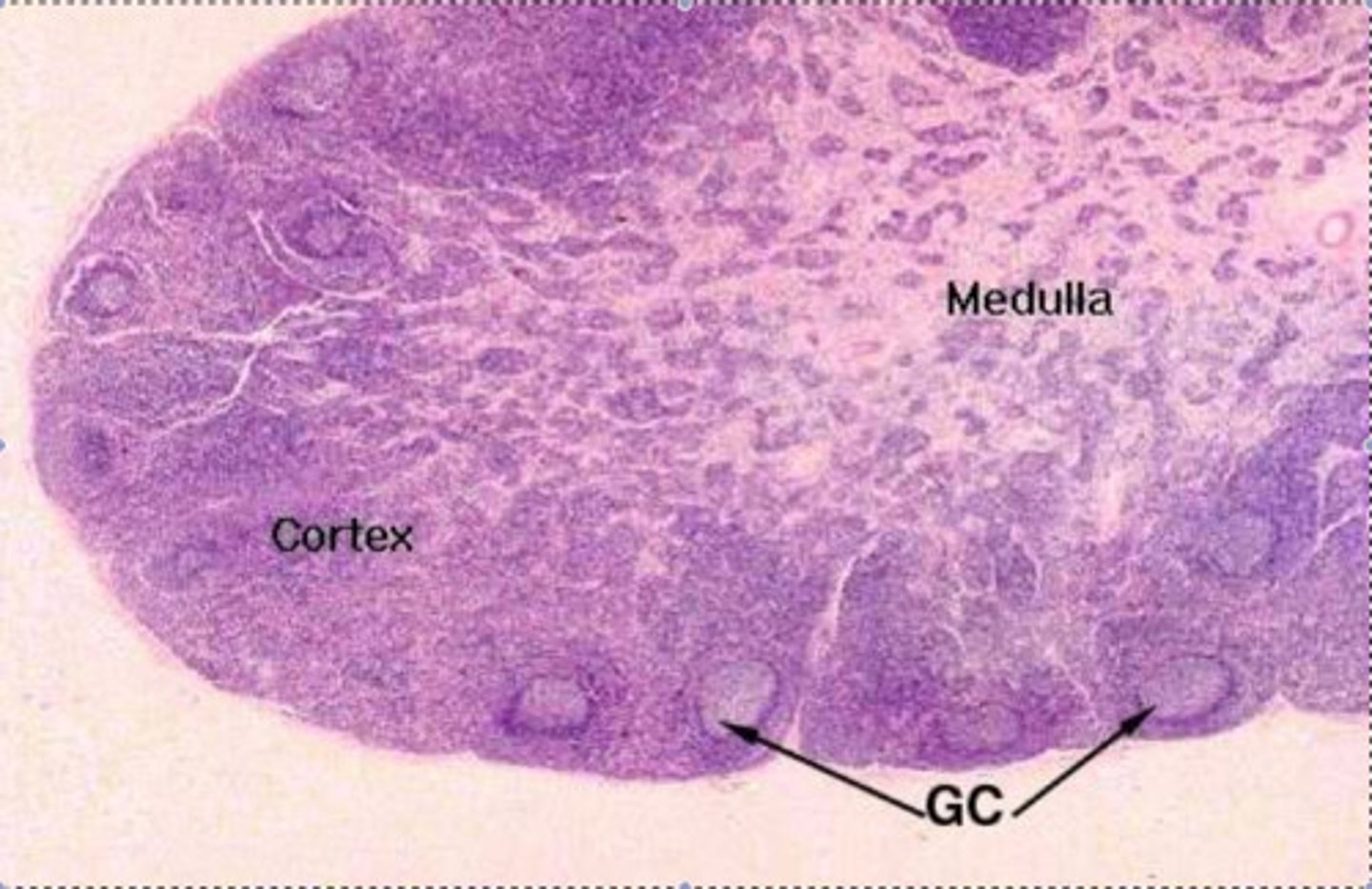
adrenal gland slide
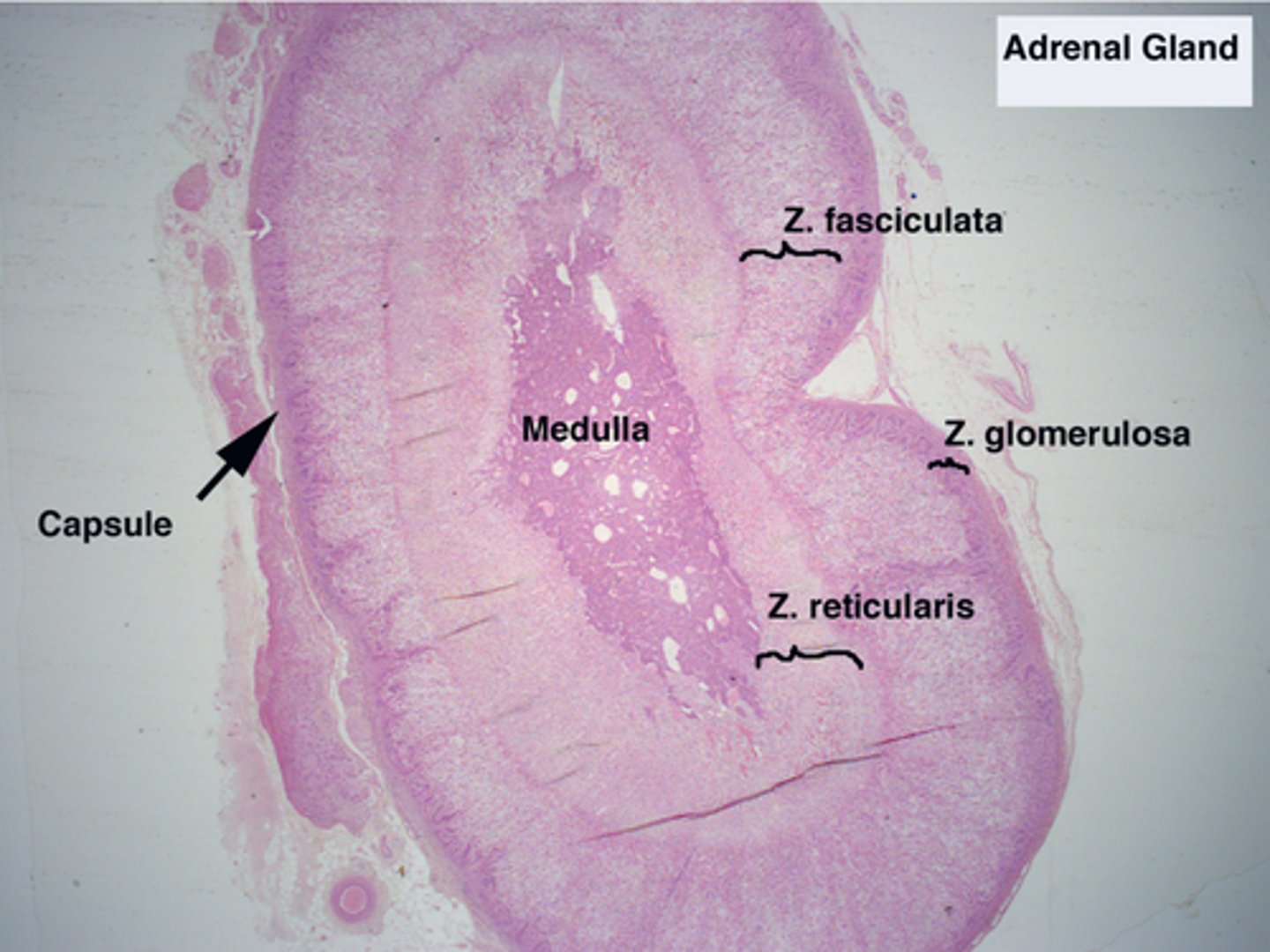
pituitary gland slide (hypophysis)
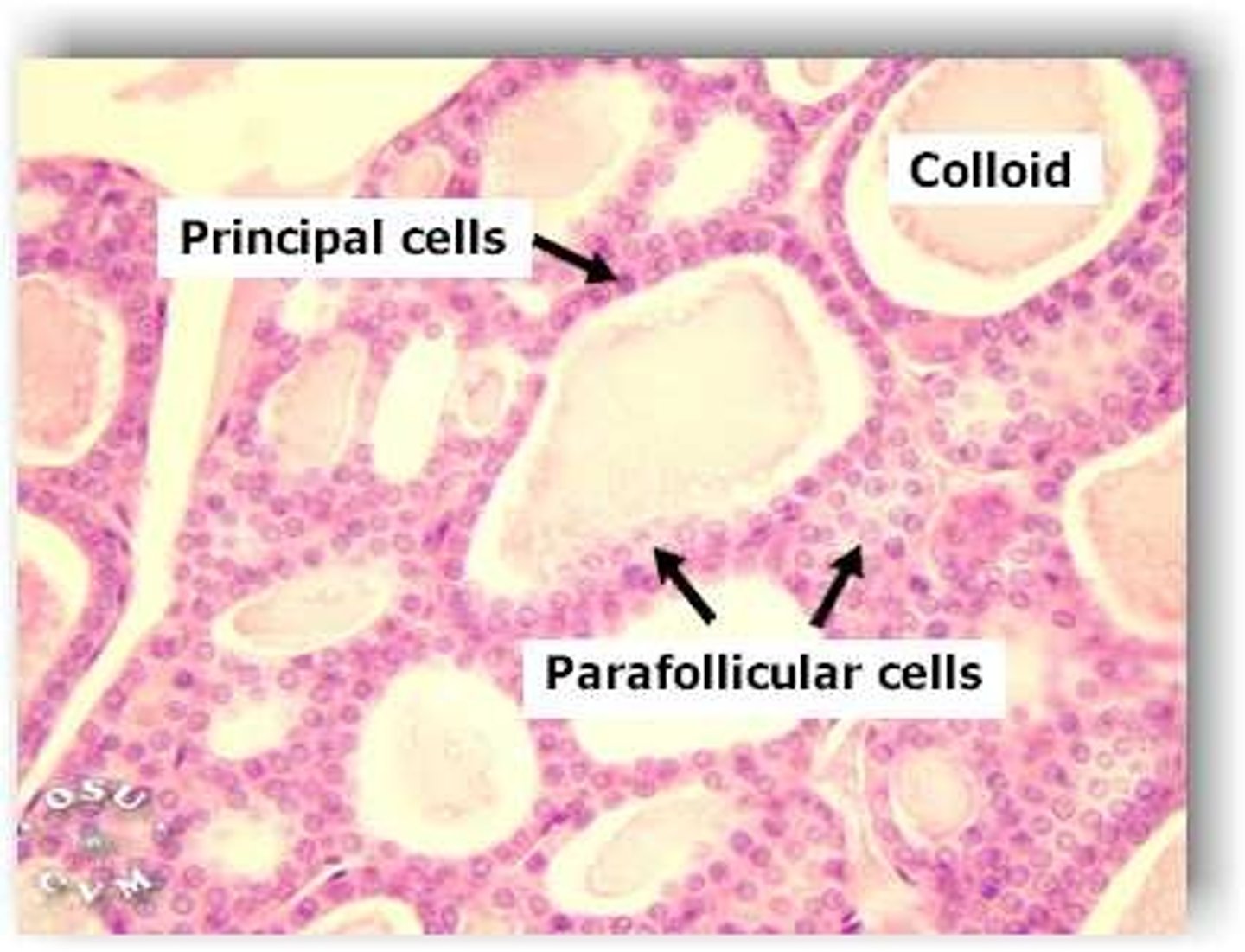
thyroid gland slide
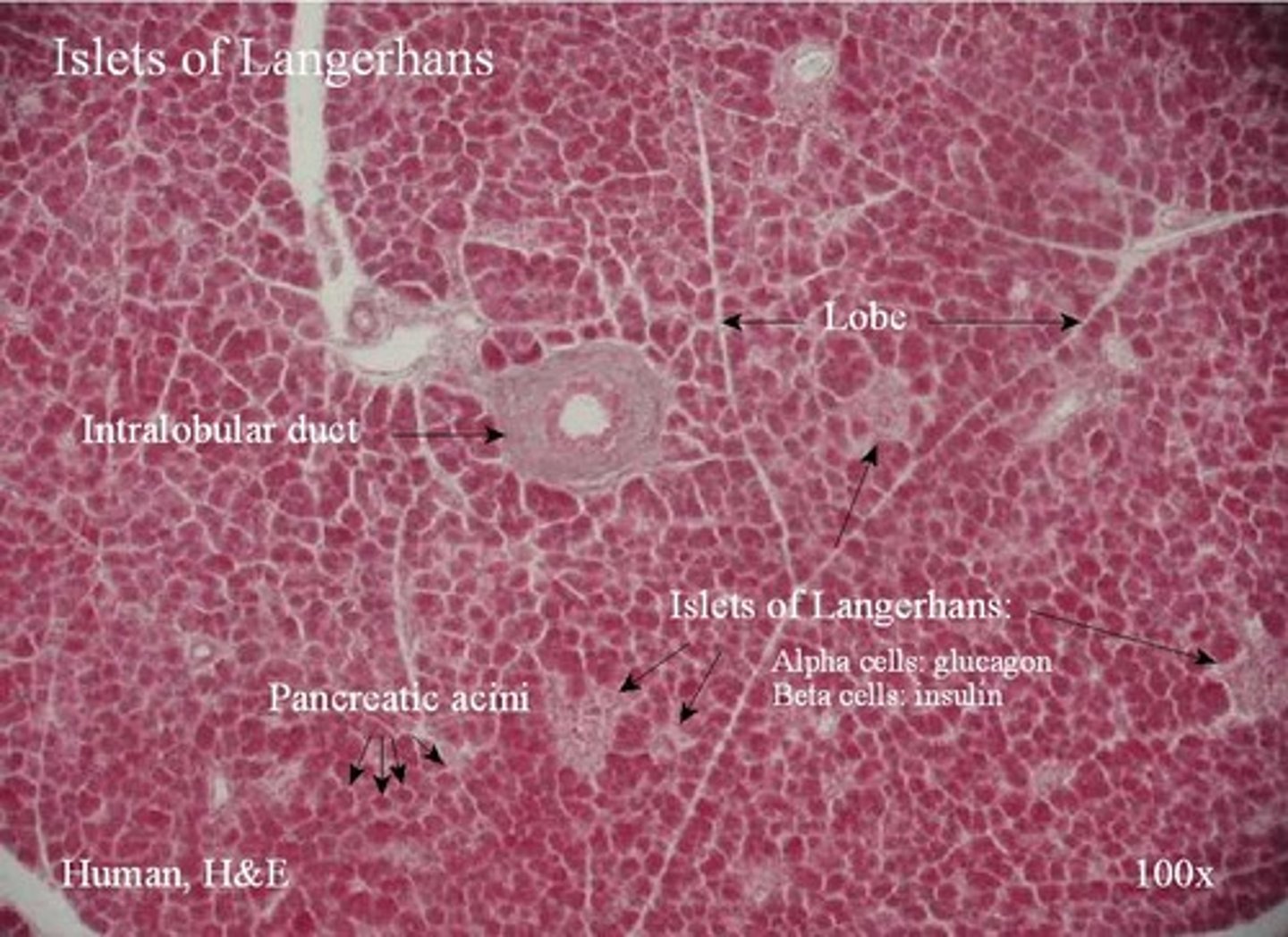
pancreas slide islets of langerhans
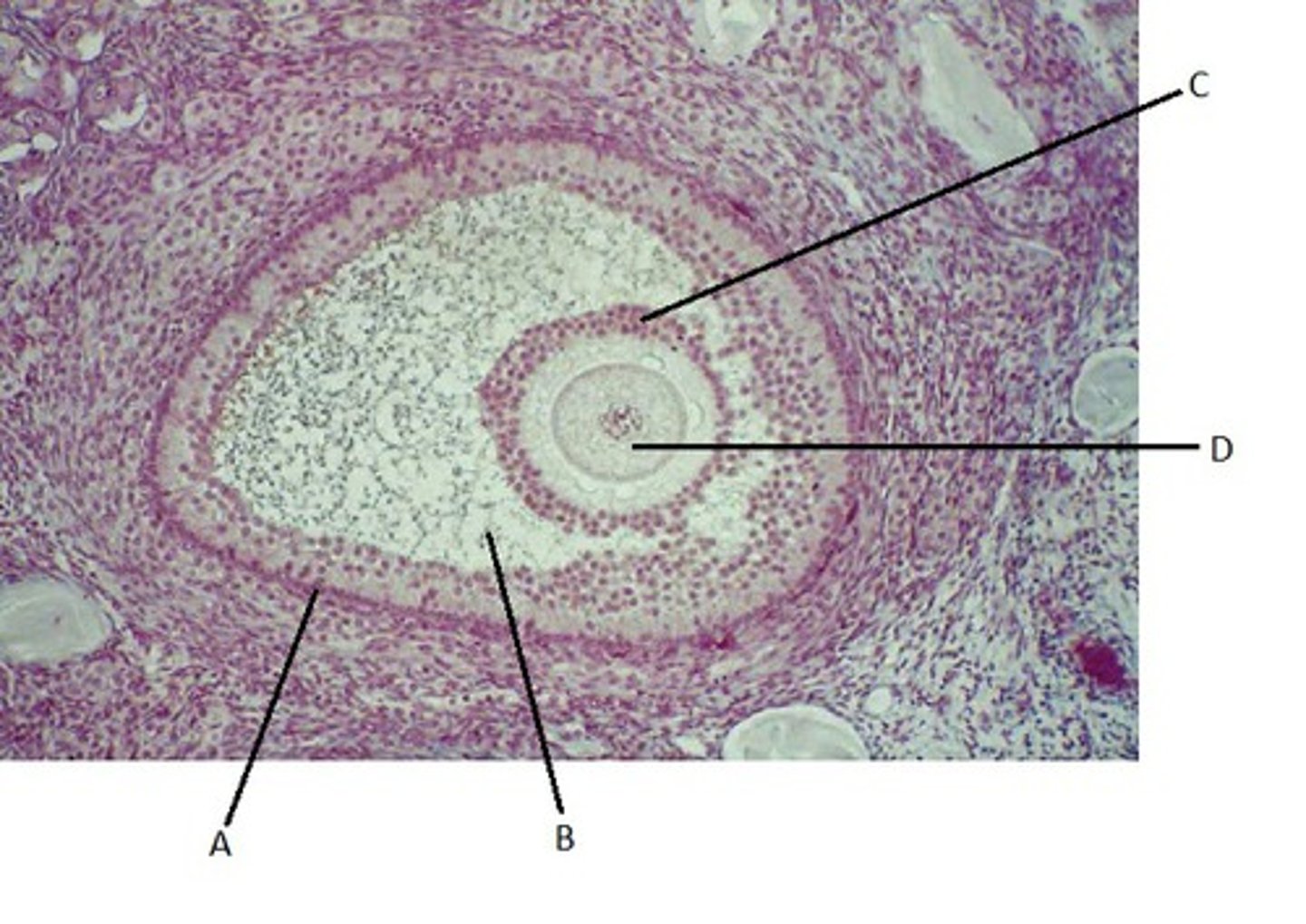
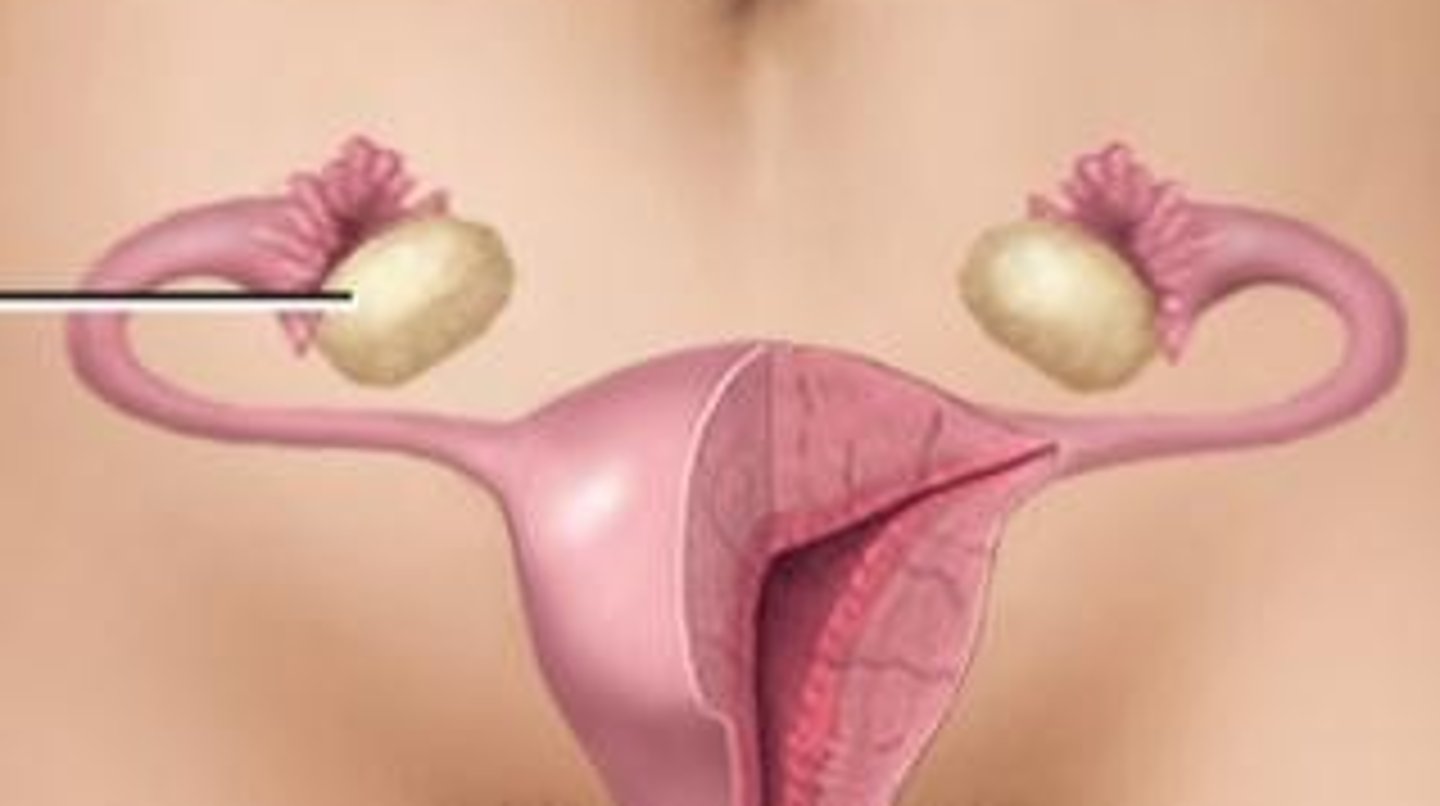
ovary follicle slide
What does adrenal gland produce
glucocorticoids-> cortisol, mineralocorticoids -> aldosterone, androgens-> DHEA & androstenedione. medulla-> catecholamines = epinephrine and norepinephrine.
