South College AVL Lab Med: Hgb/Hct, RBC - Lecture 2
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Hematopoiesis
formation of blood cells
production and turnover of blood cells is coordinated
what happens to hematopoiesis under normal conditions?
increased production of blood cells (illness, altitude, exercise, bleeding)
what happens to hematopoiesis under stress?
Erythropoiesis
production of red blood cells
hematopoieitic stem cell - myeloid stem cell - early erythroblast - late erythroblast - normoblasts - reticulocyte - erythrocyte
what is the pathway of erythropoiesis?
EPO
promotes growth of red blood cells (myeloid stem cell - early erythroblast)
B12 and folate
condenses nucleus during the late erythroblast state to the normoblasts stage
during normoblast stage
when does iron come in for hemoglobin synthesis?
looses most organelles (ex: mitochondria) and nucleus (make room for hemoglobin), flexible, biconcave, contains hemoglobin (contains iron and carries O2)
what are some key characteristics of a healthy, mature erythrocyte?
several hundred million
how much hemoglobin does one RBC contain?
heme
what specifically does oxygen bind to on hemoglobin?
100-120 days, 6-8 hrs, 7-10 days
what is the life cycle of an RBC? WBC? Platelet?
liver and spleen
where are 90% of old/damaged RBCs removed from circulation?
hemolysis in circulation
where are 10% of old/damaged RBCs removed from circulation?
contents are recycled and used again (globin, heme, iron)
what happens when old/damaged RBCs are removed from circulation?
Hemoglobin (Hgb), Hematocrit (HCT), Red blood cells (RBC - count), Mean corpuscular volume (MCV), Red blood cell distribution width (RDW)
When obtaining a CBC, what categories are we looking for?
classifications of anemia
Why is Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) and Red blood cell distribution width (RDW) important, or what do these help us diagnose?
Hematocrit (Hct)
percentage of erythrocytes in total volume of blood (Approx: 3 x Hgb (g/dL) if RBCs are normal size and normal Hgb)
RBC, Hgb, Hct
what are we following SERIALLY if we suspect bleeding and are INTEGRAL for anemia work up>
adrenal/brain/kidney/liver cancer, anabolic steroids, congenital heart disease, dehydration (severe diarrhea/burns), high altitudes, lung disease (COPD/smoking), certain meds, sleep apnea (more EPO production due to lack of O2 due to snoring)
What are some reasons as to why RBC, Hgb, and Hct values might be increased (erythrocytosis/polycythemia)?
Erythrocytosis/Polycythemia
increase in the number of red blood cells
Anemia
A condition in which the blood is deficient in oxygen carrying capacity of red blood cells, specifically hemoglobin, and/or hematocrit.
bone marrow failure, bleeding, cancer, cirrhosis, hemoglobinopathy, certain meds, pregnancy, prosthetic valves, renal disease, rheumatoid/collagen vascular disease, splenomegaly, vitamin deficiencies
What are some reasons as to why RBC, Hgb, and Hct values might be decreased (anemia)?
diuretics, gentamicin, methyldopa
what meds increase RBC, Hgb, and Hct values?
antibiotics, chemo, aspirin, indomethacin, rifampin, sulfonamides
what meds decrease RBC, Hgb, and Hct values?
underlying disease (rather than specific diagnosis)
what is anemia a sign of?
left = normal, right = abnormal
which side is normal? abnormal?
