intermolecular forces
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
what are the 3 main types of intermolecular force in order of increasing strength?
Van der Waals forces
permanent dipole-dipoles
hydrogen bonding
what are intermolecular forces?
forces that occur between molecules
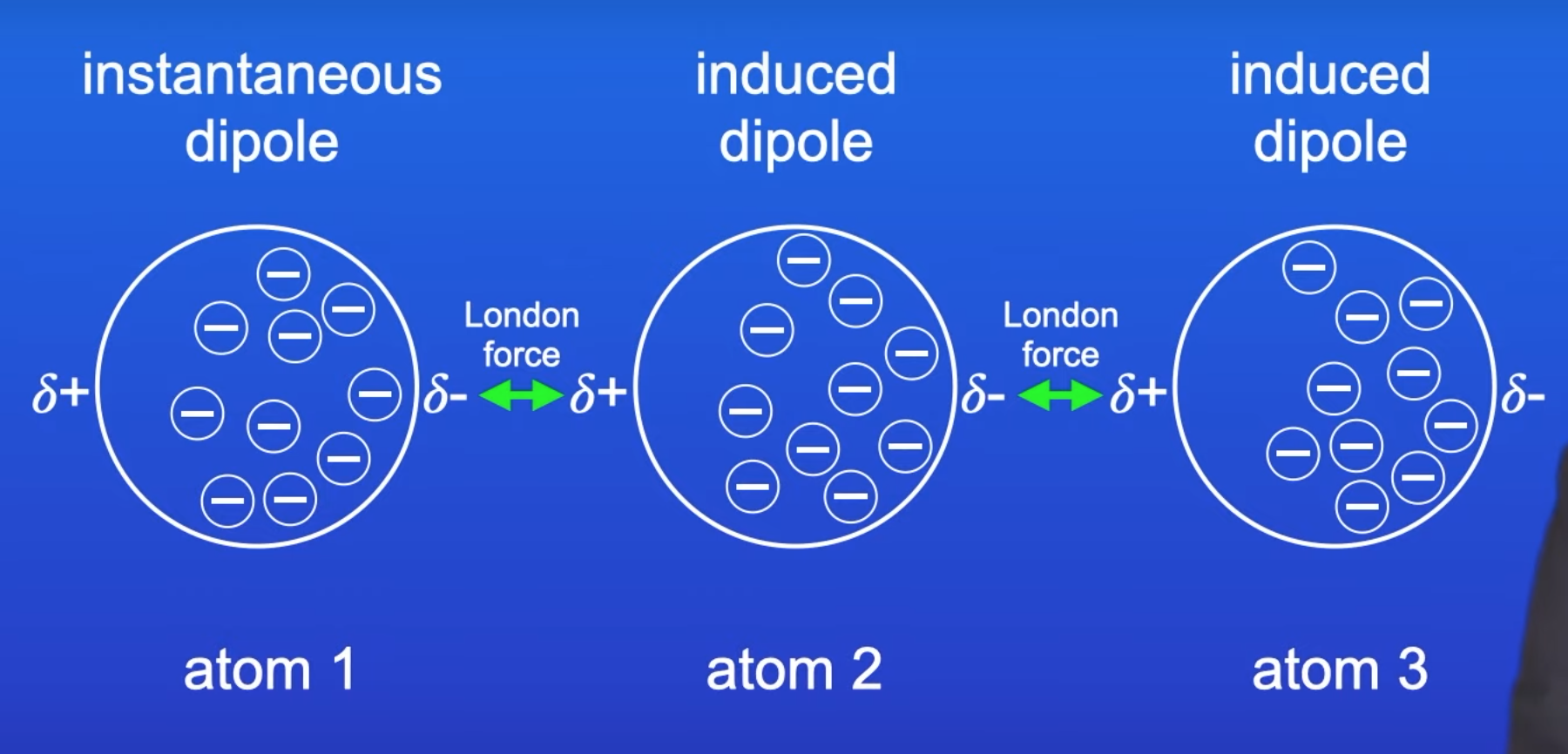
describe and explain Van der Waals forces
present in all molecular substances
occur because e- are constantly moving around and there will be an uneven e- distribution at any given moment in time
this causes a TEMPORARY DIPOLE w/in a molecule
this temporary dipole induces an INDUCED DIPOLE in a neighbouring molecule
there is then an attraction between these molecules -this is a temporary induced dipole-dipole attraction
how does increasing the size of a molecule affect bpt?
the bigger the molecule, the greater the Van der Waal forces
this is because bigger molecules have more e-
∴ greater VDWs = higher bpt
describe and explain permanent dipole-dipole attraction
occurs between polar molecules
polar molecules have permanent dipoles, meaning that one atom in a molecule is more electronegative than the other as the e-s are more attracted to it
this more electronegative atom becomes attracted to the more electropositive atom of another polar molecule
this causes a permanent dipole-dipole attraction
describe and explain hydrogen bonding
H bonded to a very electronegative atom (F, O and N)
the polar bond between the H and N/O/F leaves the H nucleus exposed as H only has 1 e-
∴ there is a strong attraction from the lone pair on the N/O/F of 1 molecule to the exposed nucleus of the other
how do we find H bonds?
H atoms bonded to a N/O/F atom
do lone pairs of e- conduct electricity? why?
no
they are localised and so not free to move