What does the pituitary produce
growth hormone, prolactin, adrenocorticotropic hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and luteinizing hormone
what does the thyroid gland produce
thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)
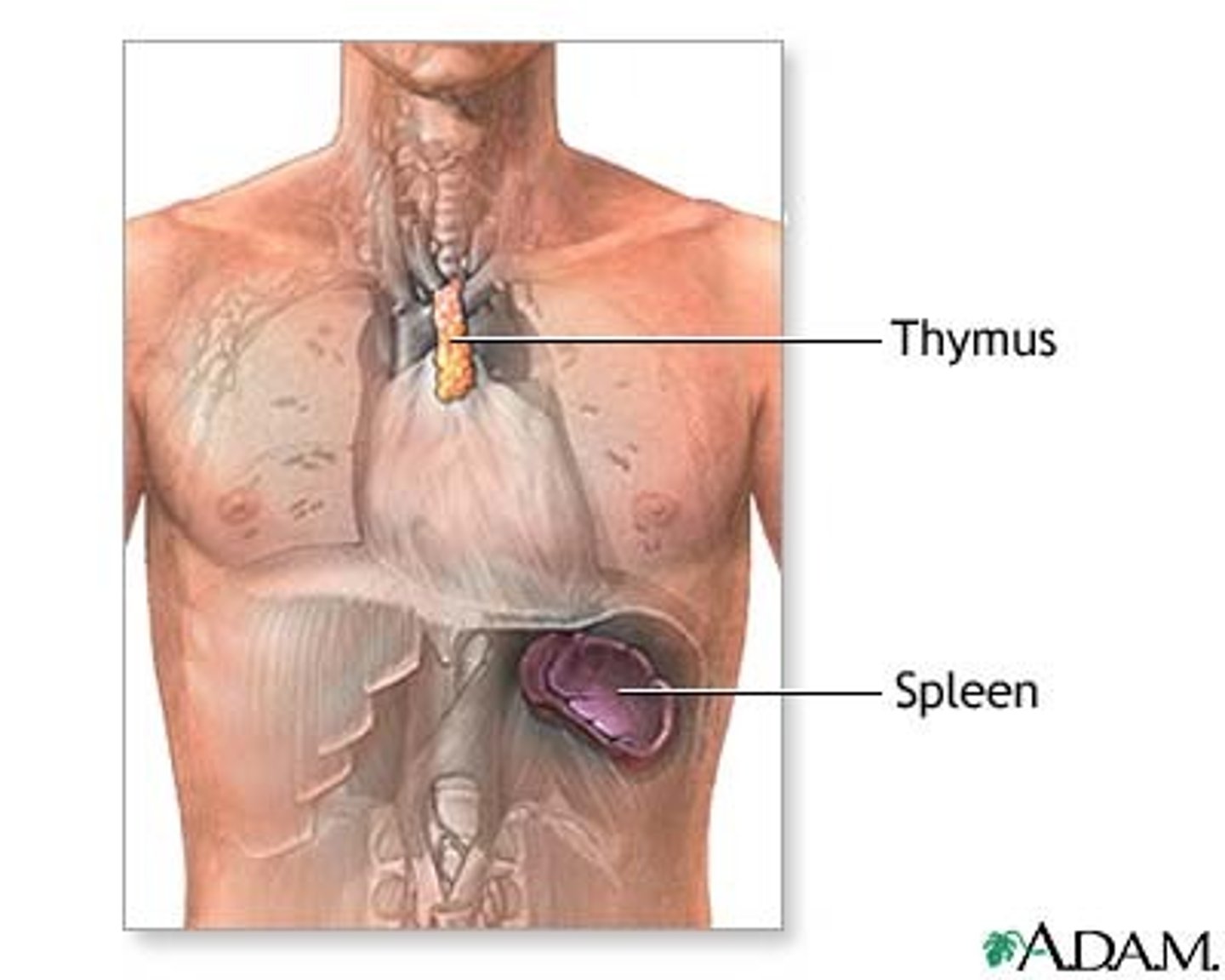
what causes an enlarged spleen
acute infections like mono, liver disease, cirrhosis, lymphoma.
Where did you see clusters of lymph nodes in the male model
Armpits, head and neck, inguinal, chest
Which of these cluster areas could you feel when examining a patient or athlete?
Head and neck
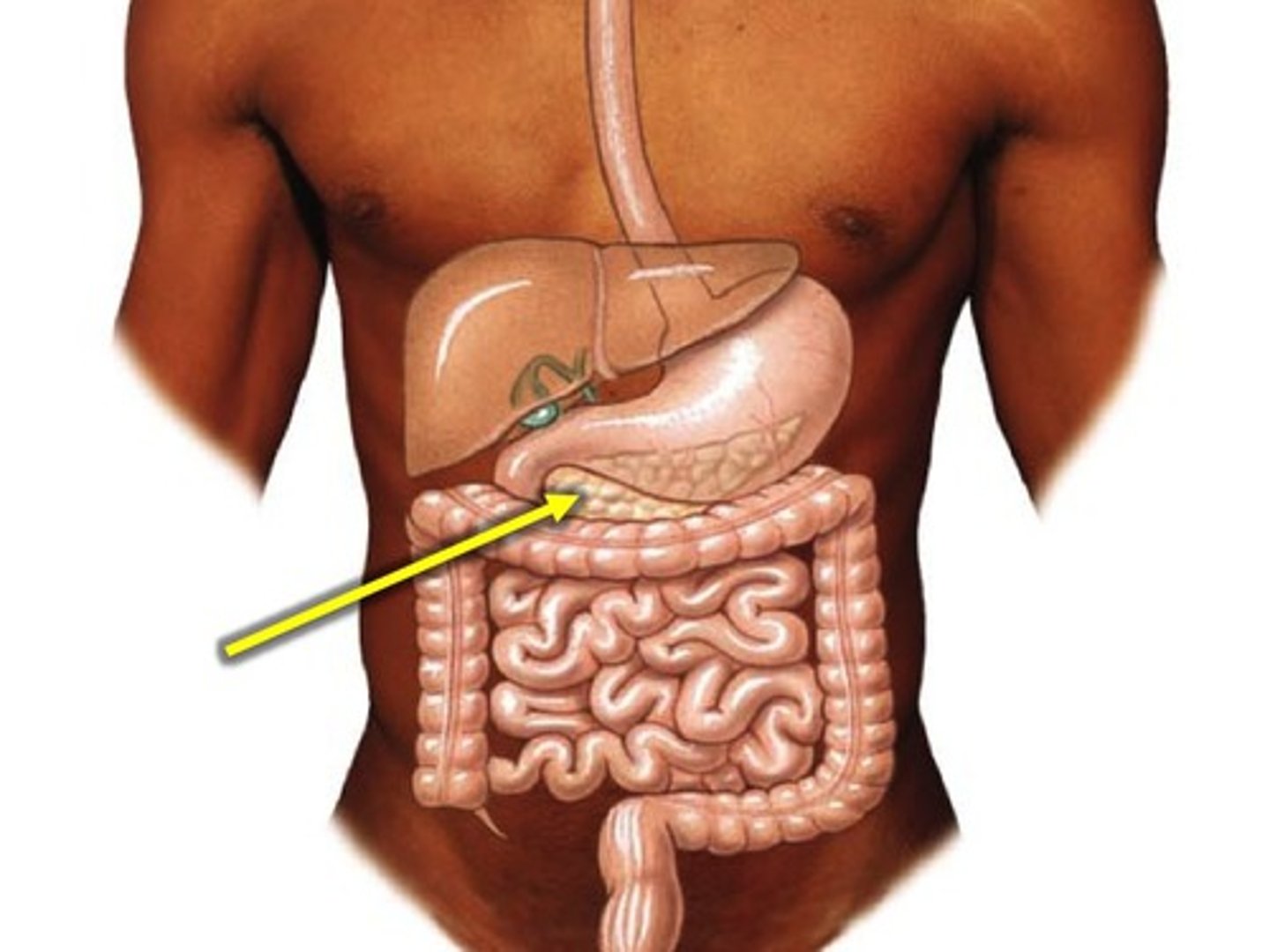
Which endocrine gland is most close to the spleen?
pancreas
Which endocrine gland is closest to the tonsils?
thyroid gland
endocrine system role in
growth, metabolism, and sexual development
common endocrine system diseases
thyroid disease and diabetes mellitus
hormone classes
lipid-derived, amino acid-derived, and peptide (peptide and proteins) hormones.
thymus
adrenal glands
pancreas
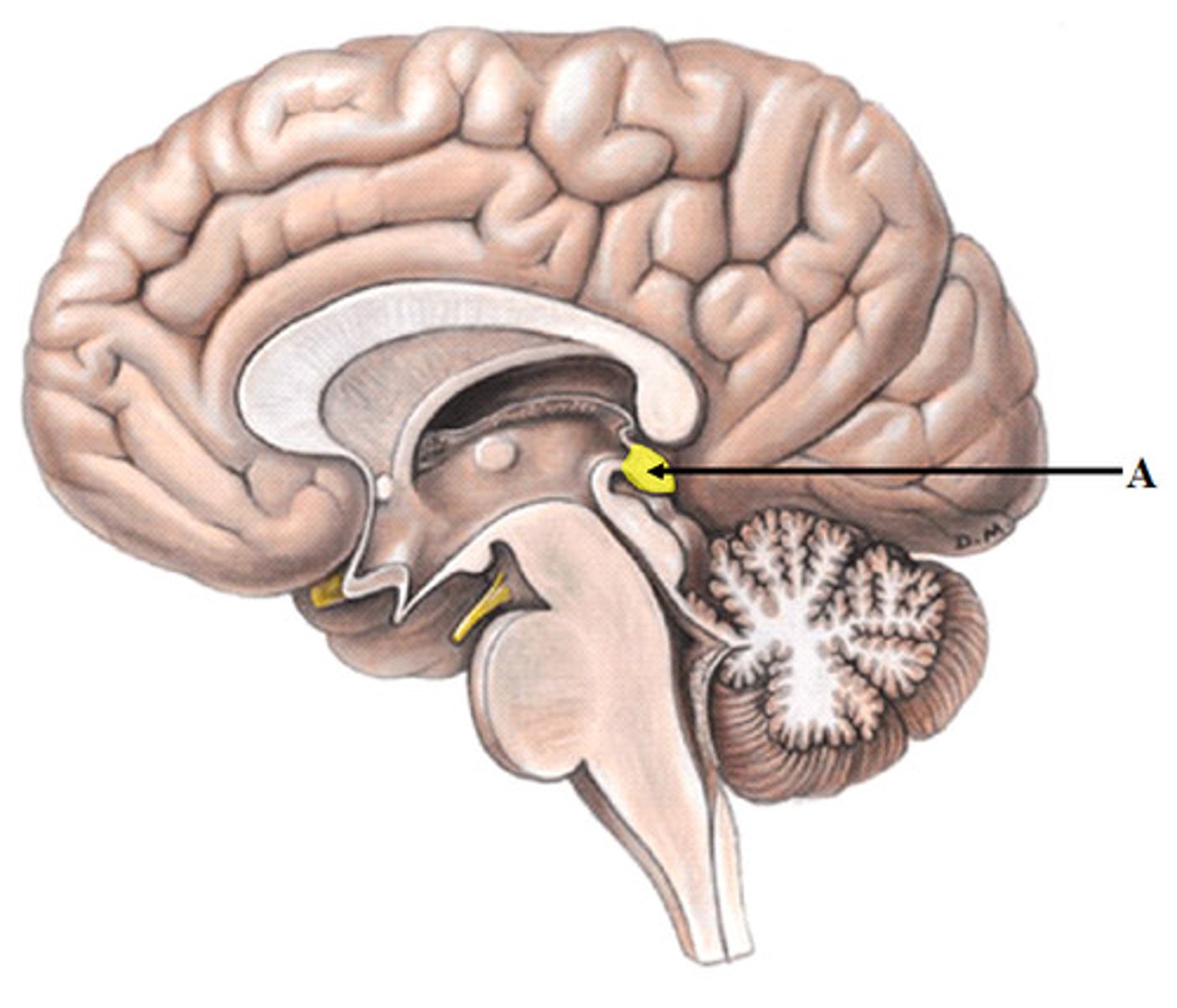
pineal gland
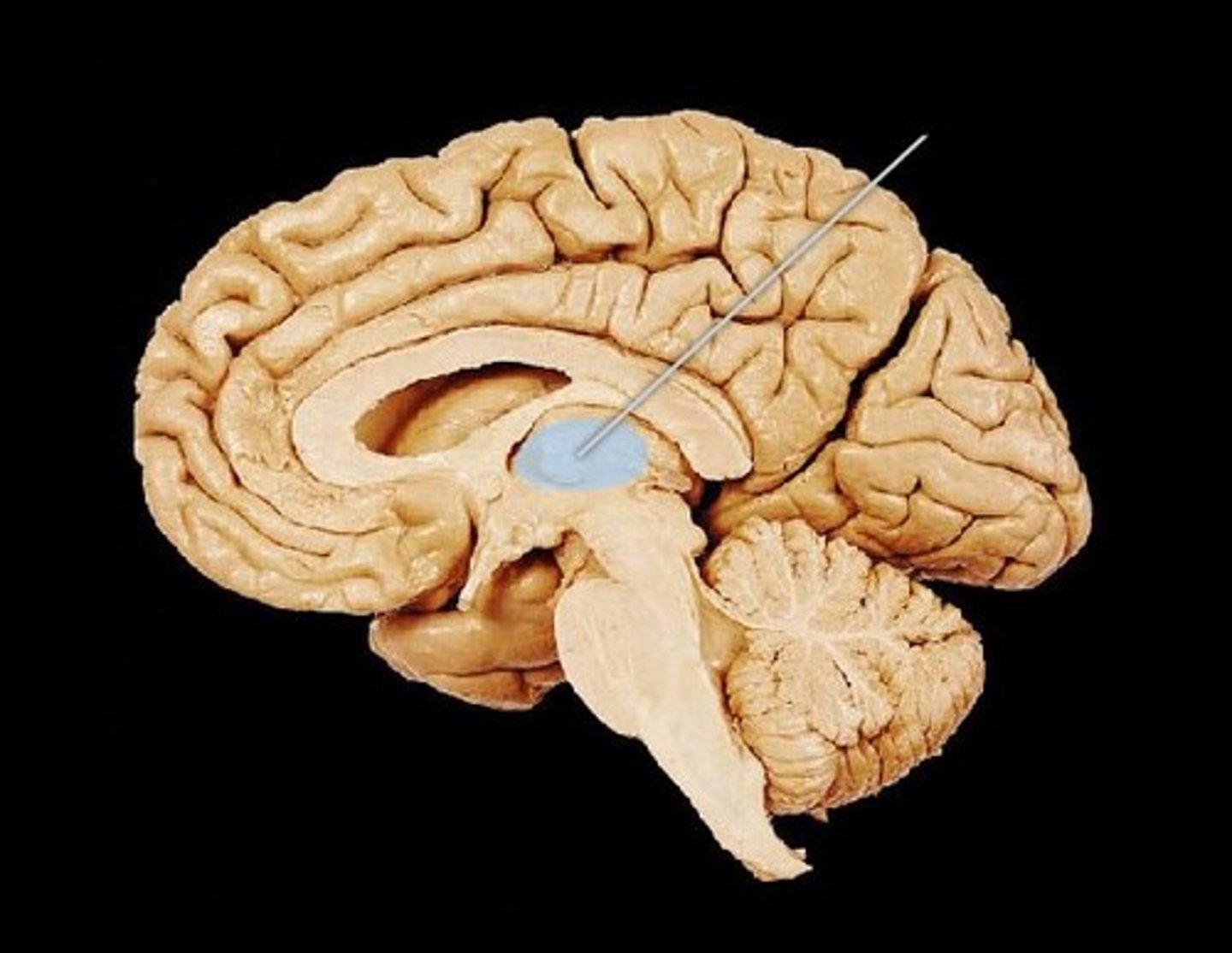
thalamus
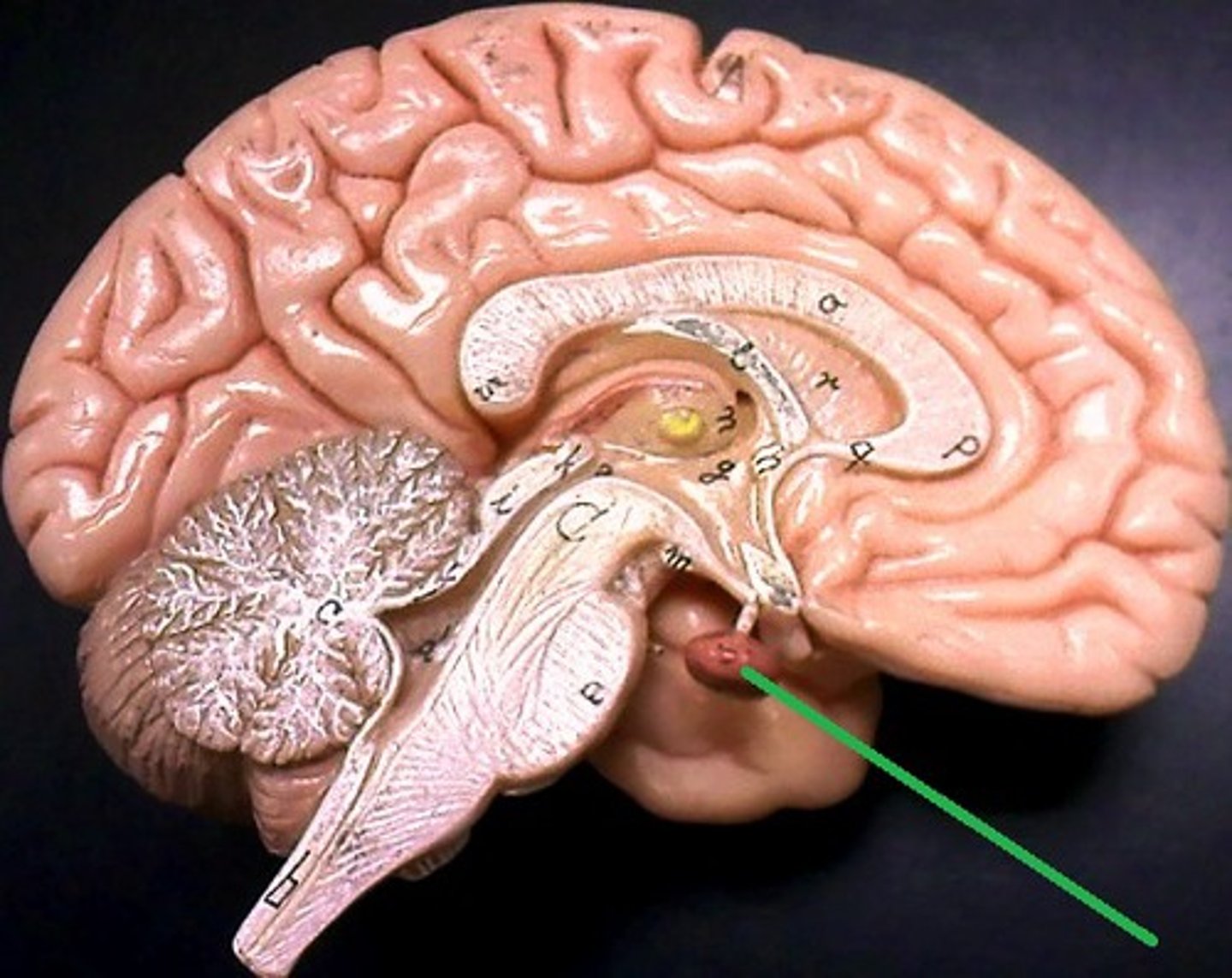
pituitary gland
thyroid gland
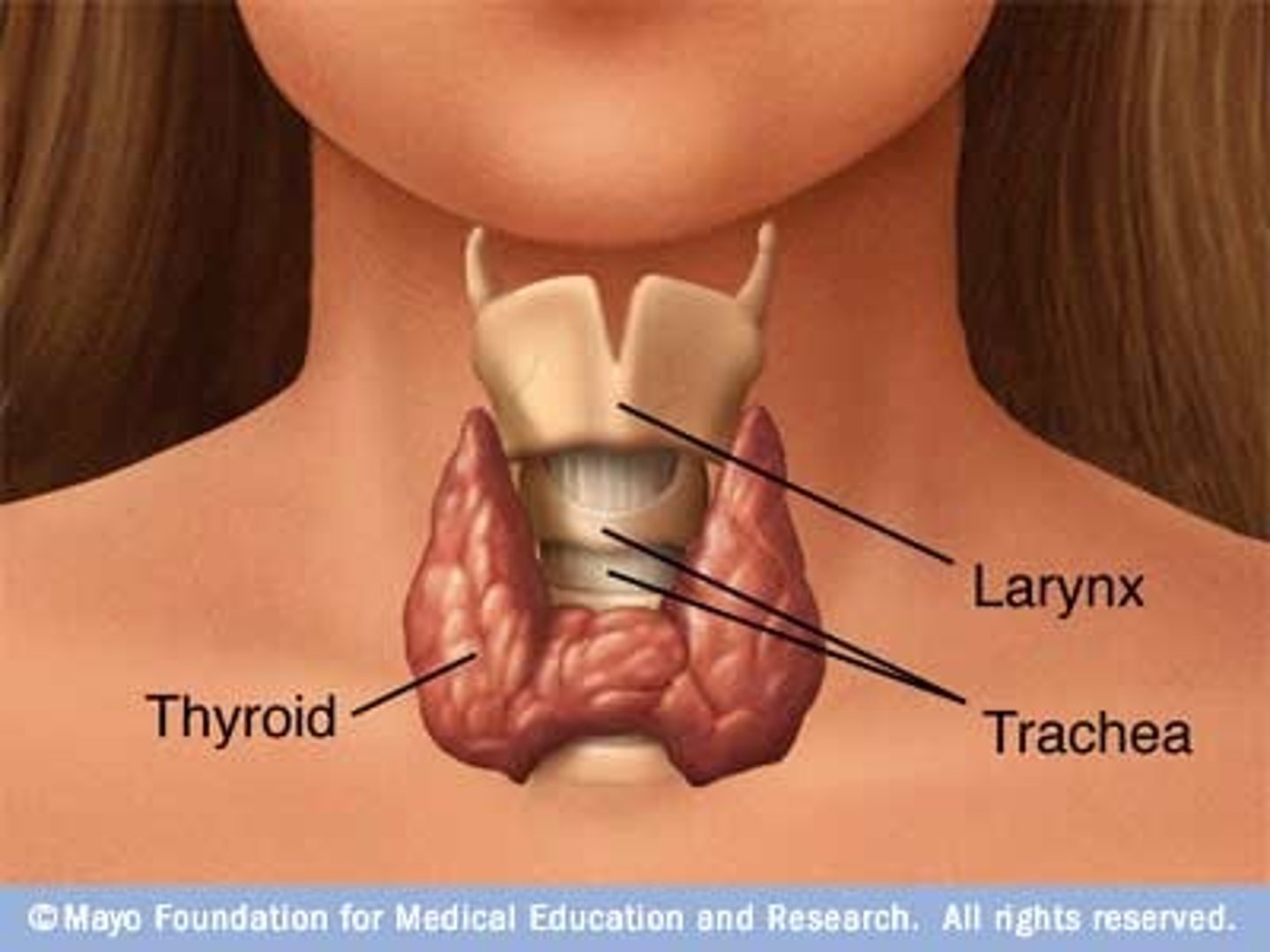
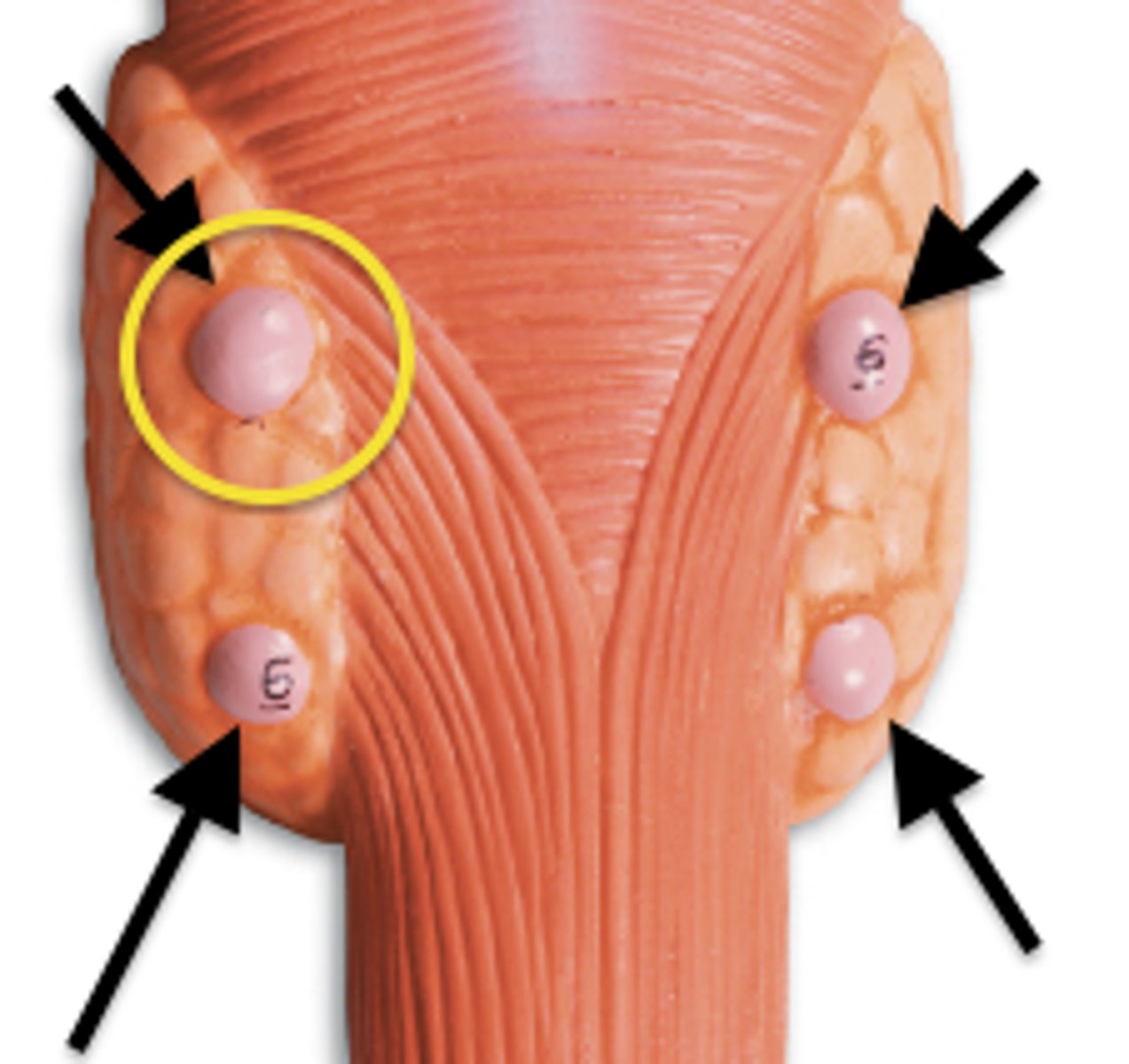
parathyroid gland
ovaries
anterior pituitary hormones
FSH, LH, TSH, STH, ACTH, and prolactin
posterior pituitary hormones
ADH and oxytocin
pancreas hormones
insulin and glucagon
adrenal gland hormones
aldosterone, cortisol, epinephrine, norepinephrine
pineal gland hormones
melatonin
ovaries hormones
estrogen and progesterone
Acromegaly
Enlarged hands and feet, excessive sweating, fatigue, muscle weakness, pain, limited joint mobility
Acromegaly lab results
Elevated levels of insulin, like growth factor I
Addison's Disease
Fatigue, increased pigment in the skin, weight loss, muscle weakness
Addison's Disease lab results
Low sodium, high potassium, high ACTH, low cortisol in the blood
Cushings Syndrome
Backache, anxiety, muscle weakness, extra fat deposits on the back of the neck and upper back (aka "buffalo hump"), females may experience irregular menstrual cycle
Cushing's Syndrome lab results
High levels of cortisol in the blood
Diabetes Insipidus
Frequent urination, excessive thirst
Diabetes Insipidus lab results
Normal blood glucose level, no glucose in the urine, low ADH level in the blood
Hyperparathyroidism
Excessive thirst, weak or broken bones, fatigue, nausea
Hyperparathyroidism lab results
High calcium and parathyroid hormone levels in the blood
Hyperthyroidism
Elevated body temp, extreme sweating, nervousness, rapid heart rate, weight loss, irregular menstrual cycle in females
Hyperthyroidism lab results
High thyroxine and low TSH in the blood
hypothyroidism
Fatigue, muscle weakness, depression, weight gain, low body temperature, intolerant of cold
Hypothyroidism lab results
Low thyroxine and high TSH in the blood
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
Acne, unwanted hair growth, weight gain, fatigue, infertility, mood changes, sleep problems
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) lab results
Elevated levels of testosterone and LH, low levels of FSH in blood
Type I Diabetes Mellitus
Frequent urination, excessive thirst, weight loss
Type I Diabetes Mellitus lab results
Glucose in urine, elevated blood glucose, islet cell antibody in the blood
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Frequent urination, excessive thirst