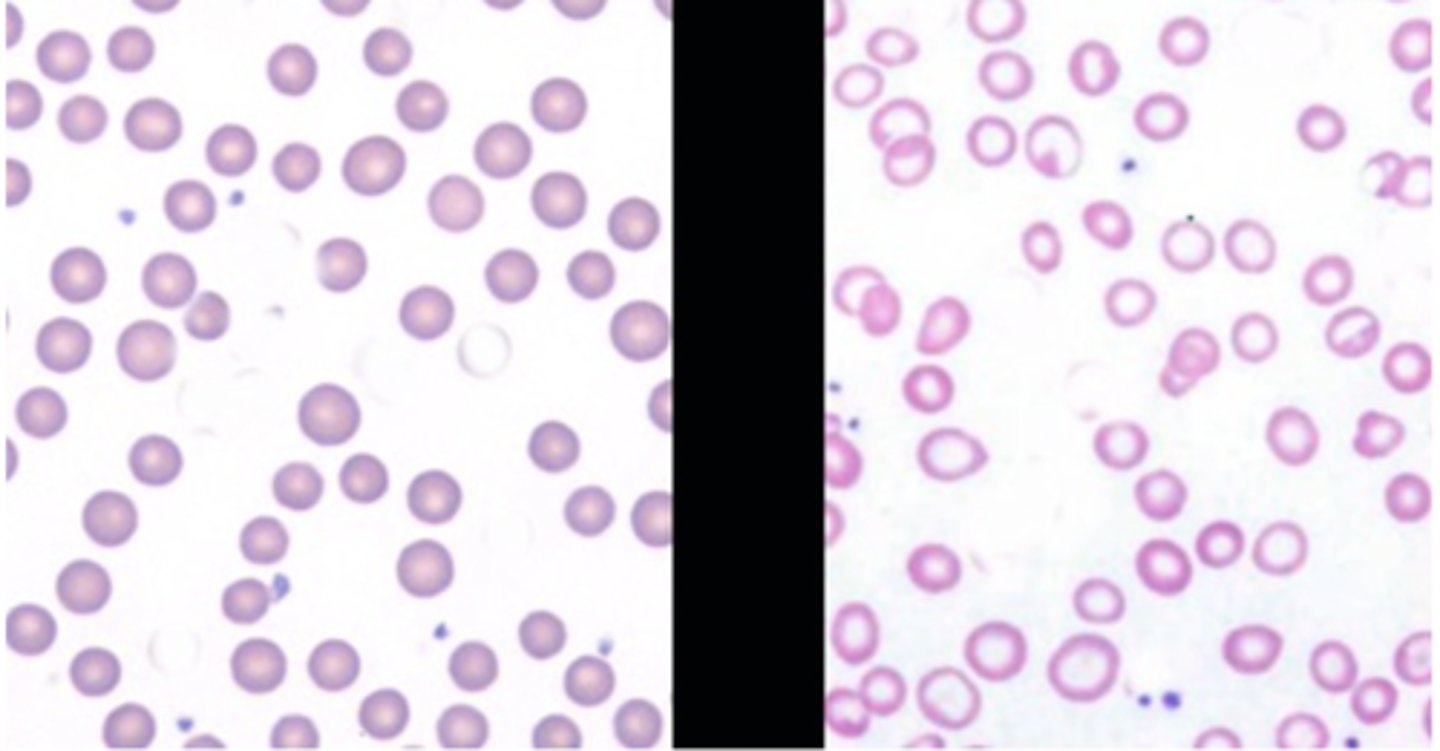
hollow - missing hemoglobin, and they are light in color
what is wrong with the RBCs on the right?
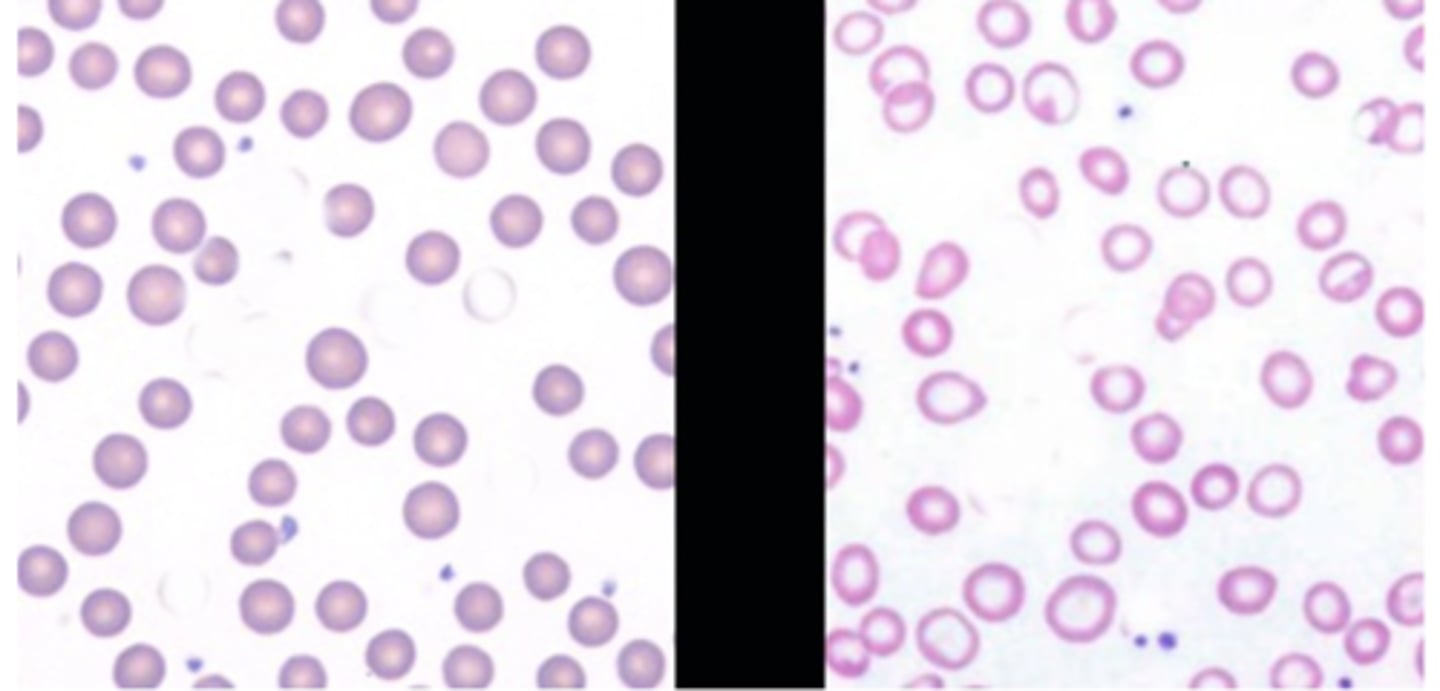
decreased production and destruction of RBCs
What are the two main reasons for anemia (pathophys)?
bone marrow damage (fibrosis/drugs), decreased marrow stimulation (renal disease/inflammation), Iron/folate/B12 deficiencies
what are three causes of decreased RBC production?
Healthy bone marrow cant keep up with blood loss or hemolysis
What causes the destruction of RBCs?
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) and Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
while still included on a CBC, which categories are we NOT too concerned about?
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)
(Hct % x 10)/RBC (million/mm3) = ?