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus lab results
Glucose in urine, elevated blood glucose, no islet cell antibody in the blood
2. Why are blood tests used to diagnose endocrine disorders?
provide important information about the levels of hormones and other substances within the bloodstream.
3. Why is it so important to consider age and sex when diagnosing an endocrine disorder?
hormone production and functions change throughout life. sex hormones vary drastically between males and females.
lymph node microscope
bile salts
produced in liver-> stored in gall bladder
bile salts function
emulsifier= aid in the mixture of oil and water
lipase
enzyme digests triglycerides and other lipids into fatty acids and glycerol digest lipids only at the border between lipid and water (or lipid droplet and water).
where is lipase produced
pancreas
milk when added to acid
more viscous
litmus crystals
blue at basic or neutral pH- pink/red at acidic pH
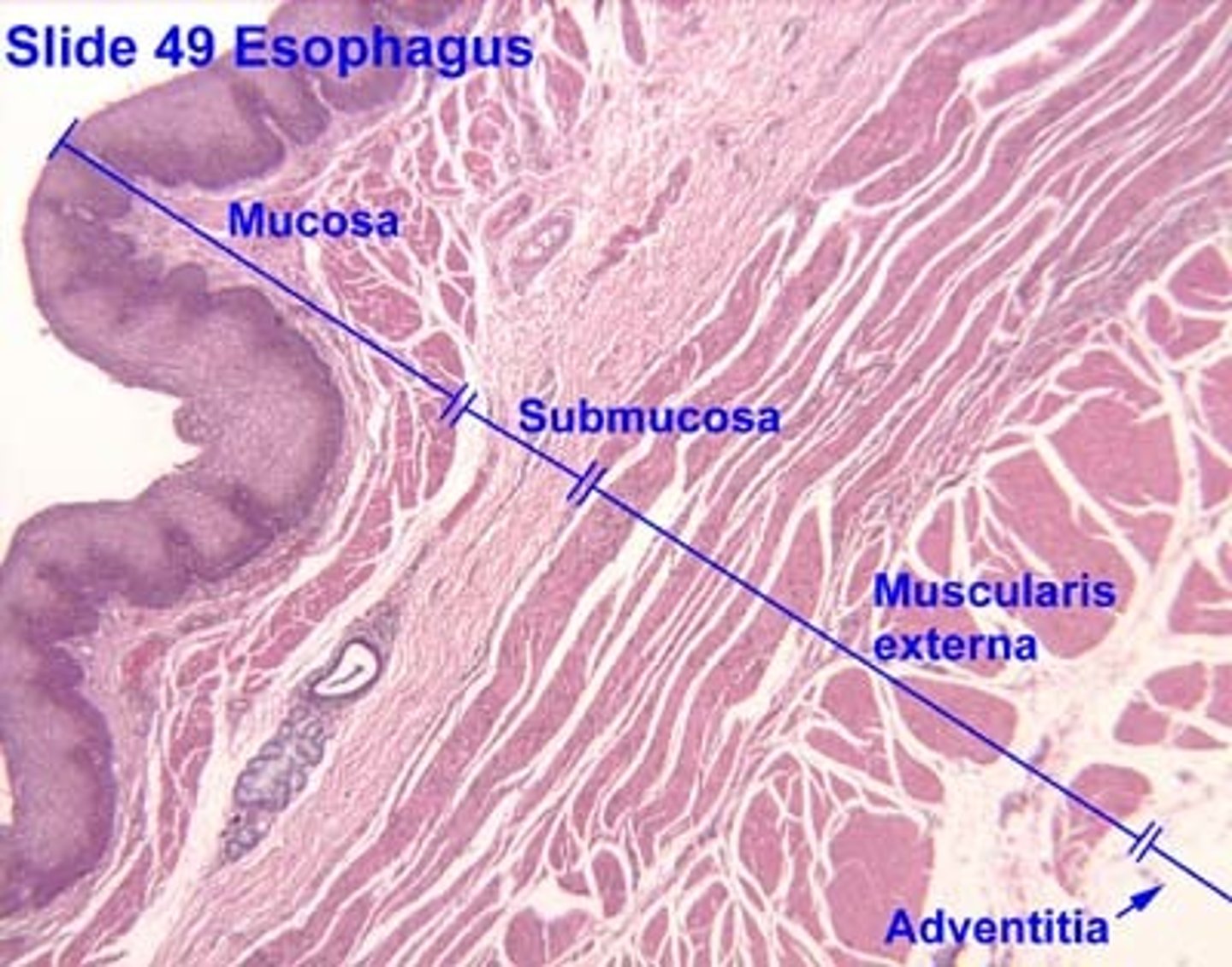
esophagus slide
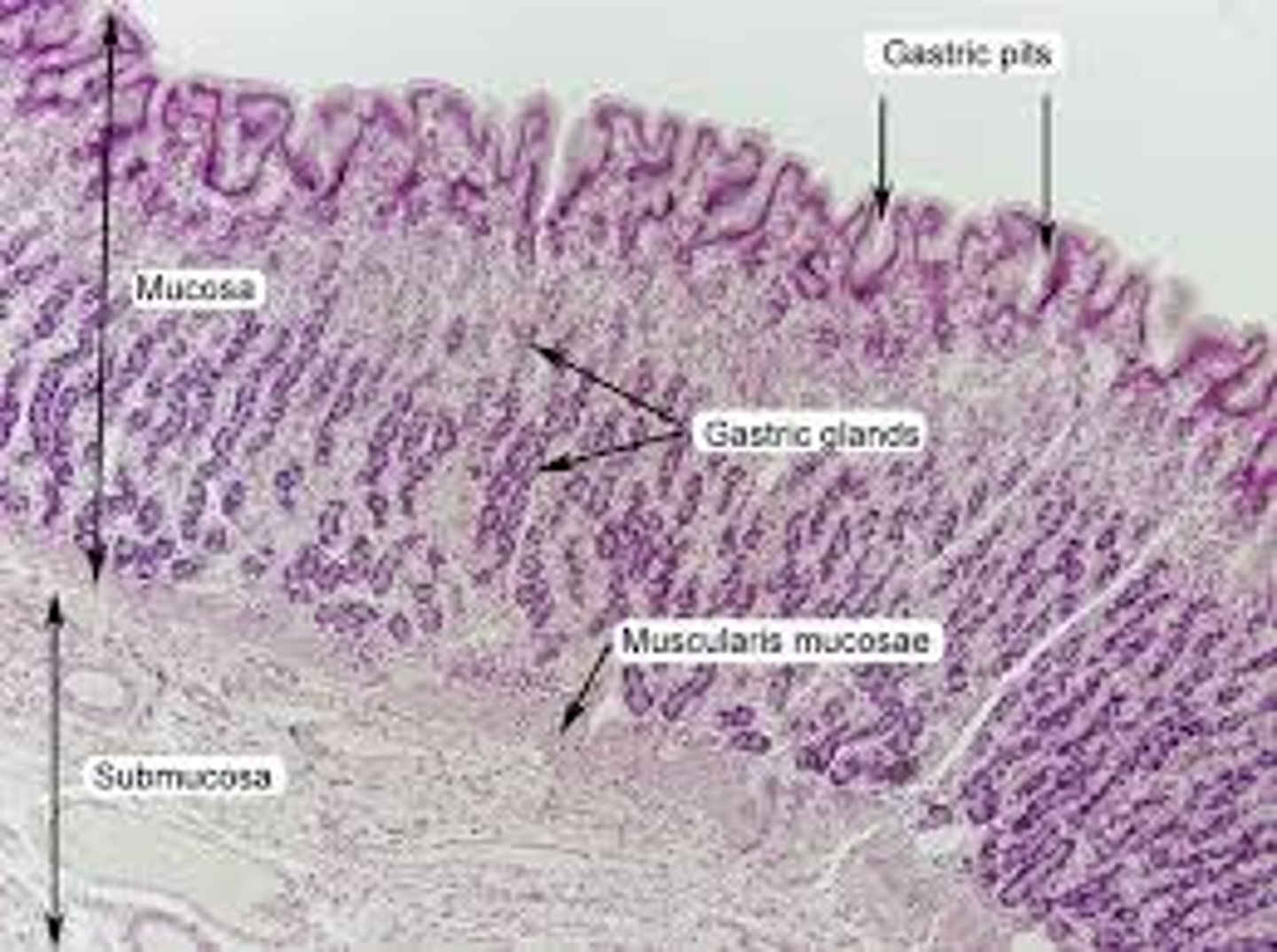
stomach slide
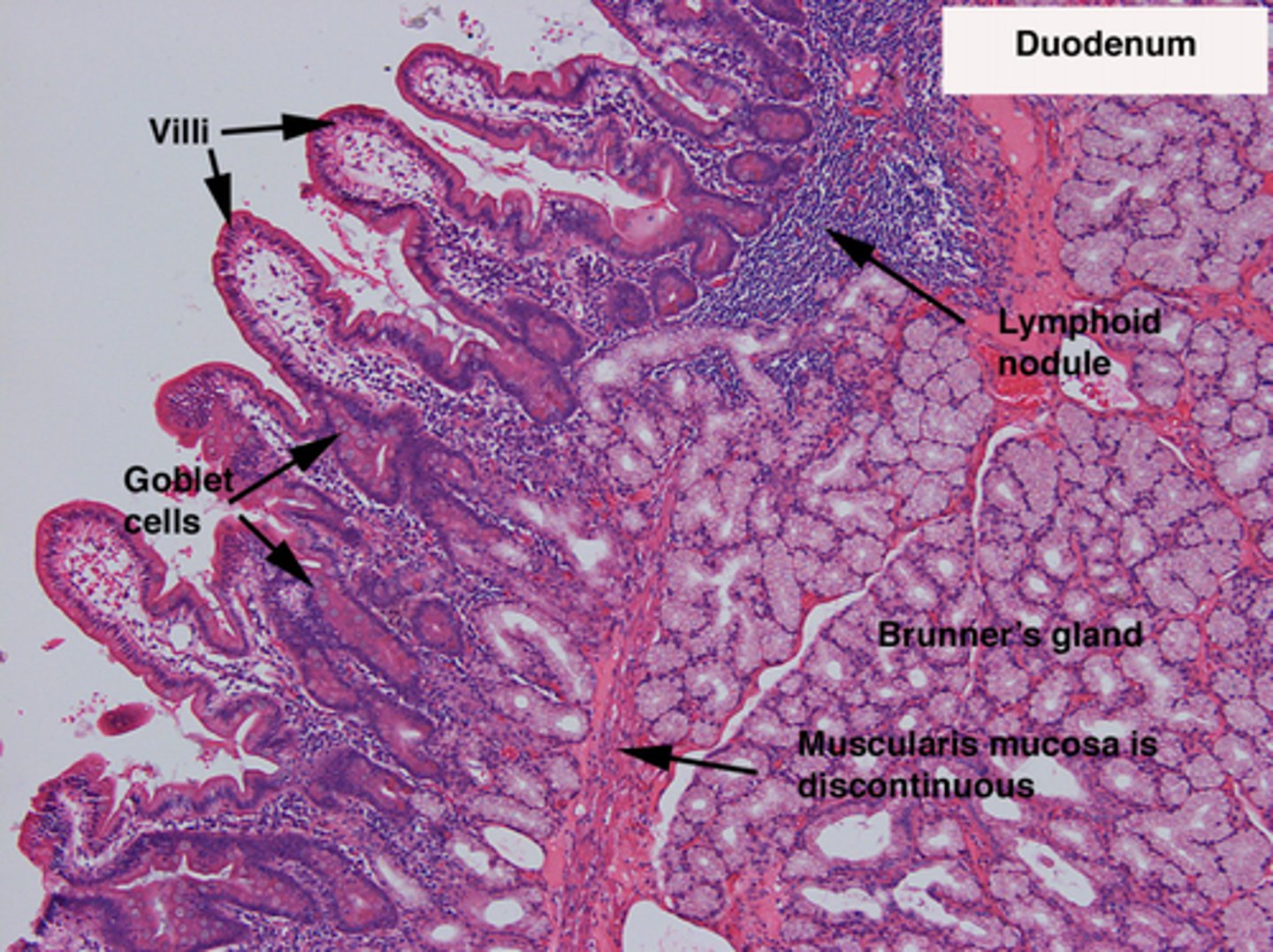
duodenum slide
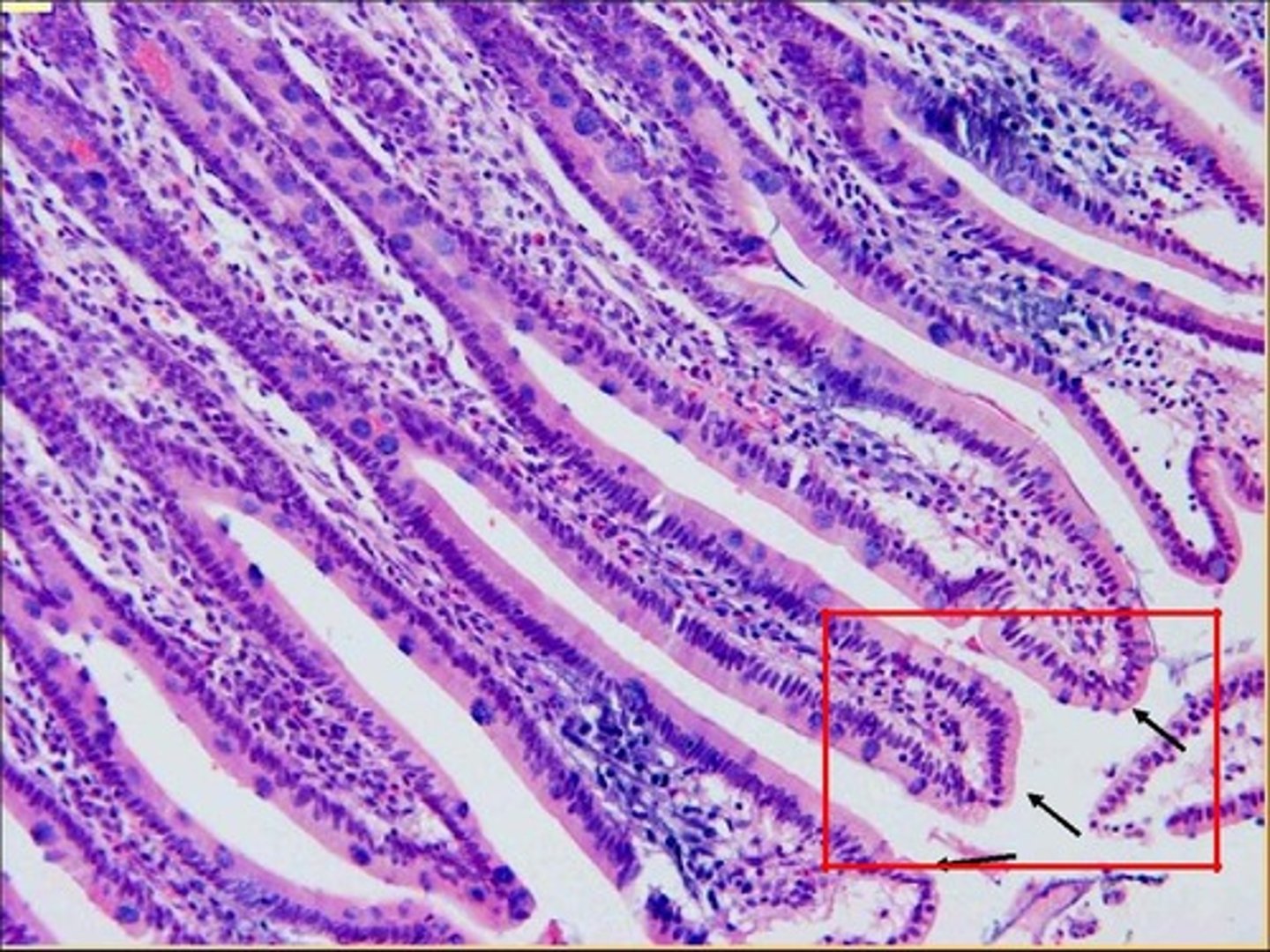
jejunum slide
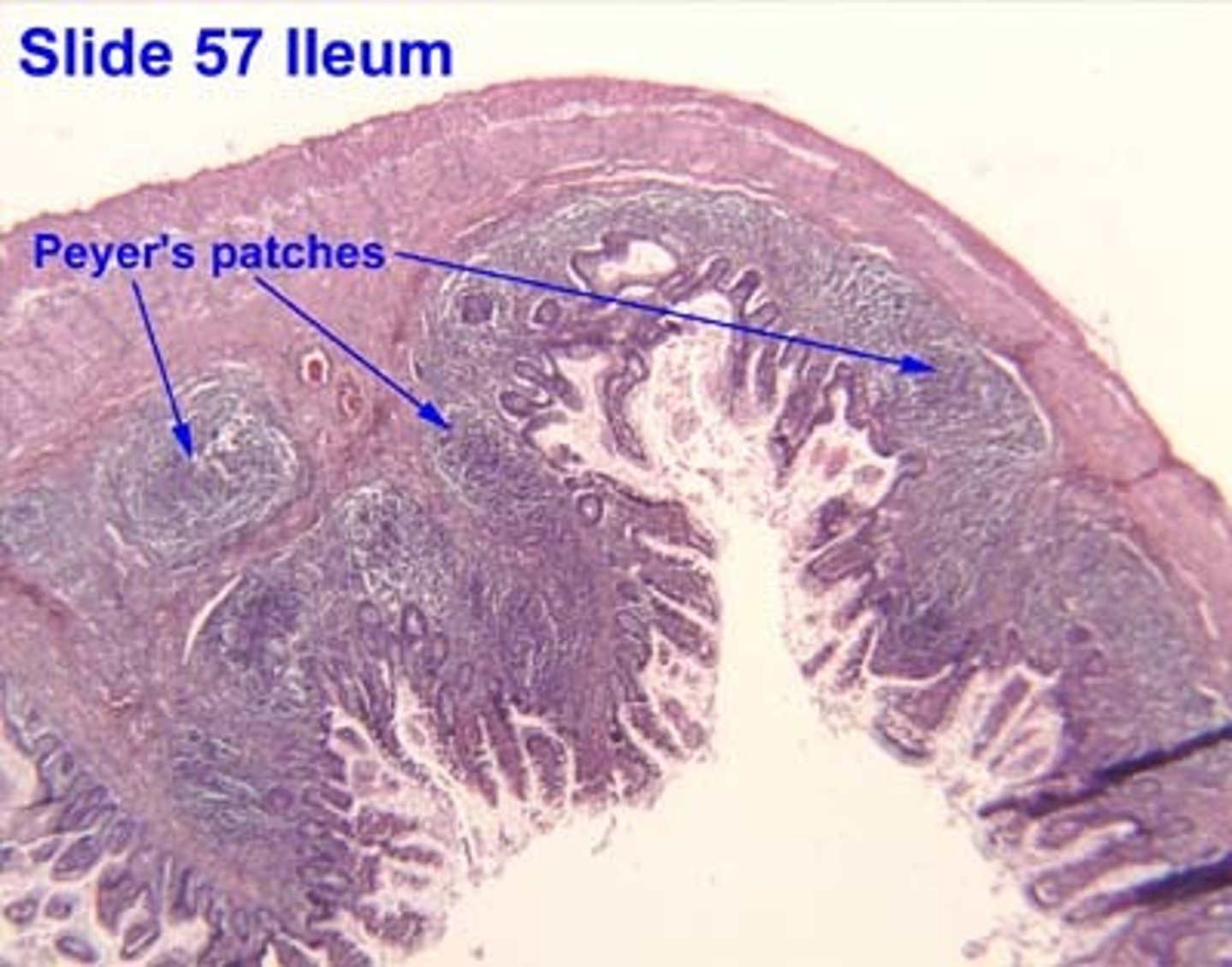
ilium slide
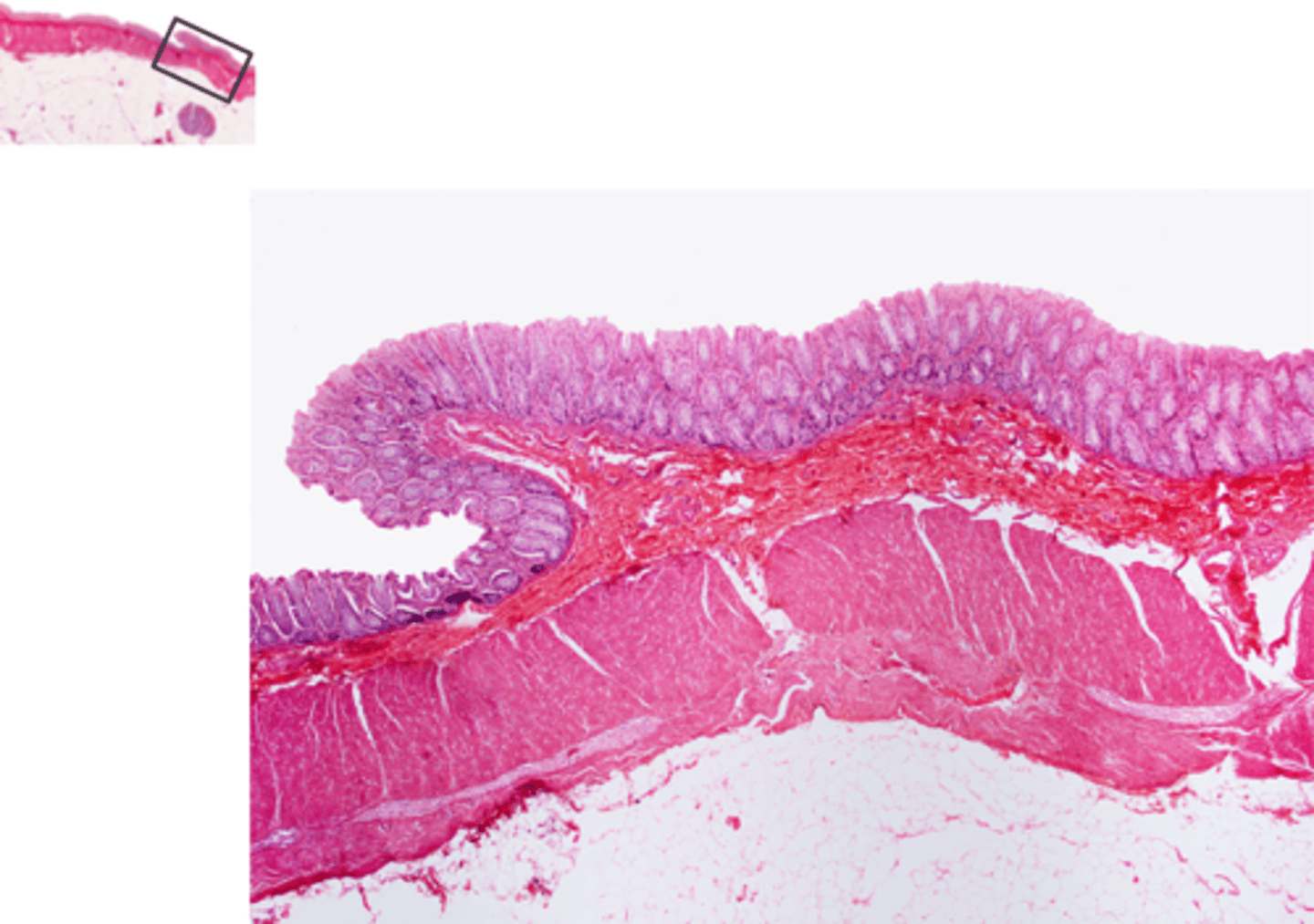
colon/ large intestine slide
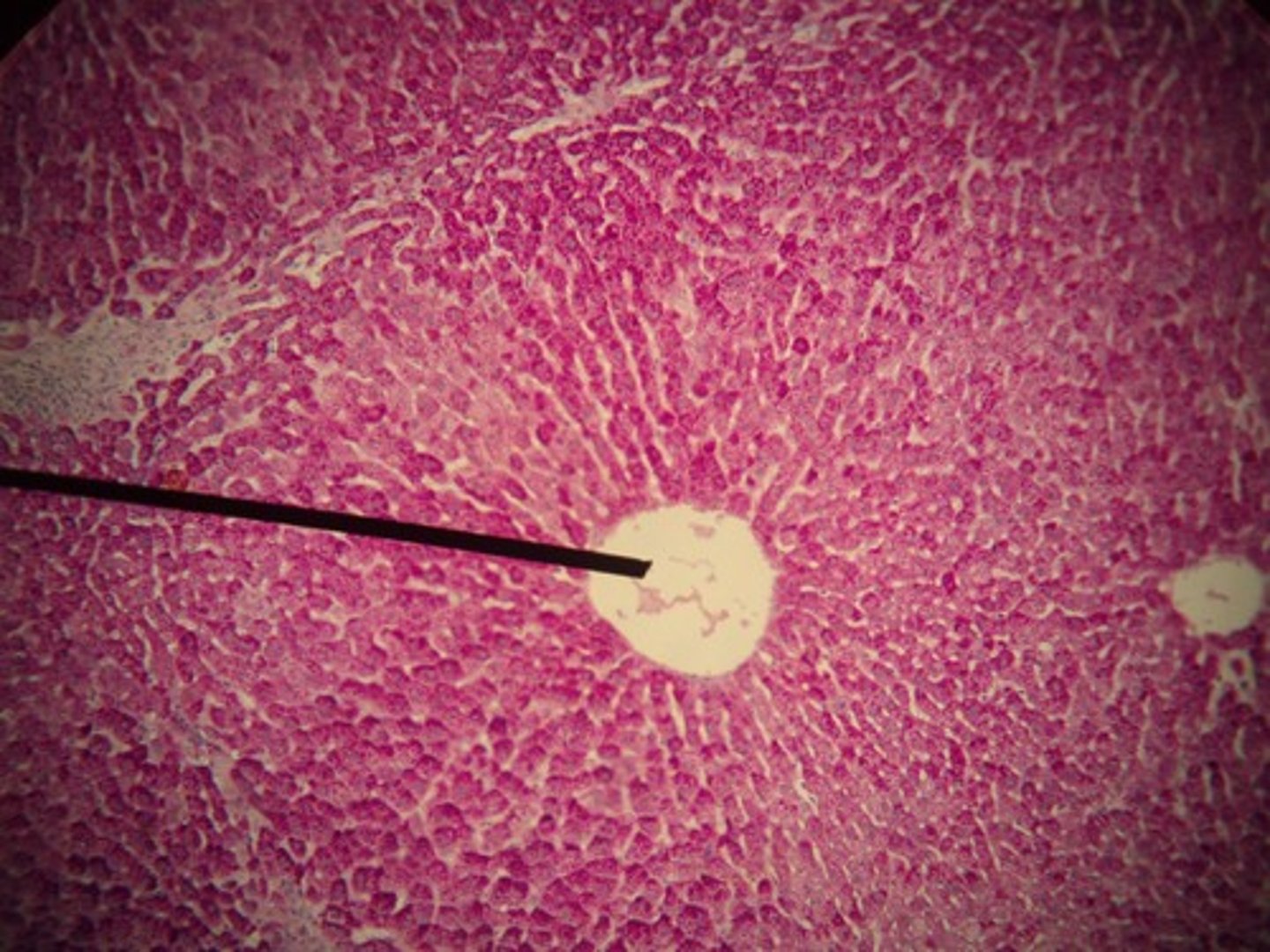
liver slide
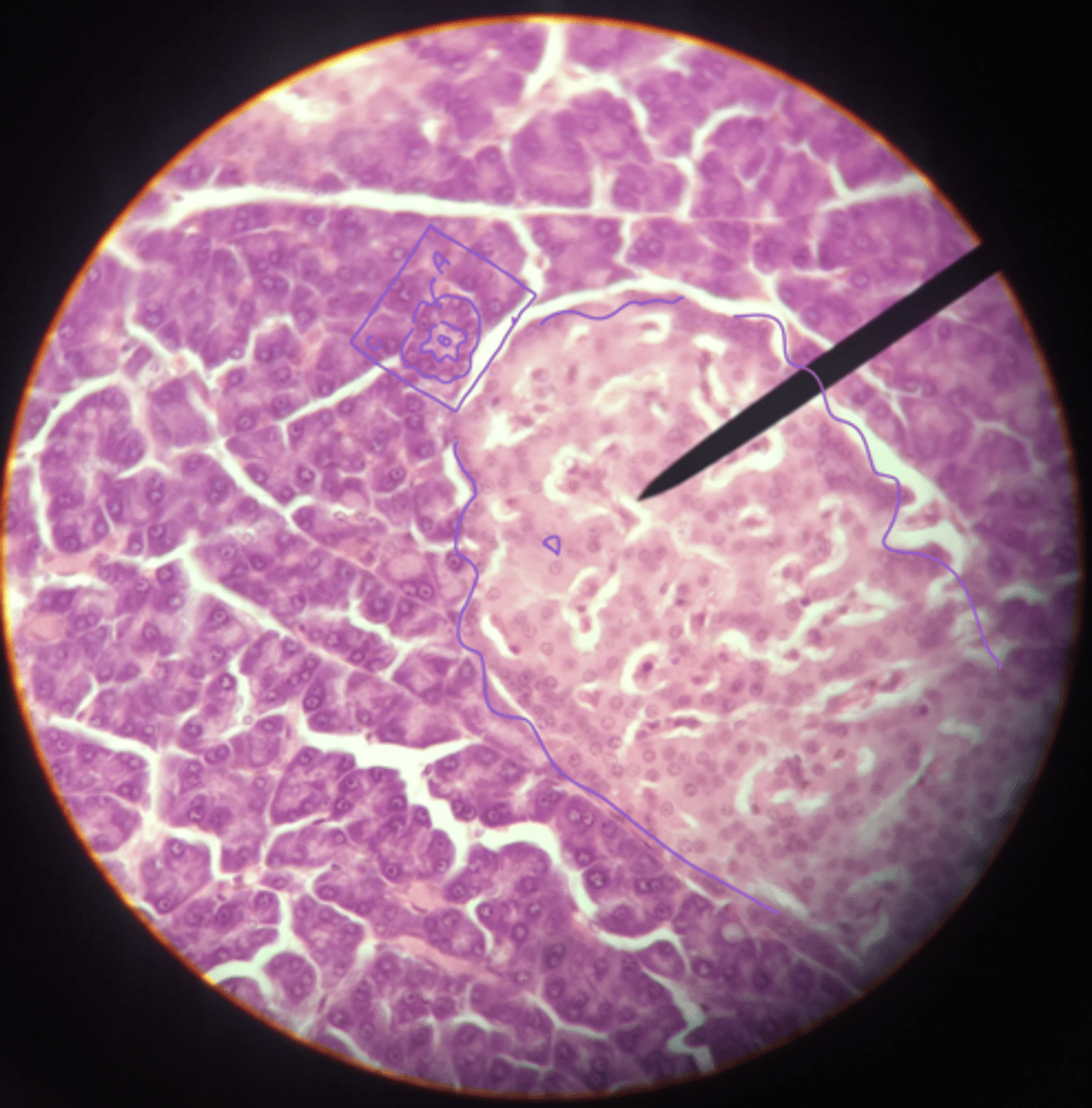
pancreas sldie
cuspid teeth function
tear food
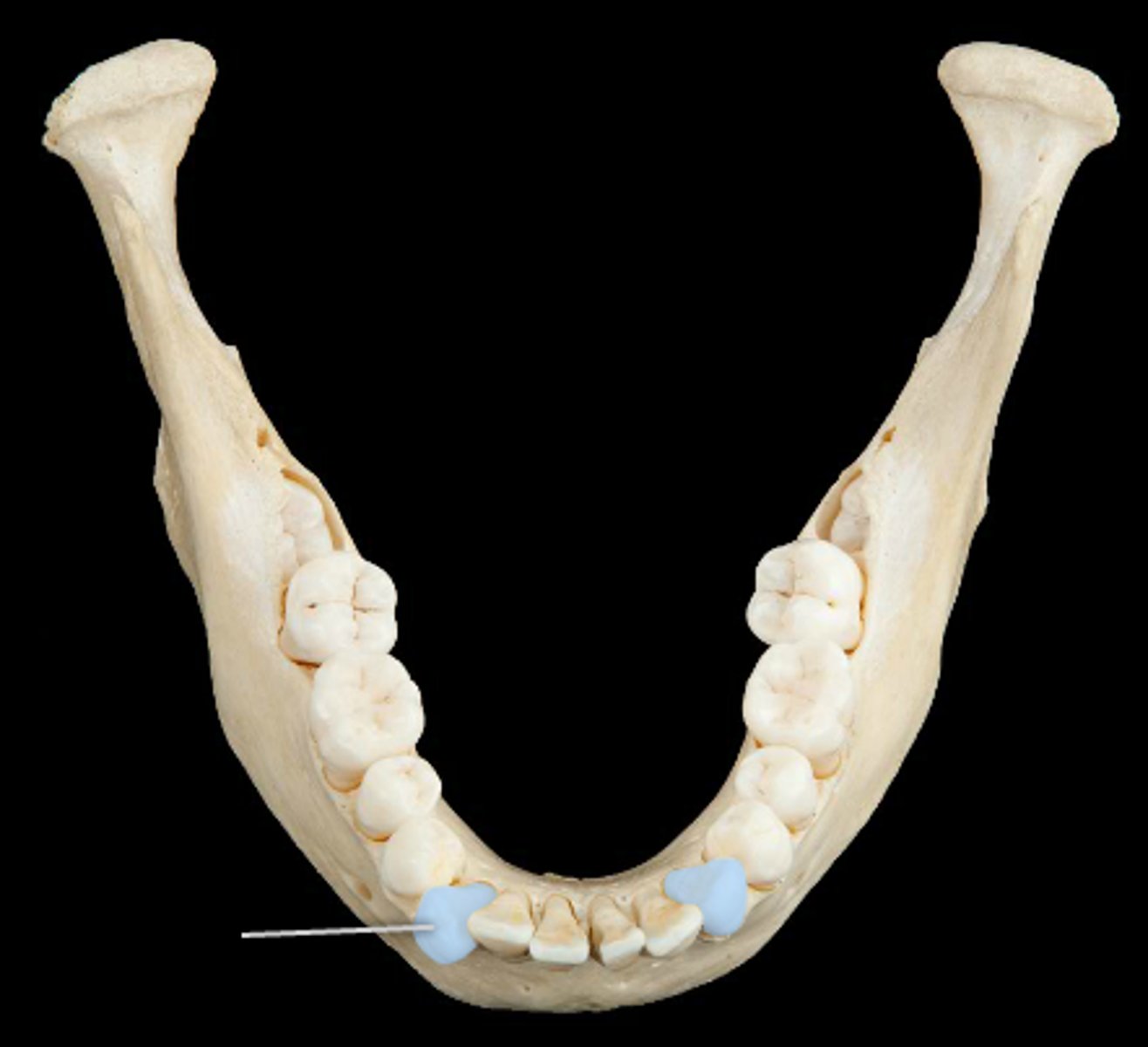
bicuspid teeth function
grinding and crushing
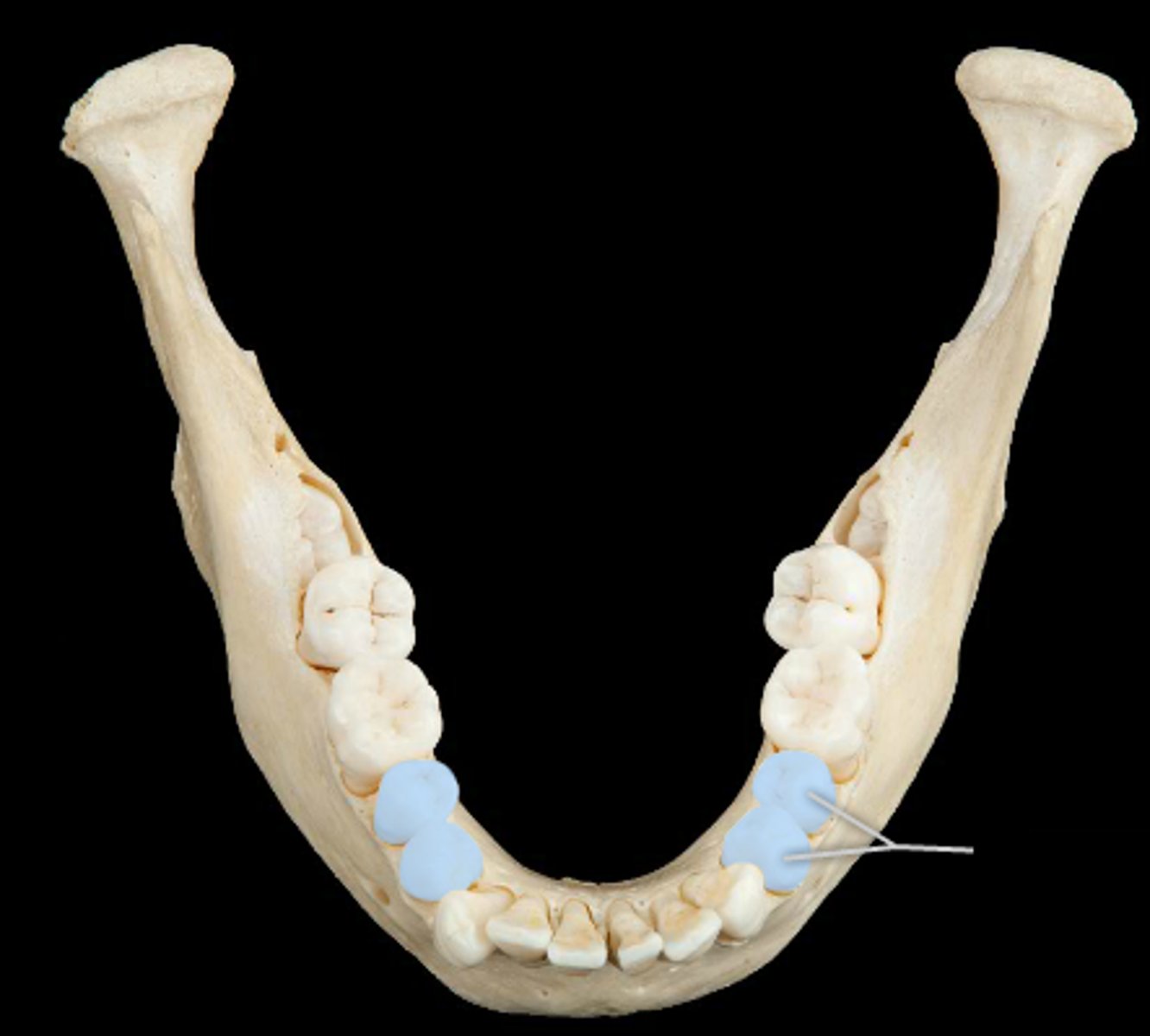