Alcohol (EtOH) use disorder, folate deficiency, hypothyroidism, chronic liver disease, certain meds, multiple myeloma, myelodysplastic syndrome, pernicious anemia, B12 deficiency
What are some reasons as to why Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) values might be high > 96 (macrocytic)?
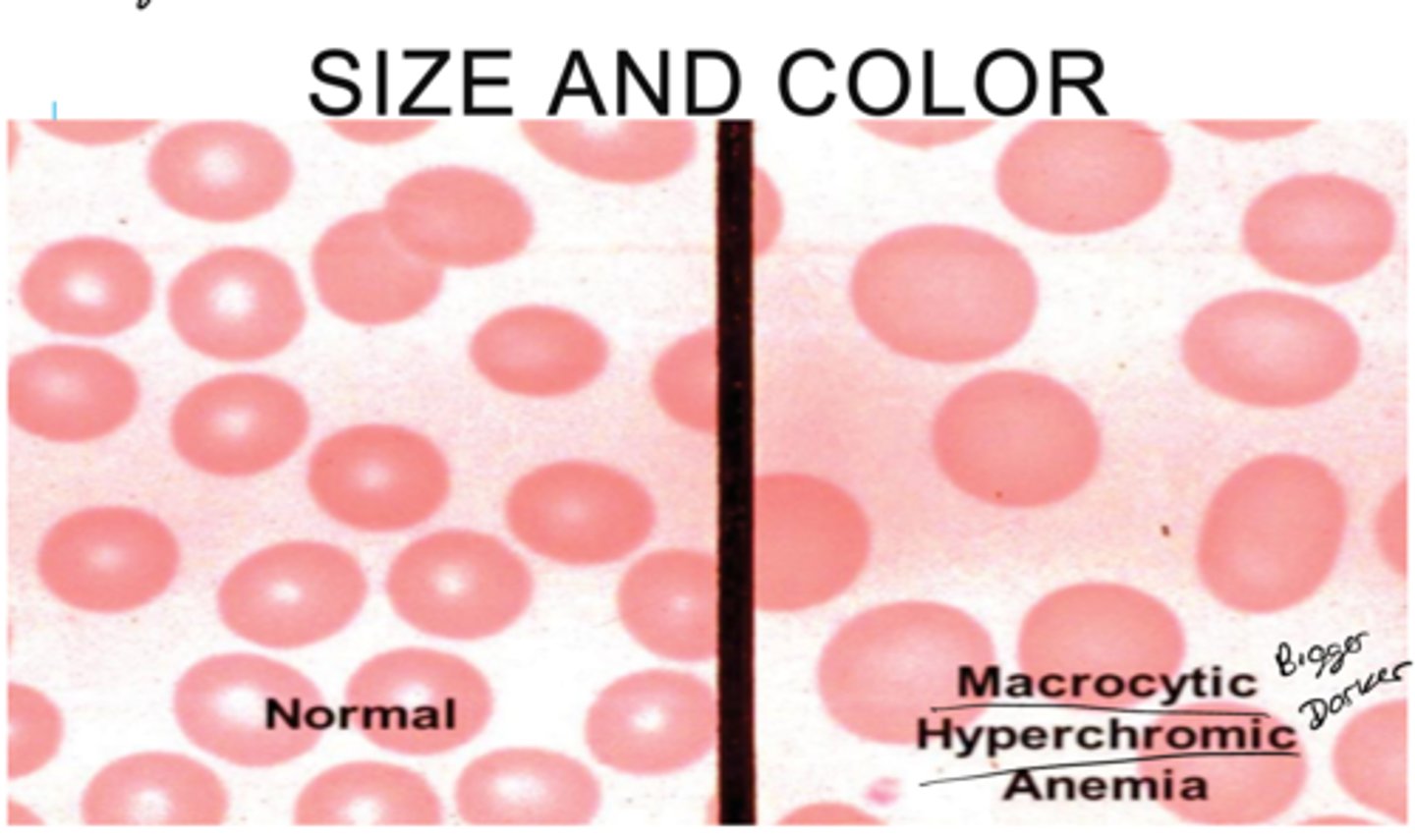
methotrexate, imuran, hydroxyurea
What meds lead to a high Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) value >96?
Alcohol use disorder and certain meds (methotrexate, imuran, hydroxyurea)
Of the problems listed for high MCV values, which have normal RBC distribution width (RDW)?
folate deficiency, chronic liver disease, multiple myeloma, myelodysplastic syndrome, B12 deficiency
Of the problems listed for low MCV values, which have elevated RBC distribution width (RDW)?
chronic disease, early B12/iron deficiency OR mixed deficiencies anemia, renal failure, sickle cell anemia
ALL elevated RDW
What are some reasons as to why Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) might be normal = 80-96 (normocytic)? RDW values?
iron deficiency anemia (most common cause of anemia), toxins/drugs, thalassemia, myelodysplastic syndrome
ALL elevated RDW
What are some reasons as to why Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) values might be low > 80 (microcytic)?
RDW values?
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC)
(Hgb (g/dL) x 100)/ hematocrit (%) = ?
decreased and normal MCHC
What are the two classifications of anemia in terms of MCHC?
hypochromic anemia
reduced hemoglobin content (lighter in color)
normochromic anemia
normal hemoglobin content (normal color)
iron deficiency and thalassemia
what are two examples of hypochromic anemia?