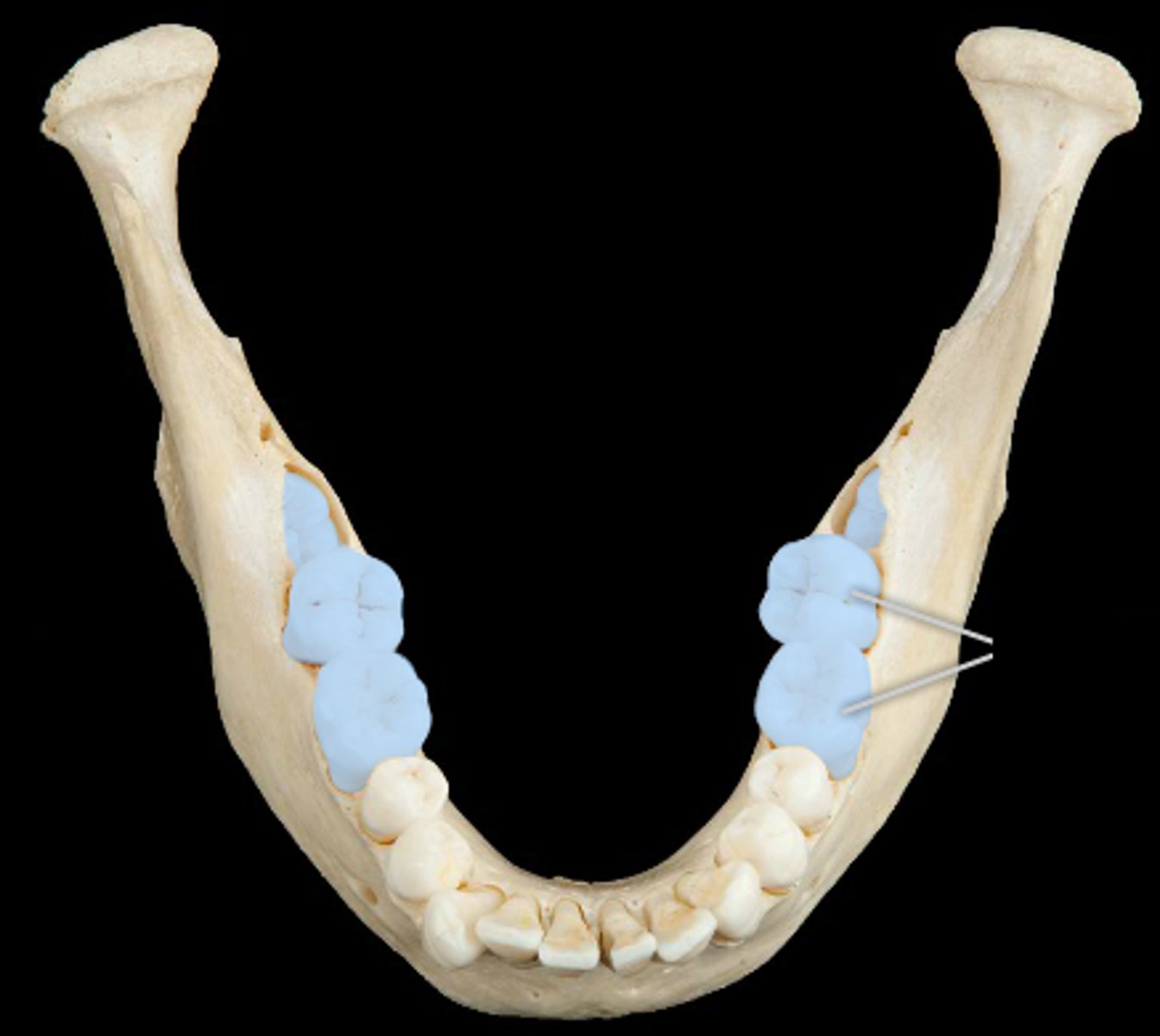
molar function
crushing and grinding
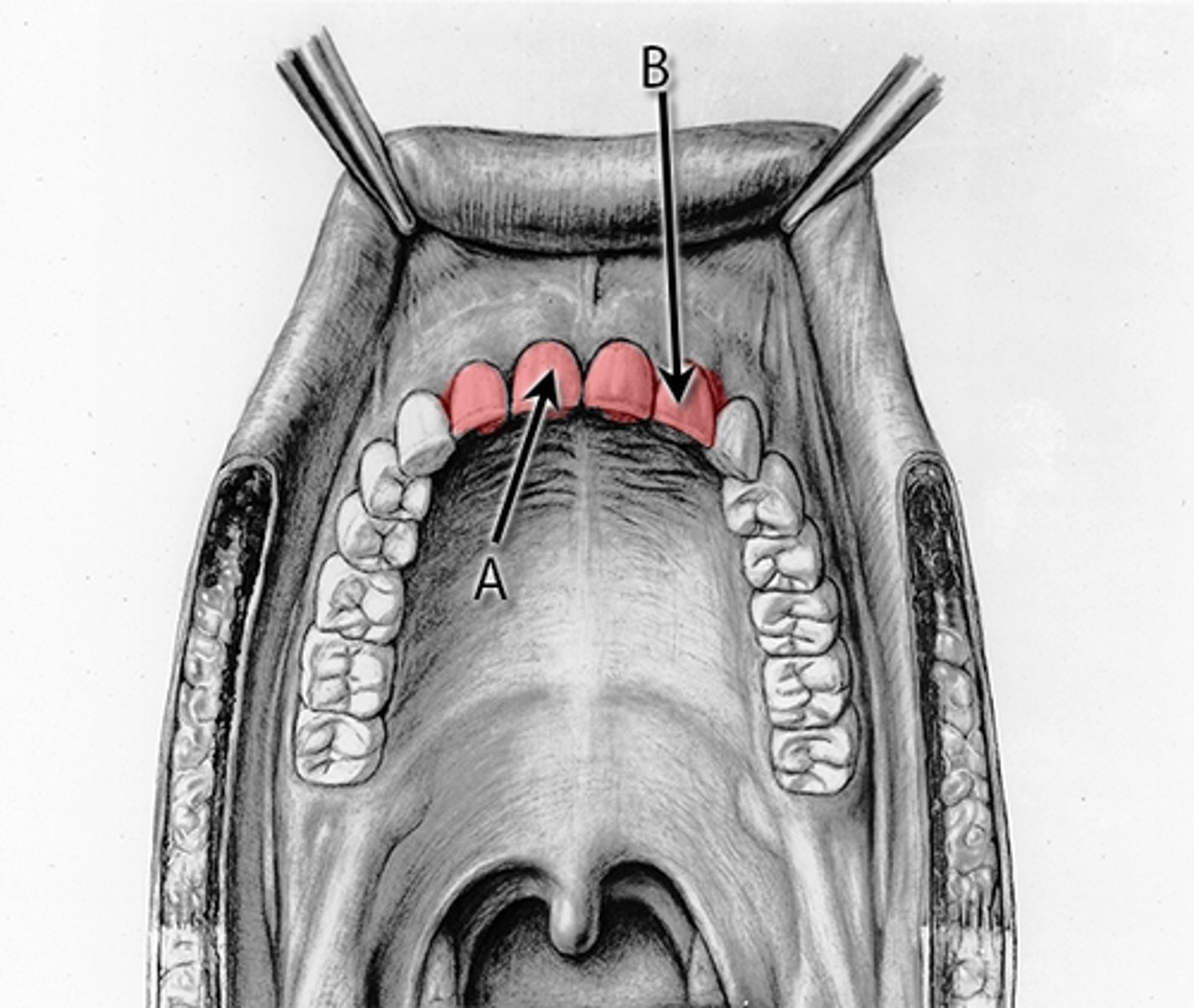
incisor function
cutting and tearing food
pyloric canal
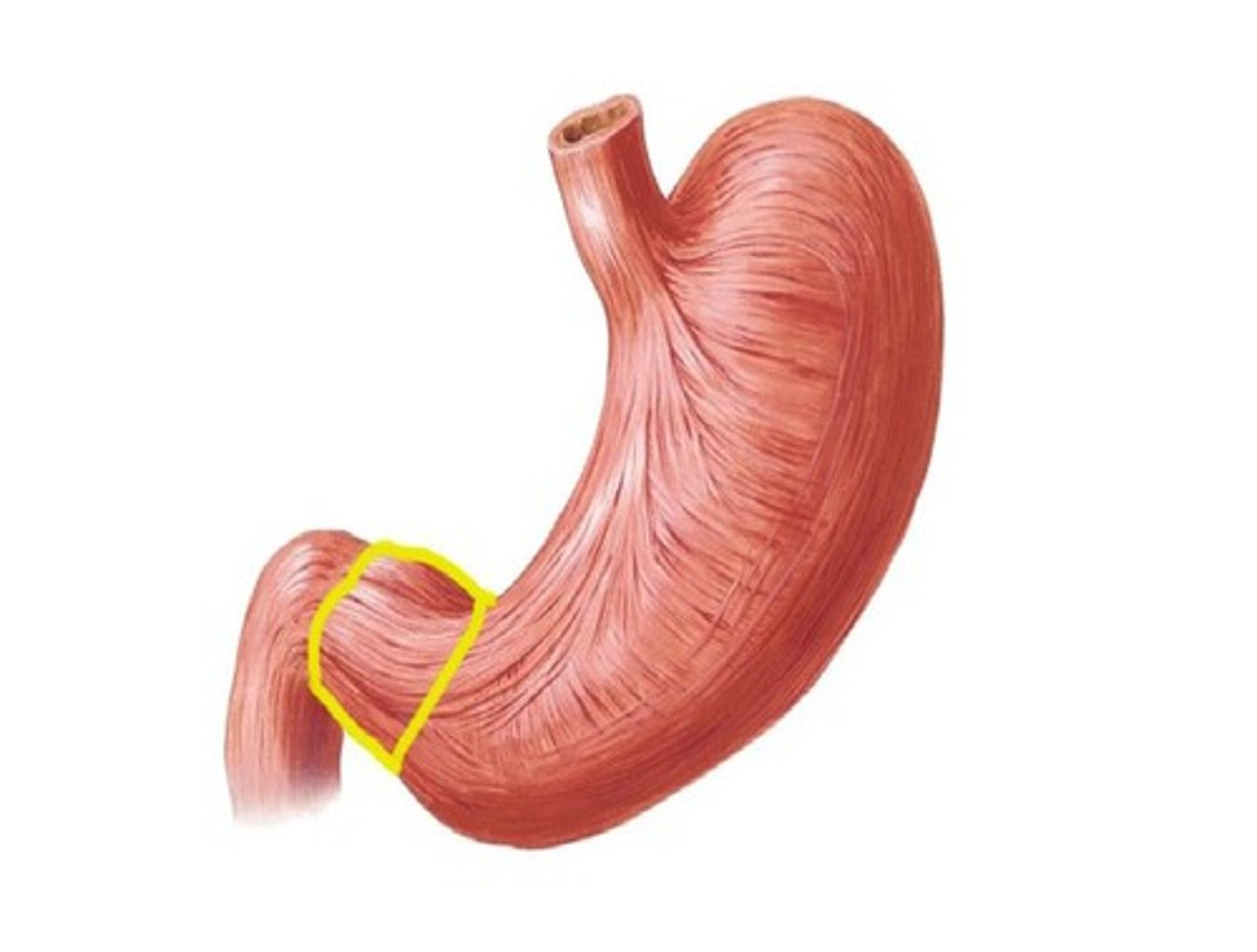
pyloric sphincter
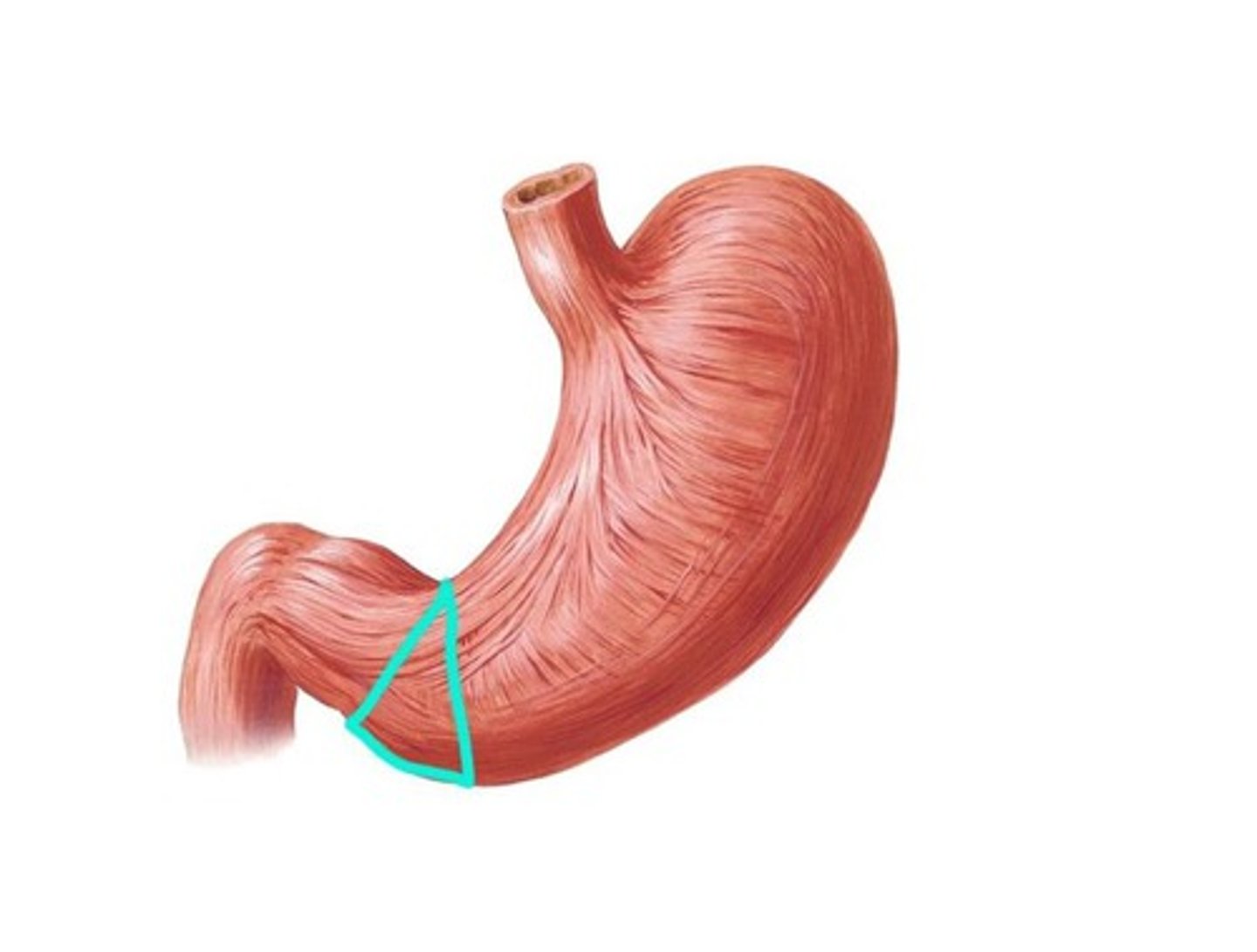
pyloric antrum
cardiac region
lesser curvature
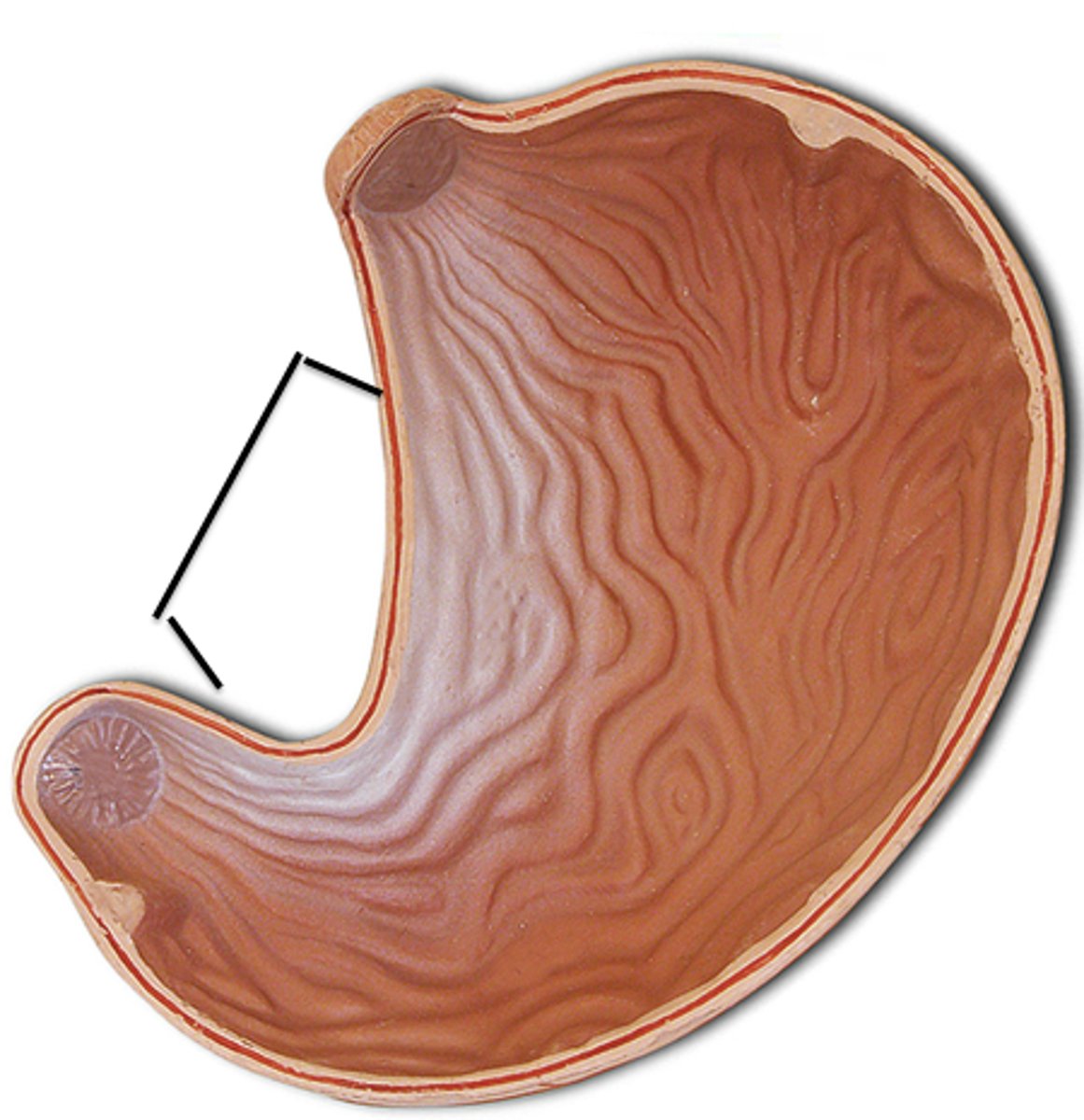
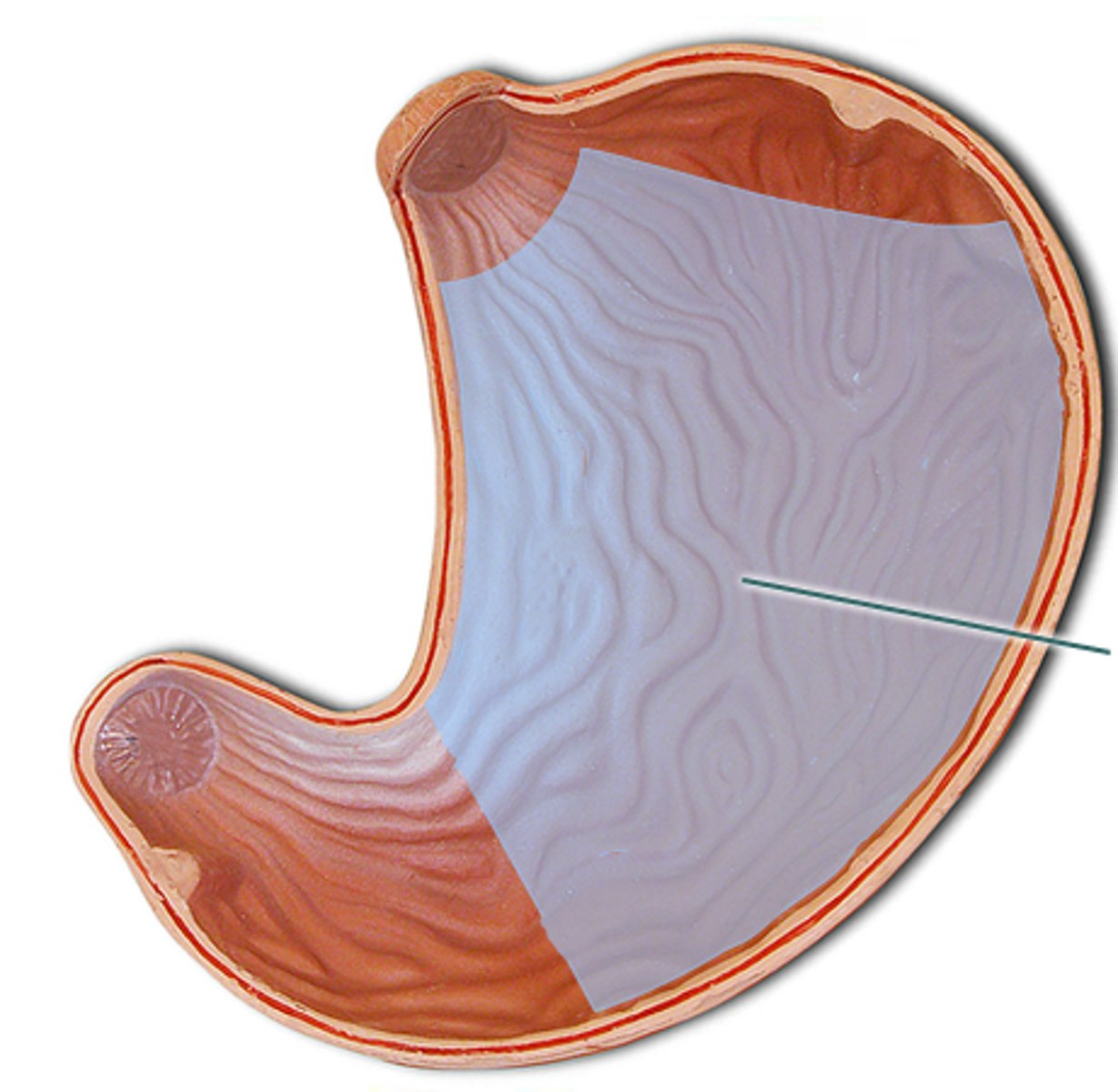
body of the stomach
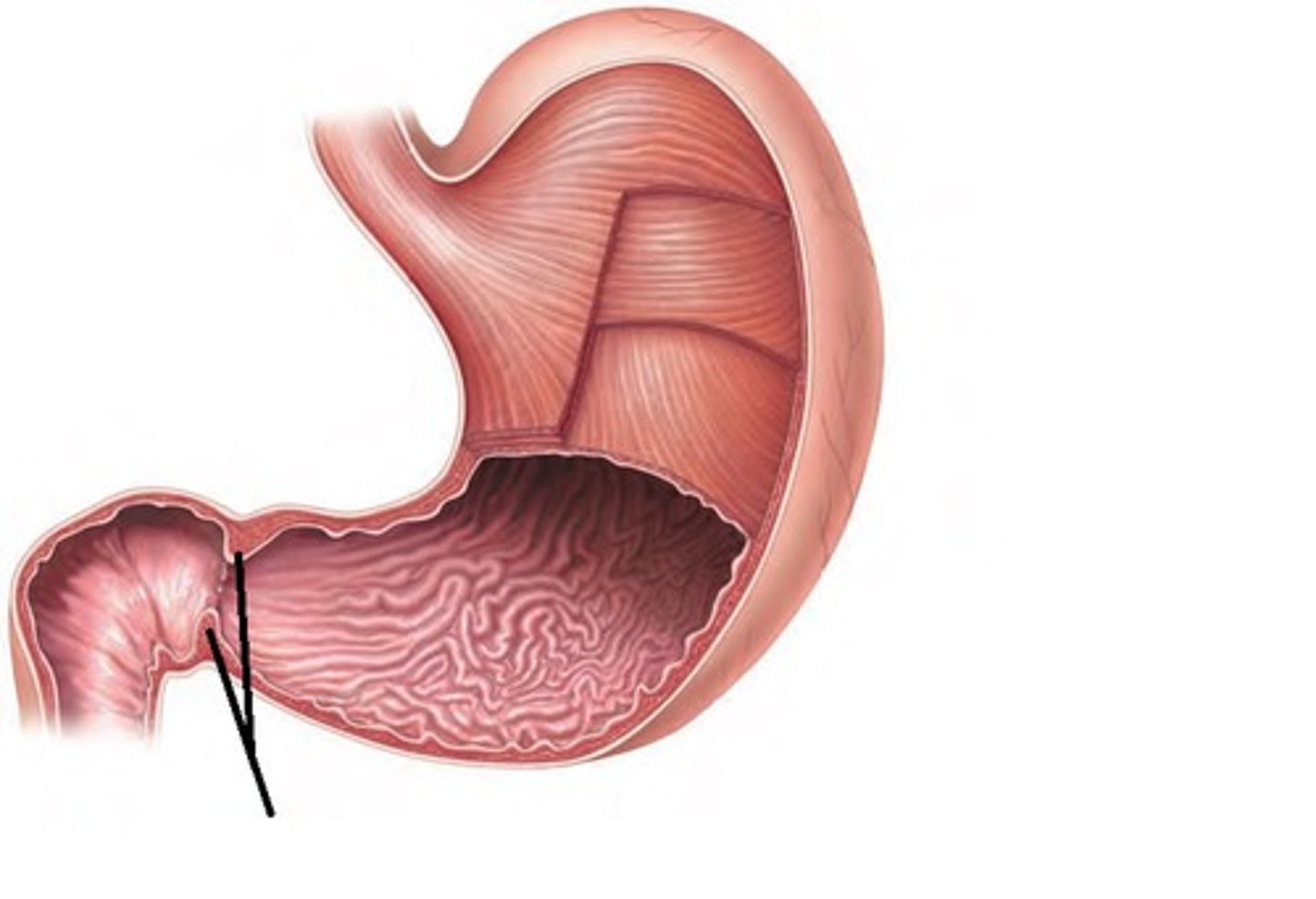
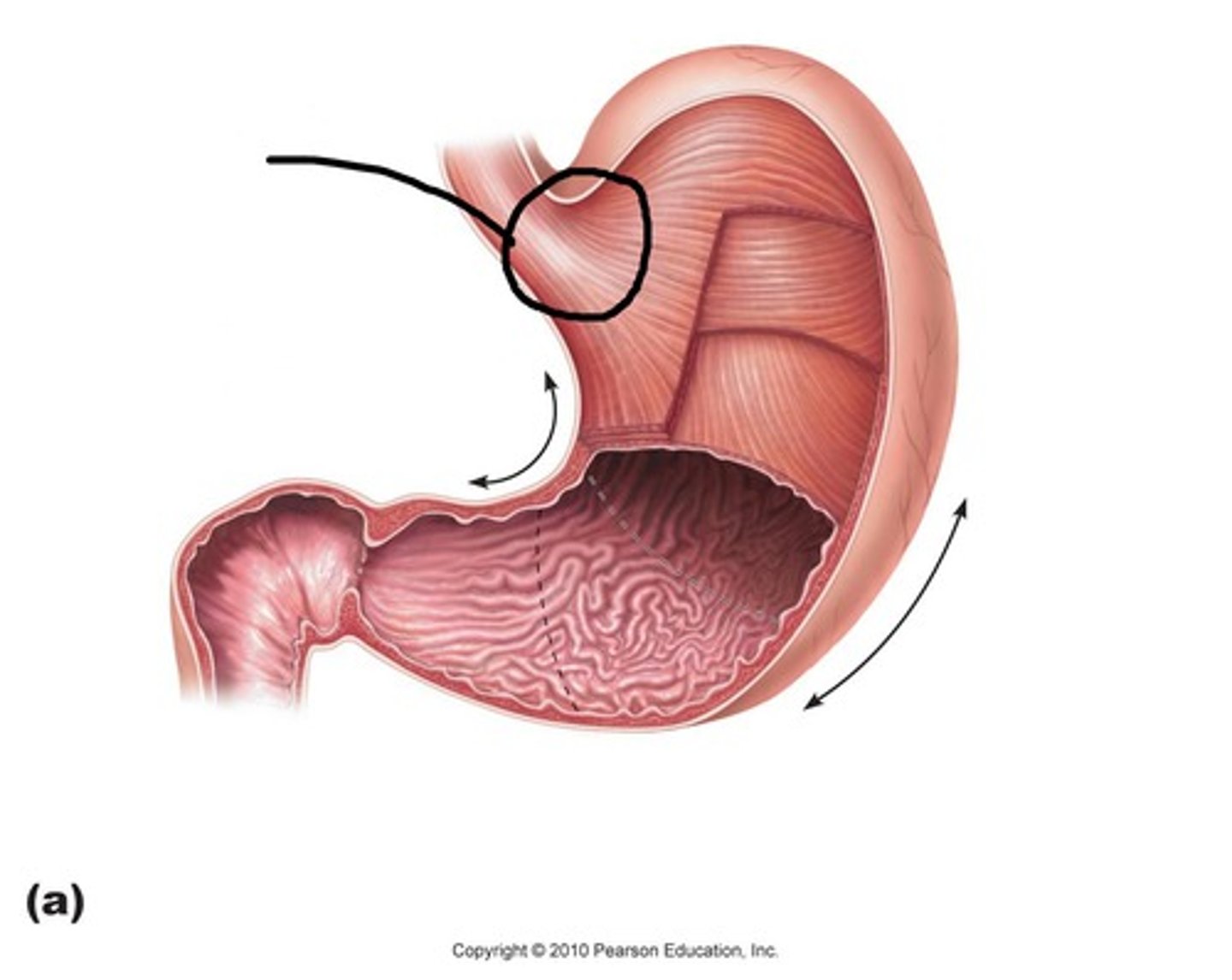
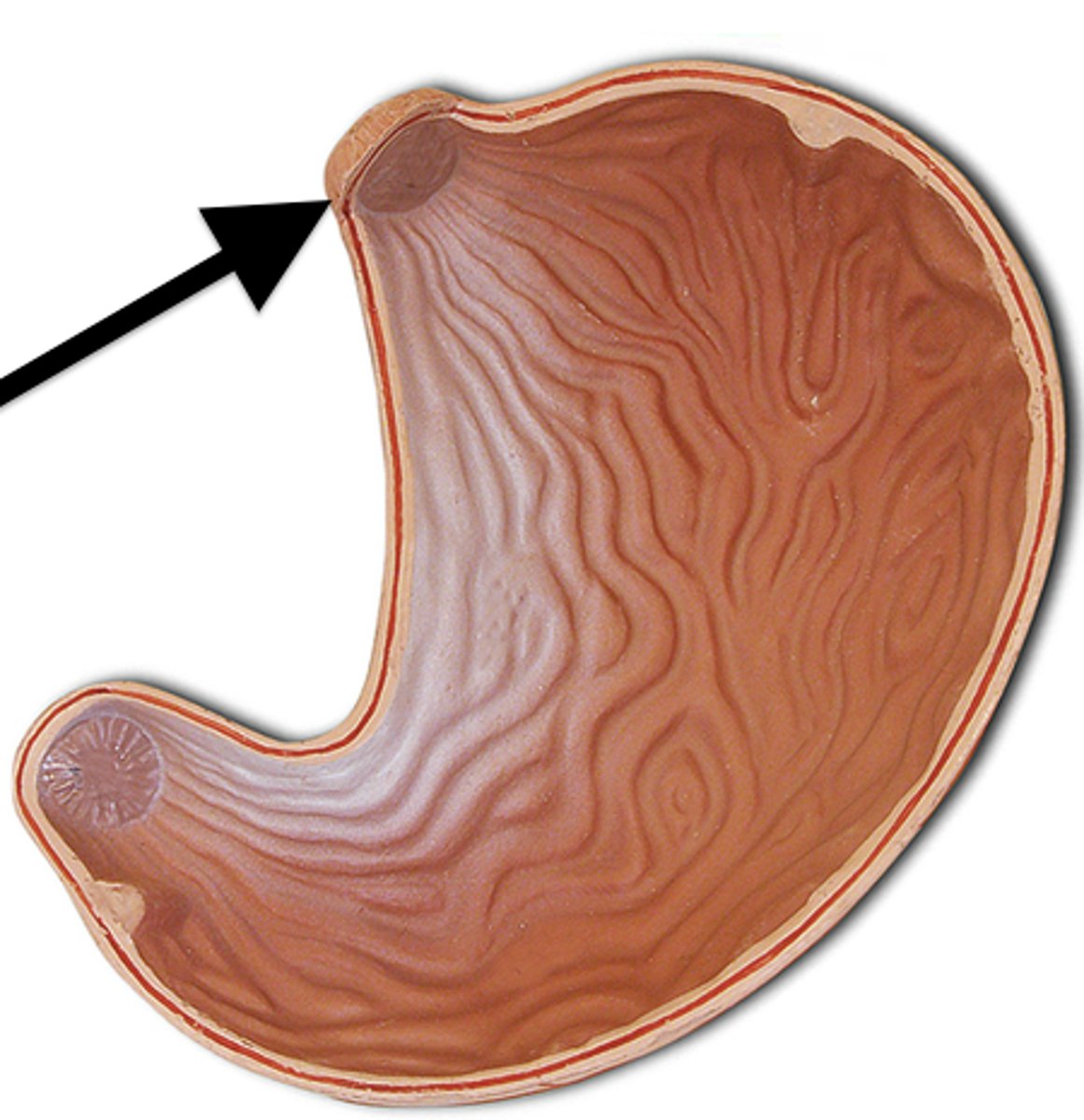
cardiac sphincter
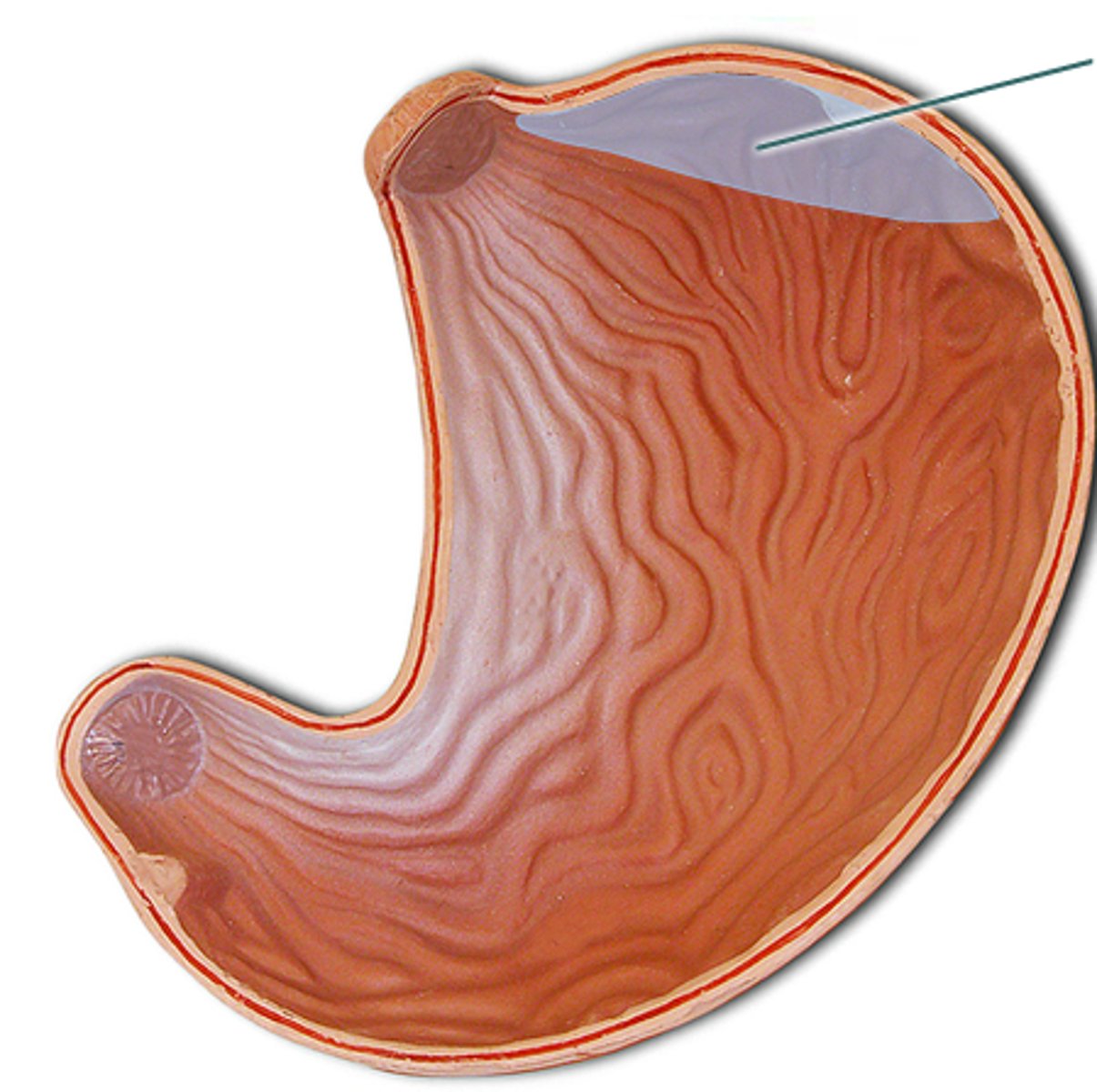
fundus of stomach
left hepatic duct
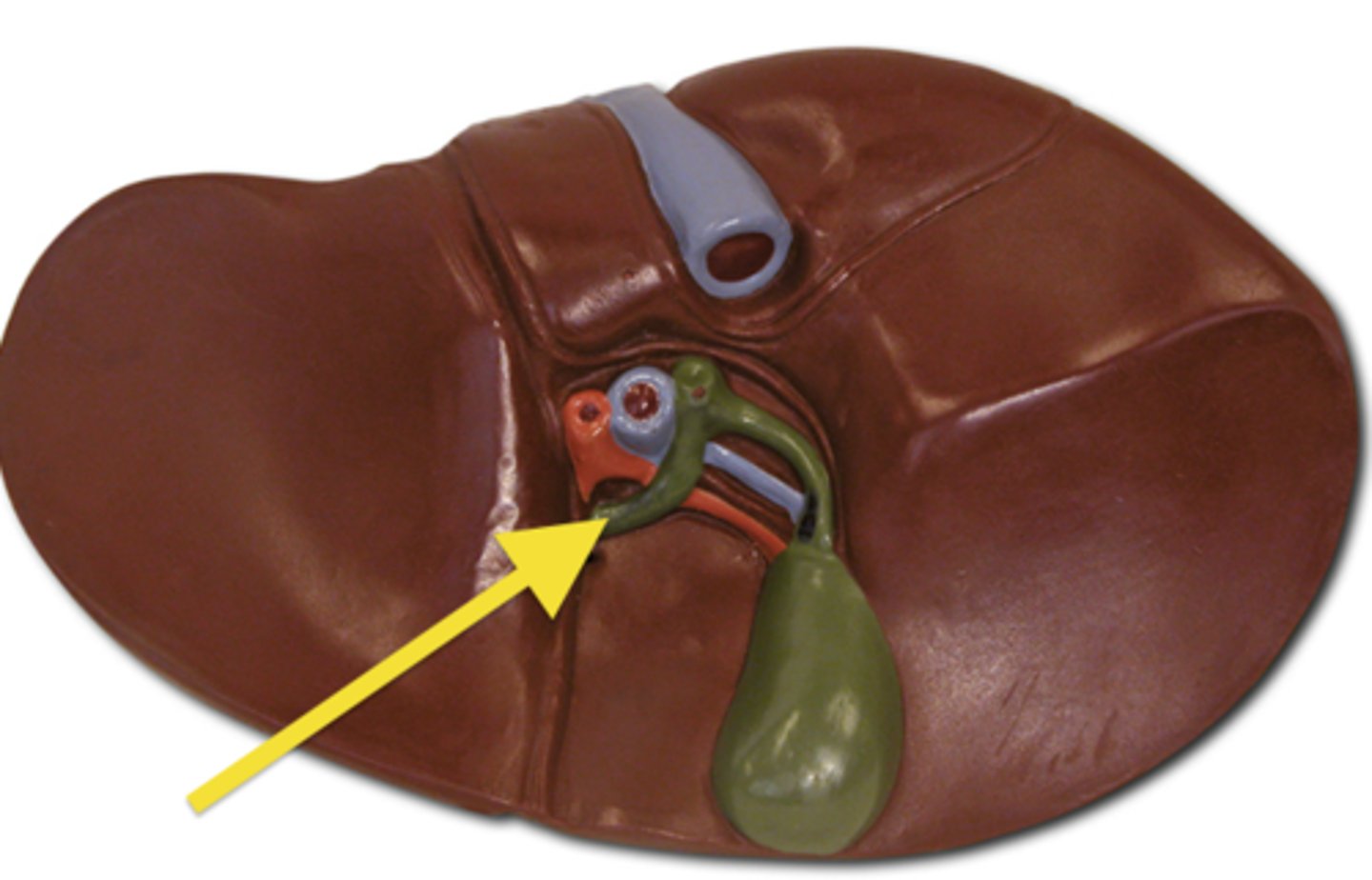

right hepatic duct
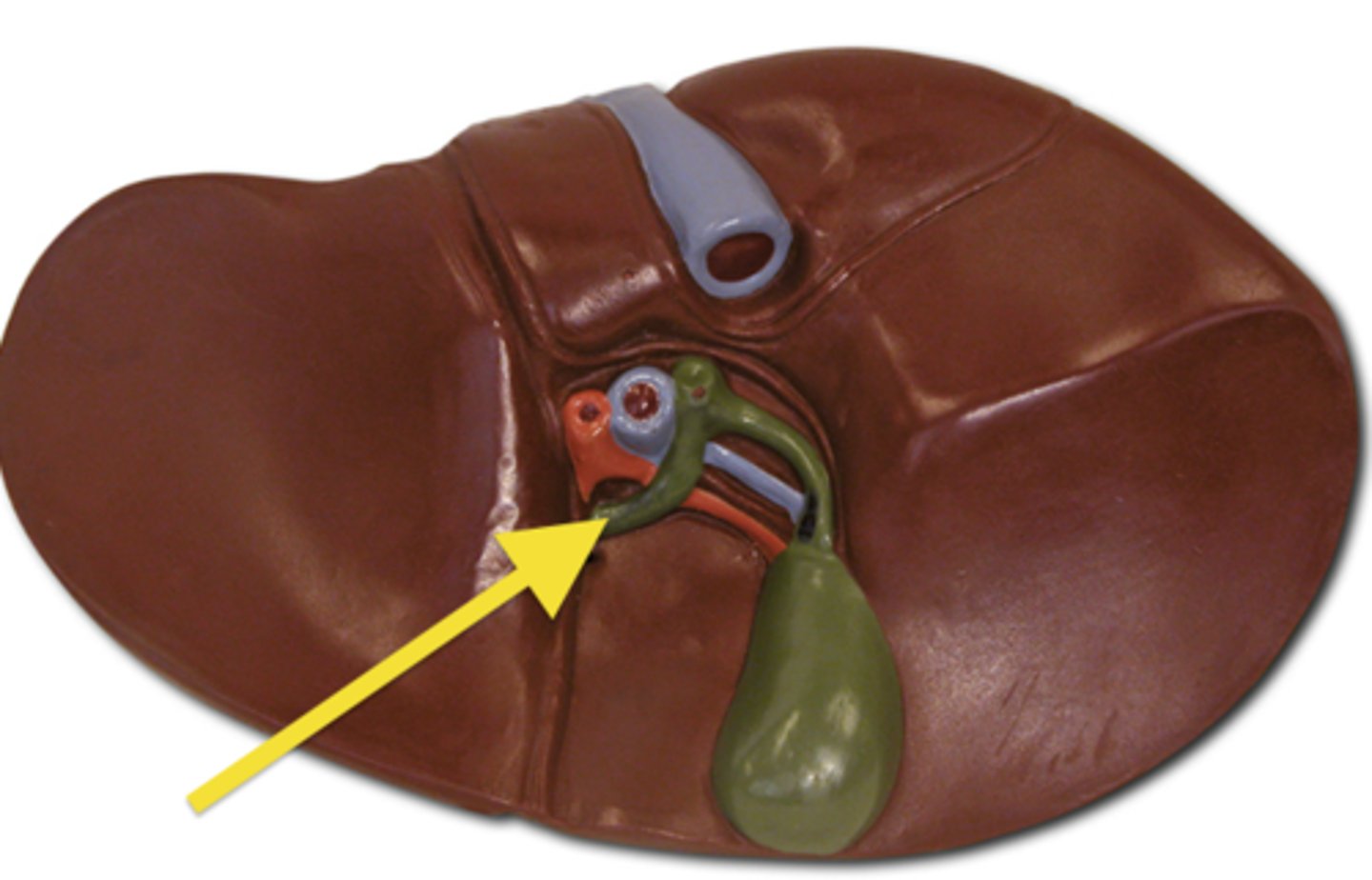

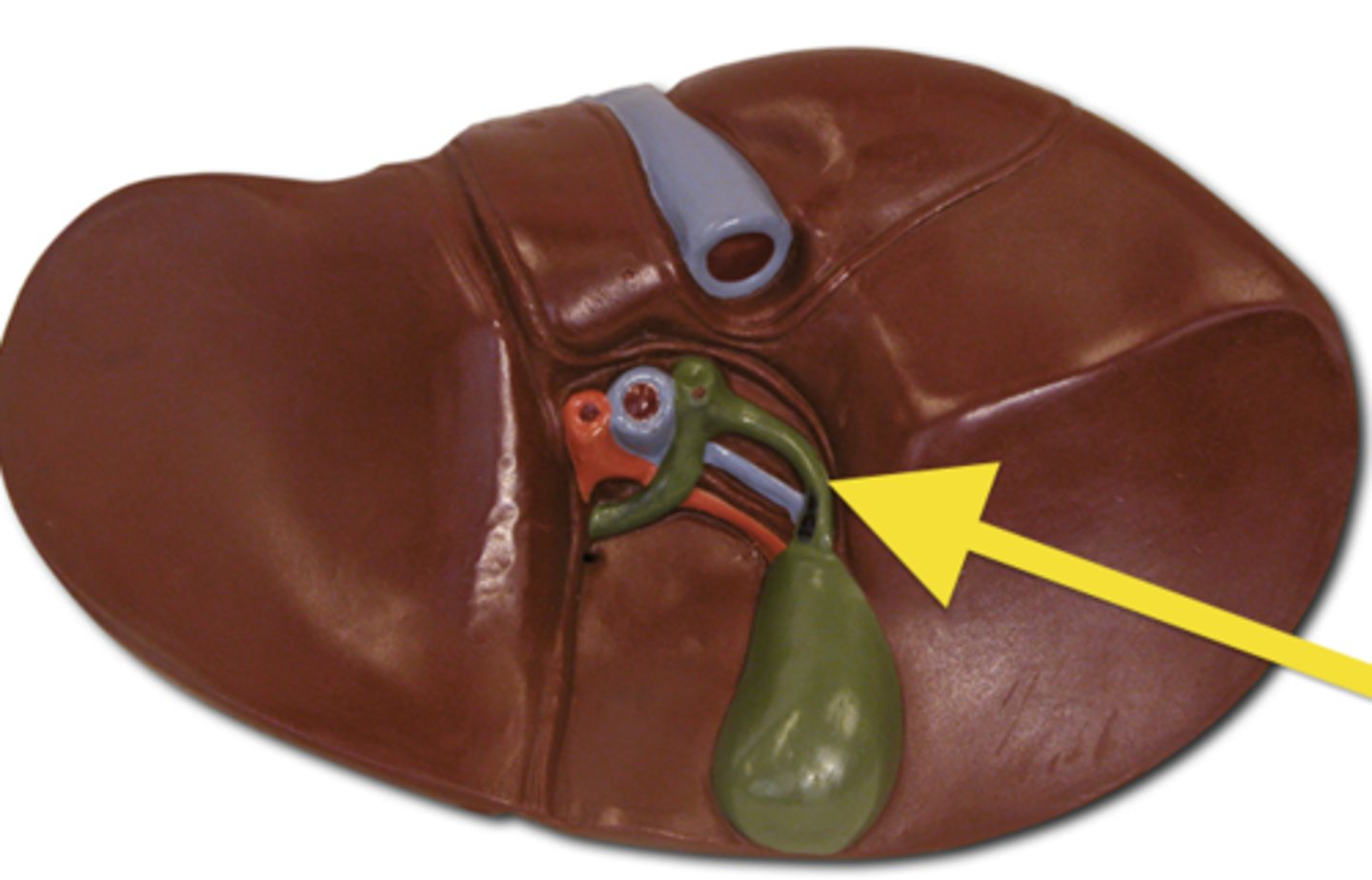
cystic duct

bile duct
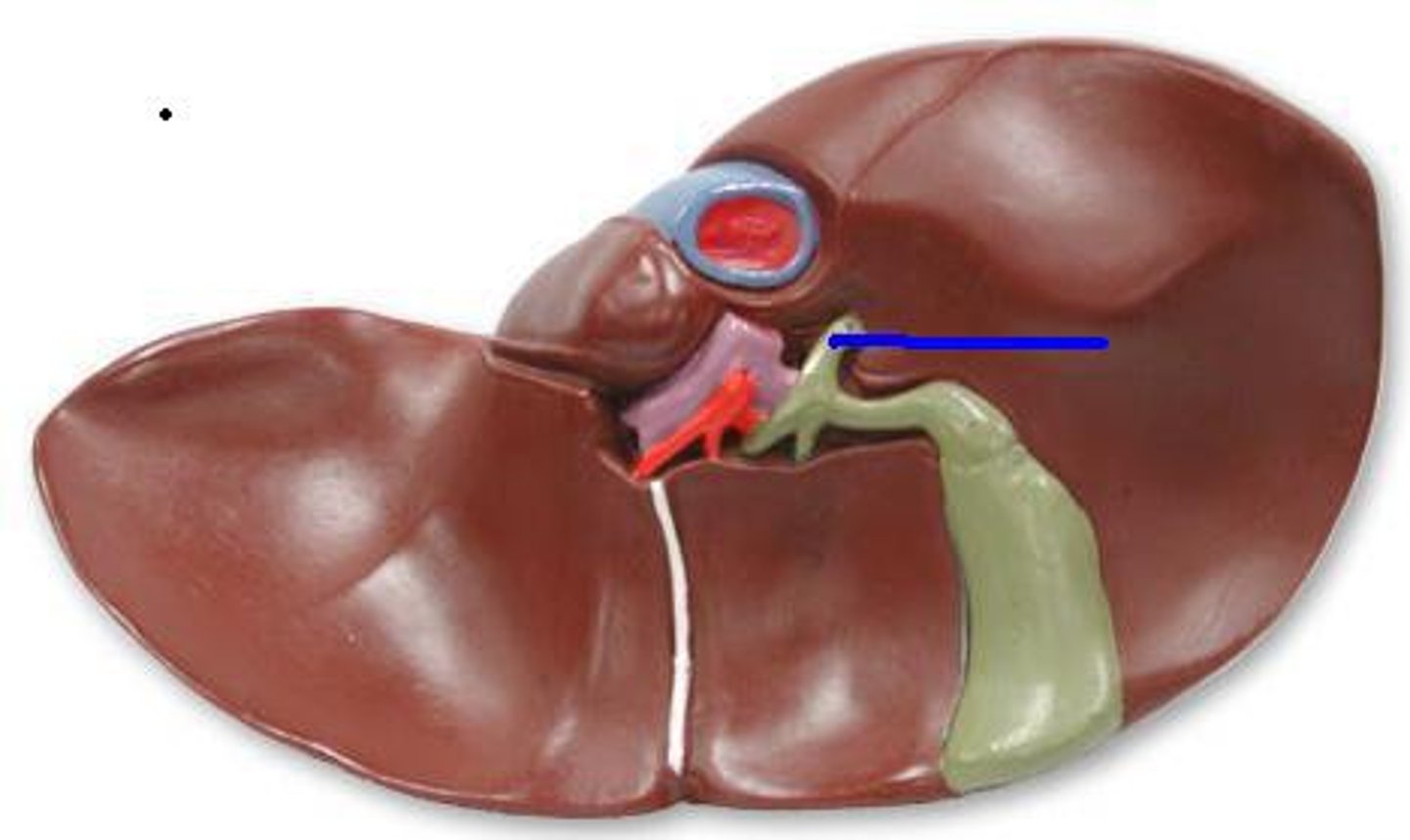
pancreatic duct
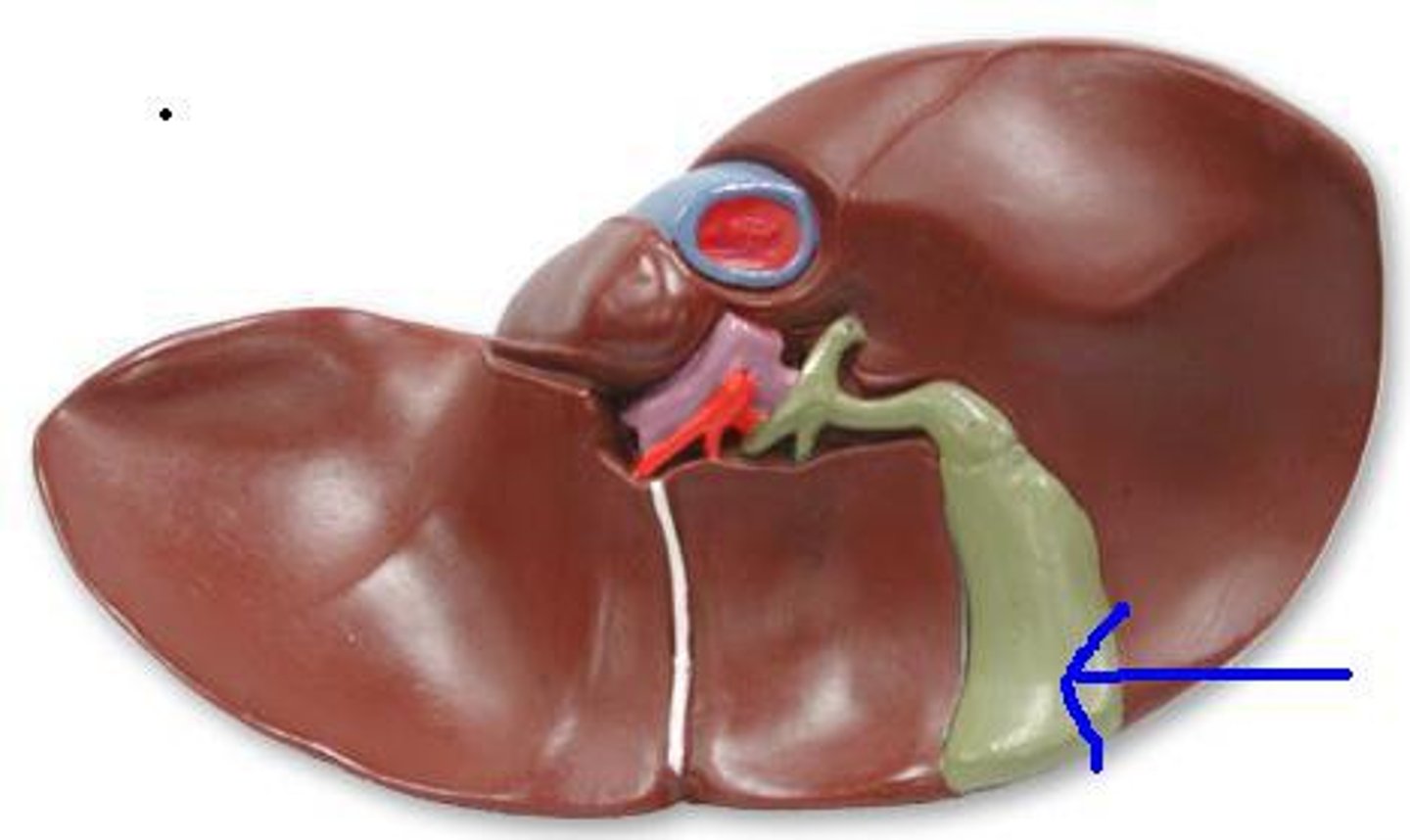
gallbladder
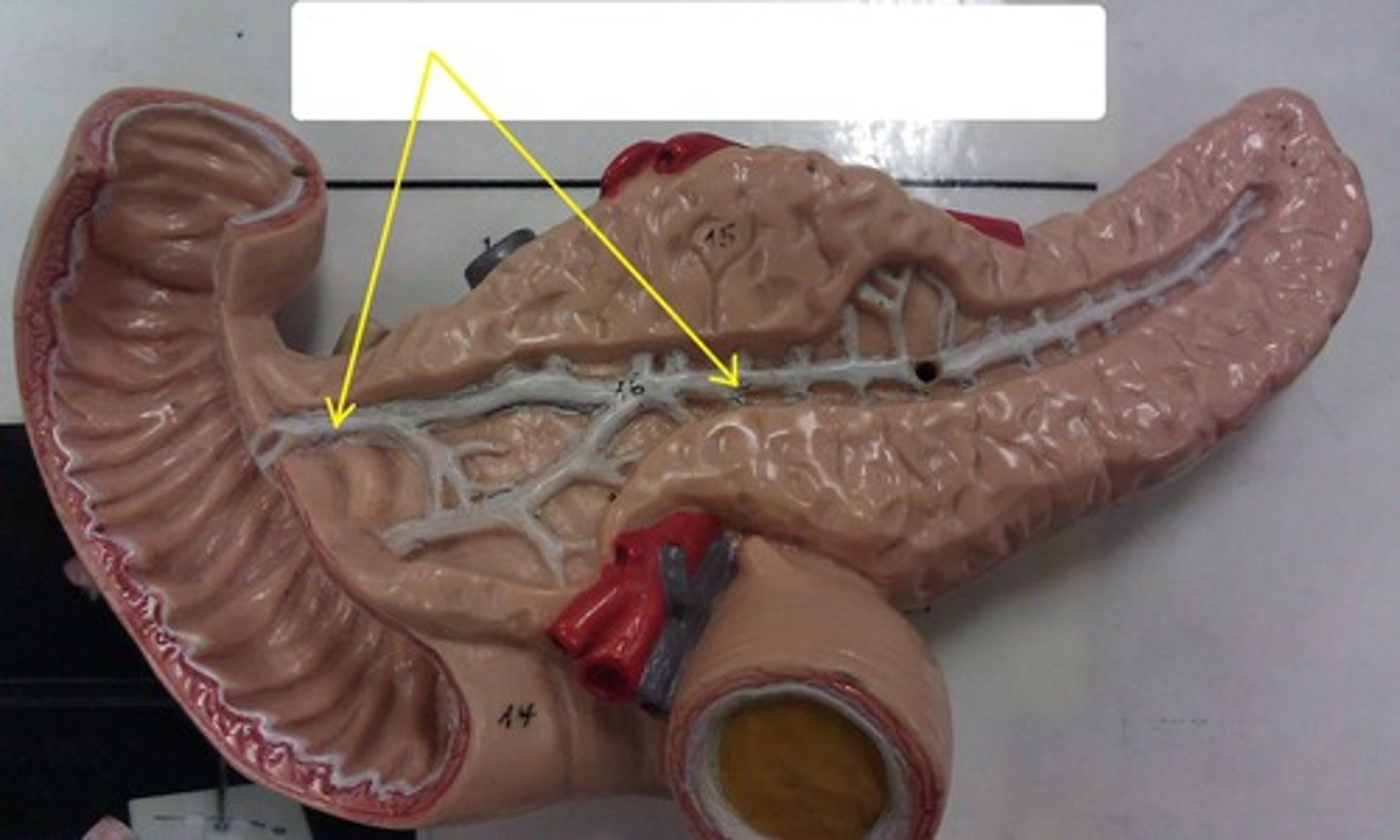
accessory pancreatic duct
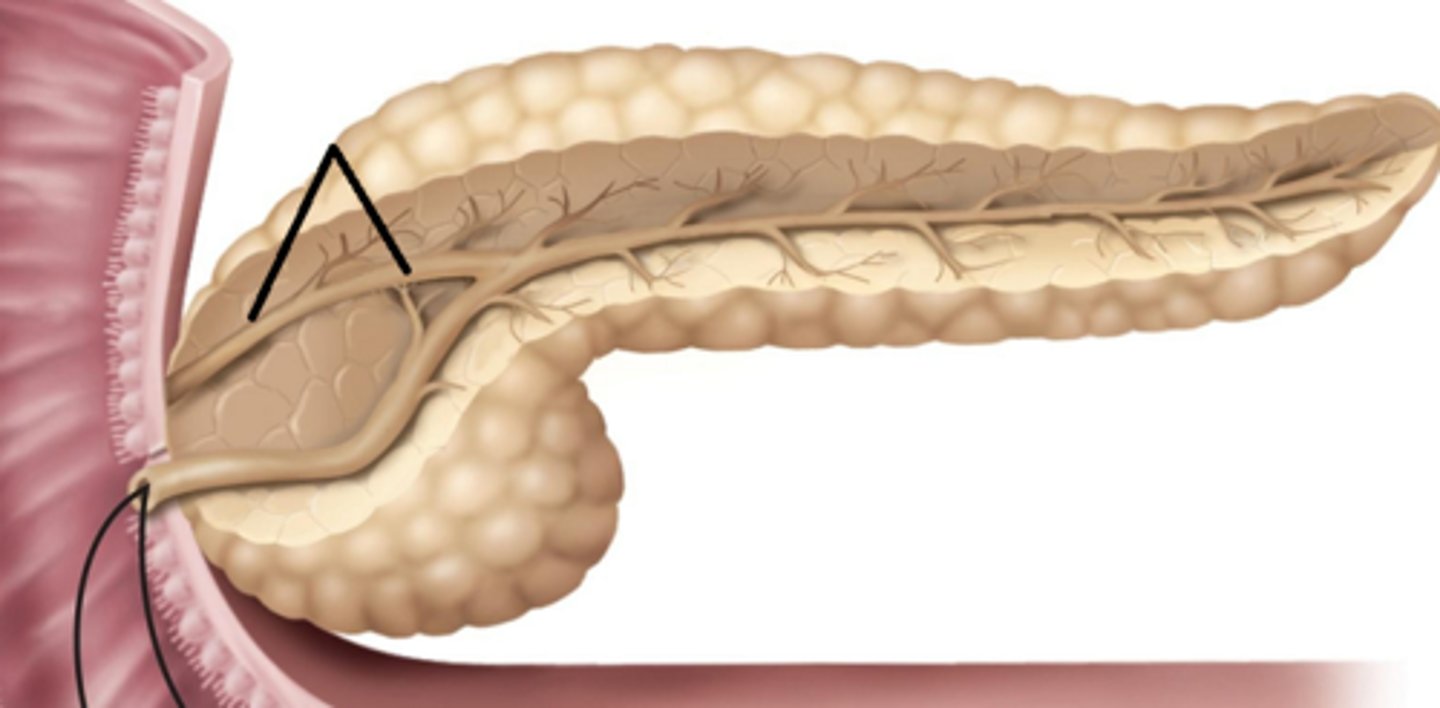