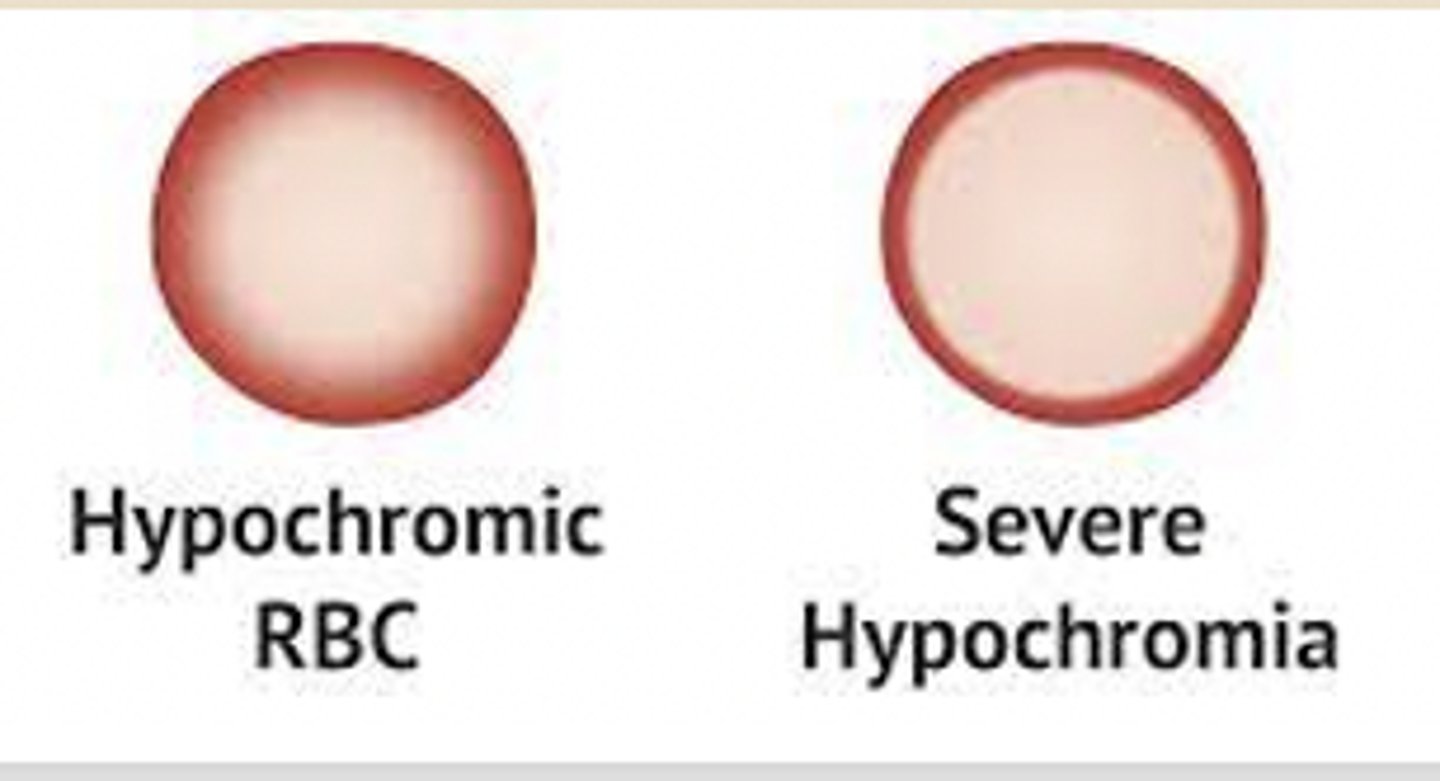
hemolytic anemia
what is an example of normochromic anemia?

RBC distribution width (RDW)
indicates the variation in size of an RBC, the degree of anisocystosis
calculated by machine using MCV and RBC values
anisocytosis
variation/unequal RBC size (can be abnormal)
results in macrocytosis and microcytosis
RDW measures this
iron deficiency anemia B12/folate deficiency anemia, hemoglobinpathies (sickle cell disease), hemolytic anemia, post-hemorrhagic anemia
What are some reasons RDW would be increased?
poikilocytosis
increase in abnormal RBCs of ANY shape where they make up 10% or more of total population
diagnosed via blood smears
flat, elongated, crescent shaped, tear-drop shaped, pointy shaped projections, etc.
poikilocystosis results in what kind of shaped RBCs?
poikilocytosis
what would these cells be an example of?

anisocytosis
what would these cells be an example of?