hepatic pancreatic ampulla
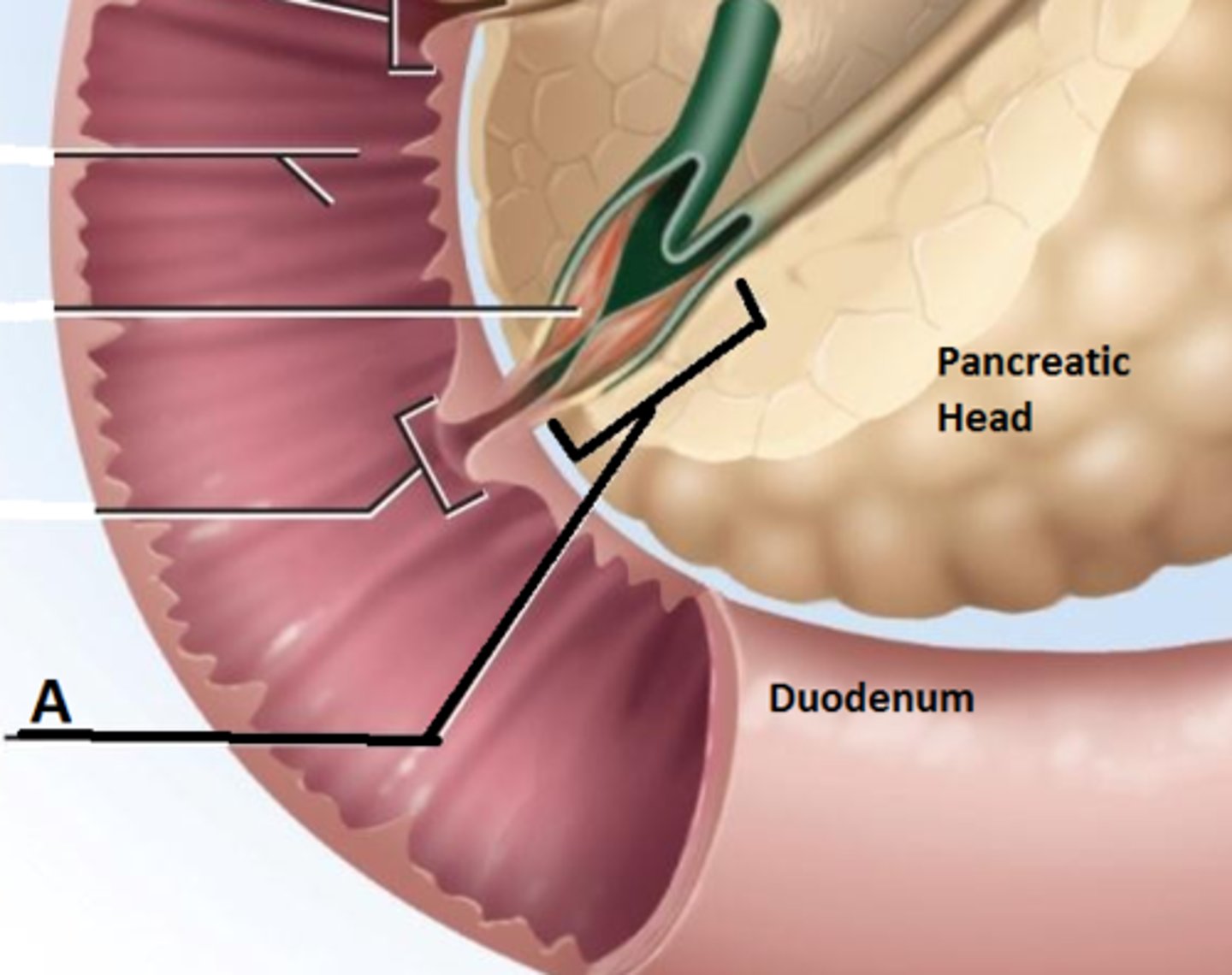
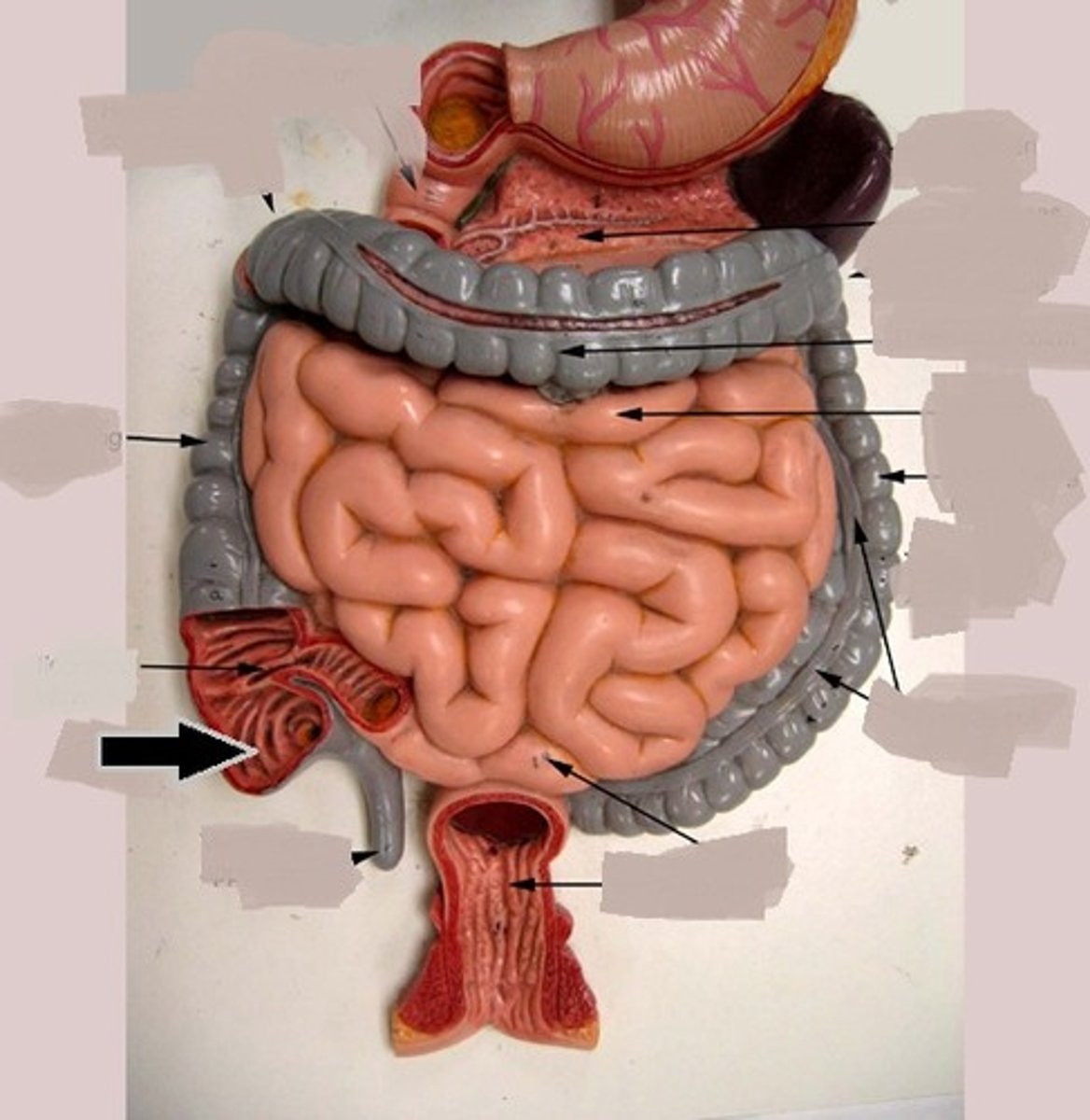
duodenum
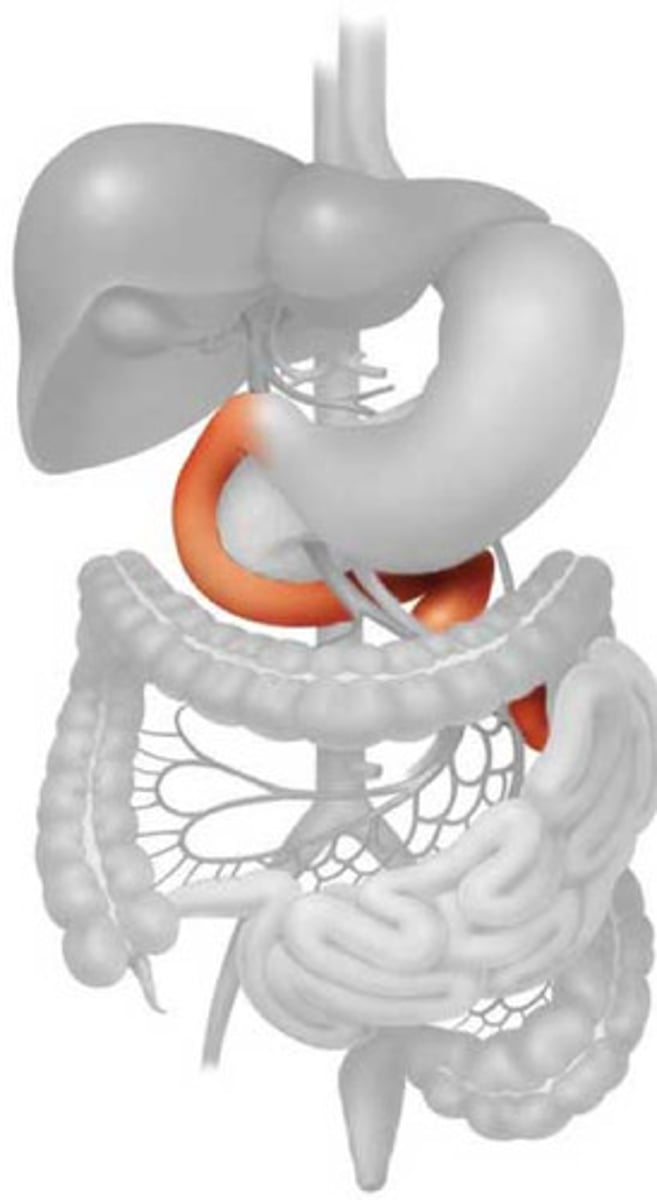
jejunum
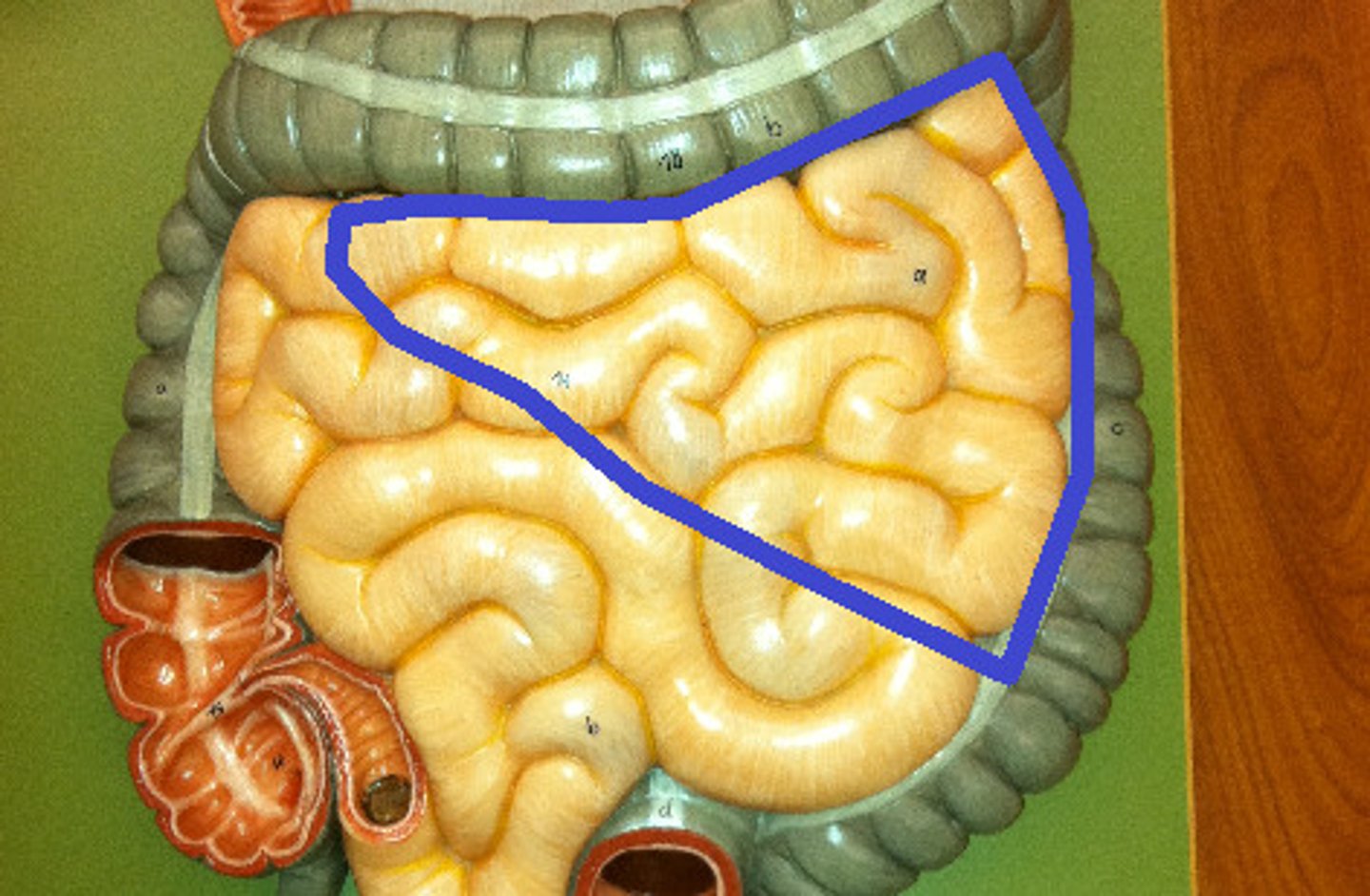
ileum
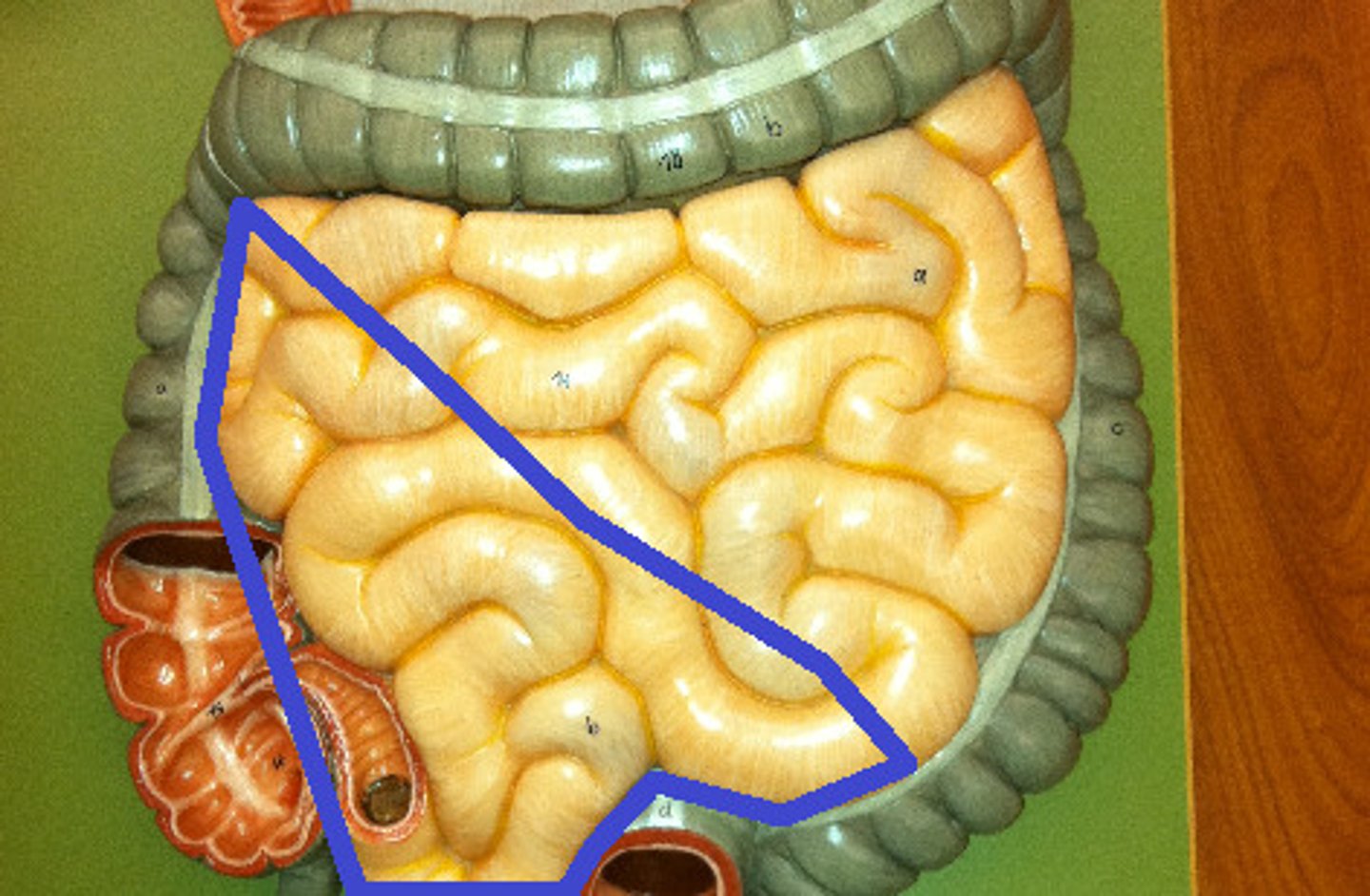
colon
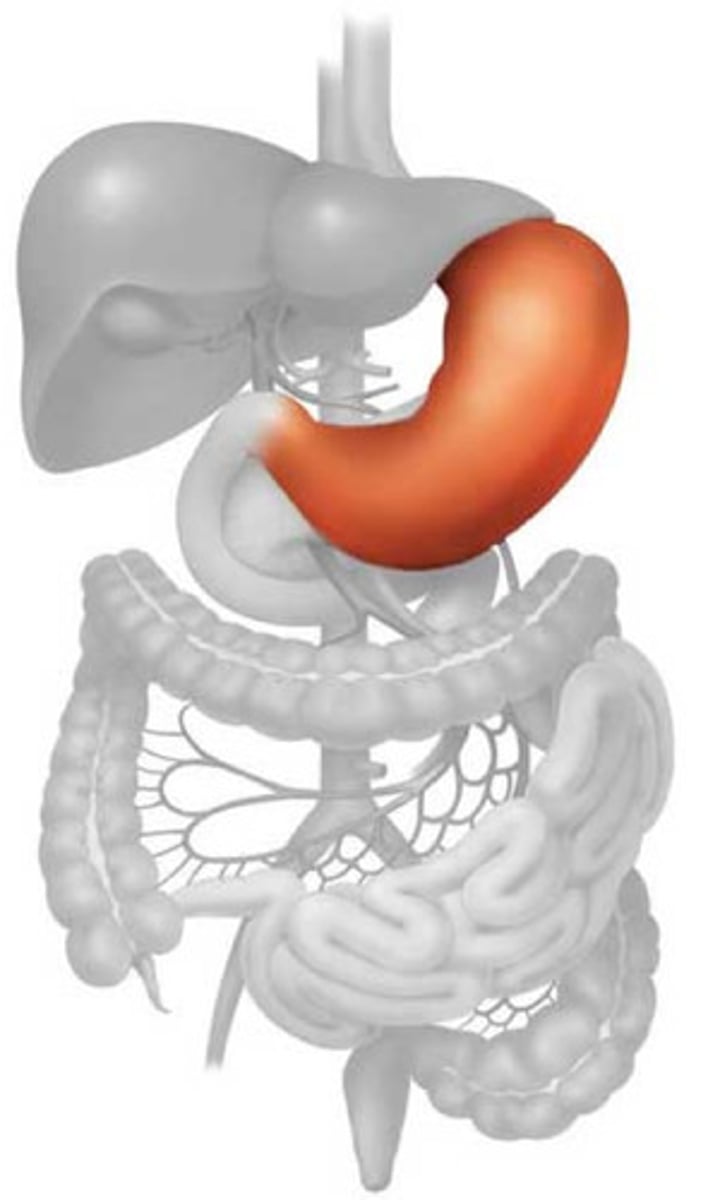
stomach
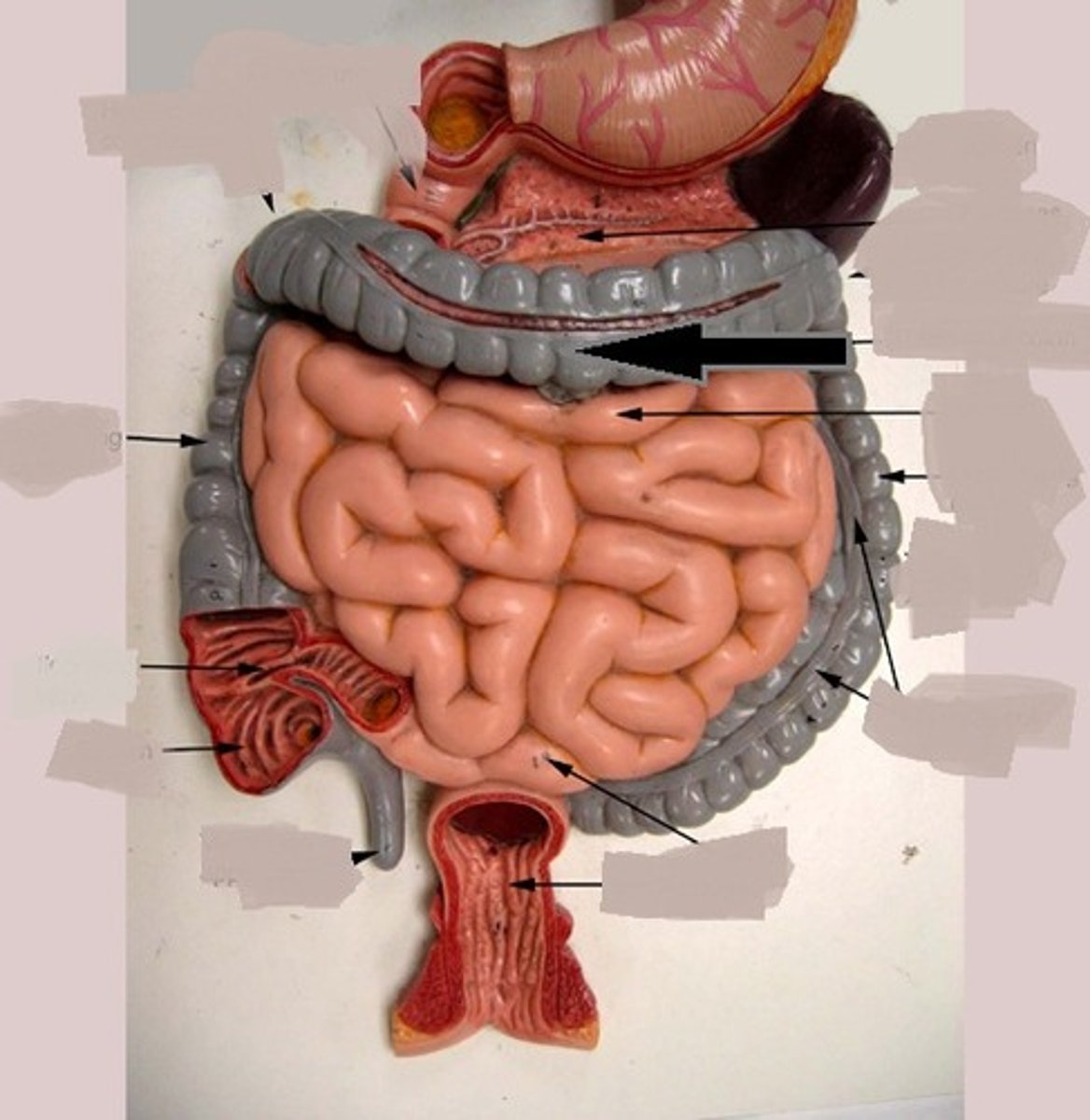
hepatic flexure
teniae coli
ascending colon
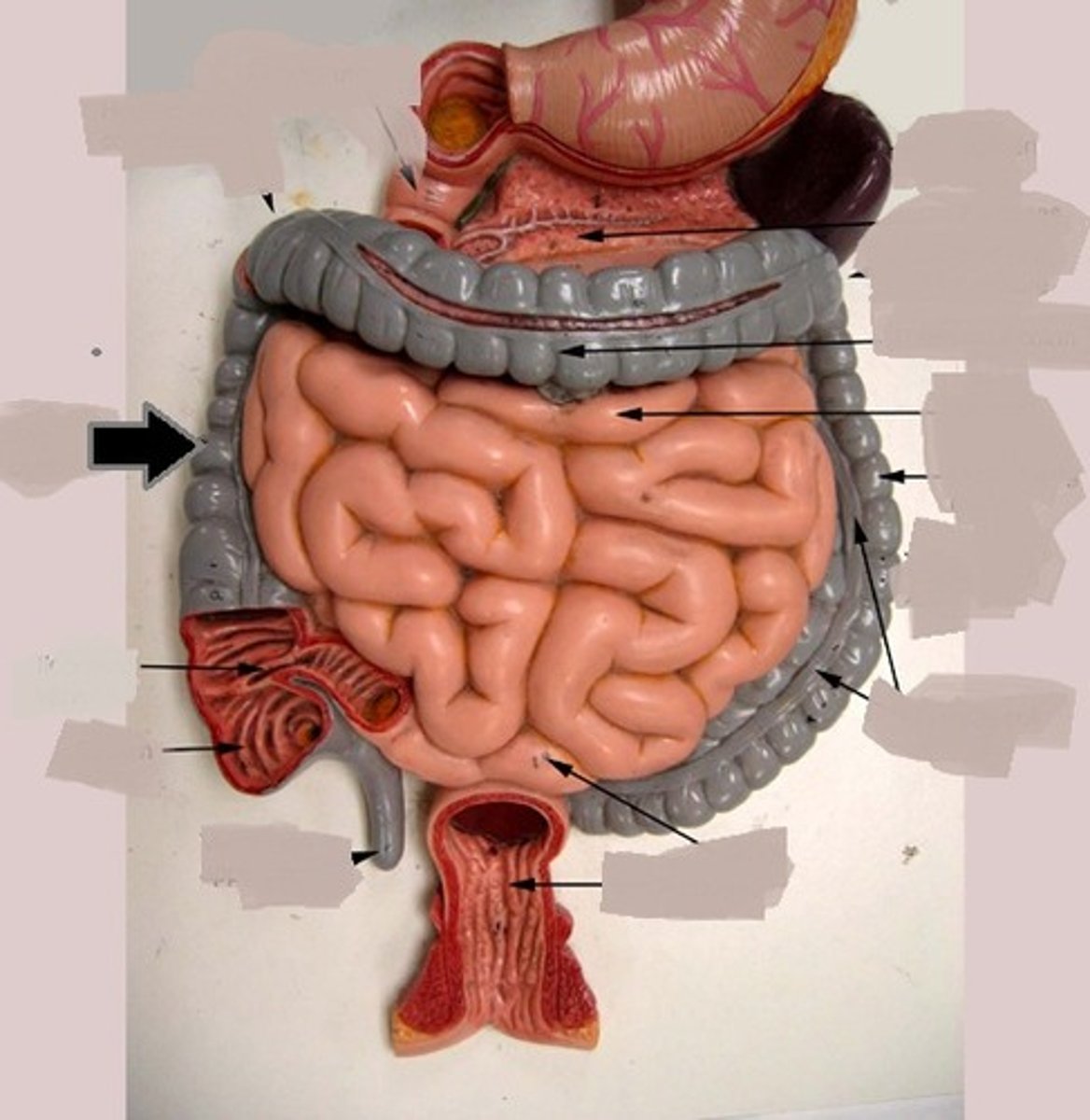
cecum
transverse colon
appendix
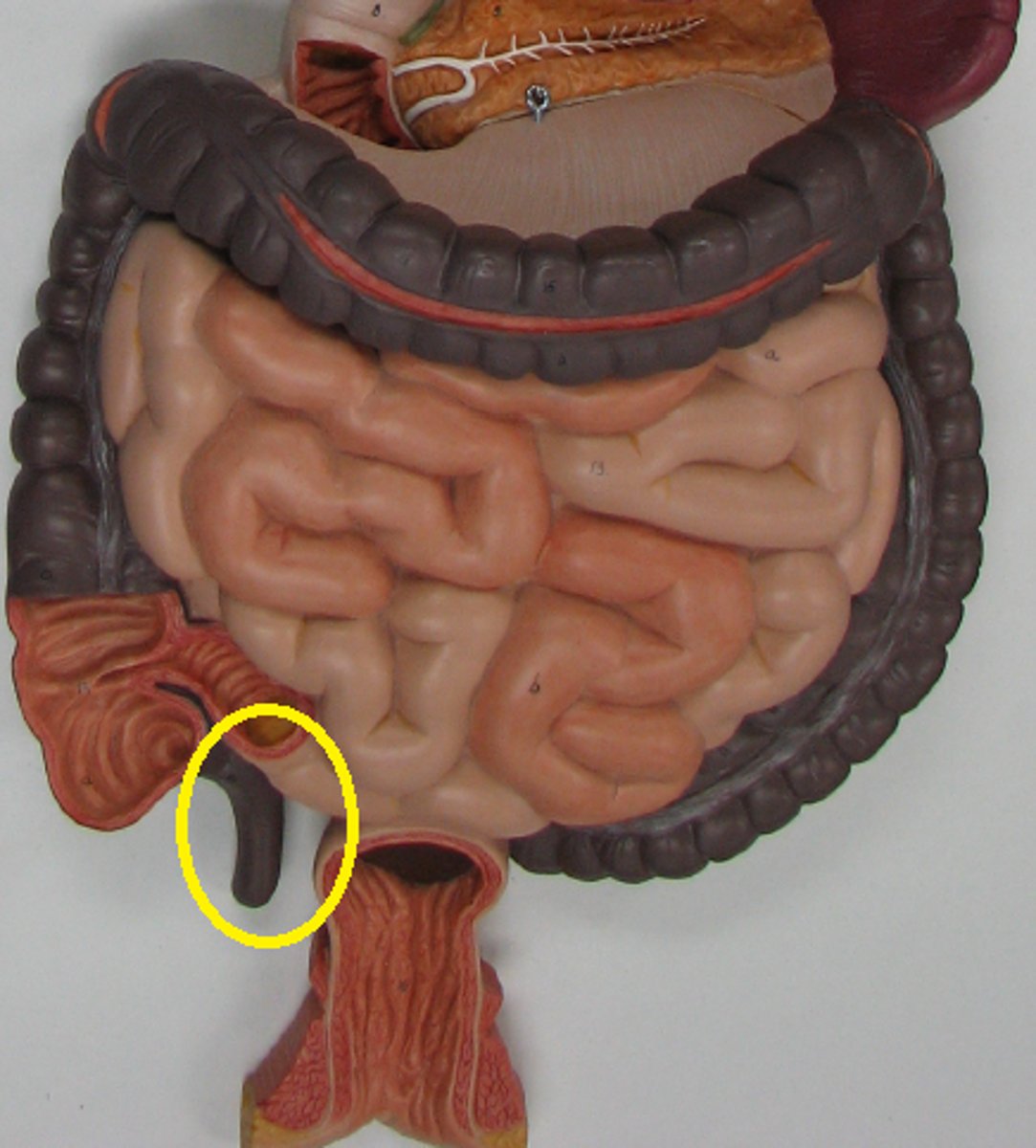
mesocolon