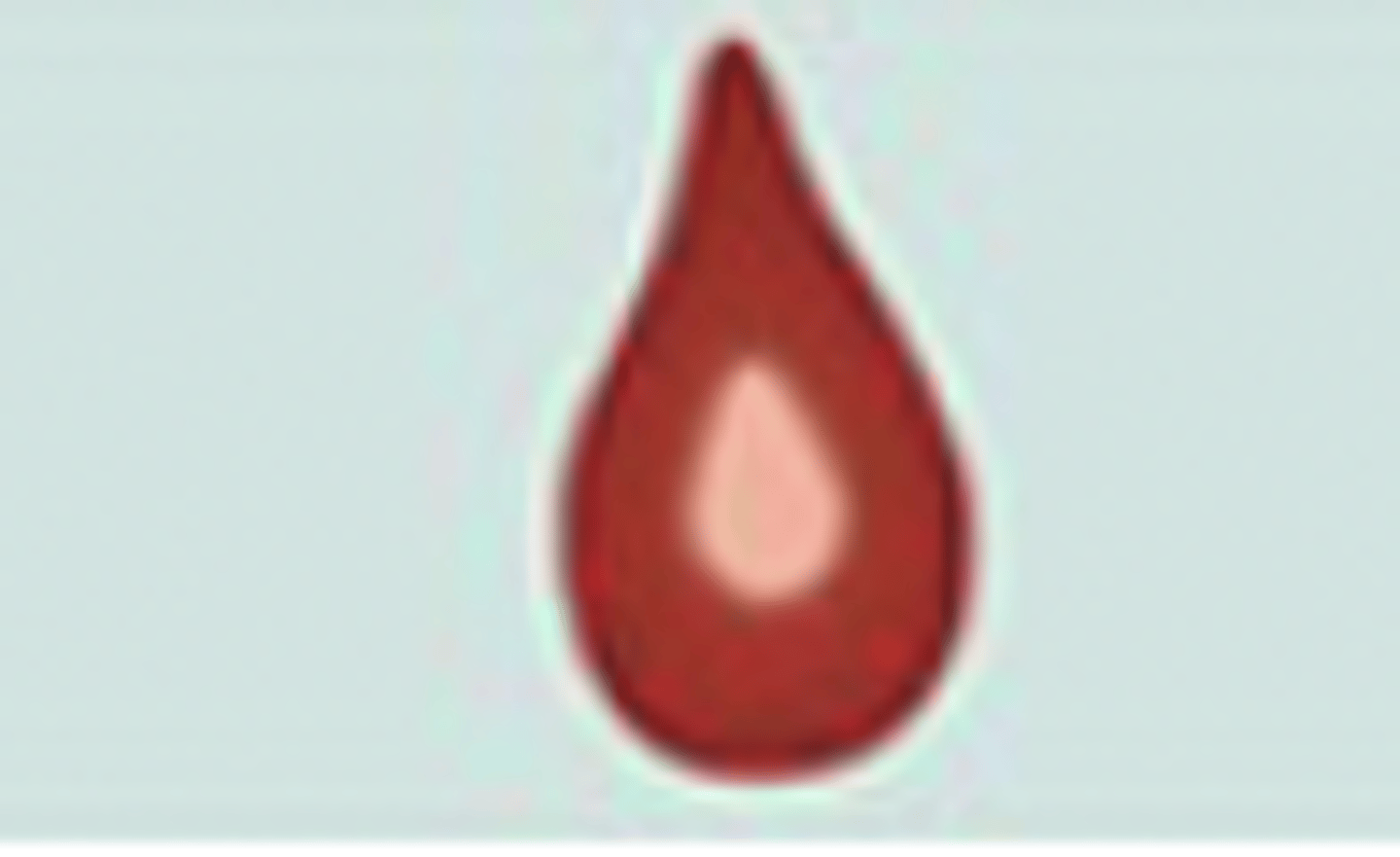
teardrop - thalassemia, anemia, marrow infiltration, splenic abnormalities
what type of abnormal RBC morphology is this?what is it indicative of?

- Hgb - slight diurnal variation (highest 8am, lowest 8pm)
- heavy smokers
- Hgb/Hct - hemodilution (overhydration)/dehydration
- pregnancy - hemodilution (Hgb/Hct decrease)
- high altitudes - Hgb/Hct increase (more O2 available)
- Abnormal RBC size - higher Hct w/ larger RBCs take up greater % of total blood volume (RBC affectd MCH and MCHC)
- WBC extremely elevated (decrease Hct - false indicate anemia - increase MCV and MCH)
- unreliable labs immediately after hemorrhaging (total blood volume of RBC will not change until replaced w/ fluids)
- extreme elevation in lipid levels (Hgb, MCV, MCHC, and MCH falsely high)
- MEDICATIONS CAN CAUSE INCREASE OR DECREASE IN ALL!!
What are some interfering factors of Hgb, Hct, and RBC?